4-Melting and Crystallisation in Geochemical Systems: Phase diagram applications
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
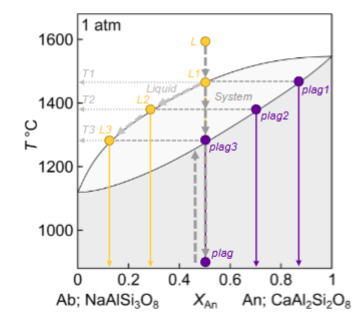
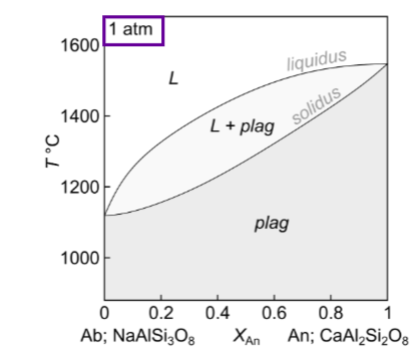
Describe where plagioclase 1,2,3 are for equilibrium crystallisation and melting:
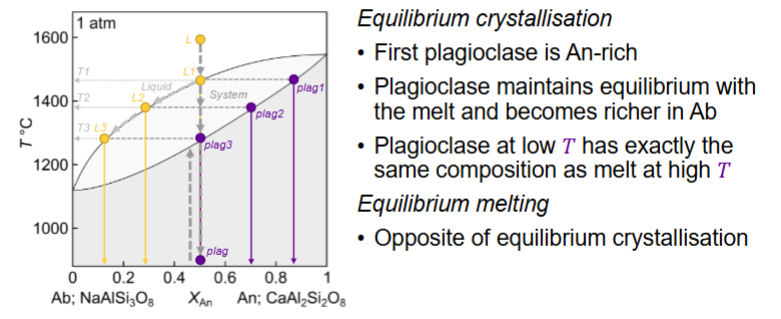
In equilibrium, the final composition is…..
the same as the starting composition
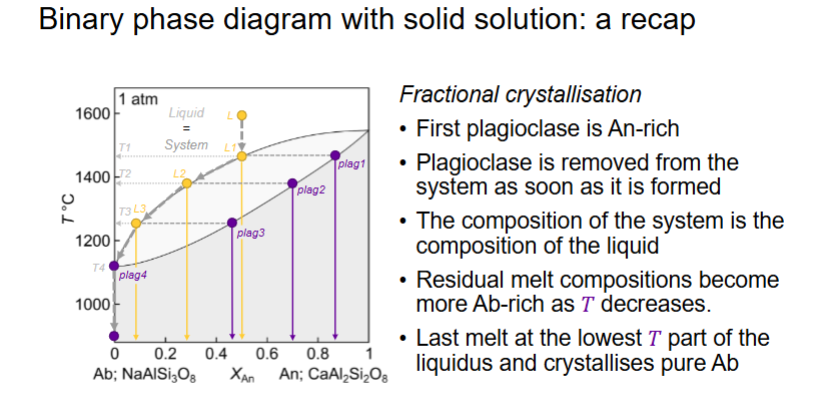
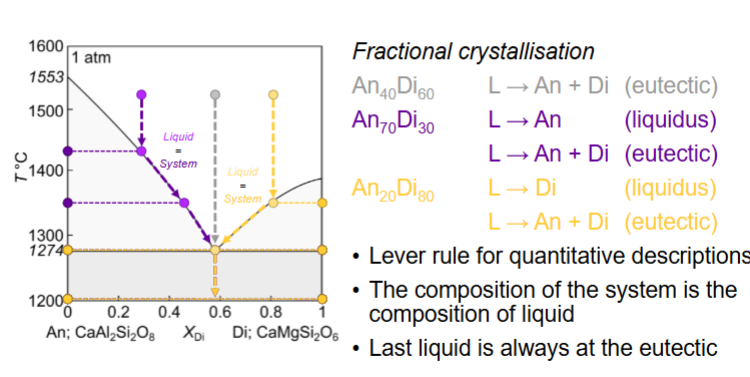
Describe for fractional crystallisation An 0.5
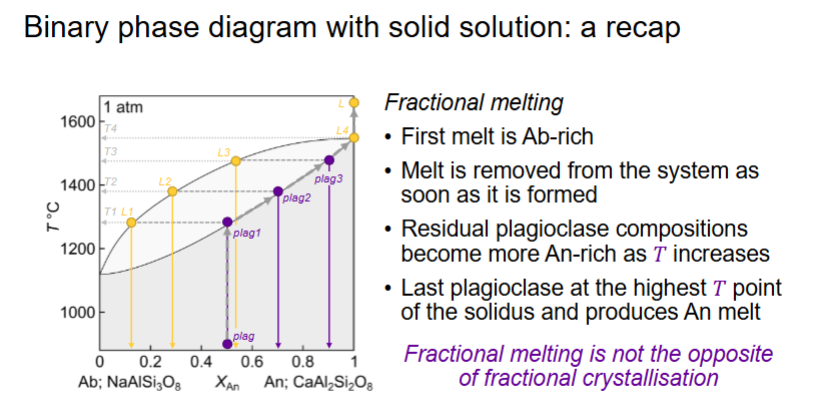
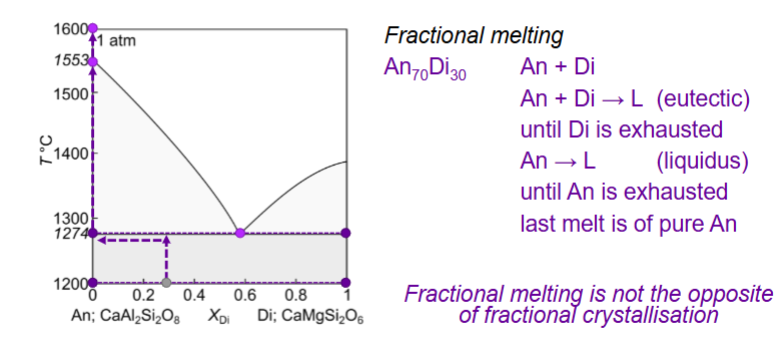
Describe for fractional melting An 0.5
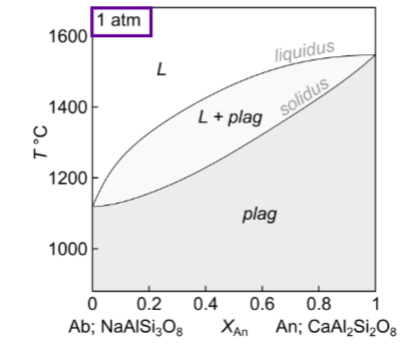
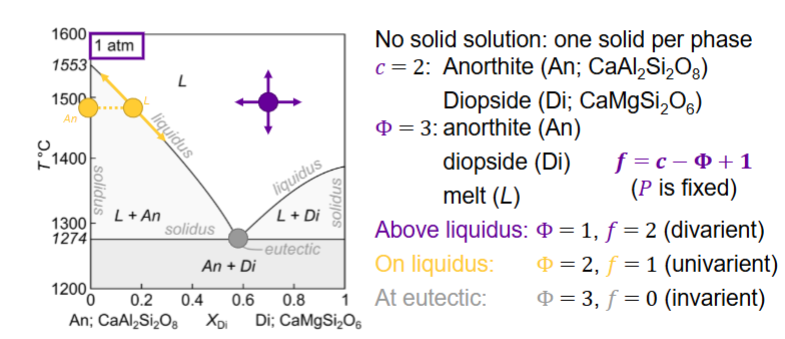
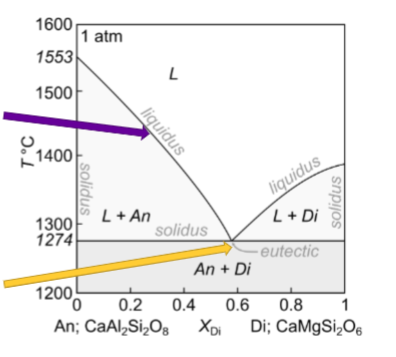
For this binary phase diagram with no solid solution: An-Di, how many components, how many phases?
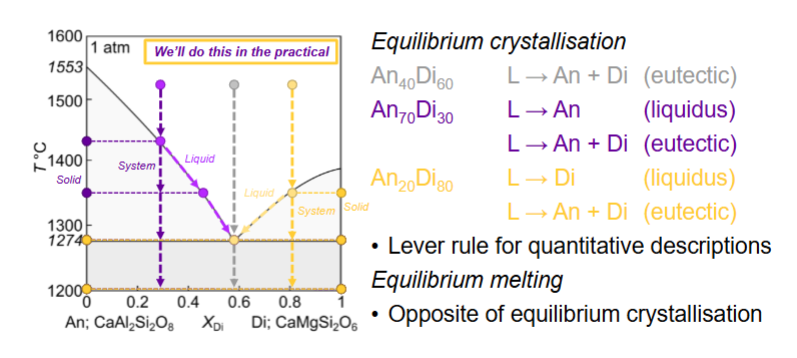
Fractional melting of An70Di30
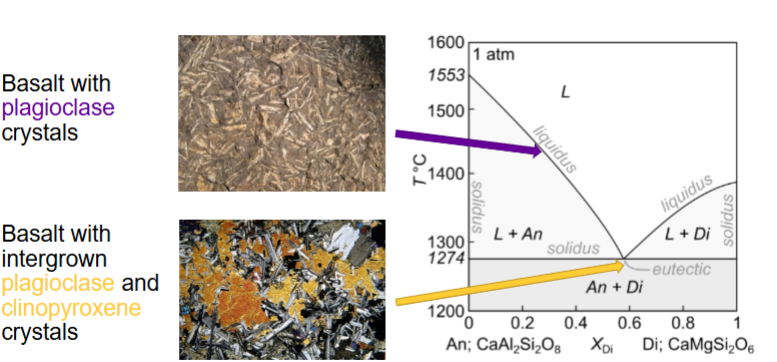
On diagram where is basalt with plagioclase and basalt with intergrown plag and clinopyroxene found?
What is a solid solution?
A solid solution is a single solid phase in which atoms of one element (or ion) can substitute for or mix with atoms of another within the same crystal lattice
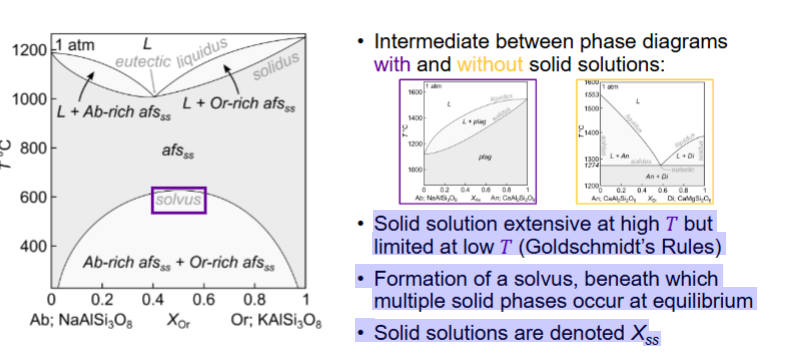
How many components and phases?
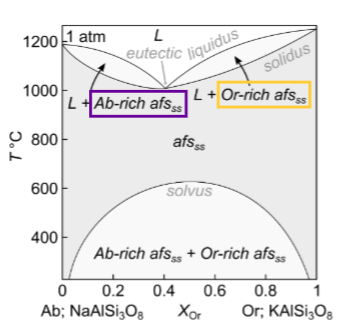
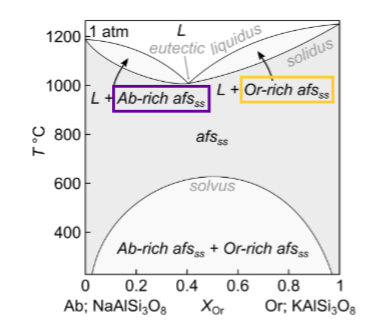
What happens for equilibrium crystallisation at Or 0.25
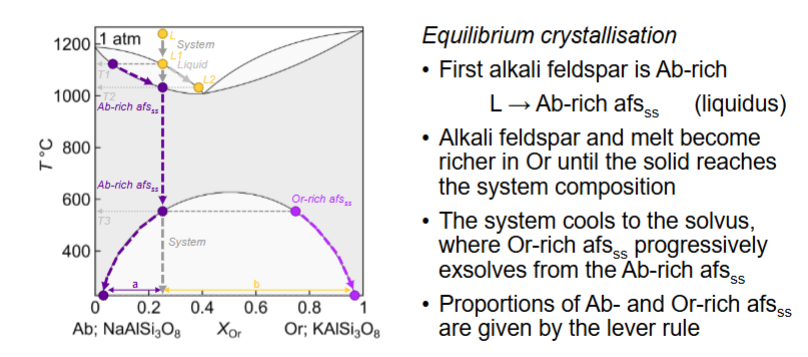
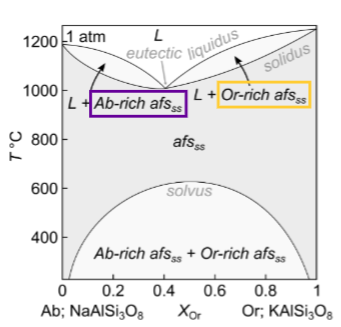
What happens for fractional crystallisation?
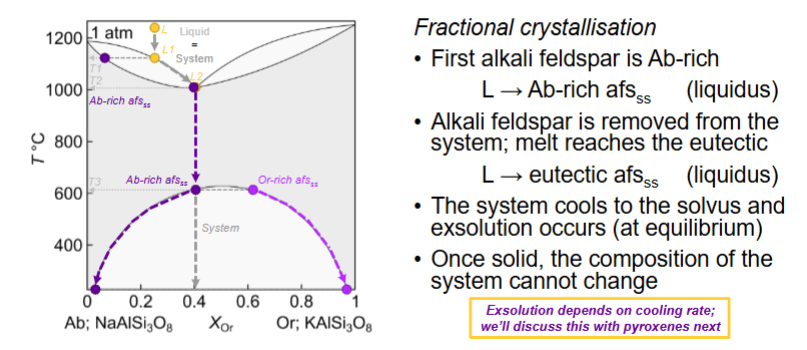
When is solid solution more extensive?
Solid solution extensive at high T (elements can substitute for each other over a wide composition range without forming separate minerals.)
Solid solution limited at low T
What is exsolution?
Exsolution is the process where a homogeneous solid solution separates (“unmixes”) into two distinct solid phases as it cools — without melting
SEPARATION OF MULTIPLE SOLIDS FROM A SINGLE SOLID PHASE
extent to which exsolution occurs depends on the cooling rate
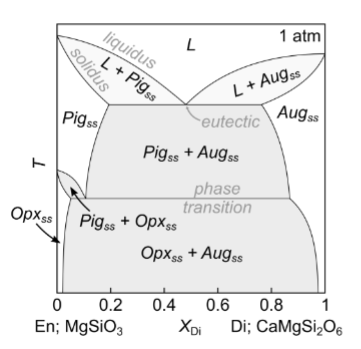
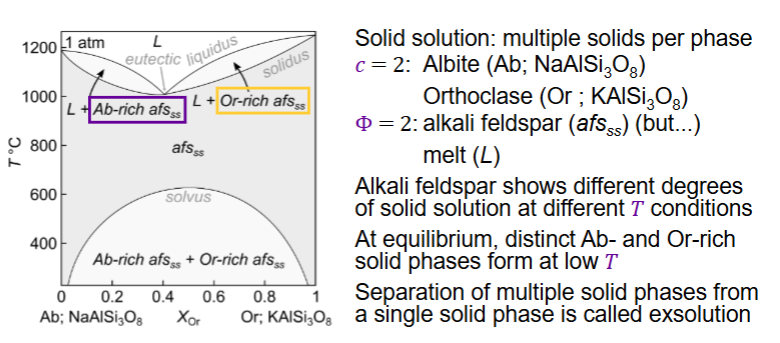
How many components and phases?
c = 2
phases phi = 4
Solvus intersects eutectic. (solvus - limit of solid-solution stability)
Characteristic rabbit ears shape
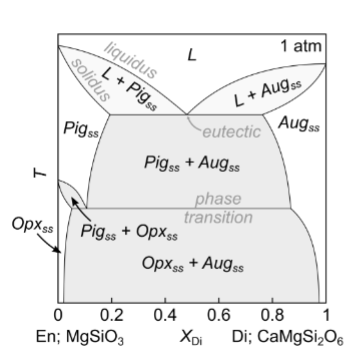
For this diagram, what happens with slow cooling?
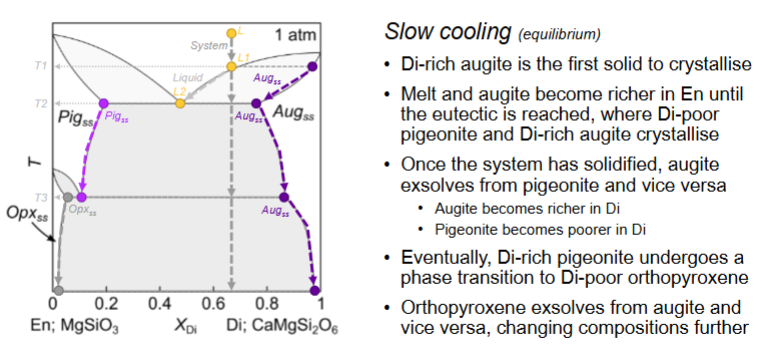
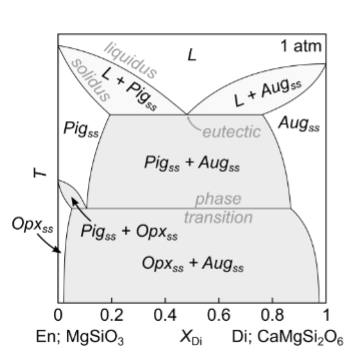
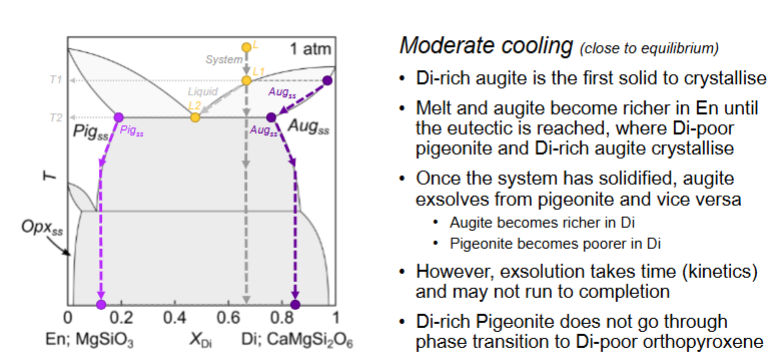
For this diagram, what happens with moderate cooling?
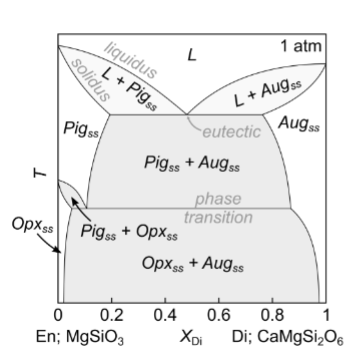
For this diagram, what happens with fast cooling?
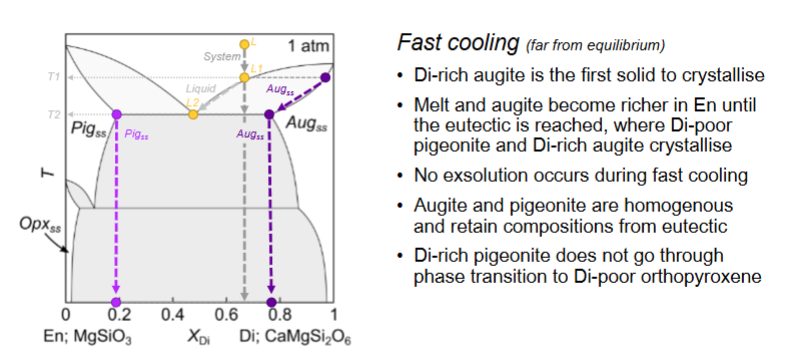
Where does each pyroxene grow?
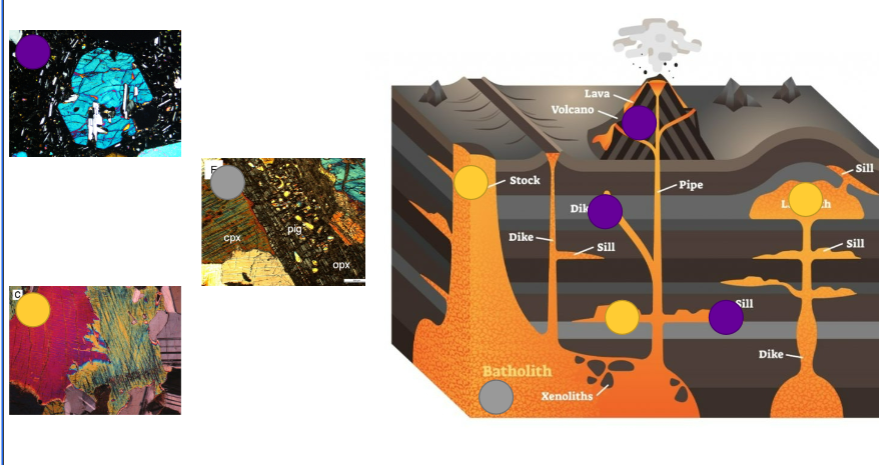
Fast cooling - volcano, dike, sill
Moderate cooling - stock, sill
Slow cooling - in big large magma environments deep down
How many components and phases?
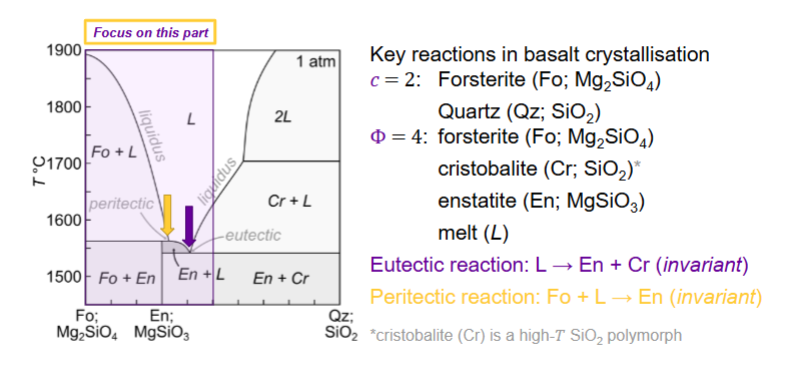
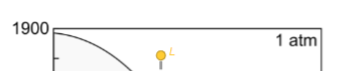
What happens for equilibrium crystallisation for here?
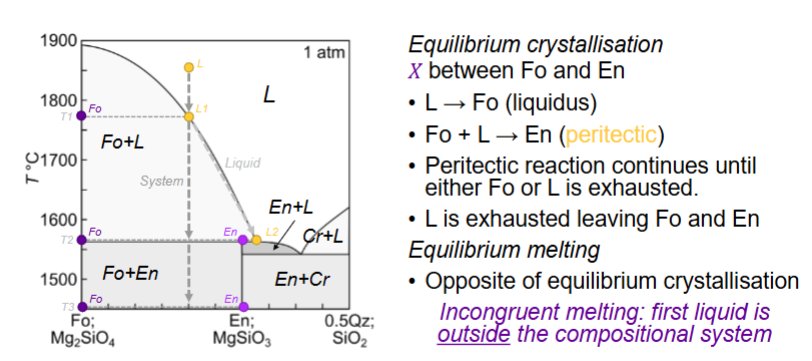
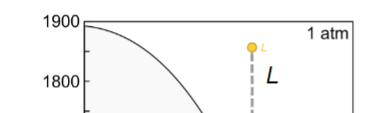
Equilibrium crystallisation for here?
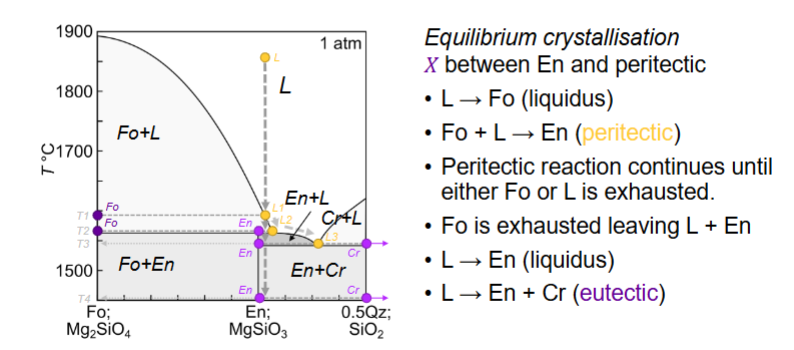
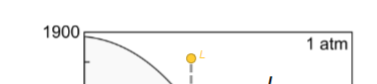
Fractional crystallisation for here?
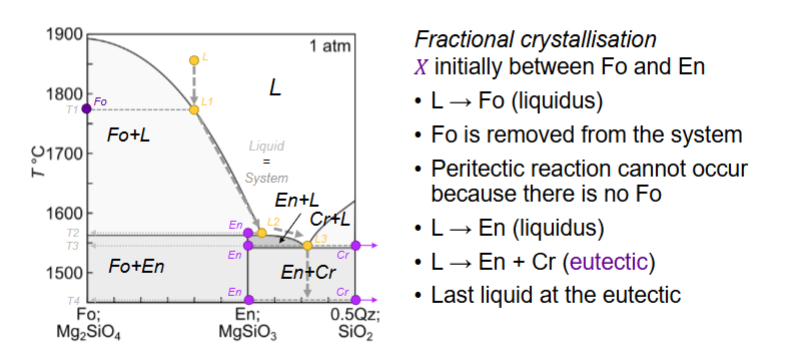
What is the peritectic?
consuming a mineral you just produced
stay at same temp until one thing is exhausted
Do peritectic reactions occur in nature?
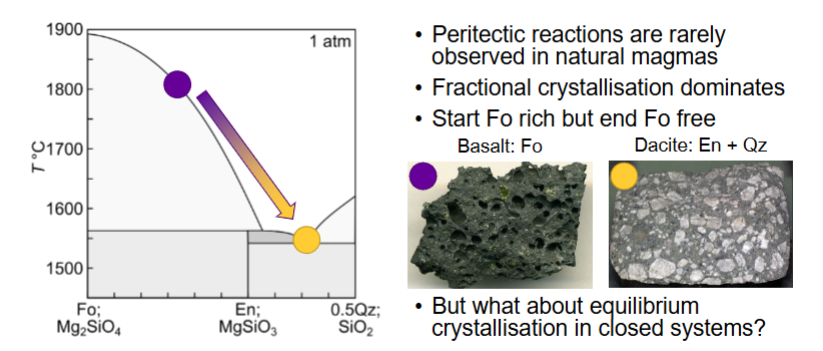
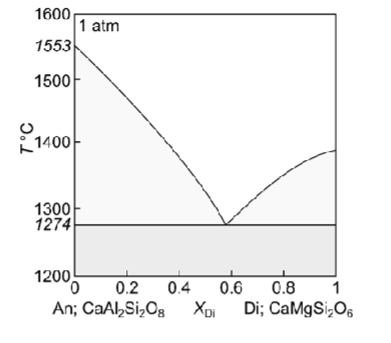
Describe equilibrium crystallisation of a liquid with XDi = 0.8

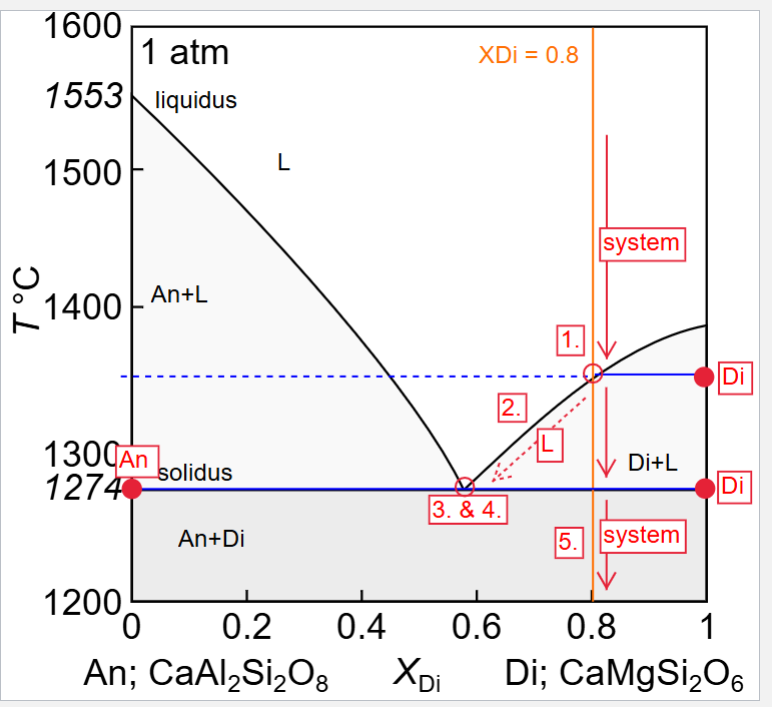
Describe fractional crystallisation of a liquid with XDi = 0.8

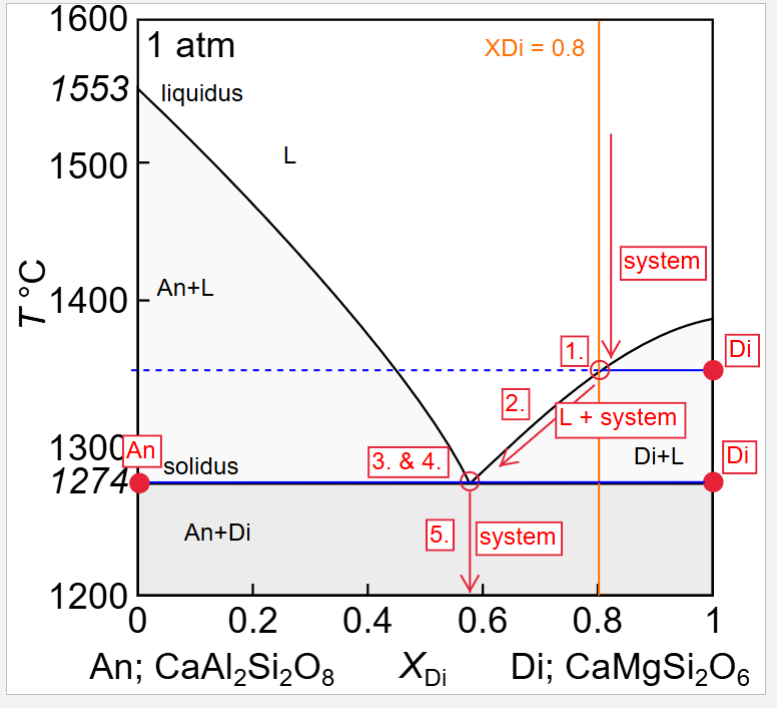
Describe fractional melting of a solid with XDi = 0.8

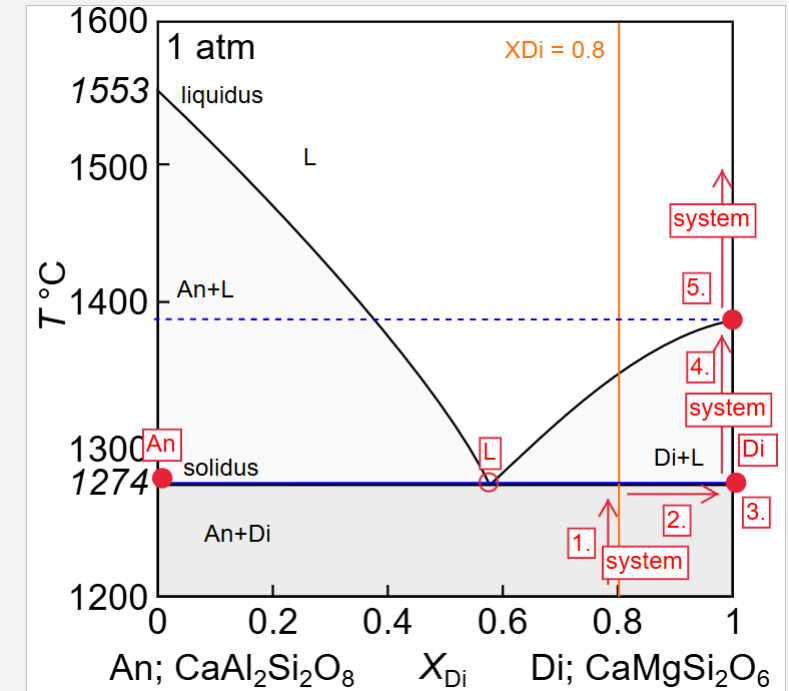
How could you distinguish between rocks produced during fractional crystallisation of liquids with initial compositions of XDi = 0.1, and XDi = 0.8 in the field?

Describe equilibrium crystallisation of a liquid with XQz = 0.32

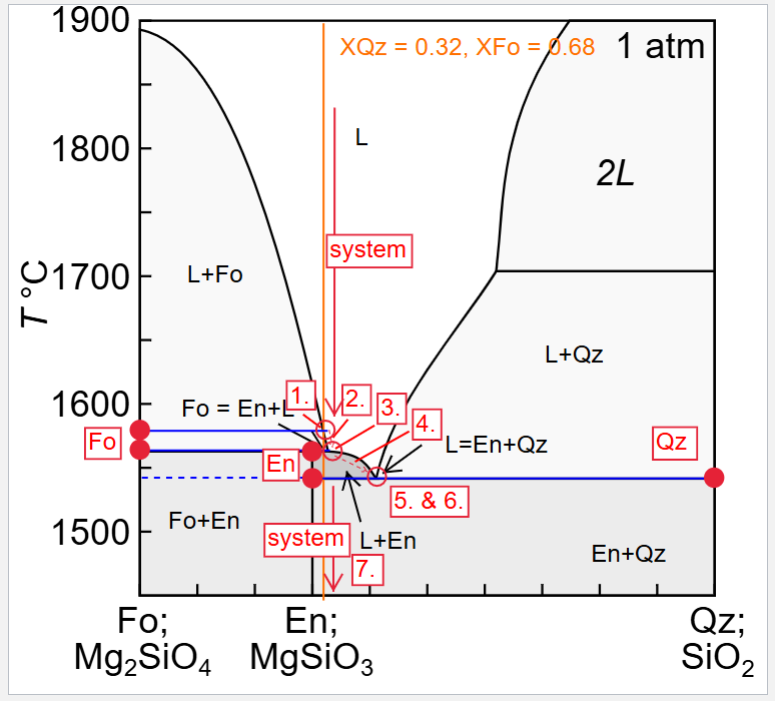
Describe fractional crystallisation of a liquid with XQz = 0.32

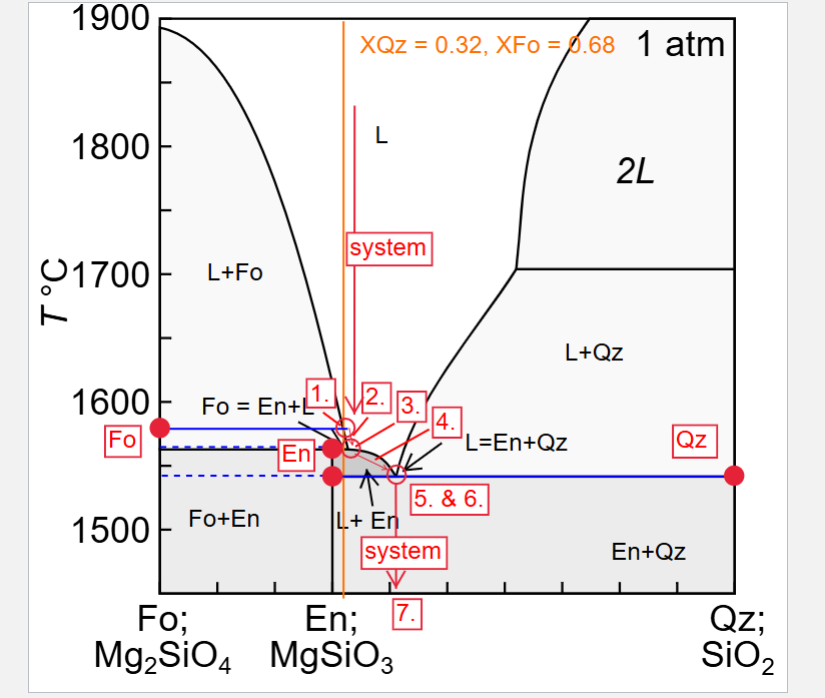
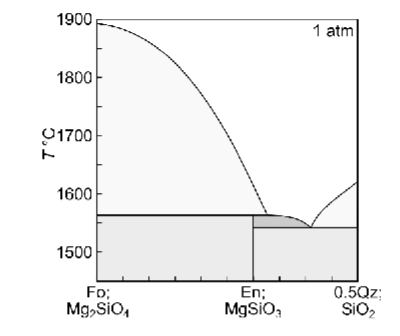
Describe fractional melting a solid with XQz = 0.32

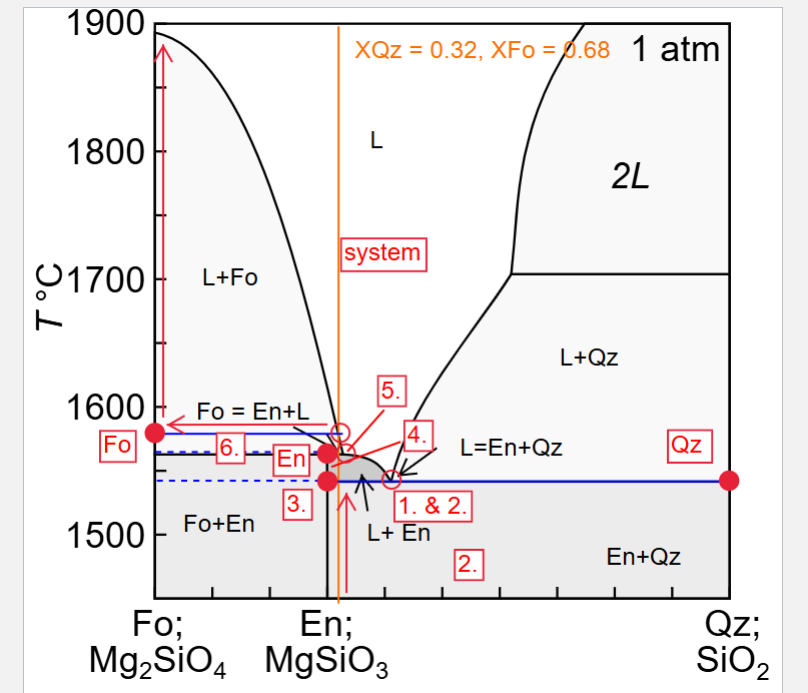
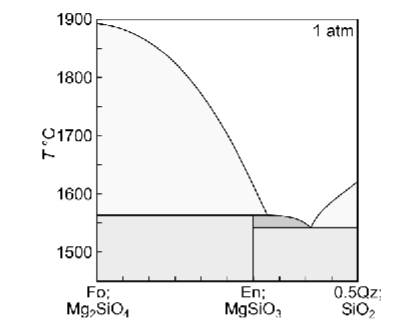
Briefly describe how each of the melting or crystallisation scenarios would differ if the system had a composition of XQz =0.28, and XQz = 0.32
