LC3117 CLE WEEK 11-14 FINAL NOTES
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intellectual Property Rights, Copyright, Trademark, Patent, Industrial Designs, Geographical Indications, Creative Commons, Fair Use
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms

INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
DEFN: Creations of the mind, like inventions, artworks, designs & symbols used in commerce
Multiple people can use them at the same time
Initial development is costly, but reproduction is cheap
5 EXAMPLES OF INTELLECTUAL OBJECTS
Musical Compositions
Poems
Inventions
Product Formula
Novels
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ISSUES
Ownership rights can be problematic
Defining creators & owners is essential
Legal protection for creators’ & owners’ interests
Safeguarding IP from unauthorised copying
Balancing interests with the public
IMPACT OF COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
Technologies made it easy to copy and distribute IP:
Compression formats for music/movie files.
Scanners for converting printed text/photos to digital.
Computer networks for distributing digitized material.
Peer-to-peer technology for file transfer.
World Wide Web for finding and downloading material.
Inexpensive digital storage media.
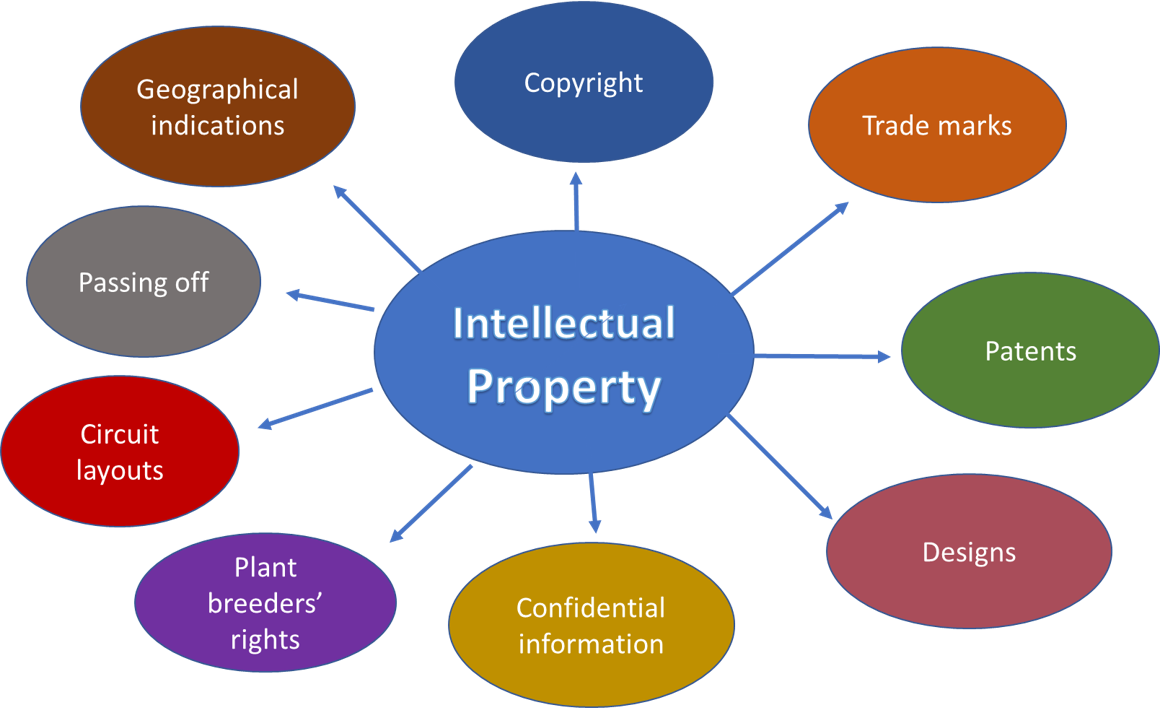
5 TYPES OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (C.P.T.ID.GI)
1. Copyright: Rights creators have over literary and artistic works, like books, music, paintings, and films.
2. Patents: Exclusive rights granted for an invention, allowing the owner to decide its use.
3. Trademark: A sign distinguishing goods or services of one enterprise from others.
4. Industrial Designs: The ornamental aspect of an article, like its shape or surface.
5. Geographical Indications: Signs on goods with a specific geographical origin and unique qualities, reputation, or characteristics. Often includes the place of origin's name.

COPYRIGHT
Creator’s rights over their literary & artistic works (e.g. books, music, art), which allows them to control the reproduction, performance & distribution of their work
Includes: Novels, poems, computer programs, newspapers, plays, choreography, musical works, sculpture, architecture, maps, technical drawings, paintings, & photographs
Lasts the author’s lifetime plus 70 years
In software, copyright can protect algorithms
E.g. ‘To Kill A Mockingbird’, ‘Borneo Bulletin’

PATENTS
Exclusive right granted for an invention, giving the owner control over how it’s used
BUT, technical details of the invention are made public
Inventions must be new & unique, involve an inventive step, & be industrially applicable
E.g. Dyson Vacuum Cleaner, A new medicine

TRADEMARKS
A unique sign like a word, phrase, or symbol that distinguishes one company’s goods or services from others
Prevents unauthorised use of these identifiers
Violations occur through infringement (unauthorised use) & dilution (blurring the distinctiveness or tarnishing the reputation)
E.g. Nike, Adidas, McDonald’s, iPhone, PlayStation
INDUSTRIAL DESIGNS
The unique appearance of a product, including its shape, pattern, or ornament
DOES NOT cover construction method
Aims to make products visually different
E.g. Coca-Cola Glass Contour Bottle, Tesla Model S

GEOGRAPHICAL INDICATIONS
Signs used on goods that link them to a specific geographic region
E.g. Champagne, France and its sparkling wines
E.g. Darjeeling Tea from Darjeeling, India
BENEFITS OF IP PROTECTION
Gives creators control over their work & prevents misuse
Rewards producers’ efforts
Encourages innovation & creativity
Enhances business’ value, turning ideas into profitable assets & generating income for the economy
LIMITATIONS OF IP PROTECTION
Society benefits when inventions are freely accessible
Balances the need to reward creators & the wider benefit of disseminating ideas
FAIR USE PROVISION (N.C.C.T.SR)
The use of copyrighted material under certain conditions
Aims to balance creators’ interests with society’s need for free idea exchanges
E.g. News reporting, criticism, comment, teaching, scholarship & research
Factors for fair use: The purpose of use, the amount use, and the impact on the potential market for the copyrighted work
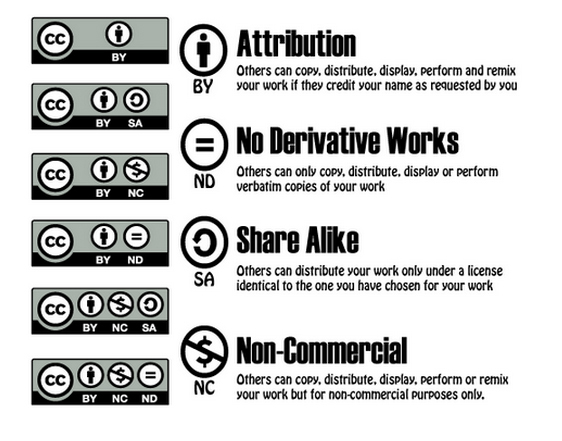
CREATIVE COMMONS
A non-profit org providing different copyright licenses, allowing creators to decide how their work is shared, used, & remixed
Aim to increase free creative content for the public

CC0 (CC ZERO)
Public dedication tool by Creative Commons, allowing creators to give up their copyright, placing their works in the worldwide public domain
Enables others to freely distribute, remix, adapt, & use the material unconditionally
CASE FOR - COPYING SOFTWARE
Over-Priced Perception
Not Perceived as Stealing (Intangible Nature)
Global Access Inequalities
CASE AGAINST - COPYING SOFTWARE
Illegal Activity (Piracy)
Economic Impact
Removes Incentive to Innovate
Malware Risk
RELATED RIGHTS
Related with copyrighted works.
Includes: sound recordings, films, broadcasting, cable programs & published editions