Organic Chemistry
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What is a saturated compound?
A compound with a single C — C bond
What are chain isomers?
Same molecular formula but the way their carbon atoms are joined are different
What is an unsaturated compound?
A compound with a double or triple CC bond
What is a homologous series?
A family of compounds with similar chemical properties whose successive members differ by the addition of CH2 group
What is a functional group?
Part of organic molecule largely responsible for molecules chemical properties e.g. OH groups
What is thee functional group and suffix for an alkene
FG: C=C
Suffix: -ene
What is the functional group, suffix and prefix for an alcohol?
FG: -OH
Prefix: Hydroxy
Suffix: -ol
What are the functional groups and prefixes for the haloalkanes?
FG: -Cl, -Br, -I
Prefix: Chloro-, Bromo-, Iodo-
What is the functional group and suffix for an aldehyde?
FG: -CHO
Suffix: -al
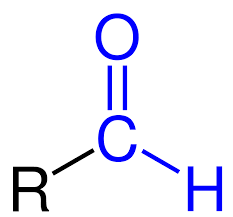
What is the functional group and suffix for a ketone?
FG: -C(CO)C
Suffix: -one
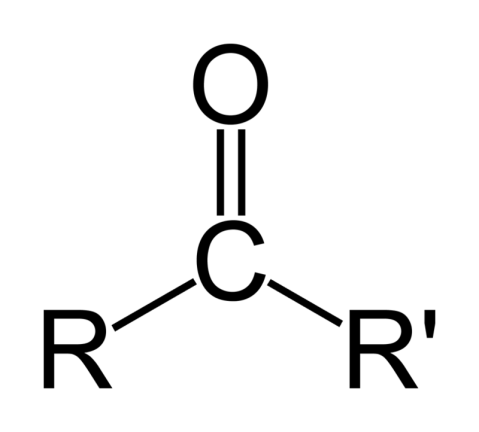
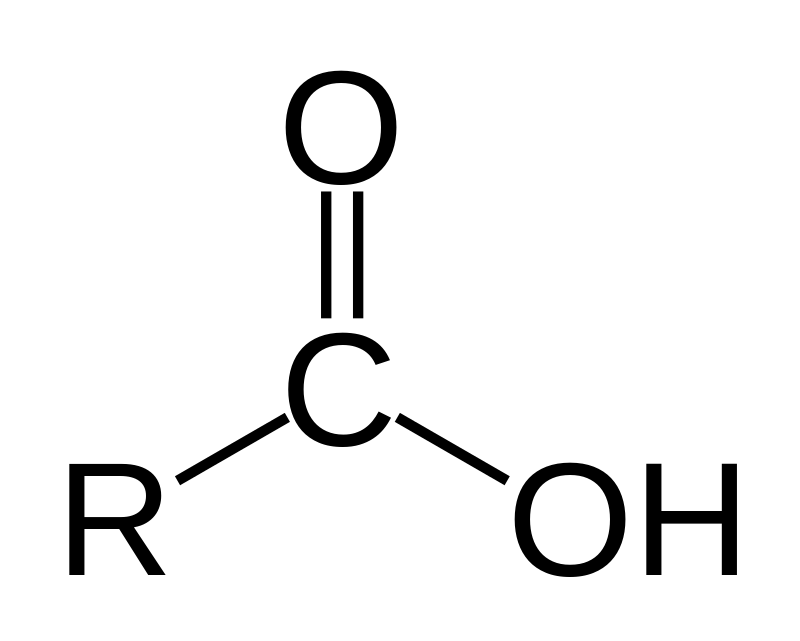
What is the functional group and suffix for a carboxylic acid?
FG: -COOH
Suffix: -oic acid
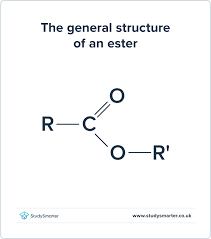
What is the functional group and suffix for an ester?
FG: -COOC
Suffix: -oate
What is the functional group and suffix of acyl chloride?
FG: -COCl
Suffix: -Oylychloride
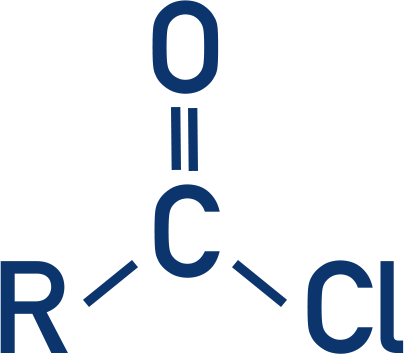
What is the functional group and prefix and suffix for amine?
FG: -NH2
Prefix: Amino
suffix: -amine
What is the functional group and suffix for Nitrile?
FG: -CN
Suffix: -Nitrile
What is aliphatic?
Carbon atoms joined to each other in unbranched or branched chains or in non-aromatic rings
What is alicyclic?
Carbon atoms joined to each other in ring structures, with or without branches
What is aromatic?
Some or all of the carbon atoms are found in benzene rings
What is general formula?
The simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series
What is structural formula?
The minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
What is displayed formula?
The relative positioning of atoms and the bonds between them
What is skeletal formula?
The simplest organic formula shown by removing H atoms from alkile chains leaving just C skeleton and associated functional groups.
What are the IUPAC rules when naming organic compounds?
Select the longest continuous carbon chain with the functional group
Number it such that the functional group gets a lower number
Number it such that alkyl groups get lower numbers
Assemble the name listing groups in alphabetical order. Prefixes are used to designate several groups of the same kind, are not considered when alphabetising
What is a structural isosmer?
A molecule with the same molecular formula but with different structures
What is a chain isomer?
Same molecular formula but with a different structure
What is a positional isomer?
Where the molecular formula is the same but the position of the functional group is different.
What is a functional group isomer?
Same molecular formula but a different functional group
What is are stereo isomers?
Molecules with the same structural formula but with different arrangement of atoms in space
What are the requirements of geometric isomers?
restriction of roation - this can be achieved by having a C=C or by having a cyclic structure
Each carbon atom of the C=C should have different groups
What is a cis isomer
Each C from the C=C has different groups
What is a Trans isomer?
Above and below there are different groups
What is Cohn-Ingold Prelog non enclature?
Used to decide how to name isomers
If groups of high priority are on the same side it is a Z isomer
If groups of high priority are on opposite sides it is an E isomer
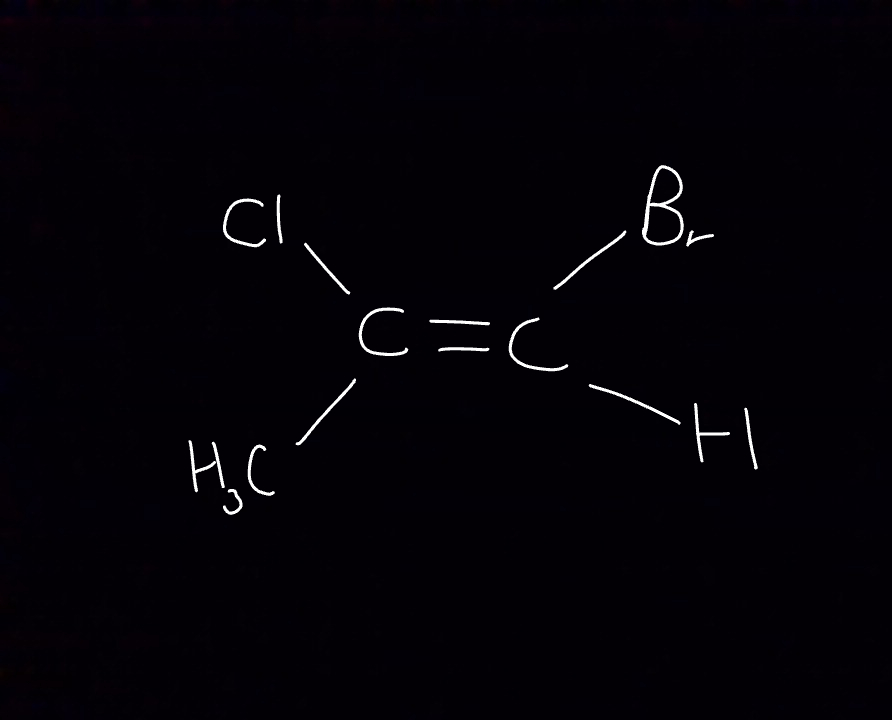
Name this isomer
Chlorine is higher priority because it has the highest atomic mass (out of chlorine and Methyl)
Bromine is higher priority because it has the highest atomic mass (out of bromine and hydrogen)
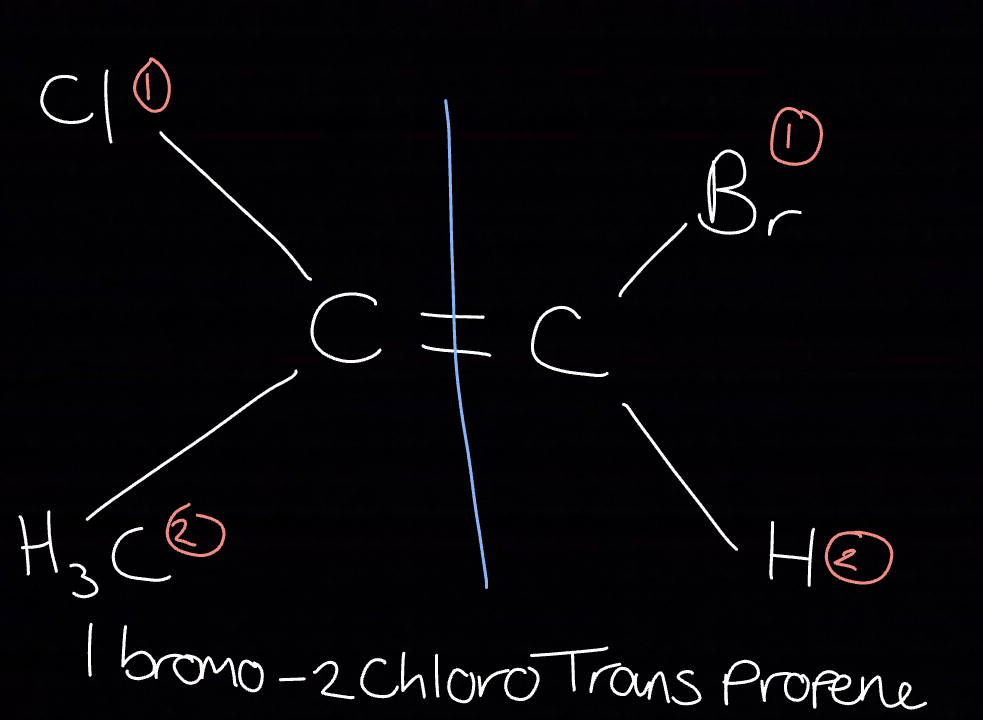
Which groups are priority?
Methyl
ClCH4

What is a carbocation?
A cation where positive charge is on a carbon atom
What is a free radical?
Species with a single unpaired electron
What does a mechanism show?
The movement of electrons
What do curly arrows show?
The movement of a pair of electrons, they start from an area where there is electrons e.g. double bond or lone pair and end where you are moving the electrons to or the formation of a new bond.
What is bond fission?
The breaking of a covalent bond
What is heterolytic bond fission?
Where the electrons are distributed unequally to form two different ions ( a cation and an anion), the double headed arrow shows the movement of a pair of electrons.

What is homolytic bond fission?
Where the bond breaks with the pair of electrons in the bond being shared equally to form 2 uncharged radicals. The dot means there is an unpaired electron on the atom.

What is sigma bonding?
A covalent bond which is as a result of the overlap of S orbitals, one from each bonding atom - the sigma bond lies directly between the bonding atom.
What is Pi bonding?
A covalent bond formed by the overlap of p orbitals on adjacent atoms, perpendicular to any sigma bond(s) between the same atoms.
What is the bonding in alkanes?
Covalent sigma bond

What is the bond angle in alkanes?
All carbons in alkanes have tetrahedral structures 109.5°
Can alkanes freely rotate and what does this mean?
Yes - because they are in a single bond they can rotate freely.
How does fractional distillation in cracking alkanes?
The longer the hydrocarbon chain the higher the boiling point. So the mixture of alkanes is boiled and the resulting vapours travel up the fractionating column where they condense and are collected.
Why is the boiling point higher when the chain length is longer?
Because as chain length increase molecules have a larger surface area and more electrons so more london forces will occur therefore more energy is needed to overcome the forces.
What happens to the boiling point of alkanes when branching increases?
The boiling point decreases because the surface area decreases because there is less surface contact.
True or false alkanes are very reactive
False because C-C and C-H σ Bonds are very strong and because the are non - polar.
What is combustion and what are the 2 different types and their word formulas?
A reaction with oxygen
Incomplete - occurs in a limited supply of oxygen, if the supply of oxygen is further limited unburnt carbon can be resulted.
Alkane + Oxygen → Carbon monoxide + Water
Complete - occurs in excess oxygen
Alkane + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water
What is halogenation of alkanes?
Homolytic free radical substitution
substituiton is a reaction in which an atom or group of atoms have been replaced by another.
What are the three steps of halogenation?
Initiation
Propagation
Termination
What happens at initiation?
In the presence of UV light, halogen molecule undergoes homolytic fission to give free radicals which are reactive species
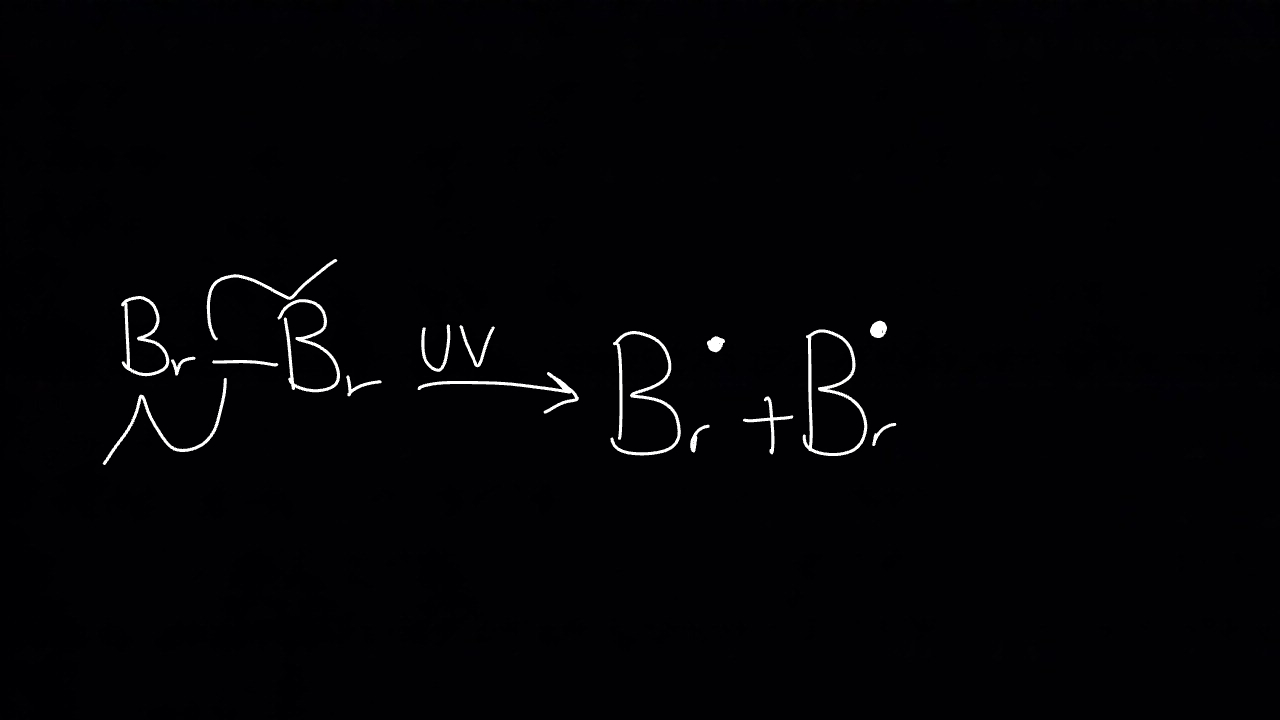
What happens during propagation?
Some radicals are used up and some radicals are formed, must have
neutral molecule + radical → neutral molecule + radical
Add radical and react with alkane
React the radical alkyl group formed with another molecule of halogen (bromine in this case)
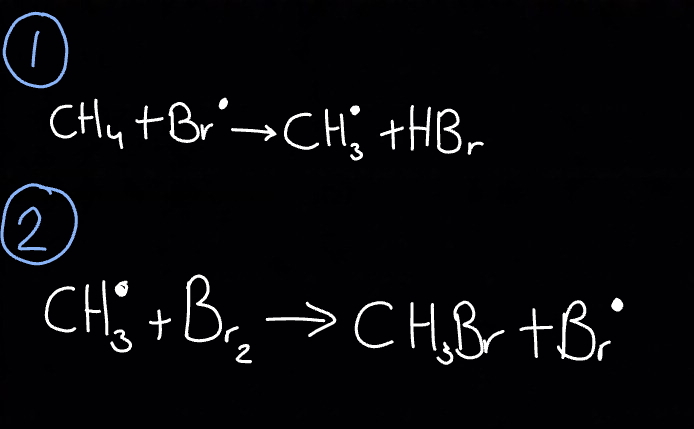
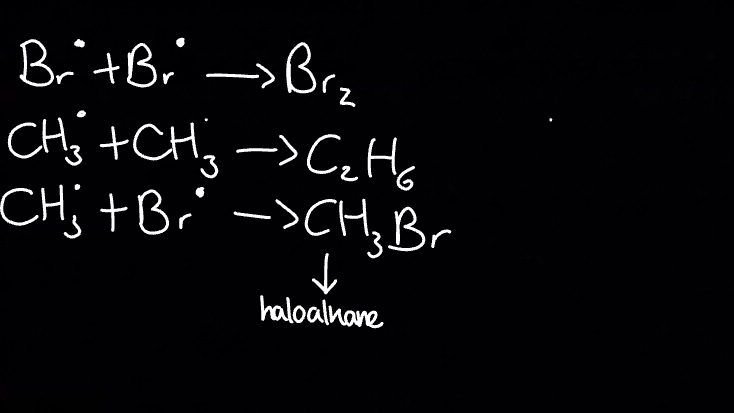
What happens during termination?
All leftover radicals reacted together
What is the bonding in alkenes?
Pi bonding
True or false for each C of the C=C bond, 3 of the 4 electrons are used in 3 pi bonds and the last electron is in an s - orbital
False for each C of the C=C bond, 3 of the 4 electrons are used in 3 sigma bonds and the last electron is in the p orbital.
How is a pi-bond formed?
From the sideways overlap of 2p orbitals. The electron density is above and below the line joining the nuclei of the bonded atoms.
What is the geometry of alkenes (around the double bond) and alkanes?
Geometry of alkenes around double bonds - trigonal planar
Geometry of alkanes - tetrahedral
Describe the rotation of the 2 carbon atoms in the C=C bond?
The pi bond locks the 2 carbon atoms of the C=C bond into position and prevents rotation.
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes?
Because of their pi bond. In the pi bond, the pi-electron density is concentrated above and below the plane of the sigma bond. Because they are on the outside of the C=C bond, they are more exposed than the sigma bond electrons so the pi bond can readily break and allow alkenes to undergo addition reactions easily.
What are the differences between bond breaking/reactions in alkenes and bond breaking in alkanes?
When alkenes react the pi bond breaks whereas when alkanes react, the sigma bond remains in tact, pi bonds are weaker than sigma bonds so have lower bond enthalpies and are broken more readily.
What is hydrogenation?
An addition reaction between an alkene and H2 over a nickel catalyst at 432K to form an alkane. The number before the hydrogen is the same as the double bonds.
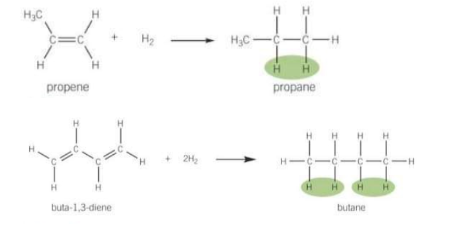
What is halogenation?
When alkenes undergo rapid addition with halogens Cl2 or Br2
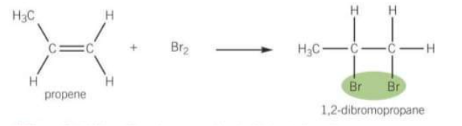
What is the test for alkenes?
Add Br2 to identify is a C=C bond is present in an organic compound. When bromine water is added the solution goes from orange to colourless.
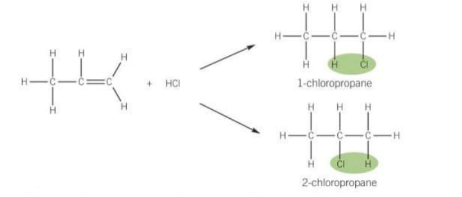
What is the hydrogen halide reaction?
When alkenes react with gaseous hydrogen halides at room temperature to from haloalkanes.
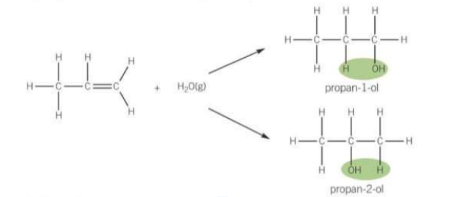
What is hydration? - reaction of alkenes
Alcohols are formed when alkenes react with steam in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst H3PO4. The steam adds across the C=C bond.
note: remember it is steam so H2O is a liquid
What is an electrophile?
An atom or a group of atoms that is attracted to an electron rich centre and accepts a pair of electrons, usually a positive ion or molecule containing an atom with a partially positive charge.
What is a nucleophile?
An atom or a group of atoms that is attracted to an electron deficient carbon atom, where it donates a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond. e.g. OH- ions water molecules, ammonia
Finish the sentance:
Alkenes take part in addition reactions to form saturated products in a mechanism called….
Electrophilic addition
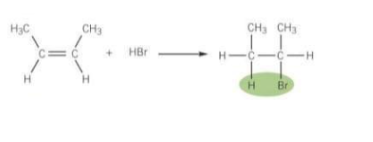
Draw and the describe the electrophilic addition of this reaction
Br is more elctronegative than H so HBr is polar and has a dipole
The electron pair in the pi-bond are attracted to the partially positive H atom, causing the C=C bond to break
A bond forms between the H atom of HBr and a C atom from the C=C bond
The H-Br atom breaks by heterolytic fission, with the electron pair going to the Br atom
A Br- ion and a carbocation is formed. The carbocation is a positively charged C atom
Br- reacts with the carbocation to form the addition product
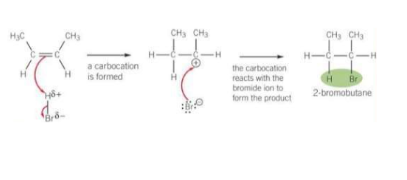
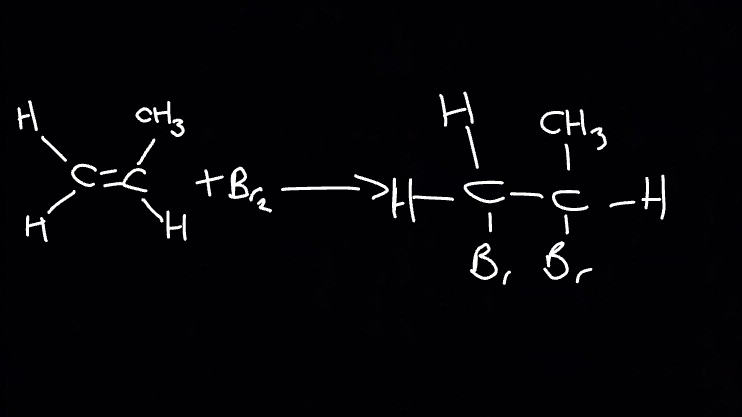
Draw and describe halogen elctrophlic addition for this reaction
Br2 is a non-polar molecule. When Br2 approaches an alkene, the pi-electrons interact with electrons in the Br-Br bond causing polarisation across the Br-Br bond in an induced dipole.
The electron pair in the pi-bond is attracted to the partially positive Br, causing the double bond to break
A bond between a C atom of the C=C bond and the partially positive Br atom is formed
The Br-Br bond breaks by heterolytic fission with the electron pair going to the partially negative Br atom forming a Br- ion and a carbocation
The Br- ion reacts with the carbocation to form the addition product.
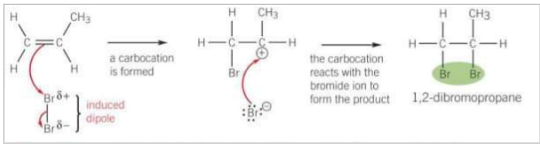
What is a carbocation?
An ion with a positively charged carbon atom
What is Markowinkoff’s rule?
When a hydrogen halide reacts with an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen of the hyrogen halide attaches itself to the carbon of the alkene with the greatest number of hydrogen atoms and the smallest number of carbon atoms.
What are the 2 possibilities in the first step of electrophilic addition: the formation of a carbocation
Primary - the positive charge is on a carbon atoms at the end of the chain
Secondary - the positive charge is on a carbon atom with 2 other carbon chains attached
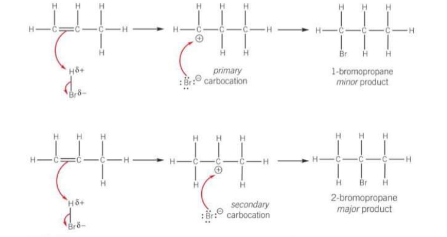
Which one is the major product and which yield is smaller
The major product is 2-bromopropane formed from the secondary carbocation
The yield for 1-bromopropane is much smaller
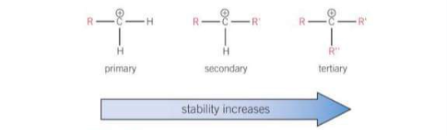
How are carbocations classified?
By the number of alkyl groups attached to the positively charged C atom
How is carbocation stability determined? Which carbocation is the most stable?
Carbocation stability is linked to the electron-donating ability of alkyl groups. Each alkyl group pushes electron density towards the positive charge of the carbocation. The positive charge is therefore spread across the alkyl groups and the more alkyl groups attched to the positively charged C atom, the more charge is spread out and the more stable the carbocation.
Tertiary carbocations are the most stable
Complete the sentance:
Addition of a ………… ….………….. to an unsymmetrical ………… forms the major product via the most stable carbocation
Hydrogen halide
alkene
What are polymers?
Large molecules formed from thousands of repeat units of smaller molecules known as monomers
What happens to alkenes when they undergo addition polymerisation?
They form long saturated chains forming no double bonds
Finish the sentence
Addition polymers have ………. Molecular masses
Addition polymers have high molecular masses
How are synthetic polymers named
After the monomer that makes then with the prefix poly
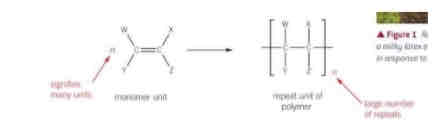
What is a repeat unit and where is the repeat unit in an addition polymer, what shows the number of repeating units?
The specific arrangement of atoms in the polymer molecule, that repeats over and over again. It is always in square brackets in an addition polymer. The letter n follows the brackets to show there is a large number of repeating units, the n is also in front of the reactant.
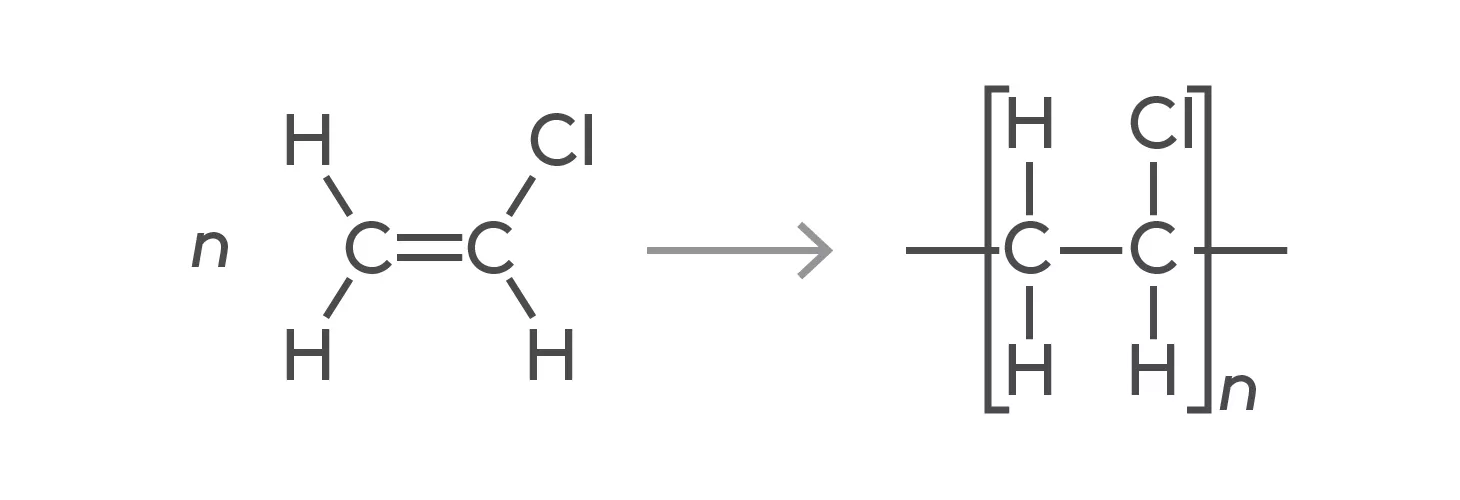
What is PVC?
poly(vinyl chloride) or poly(chloroethene), it can be prepared to make a polymer that is flexible or rigid
Why are waste polymers commonly used?
They are readily available, cheap to purchase an convenient to throw away. Their lack of reactivity makes them suitable for storing food and chemicals safely.
Why should polymers be recycled?
Because it reduces their environmental impact by conserving fossil fuels as well as decreasing the amount of waste going to landfill.
How are polymers recycled?
Discarded polymers have to be sorted by type, if they are mixed the product is unusable. Once sorted they are chopped into flakes, washed, dried and melted and the recycled polymer is cut into pellets are used by manufacturers to make new products.
Why is the disposal and recycling of PVC hazardous?
Because of the high chlorine content and the range of additives present in the polymer, it is not sustainable to put in land fill and when burnt it releases hydrogen chloride which is a corrosive gas. It also releases other pollutants like toxic dioxins.
What can waste polymers be used for if they are difficult to recycle?
As they are derived from petroleum or natural gas, they have a high stored energy value so can be incinerated to produce heat, generating steam to drive a turbine to produce electricity.
What is feedstock recycling?
It is the chemical and thermal processes that can reclaim monomers, gases or oil from waste polymers. The products from feedstock recycling resemble those produced from crude oil in refineries. These materials can be used as raw materials for the production of new polymers.
What is an advantage of feedstock recycling?
It is able to handle unsorted and unwashed polymers
What is feedstock?
The material needed to produce something in an industrial process.
What are bioplastics and why are they good?
Bioplastics produced from plant starch, cellulose, plant oils and proteins offer a renewable and sustainable alternative to oil based products.
How does the use of bioplastics help the environment?
It protects the environment and conserves valuable oil reserves.
How are biodegradable polymers broken down and what are they made from?
They are broken down by microorganisms into water, carbon dioxide and biological compounds. They are usually made from starch or cellulose or contain additives that alter the structure of traditional polymers so that microorganisms can break them down.
Why are compostable polymers good?
Because they leave no visible or toxic residues
What are bioplastics likely to be used for as technology advances?
They are likely to be used in packaging, electronics, and more fuel efficient and recyclable vehicles.
What are photodegradable polymers?
Oil based polymers that are being developed, they contain bonds that are weakened by absorbing light to start the degradation. Alternatively light absorbing additives are used.