Nervous system lecture
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
neural tissue outside of central nervous system
spinal nerves
carry impulses to and from the spinal cord
cranial nerves
carry impulses to and from the brain
interoceptors
internal senses (taste, internal pressure)
exteroceptors
external senses (touch, temp, sight, smell, sound)
proprioceptors
monitor position and movement (skeletal muscles and joints)
afferent division of peripheral nervous system
nerves bring sensory info to CNS
efferent division of peripheral nervous system
nerves carry motor commands to effectors (glands, organs and smooth muscle)
somatic nervous system
division of efferent division
Controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
division of efferent division
controls involuntary organs, glands, cardiac and smooth muscle
impulses go from hypothalamus to effectors
sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight)
the division of the autonomic nervous system that
increases heart rate, blood flow, energy, breathing, sweating, mental activity
decreases digestion and urination
parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest)
division of the autonamic nervous system that
decreases heart rate and breathing
increases urination and digestion
neurons
cells that send and receive electrical impulses
amiotic (don't divide)
last entire life
neuroglia
cells that support and protect neurons
perikaryon
neuron cytoplasm
nissl bodies
Rough endoplasmic reticulum in neurons that produce neurotransmitters
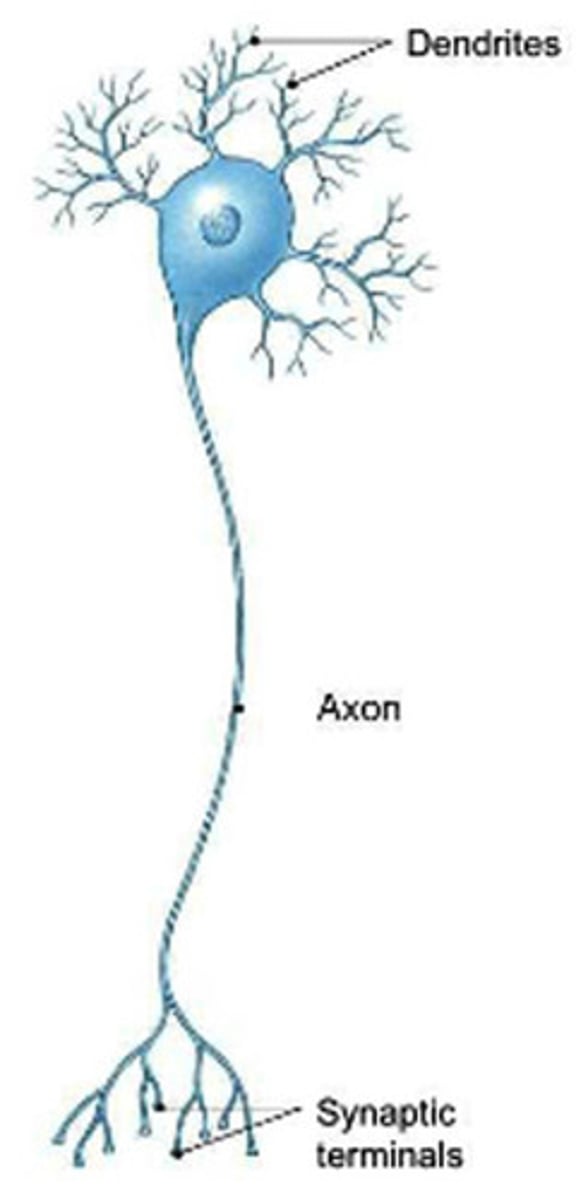
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
axons
Carry impulses away from the cell body onto the next
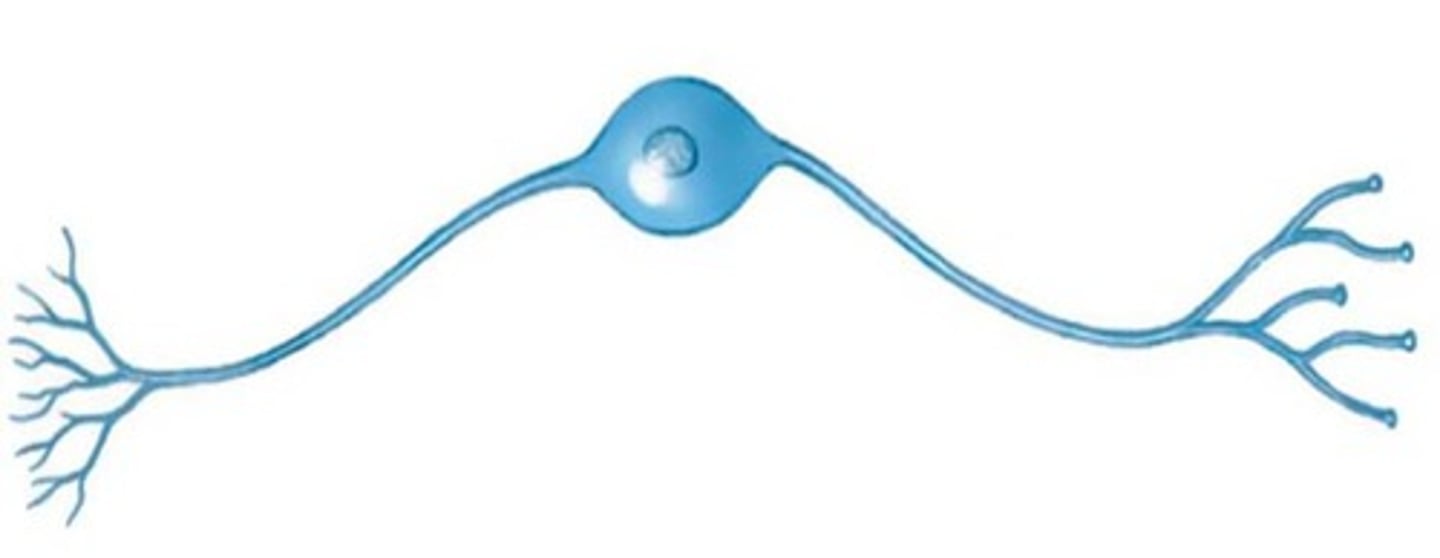
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites
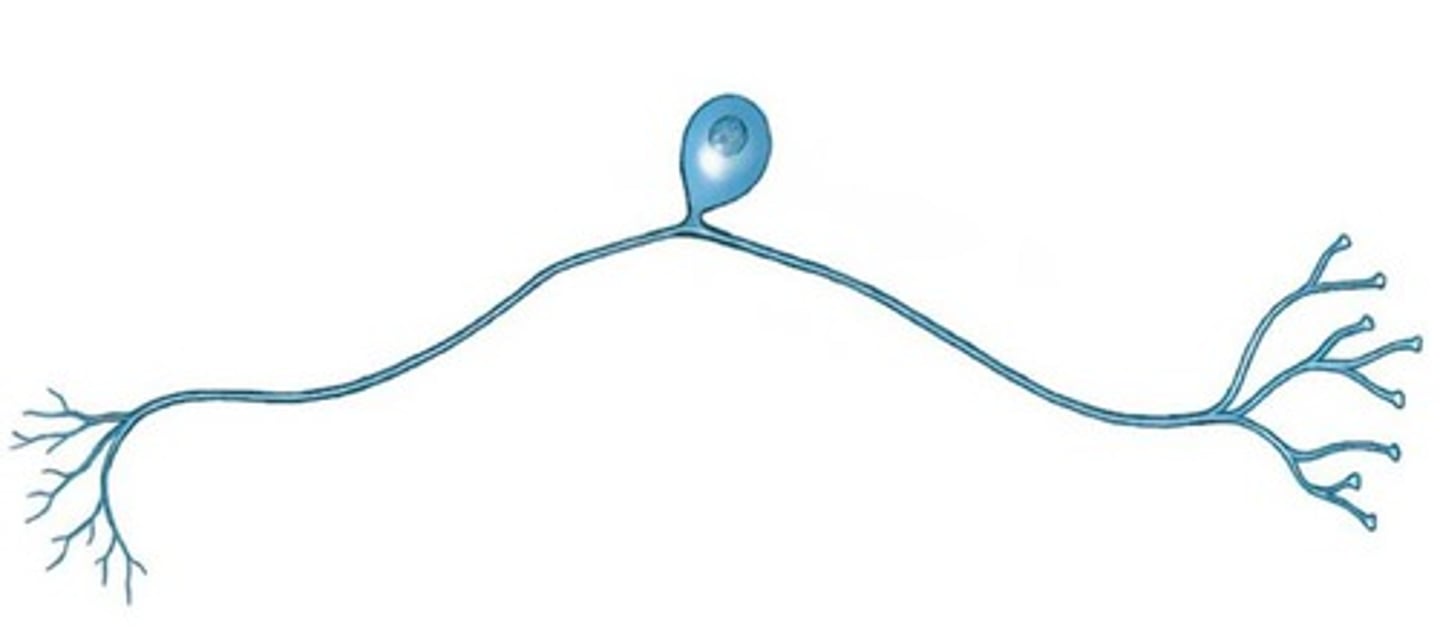
unipolar neuron
A neuron with one axon attached to its soma
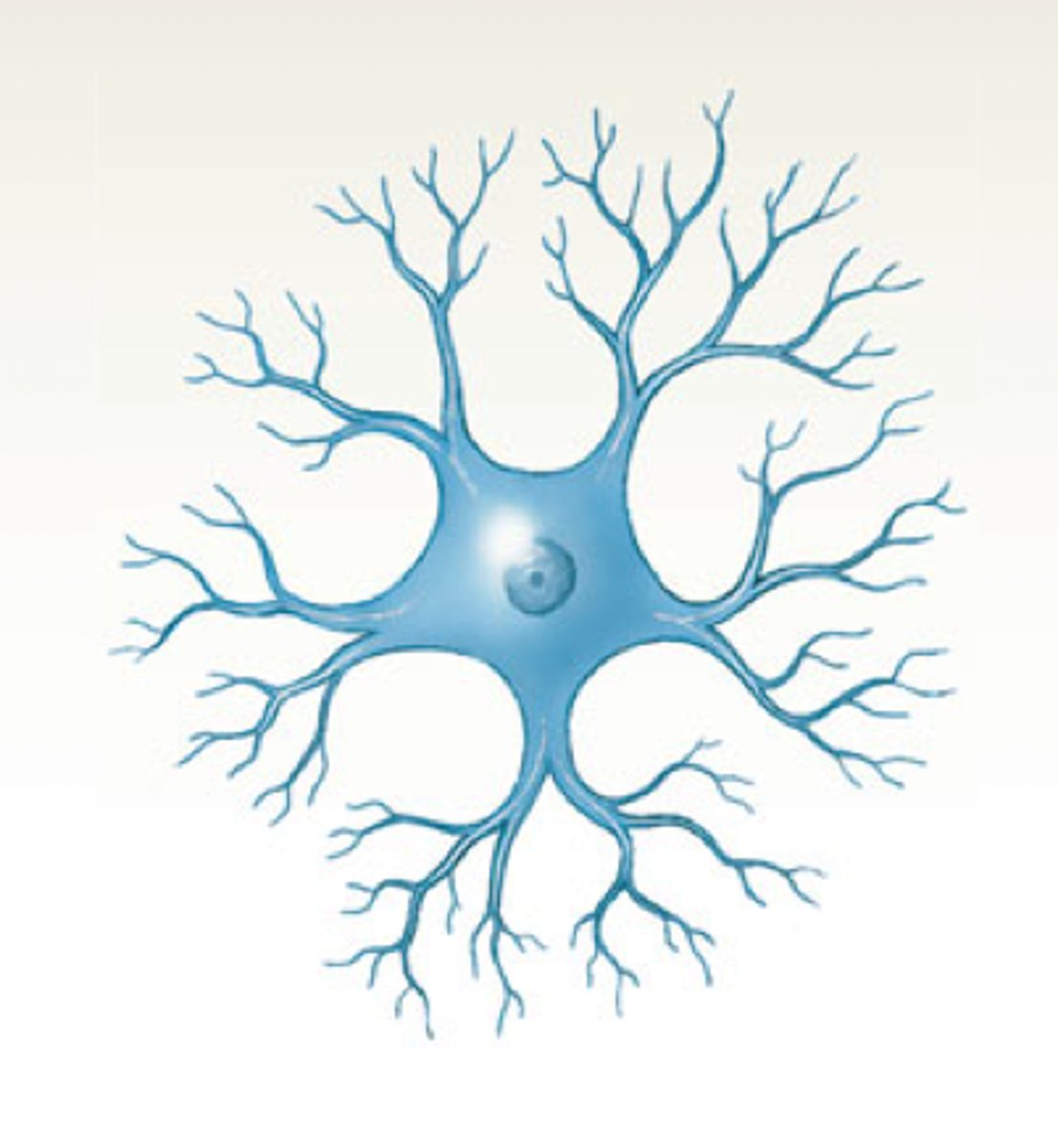
anaxonic neuron
many dendrites but no axon
bipolar neuron
one axon and one dendrite
telodendria (collaterals)
branches at ends of axons
synaptic terminals
tips of telodendria
contain vesicles with neurotransmitters
sensory neurons (afferent)
carry information to the CNS
motor neurons (efferent)
neurons that carry outgoing information from the central nervous system to the effectors
interneurons (association)
links between sensory and motor neurons. found in the brain or spinal cord
responsible for higher functions such as memory, learning and emotion
ependymal cells (CNS)
line ventricles of brain and central canal of spinal cord
secretes and circulates cerebrospinal fluis
astrocytes (CNS)
maintain blood-brain barrier and stabilizes neurons
microglia (CNS)
Migrate through neural tissue
Clean up cellular debris, waste products, and pathogens
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
produce myelin which insulates axons and increases the speed of action potentials
nodes of Ranvier (CNS)
gaps between myelin (bare axon)
Satellite cells (PNS)
protect/nourish neuron cell bodies in PNS
Function similar to astrocytes of CNS
Schwann cells (PNS)
Form myelin sheath around peripheral axons
fluid inside cell
potassium (K) and anions (A)
fluid outside cell
sodium (Na)
resting potential
-70mV
Depolarization
inside of the cell becomes more positive
greater than -70mV
hyperpolarization
inside of cell becomes more negative
more negative than -70mV
electrical impulses
when cells become more positive
chemically gated channels
Open in the presence of specific chemicals
voltage-gated channels
respond to electrical charges produced by the movement of ions
mechanically gated channels
Respond to membrane distortion (pressure)
sodium potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
graded potential
a shift in the electrical charge in a tiny area of a neuron can lead to an action potential if strong enough
graded potential depolarization
sodium enters cell through channel and cell becomes more positive which produces an elecrtical impulse
graded potential repolarization
When the stimulus is removed, sodium pumps out and membrane potential returns to normal
action potential
if graded potential reaches -55mV or more, impulse travels down entire axon
all or none principle
Refers to the fact that the action potential in the axon occurs either full-blown or not at all at -55mV
action potential depolarization
reaches -55mV and voltage gated sodium channels allow more sodium in
action potential repolarization
potential becomes more positive until reaching +30mV and sodium channels close and potassium leaves through channels but remain open until -70mV
action potential refractory period
potassium channels close and potassium goes into cell while sodium leaves
Propagation
The spread of the action potential down an axon
continuous propagation
Action potentials along an unmyelinated axon; slow
saltatory propagation
Action potential along myelinated axon
Faster and uses less energy than continuous propagation
depolarization occurs at nodes of ranvier and jumps over myelin
propagation speed factors
bigger diameter of axon and more myelin=faster
Type A fibers
myelinated, largest diameter
Type B fibers
myelinated, medium diameter
Type C fibers
unmyelinated, smallest diameter
synapse
connection between a neuron and another structure
electrical synapse
presynaptic and postsynaptic locked together at gap junctions and action potential spreads directly to postsynaptic cell
chemical synapse
Neurotransmitters released by the presynaptic cell lead to graded potential in post synaptic cell
steps of a synapse
1. action potential reaches synaptic knob and depolarizes
2. calcium releases and releases neurotransmitters across synaptic cleft
excitatory neurotransmitters
open sodium channels and depolarize postsynaptic membranes, promoting action potentials
inhibitory neurotransmitters
open potassium channels and hyperpolarize postsynaptic membranes, suppressing action potentials
Which type of receptor in your body would detect the sound of a voice of someone talking to you?
exteroceptor
A nerve impulse traveling from the CNS to a sweat gland would travel along the:
autonomic part of the efferent division
Nissl bodies are found in which part of a neuron?
cell body
During a Graded Potential, channels open allowing ________ to move into the neuron causing the cell to depolarize.
sodium
In regards to an action potential, what type of channel opens during repolarization?
voltage gated potassium channels
Sodium Inactivtion occurs during which step of an action potential?
repolarization
Which type of propagation would occur along an unmyelinated axon?
continuous