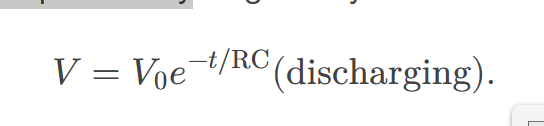Chapter 21: Circuits and DC Instruments
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
ammeter
an instrument that measures current
analog meter
a measuring instrument that gives a readout in the form of a needle movement over a marked gauge
bridge device
a device that forms a bridge between two branches of a circuit; some bridge devices are used to make null measurements in circuits
capacitance
the maximum amount of electric potential energy that can be stored (or separated) for a given electric potential
capacitor
an electrical component used to store energy by separating electric charge on two opposing plates
conservation laws
require that energy and charge be conserved in a system
current
the flow of charge through an electric circuit past a given point of measurement
current sensitivity
the maximum current that a galvanometer can read
digital meter
a measuring instrument that gives a readout in a digital form
electromotive force (emf)
the potential difference of a source of electricity when no current is flowing; measured in volts
full-scale deflection
the maximum deflection of a galvanometer needle, also known as current sensitivity; a galvanometer with a full-scale deflection of 50μA has a maximum deflection of its needle when 50μA flows through it
galvanometer
an analog measuring device, denoted by G, that measures current flow using a needle deflection caused by a magnetic field force acting upon a current-carrying wire
internal resistance
the amount of resistance within the voltage source
Joule’s Law
the relationship between potential electrical power, voltage, and resistance in an electrical circuit, given by: 𝑃𝑒=IV
Junction Rule
Kirchhoff’s first rule, which applies the conservation of charge to a junction; current is the flow of charge; thus, whatever charge flows into the junction must flow out; the rule can be stated 𝐼1=𝐼2+𝐼3
Kirchhoff’s rules
a set of two rules, based on conservation of charge and energy, governing current and changes in potential in an electric circuit
loop rule
Kirchhoff’s second rule, which states that in a closed loop, whatever energy is supplied by emf must be transferred into other forms by devices in the loop, since there are no other ways in which energy can be transferred into or out of the circuit. Thus, the emf equals the sum of the IR (voltage) drops in the loop and can be stated: emf=𝐼𝑟+𝐼𝑅1+𝐼𝑅2
null measurements
methods of measuring current and voltage more accurately by balancing the circuit so that no current flows through the measurement device
Ohm’s Law
the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance within an electrical circuit: V=IR
Ohmmeter
an instrument that applies a voltage to a resistance, measures the current, calculates the resistance using Ohm’s law, and provides a readout of this calculated resistance
Parallel
the wiring of resistors or other components in an electrical circuit such that each component receives an equal voltage from the power source; often pictured in a ladder-shaped diagram, with each component on a rung of the ladder
Potential Difference
the difference in electric potential between two points in an electric circuit, measured in volts
Potentiometer
a null measurement device for measuring potentials (voltages)
RC circuit
a circuit that contains both a resistor and a capacitor
Resistance
causing a loss of electrical power in a circuit
Resistor
a component that provides resistance to the current flowing through an electrical circuit
Series
a sequence of resistors or other components wired into a circuit one after the other
Shunt resistance
a small resistance 𝑅 placed in parallel with a galvanometer G to produce an ammeter; the larger the current to be measured, the smaller 𝑅 must be; most of the current flowing through the meter is shunted through 𝑅 to protect the galvanometer
Terminal Voltage
the voltage measured across the terminals of a source of potential difference

Voltage
the electrical potential energy per unit charge; electric pressure created by a power source, such as a battery
Voltage Drop
the loss of electrical power as a current travels through a resistor, wire or other component
Voltmeter
an instrument that measures voltage
Wheatstone bridge
a null measurement device for calculating resistance by balancing potential drops in a circuit
The total resistance of an electrical circuit with resistors wired in a series is the sum of the individual resistances
and can be calculated using the formula R_total = R1 + R2 + R3 + … + Rn.

The total resistance of an electrical circuit with resistors wired in parallel
is less than the lowest resistance of any of the components
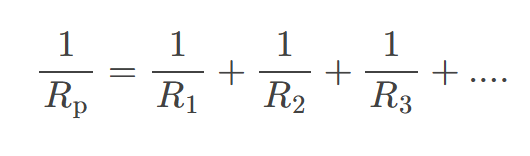
When an initially uncharged (𝑉0=0 at 𝑡=0) capacitor in series with a resistor is charged by a DC voltage source,
the voltage rises, asymptotically approaching the emf of the voltage source; as a function of time,
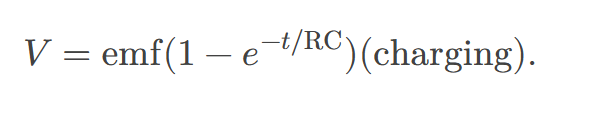
If a capacitor with an initial voltage 𝑉0 is discharged through a resistor starting at 𝑡=0
then its voltage decreases exponentially