Unit 3: Early Modern Age; Renaissance & Reformations
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Cimabue
Late medieval Italian painter whose work showed early signs of naturalism.

Giotto
Early Renaissance artist known for realistic figures and emotional expression.

Chiaroscuro
Technique using light and shadow to create depth and volume.

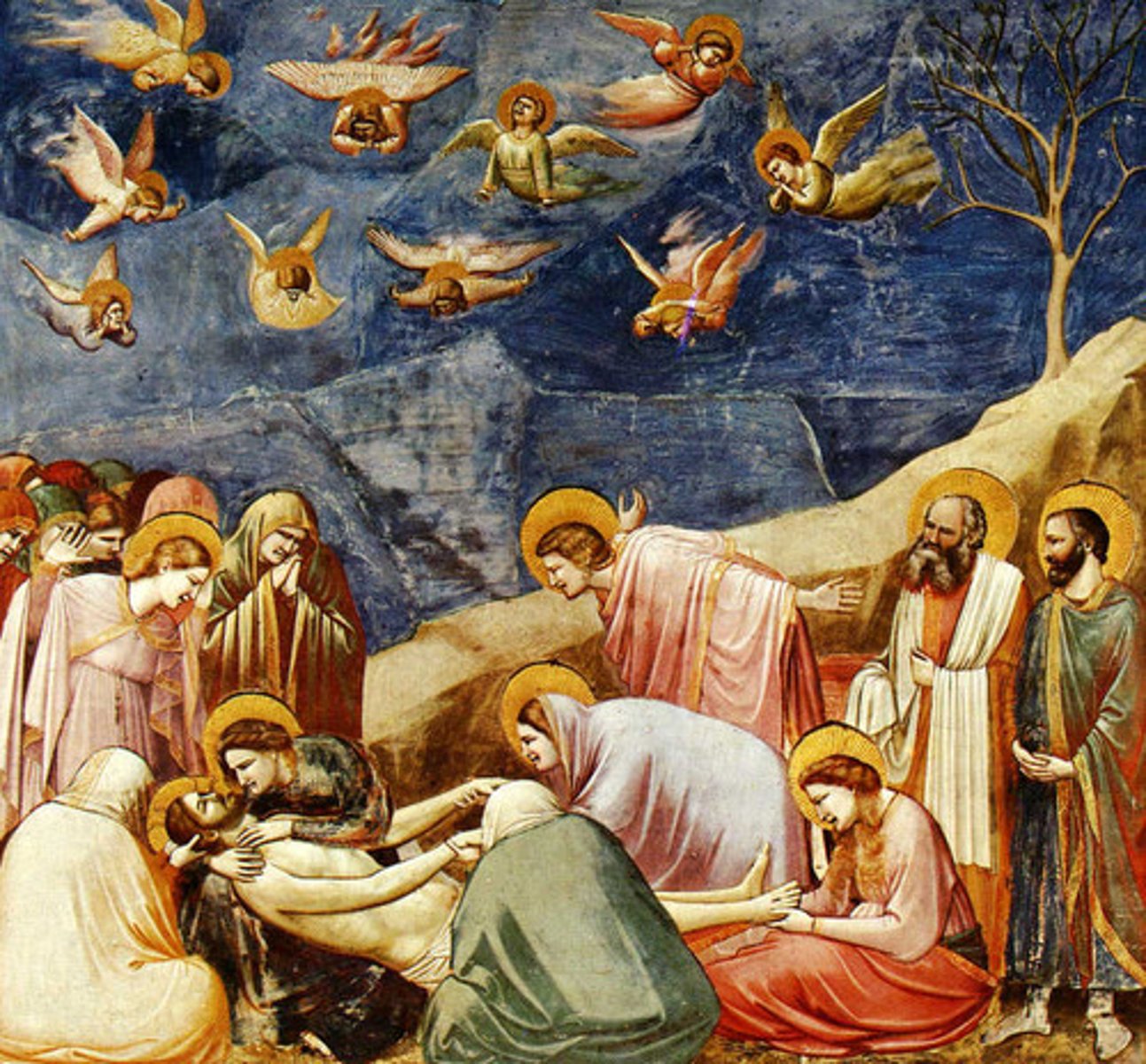
Lamentation
A scene of mourning over Christ's body; famously painted by Giotto.

Grisaille
Painting technique using shades of gray to mimic sculpture.

Patron
Wealthy individual or group who commissioned and supported artists.
Florence
Italian city-state considered the birthplace of the Renaissance.
The Medici
Influential Florentine banking family and major art patrons.
Humanists
Renaissance scholars focused on classical texts and human potential.
Petrarch
Early humanist who revived interest in classical Latin literature.
Civic Humanism
Belief in using classical learning to promote public service and civic virtue.
Women in the Renaissance
Generally had limited roles; some gained influence through writing or noble birth.
Caterina Sforza
Noblewoman and military leader known for her defiance and leadership.
Christine de Pizan
Early feminist writer who defended women's education and intellect.
Lucretia Marinella
Italian writer who challenged male views on women's nature and abilities.
Sfumato
Blending of colors and tones to create soft, hazy transitions (used by da Vinci).
Jakob Burckhardt
19th-century historian who popularized the idea of the Renaissance as a distinct era.
Titian
Leading Venetian painter known for vivid color and dynamic compositions.
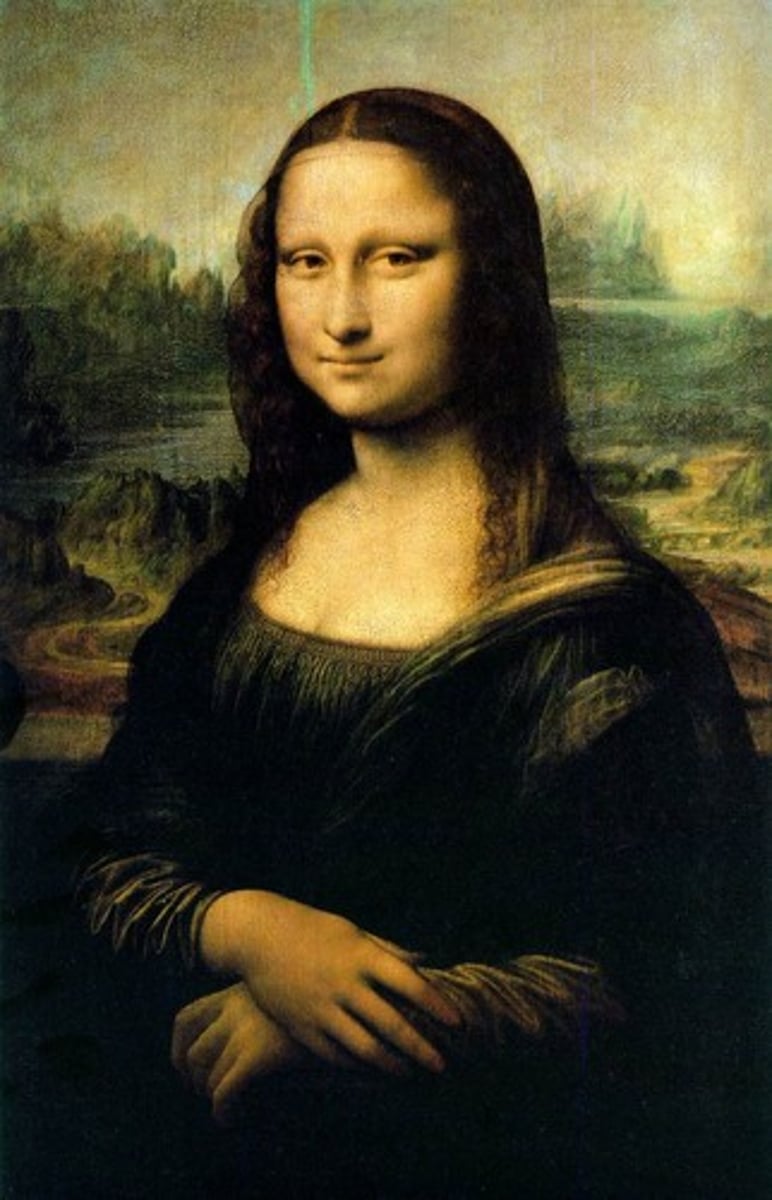
Mona Lisa
Leonardo da Vinci - noted for sfumato and enigmatic expression.

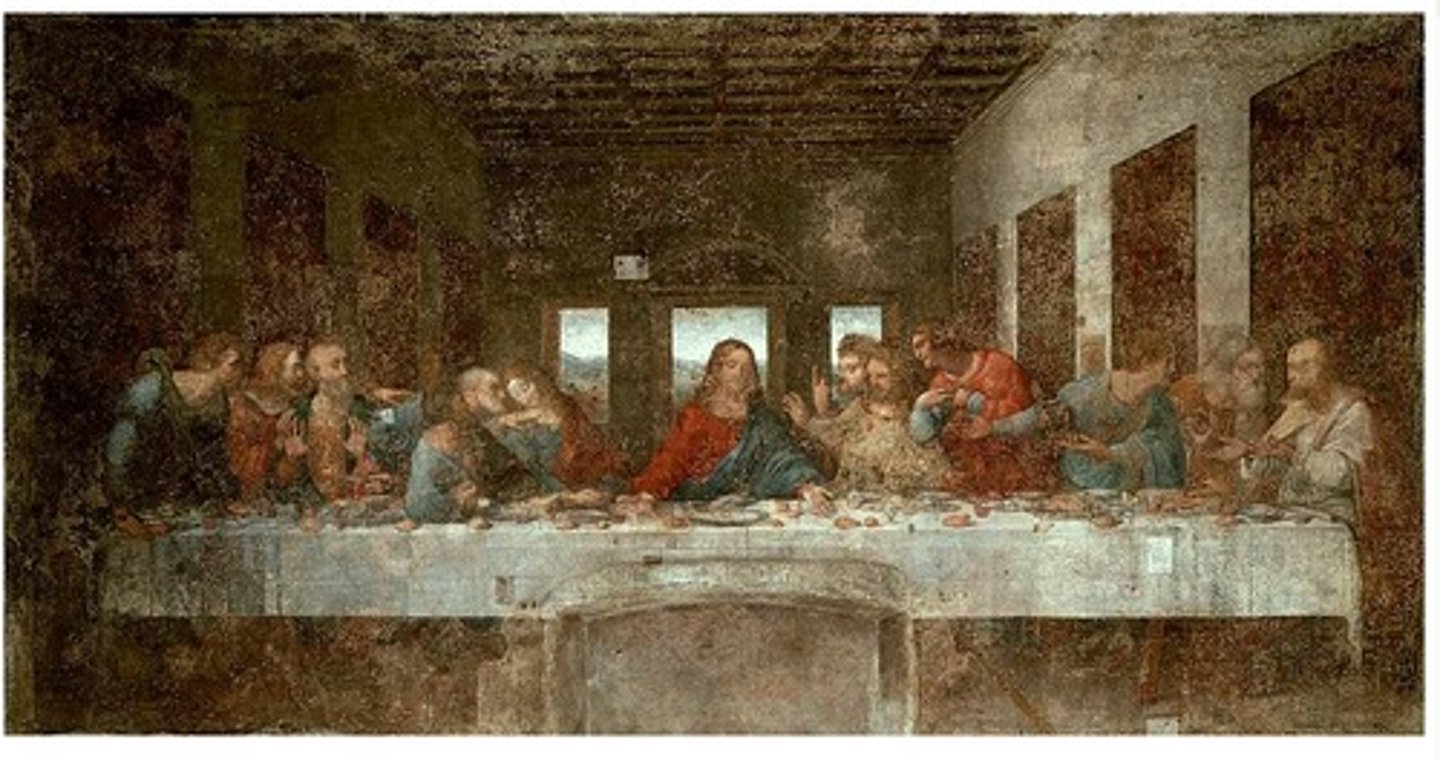
The Last Supper
Leonardo da Vinci - mural depicting Christ's final meal with his disciples.

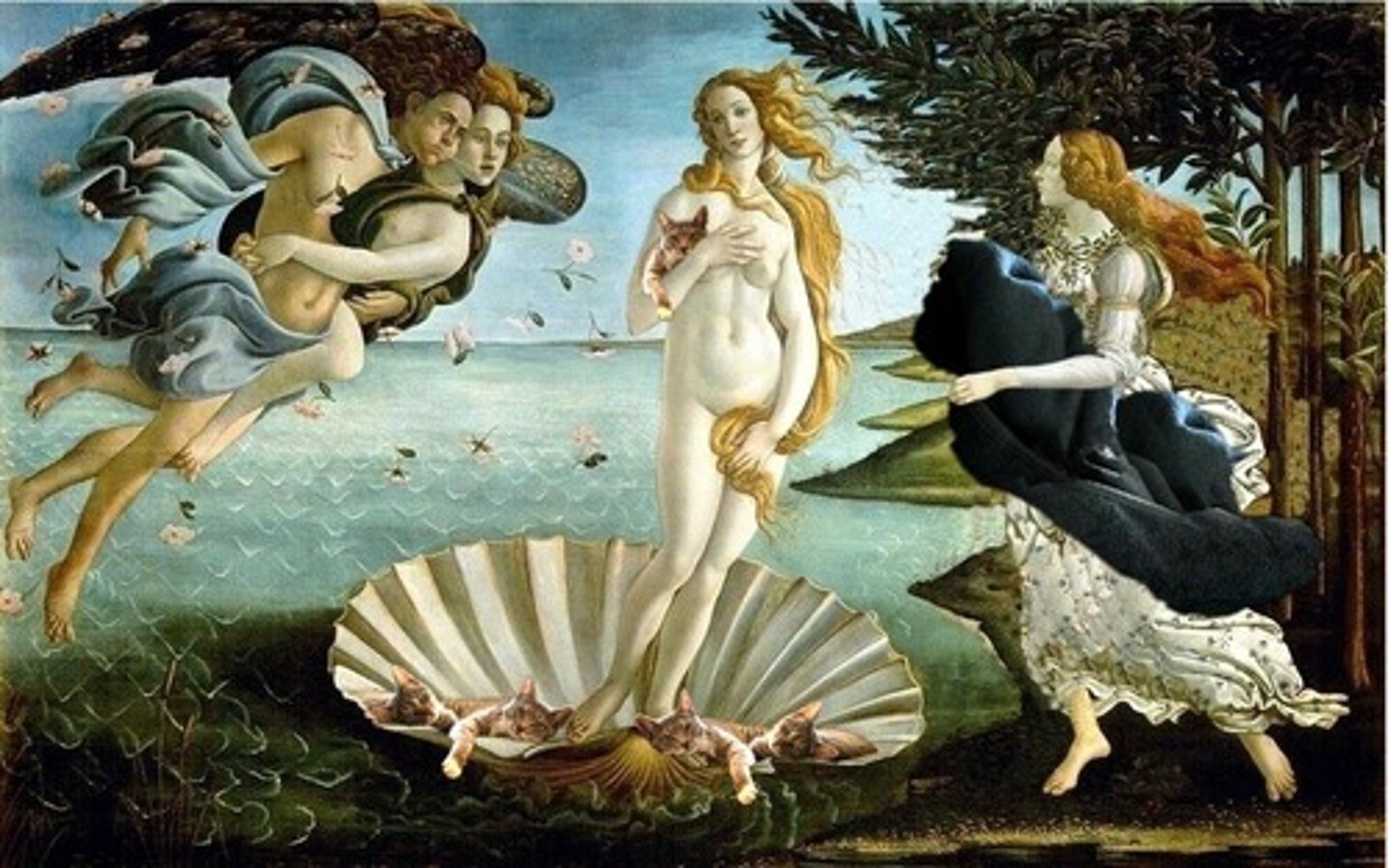
Birth of Venus
Botticelli - Mythological painting showing Venus emerging from the sea.

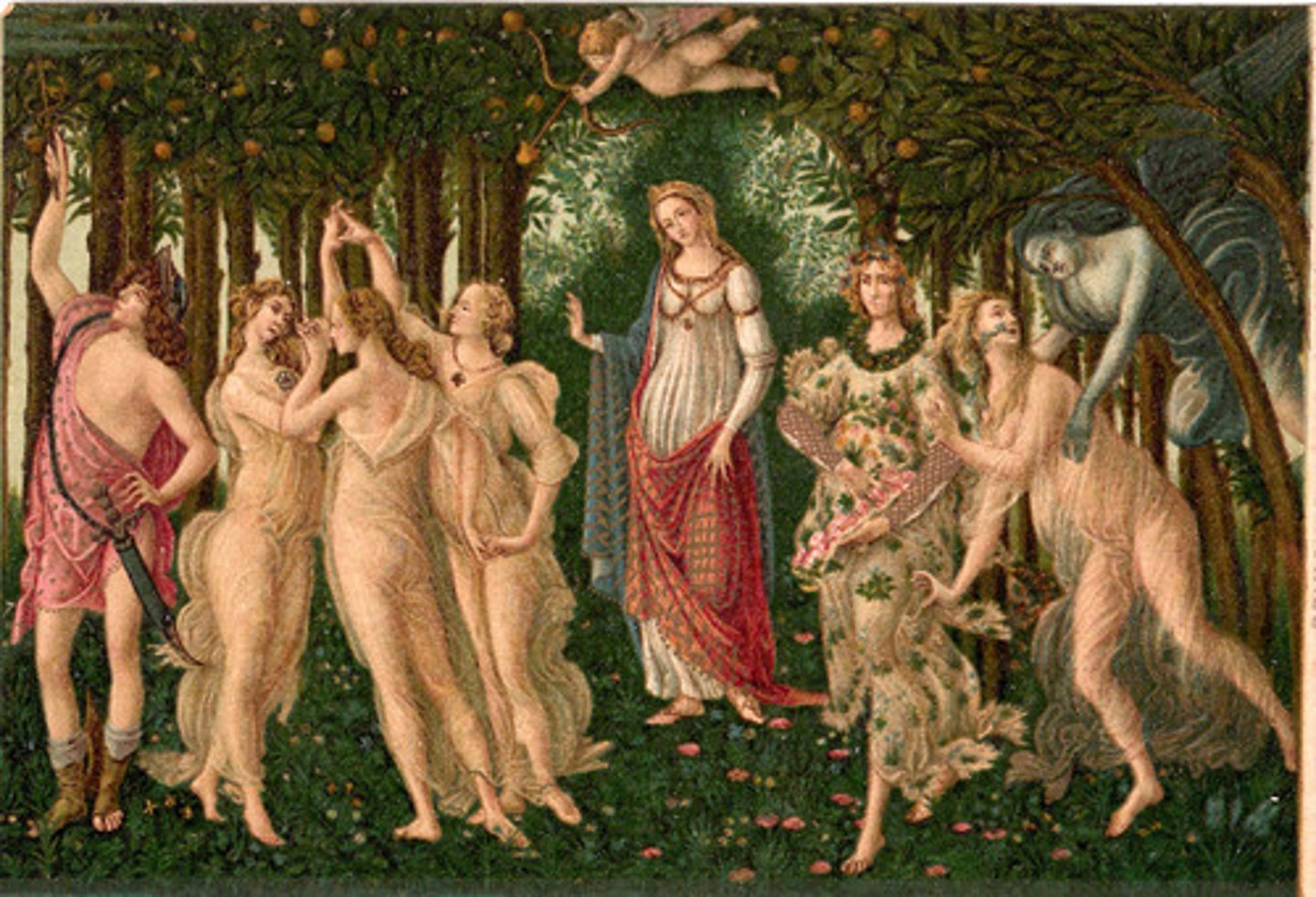
La Primavera
Botticelli - Allegorical painting celebrating spring and classical mythology.

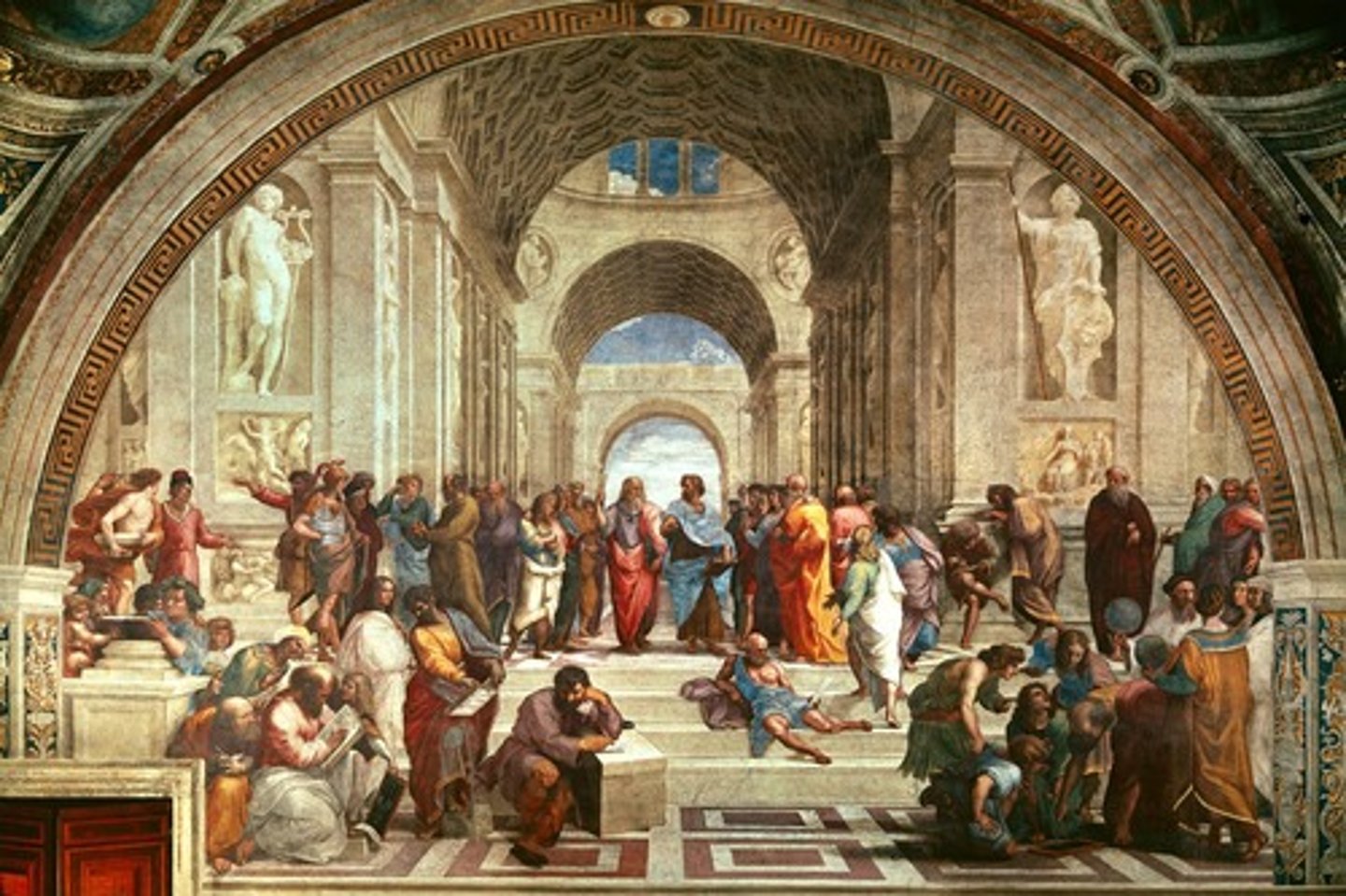
School of Athens
Raphael - fresco showing ancient philosophers, symbolizing humanist ideals.

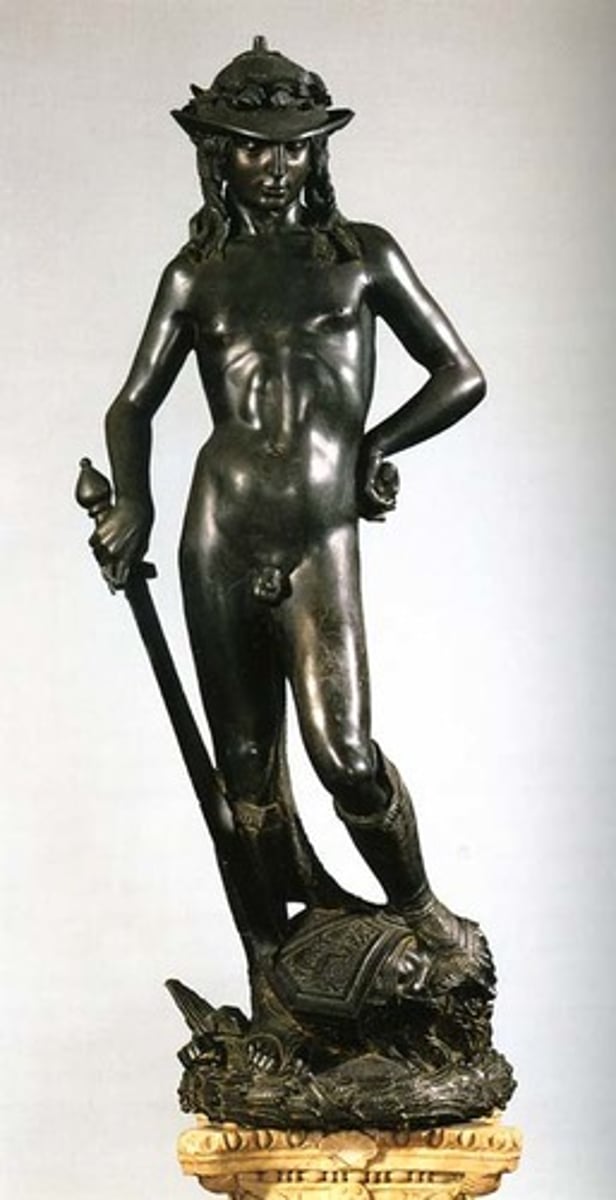
David by Donatello
Donatello - First free-standing nude statue since antiquity; early Renaissance bronze.

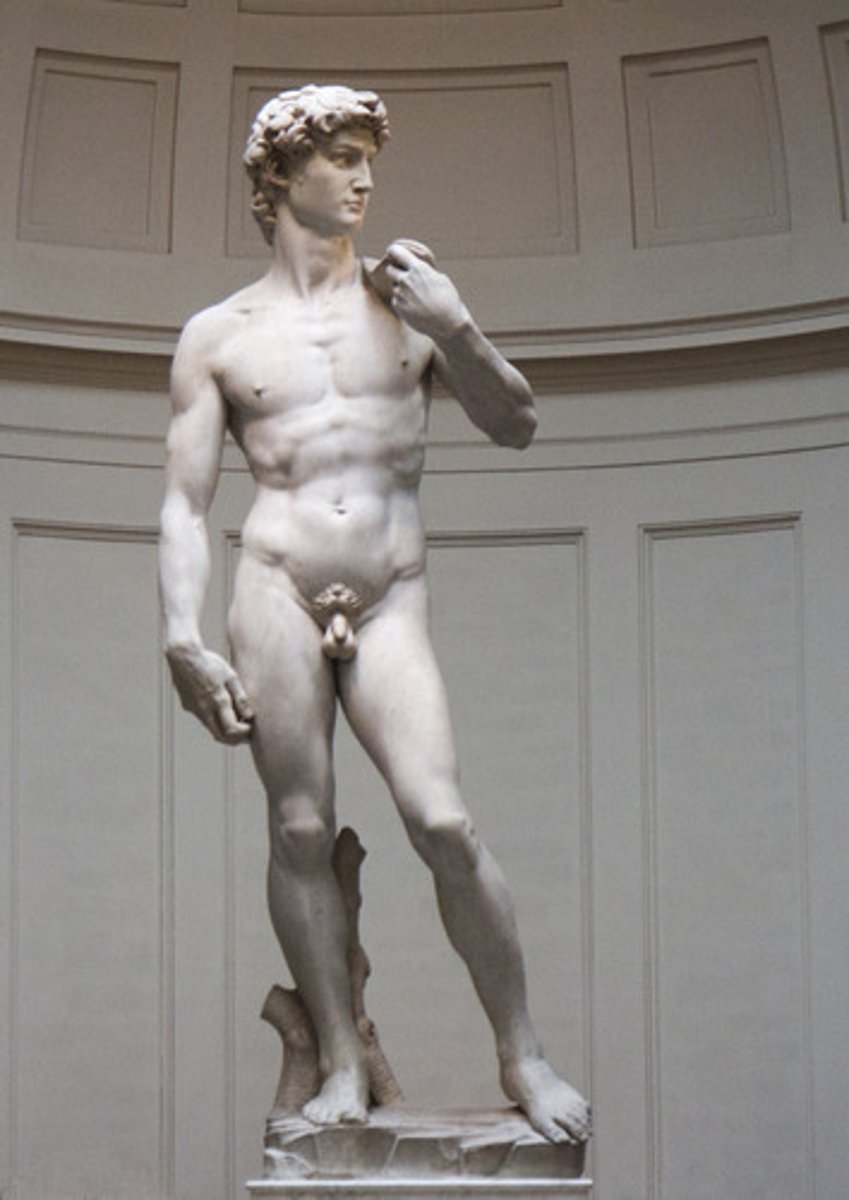
David by Michelangelo
Michelangelo - Monumental marble sculpture symbolizing strength and civic pride.

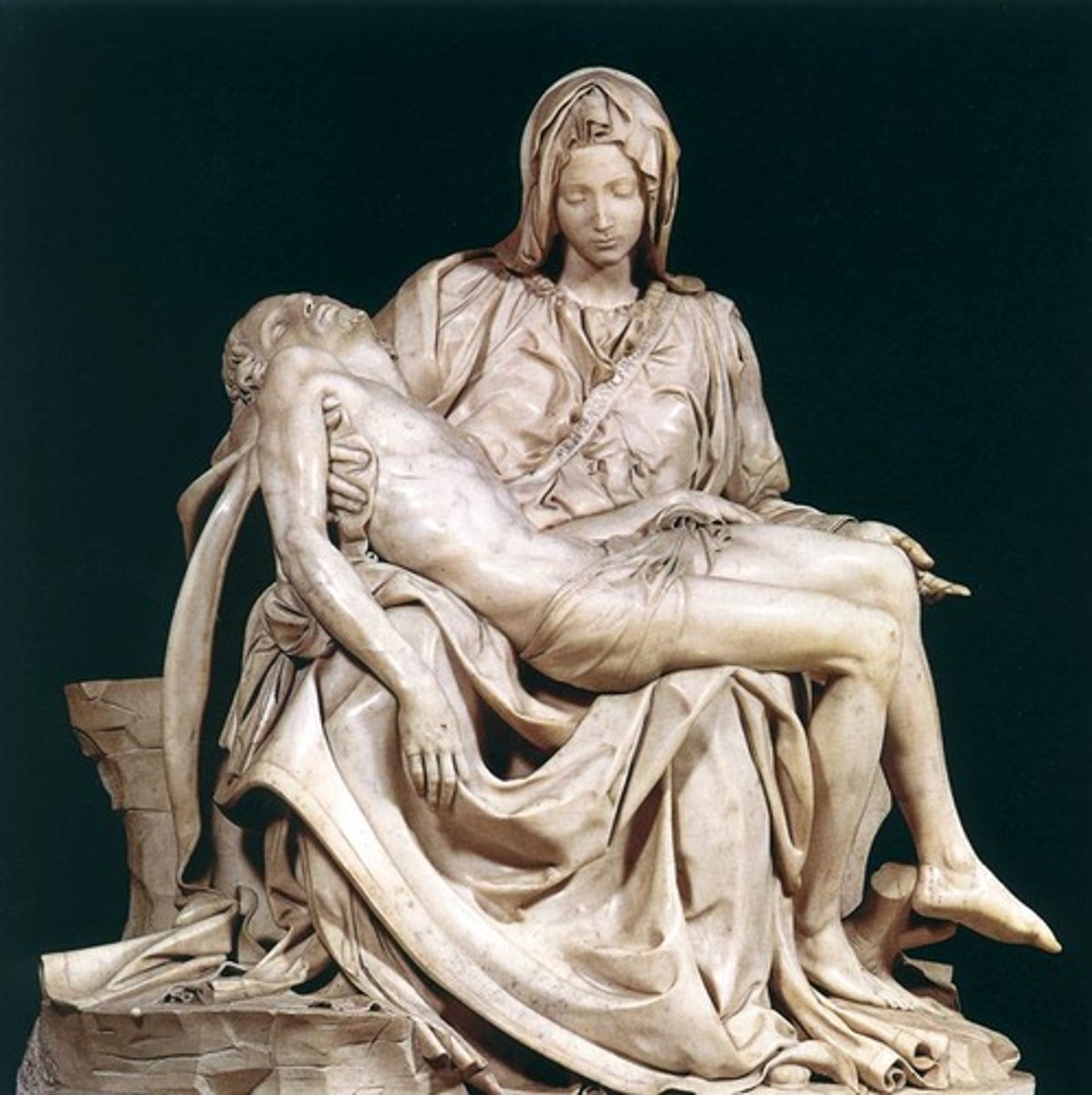
Pieta
Michelangelo - sculpture of Mary holding the dead Christ, noted for emotion and detail.

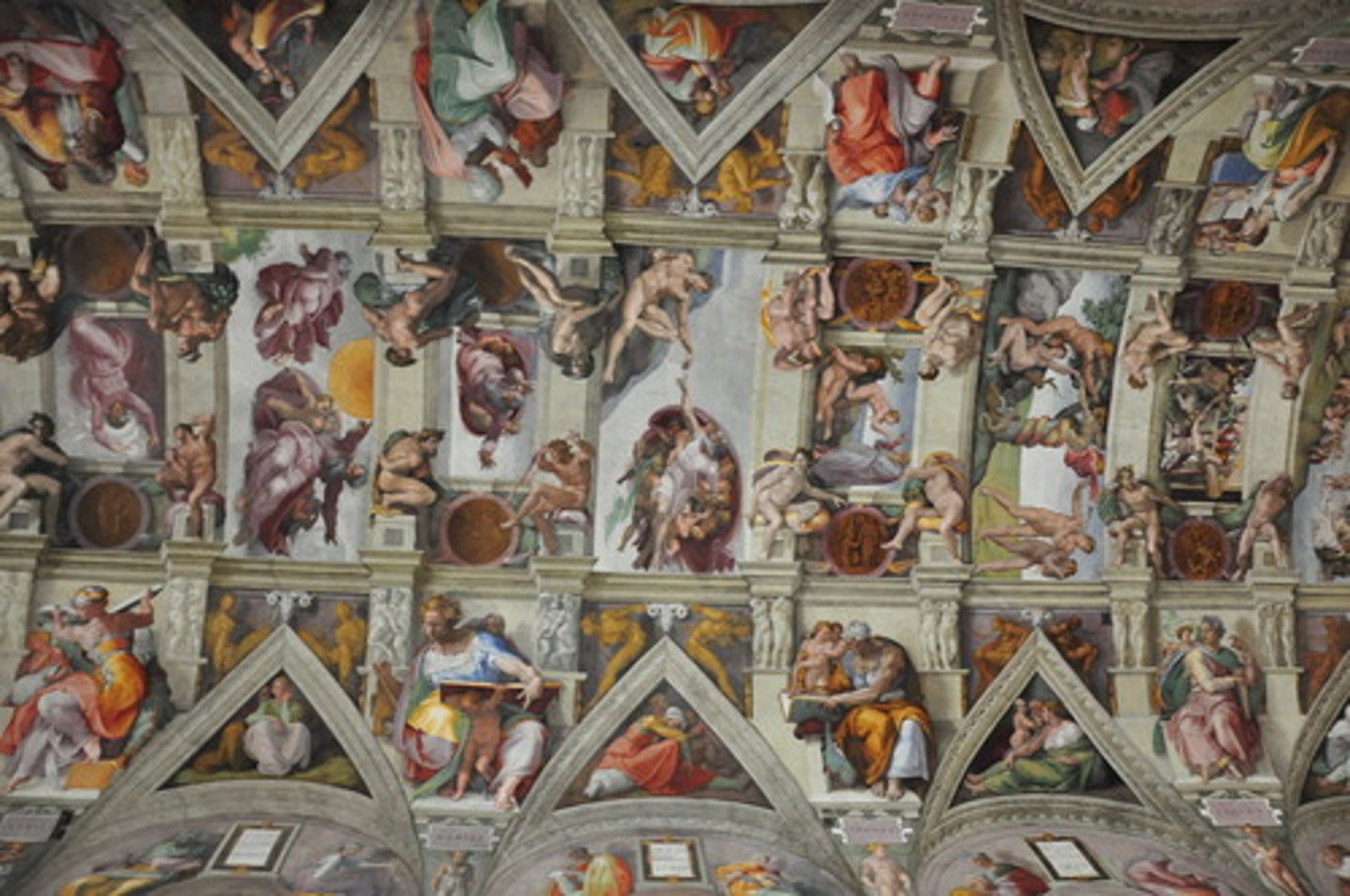
Sistine Chapel
Michelangelo - Ceiling and altar frescoes depicting Biblical scenes.

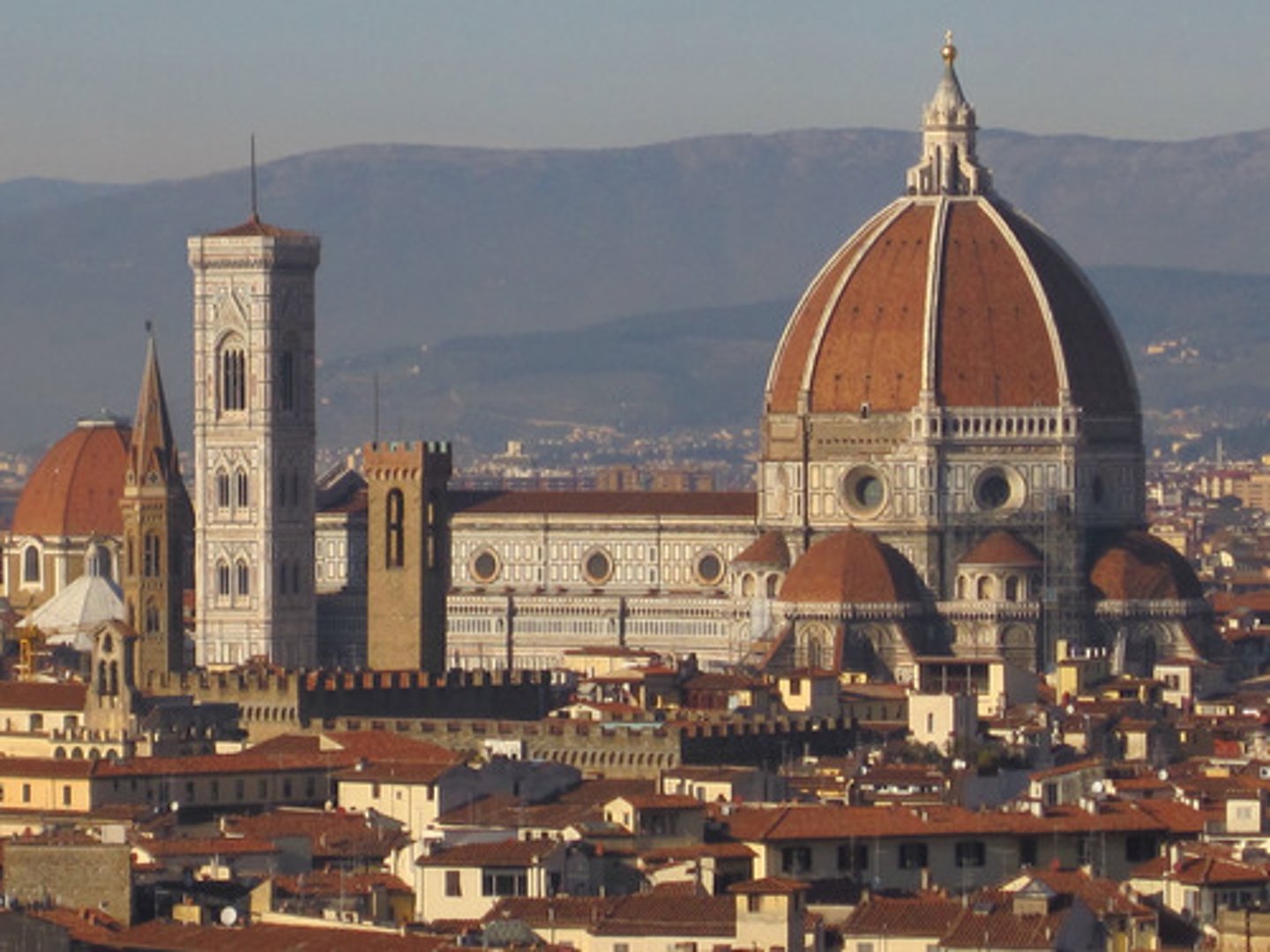
Florentine Il Duomo
Brunelleschi - Cathedral dome designed by Brunelleschi; engineering marvel of the era.

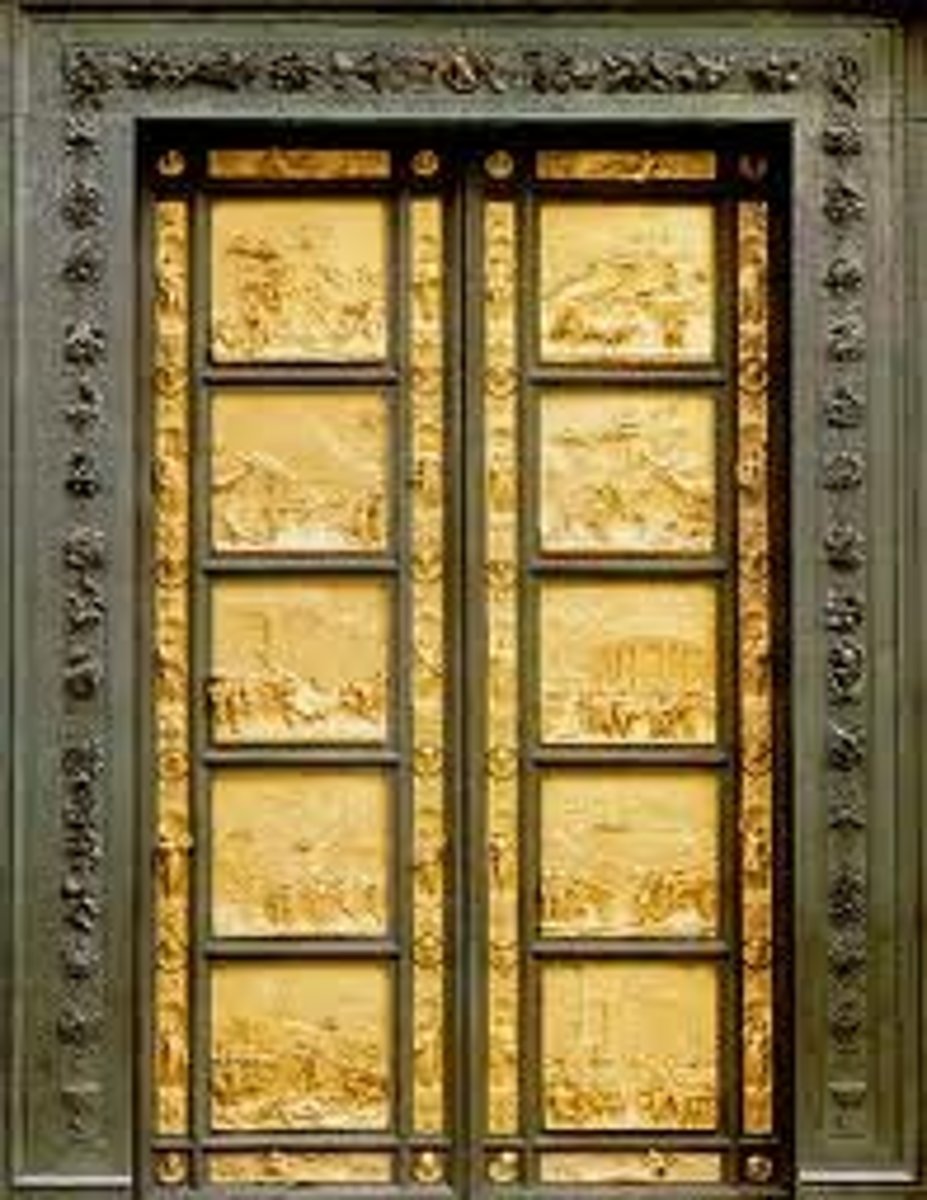
Baptistry Doors
Ghiberti - Bronze doors by Ghiberti in Florence, known for detailed reliefs.

The Prince
Political treatise by Machiavelli promoting pragmatic and sometimes ruthless leadership.
Niccolò Machiavelli
Political theorist who emphasized power, realism, and statecraft over morality.
Differences between Italian & Northern Renaissance
Northern art emphasized detail and domestic settings; more religious focus.
Jan van Eyck
Flemish painter known for oil painting techniques and realism.
Double Arnolfini Portrait
Jan van Eyck - Detailed portrait with symbolic objects, attributed to van Eyck.

Hieronymus Bosch
Dutch painter known for fantastical and moralizing imagery.
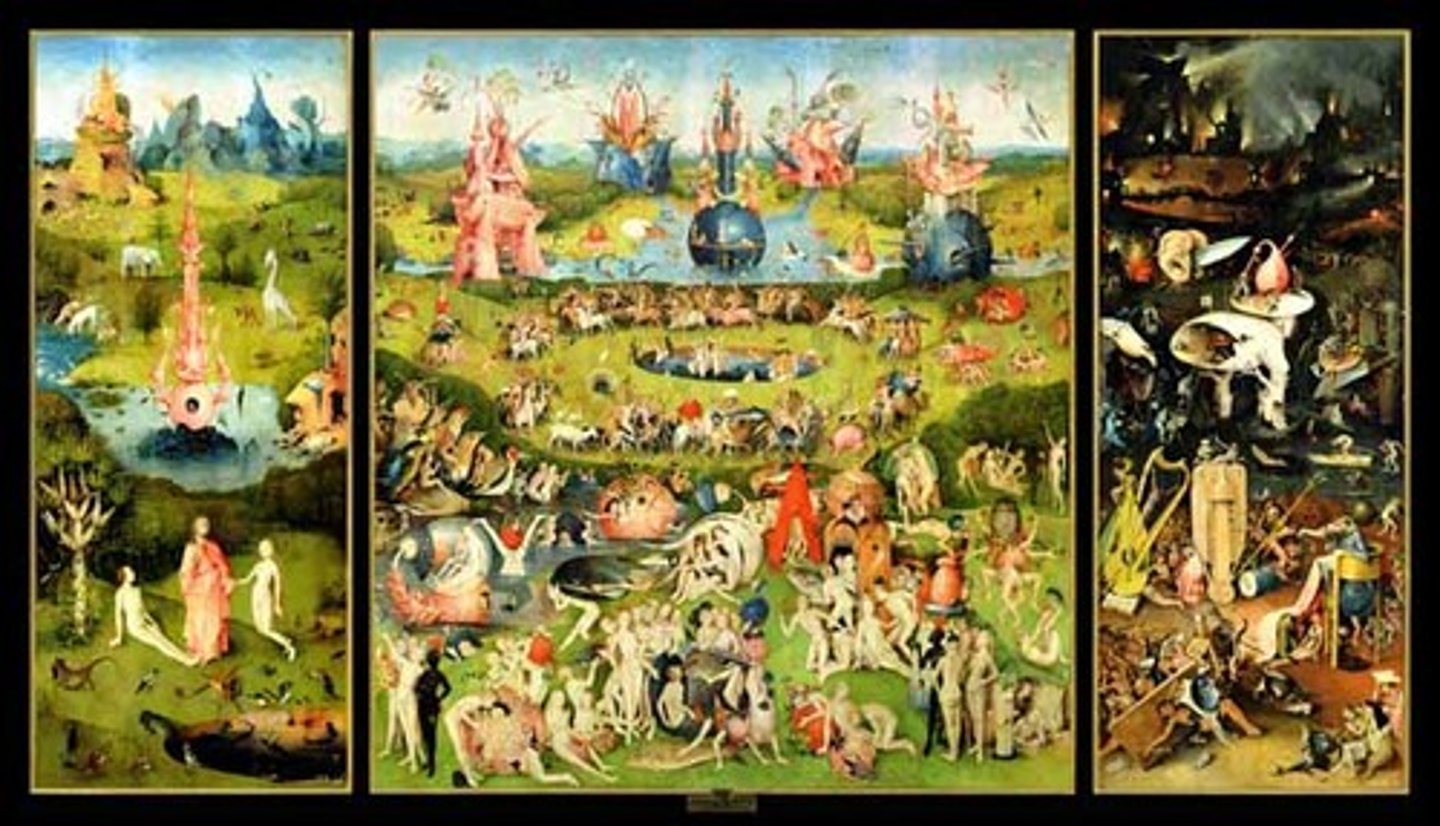
Garden of Earthly Delights
Hieronymus Bosch - Triptych by Bosch depicting paradise, sin, and damnation.

Memento mori
Artistic symbol reminding viewers of death and the afterlife.
Woodcut
Printmaking technique using carved wood blocks.
Engraving
Printmaking using incised metal plates for fine detail.
Albrecht Dürer
German artist skilled in woodcuts, engravings, and self-portraiture.
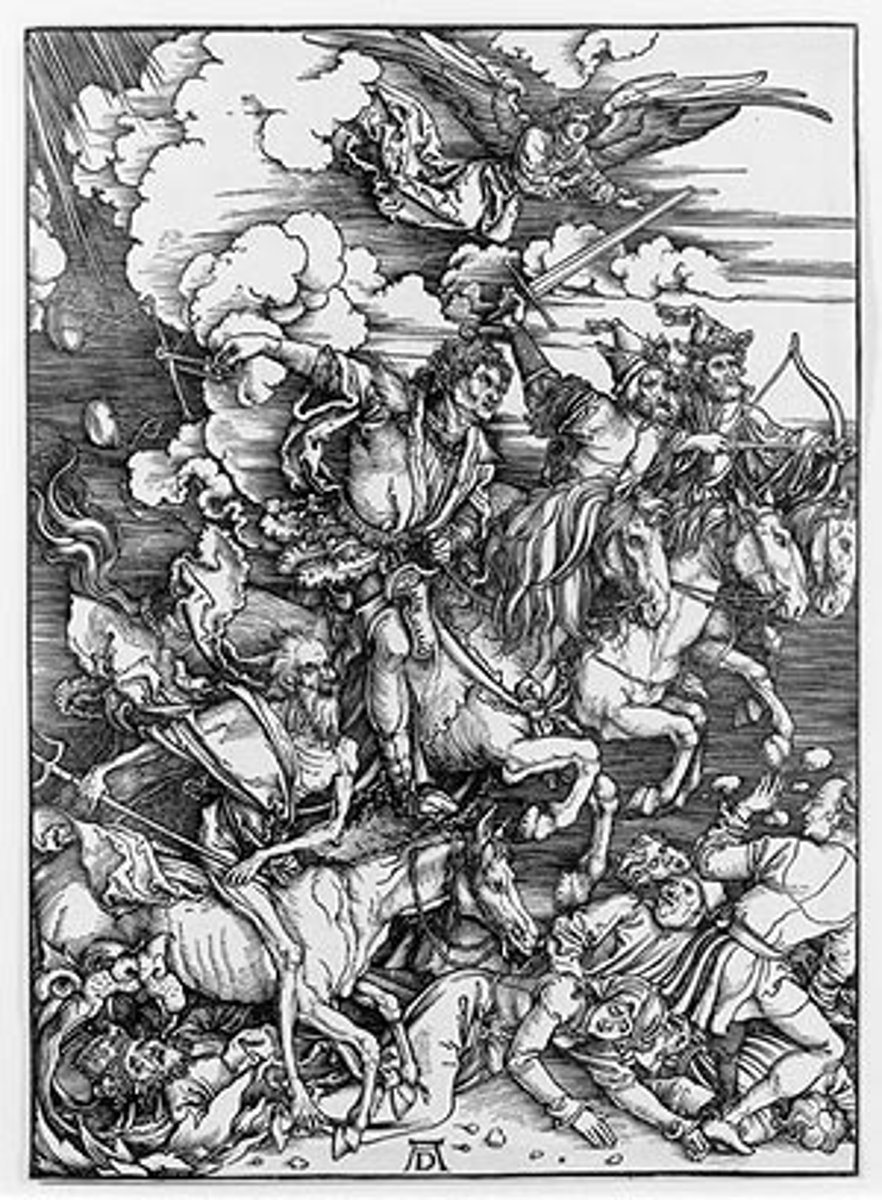
The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse
Dürer - woodcut depicting biblical end-times.

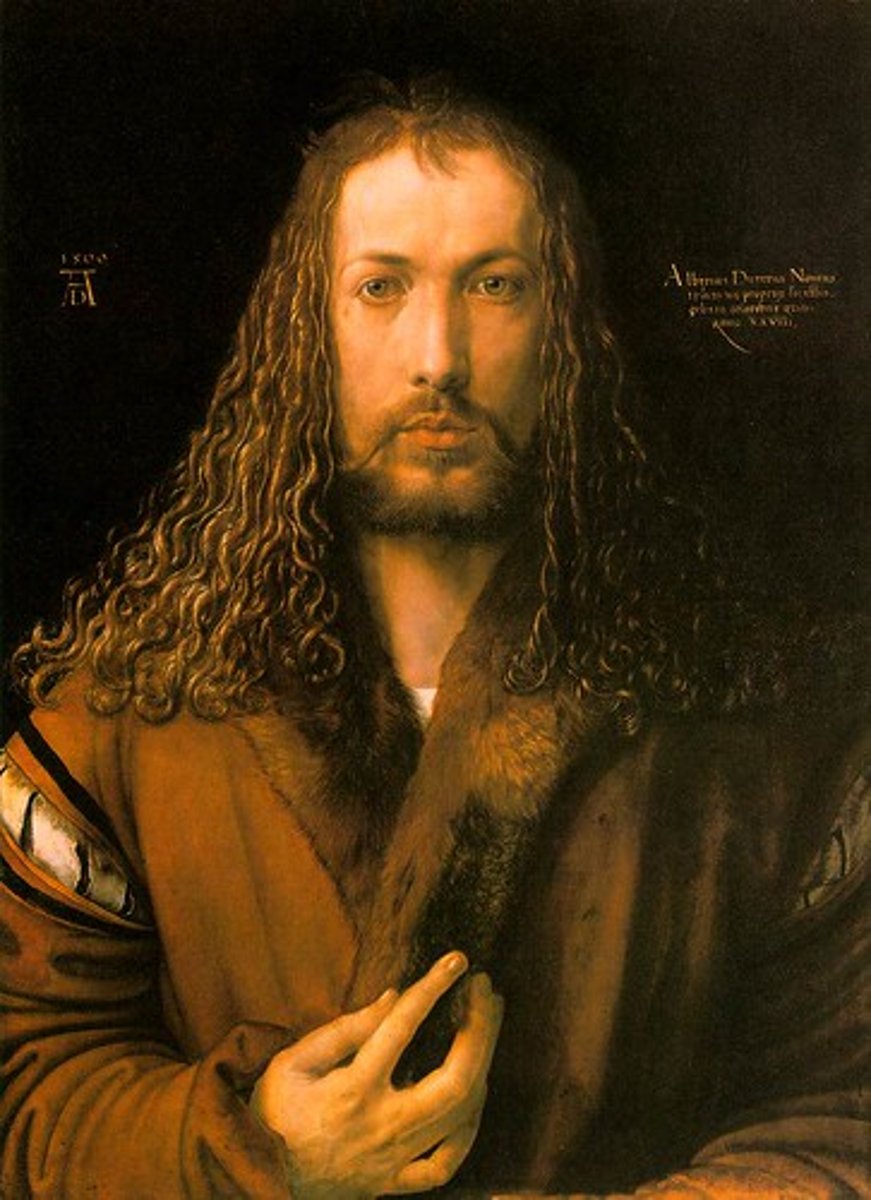
Self-Portrait at the Age of Twenty Eight
Dürer - introspective painting echoing Christ-like imagery.

Grünewald
German painter known for expressive religious works.
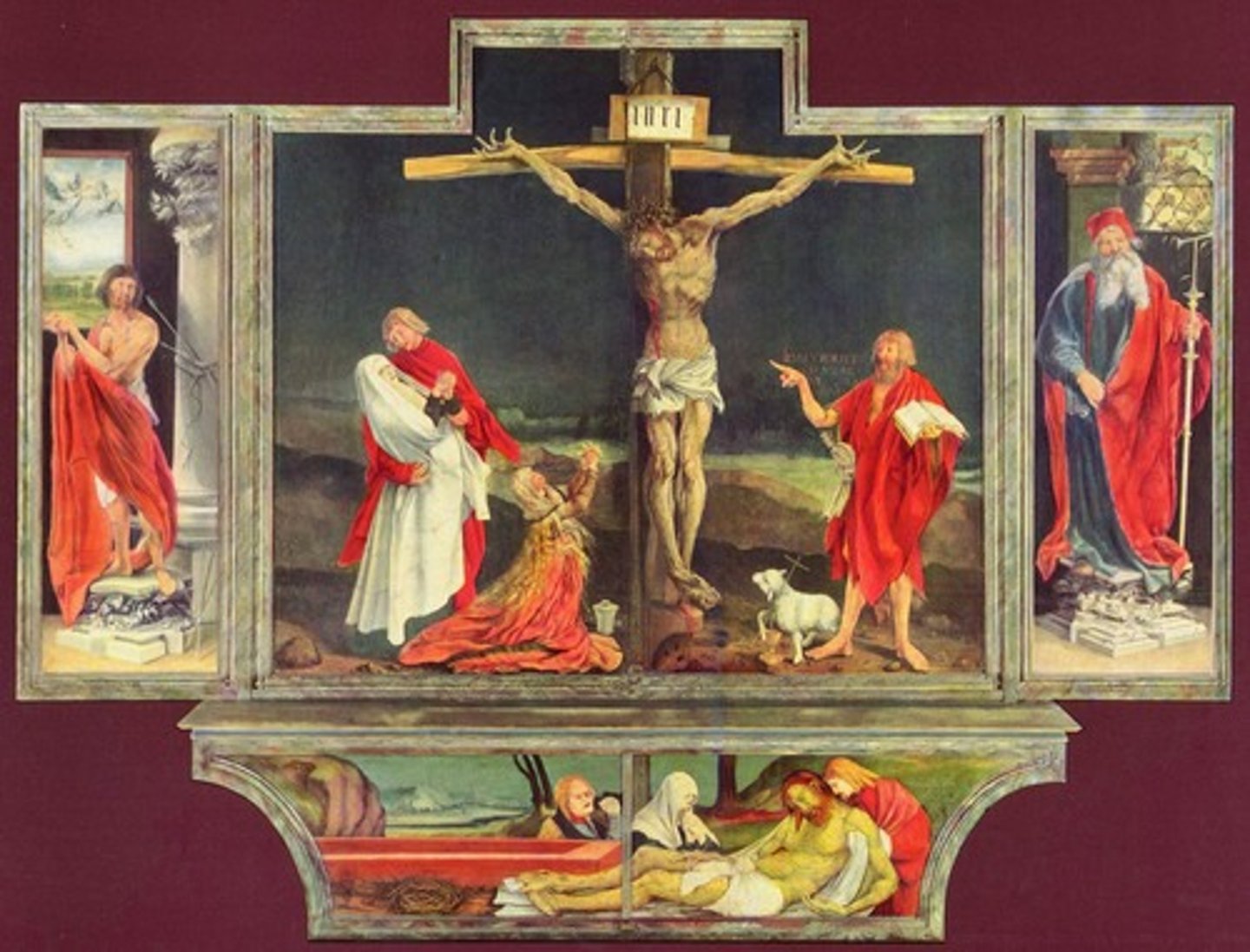
Isenheim Altarpiece
Gruenewald - altarpiece featuring vivid imagery of Christ's suffering and healing.
Hans Holbein the Younger
Portraitist of the Tudor court, known for realism.
Portrait of Henry VIII
Holbein - famous image symbolizing royal authority.

Pieter Bruegel the Elder
Dutch painter of peasant life and landscapes.
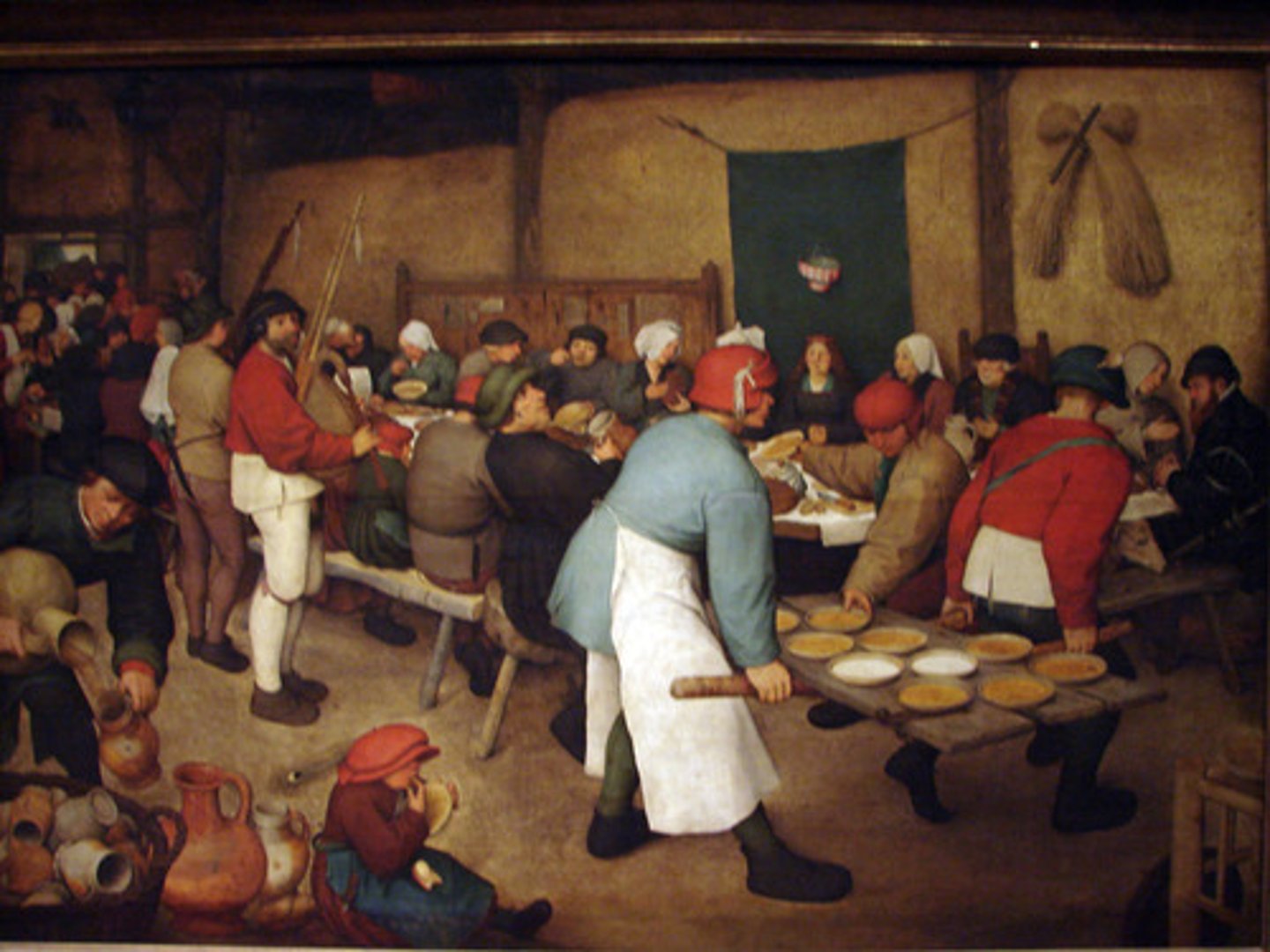
Peasant Wedding
Bruegel - painting capturing rustic festivity and everyday life.

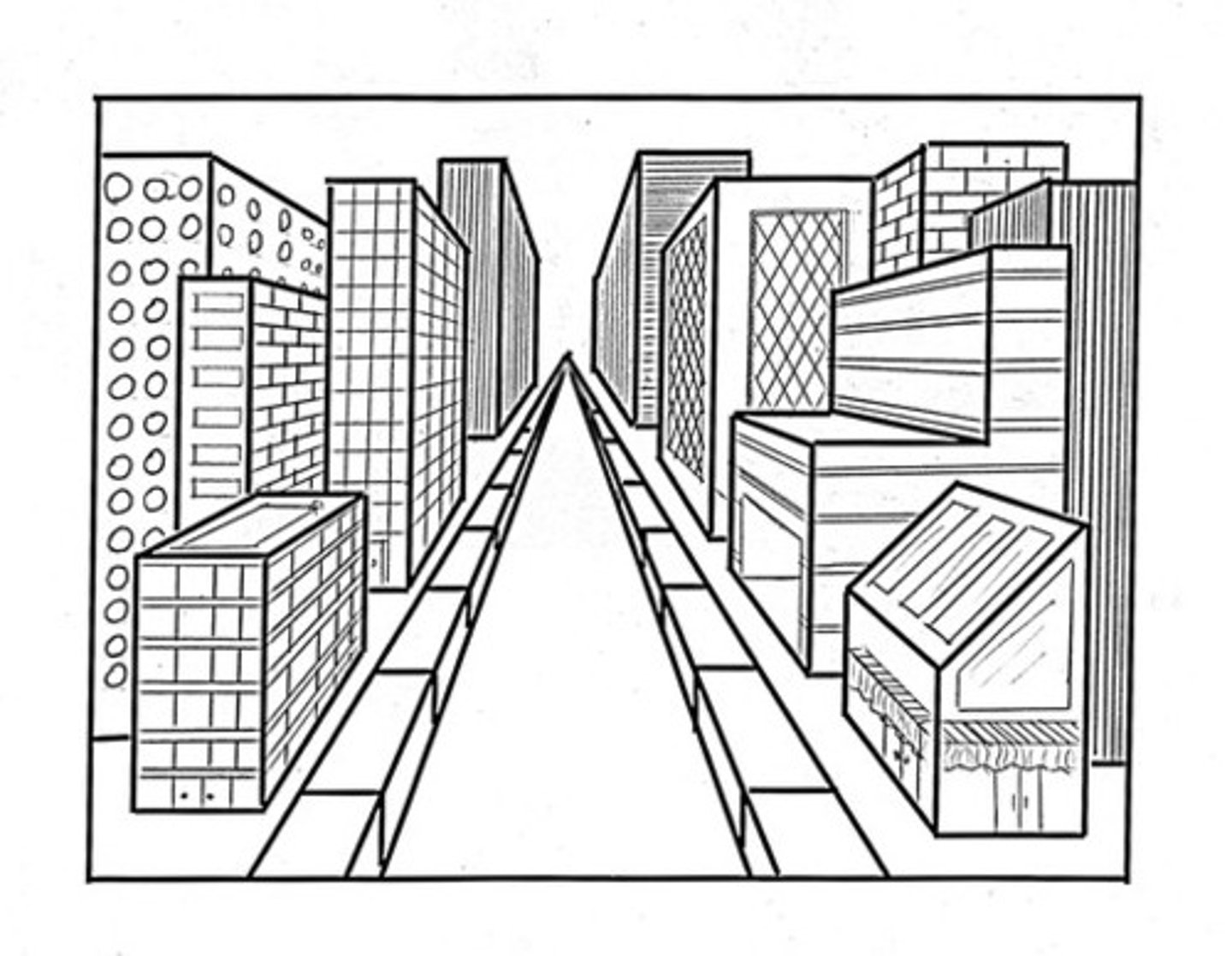
Linear perspective
Artistic technique creating depth through converging lines; mastered in Italy.
Gutenberg printing press
Invention that made books affordable and helped spread Reformation ideas.
Christian humanism
Northern humanist movement focusing on reforming Christianity through education.
Desiderius Erasmus
Dutch humanist who criticized Church corruption while remaining Catholic.
Charles V
Holy Roman Emperor who opposed the Protestant Reformation.
Indulgences
Church-issued pardons for sins, a key trigger of the Reformation.
Martin Luther
German monk who sparked the Reformation by challenging Church abuses.
German peasant revolts
Uprisings inspired by Luther's ideas, though he did not support them.
Peace of Augsburg
1555 treaty allowing German princes to choose Catholicism or Lutheranism.
John Calvin
Reformer who promoted predestination and strict moral discipline.
Doctrine of Predestination
Belief that God has already determined who will be saved.
Anabaptists
Radical reformers who rejected infant baptism and promoted separation of church and state.
Henry VIII
English king who broke from the Catholic Church and created the Anglican Church.
Anglican Church
Church of England established by Henry VIII during the English Reformation.
Impact of Reformation on music
Emphasized congregational singing and use of vernacular lyrics.
Chorale
Lutheran hymn sung in German by the whole congregation.
Vernacular
Everyday language; used in Reformation texts to reach wider audiences.
Witch trials
Persecutions intensified during the Reformation due to religious and social tensions.
Council of Trent
Catholic response to the Reformation that reformed Church practices and reaffirmed doctrine.