NU 201 Chapter 8 & 11
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Define history of health
Subjective data for health assessment
What does physical examination require the examiner to do?
Develop technical skills, the tools to gather data
What sense does the examiner use during the physical examination?
Sight
Smell
Touch
Hearing
List the skills performed one at a time IN THIS ORDER
IPPA
What does the I stand for in IPPA?
Inspection
What does inspection require during the physical examination?
Good lighting
Adequate exposure
Use of instruments to enlarge your view
What does the first P stand for in IPPA?
Palpation
what is palpation use to assess?
Texture
Temp
Moisture
Organ location and site
Swelling, vibration or pulsation
Crepitation
Presence of lumps or masses
Presence of tenderness or pain
What to parts of the hand can be used for palpation?
Fingertips
Fingers and Thumbs
When would you palpate with the finger tips?
Best for fine tactile discrimination of skin texture, swelling, pulsation, determining presence of lumps
When would you palpate with the fingers and thumbs?
Detection of position, shape, and consistency of an organ or mass
What is the ulnar of the hand best for detecting during palpation?
Best for fine detecting vibration
When is the dorsum part of the hand best for detecting during palpation?
Detection of temperature
What does the 2nd P stand for in IPPA?
Percussion
Define percussion
Tapping person’s skin with short, sharp stokes to assess underlying structures
What are the two methods of percussion?
Direct percussion and indirect percussion
what is direct percussion
The striking hand directly contacts the body wall
What is indirect percussion?
Using both hands, the striking hand contacts stationary hand fixed on person’s skin.
Describe resonant percussion sound
Over normal lung tissue
Describe hyper-resonant percussion sound
Emphysema
Describe Tympany percussion sound
Stomach (air filled)
Describe dull percussion sound
Liver, Spleen (dense organ) Pneumonia
Describe flat percussion sound
Thigh, muscle, bone or tumor
What does the A stand for in IPPA
Auscultation
Define Auscultation
Listening to sounds produced by body
What is the diaphragm used for on the stethoscope?
Used for high pitched sounds
what is the bell used for on the stethoscope?
Used for low pitched sounds
what is neuropathic pain?
Pain that does not adhere to typical phases
what is visceral pain?
Pain originates from larger interior organs
Where is somatic pain?
Comes from sources such as blood vessels, joints, tendons, muscles, and bone
Where is cutaneous pain?
Derived from skin surfaces and subcutaneous tissues
What is referred pain?
Pain that is felt at a particular site but originates form another location
What is acute pain?
Short term and self-limiting
What is chronic pain
Pain is diagnosed when pain continues for 6 months or longer
Is pain subjective or objective?
Subjective
What is pain?
Pain is whatever the experiencing person says it is
What is the most reliable indicator of pain?
Subjective report
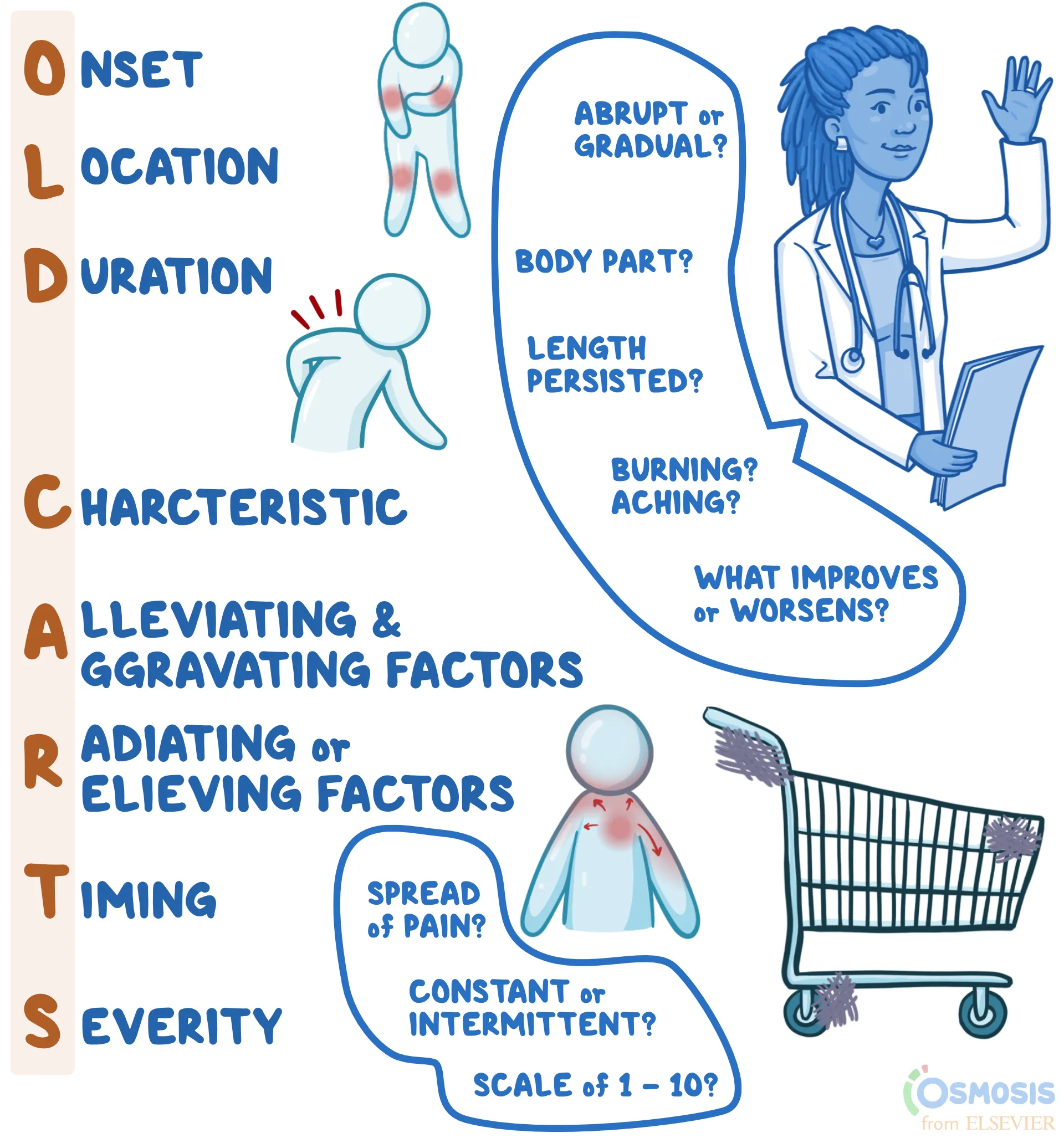
Do physical findings always support patient’s pain complaints?
NO