Visual Acuity - Clinical Skills 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Visual Acuity
Angular measurement relating testing difference to the minimal object size resolvable at that distance
-Spatial resolving capacity of the visual system
What is Visual Acuity based on?
Central Vision
Fovea
Central of Cones
Where should we measure Resolvable Acuity?
Curved Surface at the Retina
What type of measurements do we use to measure the Resolvable Activity?
Minutes and Seconds
Why do we not use Degrees or Arcs?
They are too large
Why do we use angular measurements to measure the Resolvable Activity?
Retina is a curved, NOT flat
List the reasons why we test Visual Acuity (4)
1. Determines Normalcy
2. Determines Refractive Decisions
3. Monitors Ocular Health
4. Vision Standards
In absence of Ocular Disease, how should patients see?
20/20
What Visual Acuity is better than 20/20?
20/15
Up to what age should our eyesight be better than 20/20?
50 years of age
List the reasons as to why patients may not see as well as 20/20 (3)
1. Uncorrected Refractive Error
2. Ocular Disease
3. Amblyopia
Amblyopia
Developmental disorder resulting in reduced vision
What does Amblyopia cause? (5)
1. Uncorrected (high) Refractive Error
2. Uncorrected Asymmetric Refractive Error
3. Deprivation (Ptosis/Cataract at early age)
4. Strabismic
5. Toxic/Nutritional
What is Strabismus?
Eye turn
What can Visual Acuity be used to help estimate?
Spherical Equivalent Refractive Error
-This supports your objective/subjective refraction
What can Visual Acuity be used to help monitor?
Ocular Disease
What is the main factor that decreases Visual Acuity?
Ocular Pathologies
Do certain professions have Visual Acuity requirements?
YES
-List may include Pilots, Military, Police
Do driving acuity requirements vary for each state?
YES
Who must you report to when a patient falls below the acuity requirement to drive?
DMV
List the two types of theories of the resolution of the eye:
1. Optical Limitations
2. Neural Limitations
What determines the Resolution?
Pupil
Diffraction
Pupil is too small
Refraction
Pupil is too large
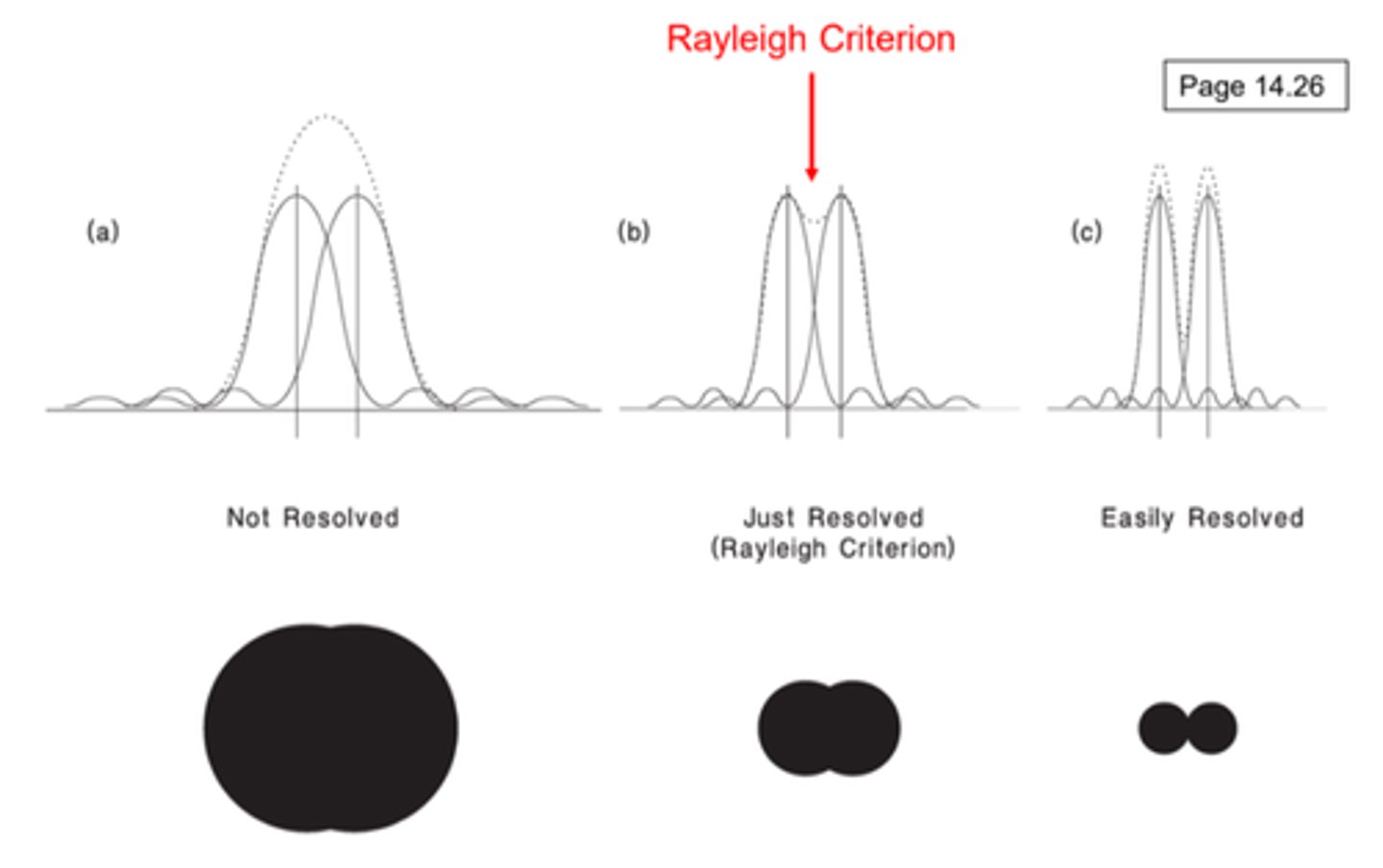
What type of limitation is Rayleigh Criterion?
Optical Limitation
Airy Disc
Central bright circular region of pattern produced by light diffracted when passing through the Pupil
Pupil
Small circular aperture in the eye
What is the pattern of an Airy Disc?
Concentric rings
Describe what has to occur when 2 Airy Discs are considered resolvable:
The center of one lies at the edge of another
What is Resolution approximated at?
1 minute of arc with optimal pupil size of 2.5 mm
Rayleigh Criterion
What type of limitation is the Receptor Theory?
Neural Limitation
Resolution is dependent on...
Packing density of retinal receptors & neural interactions
What has the best resolution?
Fovea
Why does the Fovea have the best resolution?
High density of cones
Distance between the centers of Cones separation within the Fovea
2 µm
What distance of the separation of centers of Cones permits the separation of 2 points when they fall on the center of 2 receptors?
4 µm
What resolutions do both Optical & Neural systems provide?
Around 1 minute
List the types of Visual Acuity (4)
1. Detection Acuity
2. Resolution Acuity
3. Localization Acuity
4. Identification Acuity
What are the two types of Detection Acuity?
1. Minimum Visible Acuity
2. Minimum Distinguishable Acuity
Minimum Visible Acuity (Detection Acuity) is associated with...
Brightness
Describe Minimum Visible Acuity (Detection Acuity)
Determined by the brightness of object relative to its background illumination
-Patient would NOT need to identify the object
-Image is NOT relative to the angle it subtends
What does visibility rely on?
Intensity, NOT size
What is an example Minimum Visible Acuity (Detection)?
Star
Minimum Distinguishable (Detection Acuity) is associated with...
Contrast
Contrast Discrimination
Distinguish whether light falling on photoreceptors is greater than falling on its neighbors
Describe Minimum Distinguishable Acuity (Detection Acuity)
Ability to detect an object against a plain background
-Threshold is 0.5 seconds of arc
-IE: dark line on white background
What does the width of the retinal image depend on?
Diffraction
Resolution Acuity
Ability to distinguish smallest space between two similar objects
-30 seconds of arc is threshold
-IE: dots and lines
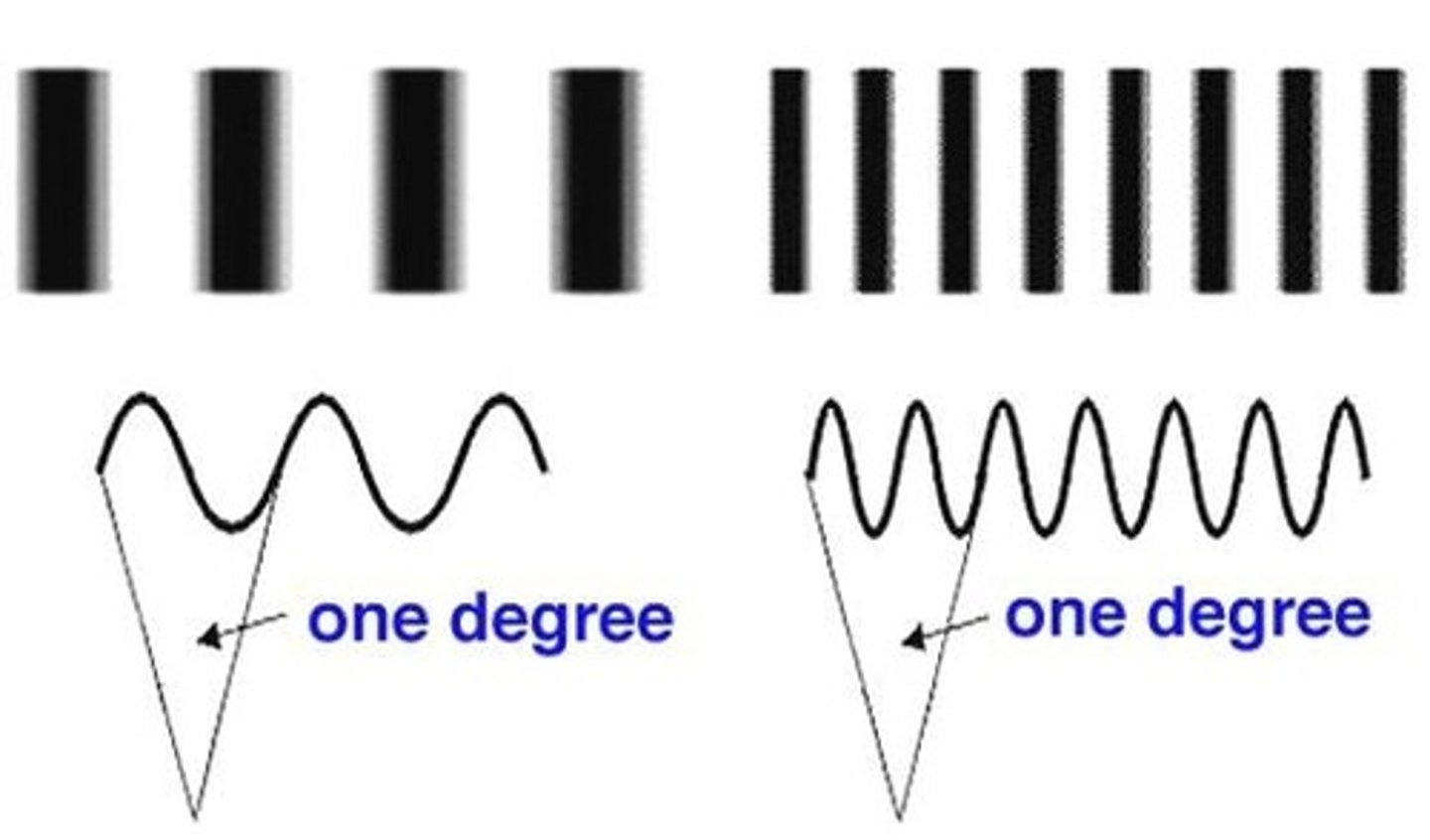
What are the clinical applications to the Resolution Acuity?
Preferential Looking and Retinometer
What happens are shapes are moved closer together?
It's harder to resolve the two shapes or gaps & it DECREASES angular size
Minimum Angle of Resolution (MAR)
The angular size of the gap between the smallest letters a patient can read
Localization Acuity
Ability to discriminate the alignment of 2 objects
-Minimum spatially discriminable
-Misalignment Acuity
-Threshold is 2-6 seconds of arc
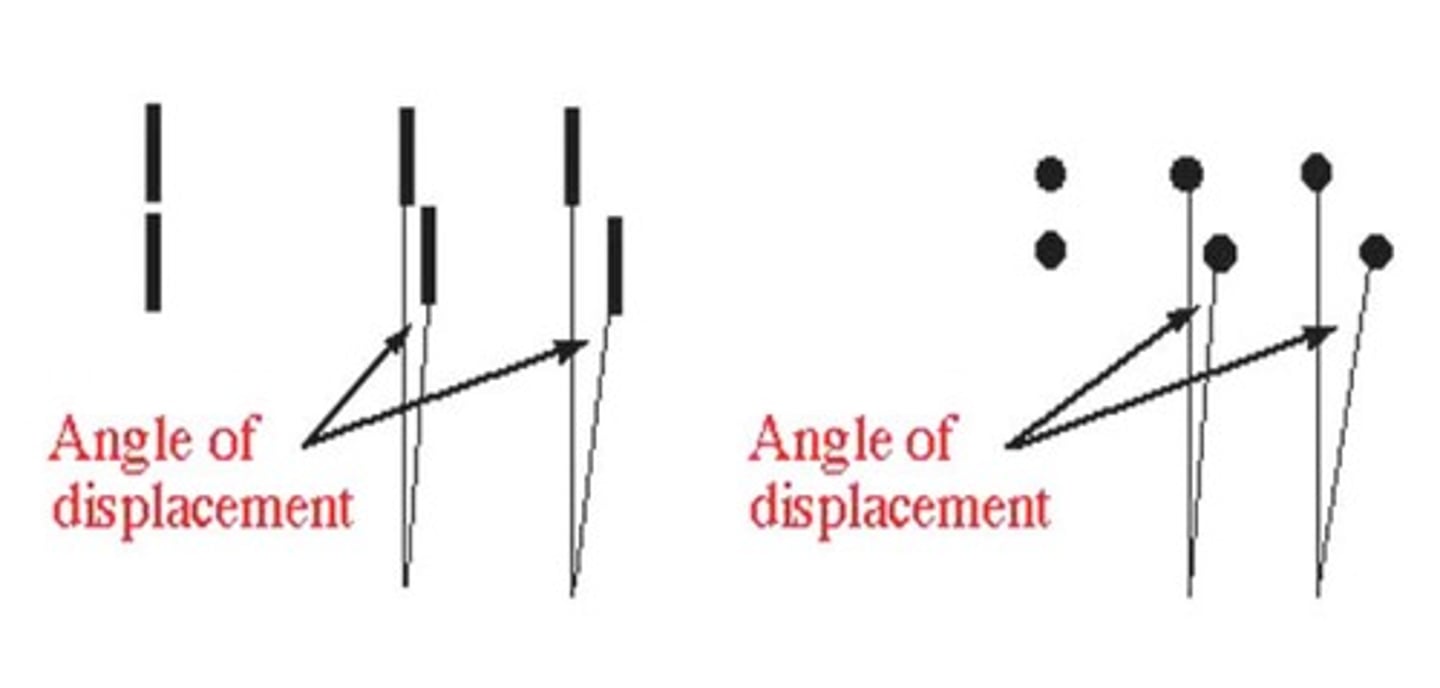
What does the angular displacement of 2 objects determine?
Acuity
Clinical Applications of Localization Acuity (4)
1. Stereoacuity
2. Keratometry
3. Lensometers
4. Applanation Tonometers
Identification Acuity
Minimum Legible Acuity - Recognition Resolution
-Patient must recognize or identify optotypes
-Threshold is 30 seconds to 1 minute of arc
Examples of Identification Acuity charts:
Snellen Acuity Chart and SOSH Chart
What is the most commonly used clinical chart?
Identification Acuity - Snellen Acuity Chart
Limitations of Snellen Acuity Chart
1. Fewer targets at the top of the chart
2. Some optotypes are more recognizable than others