Software II Concepts
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Subsystems Guidline 1
Minimize Number of Collaborations
Subsystems Guidline 2
Minimize Delegations of Subsystem Contracts
Subsystems Guidline 3
Minimize Number of Contracts
Cohesion
The degree to which all elements of a component are directed towards a single task.
High cohesion is good because if there is a change, there is a high probability that the impact will be localized.
Coincidental Cohesion
Parts of the component are unrelated.
Logical Cohesion
Elements of a component are related logically but not functionally.
Temporal Cohesion
Elements are related by timing involved.
Procedural Cohesion
Related only to ensure a particular order of execution.
Communicational Cohesion
Functions performed on the same data or to produce the same data.
Sequential Cohesion
The output of one part is the input to another.
Functional Cohesion
Every essential element to a single computation is contained in this component.
Exceptional Post Condition
Says what is true when a method throws an exception.
Process for Writing Protocols
For each class, For each contract, For each responsibility - Specify complete protocol (set of signatures) to
support the responsibility.

A Protocol
Set of signatures for methods to be implemented.
Coupling
The degree of dependence such as the amount of interactions among components.
Changes to a component are localized and do not cascade.
Content Coupling
One component modifies another.
Common Coupling
More than one component share data such as global data structures.
Problem: Difficult to determine components that edit.
External Coupling
Two components share something externally imposed.
Low = changes in external entity has little impact
Medium = Some impact (introduce interfaces)
High = Substantial impact
Control Coupling
Component passes control parameters (boolean flags) to coupled components.
Bad if control flow paths are unrelated, good if reusable.
Stamp Coupling
Component passes a data structure to another component that does not need access to the entire structure.
Problem: Requires 2nd component to know how to manipulate data, Security Risks.
Data Coupling
Component passes data (NOT DATA STRUCTURES) to other component.
Uncoupled
Completely uncoupled components are not systems.
Semi-formal Notation
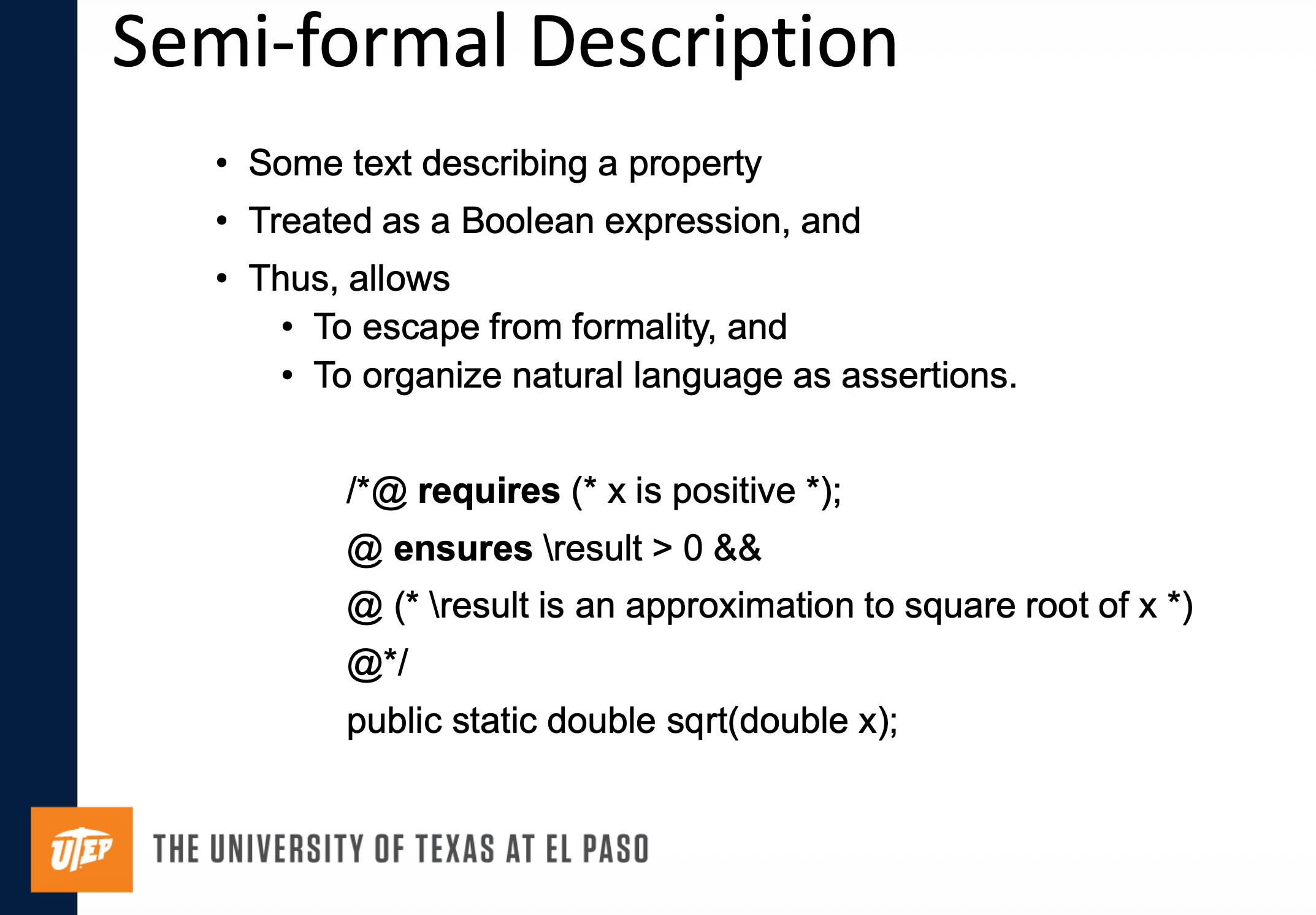
Private Responsibilities
Responsibilities not part of a contract.