Reptiles and amniotes
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Amniotes
term for reptiles, birds, and mammals
-completed transition to land
-amniote egg

Amniote egg
egg with four membranes that allows an embryo to develop away from water
-tough shell preventing water loss
-encloses amniotic sac
-contains 4 layers
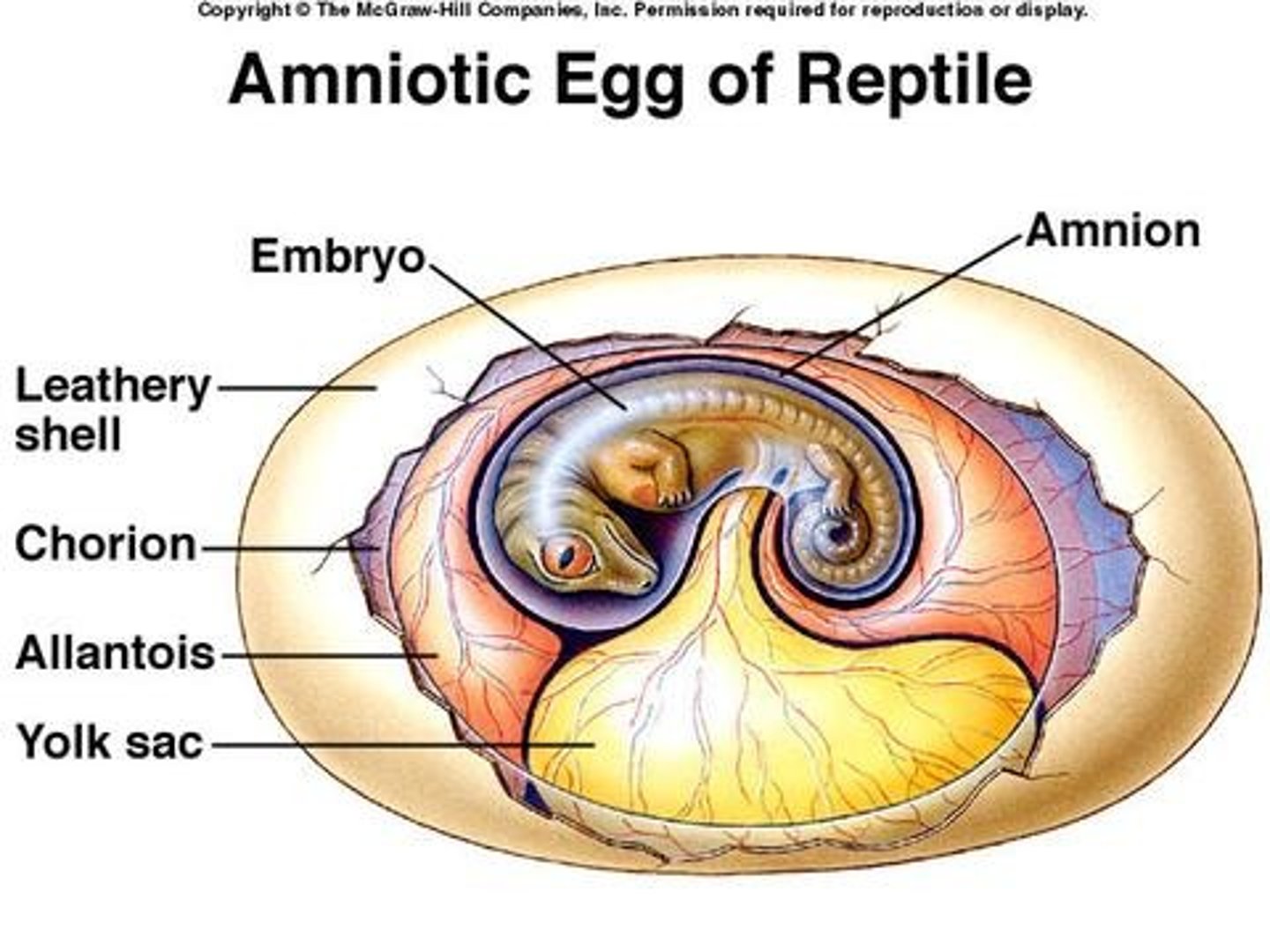
amniotic sac
term for a fluid-filled sac that cushions and protects a developing embryo and fetus
Amnion
This is the Innermost membranous sac of the egg that surrounds the developing fetus
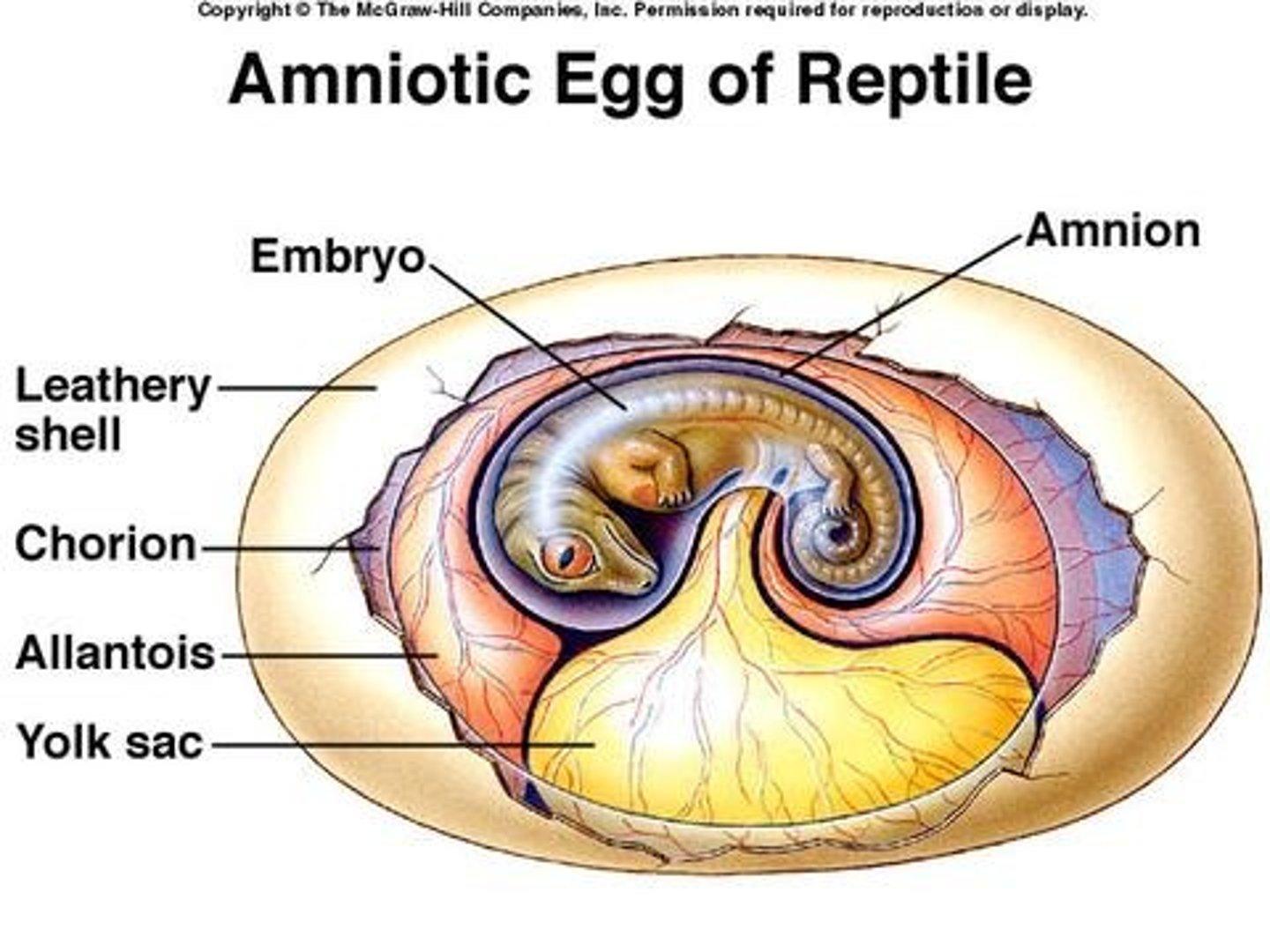
Chorion
This is the outermost layer of the two membranes surrounding the embryo in the egg; it forms the fetal part of the placenta (structures that originate from the embryo and are responsible for the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste between the fetus and the mother)
-highly vascularized
-works w/ the allantois to remove CO2 and get O2
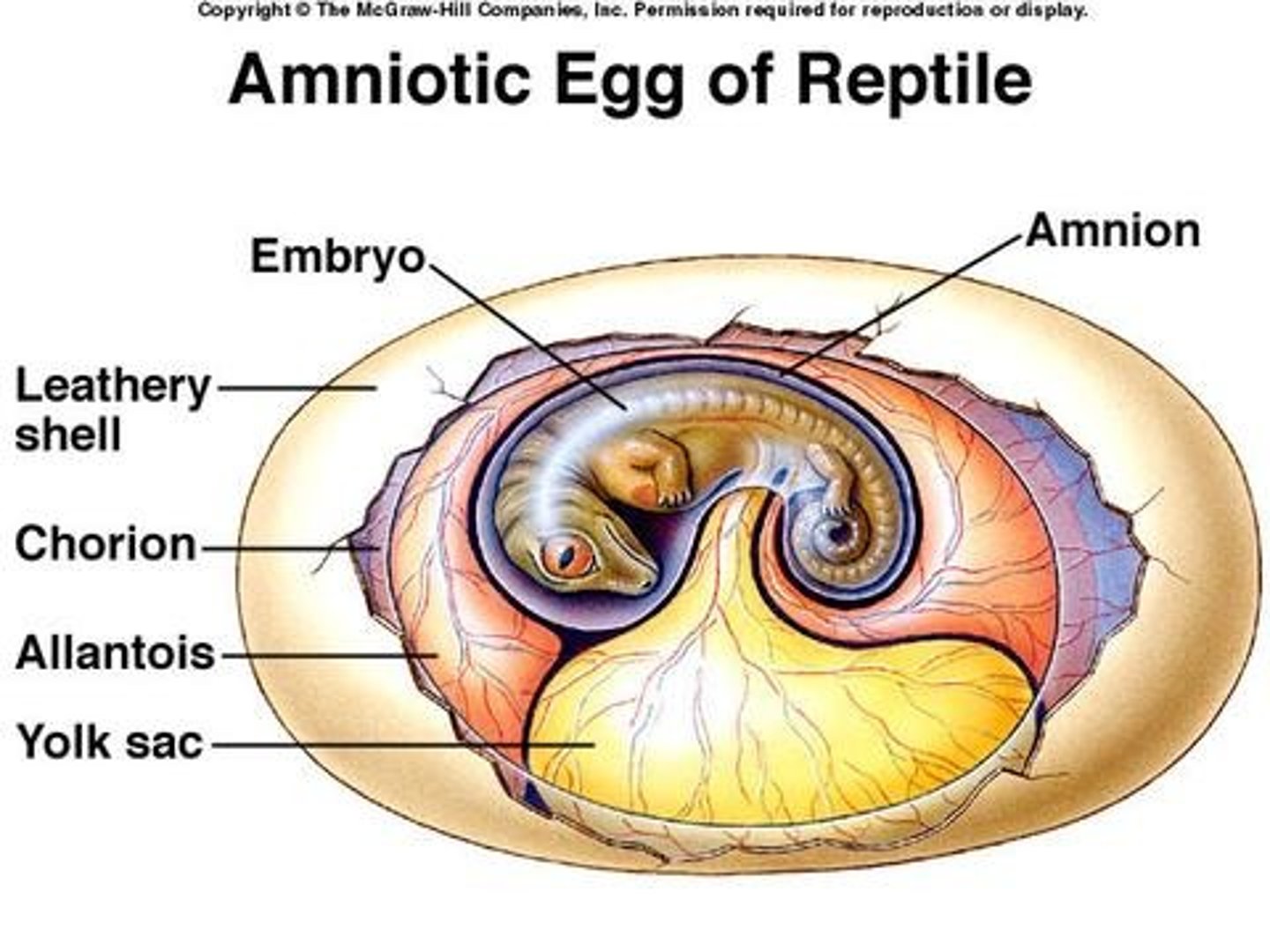
Allantois
this is involved in early fluid exchange between the embryo and the yolk sac of the egg
-stores metabolic waste
-works w/ chorion
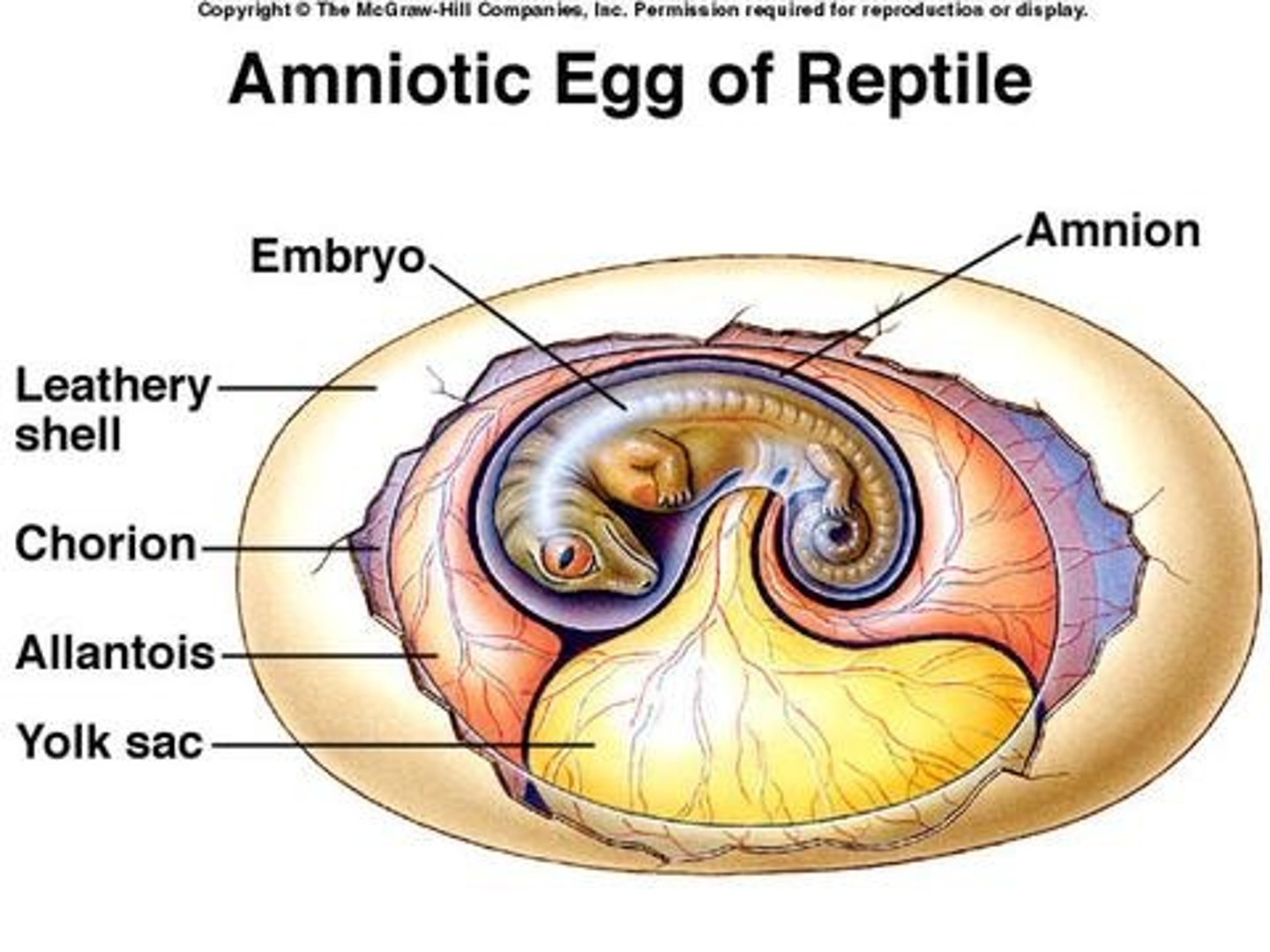
yolk sac
This is an extra-embryonic membrane that provides food for the embryo within the egg.
-stores nutrients
reptiles (characteristics)
Defining characteristics of ___:
1. amniote egg
2. keratinized epidermis
3. Aspiration breathing (negative pressure)
4. separation of pulmonary and systemic circuits
5. ectothermic
6. polyphyodont, homodont teeth
7. Vomeronasal (jacobson's organ)
8. internal fertilization
9. metanephric kidneys that excrete uric acid
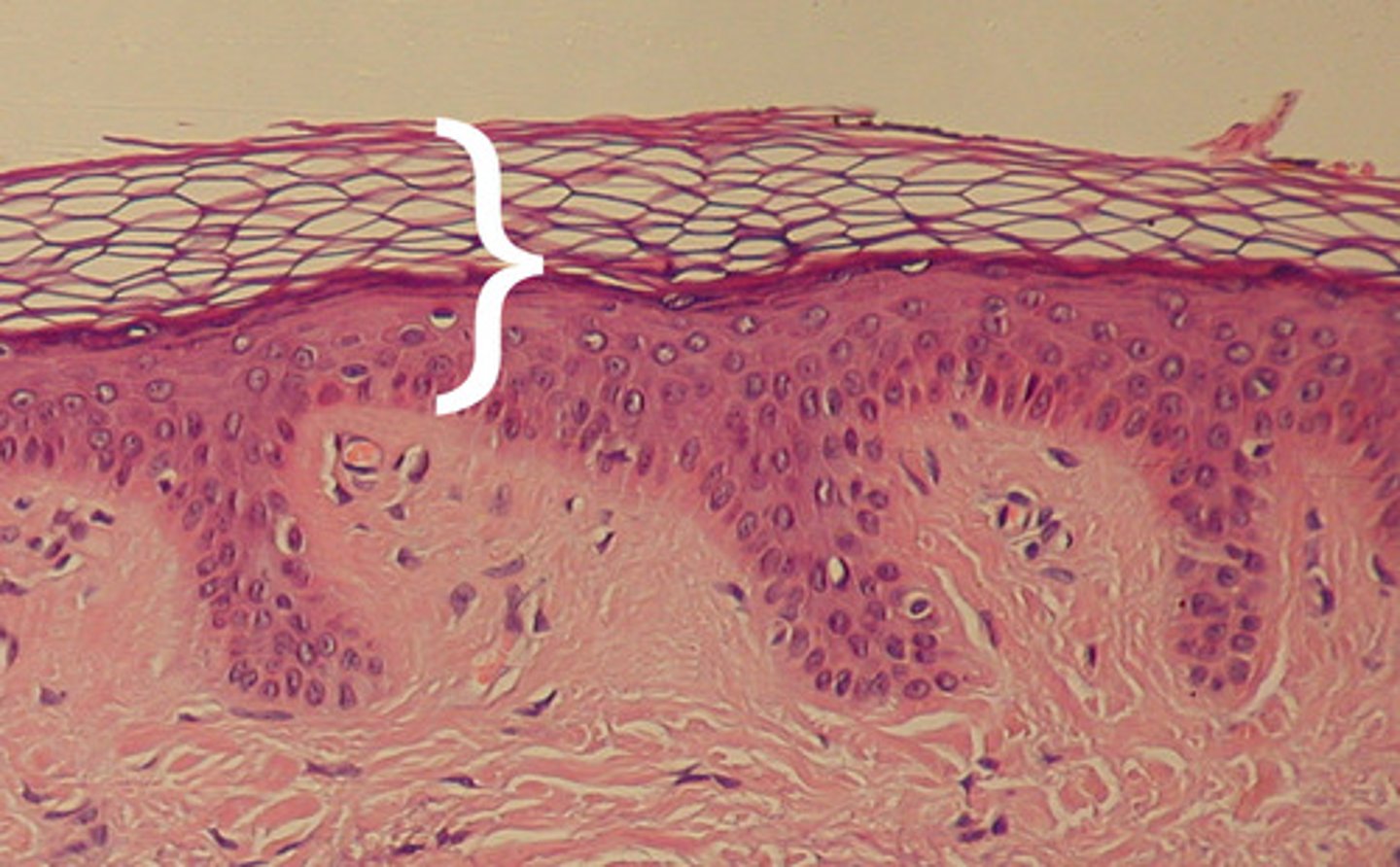
Keratinized epidermis
this type of epidermis gives reptiles thicker and water resistant skin
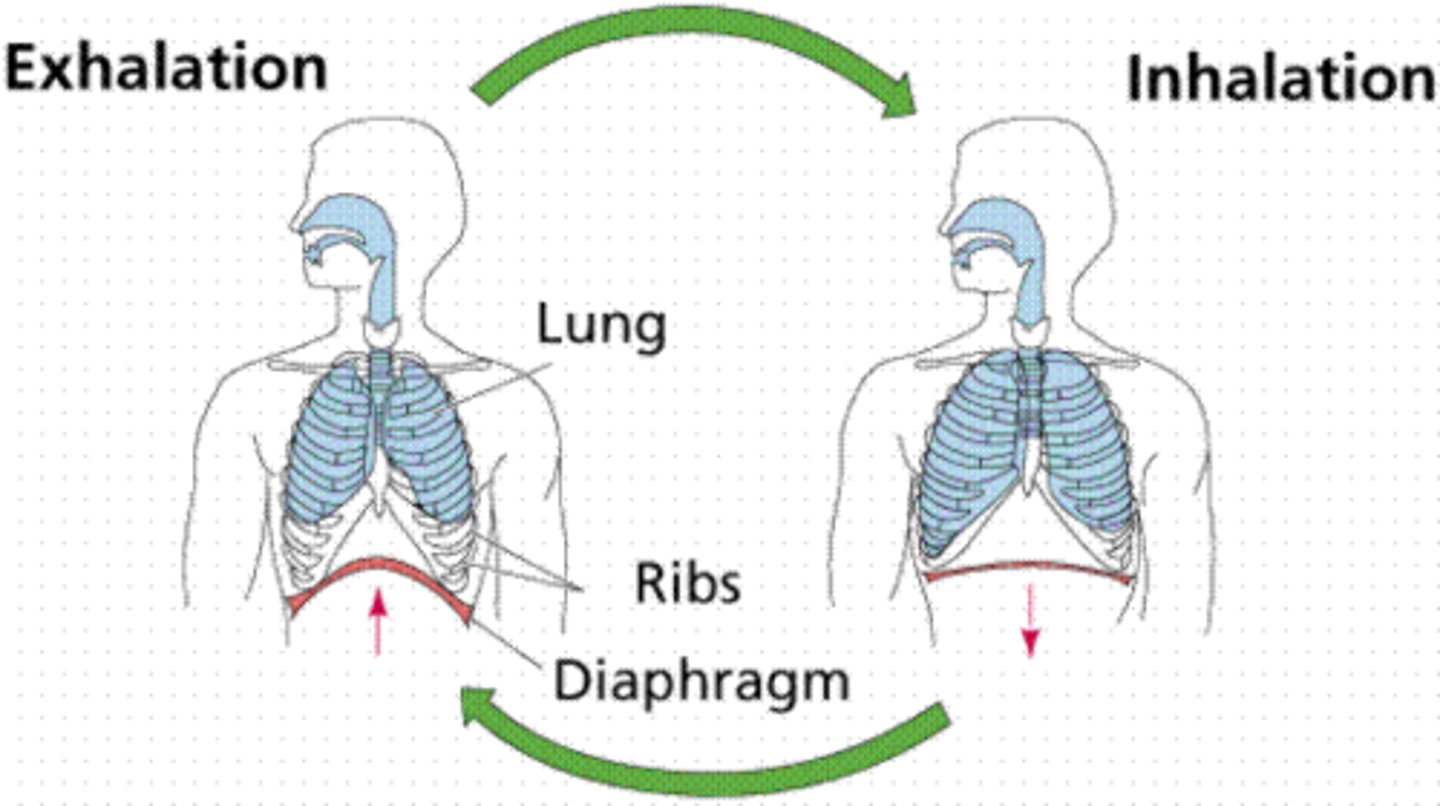
Aspiration breathing (negative pressure)
this is a breathing system in which air is pulled into the lungs when the lung volume is expanded.
ectothermic
term referring to organisms for which external sources provide most of the heat for temperature regulation

Polyphyodont
term for teeth are continuously replaced
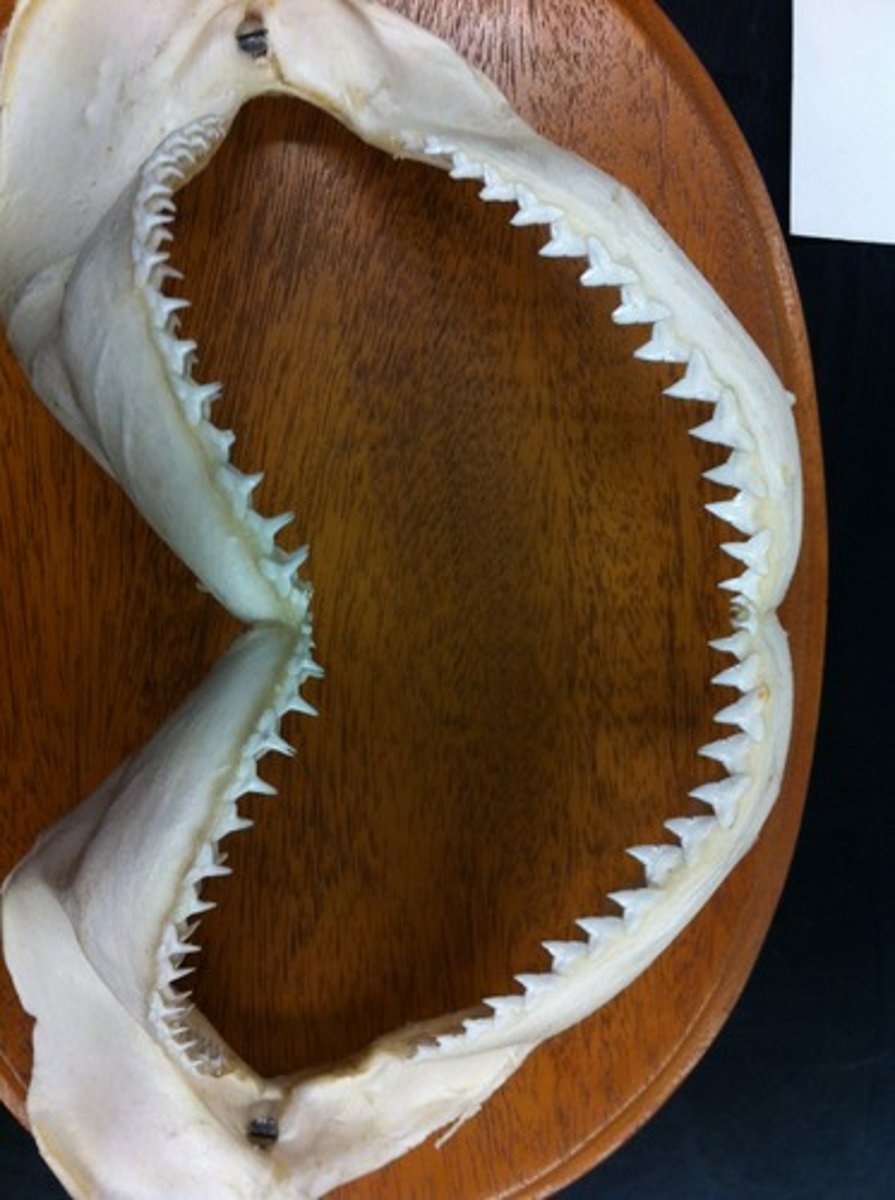

homodont
all teeth are the same
-no difference of tooth type in the jaw

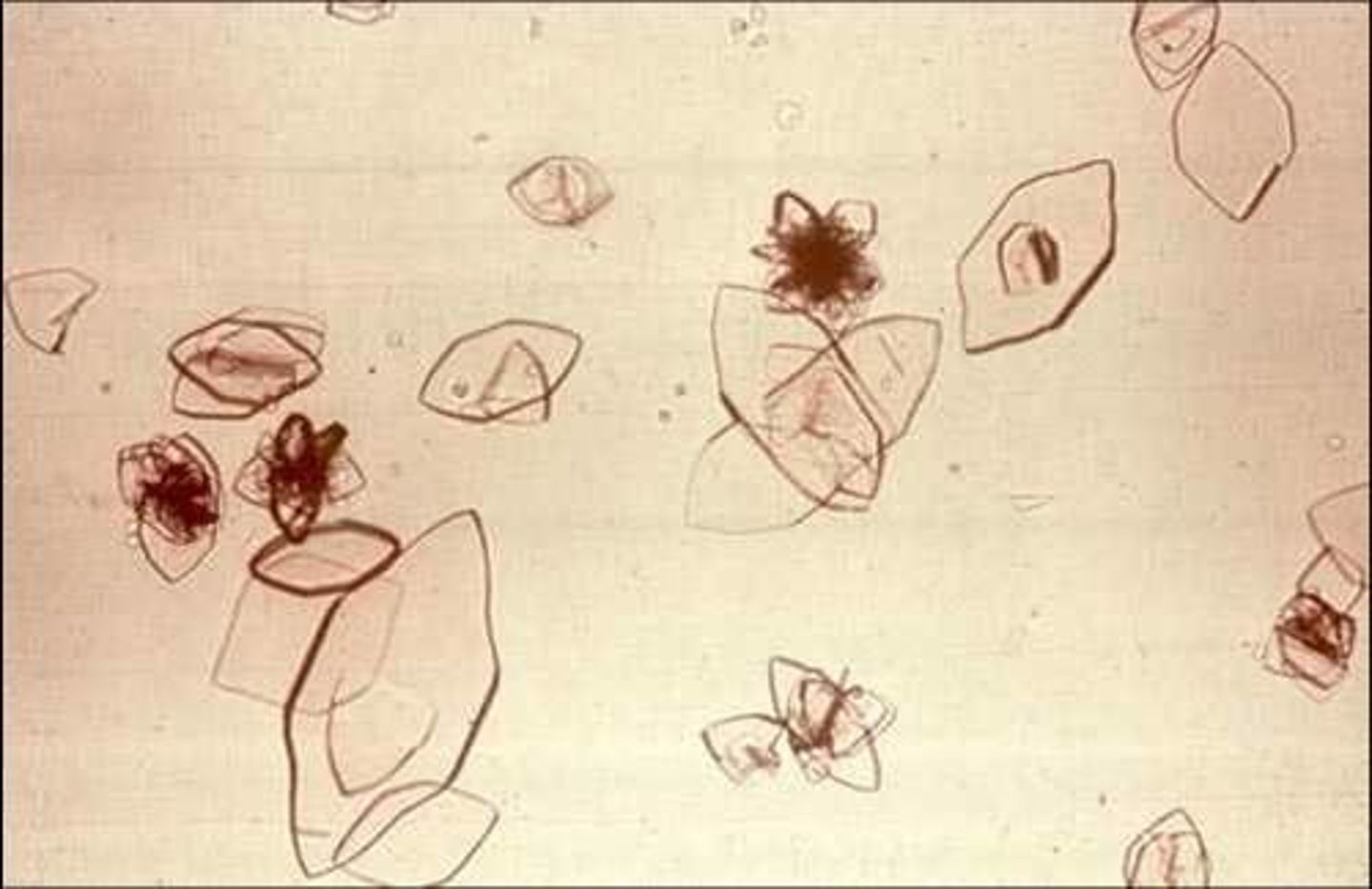
uric acid
term for nitrogenous waste excreted in the urine which is removed from the circulating blood by the kidneys

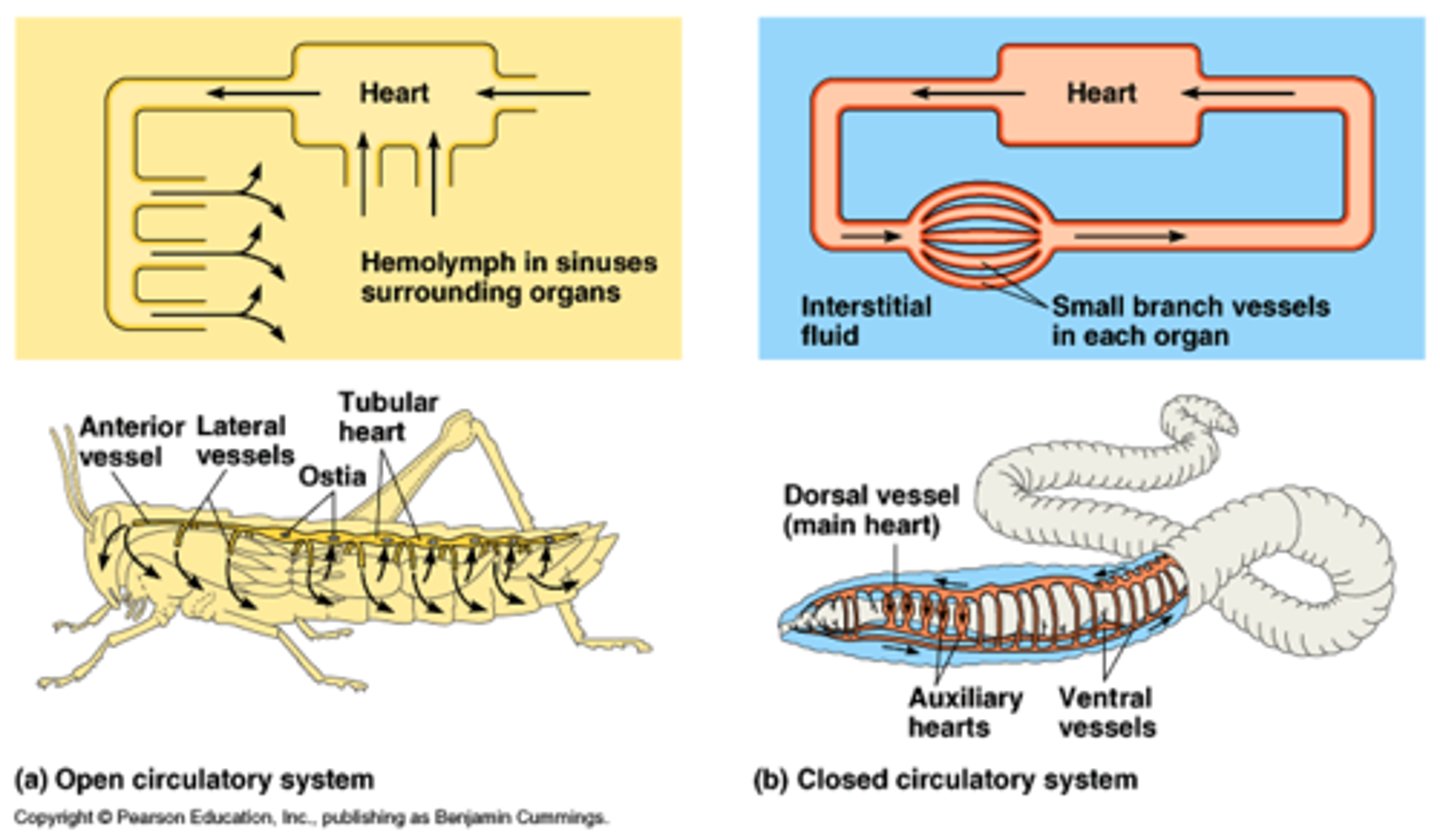
closed circulatory system
A circulatory system in which the oxygen-carrying blood cells never leave the blood vessels
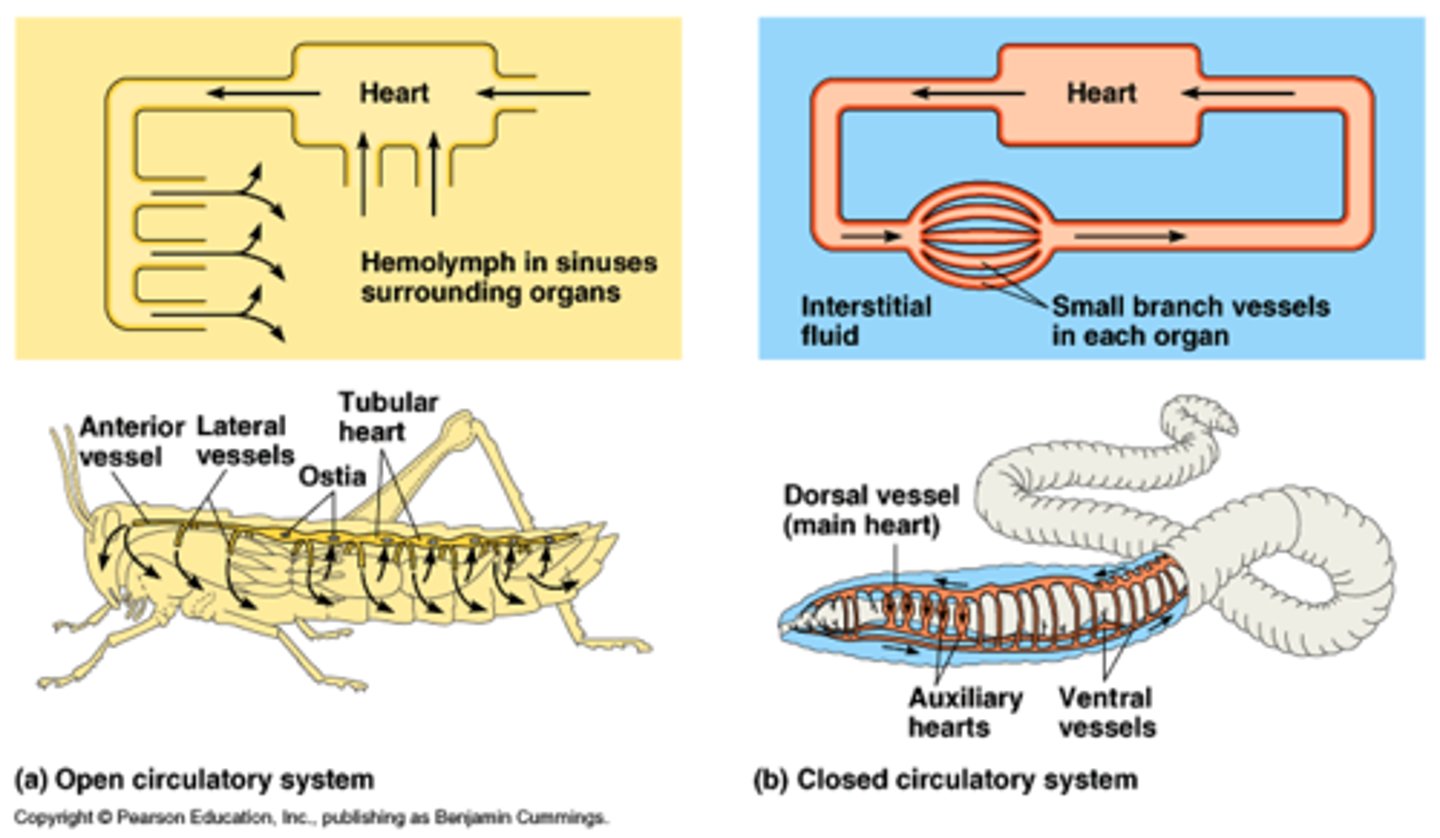
open circulatory system
A circulatory system that allows the blood to flow out of the blood vessels and into various body cavities so that the cells are in direct contact with the blood
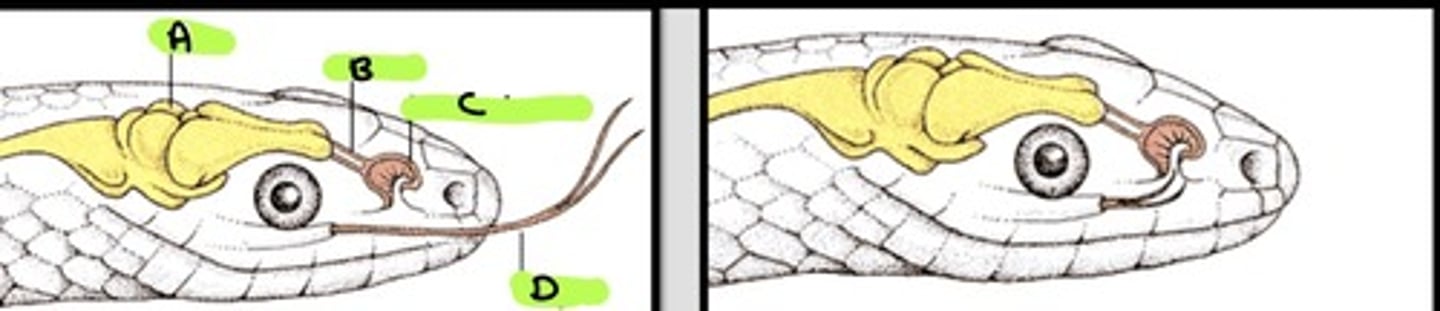
Vomeronasal (Jacobson's) organ
Organ responsible for pheromone perception in animals
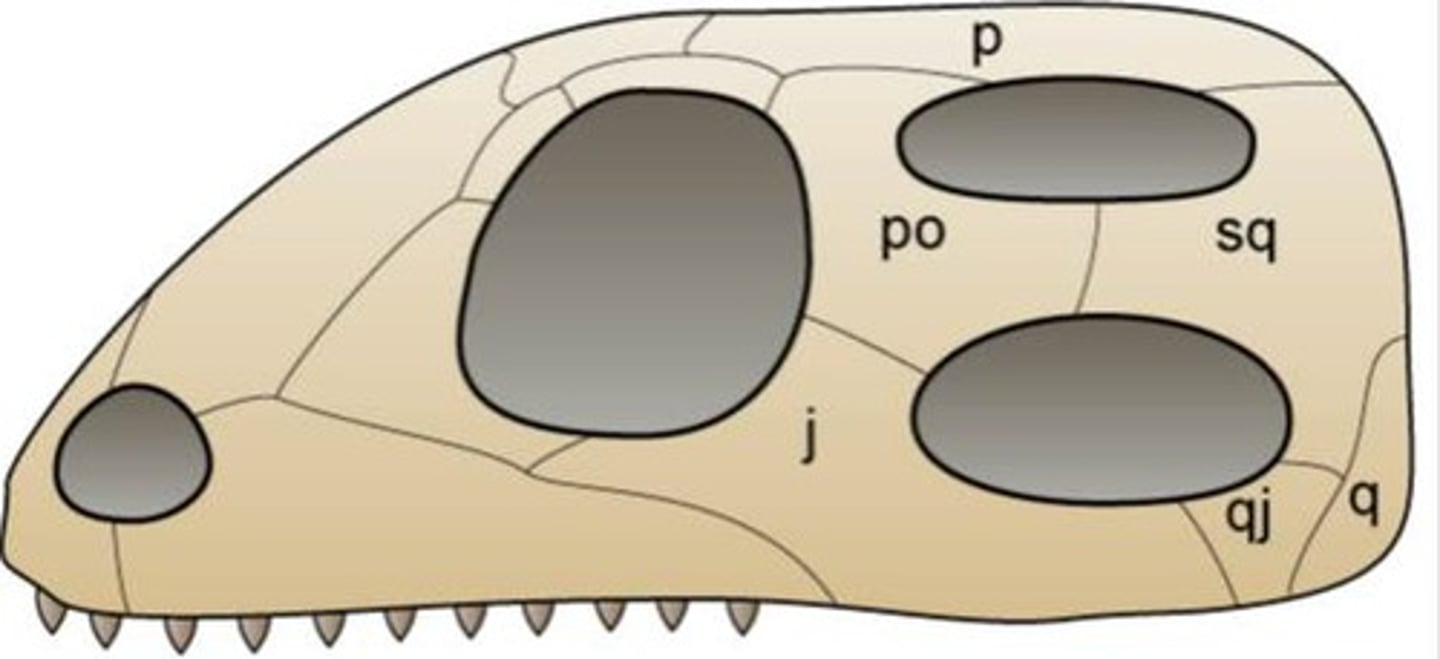
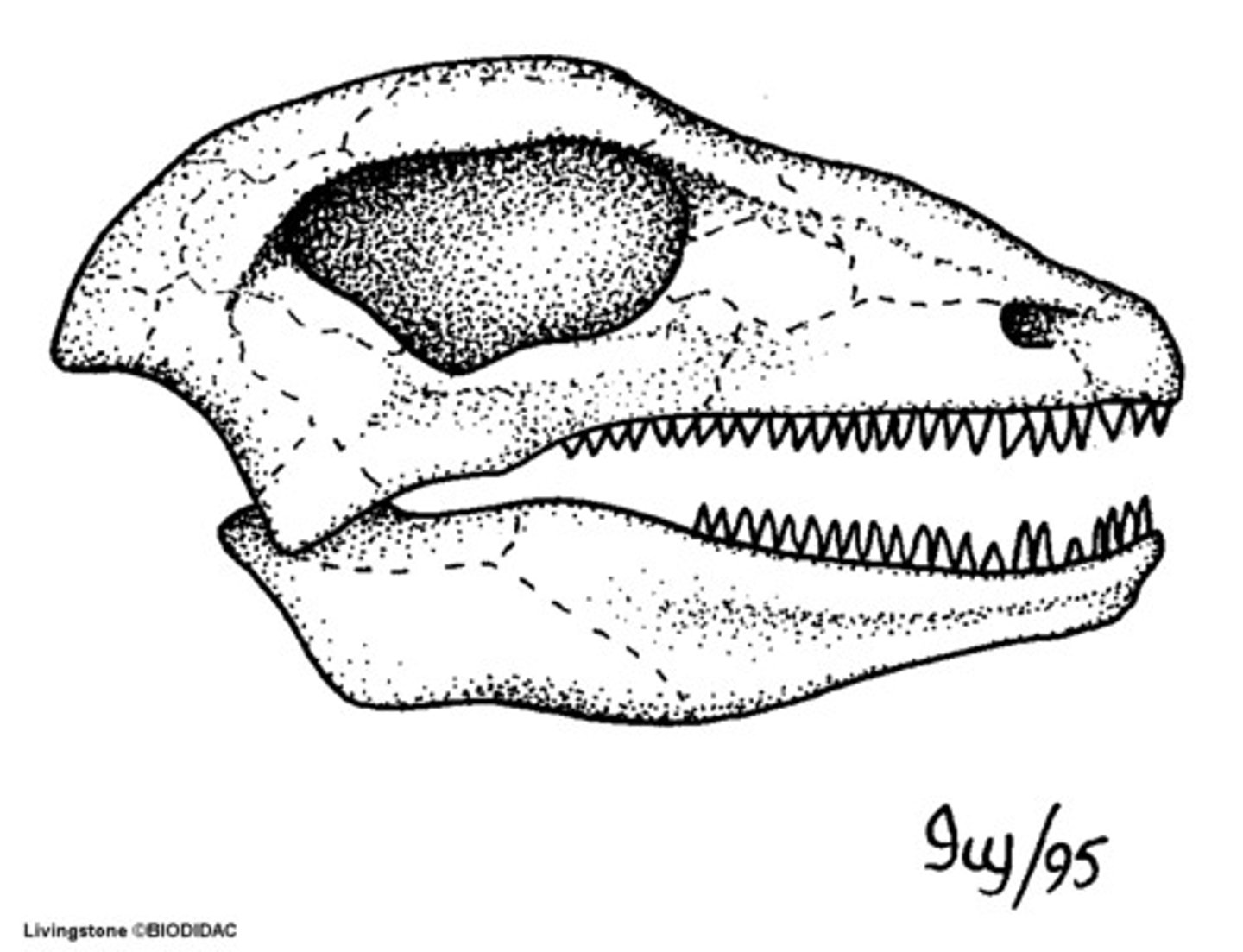
Fenestrae
term for a small natural hole or opening, especially in a bone.
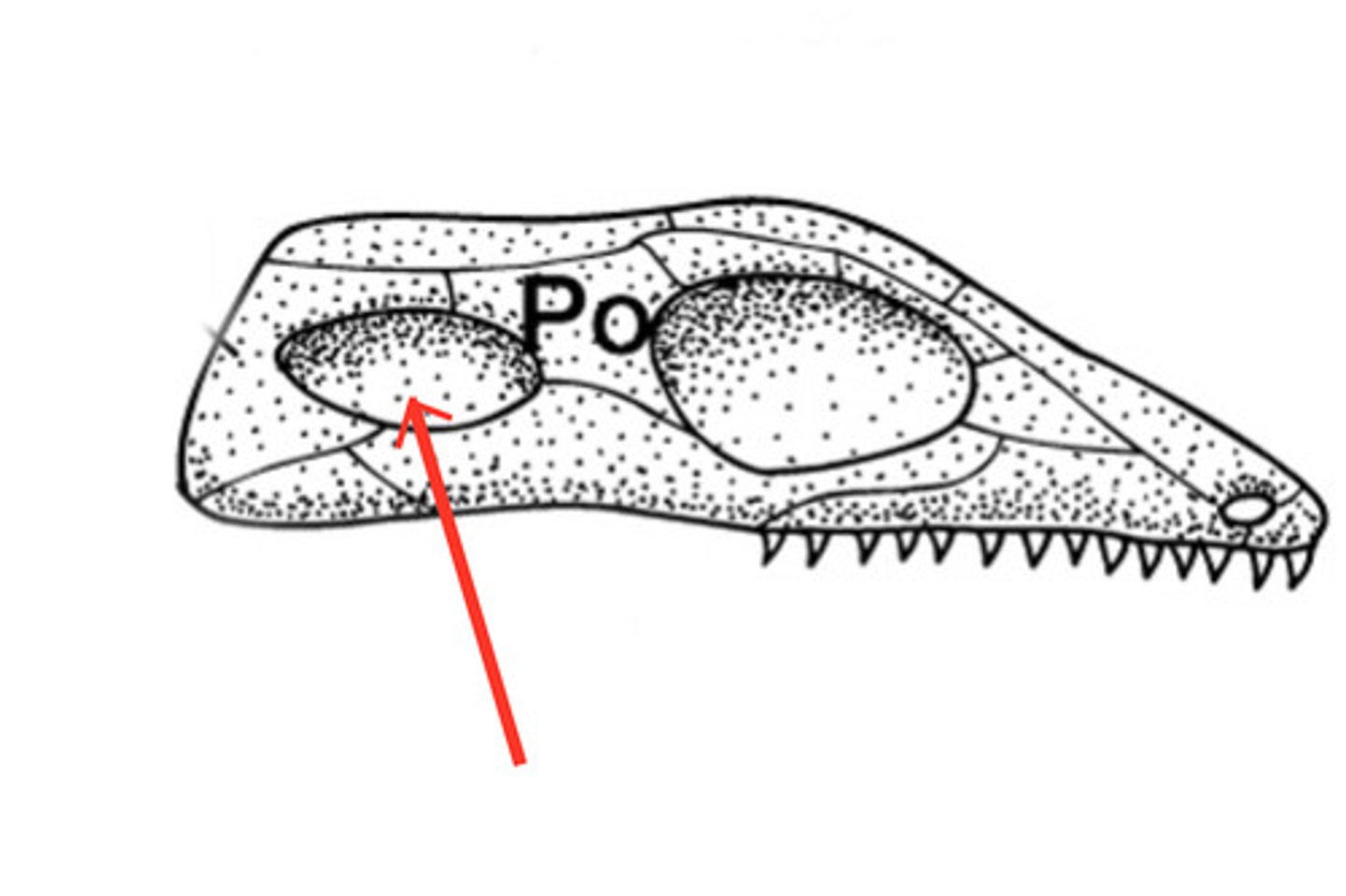
Synapsid
term for mammal having one temporal fenestra
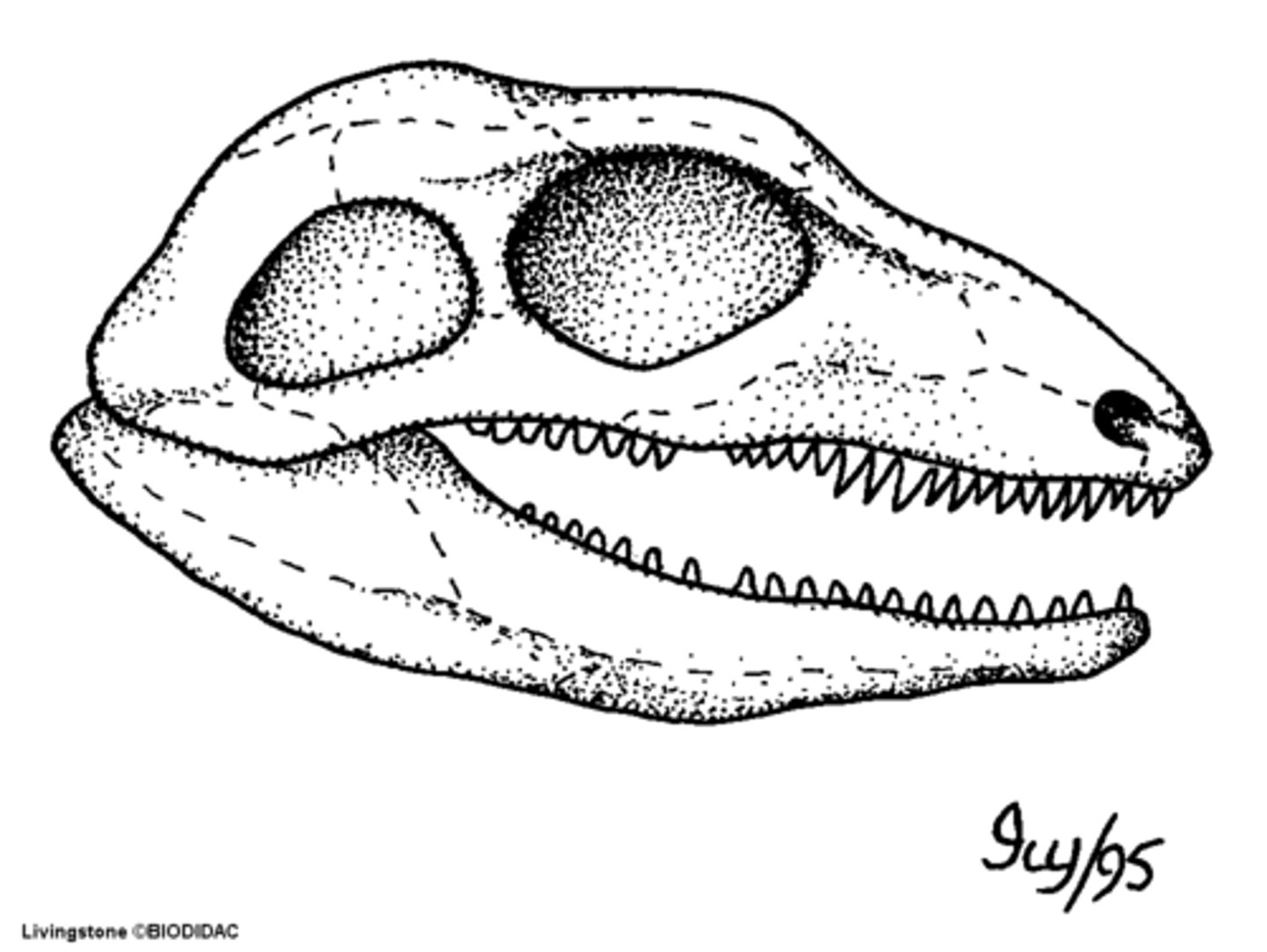
Diapsid
term for mammal have two temporal fenestra
-found in birds, reptiles, and dinosaurs.
Anapsid
term for mammal have no temporal fenestra
order testudines
this order is made of turtles
-terrestrial, freshwater and marine
-bony shell w/ dorsal carapace and ventral plastron
-temp dependent sex determination
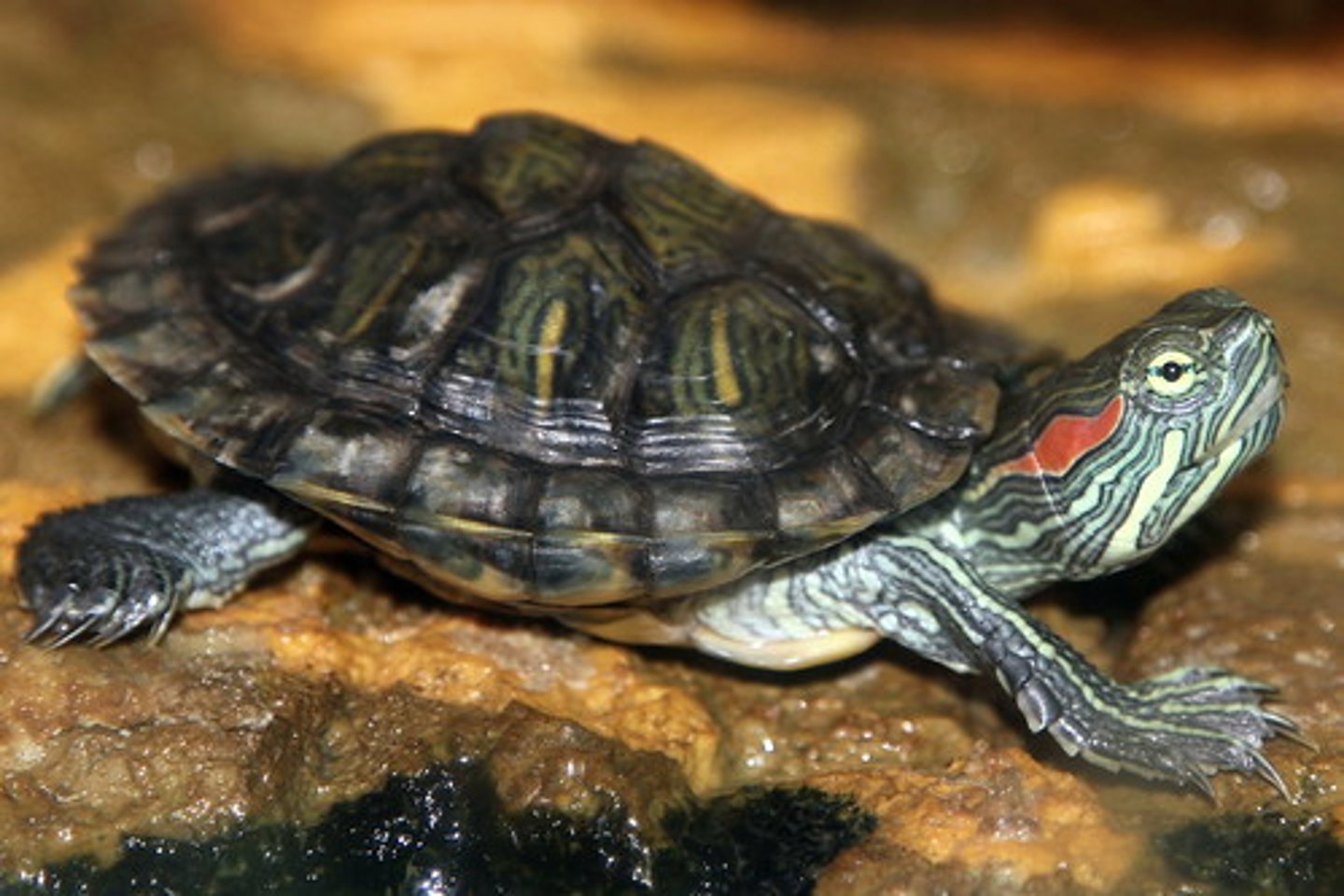

carapace
hard outer covering or case of certain organisms such as arthropods and turtles
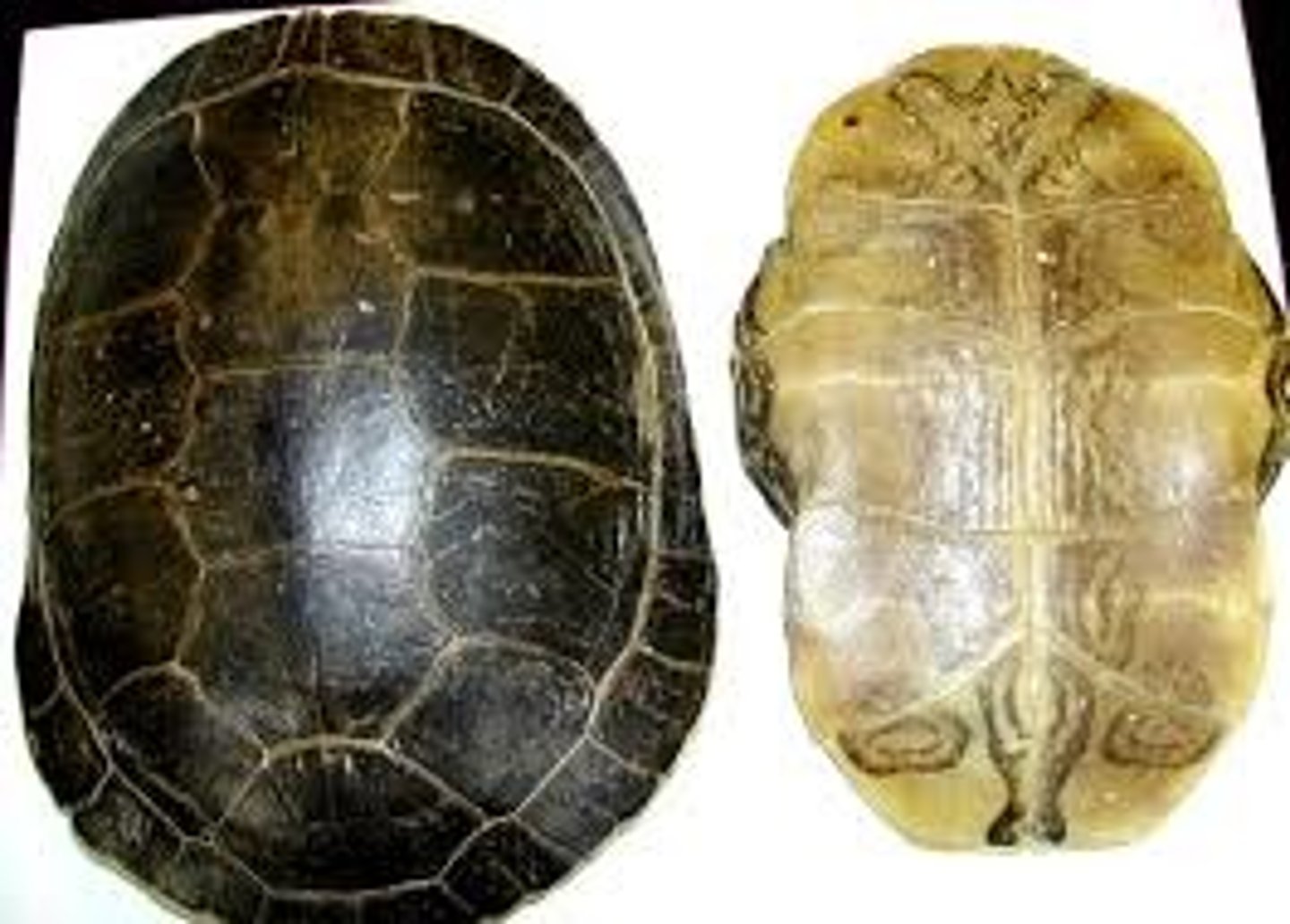

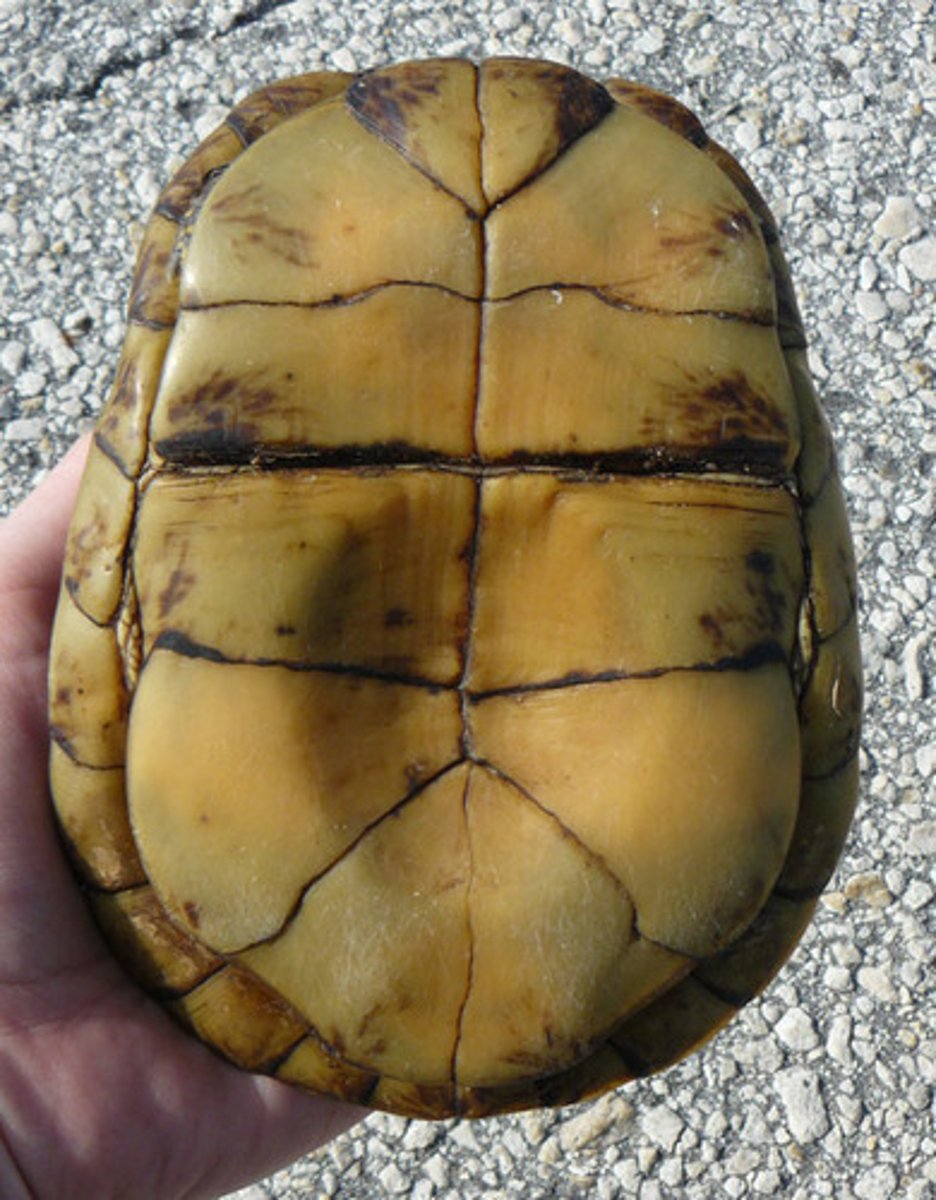
Plastron
this is the the ventral (bottom) part of a turtle's shell

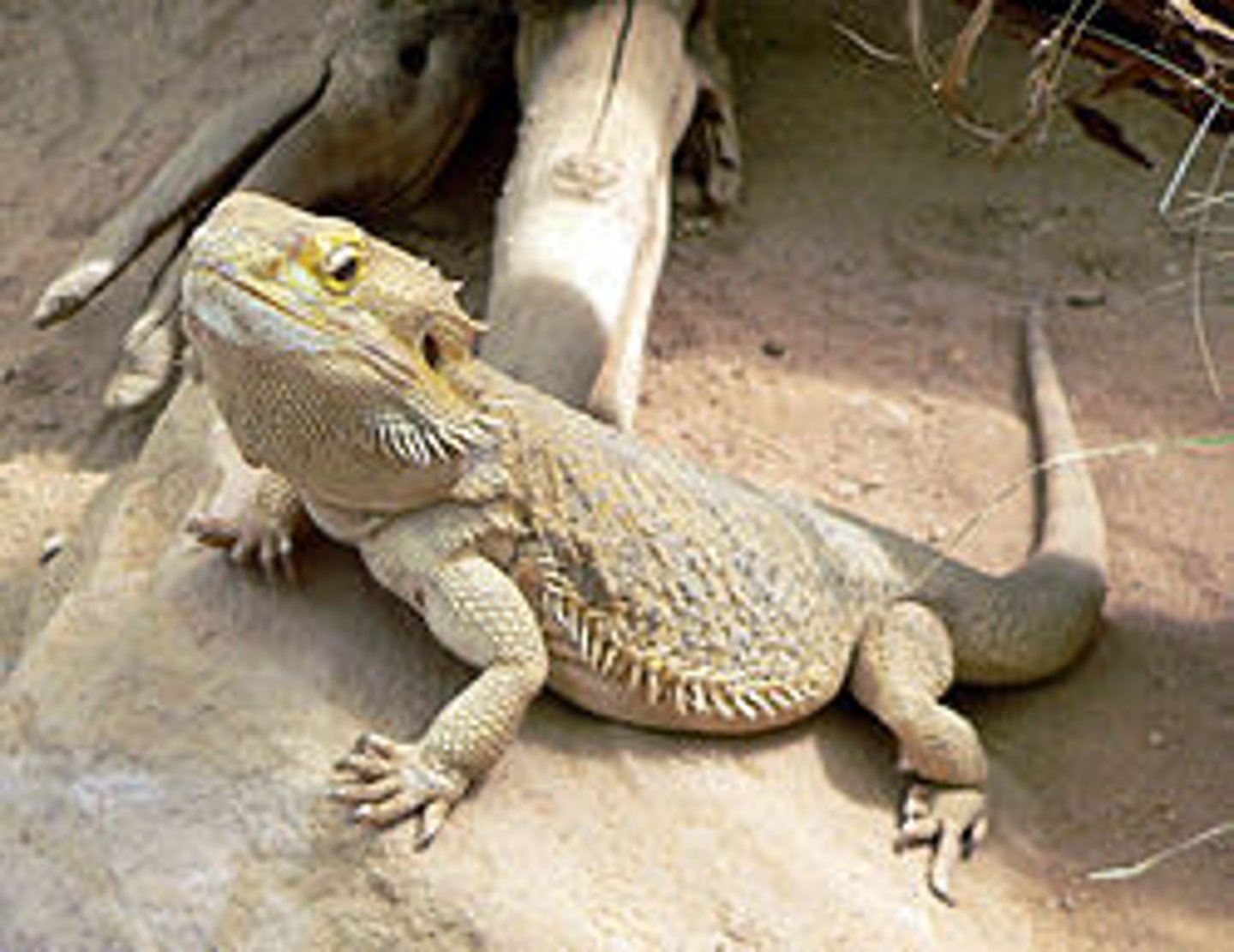
Order squamata
this order is made of lizards and snakes
-terrestrial, burrowing, freshwater, marine
-snakes a derived limbless lizards
-whole clade has modified diapsid skull
-moveable internal kinetic skull
-males w/ hemipenes

kinetic skull
term for Skulls of most reptiles that has extremely mobile joints.
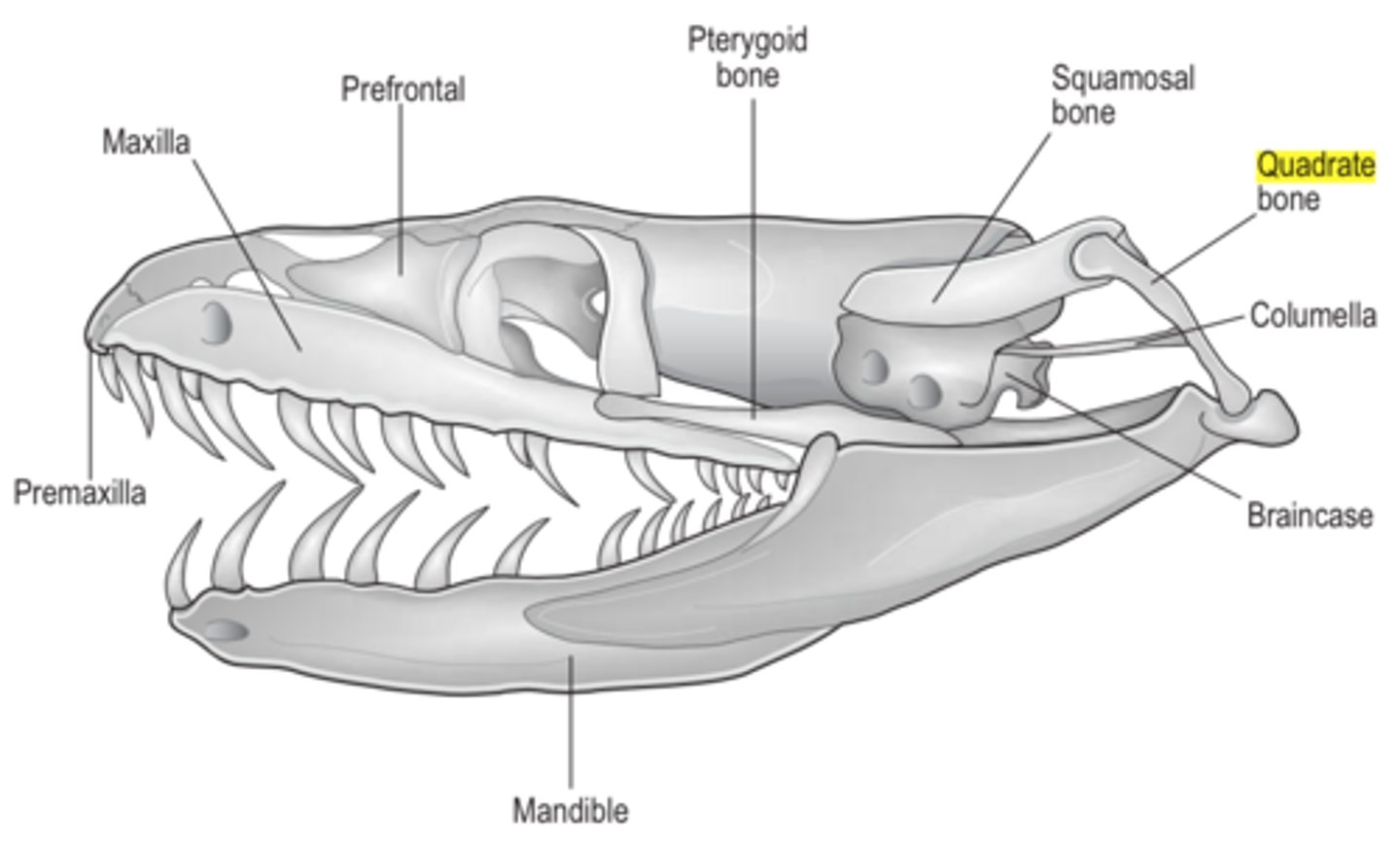
hemipenes
term for paired penises found in snakes and lizards
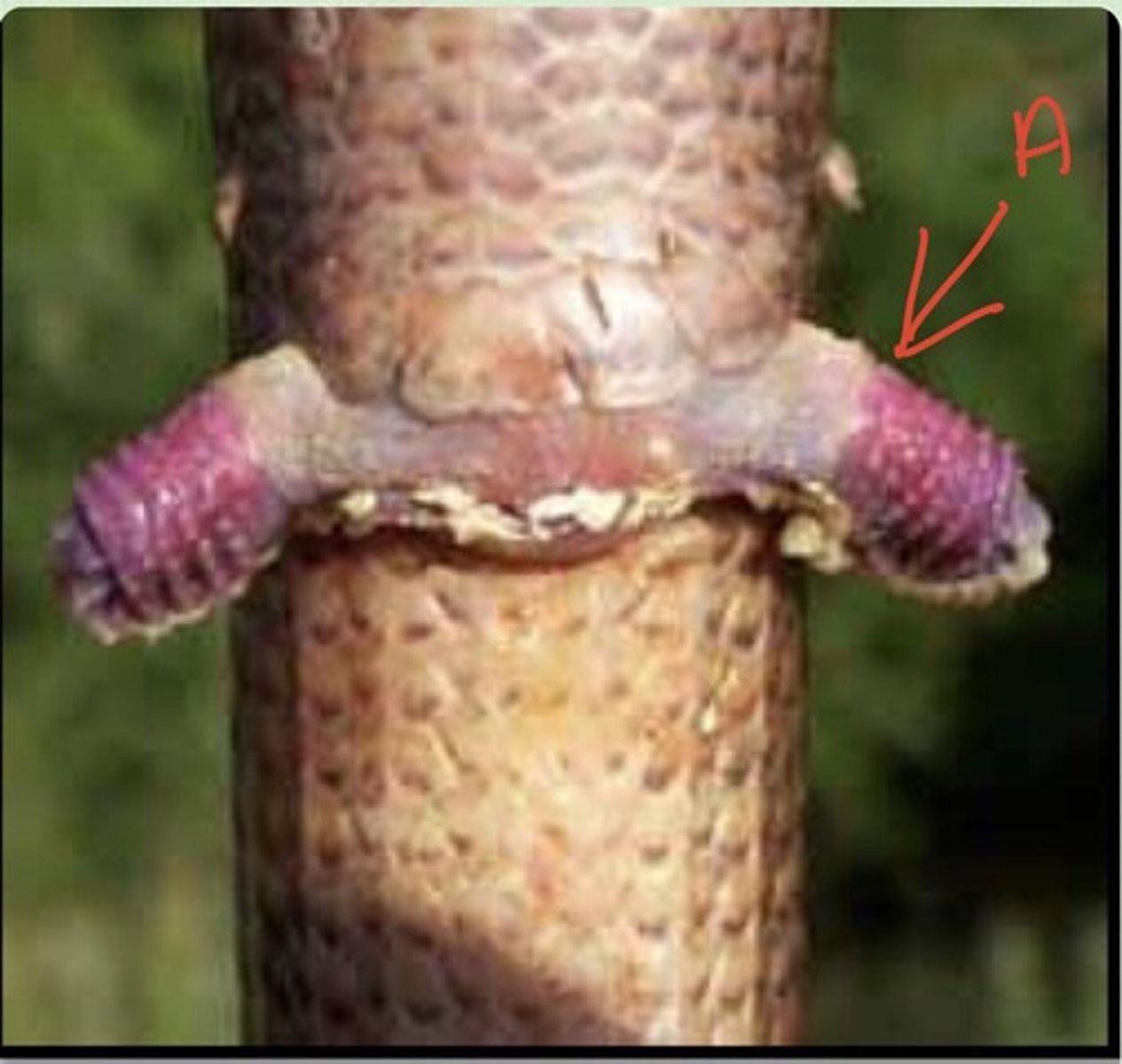

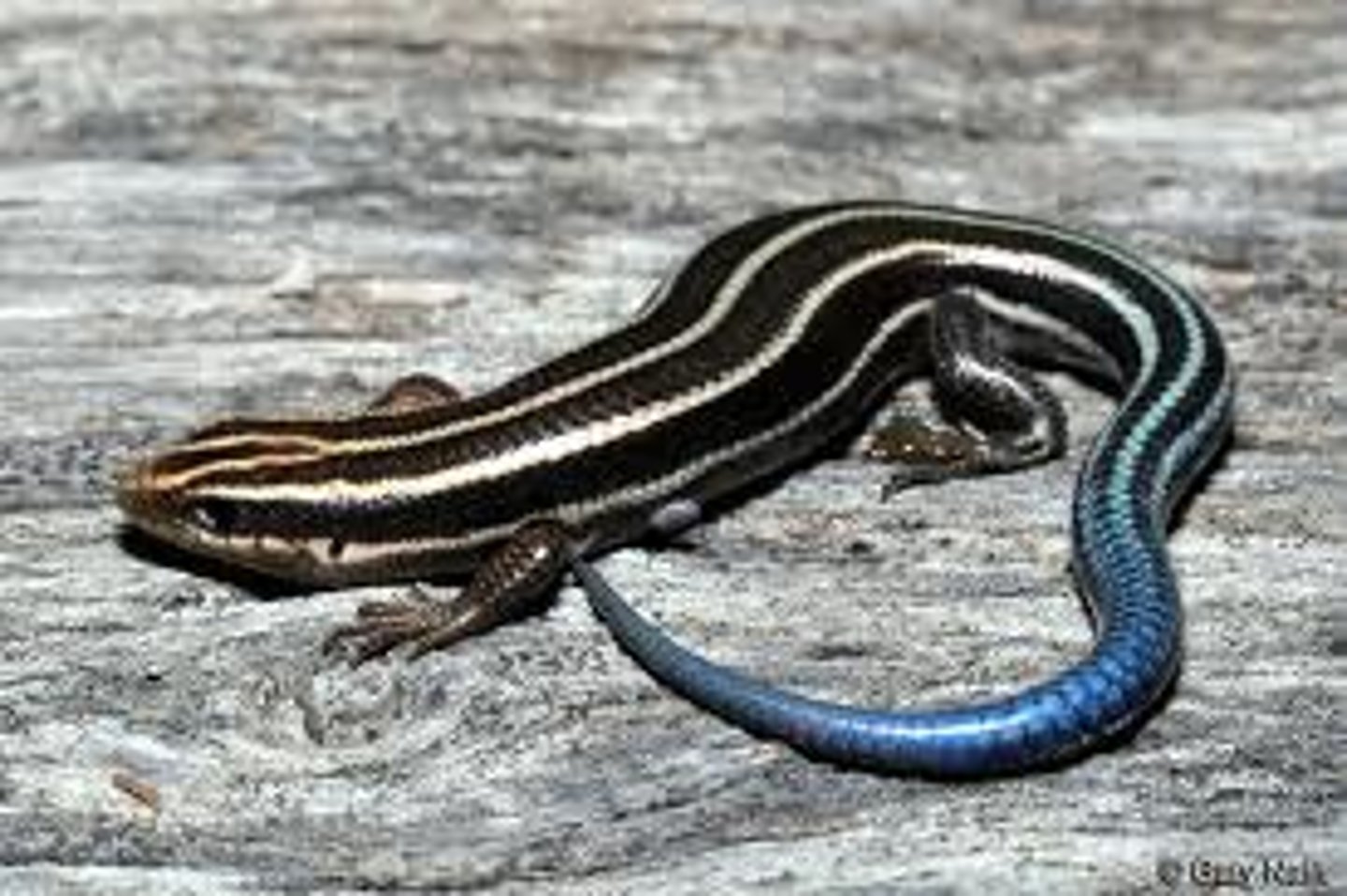
Suborder Sauria (Squamata)
this suborder is made of lizards
-part of order Squamata
-varied lifestyle, found worldwide
-oviparous, ovoviviparous or viviparous
-tongue projection in chameleons

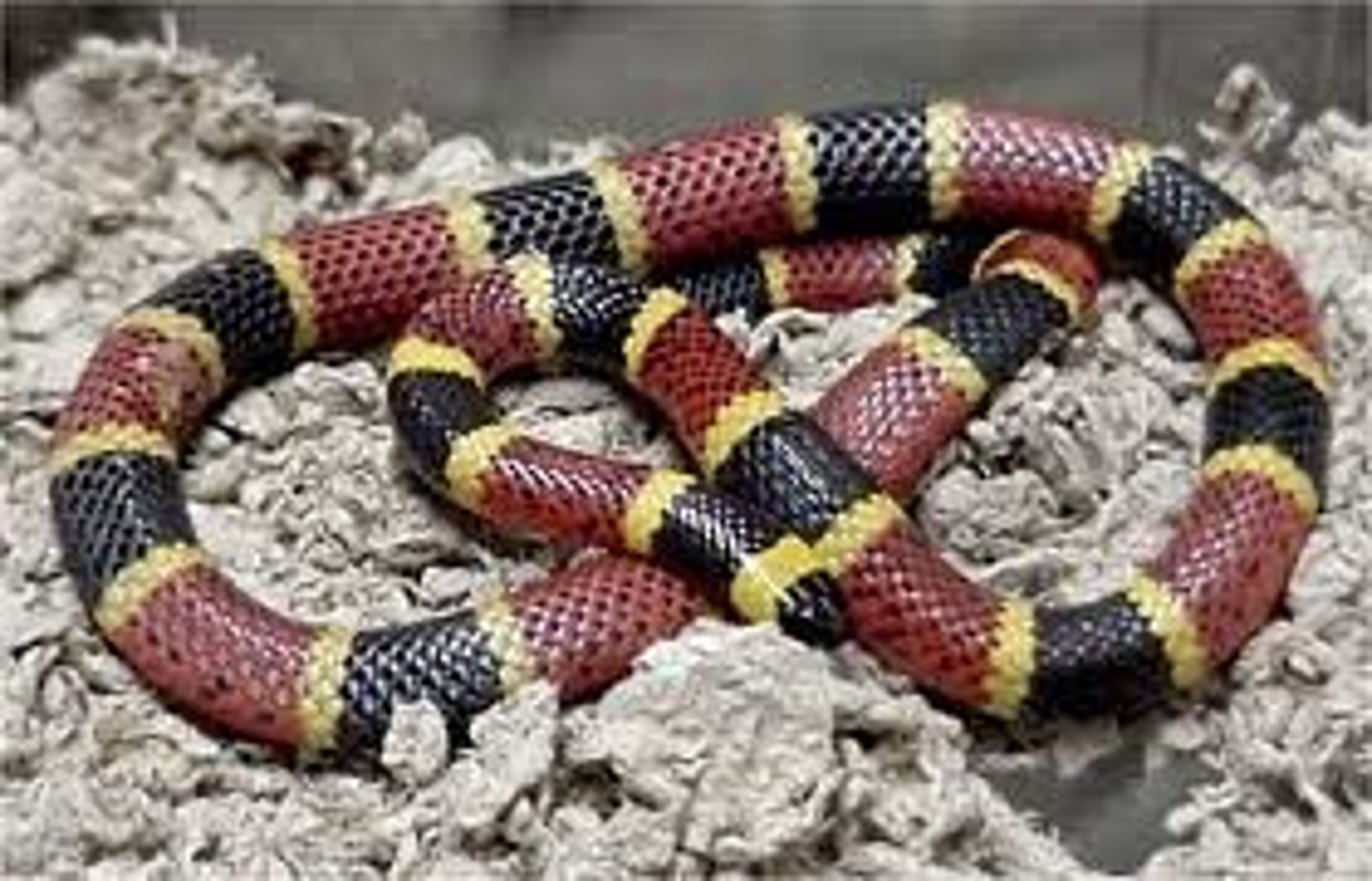
Suborder Serpentes (Squamata)
this suborder is made of snakes
-part of order Squamata
-highly modified skulls to swallow prey
-venom
-infrared sense in pit vipers
-tongue and jacobson's organ to smell
-constriction to suffocate prey

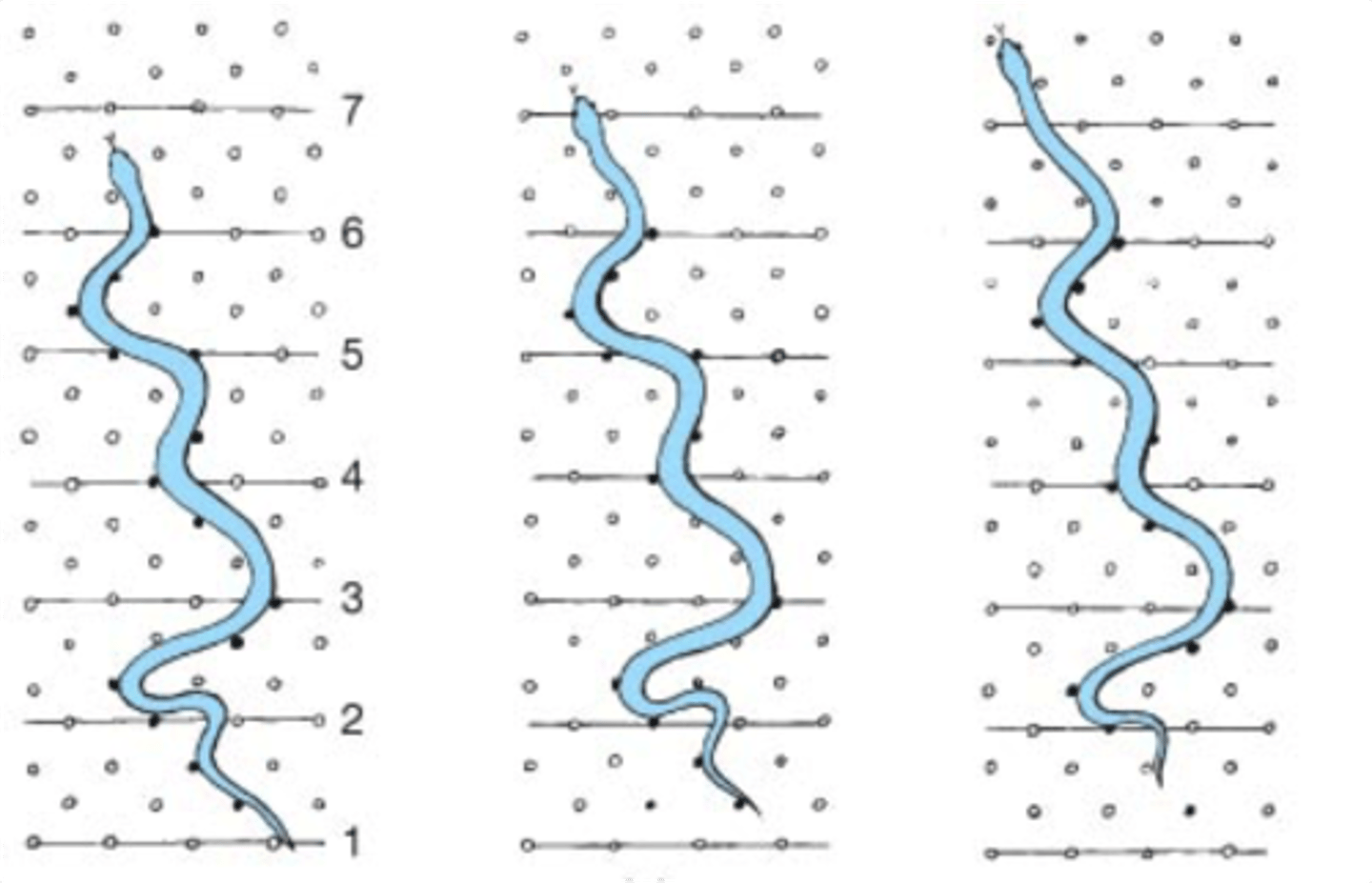
Lateral undulation (snake movement)
type of movement where snake performs a "S" shape and exerting force against surface irregularities
-lateral ungulation
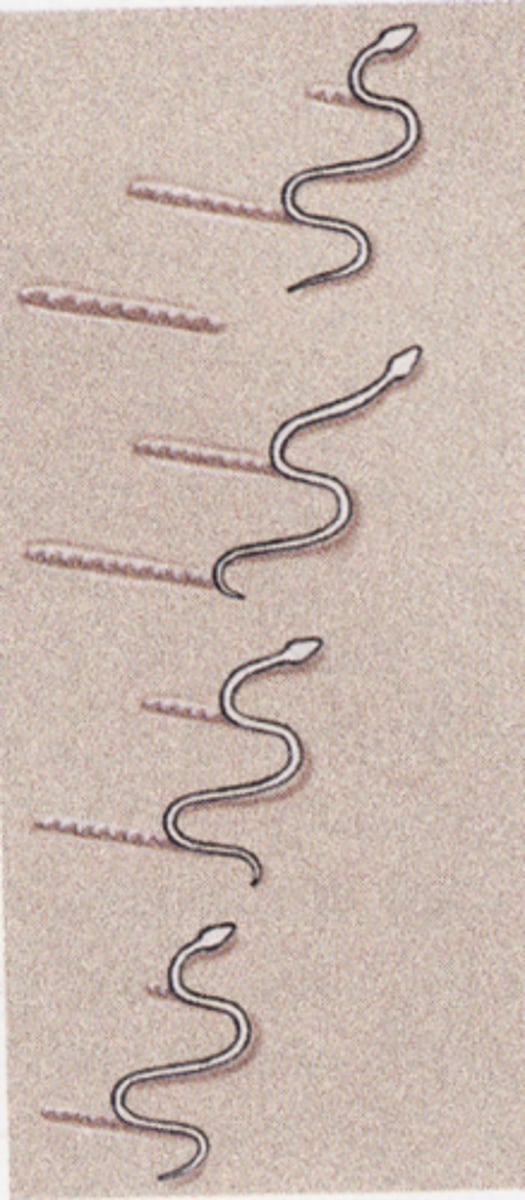
Concertina motion (snake movement)
Type of movement for snakes when on low friction surfaces, a slinky/accordion movement. In and out.
-best for narrow pathways
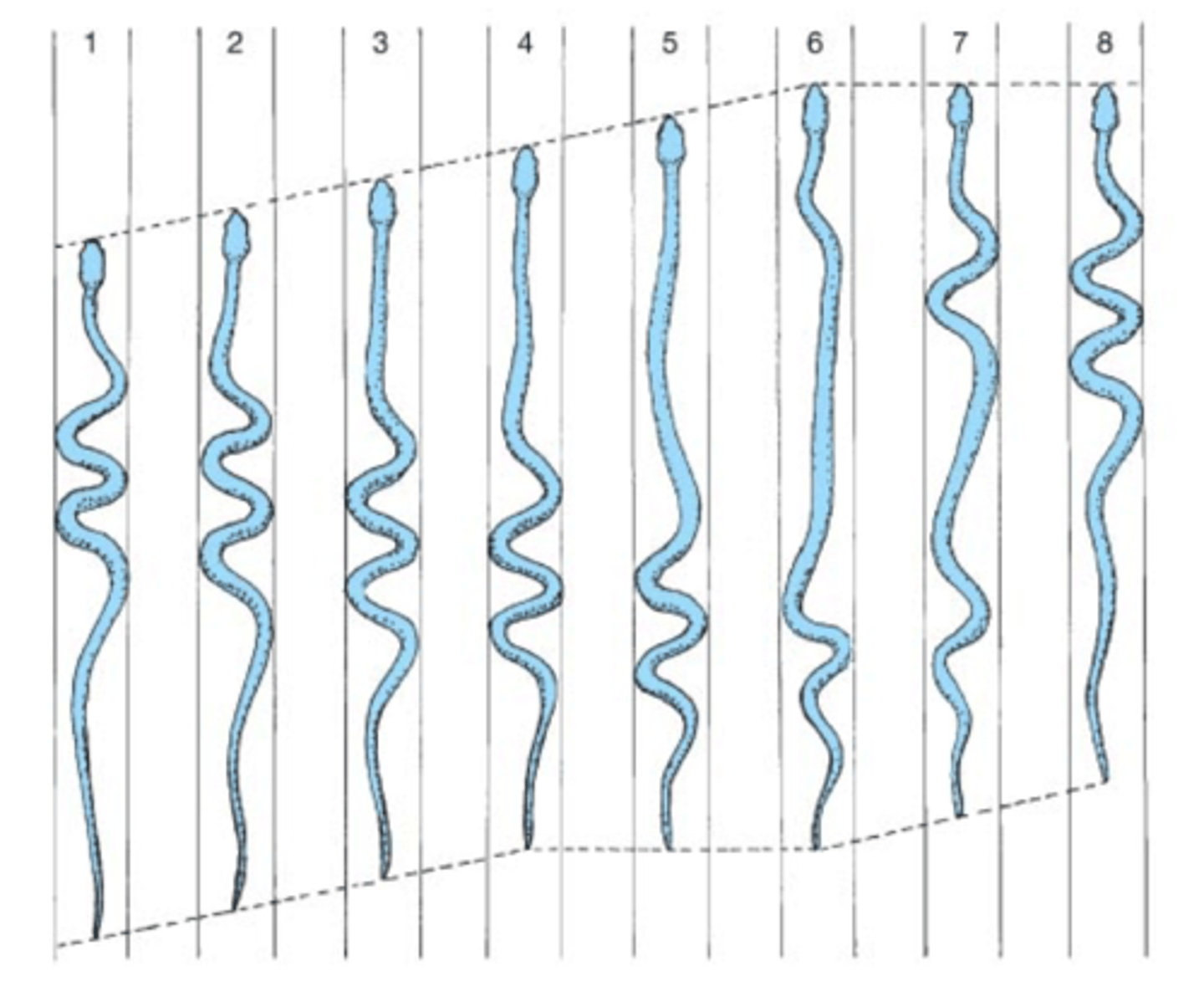
rectilinear motion (snake movement)
Type of movement in a straight line, primarily used by larger snakes like vipers, boas, and pythons. It involves the snake's belly scales alternately lifting, being pulled forward, and then pulled downward and backward, effectively "walking" the snake forward.
-larger snakes like constrictors
-like a centipede/slug

Sidewinder motion
type of movement where snakes "tumble" their body across sand dunes
Tuataras (order Sphenodonta)
These are rare lizard-like reptiles
-in order Sphenodonta
-only 2 living species
-parietal eye
-threatened by rats and grazing
-retain huge diapsid opening
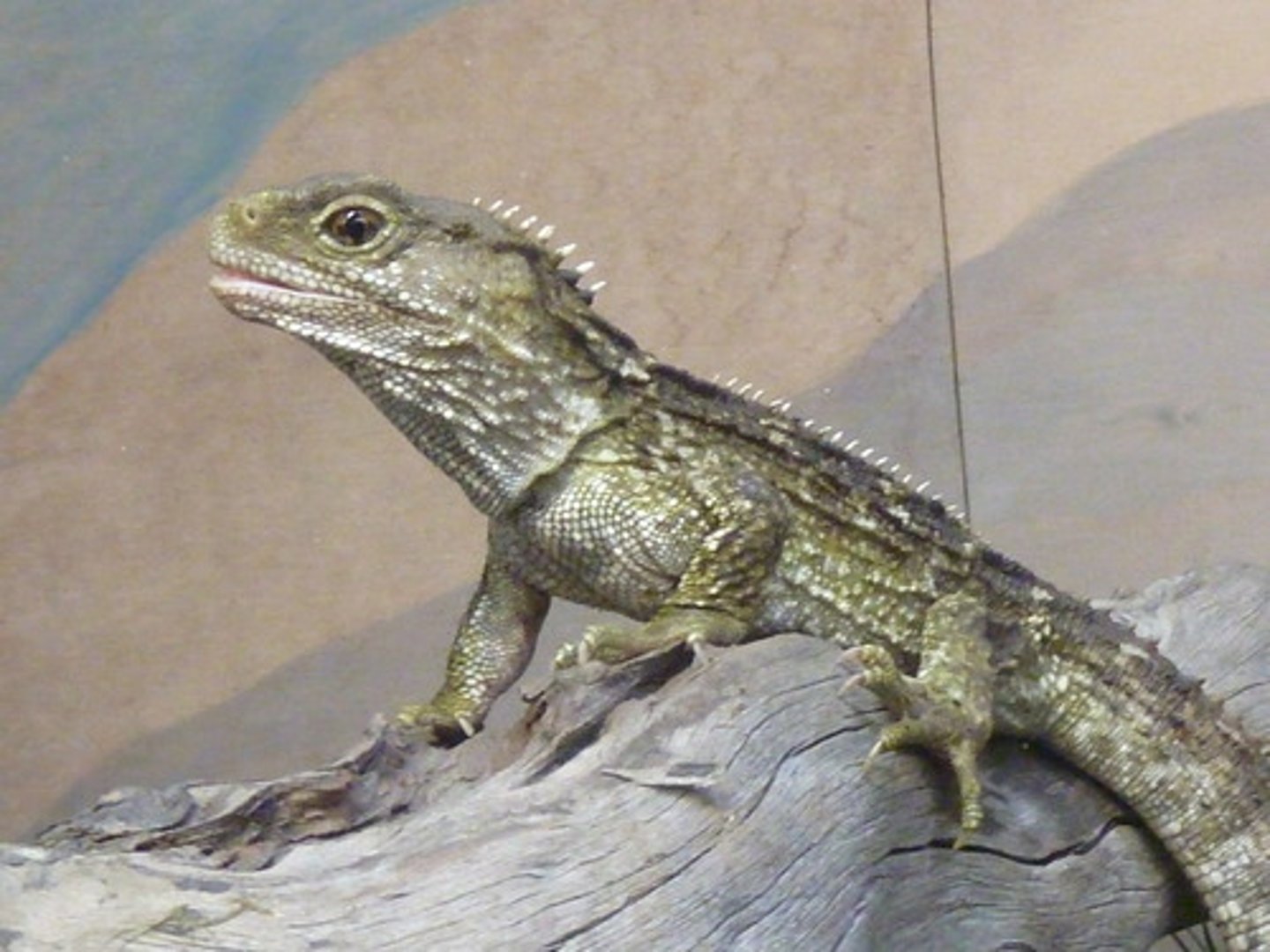

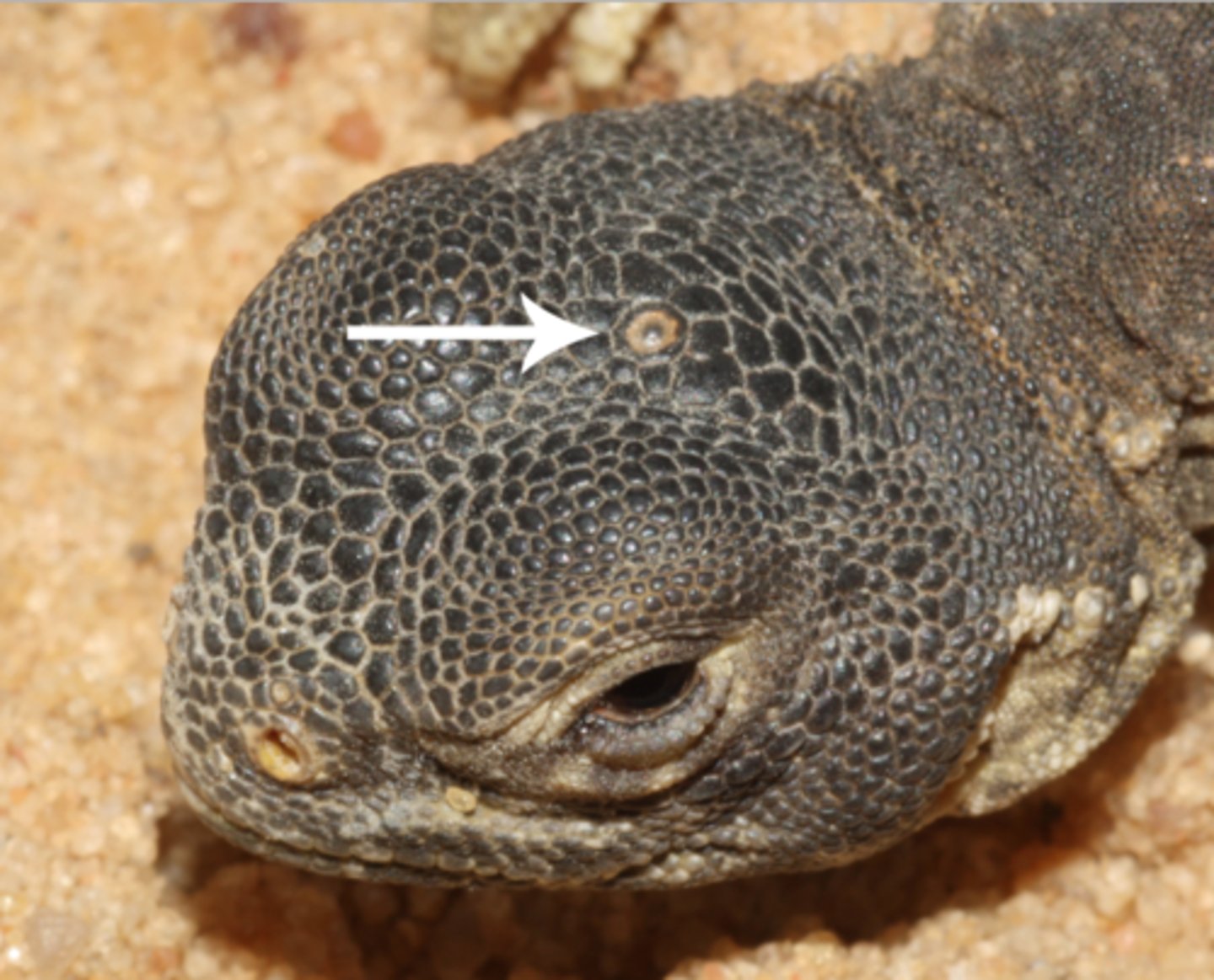
Parietal eye
Tuataras possess this on the top of their head, and use it mainly to sense radiation
-regulates day light cycles

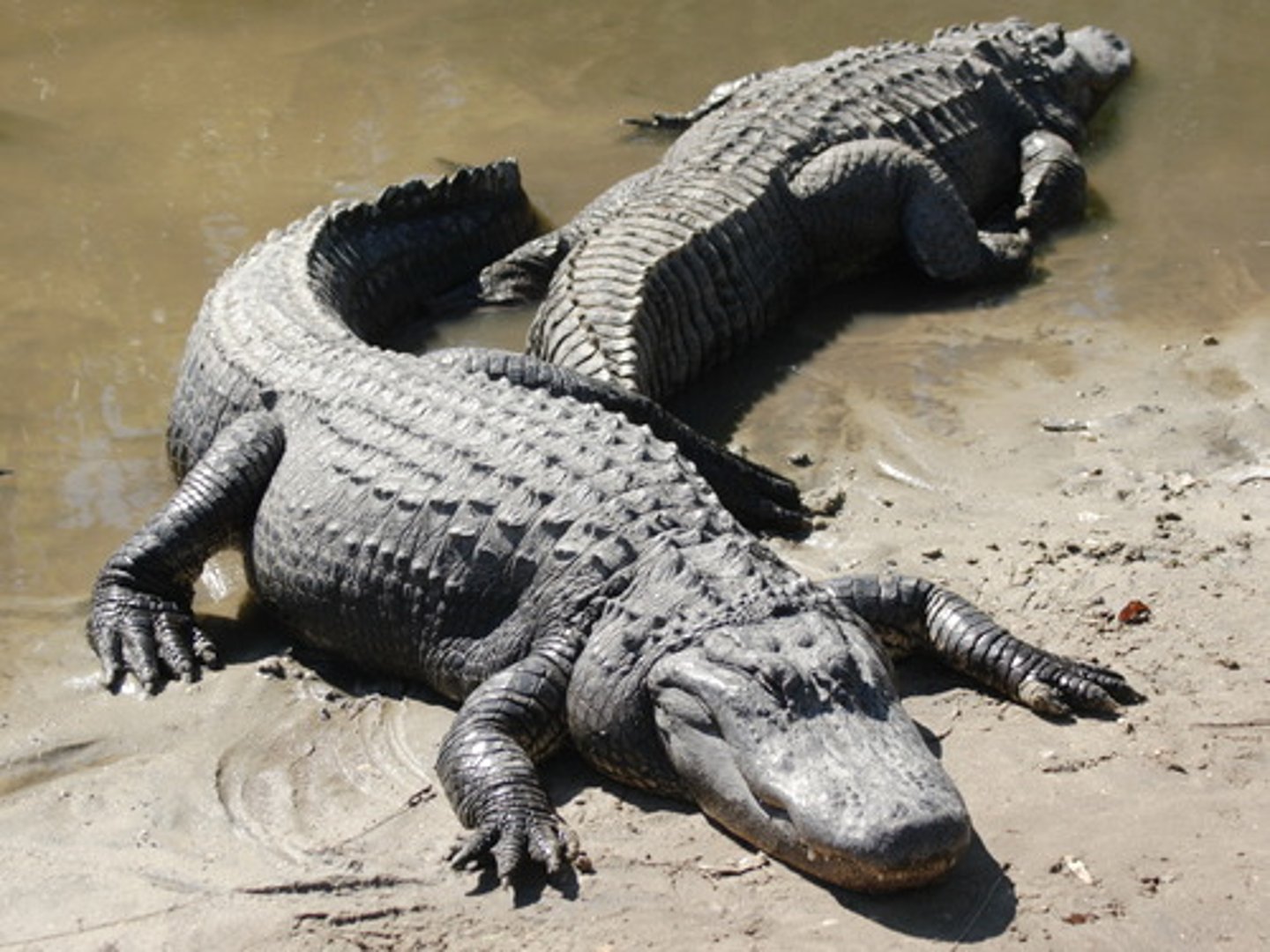
order crocodilia
this order is made of crocodiles and alligators
-part of the great archosaur radiation
-diapsid skull
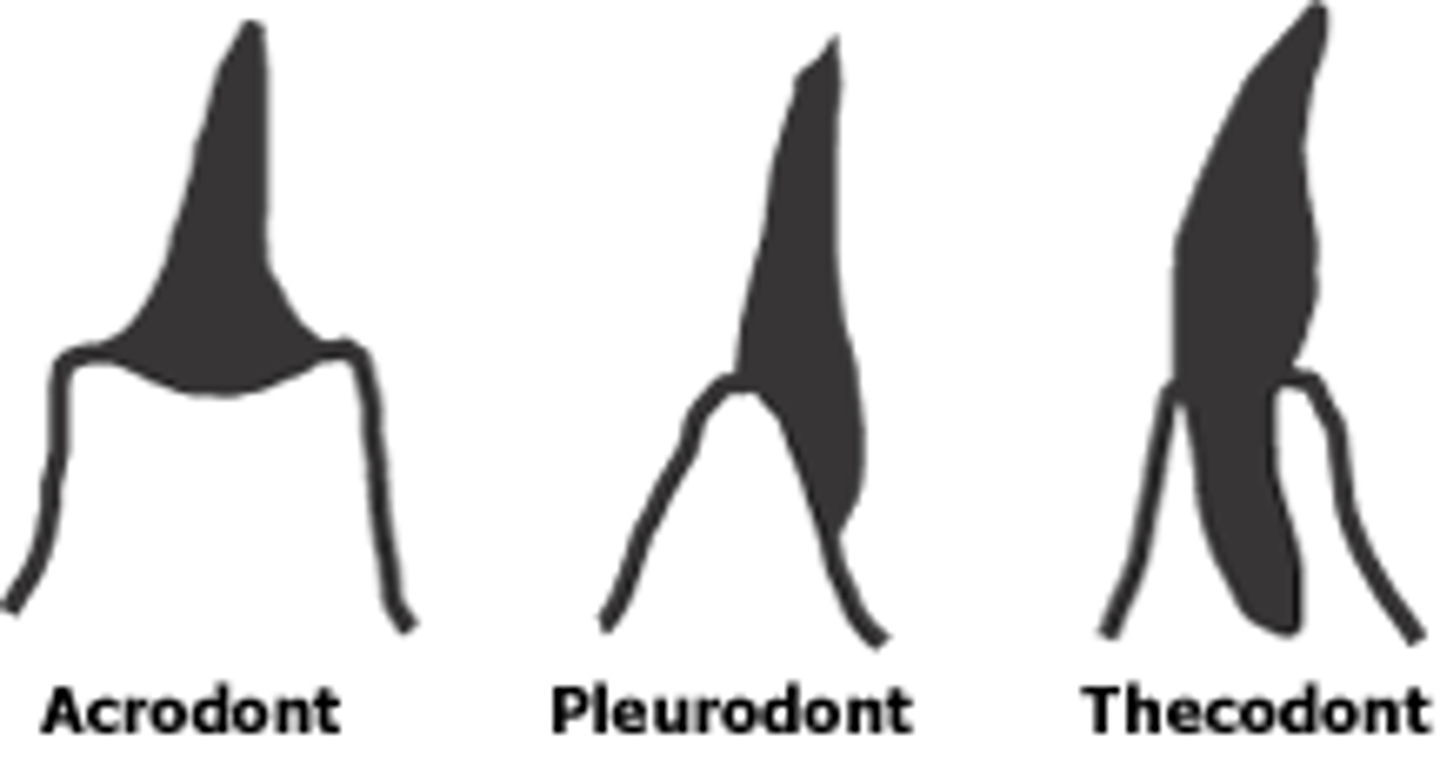
-thecodont dentition
-amphibious in saltwater and freshwater

thecodont teeth
Teeth held in sockets.
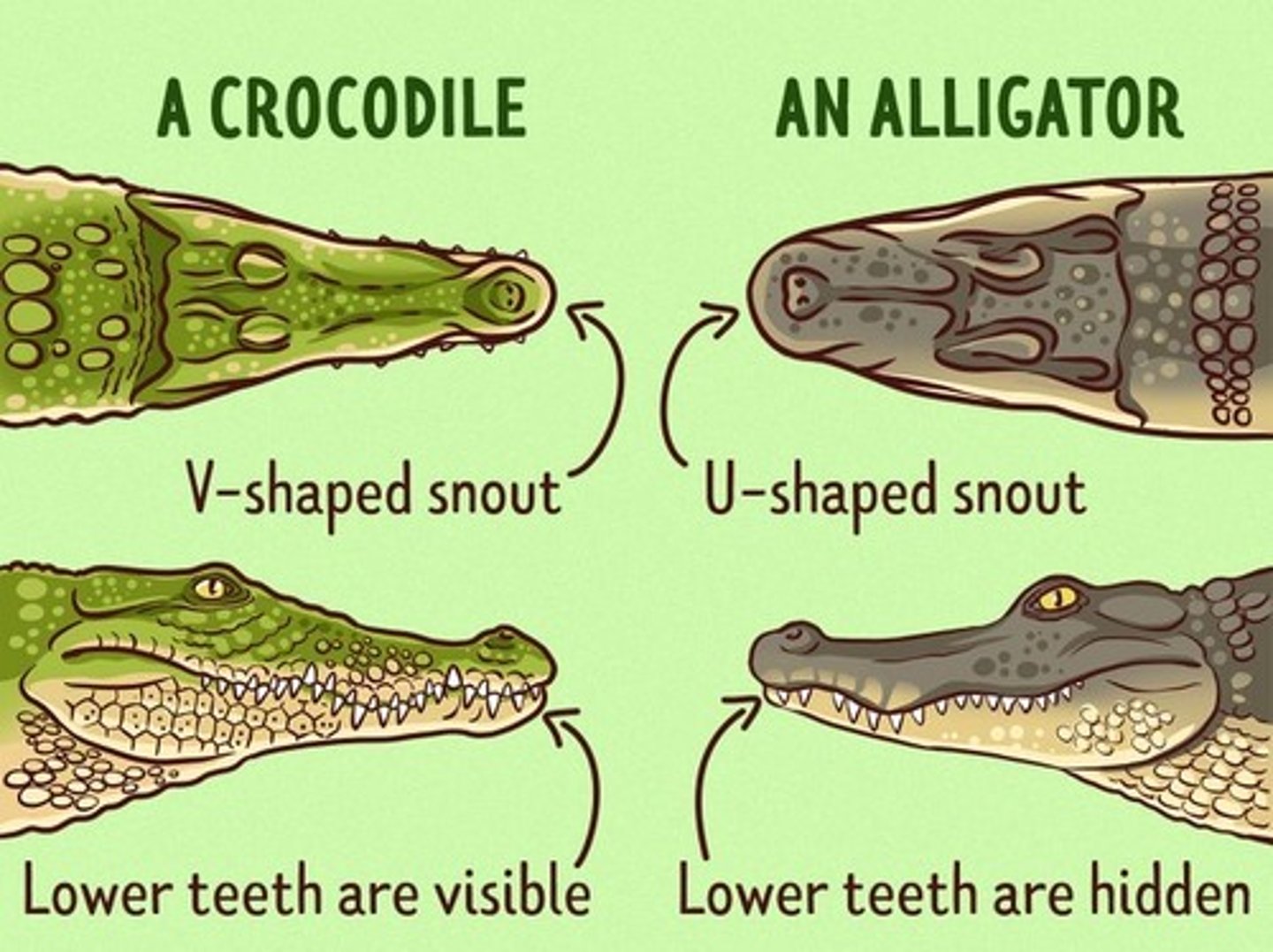
Alligator
this has a broad snout "U" shaped
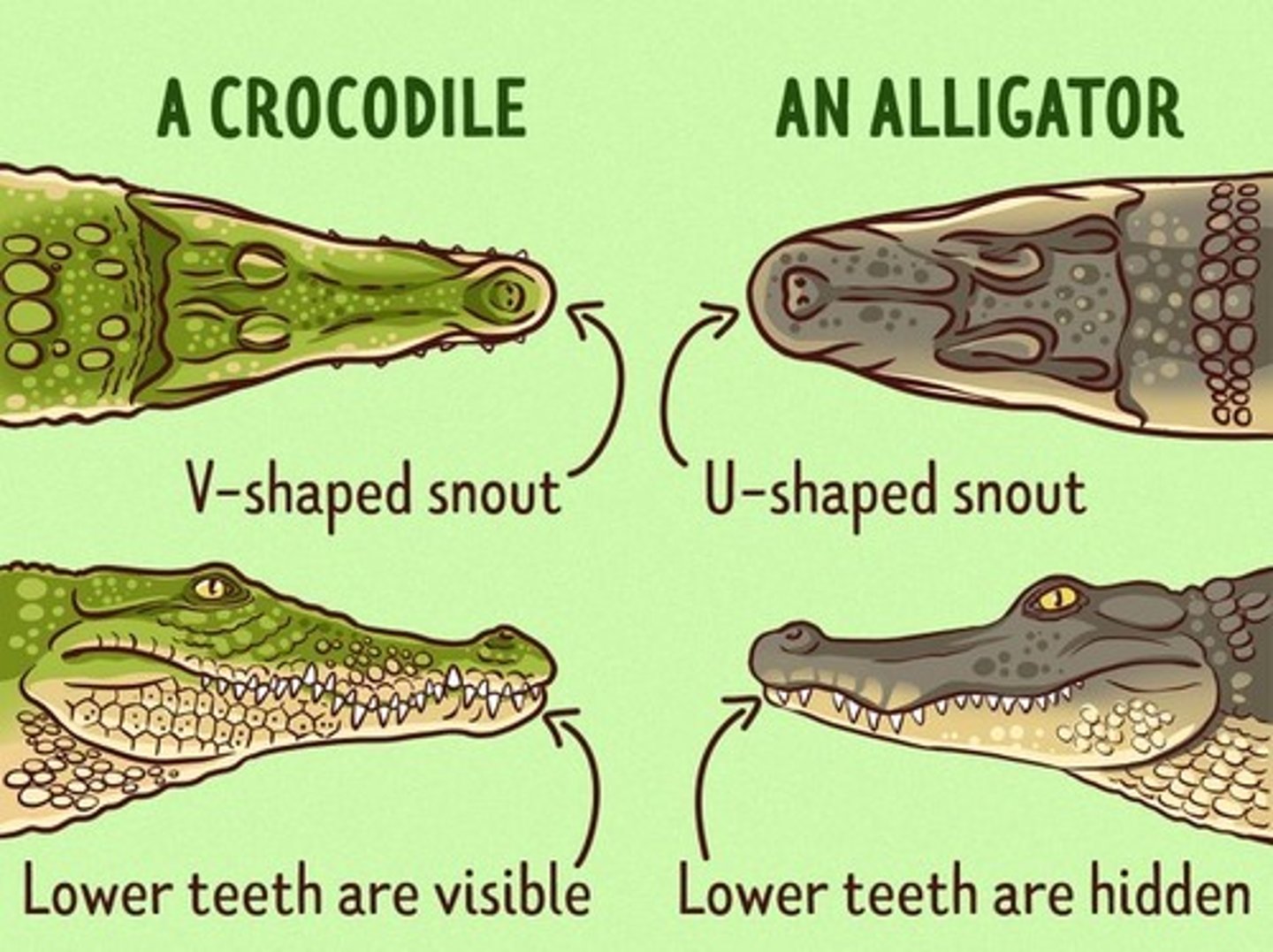
crocodile
this has a narrow snout "V" shaped
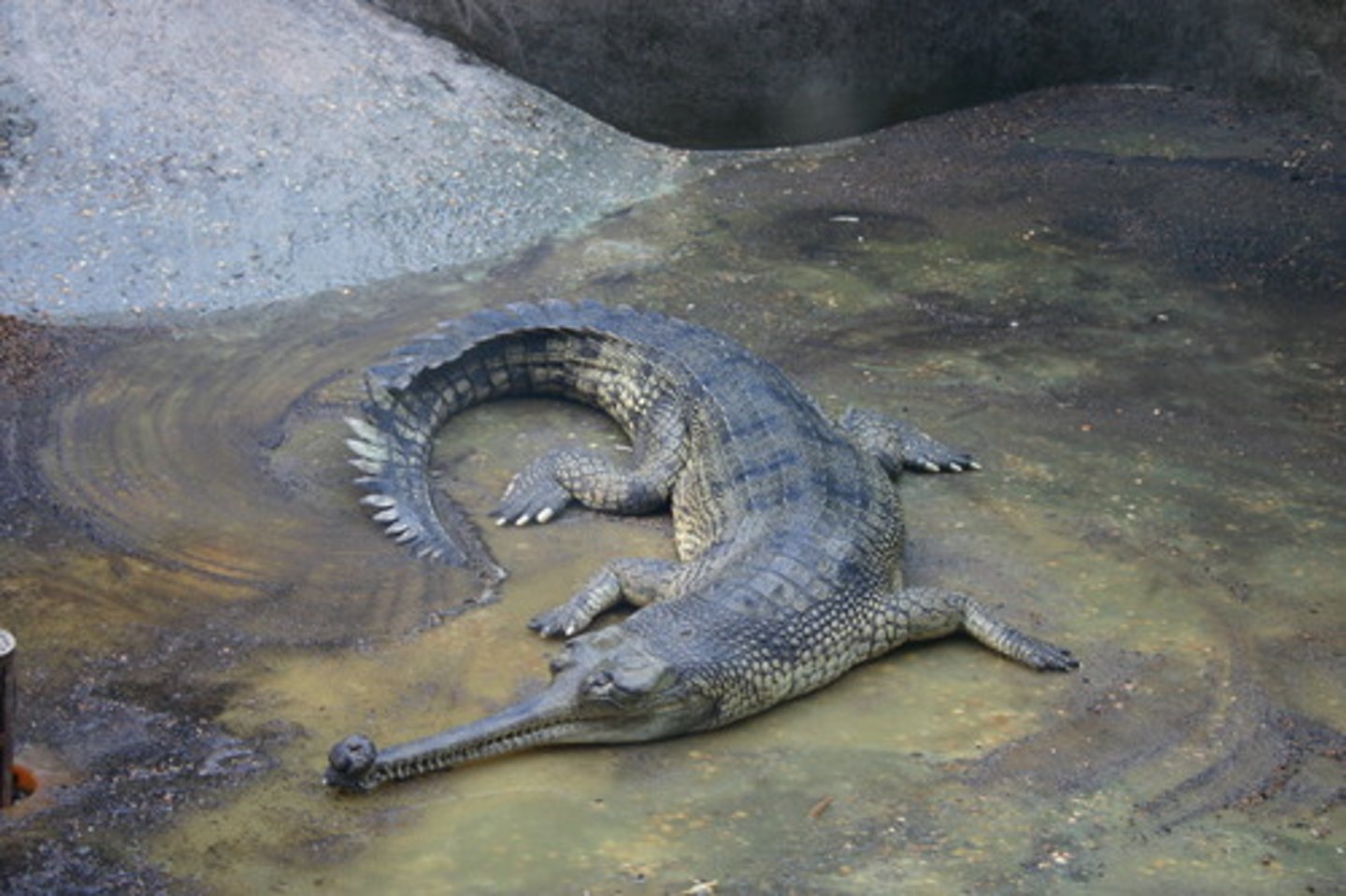
Piscivorous
term for fish eating
-eg Gharial and caiman

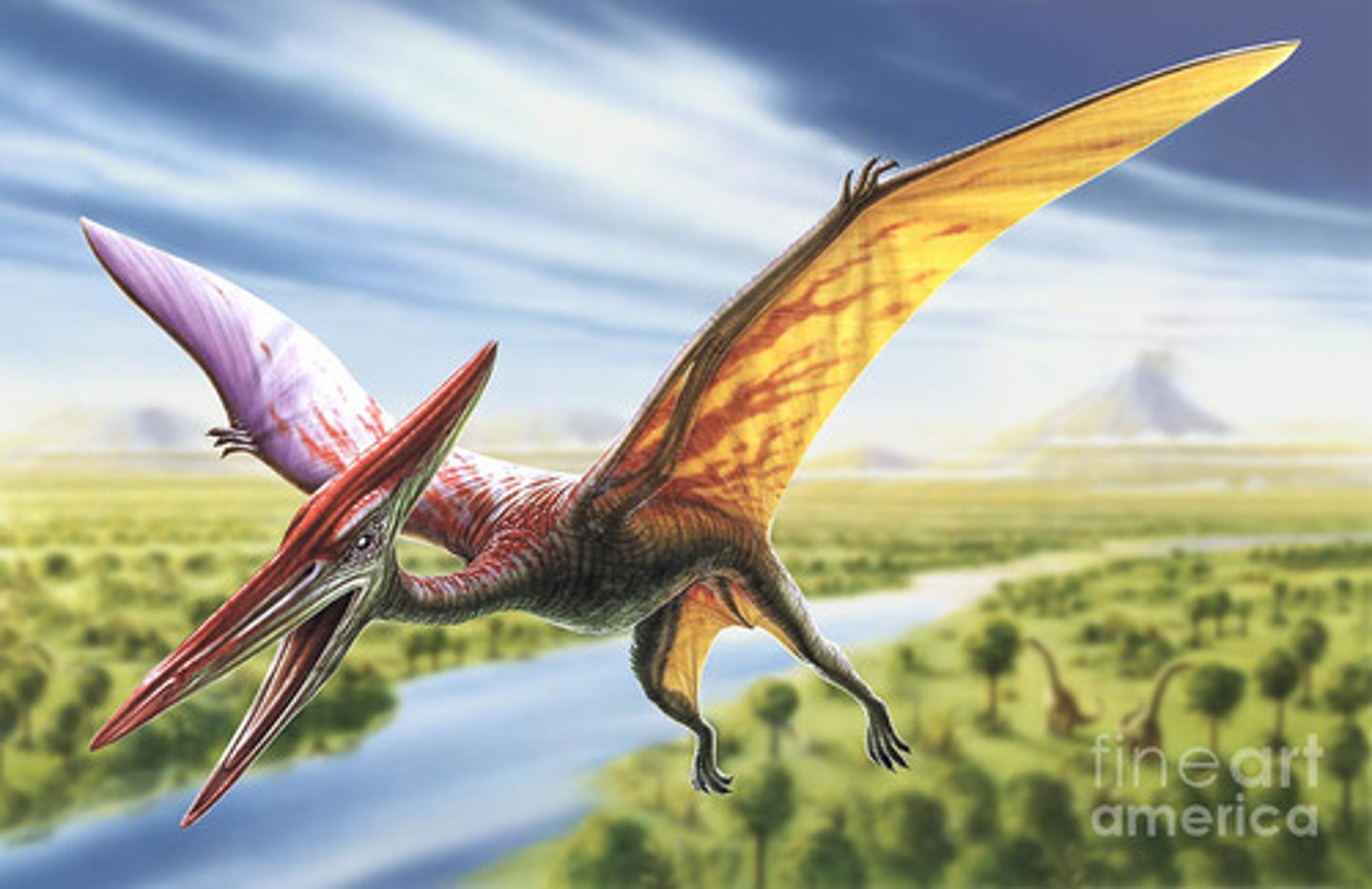
Pterosaurs
these creature were the first to evolve flight
-however, they are not a dinosaur

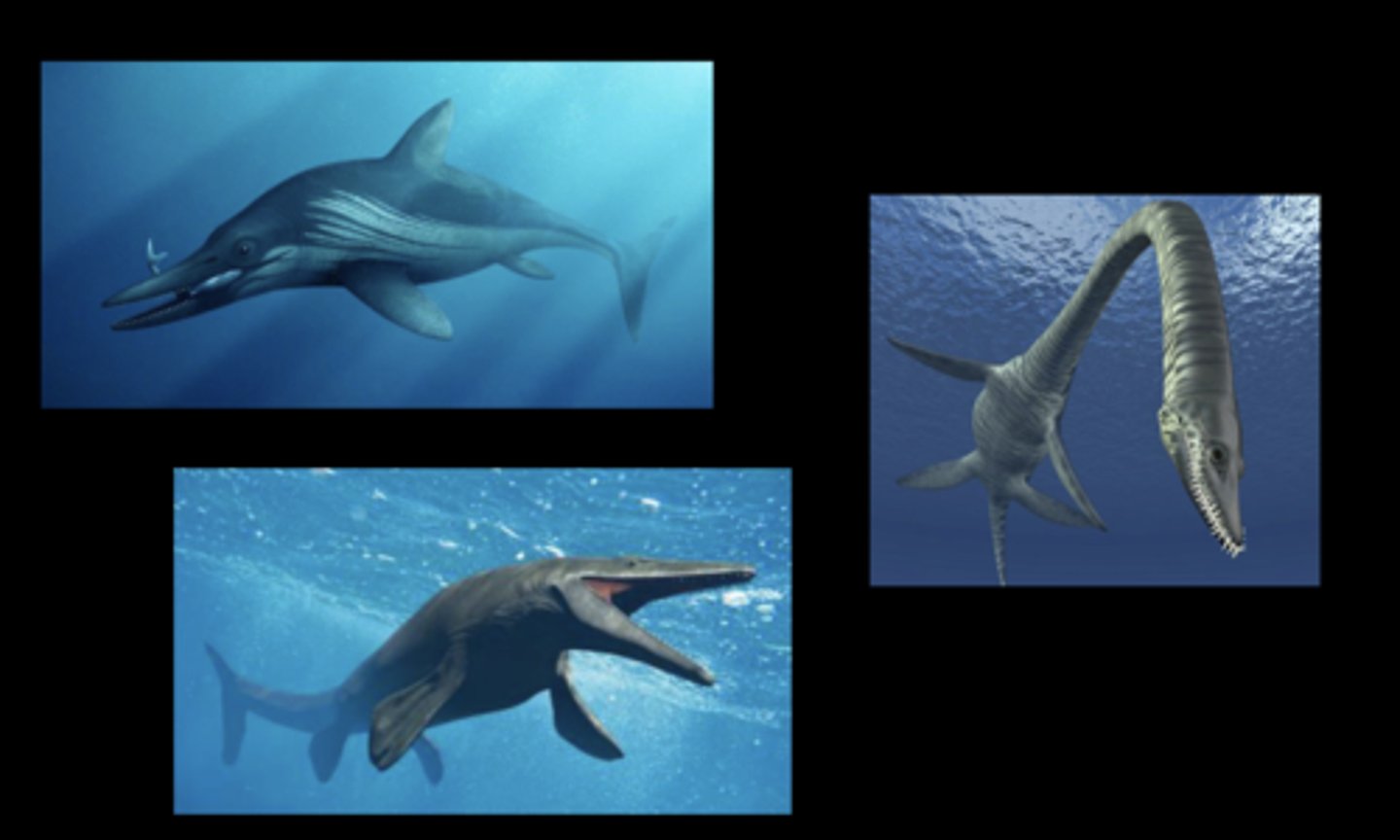
Mosasaurs, ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs (they are all what?)
these are all extinct reptiles that belong to extinct orders within class reptilia
-all were marine predators
-Ichthy were viviparous
