Properties of Gases & Kinetic Theory of Gases
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are gases made up of?
Gases are made of particles (molecules, atoms or ions) that are in constant random motion (diffusion)
Diffusion
The spreading of a gas to fill its container
Volume is sensitive to changes in….
Temperature and pressure (gases are easily compressed because they are mostly empty space)
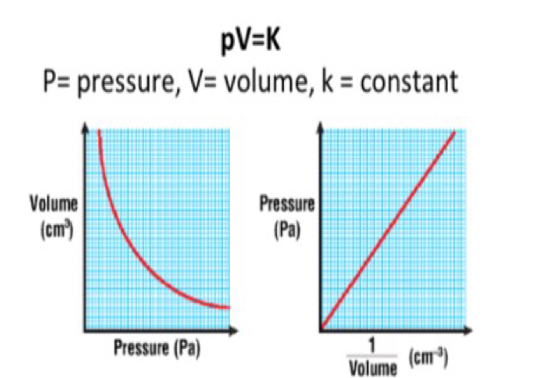
Boyle’s Law
At constant temperature the volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure (pressure increases - volume decreases and vice versa)
Charle’s Law
At constant pressure the volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its temperature (pressure increases - volume increase and vice versa)
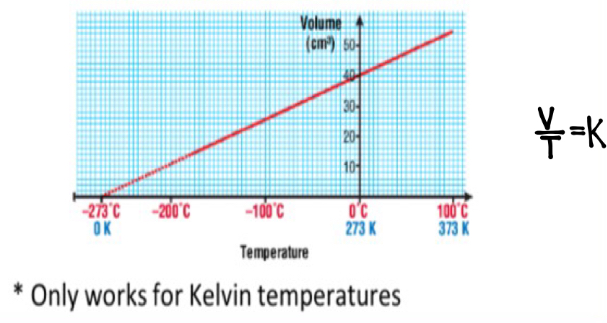
Kelvin number
+273 onto the Celsius number
Use Kelvin not Celsius
Lussac’s Law
In a reaction between gases, the volumes of any gases reacting or produced, are in the ratio of small whole numbers provided the volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure
Avogadro’s Law
Equal volumes of all gases under the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles.
Assumption 1: Kinetic Theory of Gases
Gases are made up of particles that are in continuous rapid, random motion.
Assumption 2: Kinetic Theory of Gases
There are no attractive or repulsive forces between the particles of a gas
Assumption 3: Kinetic Theory of Gases
The average kinetic energy of the particles is proportional to the temperature in Kelvin
Assumption 4: Kinetic Theory of Gases
The gas particles are so small and so widely spread out that their combined size is insignificant compared with the space that they occupy
Assumption 5: Kinetic Theory of Gases
Collisions between particles are perfectly elastic, i.e. there is no overall loss of kinetic energy in these collisions
Limitations
Contrary to assumption 2: There are van der Waals forces/ Dipole-dipole forces
Contrary to assumption 3: It is not valid under high pressure
What is an ideal gas?
One that perfectly obeys all the assumption of the kinetic theory of gases under all conditions of temperature and pressure