Unit 2 - New World Colonies (1607-1754)
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes key terms (people & groups, places & events, systems & ideas)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms

John Smith & John Rolfe
John Smith —> English soldier, explorer, colonial governor, and author. Established Jamestown Colony.
John Rolfe —> a Jamestown leader who successfully cultivated tobacco and married Pocahontas

John Winthrop
English Puritan lawyer, one of the leading figures in founding the Massachusetts Bay Colony —> the second major settlement in New England following Plymouth Colony
Led the first large wave of immigrants from England in 1630 and served as governor for 12 of the colony’s first 20 years
Gave the “City Upon a Hill” sermon

Metacom (King Philip)
Also known as Metacomet —> chief to the Wampanoag people and the second son of the sachem Massasoit
Became chief in 1662

William Bradford
English Separatist leader —> founder of the Plymouth Colony after traveling on the Mayflower in 1620
Parliament
The elected legislative body of the British government that makes laws and decisions —> mostly followed salutary neglect towards colonies, some laws like Navigation Acts(1651) targeted colonists
Indentured Servants
People who entered into a work contrsact for a set number of years in exchange for paid passage to the New World and housing for the length of work
After completion of the contract they were often given their own plot of land to farm
Declined in favor of African slavery as a consequence of Bacon’s Rebellion
Enslaved Africans
Captured and kidnapped Africans were brought to the Americas via the Middle Passage of the Triangle Trade to work on plantations
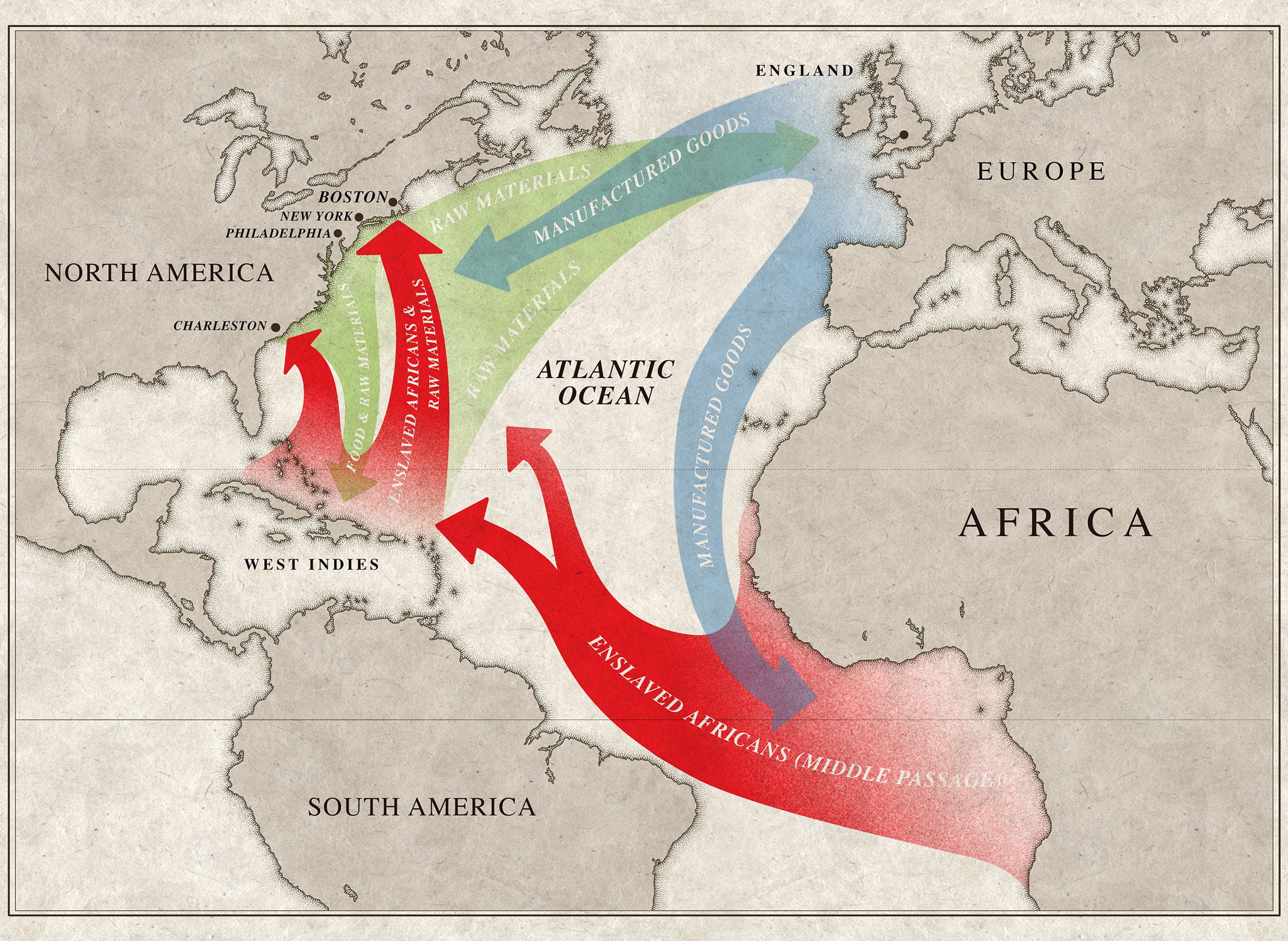

Virginia Company
A joint-stock company that received a charter to found Jamestown, Virginia in hopes of profiting from gold and silver

Bacon’s Rebellion
A rebellion of farmers and lower class groups against the colonial Virginia government which ultimately led to the deliberate institutionalization of racial slavery

Pequot War
First sustained conflict between the Pequot tribe and expanding Puritans in New England over land disputes
1636-1637
Pequots lost following Mystic Massacre

King Philip’s War
A bloody war between English colonists and their native allies against the Wampanoag of New England
1675-1676
Metacom was killed and the colonists won
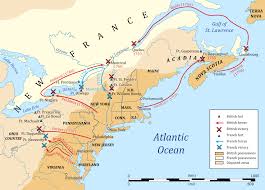
New France
A colony established in Canada (now Quebec) in 1608, that stretched down the Mississippi River
Known for fur trade, Jesuit missionaries, & friendly native relations
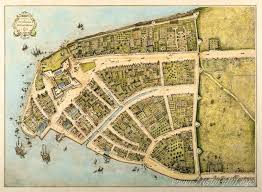
New Amsterdam
Dutch Capitol of their New Netherland colony
Noted for tolerance of religions
It failed to attract enough settlers, conquered by English in 1664, renamed New York City
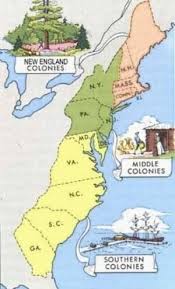
Colonial Regions
New England, Middle Colonies, and Southern Colonies
The regions developed distinct economic & social characteristics based on their geographic locations, available resources, and founding motivations
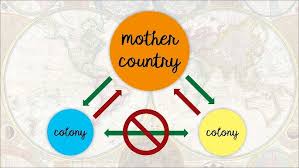
Mercantilism
Economic idea in which colonies exist to provide the mother country profit
Colonies provide raw materials and as a market to buy finished goods from mother country
Chattel Slavery
America’s version of racial slavery where people are treated as chattel (personal property) of the owner and are bought and sold as commodities
Self-Government
All 3 regions had some forms of self-government, mostly for land-owning white men
House of Burgesses(Virginia) and Mayflower Compact(Massachusetts) are early examples

Cash Crops
Crops planted to sell for profit
Southern plantations grew tobacco, indigo, and rice
Middle colonies grew grains
The North-Eastern colonies climate was too cold

1607
Jamestown Colony founded for profit
1609-1610
Starving Time in Jamestown
1619
First enslaved Africans arrive in British colonies
1620
Mayflower Ship of separatists (pilgrims) arrives
1651
Parliament passes first Navigation Act
1692
Salem Witch Trials
1739
Stono Rebellion —> large slave uprising
1754
Start of the French and Indian War