Glycogen & Glucose Metabolism
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FSHN 3600
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
Glycogenesis occurs in a ___ state and glycogenolysis occurs in the ___ state.
fed, fasted
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
In the fasted state, ___ & ___ are the predominant hormones.
glucagon, epinephrine
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
____ is in the liver and ___ is in the muscle
glucokinase, hexokinase
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
Insulin binds to receptors on ___ cells to stimulate activity of ___.
liver, PP1
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
Glucokinase is ___ by insulin.
induced
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
(T/F) The Km for hexokinase is much lower than for glucokinase.
T
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
Hexokinase is allosterically inhibited by __-__-__.
glc-6-P
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
(T/F): Bother liver & muscle tissue express glc-6-P.
F
Muscle does not express glc-6-
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
Glycolysis occurs in the ___.
Cytosol
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
The hormone ___ regulates three glycolytic enzymes: GK, PFK, and PK.
insulin
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
Glycolysis is the process of oxidizing ___ to ___.
glucose, pyruvate
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
For every one glucose molecule, ___ pyruvate molecules are generated.
2
Regulation of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
For each glucose molecule, there is a net production of molecules of NADH and __ molecules of ATP
2,2
Glycolysis
What do glucokinase (GK), Phosphofructokinase (PFK) and pyruvate kinase (PK) all have in common?
They’re unidirectional enzymes
Glycolysis
What is the substrate for GK?
glucose
Glycolysis
What is the substrate for PFK?
Fructose-6-P
Glycolysis
What is the substrate for PK?
Phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP)
Glycolysis
What is the product of GK?
Glc-6-P
Glycolysis
What is the product of PFK?
Fructose-1,6-biP
Glycolysis
What is the product of PK?
Pyruvate
What are example of allosteric regulation in glycolysis?
(+) High concentrations of ADP and NAD+ stimulate PFK
(-) High concentrations of NADH and ATP inhibit PFK
TCA Cycle
Which enzymes results in the production of CO2?
What reactions do these catalyze?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) — Pyruvate + NAD+ —→ acetyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) — Isocitrate + NAD+ —→ alpha-ketogluterate + CO2 + NADH
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (alpha-KGDH) — alpha-ketogluterate + NAD+ —→ Succinyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH
What are some examples of allosteric regulation that occur in the TCA cycle?
(+) High concentrations of ATP/ADP and NADH/NAD+ stimulate ___, ___, and __-__
(-) High concentrations of acetyl-CoA inhibit __
(-) High concentrations of citrate inhibit __.
1) PDH, IDH, alpha-KGDH
2) PDH
3) PFK
How many molecules of ATP do NADH and FADH2 yield?
1 FADH2 —→ 2 ATP
1 NADH —→ 3 ATP
Shuttle Systems
What are the two?
Hexose monophosphate shunt (HMS) and Malate-aspartate shuttle
Shuttle Systems
What is the purpose of HMS?
to generate a pentose (ribose) from a hexose to produce NADPH
Shuttle Systems
What is the mechanism of HMS?
NADP is reduced back to NADPH to support reductive process.
Shuttle Systems
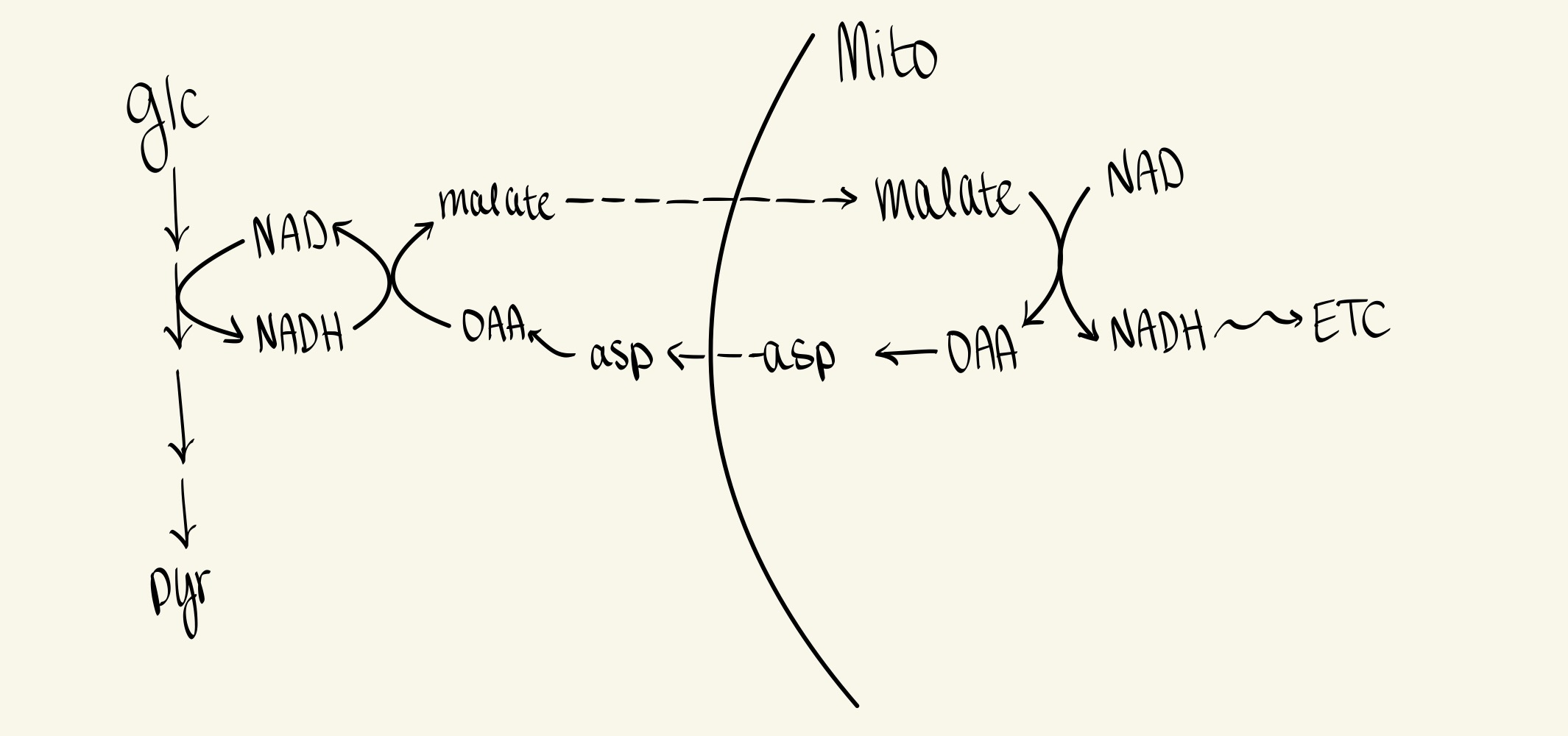
What is the purpose of malate aspartate shuttle?
To allow NADH produced in the cytosol from glycolysis to enter the mitochondria to donate its electrons to the ETC.
Shuttle Systems
What is the mechanism of malate-aspartate shuttle?
NADH in the cytosol is oxidized to NAD+ and OAA is reduced to malate. Malate enters mitochondria and reverse reaction occurs. OAA cannot cross mitochondrial membrane so it’s transaminated to aspartate in mitochondria. Aspartate cross the mitochondrial membrane and is transaminated back to OAA in cytosol.
Shuttle Systems
What is the problem with HMS?
Needs NADPH for reductive anabolic reactions and ribose to form DNA/RNA.
Shuttle Systems
What is the problem with malate-aspartate shuttle?
NADH cannot cross the mitochondrial membrane.
What substrates can be used in gluconeogenesis?
NonCHO precursors such as amino acids, lactate, and glycerol.
Where does gluconeogenesis primarily occur?
Liver
Gluconeogenesis
What is pyruvate carboxylase’s substrate & product?
Substrate: pyruvate
Product: OAA
Gluconeogenesis
What is phosphoenolpyruvate’s (PEPCK) substrate & product?
Substrate: OAA
Product: PEP
Gluconeogenesis
What is fructose-1,6-biphosphatase’s substrate & product
Substrate: Fructose-1,6-biP
Product: Fructose-6-P
What is glucose-6-phosphatase’s substrate & product?
Substrate: Glc-6-P
Product: Glucose
An example of protein regulation in gluconeogenesis:
(+) Glucagon induces PC, PEPCK, fructose-1,6-biphosphatase, & glc-6-phosphatase
Hyperglycemia:
high circulating concentrations of glucose
Polyuria:
frequent urination
Polydipsia:
excessive thirst
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs):
prolonged high circulating glucose concentrations causing protein to become glycosylated (CHO added to protein)
Type 1 diabetes:
an autoimmune condition where the immune system destroys the beta cells of the pancreas, resulting in lack of insulin
Type 2 diabetes:
lack of cellular responsiveness to insulin
in muscle and adipose tissue, GLUT4 doesn’t translocate to the cell membrane
Resistant starch:
a broad category of dietary compounds that aren’t digested and absorbed
serves as energy source for gut microbiota
How can NADH cross into the mitochondrial membrane
Malate-aspartate shuttle