Thunderstorms and Weather
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What causes a thunderstorm
A thunderstorm forms when warm air rises, and cold air sinks
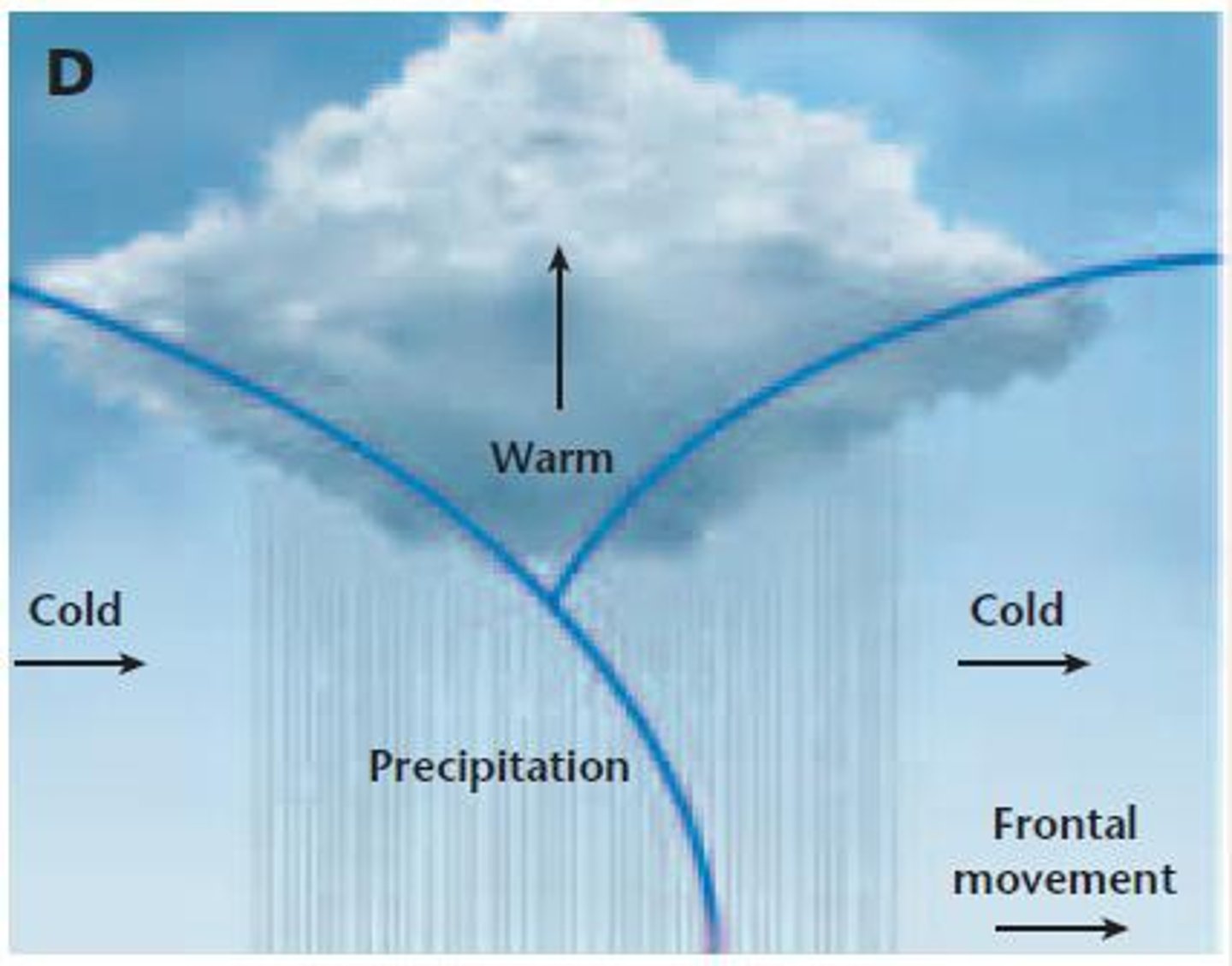
What are the stages of a thunderstorm
cumulus stage, mature stage, dissipating stage
cumulus stage
The first stage of a thunderstorm when a thunderstorm is first starting, and warm air rises to make big, fluffy clouds that grow
the mature stage
The second phase of a thunderstorm, when it is the strongest, with heavy rain, lightning, thunder, and sometimes hail falling from the big cloud.
The dissipating stage
The final stage is when the storm gets weaker, the rain slows down, and clouds start breaking apart and disappearing
What causes lightning
Inside the storm cloud, water and ice bump together and create electric charges, and when those charges build up, they form lightning.
Why does thunder occur?
rapid heating and cooling of air surrounding a lightning bolt
How does a tornado form?
A tornado forms when spinning air inside a powerful thunderstorm gets turned upright by rising warm air and touches the ground.
Why is there more than one circulation cell in the atmosphere in the Northern Hemisphere?
Earth is large and rotating, so the air breaks into three smaller circulation cells instead of one big one to move heat more efficiently.
Why do storm systems track from West to East across North America?
because the jet stream and prevailing winds high in the atmosphere blow from west to east, carrying the storms along with them.
Why do hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin near the Equator track from East to West?
Because the trade winds in that part of the world blow from east to west, pushing the storms along in that direction.
What are the two air masses that give us cold fronts and warm fronts in North America?
Cold fronts come from the Canadian air.
Warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico.
Why is water on earth so important?
Every living thing needs water
What determines waters state
Whether it is a solid, liquid, or gas. It is determined by the temperature around it.
What is humidity?
The amount of water vapor in the air
What is relative humidity?
how full the air is with water vapor compared to how much it could hold at that temperature.
What is dew point temperature
The temperature at which the air becomes cool enough for water vapor to turn into tiny droplets, like dew on grass.
What is the difference between high and low pressure?
High pressure brings sinking air and usually clear, calm weather. Low pressure brings rising air and usually cloudy, stormy weather
What is the difference between weather and climate?
The weather is the day-to-day conditions outside, like whether it is sunny or rainy today. Climate refers to the typical weather conditions in a particular location over an extended period, such as the usual cold winters and warm summers.
What is the composition of the atmosphere
The atmosphere, which is the air surrounding the Earth, is primarily composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with small amounts of other gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
How do greenhouse gases work?
Greenhouse Gases act like a warm blanket around the Earth. They let sunlight in but keep some heat from escaping, which helps keep our planet warm enough for us to live.
What are the layers of the atmosphere?
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
troposphere
the lowest layer of the atmosphere
Stratosphere
The second-lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere.
Mesosphere
The strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core
thermosphere
The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere.
Exosphere
The outer layer of the thermosphere, extending outward into space.
How do we recognize the layers of the atmosphere?
because temperature and air pressure change in specific ways as you go higher