T2 PP PMT
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
POST2017(EOS[1-18] DNAGEN[19-34](20/50) PROTEINS[35-41](15/35) INH[42-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
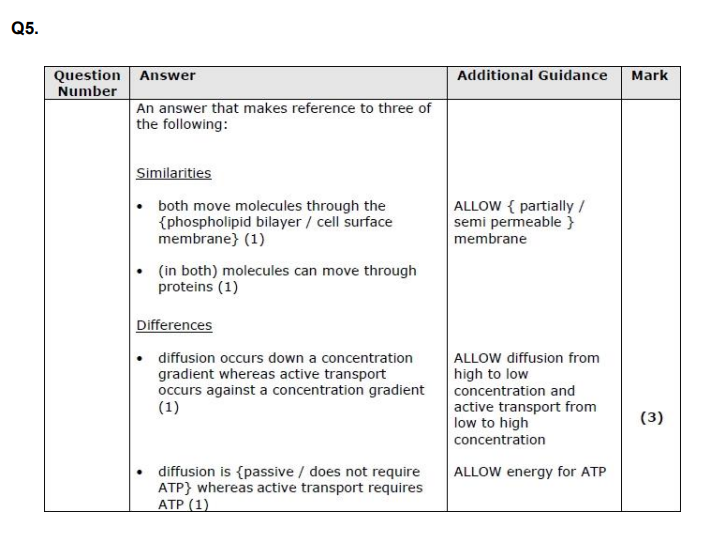
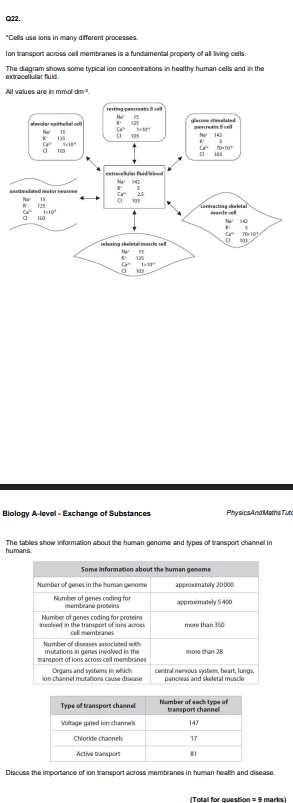
Diffusion and active transport are mechanisms by which molecules can enter cells. Compare and contrast these two mechanisms. (3)
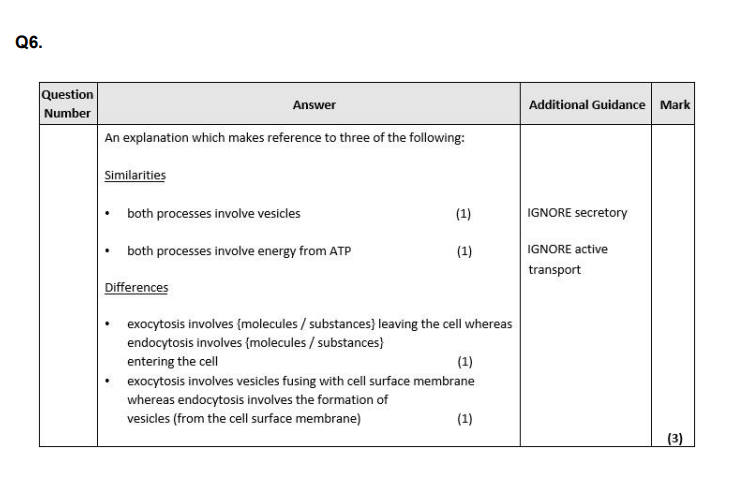
Endocytosis and exocytosis are processes that move large molecules into a cell or out of a cell. Compare and contrast the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis. (3)
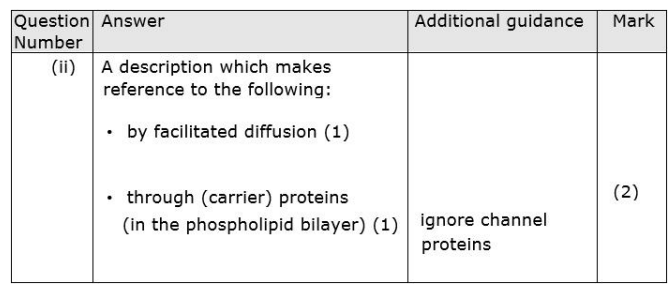
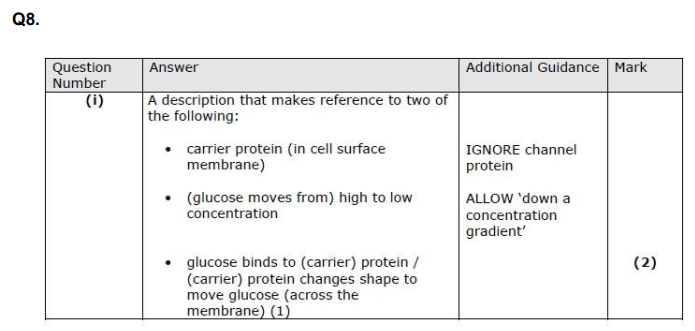
Describe how glucose molecules move into the cell. (2)
Describe how glucose moves into cells by facilitated diffusion. (2)
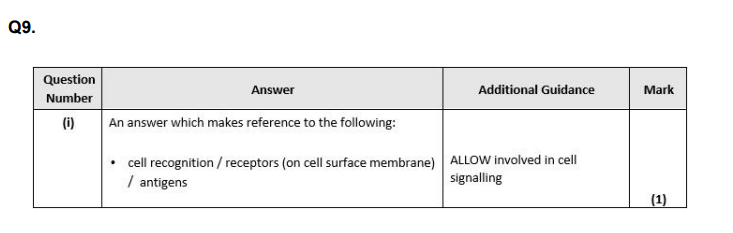
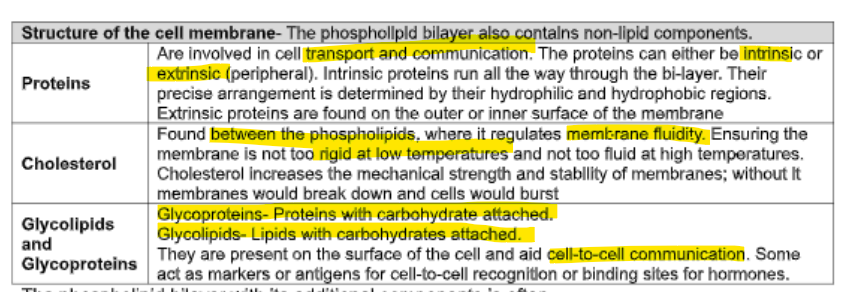
Give one function of the glycoproteins found in the cell surface membrane. (1)
Explain how the structure of a phospholipid molecule contributes to the partial permeability of a cell surface membrane. (3)

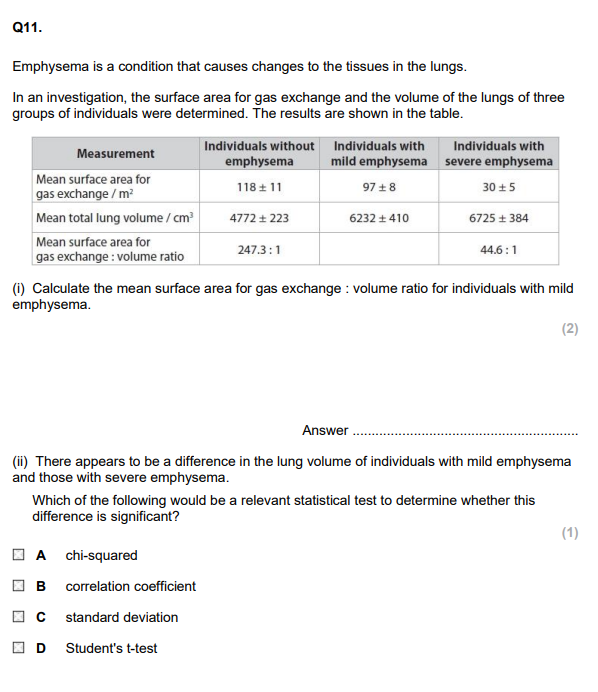
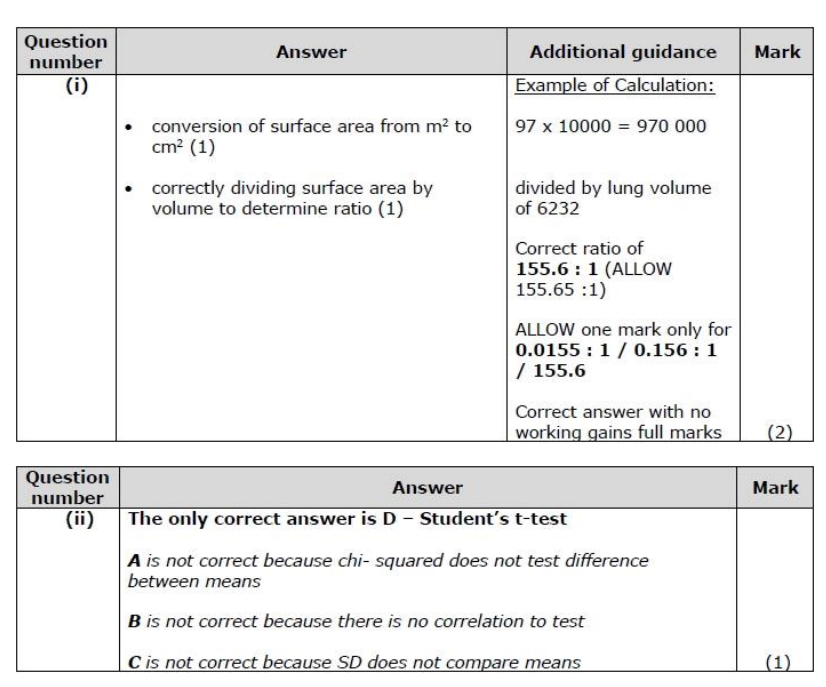
Give reasons for the variation in the lung volumes of healthy individuals. (2)
diff height/mass
diff sex
diff age
Explain why the phospholipids are arranged in two layers in a cell surface membrane. (3)
Describe the function of carrier proteins in a cell surface membrane. (4)
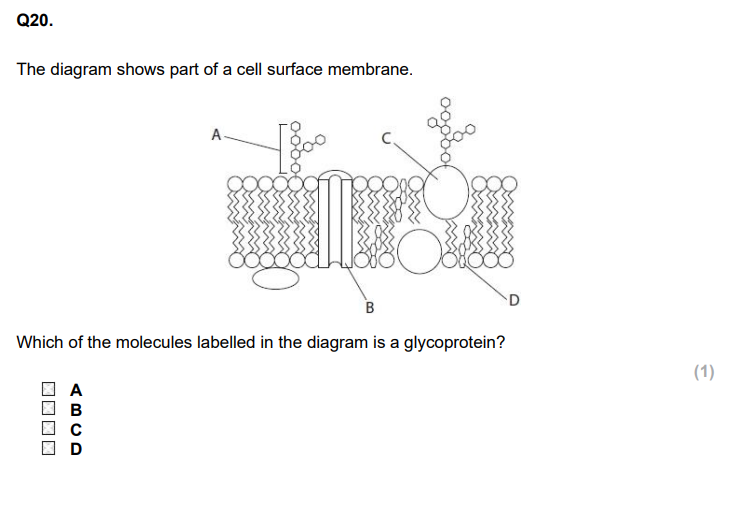
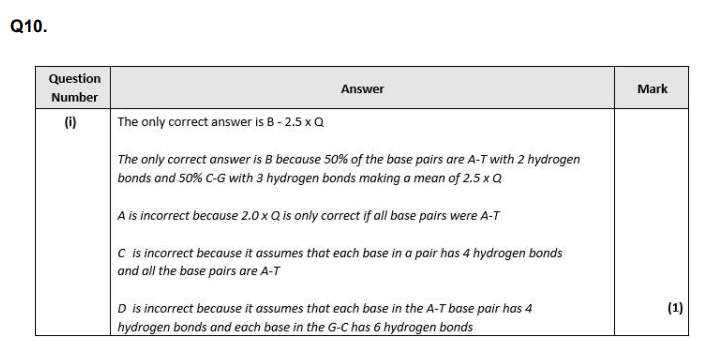
C
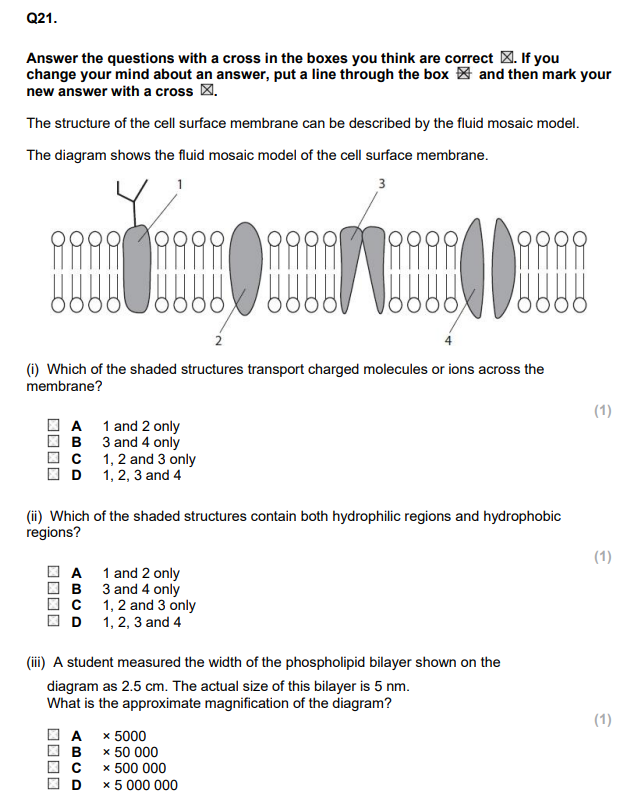
??
BD
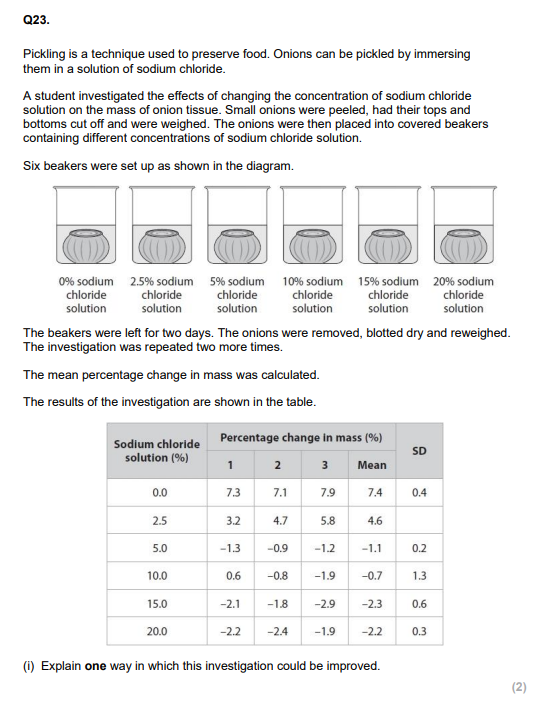
Calculate the standard deviation for the 2.5% sodium chloride solution. (2)
Deduce the effect of increasing the concentration of sodium chloride on the change in mass of the onion tissue. (3)
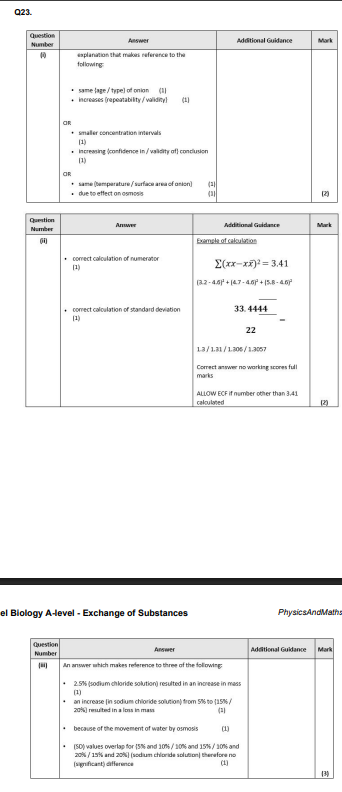

D
B
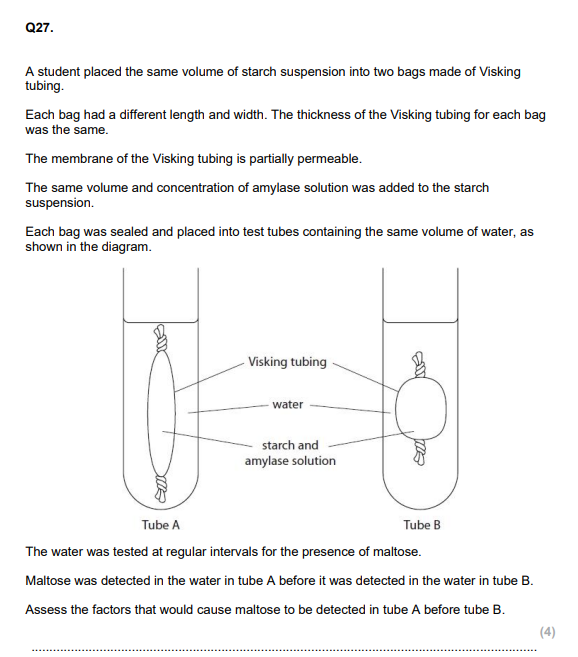
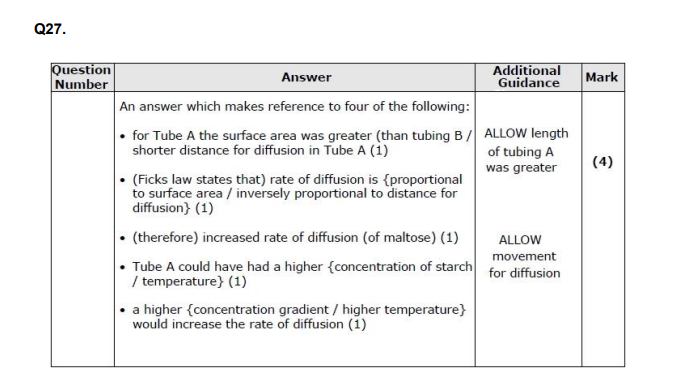
Describe the structure of the cell surface membrane. (3)
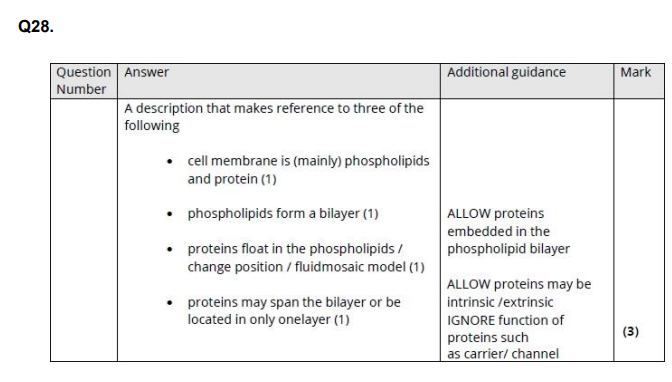
Explain how the structure of the human lungs enables rapid gas exchange. (4)
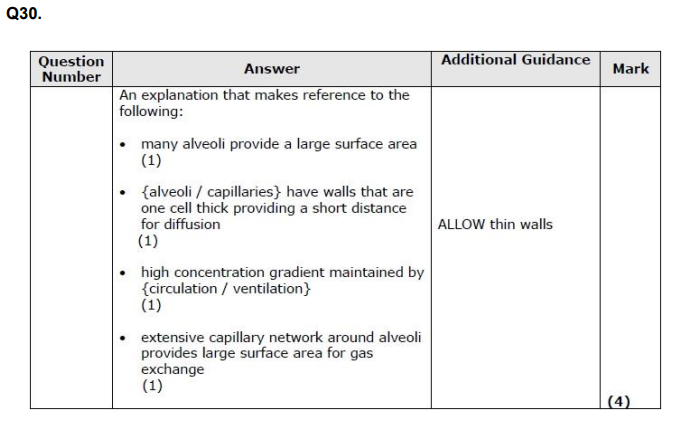
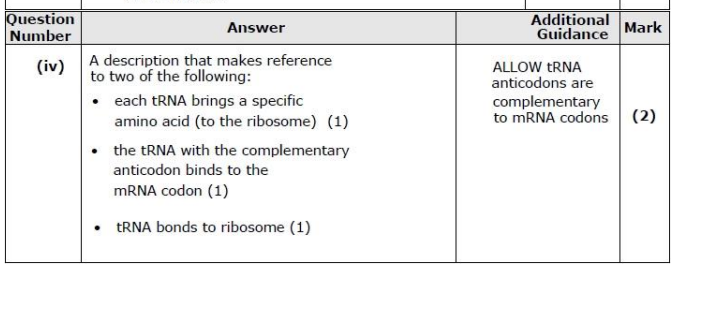
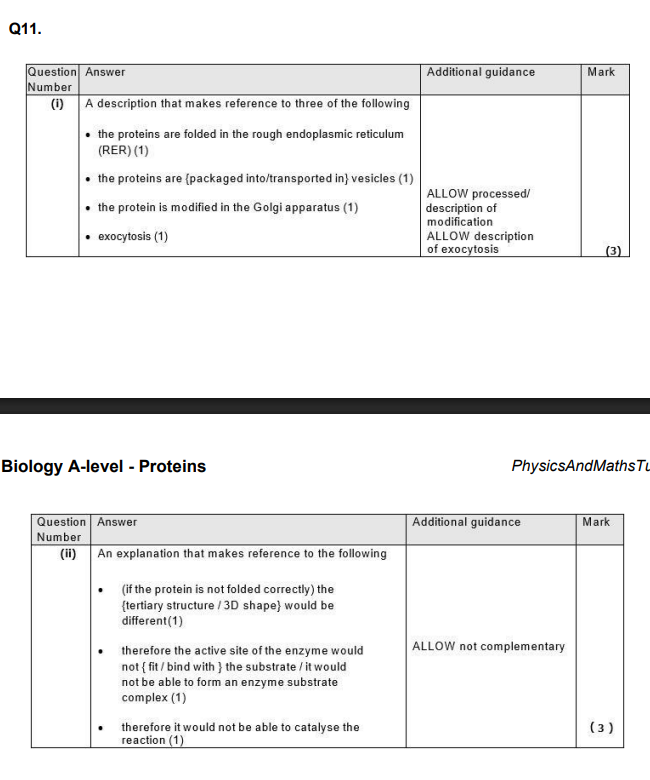
Describe the role of the tRNA in the production of the protein part of a glycoprotein. (2)
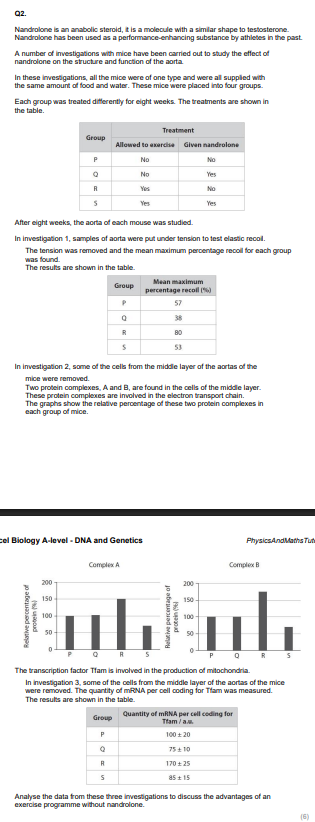
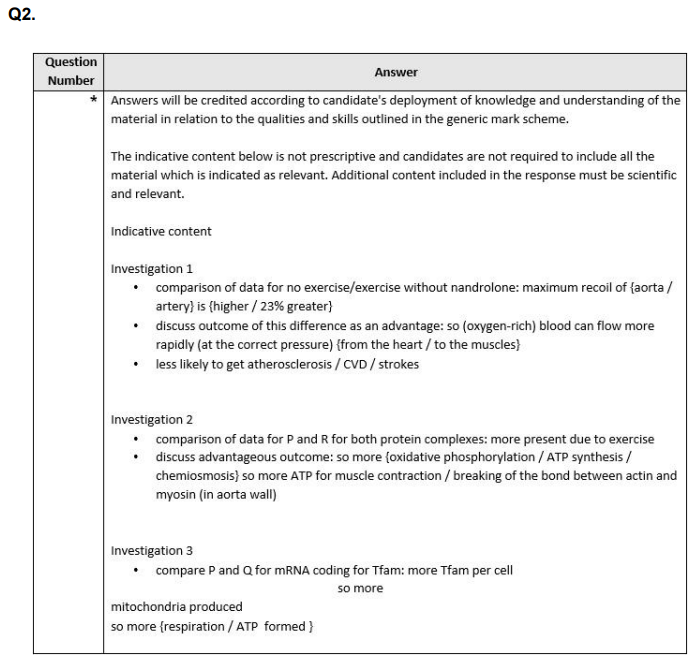


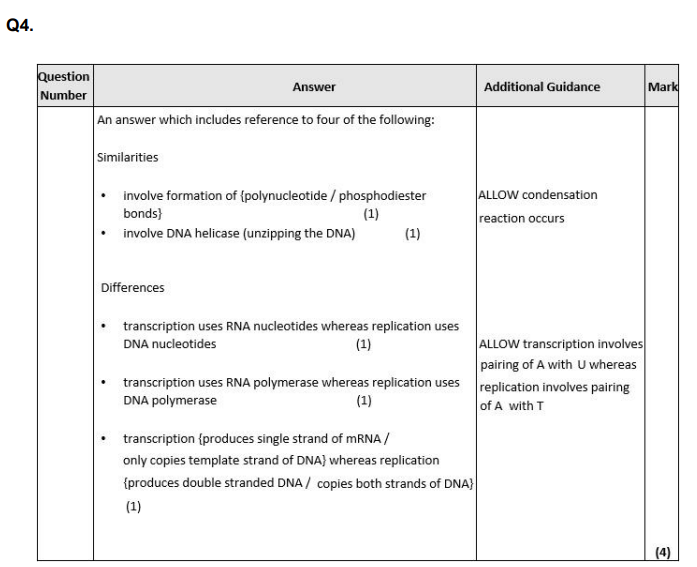
Q4. The synthesis of mRNA occurs in a process called transcription. Compare and contrast the process of transcription with the process of DNA replication. (4)
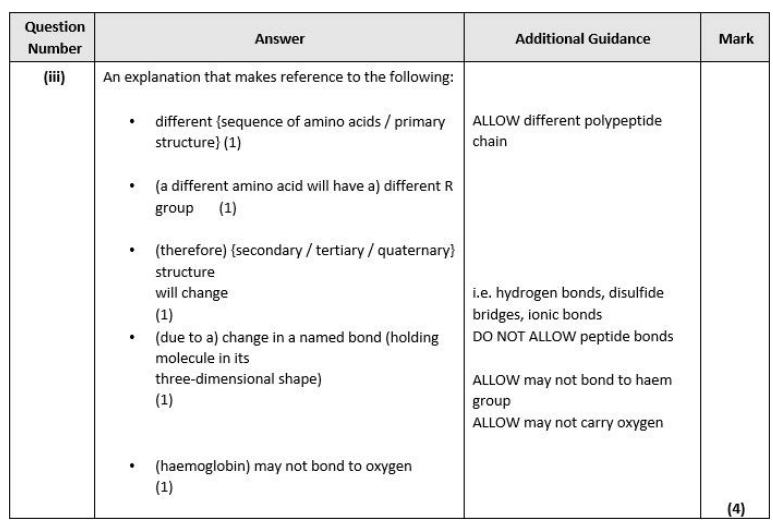
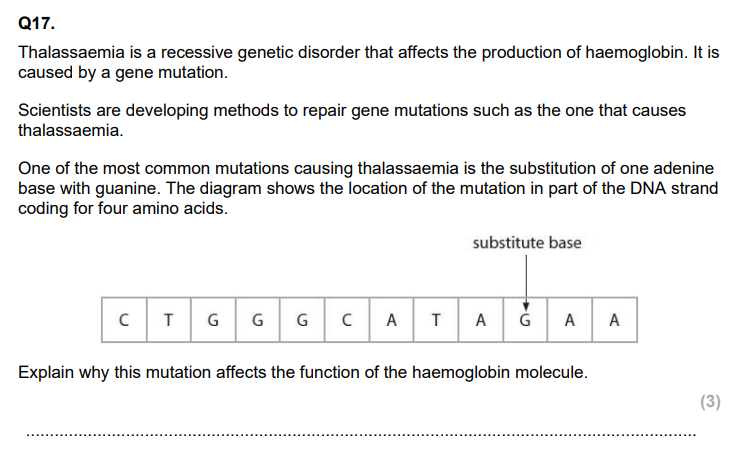
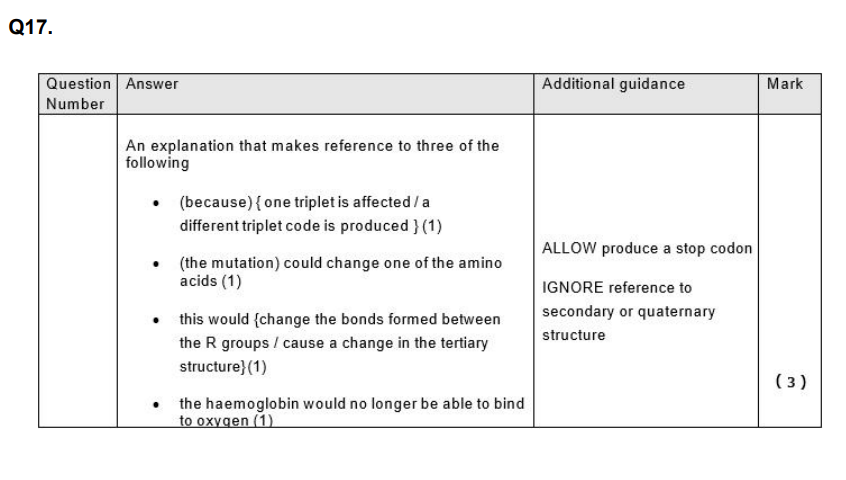
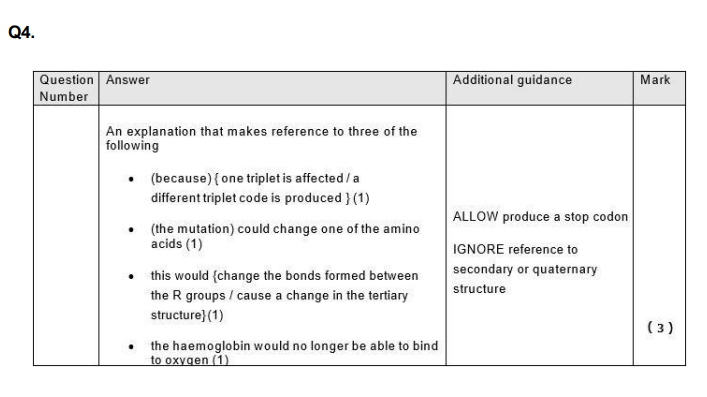
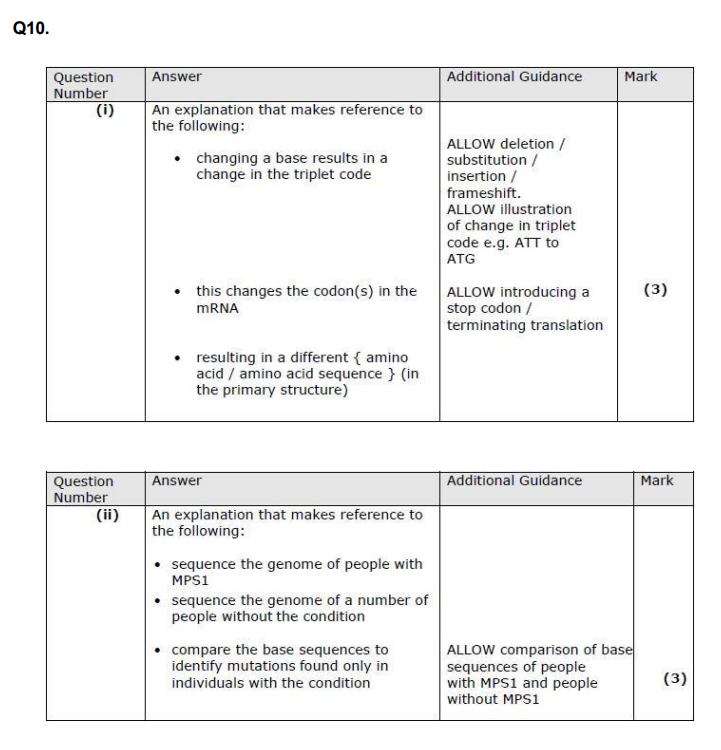
Explain how a change of one amino acid could lead to a change in the structure and properties of the haemoglobin protein. (4)
Leptin is a protein hormone with a role in the control of appetite in humans. The leptin gene is located on chromosome 17.
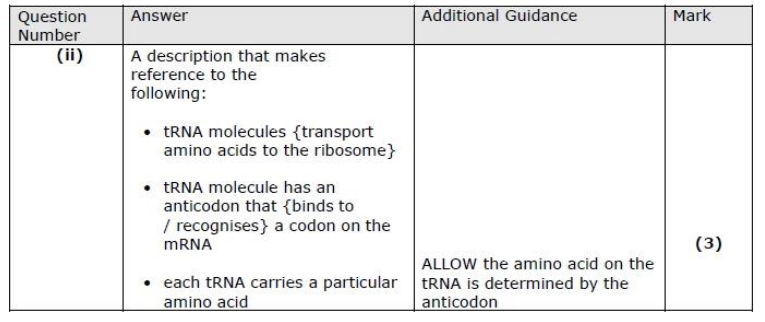
(ii) Describe the role of tRNA in the production of leptin. (3)
Leptin is a protein hormone with a role in the control of appetite in humans. The leptin gene is located on chromosome 17.
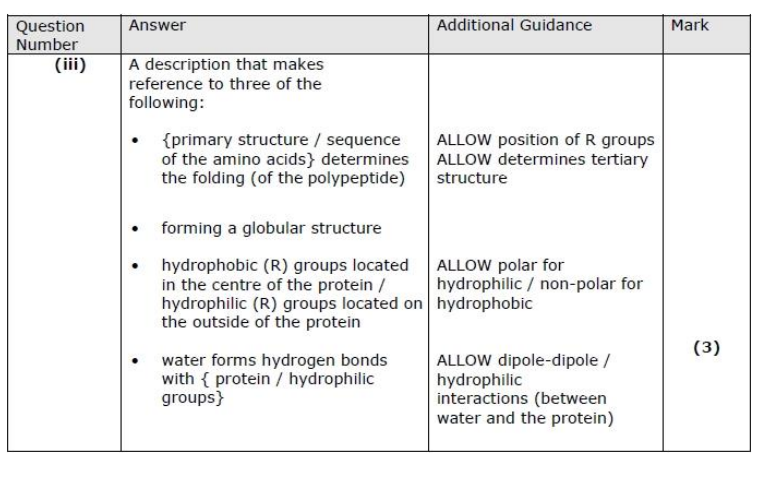
Describe how the primary structure of leptin enables it to be soluble in water. (3)

!
Describe how mRNA is synthesised at a template strand of DNA. (2)

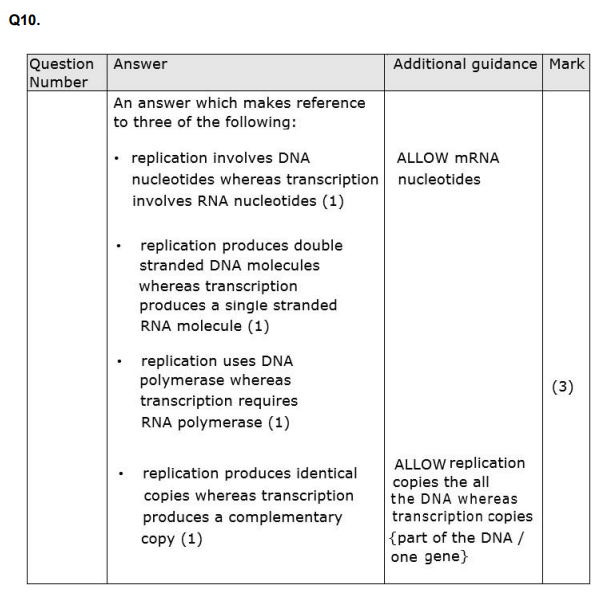
Q10. Give three differences between replication of DNA and transcription of DNA. (3)



A human gene is 27 000 base pairs long. In this section of double-stranded DNA there are 4050 nucleotides containing the base cytosine.
C
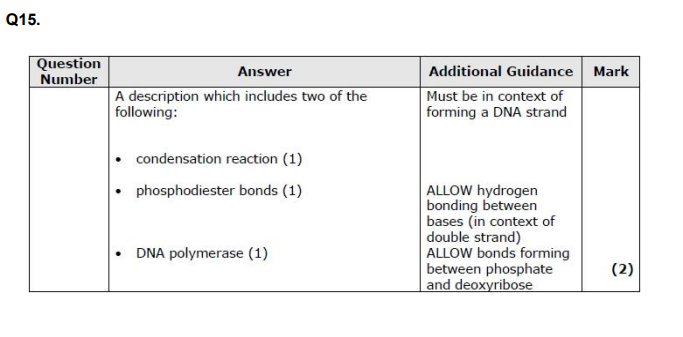
Describe how nucleotides join together to form DNA. (2)



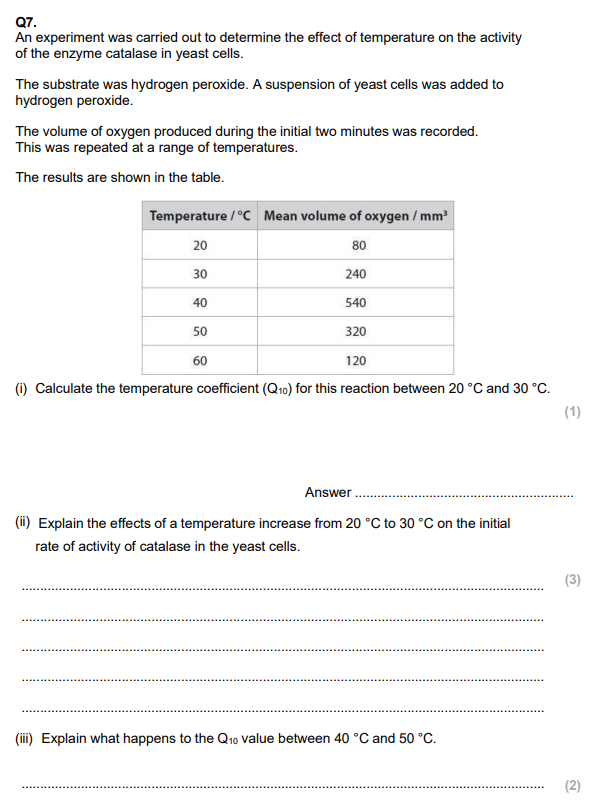
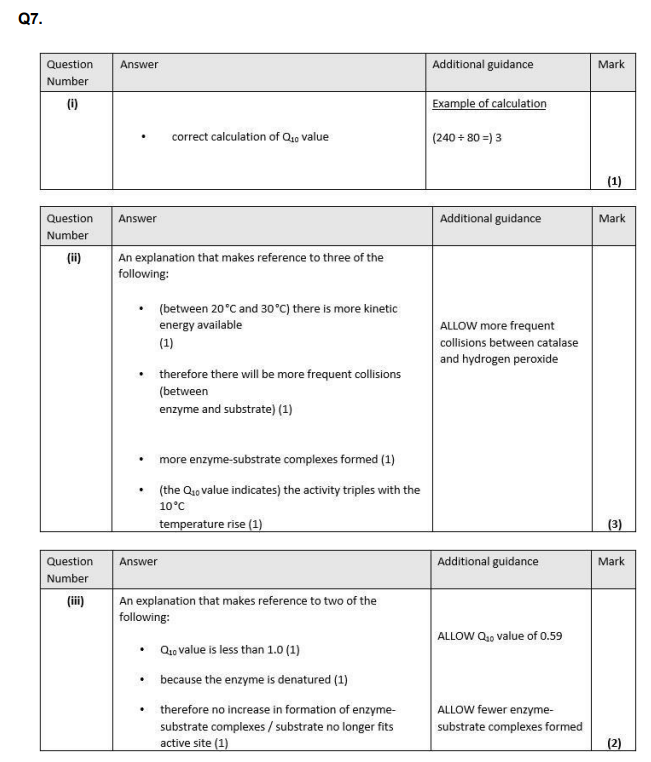

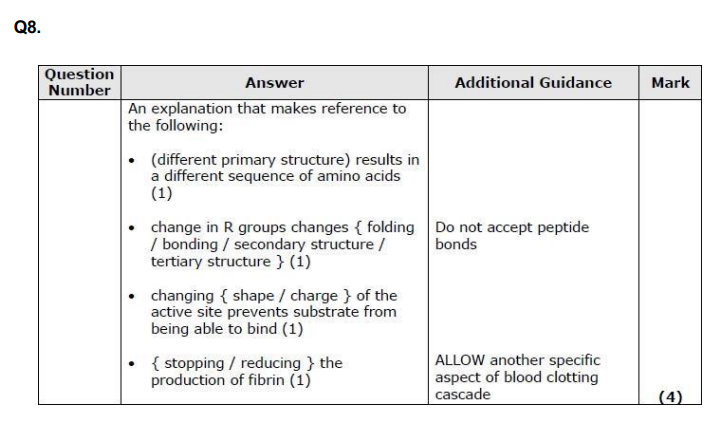
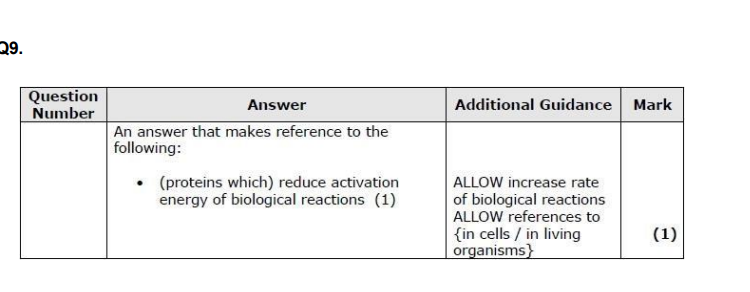
State why enzymes are described as biological catalysts. (1)


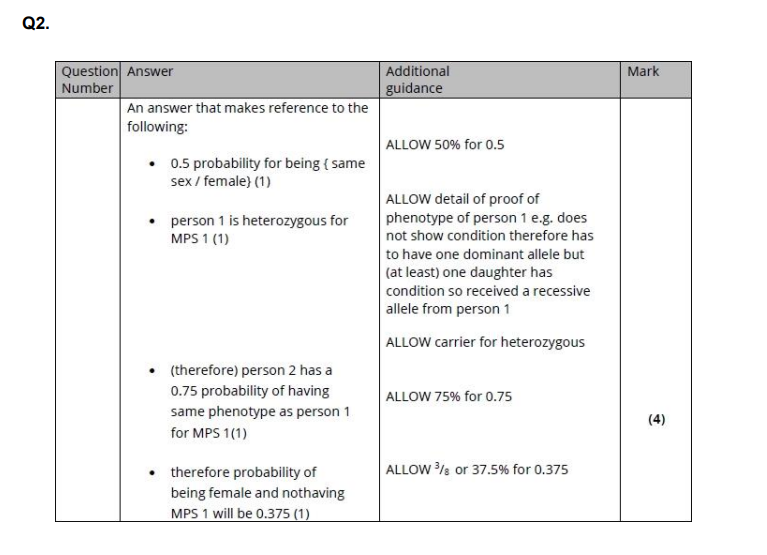

?


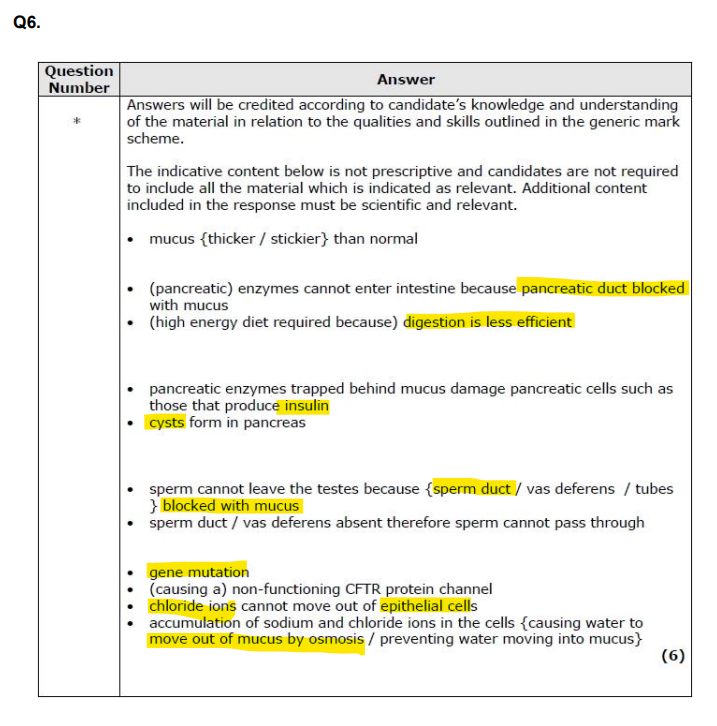
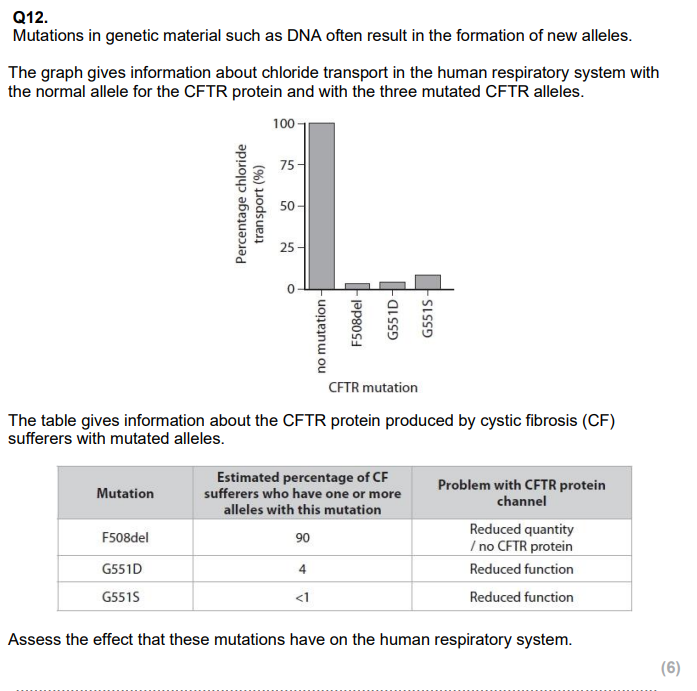
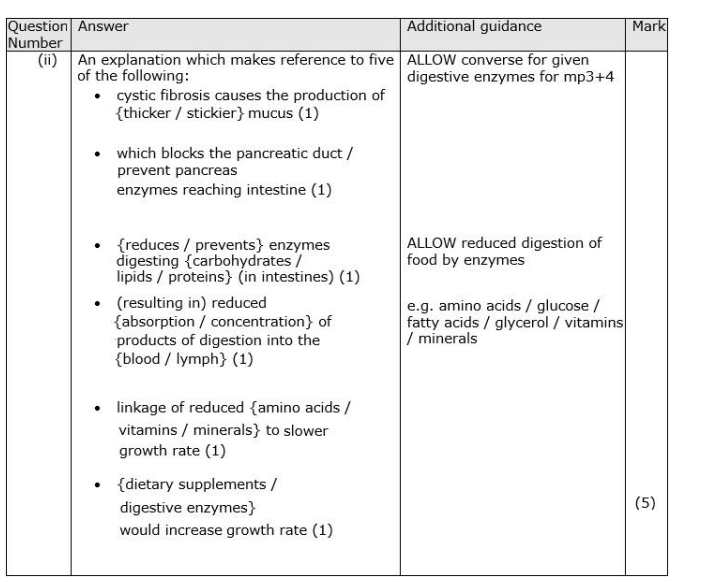
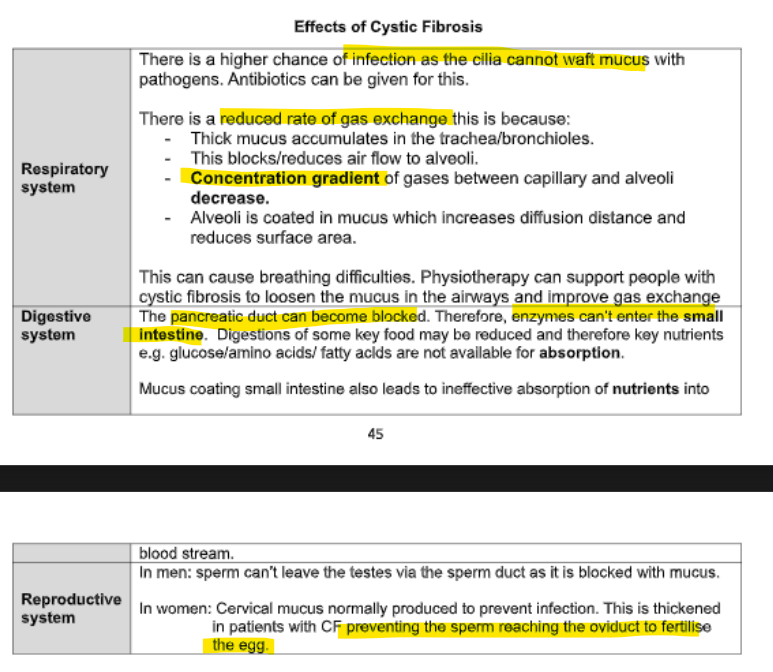
Explain why cystic fibrosis affects the rate of oxygen uptake in the lungs. (3)
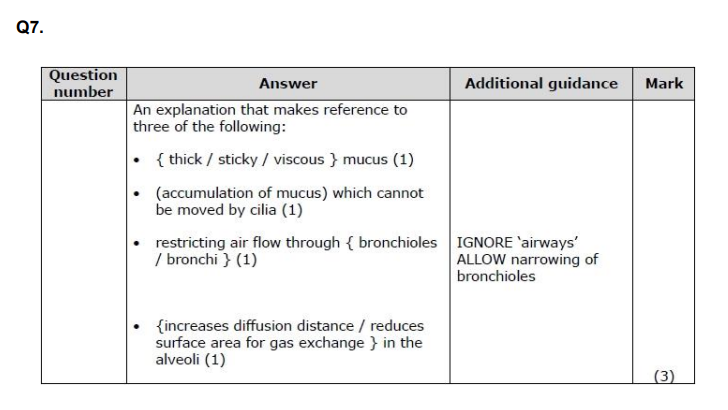
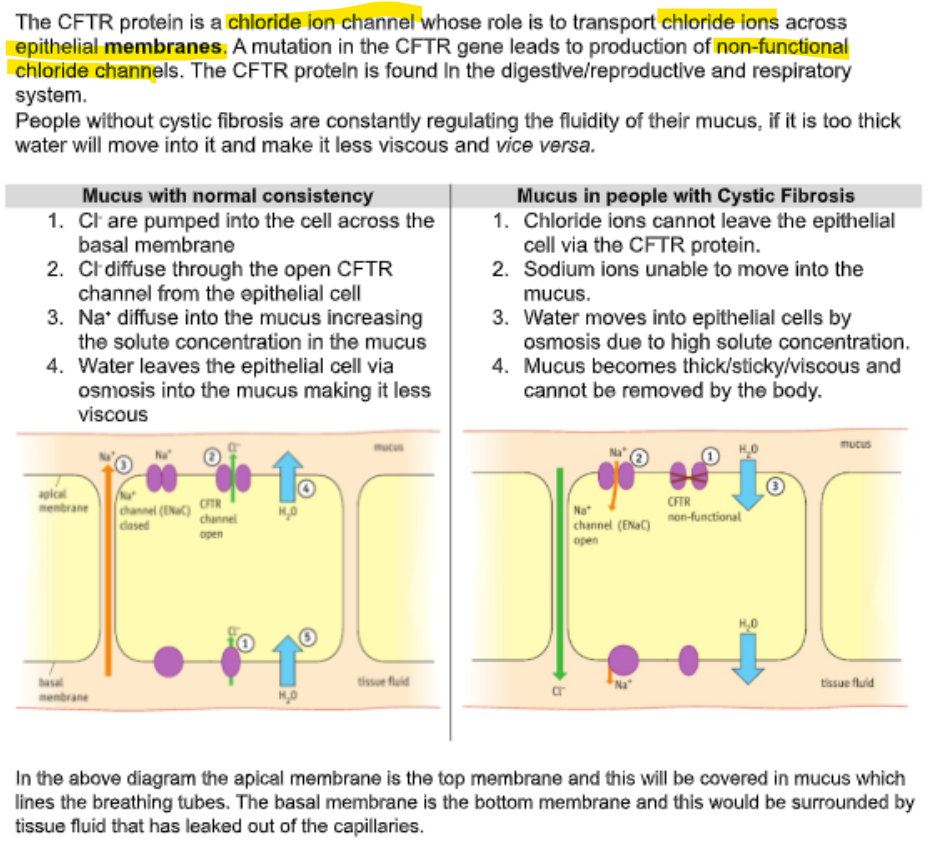
Explain why thicker mucus is produced if the functioning of the CFTR channel protein is impaired. (2)
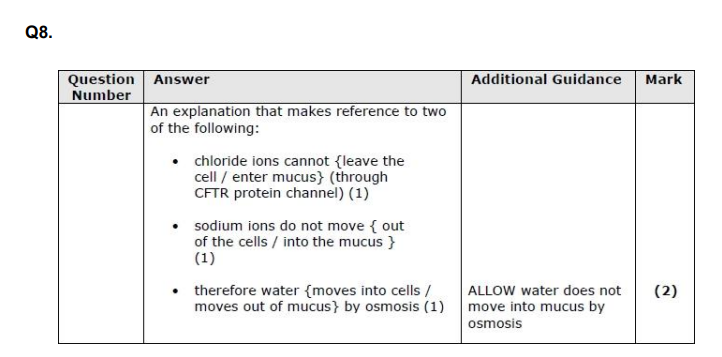

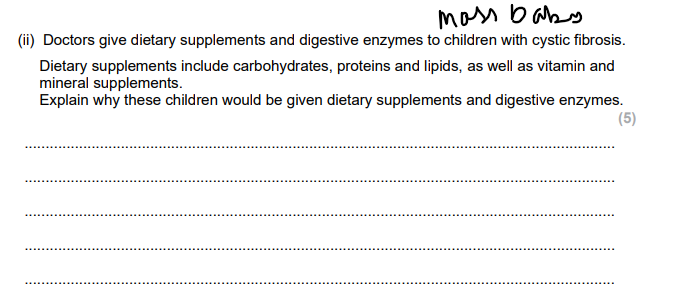

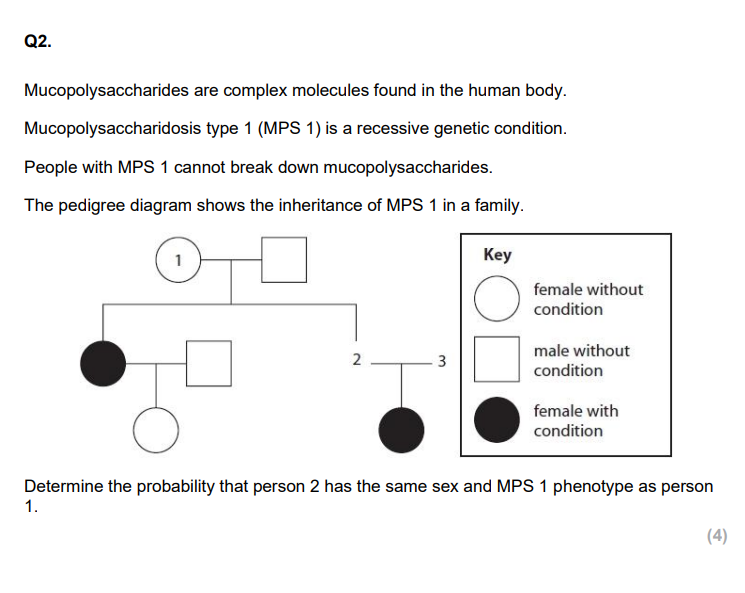
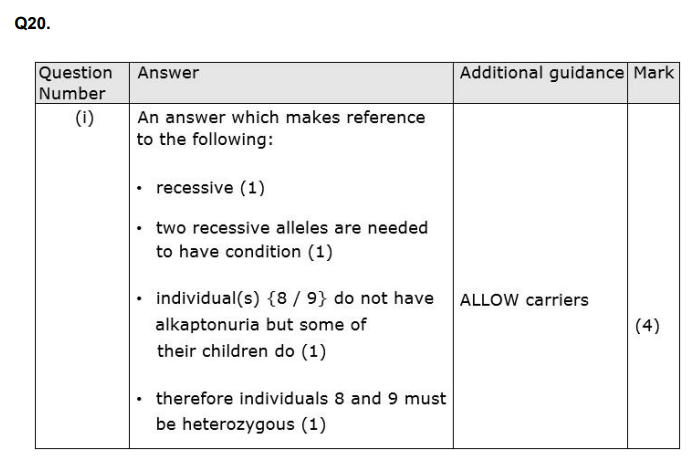
Explain why this couple may choose not to have this test. (3)
Explain what is meant by an inherited recessive disorder. (2)

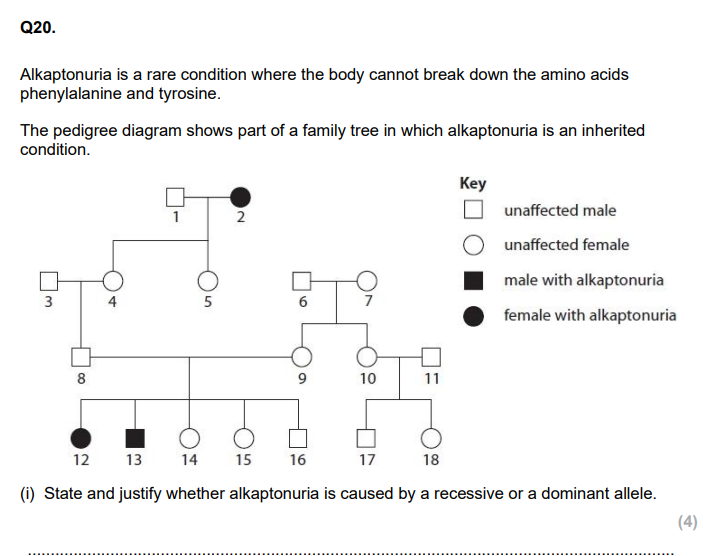


properties of lungs (4)
spongy - gas pockets to allow for gas exchange
red - lots capillaries
thin membrane - short diffusion distance
alveoli - inc SA
lungs role
The role of lungs is to maximise gas exchange while minimising the loss of water across the exchange surface
whats the trachea
Trachea
The trachea is the tube that allows air to travel to the lungs
It contains c-shaped rings of cartilage that ensure that the tube remains open at all times and does not collapse
The c-shape prevents any friction from rubbing with the oesophagus located close behind, as well as providing increased flexibility when food is being swallowed
There is a layer of mucus covering the lining of the trachea that helps to trap dust and pathogens, preventing them from entering the lungs where they could cause infection
Tiny hairs called cilia are also found on the lining of the airways, where they waft mucus towards the top of the trachea, removing any trapped particles and pathogens from the airways
bronchi?
Bronchi
Bronchi (singular bronchus) have a similar structure to the trachea but they have thinner walls and a smaller diameter
The cartilage rings in the bronchi are full circles rather than c-shaped
alveoli?\
Alveoli
Groups of alveoli are located at the ends of the bronchioles
single layer of flattened, or squamous, epithelium
The squamous epithelium forms the alveolar wall and is very thin and permeable for the easy diffusion of gases
The alveoli are surrounded by elastic fibres, allowing them to stretch during inhalation
Alveoli are surrounded by an extensive capillary network
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the capillaries and into the alveoli to be exhaled, while oxygen diffuses from the alveoli and into the capillaries to be carried around the body
A layer of moisture lines the alveoli, facilitating the diffusion of gases
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are able to dissolve in the layer of moisture, so exchange occurs in solution rather than with the air inside the alveoli
bronchioles?
Bronchioles
Carry air to the alveoli – the tiny air sacs where gas exchange happens.
Control airflow – they can constrict or dilate to regulate how much air reaches different parts of the lung.
Filter, warm, and moisten air – like the rest of the respiratory tract, bronchioles help condition the air before it reaches the alveoli.
Bronchioles are narrow, self-supporting tubes with thin walls
There is a large number of bronchioles present in the gas exchange system
Each one varies in size, getting smaller as they get closer to the alveoli
The larger bronchioles possess elastic fibres and smooth muscle that enable adjustment of the size of the airway to increase or decrease airflow
The smallest bronchioles do not have any smooth muscle but they do have elastic fibres
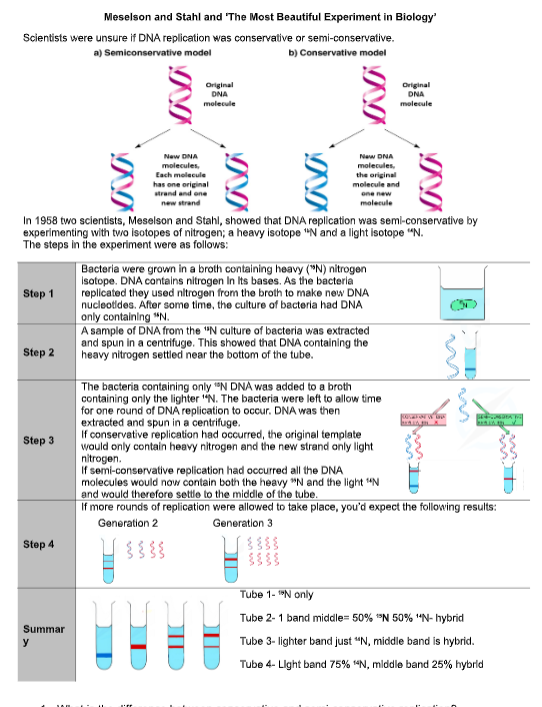
explain DNA replication

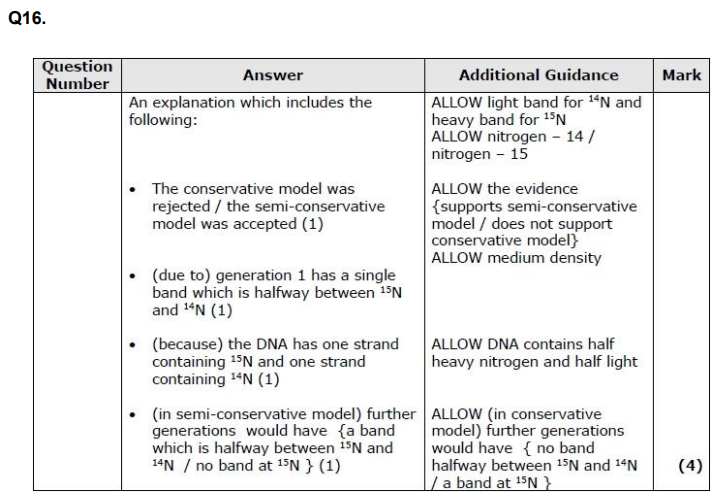
Meselson and stahl?
explain base sequences

5 factors of genetic code
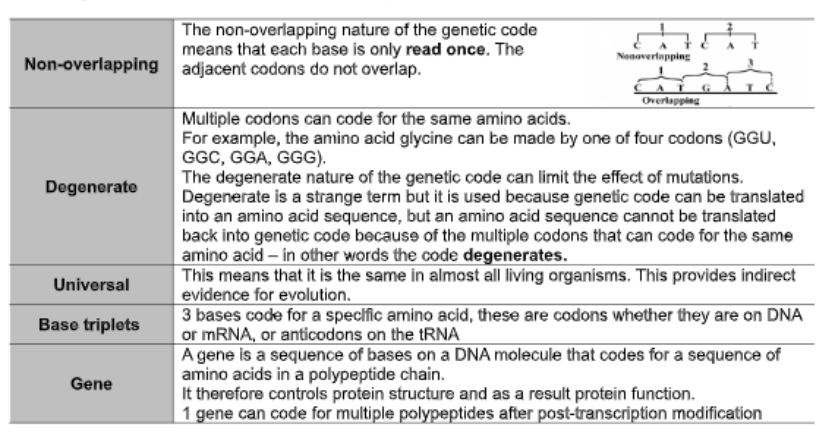
explain trancription

what is post transcriptional modification

explain trasnlation
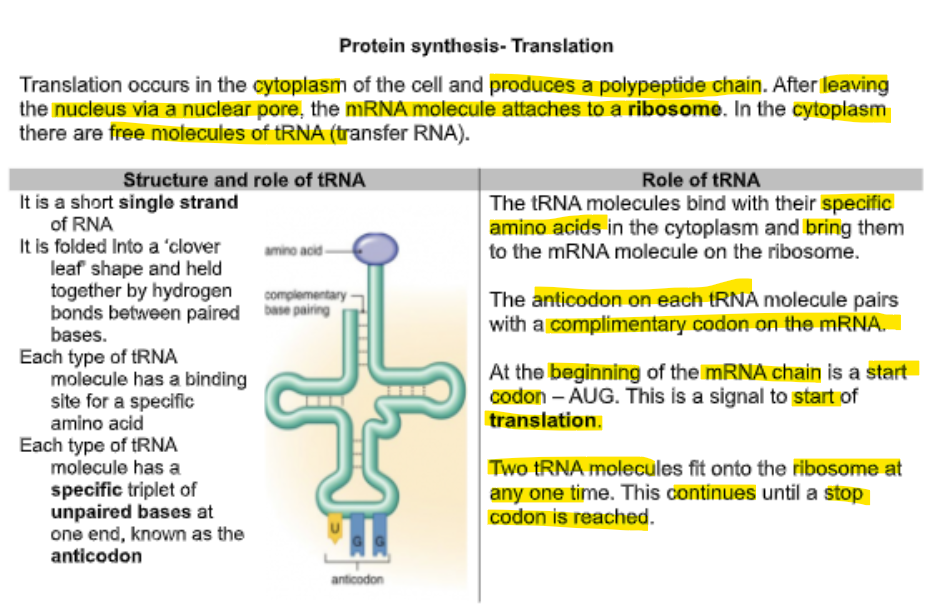
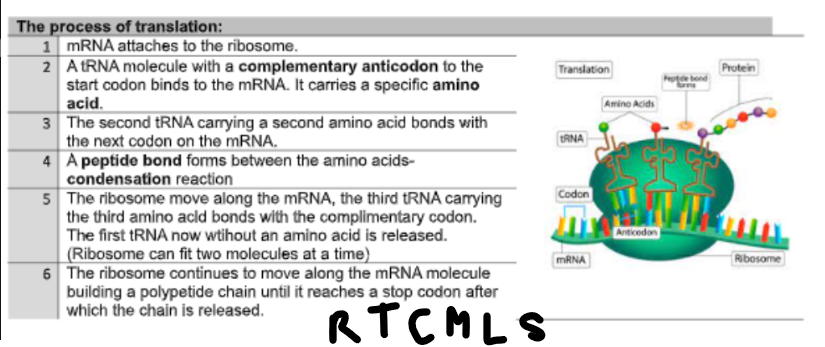
process of translation
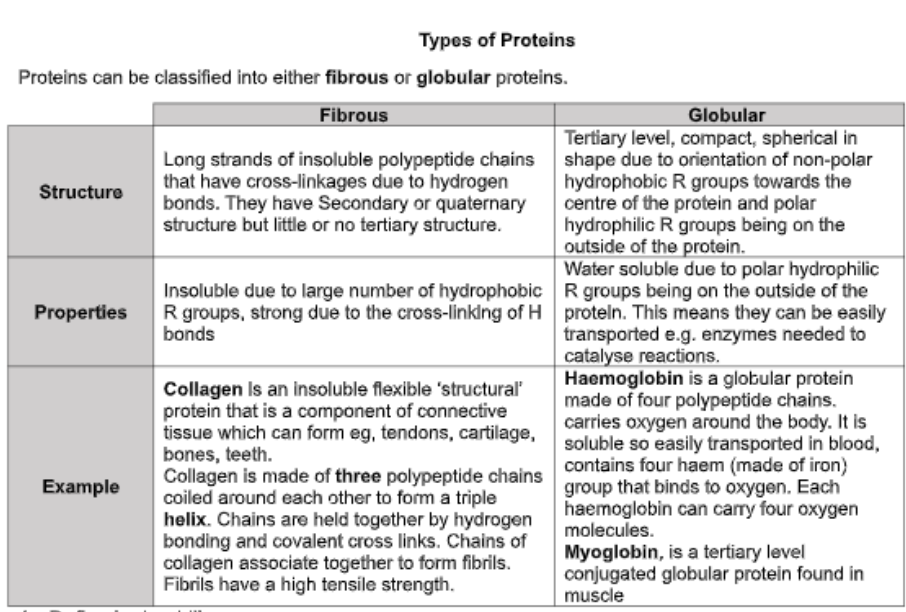
compare fibrous and globular proteins!!!!!
what extra things in cell membrane
differences between carrier and channel proteins?

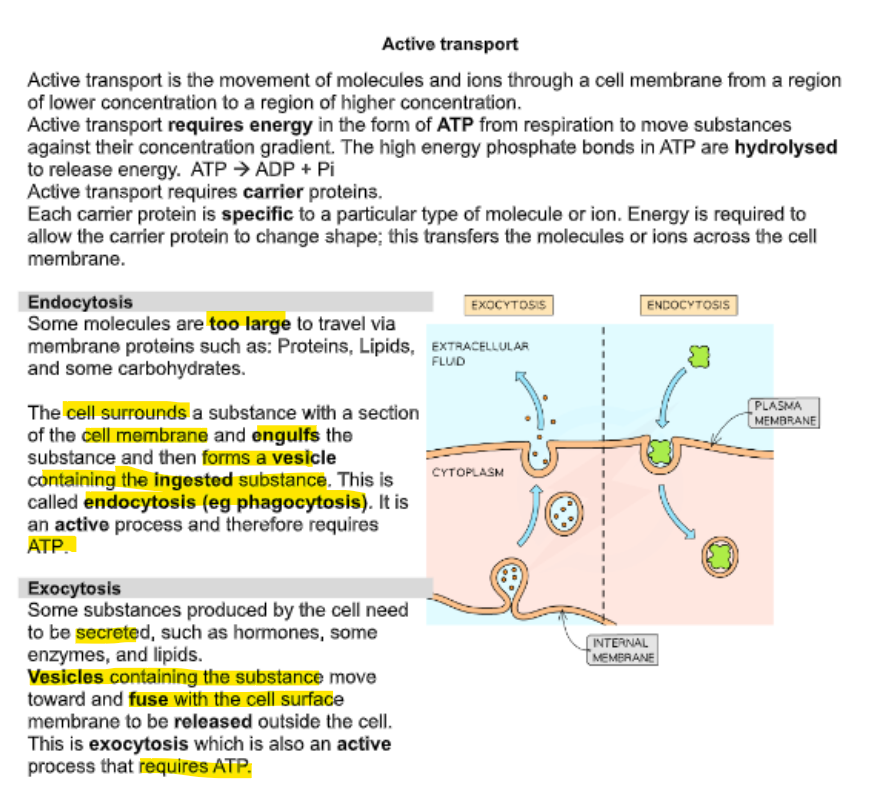
describe active transport
how are mammalian lungs adapted

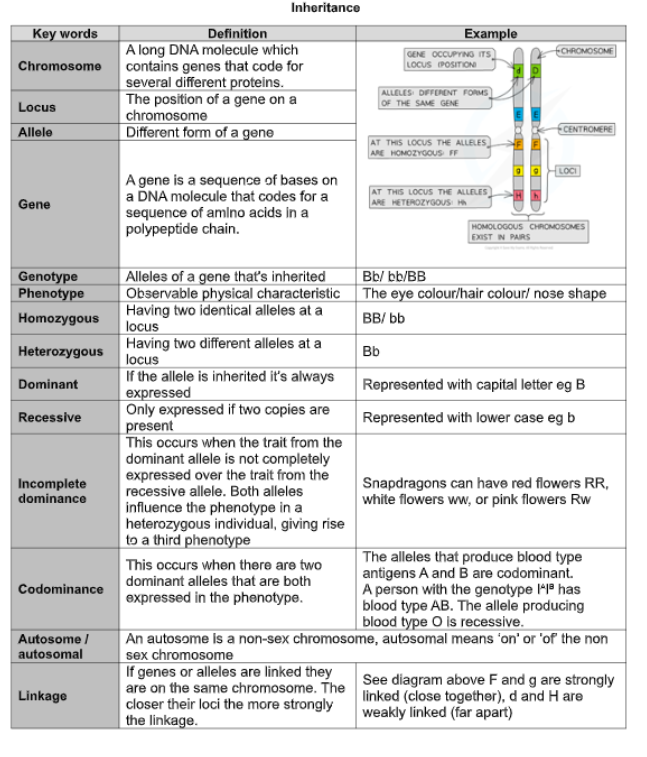
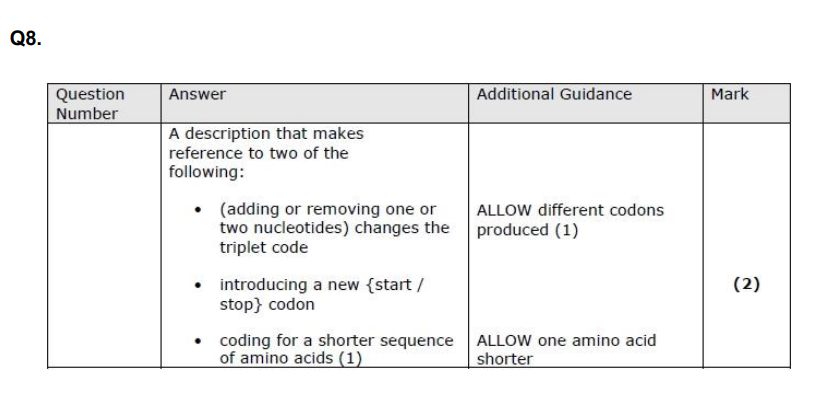
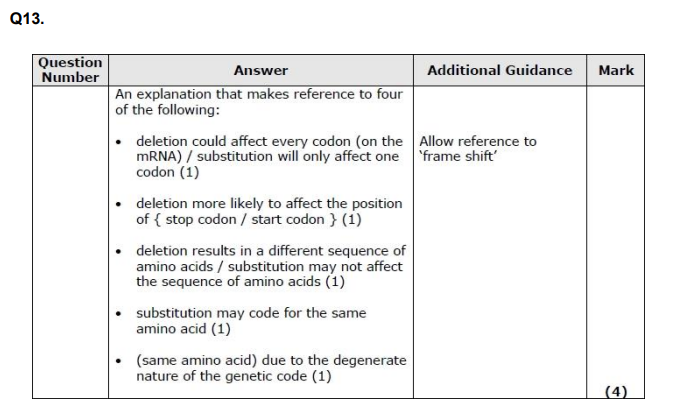
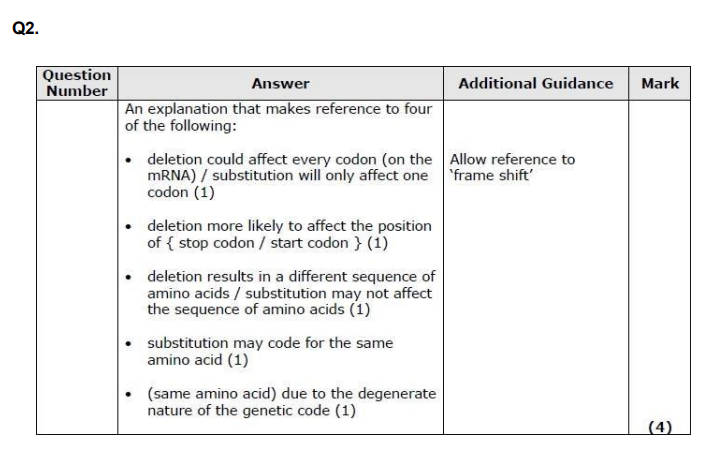
examples of mutation to gene
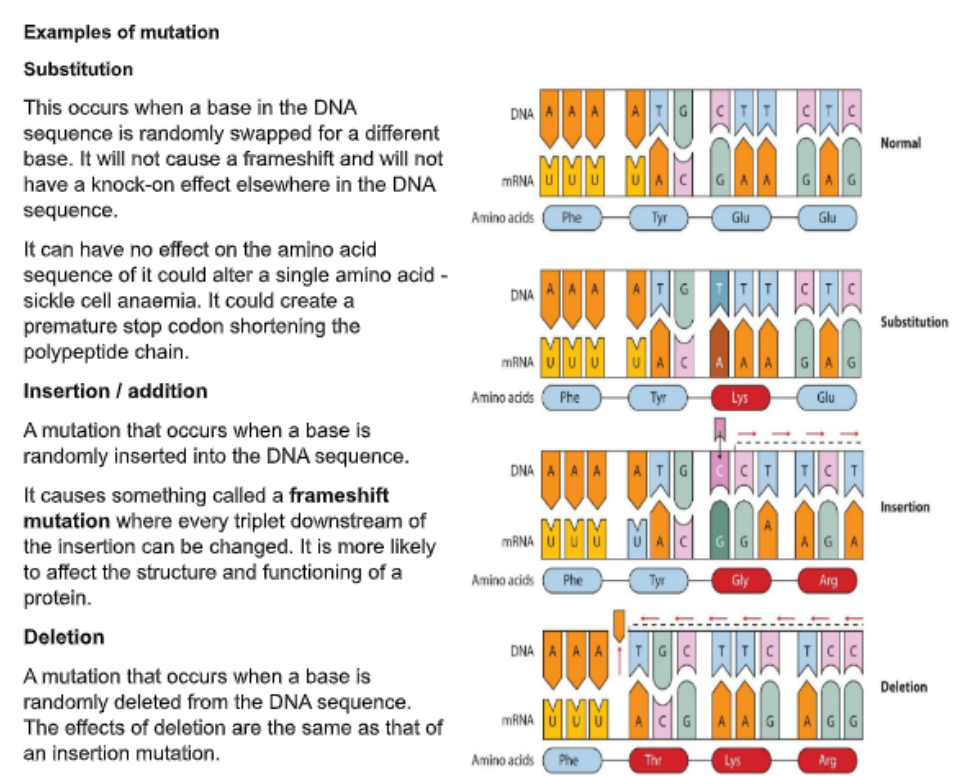
what is cystic fibrosis caused by?
effects of cystic fibrosis
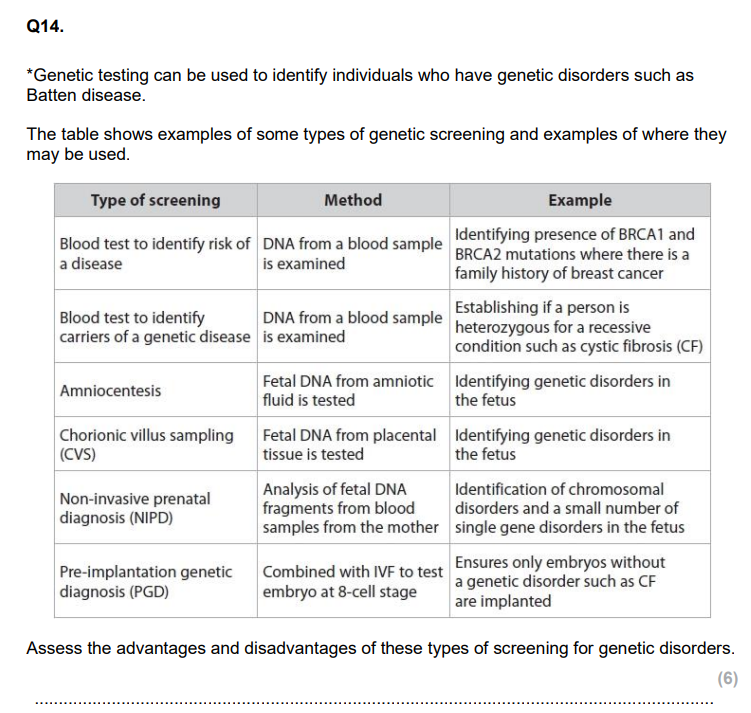
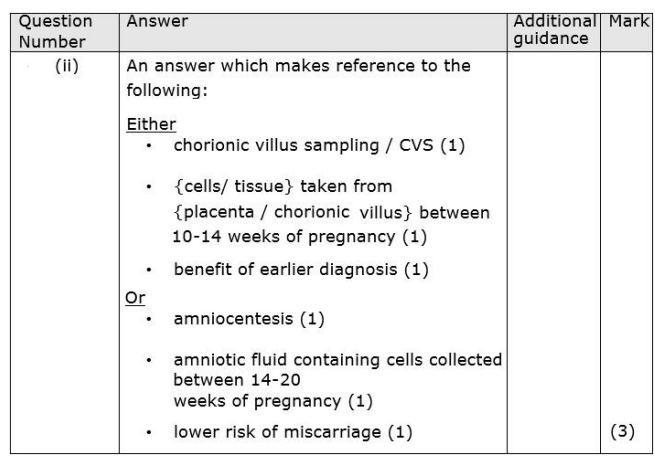
explain genetic screening
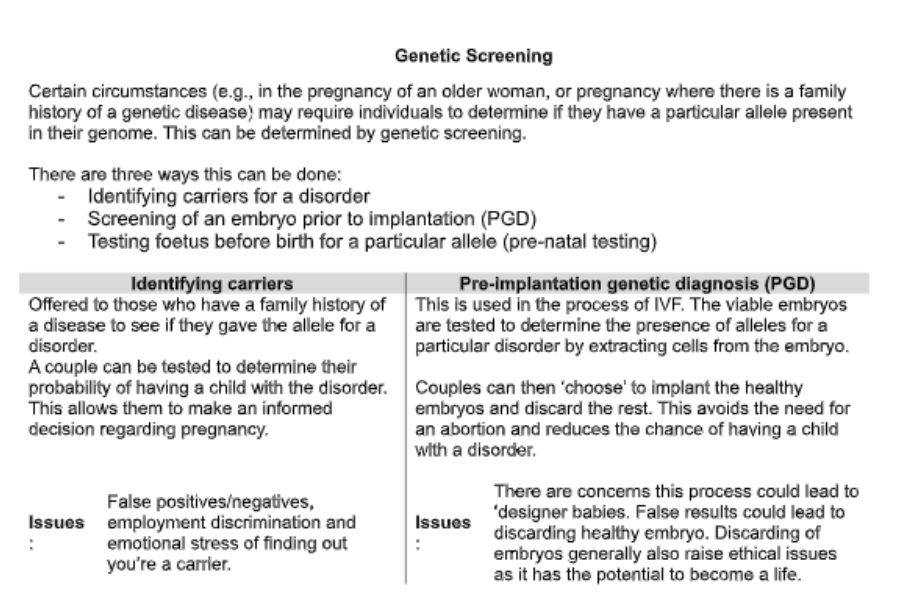
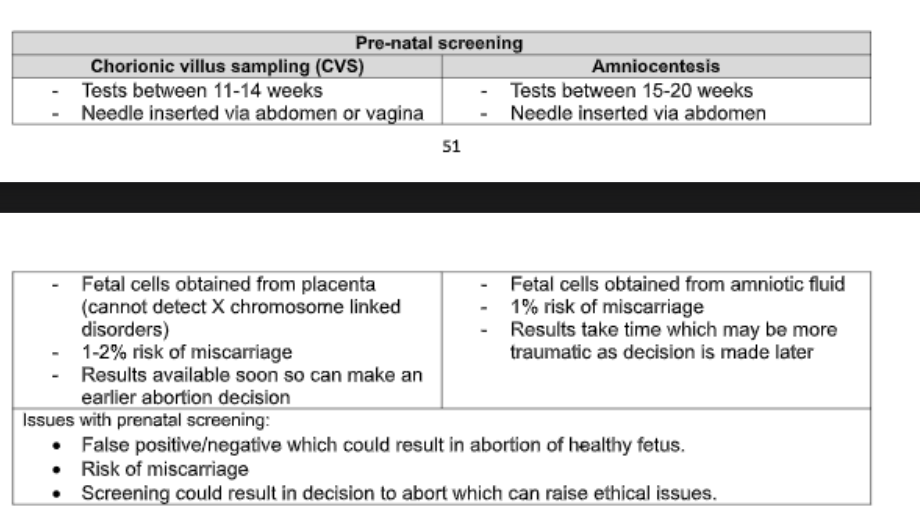
pre-natal screening?