Radioactivity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
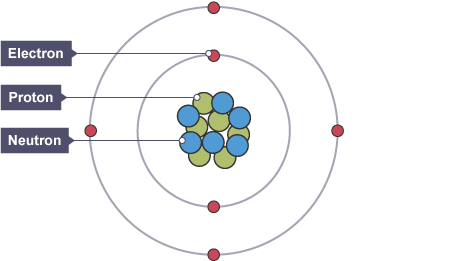
Describe the structure of an atom
- atoms have a positively charged nucleus made up of positive protons & neutral neutrons
- the nucleus is surrounded by shells which contain negative electrons that orbit the nucleus
What is the atomic number?
the number of protons an atom has
(number of protons = number of electrons because atoms are neutral)
What is the mass number?
the total number of protons & neutrons an atom has
What is an isotope?
atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
What is radioactive decay?
- when an unstable nucleus loses energy by emitting ionising radiation to become more stable
- this is a random process
What is radioactivity?
the emission of ionising radiation when an unstable nuclei decays
What are the units for radioactivity?
becquerels (Bq)
1 becquerel = 1 decay per second
What are the properties of alpha radiation?
Type of particle: helium nucleus (large, heavy, slow moving)
Relative mass: 4
Relative charge: +2
Ionising ability: strong
Penetrating power: weak
Absorbed by: a few mm of paper
What are the properties of beta radiation?
Type of particle: electron (high kinetic energy, fast moving)
Relative mass: 1/2000
Relative charge: -1
Ionising ability: medium
Penetrating power: medium
Absorbed by: a few mm of aluminium
What are the properties of gamma radiation?
Type of particle: electromagnetic wave
Relative mass: 0
Relative charge: 0
Ionising ability: weak
Penetrating power: strong
Absorbed by: several cm of lead, a few m of concrete
Why does alpha radiation have strong ionising ability & weak penetrating power?
because alpha particles are large, heavy & slow moving
- this gives them strong ionising ability as they have lots of collisions with atoms & therefore can ionise them
- this gives them weak penetrating power because most of their kinetic energy is used up in ionisation & they are difficult to absorb due to their large mass
Why does gamma radiation have weak ionising ability & strong penetrating power?
because gamma rays are fast moving & have no mass, just energy
- this gives them weak ionising ability as it is difficult for them to collide with atoms & therefore ionise them
- this gives them strong penetrating power as they have lots of energy & can quickly penetrate a long way into a material without being stopped
What happens when a nucleus emits an alpha particle?
mass number decreases by 4
atomic number decreases by 2
nuclear charge decreases by 2

What happens when a nucleus emits a beta particle?
mass number stays the same
atomic number increases by 1
nuclear charge increases by 1
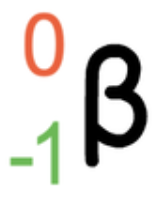
What happens when a nucleus emits a gamma particle?
mass number stays the same
atomic number stays the same
nuclear charge stays the same

What happens when a nucleus emits a neutron?
mass number decreases by 1
atomic number stays the same
nuclear charge stays the same

How can ionising radiation be detected?
Geiger-Muller tube
photographic film
What is the count rate?
the number of decays recorded each second by a radioactive detector
What is background radiation?
the low-level ionising radiation that is produced & present all of the time
What are some sources of background radiation?
from Earth → rocks, food & drink, fallout from nuclear weapon testing, nuclear power plants, x-rays & MRI scanners
from space → cosmic rays
What is half-life?
the time taken for half of a radioactive nuclei to decay
What are some uses of radioactivity in industry?
long half-life alpha emitters are used in smoke detectors → alpha particles cause a current in the detector & if smoke enters, some alpha particles will be absorbed causing the current to drop which then triggers the alarm
long half-life beta emitters are used for thickness monitoring of metal sheets → a source & receiver are placed on either side of the sheet during its production & if there is a drop or rise in beta particles detected, the thickness of the sheet has changed & needs to be adjusted
What are some uses of radioactivity in medicine?
sterilisation of equipment → gamma emitters can kill any bacteria or parasites on equipment through its protective packaging which eliminates the risk of contamination & makes the equipment safe to use in operations
diagnosis → short half-life gamma emitters are used as tracers in medicine because they concentrate in certain parts of the body (the half-life must be long enough for diagnostic procedures to be performed but short enough to not remain radioactive for too long)
treatment → some gamma emitters can be used to destroy tumors with a high dose of radiation
What is contamination?
when a radioactive source has been introduced into or onto an object
the contaminated object becomes radioactive for as long as the source is still in or on it
What is irradiation?
when an object is exposed to a radioactive source which is outside the object
the irradiated object does NOT become radioactive
What are some safety measures to avoid contamination or irradiation?
- minimising the time of exposure to radiation
- keeping the biggest distance possible from the radioactive source
- use shielding against radiation (e.g. protective clothing made from dense materials like lead)
- dispose radioactive waste from nuclear reactors carefully (e.g bury it in sealed drums deep underground & remotely handle it after it has been cooled)