Movement of blood and fluids
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Which type of circulation comes from the left side of the heart?
Systemic
Which type of circulation comes from the right side of the heart?
Pulmonary
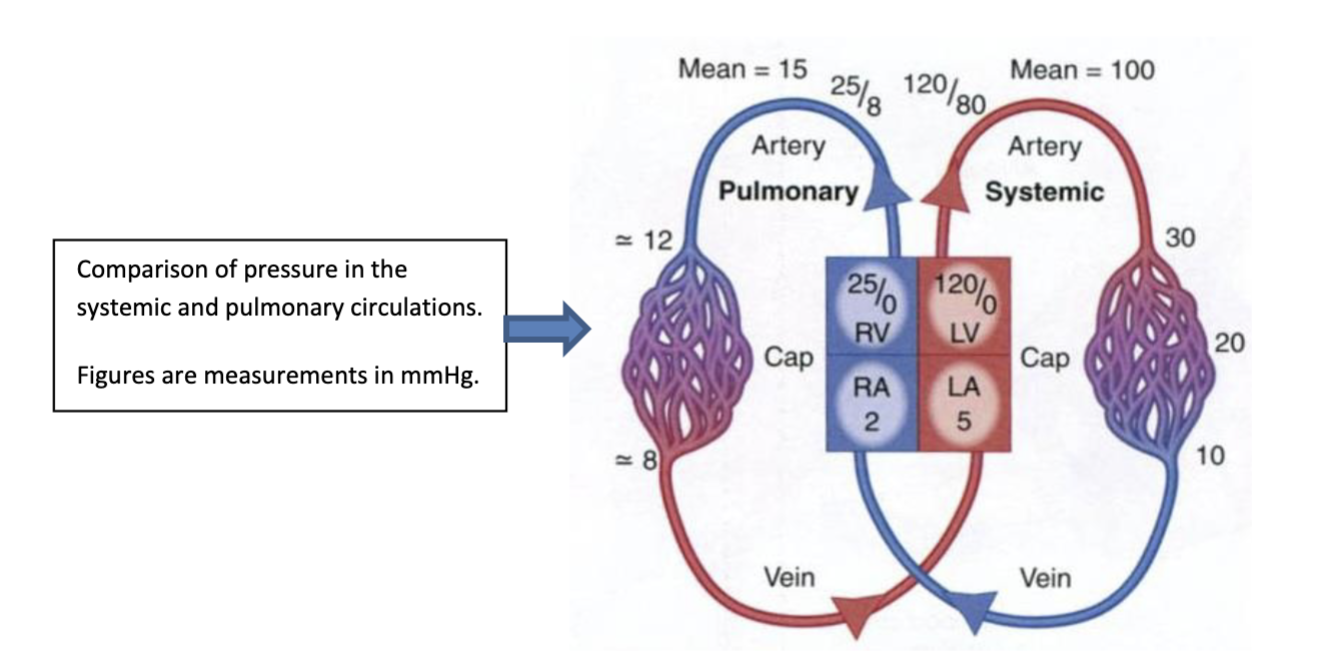
Is systemic or pulmonary circulation higher pressure? Why?
Systemic as the left side of the heart (left ventricle) is a much stronger pump than the right
Define bulk flow
Movement of the fluid from high to low hydrostatic pressure
Is bulk flow or diffusion faster over long distances?
Bulk flow
Define hydrostatic pressure
Pressure that a fluid exerts on a container (e.g. blood on a blood vessel). Fluid moves from high to low hydrostatic pressure.
Describe how blood moves by bulk flow along vessels
Since hydrostatic pressure is much higher in the arteries near the heart than it is in the atria, blood flows in the right direction
What is perfusion pressure
The difference in pressure between two points in a blood vessel (also pressure needed for blood to move through that vessel)
Which vessels’ walls does bulk flow occur across
Capillaries (and sinusoids and post-capillary venules)
Describe bulk flow across vessel walls
At the arterial end: intravascular hydrostatic pressure exceeds extravascular hydrostatic pressure and oncotic pressure, blood moves out
At the venous end: overall, extravascular hydrostatic pressure and oncotic pressure exceed intravascular hydrostatic pressure, blood moves in

What is the name for bulk flow out of a vessel?
Filtration
What is the name for bulk flow into a vessel?
Absorption
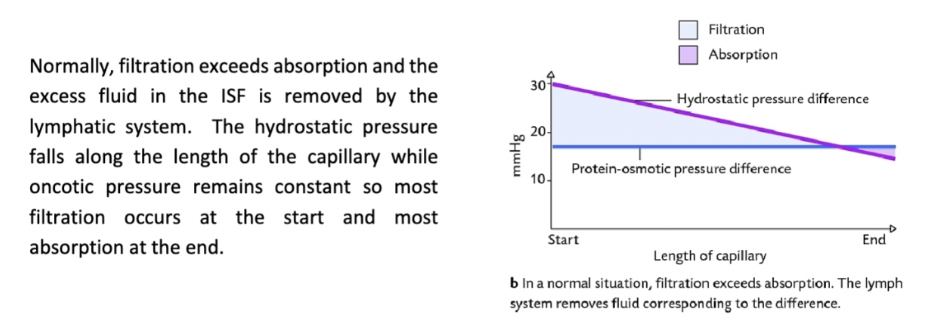
Why does their tend to be more filtration than absorption?
Intravascular hydrostatic pressure tends to exceed extravascular hydrostatic pressure which leads to more bulk flow out of capillaries than into them (filtration > absorption).
Define diffusion
Tendency of solutes to move down a concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (of solute) until the concentrations are equal
Name four factors affecting diffusion and how they affect it.
Diffusion coefficient: higher = faster diffusion
Concentration gradient: steeper = faster
Surface area for diffusion: larger SA = faster
Distance for substance to travel to target cell: longer = slower
Define osmosis
Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane from low to high osmotic pressure
Define osmotic pressure. What is the effect of high osmotic pressure?
The pressure exerted by osmotic particles (e.g. solutes) - the drive for water to move into a solution by osmosis.
High osmotic pressure draws water in.
What is oncotic pressure?
The osmotic pressure plasma proteins exert in blood (also called colloid/protein osmotic pressure)
How does oncotic pressure vary throughout the circulation?
It doesn’t - constant throughout the circulation.
Is intravascular or extravascular oncotic pressure generally higher? What effect does this have?
Intravascular oncotic pressure is generally higher which draws water into the blood.
What generates perfusion pressure?
The fact that hydrostatic pressure in the arteries is higher than those in the atria/veins returning to the atria.
How can hydrostatic pressure of a fluid in a container be changed?
Altering volume of fluid or the size of the container.
Less fluid or a larger container = lower hydrostatic pressure
What effect does vasoconstriction of arterioles have on hydrostatic pressure upstream and downstream?
Increases pressure upstream as less blood can get through.
Decreases pressure downstream in capillary beds as there is less blood in the same volume of vessels.
What effect does vasodilation of arterioles have on hydrostatic pressure upstream and downstream?
Decreases pressure upstream as it is easier for blood to flow through.
Increases pressure downstream in the capillary bed as there is more blood in the same volume of vessels.
What is Starling’s law of capillaries?
What is the Starling equation?
Hydrostatic pressure and oncotic pressure differences across the vessel wall balance to determine the movement of fluid.
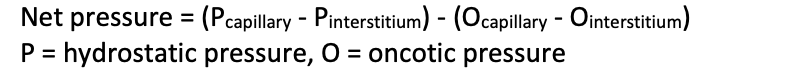
So Net pressure = effect of hydrostatic pressure pushing out - effect of oncotic pressure pulling in
Negative answer = water absorbed into the capillary
How would dilation of the arterioles feeding the capillary bed change the balance of filtration and absorption?
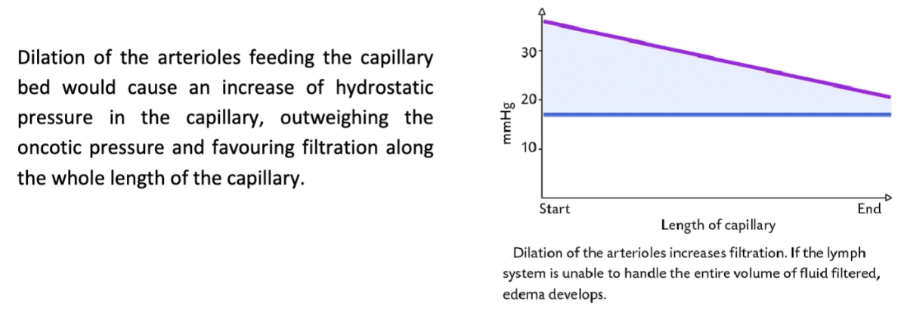

How would constriction of the arterioles feeding the capillary bed change the balance of filtration and absorption?
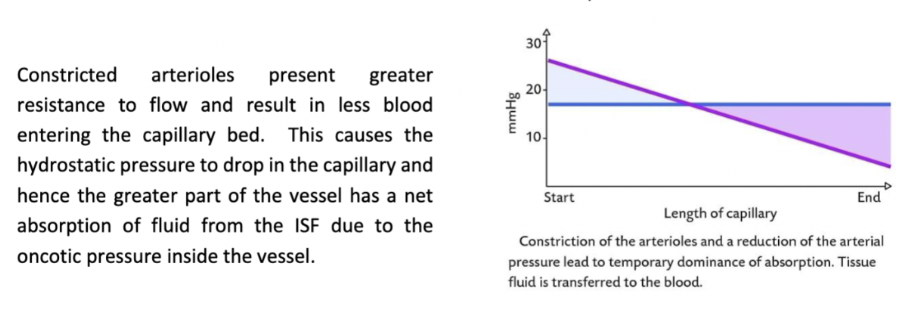

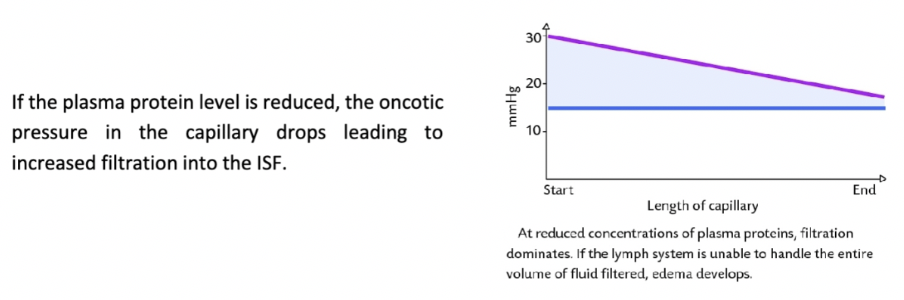
How would a reduction of the plasma protein level in the blood change the balance of filtration and absorption?