Bacteriology - Exam 1: Shape, Color, and Nasties
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
277 Terms
What are the stages of infection of a pathogen?
Entry,
Adherence,
Invasion,
Colonization, and
Growth
The balance between normal microbiota and the host is the definition of ____
Health
What are Koch's postulates?
1) Same pathogen present in every case
2) Pathogen is isolated in pure culture
3) Isolated pathogen causes same disease
4) Pathogen is re-isolated from newly infected animal
What are Koch's postulates trying to convey?
That there is a cause and effect relationship between a specific microorganism and it's disease
Where might you find Staphylococcus normally?
On the skin
Where might you find Mycobacterium normally?
In the lungs
Where might you find Clostridium normally?
In the intestinal tract
Staphylococcus epidermis living on your skin is an example of _____
Commensalism
The normal flora has a protective function against pathogens, which is called _______
Bacterial antagonism
(Compete for attachment)
How do probiotics perform bacterial antagonism?
Competitive exclusion, by growing more "good" bacteria so that "bad" bacteria can't take over
The process and mechanisms of disease development is called _______
Pathogenesis
The capacity/potential of an organism to cause a disease is called _____
Pathogenicity
The relative pathogenicity of an organism (LD_50, ID_50) is called _____
Virulence
The ability to enter and spread in the host is called ____
Invasiveness
The dose required to produce a demonstrable infection in 50% of the test animals is called _____
Infective dose
The number of microbes in a dose that will kill 50% of test animals is called ____
Lethal dose
What pathogens cause disease in normal hosts?
Frank (true) pathogens
An ______ pathogen only causes disease when the conditions are favorable
Opportunistic
What type of pathogens can grow inside and outside of cells, and can be grown in bacteriological media?
Facultative intracellular pathogens
______ intracellular pathogens can only be cultured in tissue culture media
Obligate
What is the difference between a primary and a secondary infection?
A primary infection is of a healthy host, while a
Secondary infection is one immediately following another
A sporadic disease occurs how often?
Occasionally

An endemic disease occurs how often?
Consistently in a population
An epidemic disease affects how many people?
Occurs in a large number of individuals in a population
A pandemic disease occurs _________
Worldwide
If an acute disease has a rapid onset, is usually severe, and lasts for a short period, what is a peracute disease?
Acute, but to a higher degree

If a disease spreads due to bacteria in the circulation, it is defined as ______
Systemic
If a local infection enters the circulation, affecting other parts of the body, it is defined as _____
Focal
If there is bacteria circulating in the blood, it is called ________, but if the bacteria is multiplying in the blood, it is ________
Bacteremia;
Septicemia
The period between entry and appearance of symptoms is the ___________ period
Incubation
T/F: Bacteria have peptidoglycan, and Eukarya do not
True
Do bacteria and eukarya have the same type of ribosomes?
No.
Bacteria has 70S, and
Eukarya has 80S
How many RNA polymerase do bacteria have? What about eukarya?
Bacteria have one, and
Eukarya have three
Why are differences between bacteria and Eukarya useful?
Drugs can target one and not the other
Recall the main characteristics of Prokarya
They
lack a nucleus, have a
Complex cell wall, have
Circular chromosomes, and are
Asexual
What color do gram negative bacteria stain?
Eosinophilically
What are three common bacterial shapes?
Cocci, Bacilli, and Spirilla
What is the quick and easy stain for you to perform to help identify bacteria!?
Gram stain!
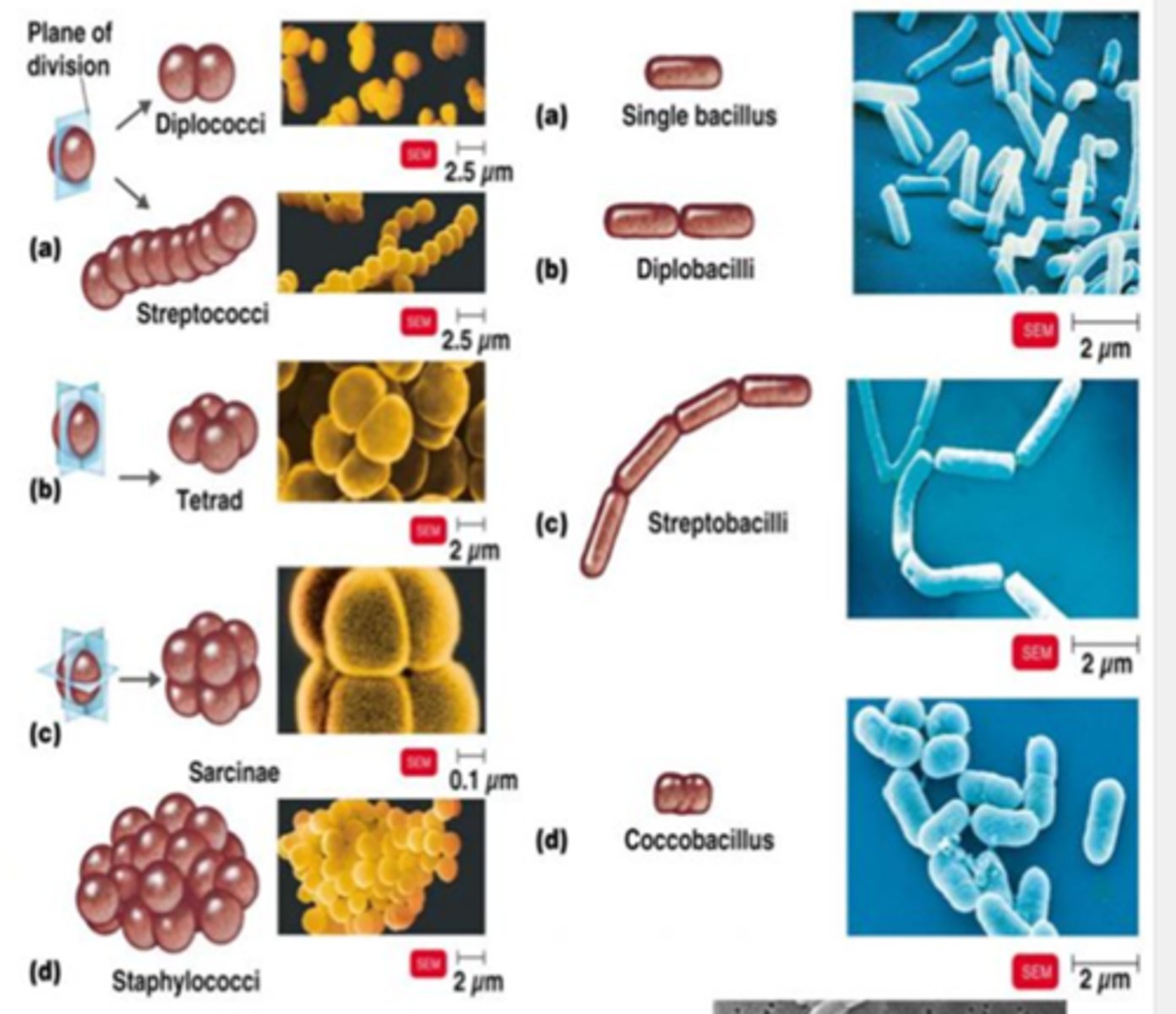
Bacteria with a single flagella are called ________
Monotrichous
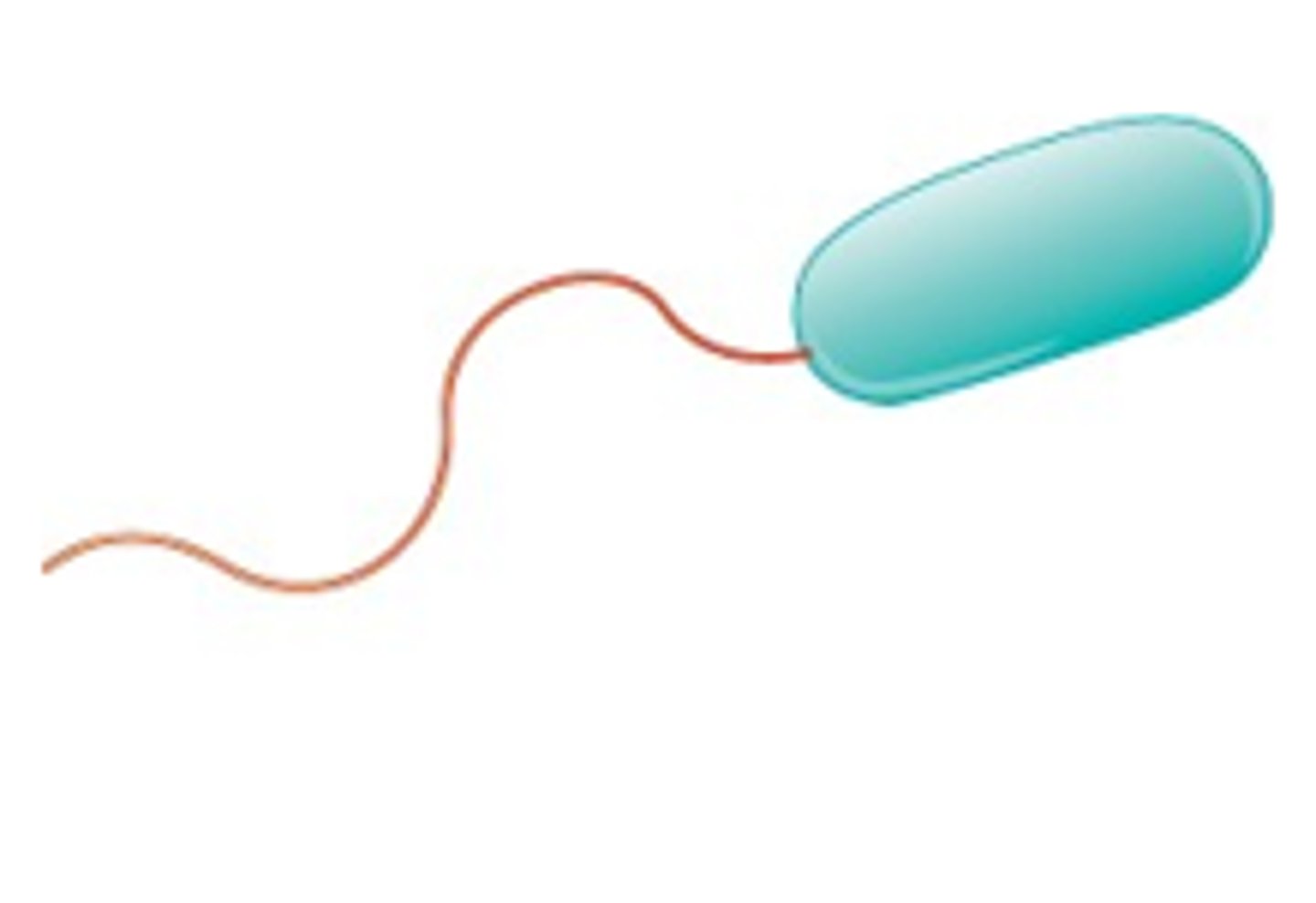
Bacteria with a flagella at each end is called _______
Amphitrichous
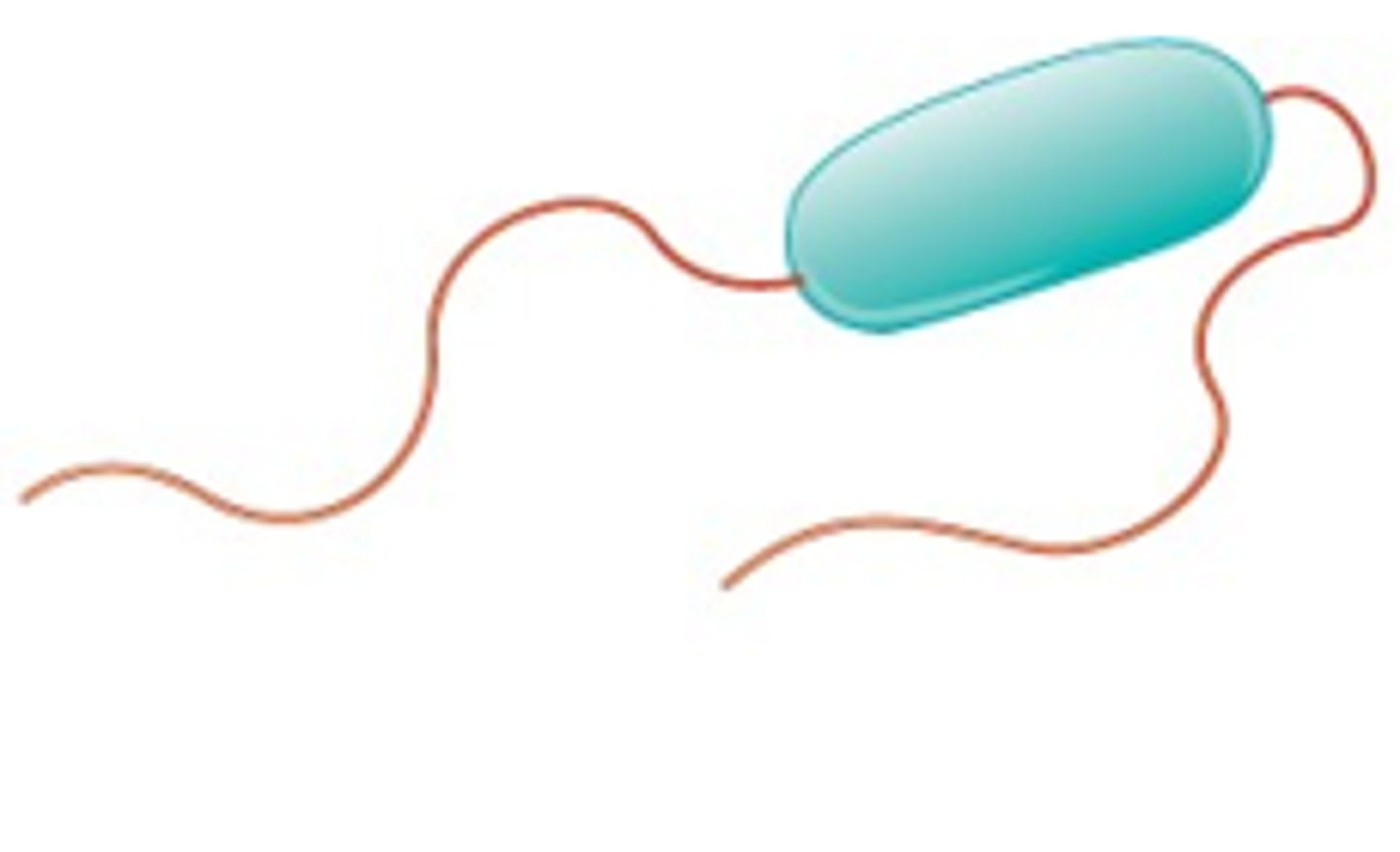
Bacteria with flagella organized into a clump (or clumps) is called _______
Lophotrichous
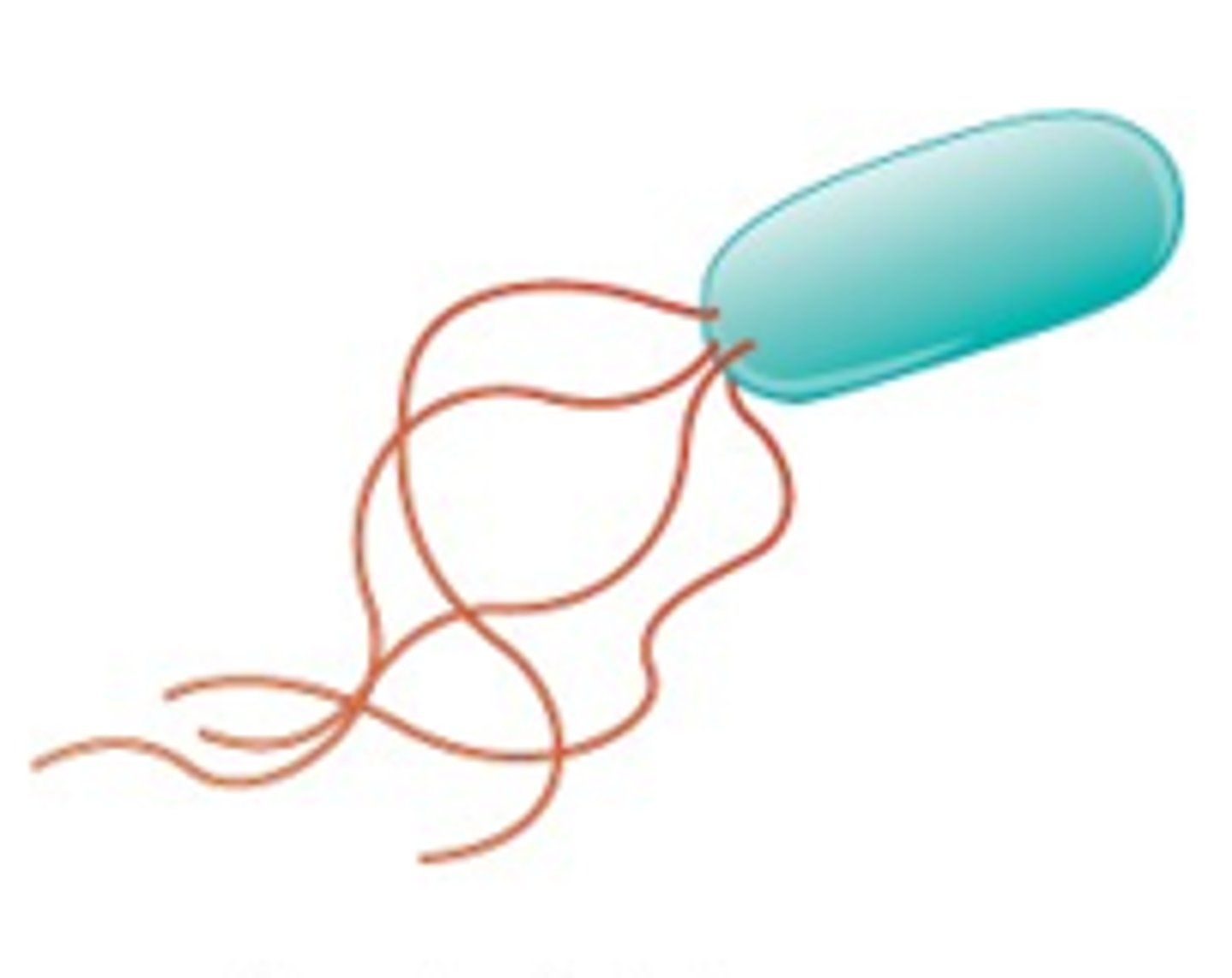
Bacteria with flagella all over is called ______
Peritrichous
Flagella help bacteria perform ______ by moving towards attractants or away from repellents
Chemotaxis
What are the three parts of the flagella?
The basal body, the filament (tail), and the hook
The filament is comprised of protein subunits called _______
Flagellin
T/F: Flagellins are highly immunogenic
True, the immune system recognizes and attacks them

Some bacteria randomly switch between protein types to disguise itself from the immune system, called ______
Phase variation
Flagellar motor of plain filaments turns in which clock direction by default?
Counterclockwise
T/F: A bacteria with counterclockwise rotating flagella will always rotate that way
False, can switch in response to a signaling molecule, causing a "tumble"
_______ is the ability to move in response to environmental stimuli
Tactic response
What are the two important considerations of the tactic response in E. coli?
The length of the run, and
The direction of the run
The presence of what determines the length of the run?
Attractants cause a decrease in tumble frequency, leading to a longer run.
Repellents cause an increase in tumble frequency, leading to a shorter run.
What kind of flagella do spirochetes have?
Internal flagella, located in periplasm between the membranes
What affect do internal flagella have on effectiveness in virulence?
They are highly invasive and virulent as they can burrow through barriers
Protein filaments on the cell surface that are short, straight, and fragile are _____
Pili
Pili are found in what gram of bacteria?
Gram Negative
What are the two biggest functions of pili?
Adhesion and conjugation (fun time)

Type 1 pili are primarily for the function of _____
Adhesion for infection/colonization
T/F: Pili are continually produced after colonization
False, don't need them anymore
Sex pili are used for the transfer of _____ between bacteria
F plasmids, which is an extrachromosomal DNA molecule
T/F: The donor and recipient both retain a plasmid after conjugation
True
Are plasmids necessary for bacteria to be pathogenic?
Yes, many bacteria require plasmids to be pathogenic
The general term for material external to the wall is the _____
Glycocalyx
What are the roles of the glycocalyx?
To protect from phagocytosis, and for
Nonspecific attachment (form a biofilm)
What is exopolysaccharide (EPS)?
A carb-rich substance secreted outside the cell wall to protect against desiccation and phagocytosis, and is important in adhesion and biofilm formation
What is the slime layer?
It is loosely adhered EPS, meaning that it can easily be washed off
What is the S-layer (Surface layer)?
It is a glycoprotein lattice that is TIGHTLY ADHERED to the cell envelope, which provides structural support and acts like armor
What is the thick ,structured layer of repeating glycoproteins at the cell surface?
The Capsule
What bonds attach the capsule to the cell?
Covalent bonds
What is the clinical use of a capsule?
It is useful for stereotyping, since it is surface-exposed, antigenic, and highly variable
How does the capsule play a role in immune evasion?
It prevents recognition by leukocytes
How does the capsule play a role in complement resistance?
It blocks C3b deposition, thus reducing opsonization
How does the capsule play a role in persistence and dissemination?
Bacteria with capsules survive longer in tissues
What is the primary role of the capsule?
Anti-phagocytic properties

Want more info?
What is the function of a bacterial cell wall?
it protects from osmotic stress (doesn't explode like a water balloon)
Why would antibiotics target the cell wall?
To cause osmotic apoptosis
What is included in gram positive cell walls?
A thick layer of peptidoglycan
What is included in gram negative cell walls?
A thin layer of peptidoglycan surrounded by an outer membrane
Why does the amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall determines the gram reaction?
Gram-positive bacteria stay purple because their thick peptidoglycan traps the crystal violet–iodine complex. Gram-negative bacteria lose the dye after decolorization, so they take up the counterstain safranin and appear pink.
What is the role of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall?
It provides strength and rigidity
The strength of peptidoglycan is due to the ________ bonds between peptides and glycan
Covalent
How do antibiotics, such as penicillin, affect peptidoglycan and kill bacteria?
They interfere with peptidoglycan synthesis, causing the cells to swell and burst
In gram positive bacteria, there is often an additional __________ connecting the L-R3 and D-alanine, as opposed to gram negative bacteria, which are linked directly
peptide bridge
What is the precursor to the amino acid Lysine, which is unique to prokaryotes and required for cell wall synthesis?
Diaminopimelic acid (DAP)
What are the bi-functional enzymes that play a role in wall synthesis by making cross links in peptidoglycan?
Penicillin-binding proteins
What is the major polymer of gram positive cell walls?
Peptidoglycan
What is found in all gram positive bacteria and bound to peptidoglycan?
Teichoic acid
(unique to gram positive)
What is the role of teichoic acids in gram positive bacteria?
They provide structural stability, regulate ions, aid adhesion, and act as antigens recognized by the immune system.
_________ are teichoic acids bound to membrane lipids and NOT covalently bound to peptidoglycan
Lipoteichoic acids
(Many gram positive bacteria don't have lipoteichoic acid)
Bacteria with ________ in the cell wall are called acid-fast bacteria
Mycolic acids
T/F: Acid fast cell walls are complex and are difficult to treat
True
What is the role of mycolic acids in the cell wall?
They protect from desiccation, hydrophobic antimicrobials, acids, and bases
What is a key characteristic of mycolic acids?
They are very waxy
Mycolic acids may be bound to _____, forming a compound called cord factor
Trehalose
What are the challenges to treating acid fast infections?
They are waxy, which is a hydrophobic drug barrier,
They grow slowly, meaning it requires longer treatment,
They survive intracellularly, so they hide from macrophages,
They have a latent state, making them resistant to drugs, and
They are intrinsically resistant to many drugs
What color do acid fast bacteria stain?
They don't stain any color
Gram negative cell walls have a peptidoglycan layer with an overlaying ______
Outer membrane
T/F: The gram negative cell wall acts as a selective barrier, has phage receptors, and has pathogenic properties
True
What lies between the two cell membranes ?
The periplasm