Chapter 1: Exam on 9/24 Measurement of Work, Power, and Energy Expenditure
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
9/8-9/19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
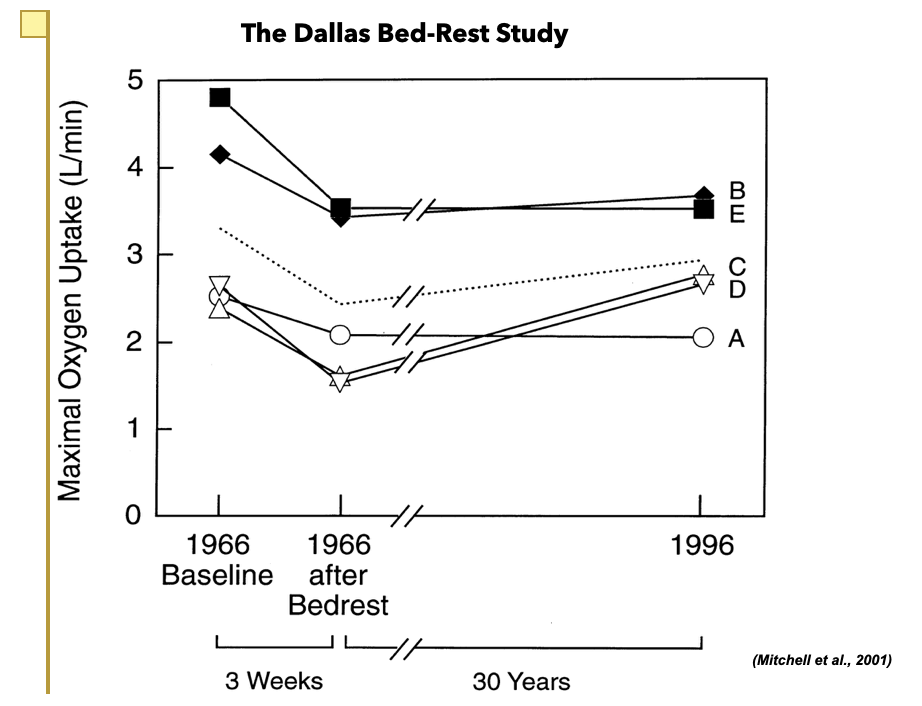
What does this graph measure and what are the results?
Measures VO2 max
Shows that being in a sedentary lifestyle for 3 weeks was physiologically worse for your body than aging 30 years because there was a more significant decrease of their VO2 max than over the course of 30 years
Objectives for Ch1
Work and power (only minimal info is needed to solve for these values) during several modes of exercise
cycle ergometry
bench step
staircase
treadmill
upside down pushups
Energy expenditure
calorimetry
what is VO2?
estimating and applying VO2
What is the equation for work and its SI units?
Work = force * distance
SI units are Work (J) = force (N) * distance (m)
Calculate work in J: lifting a 10kg weight up a distance of 2m
Force
1kg = 9.81 N
10kg = 98.1 N
Distance
2m
Work = Force * distance
98.1N * 2m = 196.2 N*m = 196.2 J
What is power known as? How do you calculate power? What are the SI units for power?
Power, also known as “work rate,” is the rate of the work performed
Power = work/time
SI units
Power (W) = work (J) / time (s)
Calculate the power in W when performing 20,000 J of work in 60s
Power (W) = work (J) /time (s)
Power = 20,000J / 60s = 333.33 J/s = 333.33 W
Calculate work for vertical jump with the following data:
155lbs, jumped 2.25ft high in 1.46s
155 lbs * 0.454 → 70.37 kg
2.25 ft → 0.6858 m
Work = Force * Distance
Force = 70.37 kg * 9.81 N = 690.3297 N
Work = 690.3297 N * 0.6858 m = 473.428 Nm = 437.428 J
Calculate work for wall sit with the following data:
62kg, 2.5 ft, 141 s
There is no work because there was no change in distance
Which athlete is the most powerful?
Athlete 1: bench press (1m), 880 lbs, took 3 seconds
Athlete 2: bench press (1m), 200 lbs, took .5 seconds
Athlete 1:
Work = (force)(distance)
(880 lbs)(0.454) = 399.52kg
force = (399.52kg)(9.81N) = 3919.2912 N
work = (3919.2912 N)(1m) = 3919.2912 Nm = 3919.2912J
Power = work/time
3919.2912J / 3s = 1306.43 J/s = 1306.43W
Athlete 2:
Work = (force)(distabce)
(200 lbs)(0.454) = 90.8kg
force = 90.8kg (9.81N)= 890.748N
work = (890.748N)(1m) = 890.748J
Power = work/time
890.748 J / .5s = 1781.496 J/s = 1781.496 W
Athlete 2 is more powerful than athlete 1.
What is egometry? What there must be in order to calculate those values?
Measurement of work or power output
to calculate work or power, there has to be a force moving against some resistance (person’s body weight moving up a step against gravity, pedaling a stationary bike when there is resistance applied to the wheels)
What is an erogmeter? What are some examples of these?
device used to measure work (give people exercise to track their bodily responses)
bench step ergometer (stepping up and down a step at a specified rate)
cycle ergometer
arm ergometer
treadmill
When running up a flight of stairs, what do you need in order to calculate work and power?
body mass (force)
height of the step (distance)
how many steps total
time
For a bench step, calculate the work and power:
70kg subject, 0.3 m step, 30 steps/min for 10 mins
Work = (force)(distance)
force = (70kg)(9.81N) = 686.7N
distance = (0.3m step)(30steps/min)(10min) = 90m
work = (686.7N)(90m) = 61,803Nm = 61,803 J
Power = work/time
61,803J / 600s = 103 J/s = 103 W
When using a stationary bike (cycle ergometer), what are the force and distance?
Force is the resistance on the pedals (how much you are pushing against the pedals. in this case, body mass IS NOT the force)
Distance is the revolutions/min times the circumference of how much traveled per revolution (flywheel is 6m / rev)
On a cycle ergometer, calculate the work and power:
1.5kg resistance, 6m/rev, 60 rev/min for 10 mins
Work:
1.5kg (9.81N) = 14.7N
(14.7N)(6m/rev)(60rev/min)(10min) = 52,920Nm = 52,920J
1.5kp (6m/rev)(60rev/min)(10min) = 5,400kpm
Power:
52,920J / 600s = 88.2 J/s = 88.2 W
5,400kpm / 10 min = 540 kpm/min (0.163) = 88.2 W
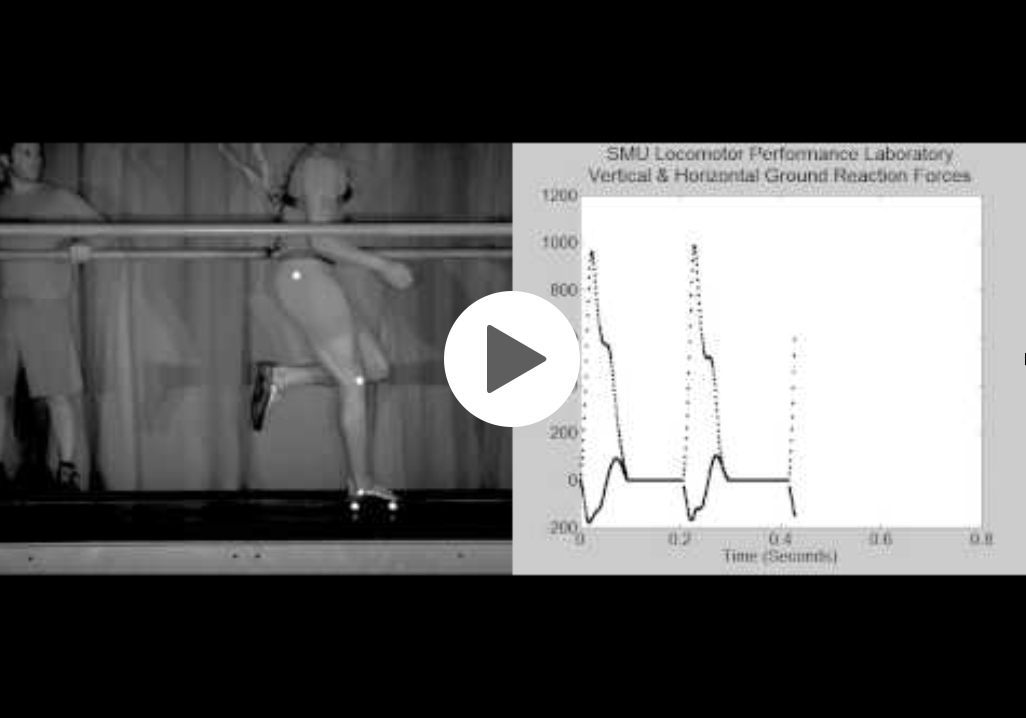
What is this measuring? What is the force and distance on a flat treadmill?What does it prove?
Every time their foot hits the treadmill, their force is measured in 3 different ways: front and back (dark lines), up and down (dotted lines), and right and left
Force = body mass
Distance = hip sensor (up and down distance)
If you ran 10 meters, the work and power is 0 because it is not the horizontal distance that you use when running; rather, it is the vertical distance (how far you go up). that is why on the graph, the dark lines (front and back) have net zero.
It is physically impossible to calculate work and power on a flat surface without expensive equipments