Clastic Coasts and Estuaries
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Coasts
Erosional-Depositional systems with morphologies being very variable from cliffs of bedrock to gravelly or sandy beaches to lower energy lagoons or tidal flats.
Erosional coastlines
Also known as reflective coasts, have relatively steep gradients where much of energy wave is reflected back into the sea from the shoreline.
Depositional coastlines
Also known as dissipative coasts, have relatively gentle gradient and much of wave energy is dissipated in the shallow water and, with supply of sediment, can be sites of accumulation.
Rock types exposed along the shore
Supply of sediment
Intensity of waves
Tidal range
Nature of coastline currents
Climate
Sea level changes
Stability of sinking or rising coasts
Factors affecting Shoreline Features (8)
Erosional coastal landforms
Sea cliffs, wave-cut notches, caves, sea stacks, sea arches are ________ coastal landforms.
Depositional coastal landforms
Beaches, barrier, spit, lagoon, tombolo are _________ coastal landforms.
Beach
Coastal landforms where wave energy is strong, with sand or gravelly material may be reworked on the foreshore forming low-angle stratification of well-sorted and well-rounded sediments.
Berm
A ridge of sand that separates the foreshore from the beach.
Dune ridge
Coastal dunes that form lying parallel to the shoreline and may build up to form dune complexes.
Coastal plains
Low-lying areas adjacent to the sea.
Strand plains
Sandy coastlines where an extensive area of beach deposits lie directly adjacent to coastal plains.
Barrier
Sediments that separate the open sea from a lagoon that lies between the barrier and the coastal plain.B
Beach spit
Barriers composed of sand and/or gravel and largely built by wave action.
Welded barrier
Barriers partially attached to the land.
Barrier island
Barriers that are wholly attached to the land and completely encloses a lagoon.
Wave energy is high and tidal range is small.
Abundant supply of sand or gravel to match or exceed any losses from erosion.
Formation Conditions for Barrier Systems (2)
Lagoons
Coastal bodies of water that have very limited connection to the open ocean, only through a channel to the sea or via seepage through a barrier.
Washover deposits
Coarser sediments that may enter when storms wash sediments over the barrier.
runoff or rainfall
estuary
shallow
fine, clastic, suspended
Mangroves
open ocean
low, brackish
hypersaline
mudstone, wave-rippled sand
Characteristics of Lagoons
Freshwater lagoons are supplied by ______ or ______.
Part of an _______ system if fed by a river.
Typically, very _______ (in terms of depth)
_____-grained ______ sediments are supplied as ______ load in seawater entering the barrier or from adjacent coastal plains.
_________ colonize shallow fringes and act as sites for sediment accumulation.
Limited connection to the ________ with:
____ salinity, _______ water in areas of high rainfall or runoff.
________ water in arid settings which leads to precipitation of evaporate minerals.
Have successions typically ________, organic-rich and thin ________ beds.
marine
lagoonal, marine
Evidence Used to Distinguish Lagoons from Lakes:
Fossil assemblage of ______ influence.
Facies association with ______ deposits occur above or below beach/barrier island sediments and fully _______ shoreface deposits.
Estuaries
The marine-influence portion of the seaward portion drowned river valley that occurs due to sea level rise.
freshwater, seawater
river, marine
river, wave and tidal
mouth
drowned river valley
transgression
Characteristics of Estuaries
Region where _________ and _________ mix.
Sediments are supplied by both ______ and _______.
Transport and deposition of sediments are done by combinations of ____, _____, and ______ processes.
Common features at the ______ of rivers.
Different from deltas due to sedimentation occurring within the ___________.
Temporarily existing due to only occurring during ___________.
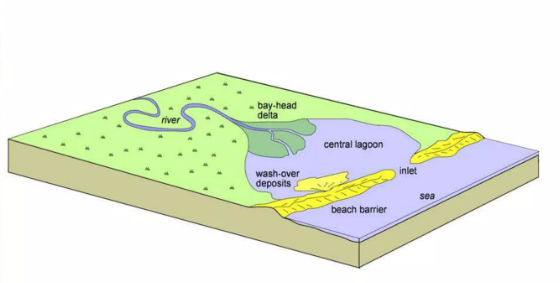
Wave-dominated Estuary
An estuary system dominated by wave processes and comprised of a bay-head delta, central lagoon, and beach barrier.
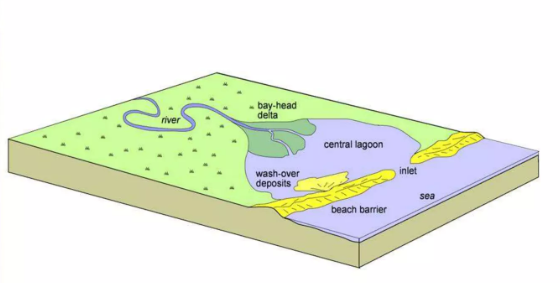
Bay-head delta
The zone where fluvial processes are dominant.
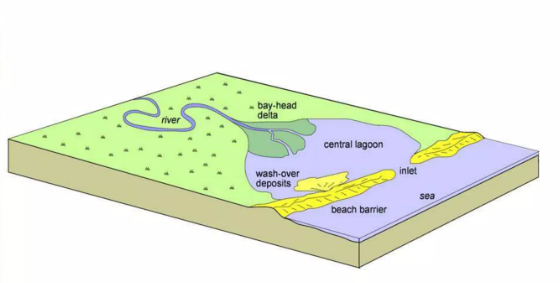
Central lagoon
The lowest energy part of the estuarine system where the river flow rapidly decreases and the wave energy is mainly concentrated at the barrier bar, therefore, a region of fine-grained deposition often rich in organic.
Salt-water marsh
A central lagoon that becomes filled with sediment crossed by channels where wave-ripples form and draped with mud.
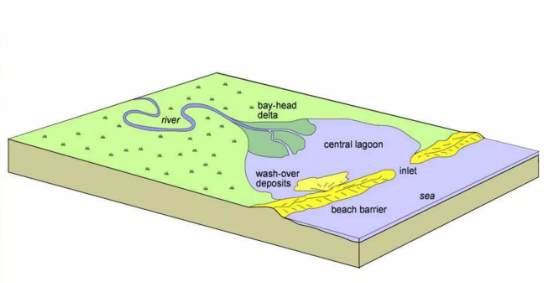
Barrier
Formed in the outer zone of the estuary where the wave action reworks marine sediments.
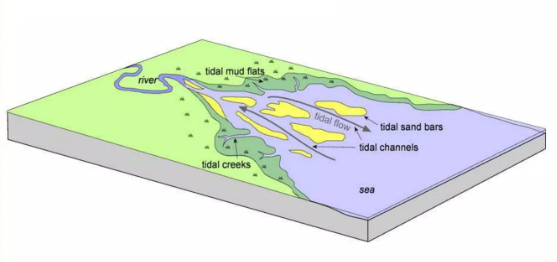
Tide-dominated Estuary
An estuary system where tidal processes may dominate in mesotidal and macrotidal coastal regime, which forms a funnel-shaped estuary which tends to increase the flood tidal current strength, and low gradient tidal channels adopting a meandering form in the inner part of the estuary.
heterolithic, bioclastic, lag
In a tide-dominated estuary, deposits in the point bar are ________, with _______ debris being common among the gravelly detritus deposited as _______ deposits on the channel floor.
Estuary - waterbody
Delta - landform
Estuary vs. Delta (Classification)
Estuary - mixing of freshwater and saltwater
Delta - deposition of sediment carried rivers along its mouth
Estuary vs. Delta (Mode of formation)
Estuary - brackish water
Delta - freshwater or saltwater
Estuary vs. Delta (Water salinity)
Estuary - fewer sediment deposits
Delta - larger sediment deposits
Estuary vs. Delta (Sediment input)
Estuary - narrower & elongated
Delta - wider & fan-shaped
Estuary vs. Delta (Geomorphology)
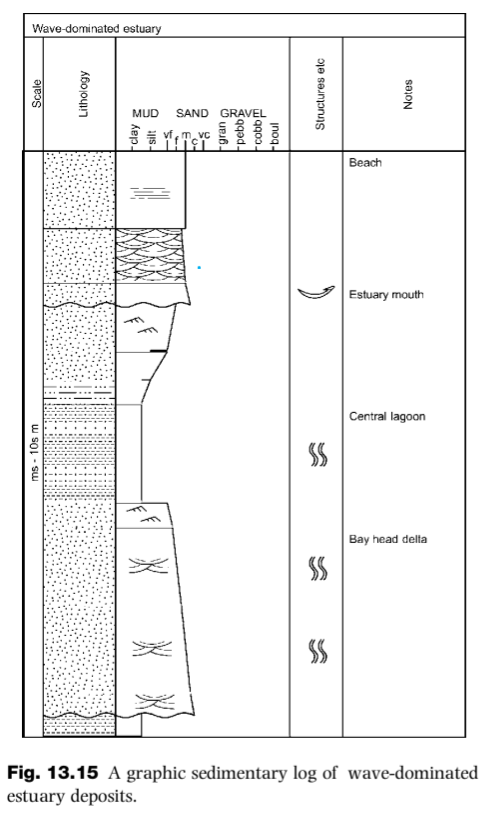
Wave-dominated estuary deposits
Estuary with facies deposits (top to bottom):
Beach
Estuary mouth
Central lagoon
Bay-head delta
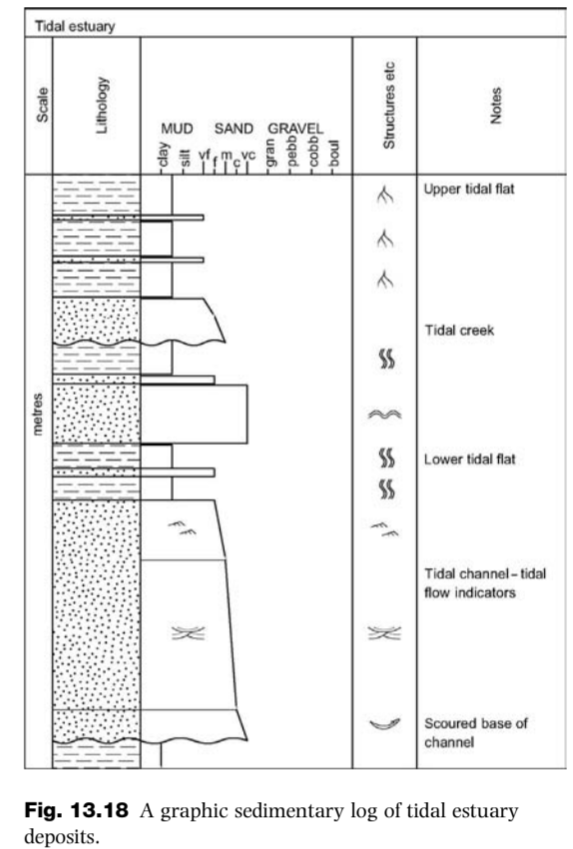
Tidal-dominated estuary deposits
Estuary with facies deposits (top to bottom):
Upper tidal flat
Tidal creek
Lower tidal flat
Tidal-channel
Scoured base of channel
Sand & Conglomerate
Lithology of Beach/Barrier
Mainly mud with some sand
Lithology of Lagoon
Mud, sand, and less commonly, conglomerate
Lithology of Tidal Channel
Mud and sand
Lithology of Tidal Mudflats
Mature quartz sands and shelly sands.
Mineralogy of Beach/Barrier
Variable.
Mineralogy of Lagoon
Variable
Mineralogy of Tidal Channel
Clay and shelly sand.
Mineralogy of Tidal Mudflats
Well-sorted, well-rounded clasts
Texture of Beach/Barrier
Fine-grained, moderately to poorly sorted
Texture of Lagoon
May be well-sorted in high energy settings
Texture of Tidal Channel
Fine-grained, not diagnostic
Texture of Tidal Mudflats
Elongate lenses
Bed geometry of Beach/Barrier
Thinly bedded mud with thin sheets and lenses of sand.
Bed geometry of Lagoon
Lenses with erosional bases
Bed geometry of Tidal Channel
Tabular muds, with thin sheets and lenses of sand
Bed geometry of Tidal Mudflats
Low-angle stratification and wave reworking
Sedimentary structures of Beach/Barrier
May be laminated and wave rippled
Sedimentary structures of Lagoon
Cross-bedding, cross lamination and inclined heterolithic stratification
Sedimentary structures of Tidal Channel
Ripple cross-lamination and flaser/lenticular bedding
Sedimentary structures of Tidal Mudflats
Mainly wave-formed structures.
Paleocurrents of Beach/Barrier
Rare, not diagnostic
Paleocurrents of Lagoon
Bimodal in tidal estuaries
Paleocurrents of Tidal Channel
Bimodal in tidal estuaries
Paleocurrents of Tidal Mudflats
Robust shelly debris
Fossils of Beach/Barrier
Often monospecific assemblages of hypersaline or brackish tolerant organisms.
Fossils of Lagoon
Shallow marine
Fossils of Tidal Channel
Shallow marine fauna and salt marsh vegetation
Fossils of Tidal Channel
Not diagnostic.
Color of Beach/Barrier
May be dark due to anaerobic conditions.
Color of Lagoon
Not diagnostic
Color of Tidal Channel
Often dark due to anaerobic conditions
Color of Tidal Mudflats
May be associated with coastal plain, lagoonal or shallow-marine facies.
Facies Associations of Beach/Barrier
May be associated with coastal or beach barrier deposits.
Facies Associations of Lagoon
May be overlain by fluvial, shallow marine, continental or delta facies.
Facies Associations of Tidal Channel
May be overlain by shallow marine or continental facies.
Facies Associations of Tidal Mudflats