Understanding Anxiety Disorders and Their Treatments
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Anxiety Disorders
Include Generalized Anxiety, Panic, Agoraphobia, Social Anxiety.
Anxiety
Emotional state with physical tension and apprehension.
Subjective Unease
Personal feeling of discomfort or worry.
Free-Floating Anxiety
Anxiety not linked to a specific trigger.
Maladaptive Anxiety
Excessive anxiety negatively affecting cognitive performance.
Fear
Normal emotion activating flight-or-fight response.
Panic
Abnormal fear response, often leading to panic attacks.
Flight-or-Fight Response
Physiological reaction to perceived threat.
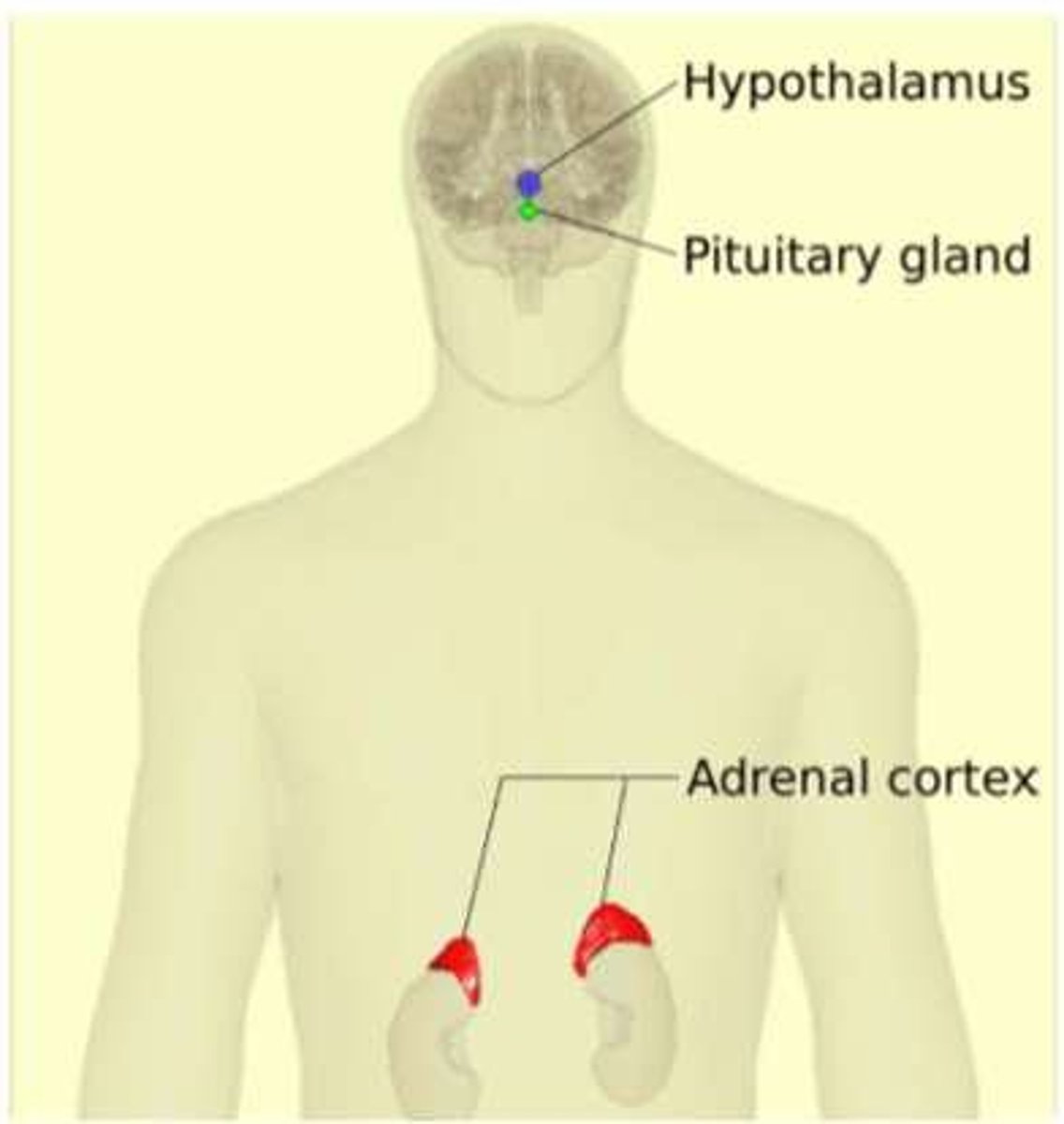
HPA Axis
Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis regulating stress response.
Physiological Changes
Increased heart rate, blood pressure, and metabolism.
Emotional Changes
Feelings of dread, terror, or irritability during stress.
Cognitive Changes
Anticipation of harm and exaggerated danger perception.
Behavioral Changes
Escape, avoidance, aggression, or freezing in response.
Panic Attack
Abrupt intense fear with physical symptoms.
Physical Symptoms of Panic
Heart palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath.
Cognitive Performance
Ability to concentrate and process information.
Moderate Anxiety
Can enhance performance and motivation.
Extreme Anxiety
Can lead to impaired focus and functioning.
Tension Symptoms
Fidgeting and looking worried as anxiety indicators.
Dysregulated Response
Flight-or-fight activated by non-threatening stimuli.
Emergency Response
Panic attacks may mimic heart attacks.
Anticipation of Harm
Cognitive distortion leading to excessive worry.
Anxiety Attack
State of very high anxiety without clinical definition.
Anxiety Disorders
Disorders differentiated by fear-inducing objects or situations.
Co-morbidity
High occurrence of multiple anxiety disorders together.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Chronic anxiety across various situations, not specific.

Uncontrollable Worry
Excessive anxiety about multiple life aspects.
Physiological Symptoms
Physical effects like muscle tension and sleep disturbances.
Chronic Restlessness
Persistent inability to relax or remain still.
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
Subset of symptoms required for disorder diagnosis.
Distress or Impairment
Significant disruption in functioning due to symptoms.
Lifetime Prevalence
8.7% of Canadians affected by GAD in 2012.
Yearly Prevalence
2.6% of Canadians affected by GAD in past year.
Chronic Illness
Condition lasting long periods, often symptom-free phases.
Repetitive Negative Thinking
Common feature in mental disorders, including anxiety.
Worry
Chain of negative, uncontrollable thoughts and images.
Rumination
Repetitive focus on distressing thoughts or memories.
Cognitive Function
Mental processes affected by negative repetitive thinking.
Psychological Treatments
Therapies aimed at alleviating anxiety symptoms.
Drug Treatments
Medications used to reduce anxiety symptoms.
Efficacy of Treatments
Effectiveness measured by symptom remission rates.
Placebo Effect
Response to treatment not due to active intervention.
Study Efficacy Example
Drug efficacy 63% vs placebo 38% for GAD.
GAD
Generalized Anxiety Disorder, characterized by excessive worry.
Benzodiazepines
Mild tranquilizers enhancing GABA for anxiety relief.
GABA
Neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve transmission in the brain.
Anxiolytic
Substance that reduces anxiety symptoms.
SSRIs
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors, increase serotonin availability.
SNRIs
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors, affect serotonin and norepinephrine.
Paroxetine
SSRI used to treat GAD, marketed as Paxil.
Venlafaxine
SNRI used to treat GAD, marketed as Effexor.
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)
Psychological treatment focusing on cognitive distortions and coping.
Worry Process
Cognitive pattern where patients avoid confronting threats.
Mindfulness Techniques
Meditational practices aimed at increasing present-moment awareness.
Short-term Relief
Immediate anxiety symptom reduction, lasting hours.
Long-term Efficacy
Sustained effectiveness of treatment over extended periods.
Dependence
Condition of relying on a substance for normal function.
Drowsiness
Common side effect of benzodiazepines affecting alertness.
Cognitive Distortions
Faulty thinking patterns contributing to anxiety.
Therapeutic Techniques
Methods used to manage and treat anxiety symptoms.
Placebo Effect
Improvement in symptoms due to belief in treatment.
Ontario Prescription Rates
1 in 18 Ontarians prescribed benzodiazepines in 2019.
Coping Techniques
Strategies to manage anxiety and stress effectively.
Acceptance of Distress
Psychological approach to tolerate uncomfortable thoughts.
Research Evidence
Data supporting the effectiveness of treatment methods.
Panic Disorder
Involves panic attacks and anxiety about future attacks.
Panic Attack
Intense emotional state with physical and psychiatric symptoms.
Expected Panic Attack
Occurs in response to a specific fear situation.
Unexpected Panic Attack
Occurs randomly without a specific trigger.
Agoraphobia
Fear of situations where escape may be difficult.

Panic Disorder Criteria
Requires panic attacks and anxiety over future attacks.
Physical Symptoms
Physiological reactions during a panic attack.
Psychiatric Symptoms
Mental health reactions during a panic attack.
Cognitive Problems
Difficulty concentrating during tests due to anxiety.
Self-Medication
Using substances to cope with panic and anxiety.
Comorbidity
High occurrence of panic disorder with substance abuse.
Distress Definition
Patient's distress defines abnormality, not functionality.
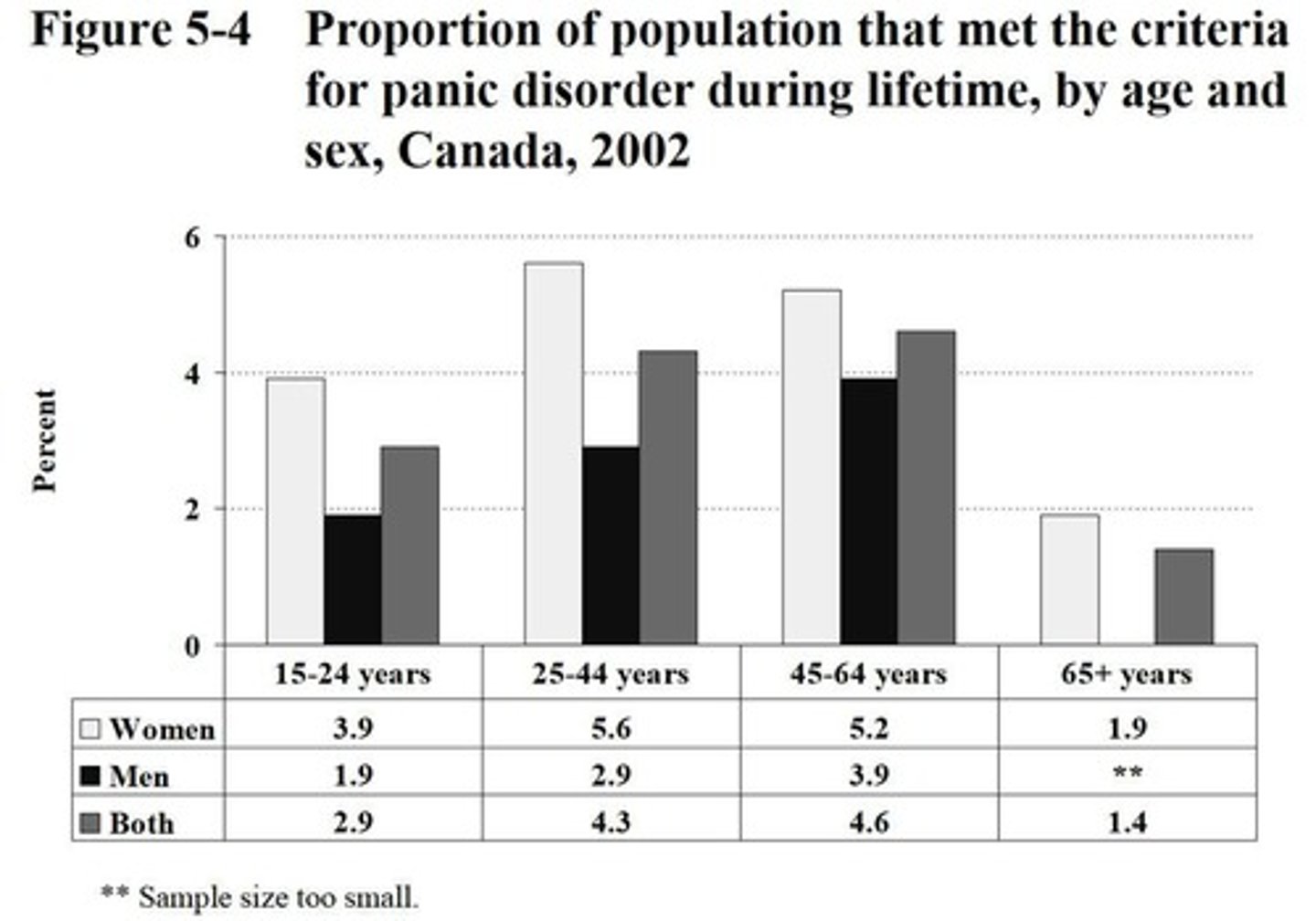
Prevalence in Canada
1.6% 12-month and 3.7% lifetime for panic disorder.
Agoraphobia Prevalence
0.7% 12-month and 1.5% lifetime for agoraphobia.
Panic Attack Consequences
May lead to avoidance of tests and lectures.
Safe Space Preference
Desire to be in safe environments during attacks.
Agoraphobia Independence
Can persist without recent panic attacks.
Avoidance Behavior
Avoiding situations to prevent panic attacks.
Intense Fear
Severe anxiety experienced during panic attacks.
Phobia Origin
Greek: agora (marketplace) + phobia (fear).
Panic Symptoms Unpredictability
Uncertainty leads to prolonged avoidance behavior.
Panic Disorder
Anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent panic attacks.
Agoraphobia
Fear of situations where escape might be difficult.
Prevalence
Frequency of panic disorder in a population.
Lifetime Prevalence
Percentage of individuals affected over their lifetime.
12-Month Prevalence
Percentage of individuals affected in the past year.
Cognitive Problems
Difficulties in thinking due to high anxiety.
Avoidance Behavior
Avoiding situations that trigger anxiety symptoms.
Chronic Disorder
Condition that persists over a long period.
Wax and Wane
Symptoms that fluctuate in intensity over time.
Gender Differences
Panic disorder prevalence is higher in females.
Sociocultural Factors
Influence of race and ethnicity on prevalence rates.
High-Potency Benzodiazepines
Fast-acting drugs like Xanax for anxiety treatment.
SSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for treating anxiety.
SNRIs
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors for panic disorder.