Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Bonds, Water, and Organic Molecules in Biology
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is a chemical bond?
An interaction between two atoms that results in them being chemically linked.
What are the two major types of chemical bonds?
Ionic and covalent.
What is the octet rule?
An atom is stable when its valence shell is completely full.
What are molecules?
Groups of atoms associated with each other through bonds.
Give examples of common molecules.
Carbon dioxide (CO2), glucose (C6H12O6), water (H2O), sodium chloride (NaCl).
What are nonpolar molecules?
Molecules that contain a high number of nonpolar covalent bonds and few polar covalent bonds, such as lipids.
What are polar molecules?
Molecules that contain a moderate number of polar covalent bonds, including carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and water.
What are hydrogen bonds?
Electrical attractions between a polar covalently bound hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in water?
They hold water molecules together and stabilize large molecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
What is the significance of water in the human body?
Water makes up 70% of body mass and is the universal solvent, facilitating metabolic reactions and transport of substances.
What does 'like dissolves like' mean?
Polar substances mix well with other polar substances, while nonpolar substances mix well with other nonpolar substances.
What are hydrophilic substances?
Polar chemicals that mix with water.
What are hydrophobic substances?
Nonpolar chemicals that do not mix with water.
What is solvency?
The ability of water to dissolve matter.
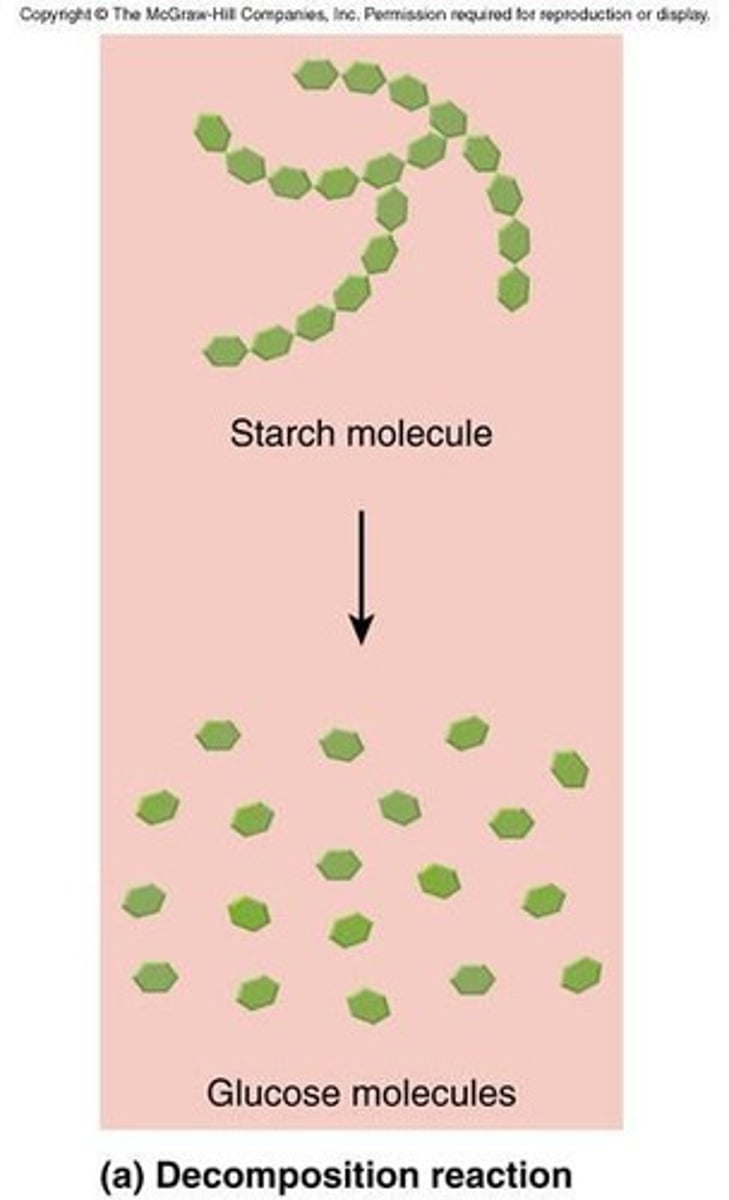
What are catabolic reactions?
Decomposition reactions that release energy into the environment.
What are anabolic reactions?
Synthesis reactions that store energy from the environment to create bonds.
What is activation energy?
The energy required to bring reactants together for a chemical reaction to occur.
What are organic molecules?
Molecules that contain carbon and are unique to living systems.
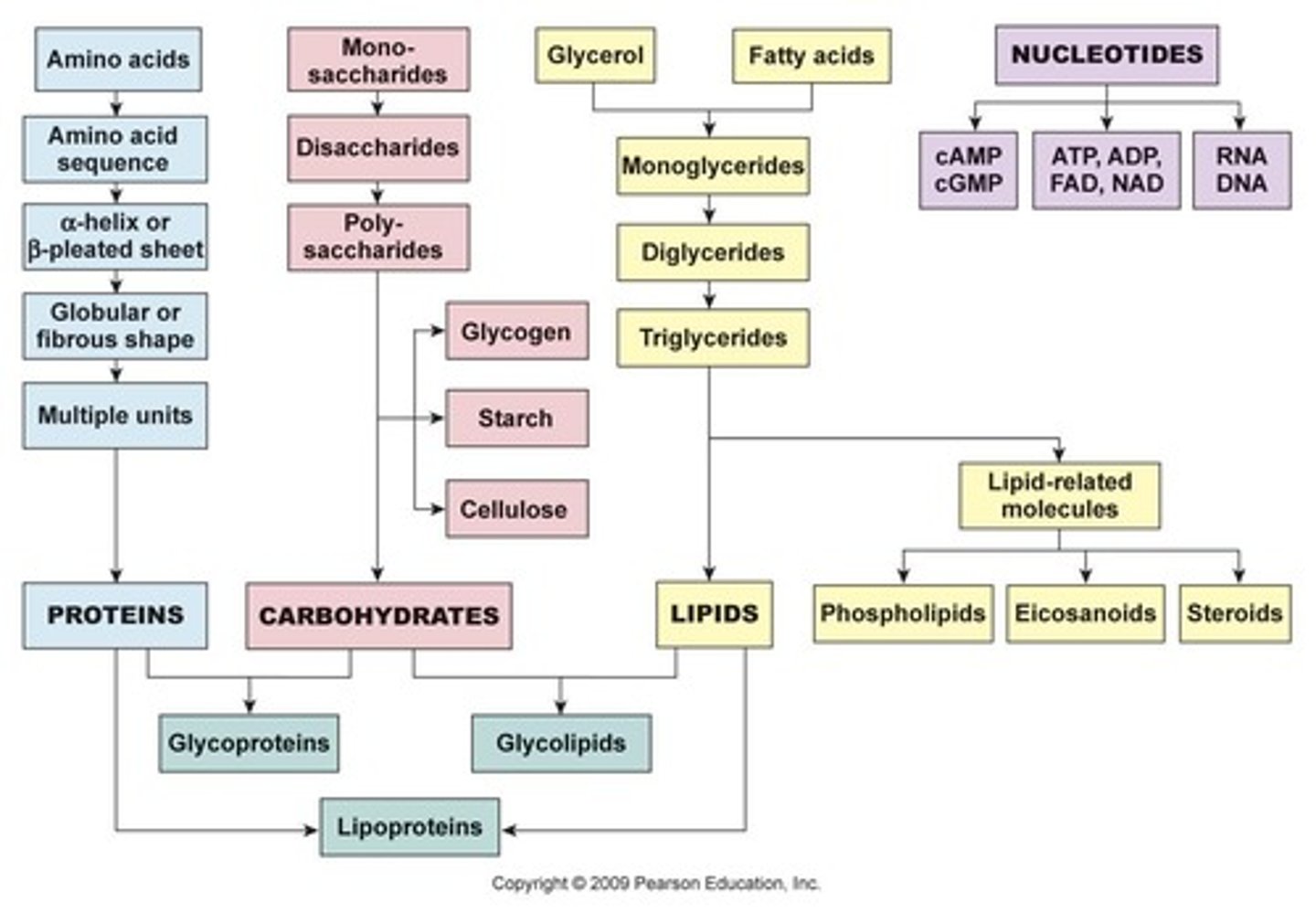
What are the four classes of organic macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What are monomers?
Small molecular subunits that make up macromolecules.
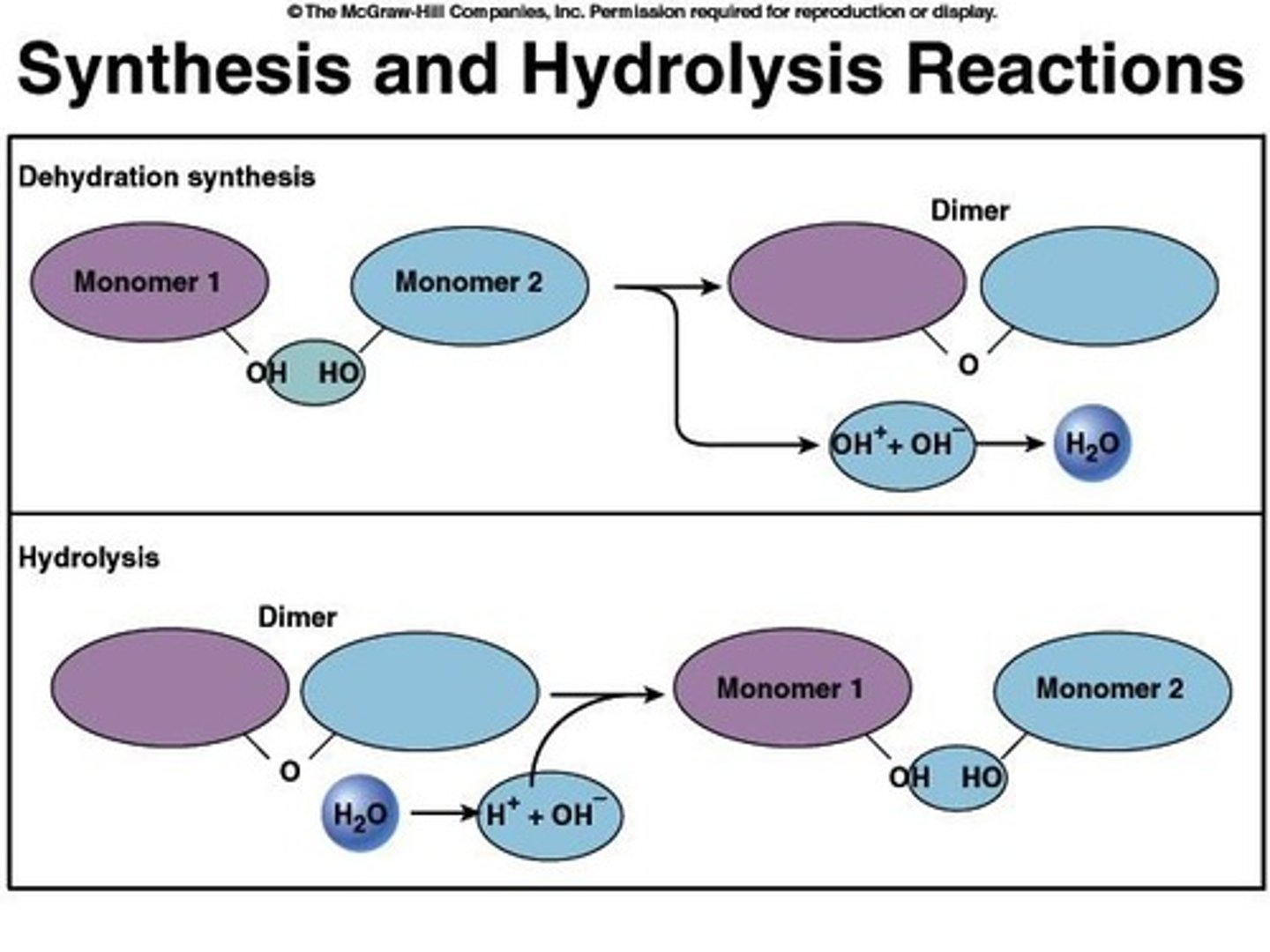
What is dehydration synthesis?
The process of covalently bonding two monomers together by removing a water molecule.
What is hydrolysis?
The process of splitting a polymer by adding a water molecule.
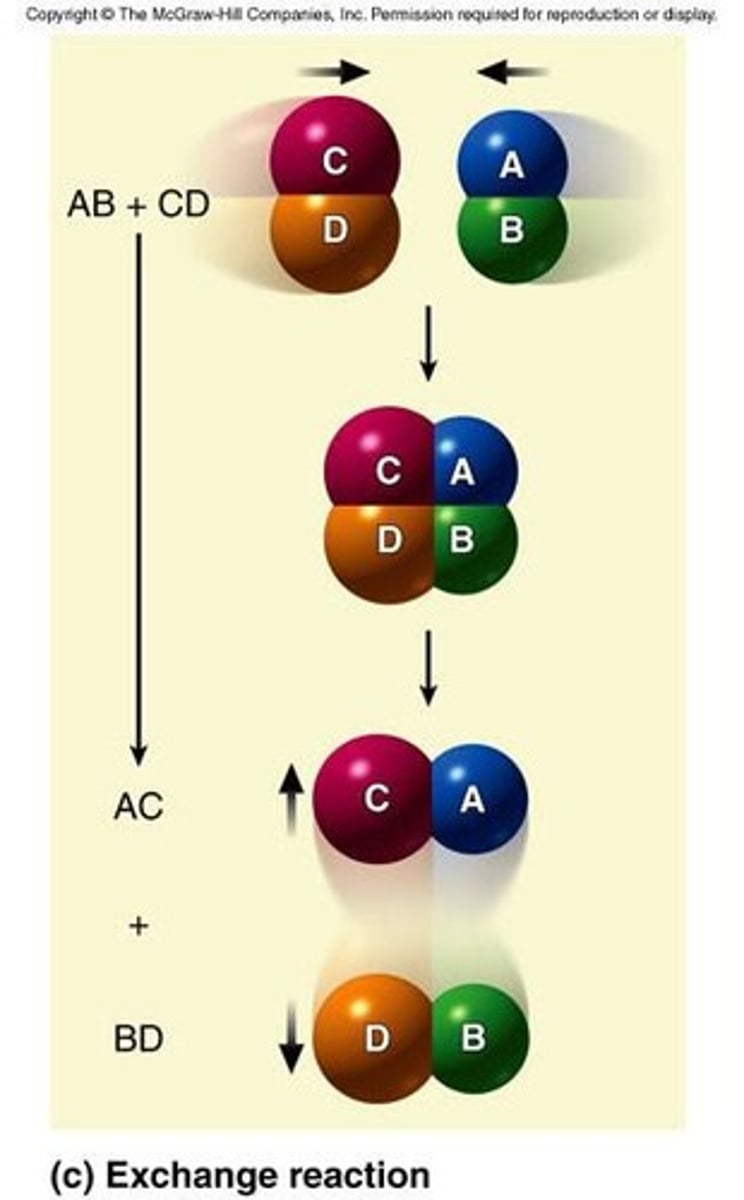
What are exchange reactions?
Reactions where two molecules collide and exchange atoms or groups of atoms.
What are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions?
Reactions that involve the transfer of electrons from one atom or molecule to another.
What happens to reactants that lose electrons in a chemical reaction?
They become oxidized.
What is the mnemonic for remembering oxidation and reduction?
LEO (Loss of Electrons is Oxidation) and GER (Gain of Electrons is Reduction).
In the reaction Na + Cl → Na+ + Cl-, what is the oxidation state of Na and Cl?
Na is oxidized and Cl is reduced.
What factors determine the rate of chemical reactions?
Concentration of reactants, temperature, and presence of catalysts.
How does increasing the concentration of reactants affect reaction rates?
It increases the rate due to more collisions.
What role do catalysts play in chemical reactions?
They bring reactants together faster, increasing reaction rates.
What are carbohydrates primarily composed of?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
What suffix do carbohydrate names typically end with?
-ose.
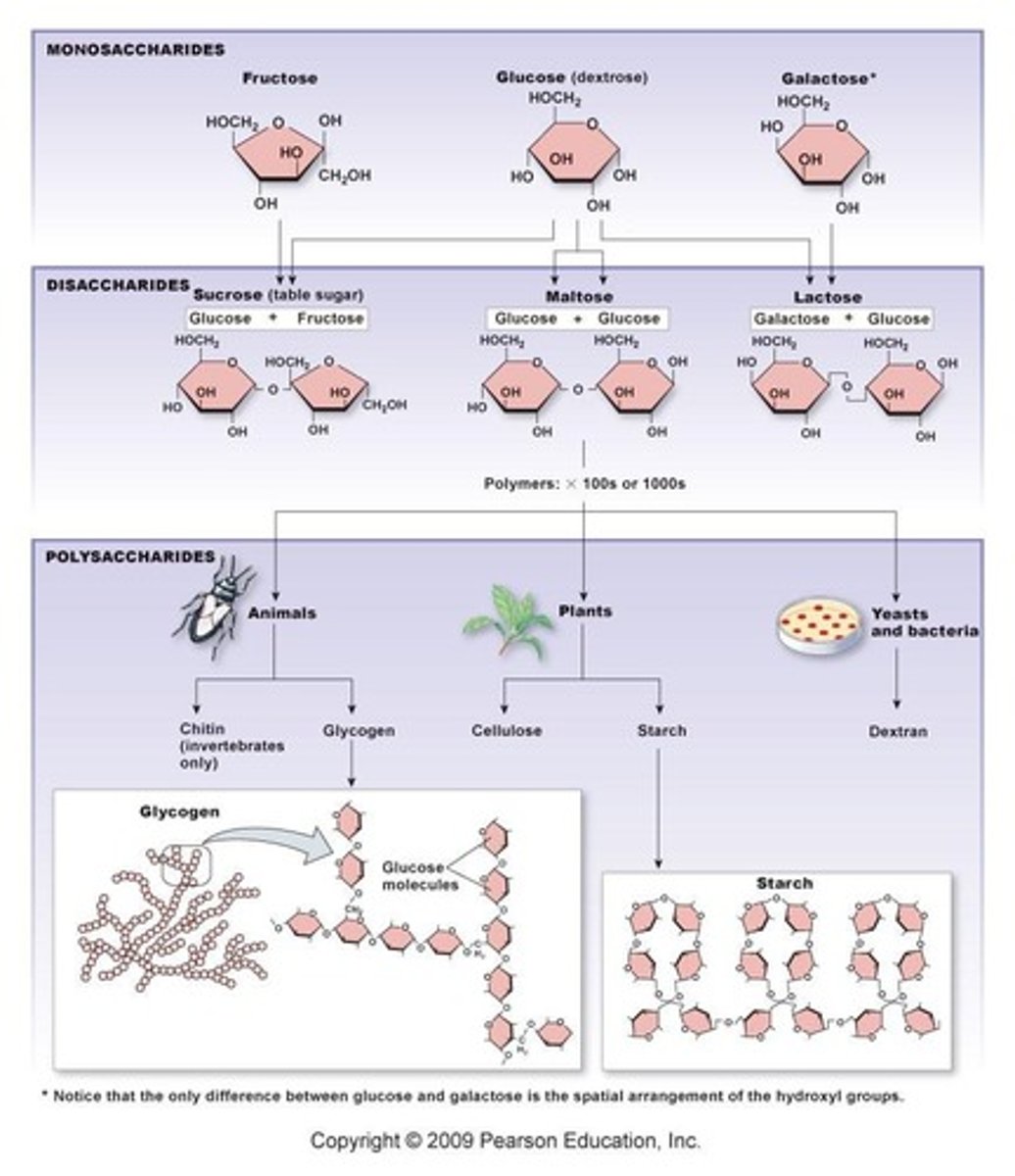
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides.
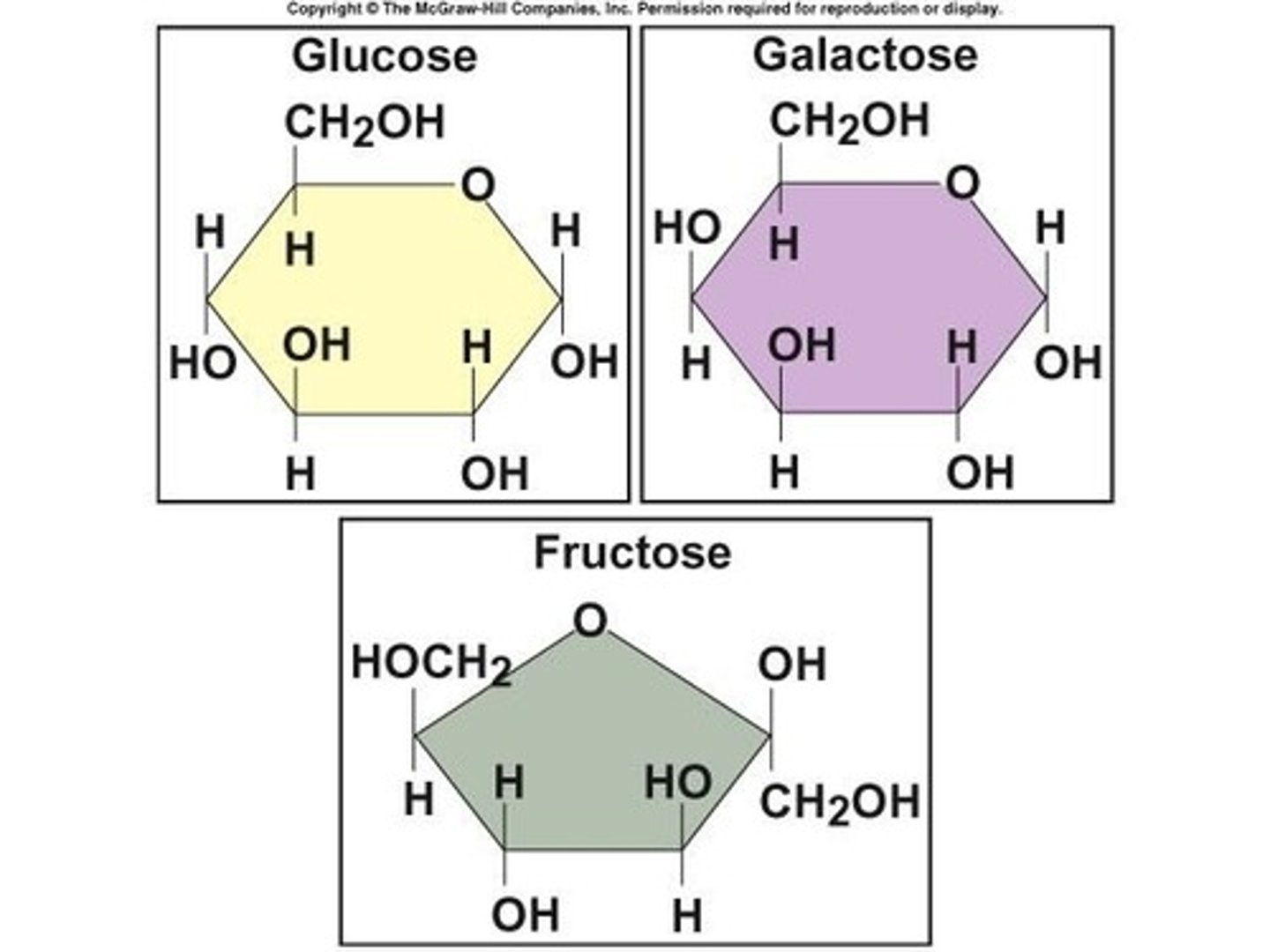
What is the most biologically important monosaccharide?
Glucose.
What is the general atomic ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in carbohydrates?
1:2:1.
What are disaccharides composed of?
Pairs of monosaccharides covalently bonded together.
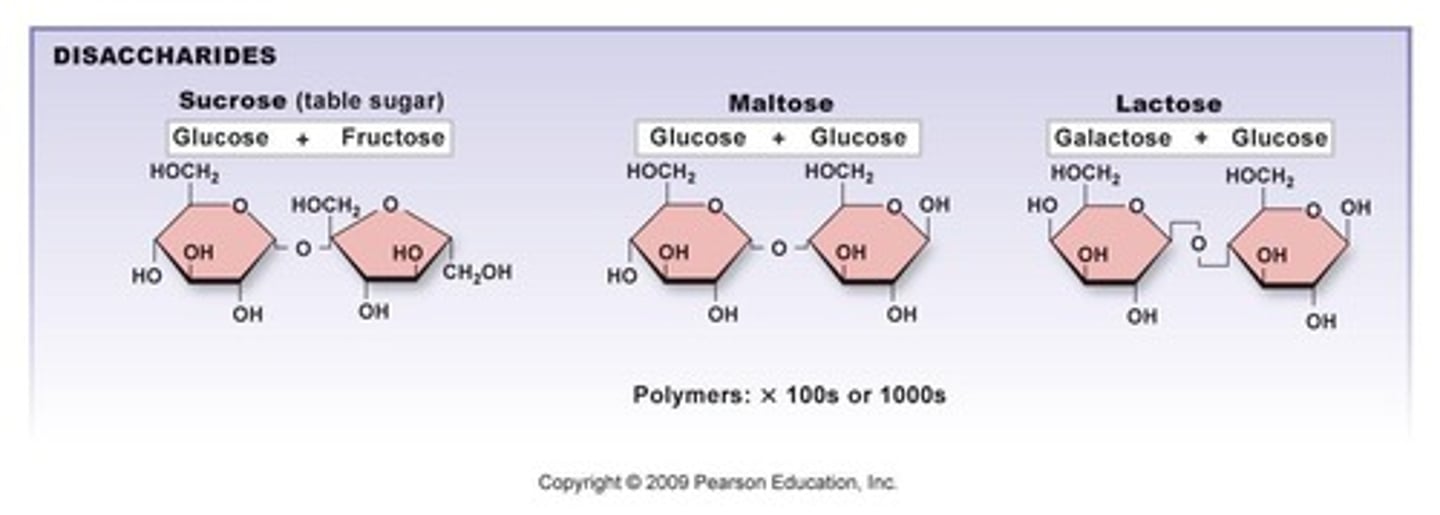
Name the three major disaccharides.
Sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), maltose (glucose + glucose).
What are polysaccharides made of?
Long chains of glucose.
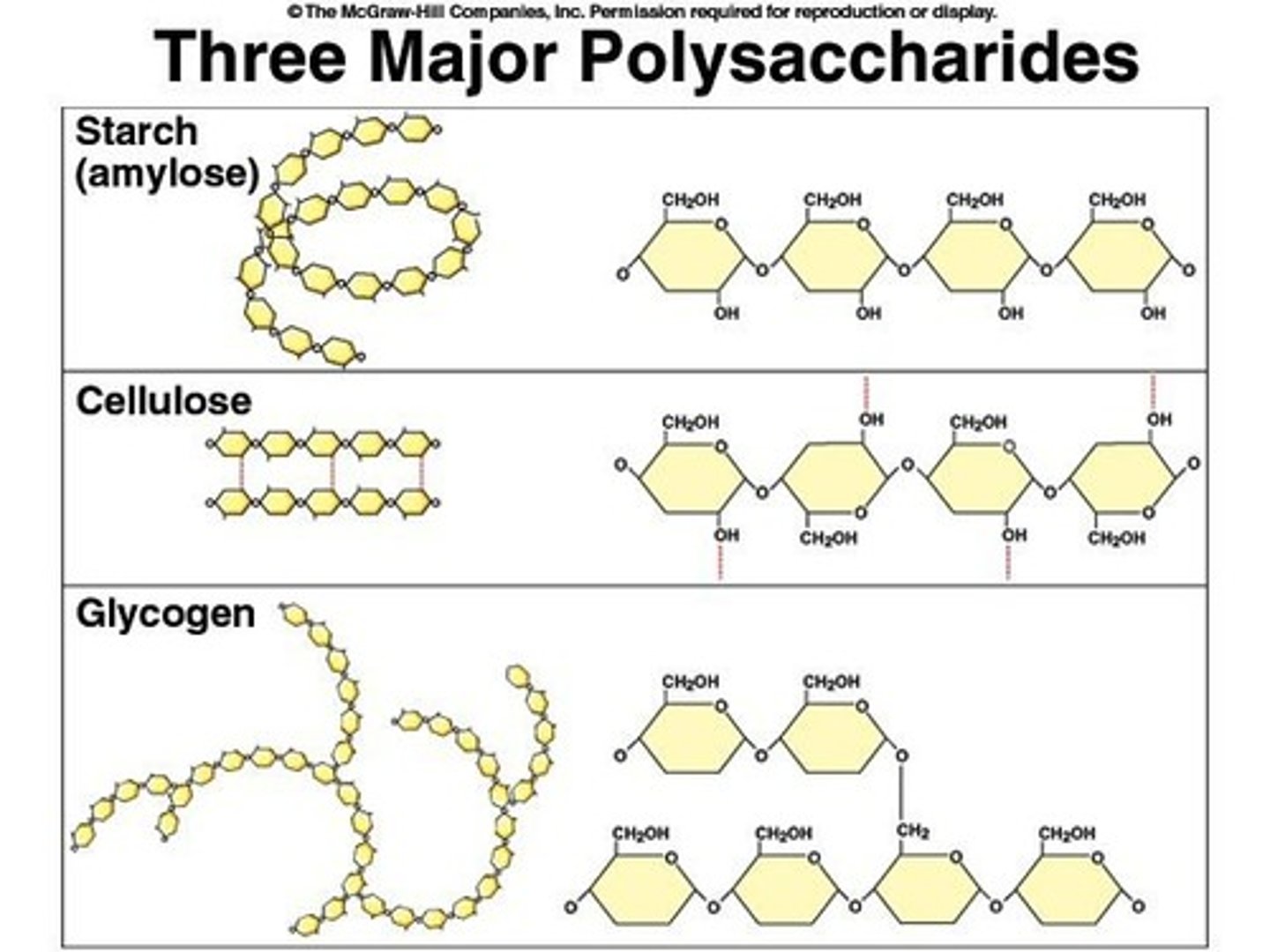
What is starch and its function?
A form of stored carbohydrates produced by plants, serving as the main source of dietary carbohydrates.
What is glycogen and its role in the body?
A polysaccharide synthesized from excess glucose, hydrolyzed to glucose between meals for energy.
What are lipids primarily composed of?
Carbon and hydrogen, making them nonpolar organic molecules.
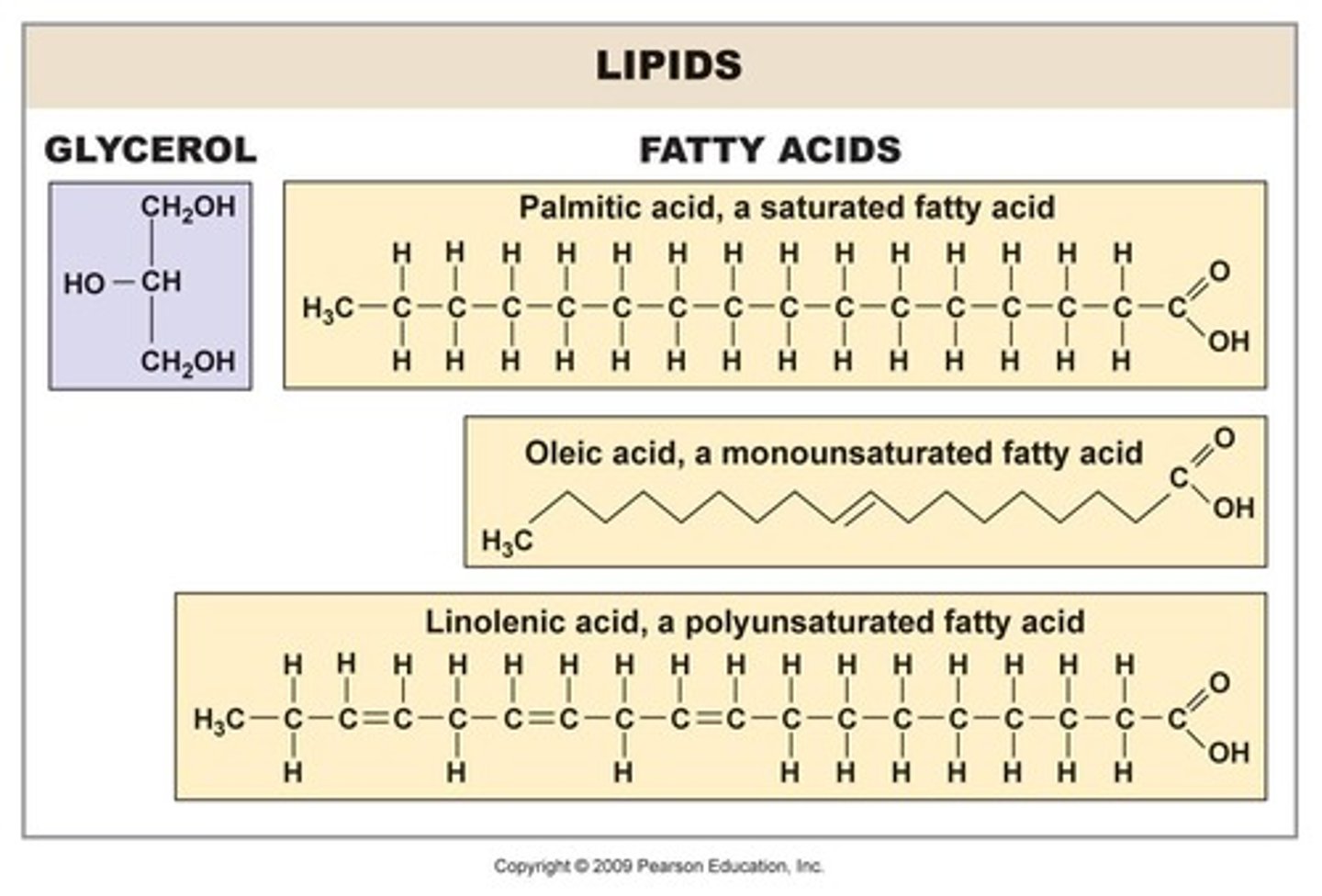
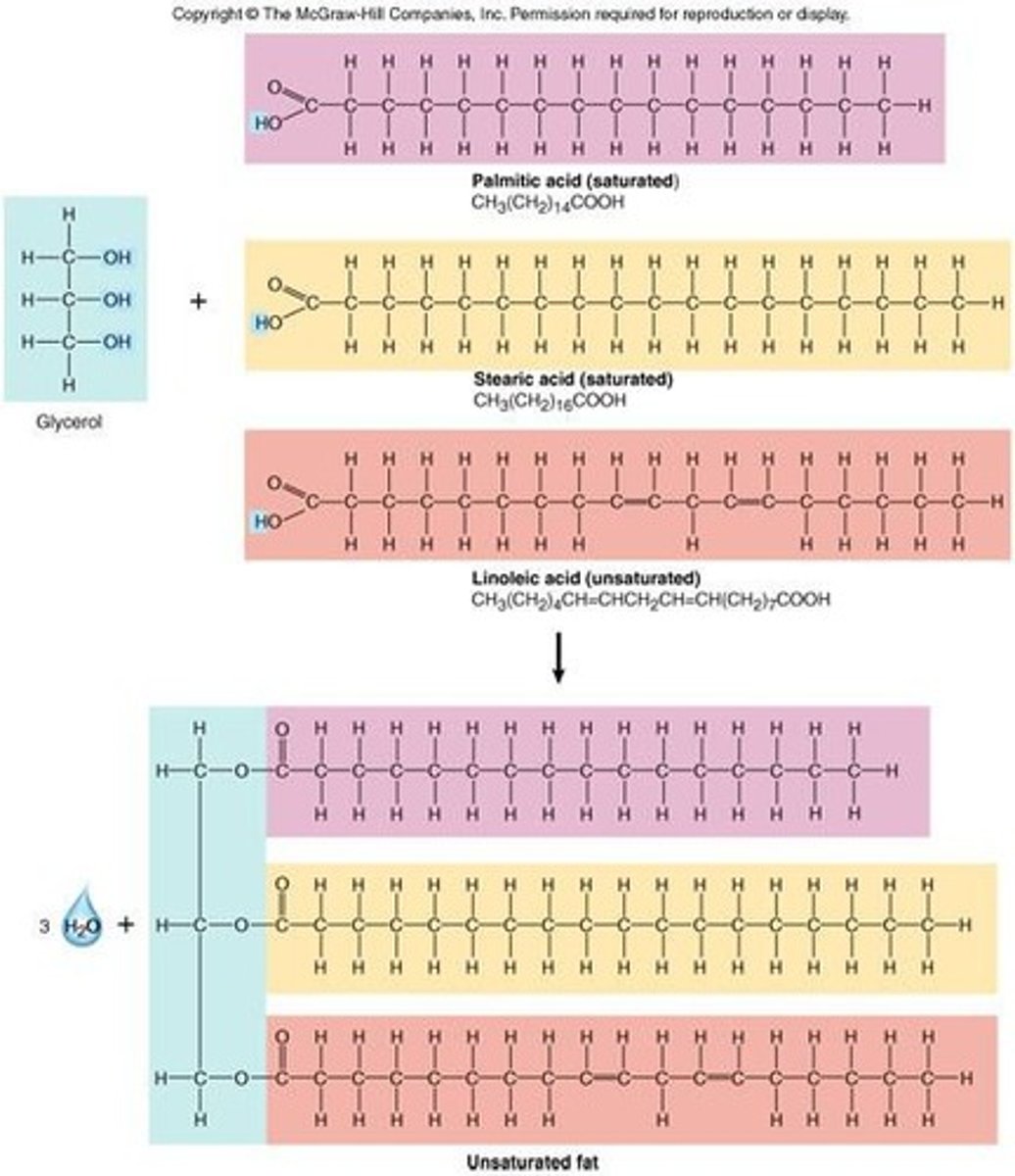
What are the two functional groups at each end of a fatty acid?
Carboxylic acid group and methyl group.
What distinguishes saturated fatty acids from unsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature and have no double bonds; unsaturated fatty acids contain at least one double bond.
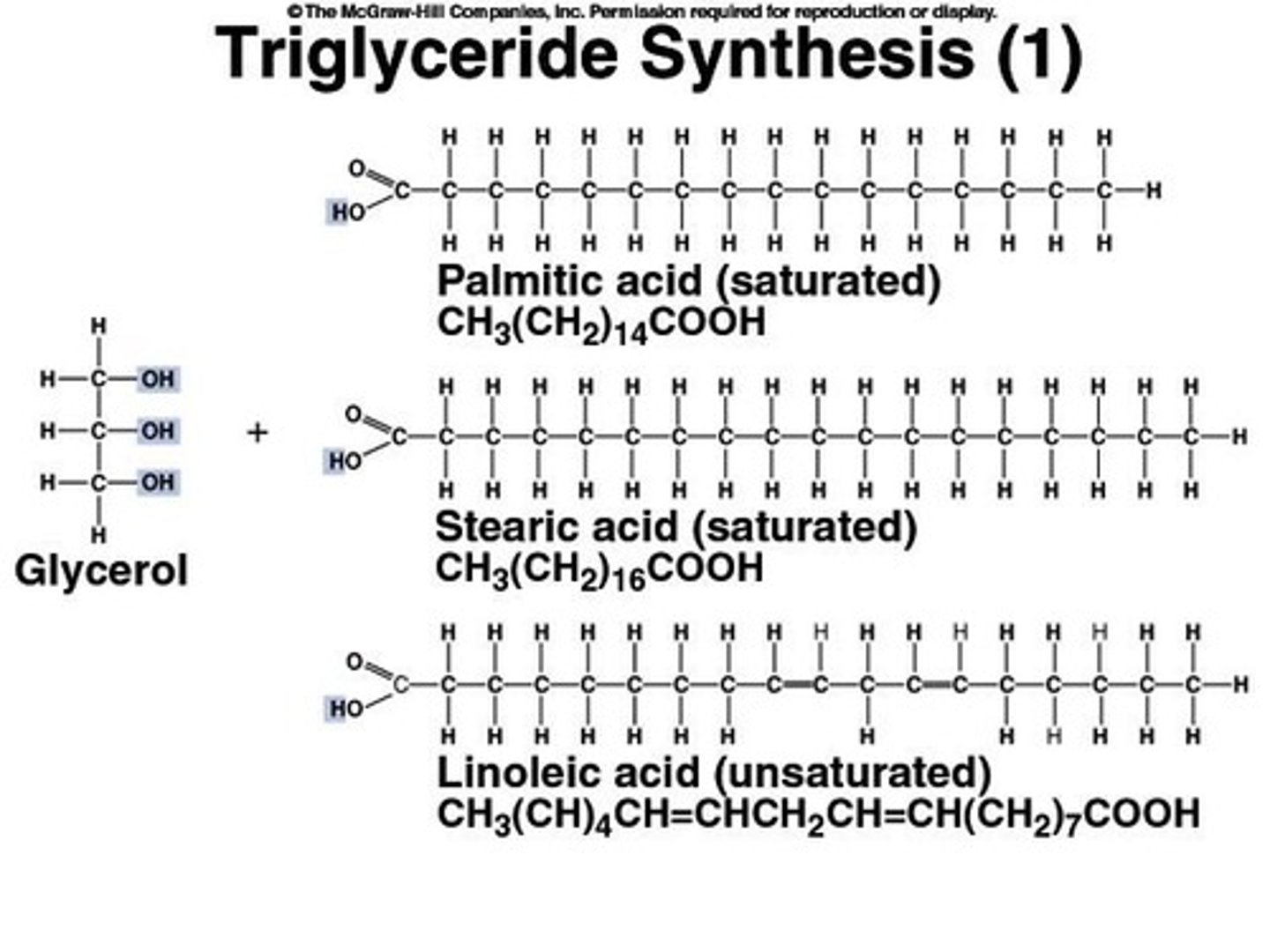
What are triglycerides and their functions?
Lipids made of three fatty acids bound to glycerol, used for energy storage, insulation, and protection.
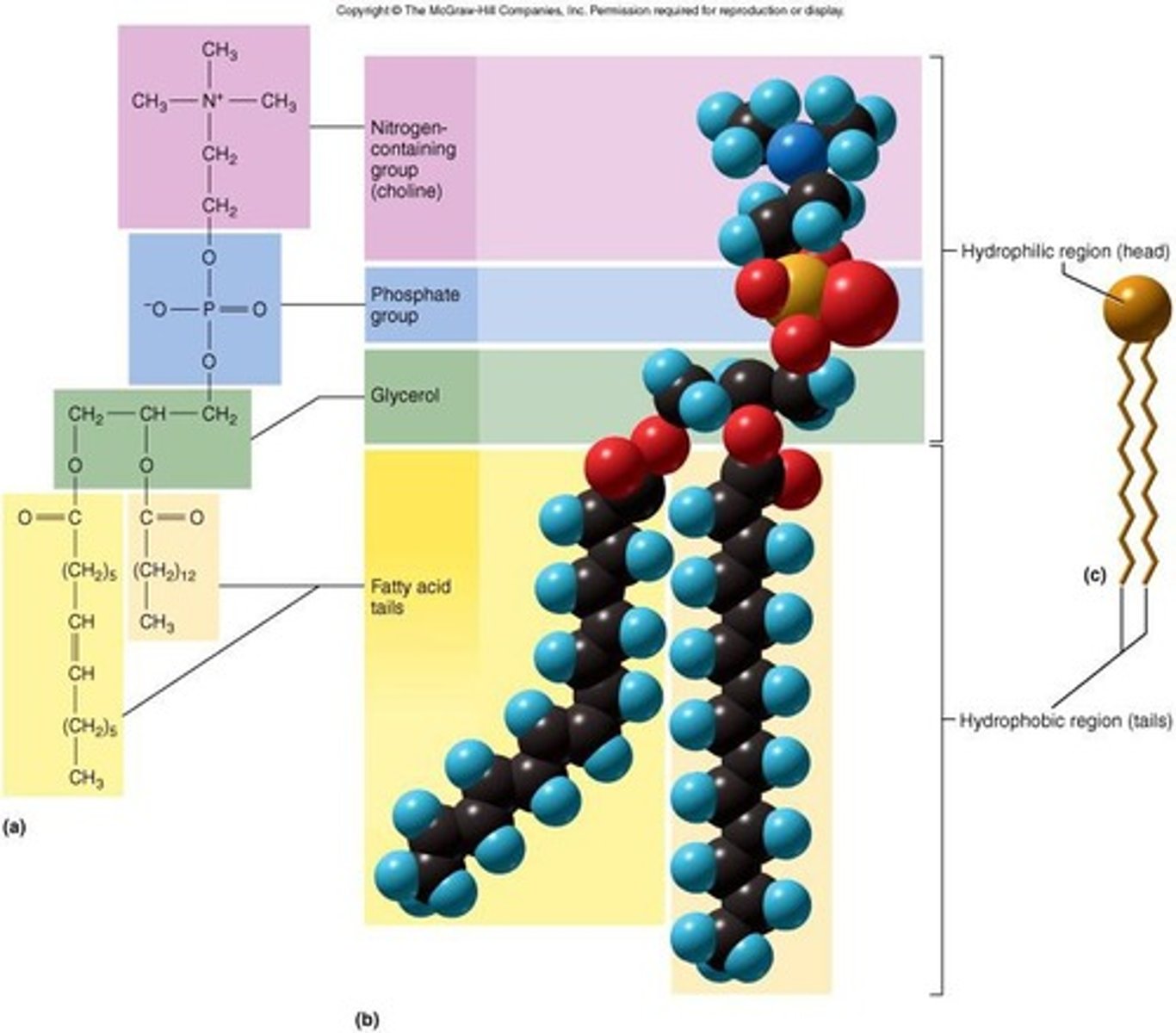
What is the structure of phospholipids?
Consist of 1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and 1 phosphate group.
What is the primary function of proteins in the body?
They perform all body functions, including catalysis, communication, and structural integrity.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids.
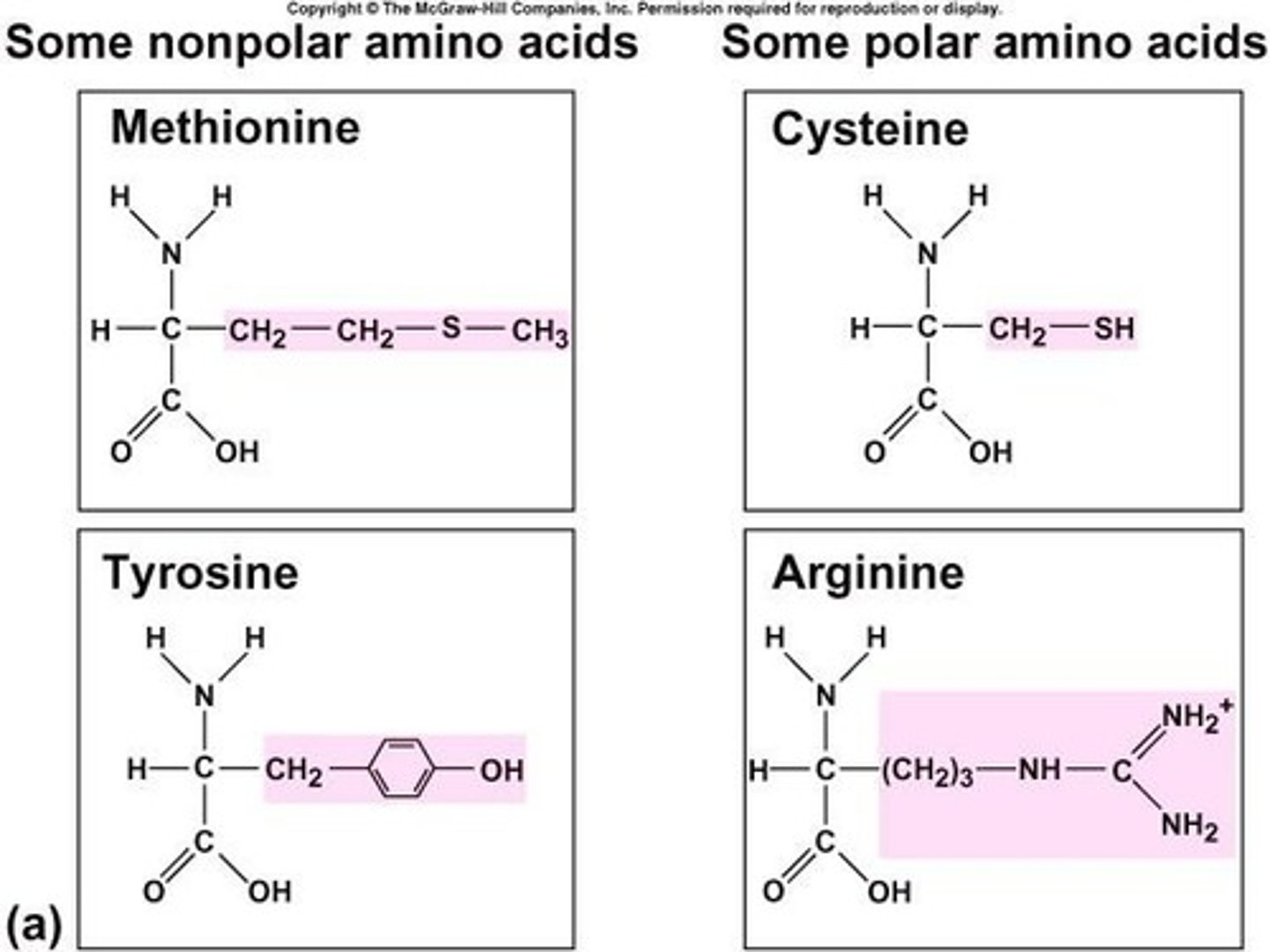
How many different amino acids are used to create proteins?
20 different amino acids.
What are the two groups of amino acids based on their necessity in diet?
Essential (cannot be synthesized) and nonessential (can be synthesized).
What are the four levels of protein structure?
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures.
What is denaturation in proteins?
A drastic conformational change caused by breaking hydrogen bonds, impairing or losing function.
What is the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions?
They speed up reactions by lowering activation energy and are specific to substrates.
What are nucleic acids and their two major classes?
Largest molecules in the body, with two classes: DNA and RNA.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
A nitrogen-containing base, a sugar, and a phosphate group.
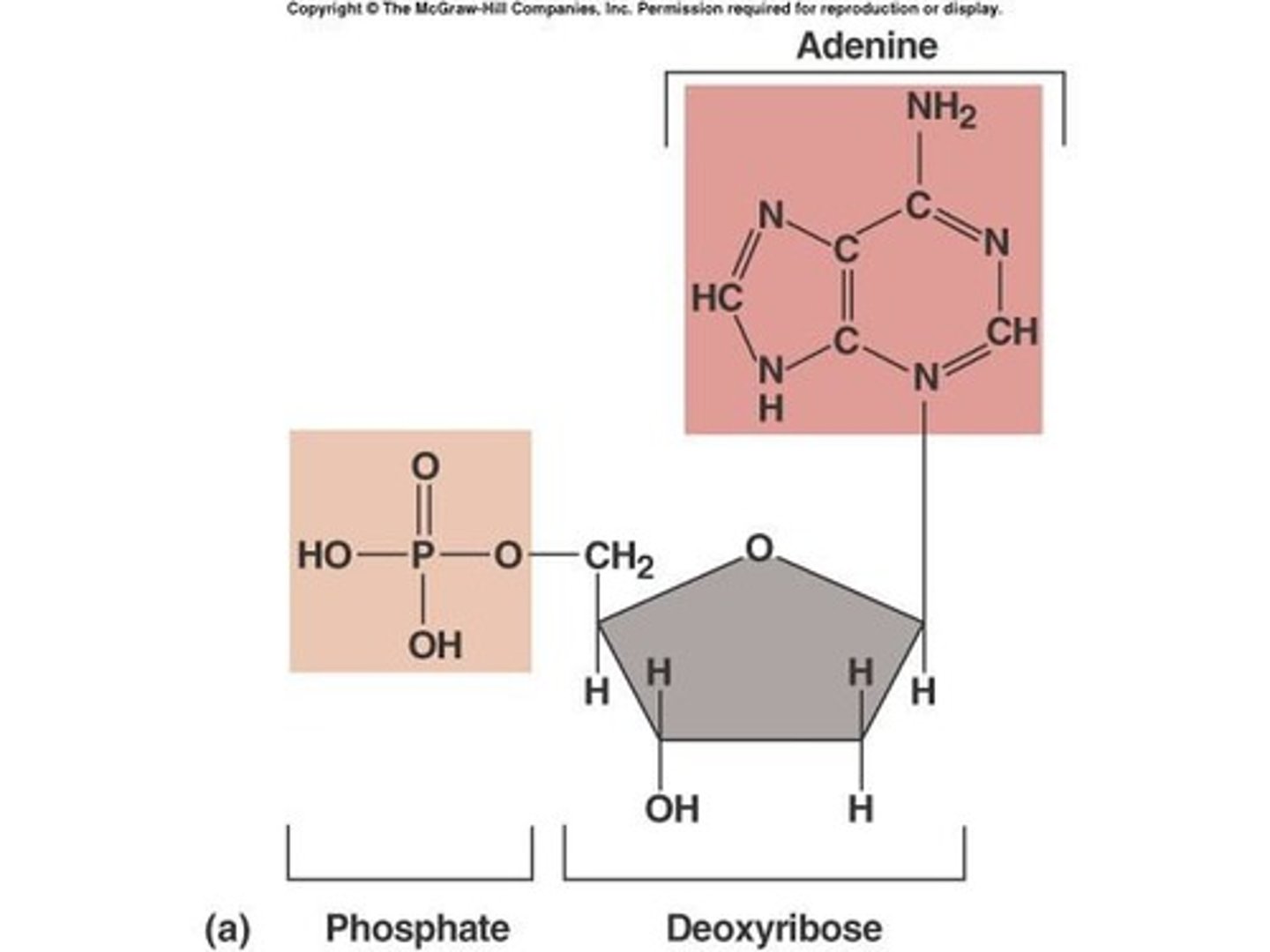
What is the structure of DNA?
A double-stranded helical molecule held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotides.
What is ATP and its function?
A nucleotide derivative that serves as a source of immediately usable energy for the cell.