Unit 1: Biochemistry - #2 Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Three Types of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides, Disaccharides and Polysaccharides
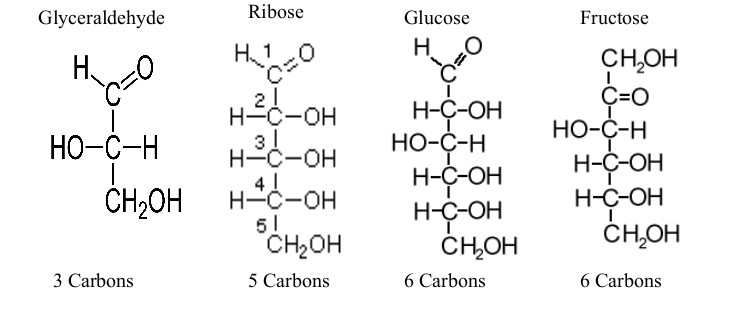
Monosaccharides
“Mono” is single, “Saccharide” is sugar
Simplest sugar
Have ratio of C:H:O = 1:2:1
Distinguished from one another by:
Carbonyl group: either aldehyde or ketone
Length of Carbon chain
What happens when Carbohydrates dissolve in water?
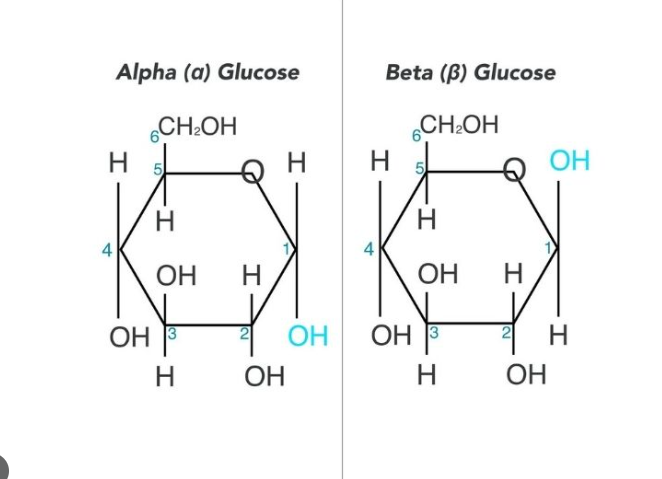
Monosaccharides with five or more carbons are linear in dry state, but form rings when dissolved in water
Example: When glucose dissolves in water, the -OH group at carbon 5 reacts with the aldehyde group at carbon 1 to form a closed ring
Beta-Glucose
50% chance the -OH group at Carbon 1 will end up above the plane of the ring
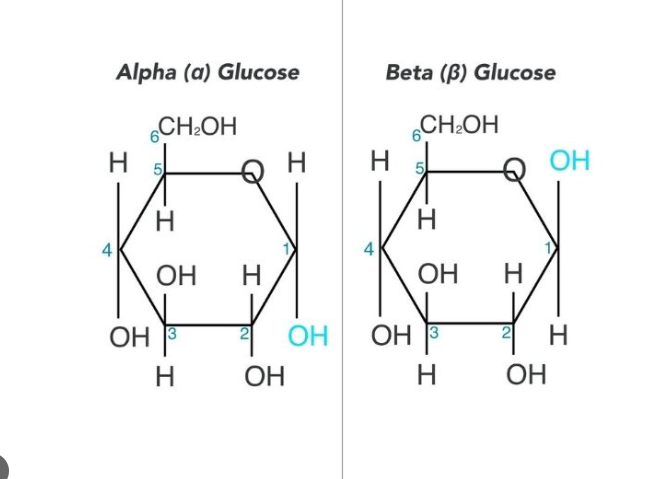
Alpha-Glucose
50% chance the -OH group at Carbon 1 will end up below the plane of the ring
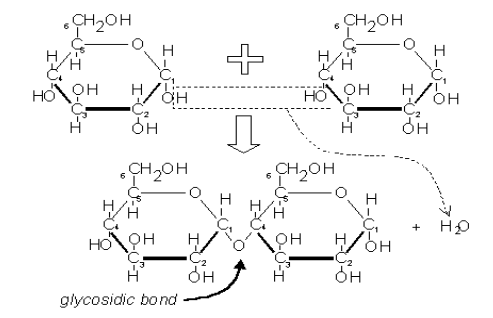
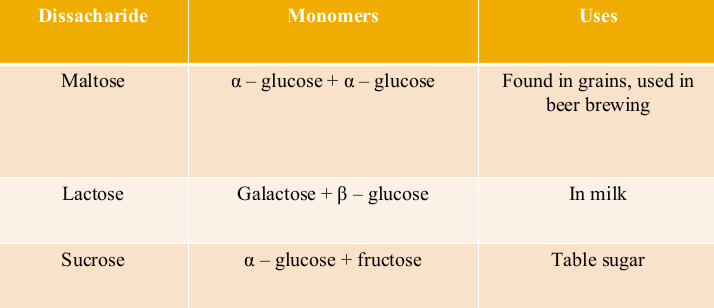
Disaccharides
Sugars containing two (disaccharides) simple sugars
Linked together by a 1-4 glycosidic linkage: A covalent bond between 2 monosaccharides by a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis)
The hydroxyl group of carbon 1 of the glucose molecule links with the hydroxyl group of carbon 4 of the adjacent molecule:
Disaccharide Chart
Polysaccharides
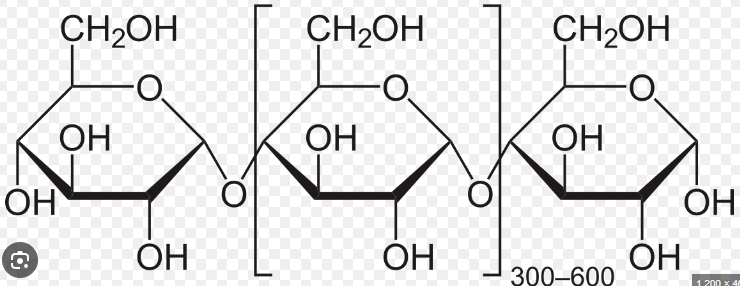
Formed by linking monosaccharides (several 100 to several 1000) by glycosidic linkages
Can be straight chained, or branched
Very polar due to many hydroxyl groups
Hydrophilic but will not dissolve due to large size
Have two important biological functions:
Energy storage (starch and glycogen)
Structural support (cellulose and chitin)
Starch
Main form of energy storage in plants
Plants produce starch by linking excess glucose molecules together
Two types: Amylose & Amylopectin
Amylose
No branches, all 𝛂-1, 4-glycosidic linkages
Amylopectin
Branched, 𝛂-1, 4-glycosidic linkages for main chain and 𝛂-1, 6-glycosidic linkages for branches
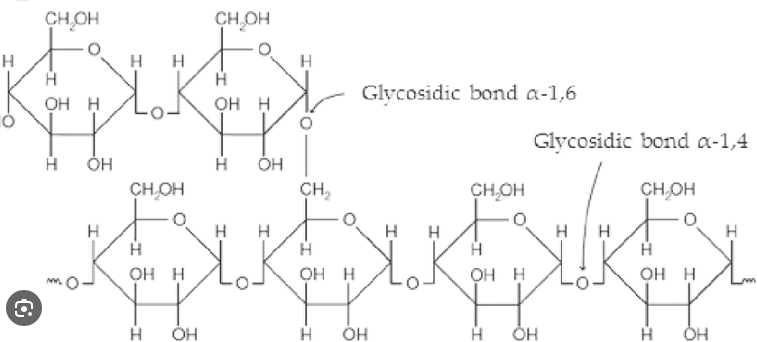
Glycogen
Storage polymer in animals (muscle and liver)
Glycogen stores small; depleted in a day if not replenished
Highly branches: (𝛂 1-4) linked glucose main chain with (𝛂1-6) linked branches
More branching and more compact than amylopectin (starch)
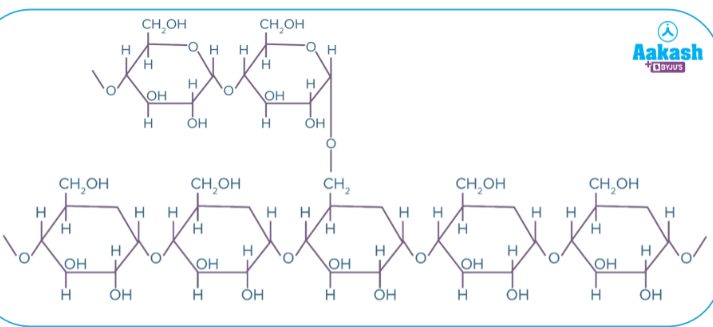
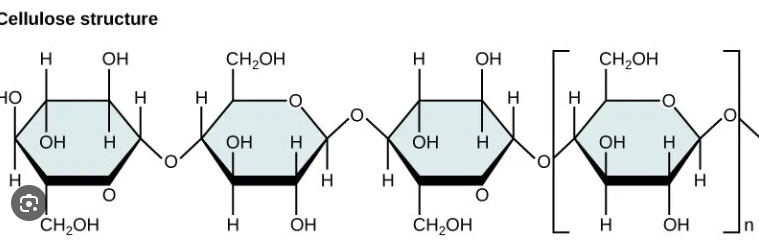
Cellulose
Major component of cell walls
Straight chain polymer of beta-glucose held together by ꞵ-1-4 glycosidic linkages, where every other glucose molecule is inverted
Humans cannot digest cellulose because they lack an enzyme to hydrolyze ꞵ-1-4 linkage (roughage)
Provides rich supply of energy for organisms who can break it down