AQA Trilogy Chemistry - C9 Crude Oil and Fuels
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Crude Oil
a finite resource found in rocks
a mixture of many different carbon compounds
formed over millions of years of remains of tiny sea animals and plants that were buried in mud
layers of rock was laid down on top creating the conditions (high pressure and temp in the absence of oxygen) to make crude oil
Hydrocarbon
a compound containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms
Alkanes
saturated hydrocarbons
all the carbon-carbon bond are single covalent bonds
CnH(2n+2)
First 4 Alkane Molecules
MAIDEN - methane
ERLEGH - ethane
PUPILS - propane
are the BEST - butane
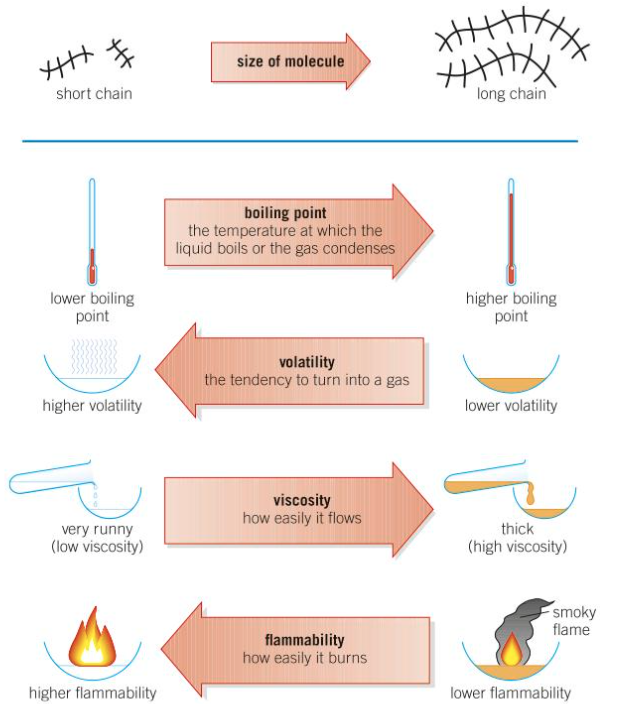
Impact of the properties of hydrocarbon depending on chain length of molecule
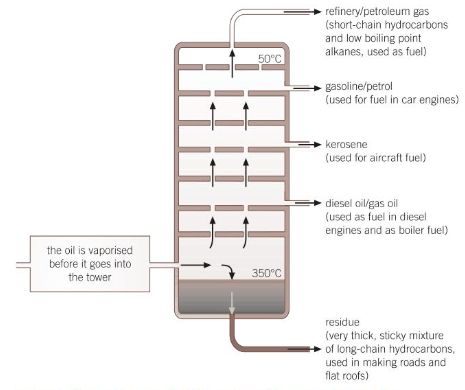
Fractional Distillation
crude oil is separated into hydrocarbons with similar boiling points called fractions
Complete Combustion
fuel + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+ energy)
the carbon and hydrogen in the fuel are oxidised completely when burned like this
Incomplete Combustion
fuel + oxygen → carbon monoxide + carbon + water (+ energy)
happens when there is a poor supply of oxygen
Cracking Hydrocarbons
breaking longer, less useful hydrocarbons into smaller, more useful hydrocarbons
cracked as thermal decomposition (chemical reaction that happens when a compound breaks down when heated) reactions take place
Alkene
unsaturated hydrocarbon
have at least one double bond between their carbon atoms
C=C
Cracking in a lab
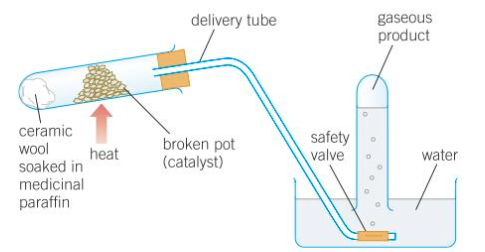
Test for Alkanes and Alkenes
a positive test for alkenes is that it turns orange bromine water colourless
alkanes don’t react with bromine water