PSY124 attitudes and persuasion
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
attitude
A positive, negative, or mixed reaction to a person, place,object or idea;
multidimensional;
explicit (aware)/ implicit (not aware)
dispositional attitudes
tendency to be more positive or negative in their attitudes.
genetic (parents) and learning( experience)
evaluate conditioning
a stimulus can be shaped by its association with something you already like or dislike
attitude scales
series of self-report questions measuring your attitude toward something
bogus pipeline
phony lie detector used to increase honest self response
covert measures/non verbal
person is unaware of mesurement/unable to control it
Implicit association test (IAT)
measures the relative reaction time it takes to associate concepts together
could be:
in-group positivity
stereotypes
awareness of privilege
Theory of Planned Behavior
Specific Attitude + Social Norms + Perceived Control → Intention → Specific Behavior
attitude strength
self interest
personal values
close others
source effects
Characteristics of the person delivering the message
credibility
must be competent and trustworthy
likeability
must be similarity to self and attractiveness
sleeper effect
if a source seems unreliable at first, its message can start to seem more believable later (soc media)
discounting cue hypothesis
we ignore unreliable sources at first, but as time passes, we forget who said it and only remember the message → so we start to believe it more.
2 routes of persuasion
central - rational, see a message strength
peripheral - mental shortcuts, surface cues
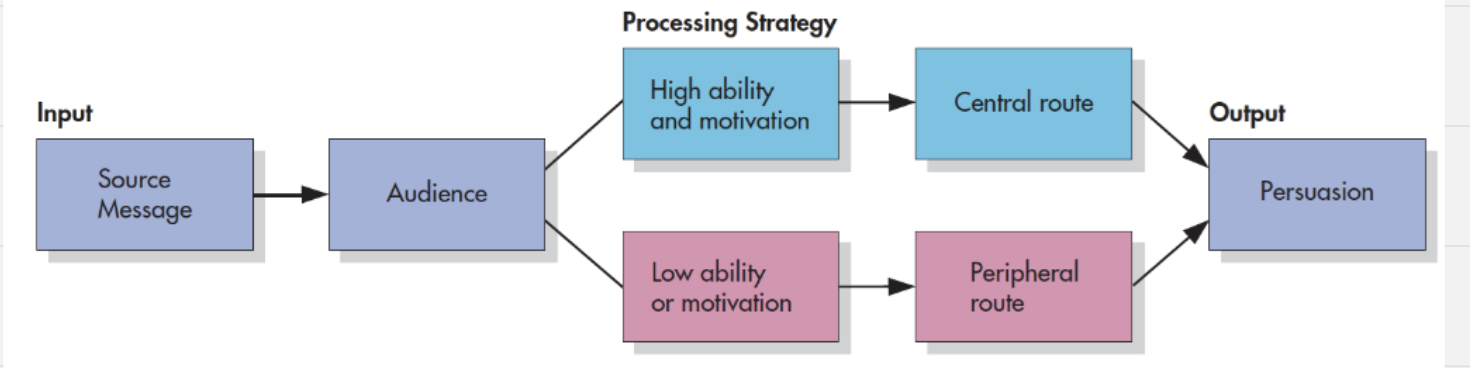
2 routes of persuasion
timing effect
primacy: if messages are close together, the 1st is more persuasive
recency: if messages are spaced out, the latter is more persuasive
fear appeals
can be effective,but must give instruction on what to do
positive emotions
good mood can enhance persuasion via peripheral route
audience factors
need for cognition - prefer thinking
psychol reactance - you trying to persuade me, i will resist it
inoculation hyp - a small “dose” of the opposing view builds resistance to stronger persuasion later
cognitive dissonance th
Feeling uneasy when your actions don’t match your beliefs, which pushes you to reduce the mismatch.
(it happens when what you do doesn’t fit what you believe)
Insufficient Justification:
the beh was freely chosen/done without any real rewards
Insufficient deterrence
the beh was done without real punishment
options to reduce dissonance
change the attitude/ beh
change your perception of the beh
create a beh-supporting cognition
minimize the importance of dissonance
reduce perceived choice
Justifying Effort and Cost
tend to like something more if it cost us dearly
Justifying Decisions
exaggerate the positive features of what we chose and the negative features of what we did not choose
cognitive dissonance (new look)
negative consequences of beh
personal responsibility outcomes (freedom of choice)
physiological aroussal occurs
attribution of arousal to beh