BIO Exam II with David
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1. Coenzyme A is an organic molecule which
a. Carries hydrogen atoms to and from substrates in glycolysis
b. Carries a phosphate group to ATP in glycolysis
c. Carries 2 and 4 carbon molecules in the Citric Acid cycle
d. Transfers electrons as part of the electron transport chain
c
2. The presence of Cytochrome oxidase in mitochondria is the reason
a. NAD+ must be regenerated by fermentation
b. Oxygen is required by most cells
c. Pyruvate accumulates during glycolysis
d. Pantothenic acid is required in the diet of animals
b
3. Cyanide is a deadly poison because it
a. Irreversibly binds to and inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase
b. Prevents lactate dehydrogenase from regenerating NAD+
c. Binds to mitochondrial cytochromes
d. Binds to coenzyme A in the Citric Acid cycle
c
4. This enzyme in the mitochondrial electron transport chain regenerates the NAD+ to keep glycolysis and the Citric Acid cycle going if oxygen is available in cells.
a. Pyruvate kinase
b. NADH dehydrogenase
c. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
d. Succinyl-coenzyme A synthetase
b
5. Mitochondrial ATP synthase produces ATP as
a. Protons move through channels in the enzyme
b. Hydrogen atoms are added to pyruvate
c. Organic acids are converted to CO2
d. Water molecules are converted to H2 and O
a
1. The structure of DNA was found to be a double helix held together by hydrogen bonds using this method.
a. Computer modeling of lowest molecular free-energy states
b. Transmission electron microscopy of DNA strands
c. X-ray diffraction of DNA strands
d. Fluorescence microscopy of chromosomes
c
2. If the sequence of one strand of DNA is 5’-TATAGAC-3’, the complementary strand must read (5’- to 3’):
a. TATAGAC
b. GTCTATA
c. CGTGACA
d. TGTCACG
b
3. The enzyme helicase catalyzes this reaction.
a. Covalently joins DNA pieces end-to-end
b. Removes incorrect bases from new DNA
c. Separates parental DNA strands
d. Adds new nucleotides to a DNA chain
c
4. A primer is needed to start DNA replication because:
a. DNA synthesis releases a considerable amount of free energy
b. There is no template present initially to guide which nucleotides are to be incorporated into the new strand
c. The first nucleotide must be attached to a 3’-OH group
d. The direction of DNA synthesis changes during replication
c
5. DNA synthesis on the lagging strand of DNA during replication:
a. Is generally in the 3’ to 5’ direction
b. Is in short, disconnected segments
c. Requires regions of double-helical DNA as templates
d. Produces a continuous, long chain of nucleotides
b
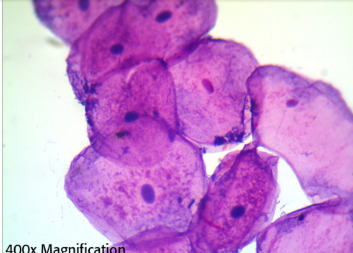
Which of the following processes cannot be occurring in these human epithelial cells, viewed with a light microscope?
a. DNA synthesis in chromosomes
b. protein synthesis in the rough ER
c. separation of sister chromatids
d. transcription of mRNAs
c
2. What kind of mutation in a somatic cell would be the least dangerous for a person?
a. A tumor suppressor gene mutates to make a non- functional tumor suppressor protein.
b. A proto-oncogene mutates to produce a non- functional proto-oncogene protein.
c. A proto-oncogene mutates to produce an overly active proto-oncogene protein.
d. A tumor suppressor gene is deleted entirely
Bcc
3. Normal cells
a. Survive if they are not attached to surfaces
b. Remain in metaphase indefinitely
c. Usually do not divide once they differentiate
d. Divide an infinite number of times
c
4. Short answer question: Why is it essential that each chromatid becomes attached to a spindle fiber before the dividing cell completes metaphase and moves on to anaphase?
to prevent unequal chromosome distribution in daughter cells.
1. This event occurs during anaphase of the first meiotic division (Anaphase I).
a. Sister chromatids separate from each other
b. Homologous chromosomes separate from each other
c. DNA replication of homologous chromosomes takes place
d. The cytoplasm of a dividing cell is partitioned into diploid gametes.
B
2. During prophase of meiosis,
a. Chromosomes disperse, becoming invisible
b.Spindle fibers disappear
c. Sister chromatids separate from each other
d.Homologous chromosomes pair up
d
3. This is the first stage of meiosis when haploid cells are first formed.
a. Anaphase II
b.Metaphase I
c. Telophase I
d.Metaphase II
c
4. This event occurs only during meiosis, but not during mitosis.
a. Spindle fiber formation
b. Synapsis
c. Dissolution of nuclear envelope
d. Movement of chromatids to opposite poles
b

5. This onion root tip cell is in the _____ Stage of mitosis.
a. Telophase
b. Metaphase
c. Anaphase
d. Prophase5. This onion root tip cell is in the _____
S
c
Think of a commonplace event or game which represents the process of
the first cell division of meiosis.
1. Phenylketoneuria (PKU) is caused by a recessive allele (p). A man and a woman, both heterozygous, marry. What is the probability that a child of theirs will have the normal phenotype?
a. 0%
b. 25%
c. 75%
d. 100%
2. Polydactyly (6 digits on hands or toes) is a dominant trait. A polydactylous man marries a normal woman. What proportion of their children would be polydactylous?
a. 25%
b. 50%
c. 75%
d. 100%
3. In Labrador Retrievers, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b) and normal vision (N) over blindness (n). Assume independent assortment. If a brown, blind female mates with black, sighted male and they have a black , blind puppy, what was the genotype of the male?
a. BBNn
b. BbNn
c. BbNn
d. Cannot be determined