3&4: Properties of Sound Waves and Wave Interference
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Audible Sound Waves
Sound wave in range of human hearing, 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Infrasonic Waves
Sound wave with a frequency below 20 Hz.
Ultrasonic Waves
Sound wave with a frequency above 20,000 Hz (20 kHz); used for ultrasounds in medical applications.
Speed of Sound
The speed of sound through air depends on the density of the air and its temperature.
Speed Increase Rate
The speed increases by 0.606 m/s for every increase of 1 °C.
Mach Number
The ratio of the airspeed of an object to the local speed of sound.
Mach 1
Means the object is travelling at the speed of sound.
Mach 2
Is twice the speed of sound.
Sound Barrier
When an object moves at the speed of sound, the sound waves emitted build up producing very dense air, or intense compressions, called the sound barrier.
Sonic Boom
Produced when an aircraft breaks the sound barrier.
Speed of Sound in Glass (Pyrex)
5170 m/s.
Speed of Sound in Steel
5000 m/s.
Speed of Sound in Water
1496 m/s.
Speed of Sound in Wood (maple)
4110 m/s.
Sound Intensity
The amount of sound energy being transferred per unit area; unit W/m².
Loudness
Describes how humans perceive sound energy; depends on sound intensity.
Threshold of Hearing
Ranges from 1 x 10^-12 W/m² to about 1 W/m².
Decibel (dB)
Unit used to deal with the large range of sound intensity.
Sound Intensity Increase
Each increase of 10 dB is a 10 times increase in sound intensity.
Sound Intensity at Threshold of Human Hearing
1 x 10^-12 W/m² corresponds to 0 dB.
Sound Intensity of Library
1 x 10^-7 W/m² corresponds to 50 dB.
Sound Intensity of Alarm Clock
1 x 10^-6 W/m² corresponds to 60 dB.
Sound Intensity of Rock Band
0.1 W/m² corresponds to 110 dB.
Sound Intensity of Power Saw
1.0 W/m² corresponds to 120 dB.
Sound Intensity at Threshold of Pain
10 W/m² corresponds to 130 dB.
Distance and Sound Level
As a sound wave expands from its source, the energy per unit area decreases and it sounds quieter.
Sound Safety Guidelines
Sound levels greater than 100 dB that persist for more than a few minutes will harm your hearing.
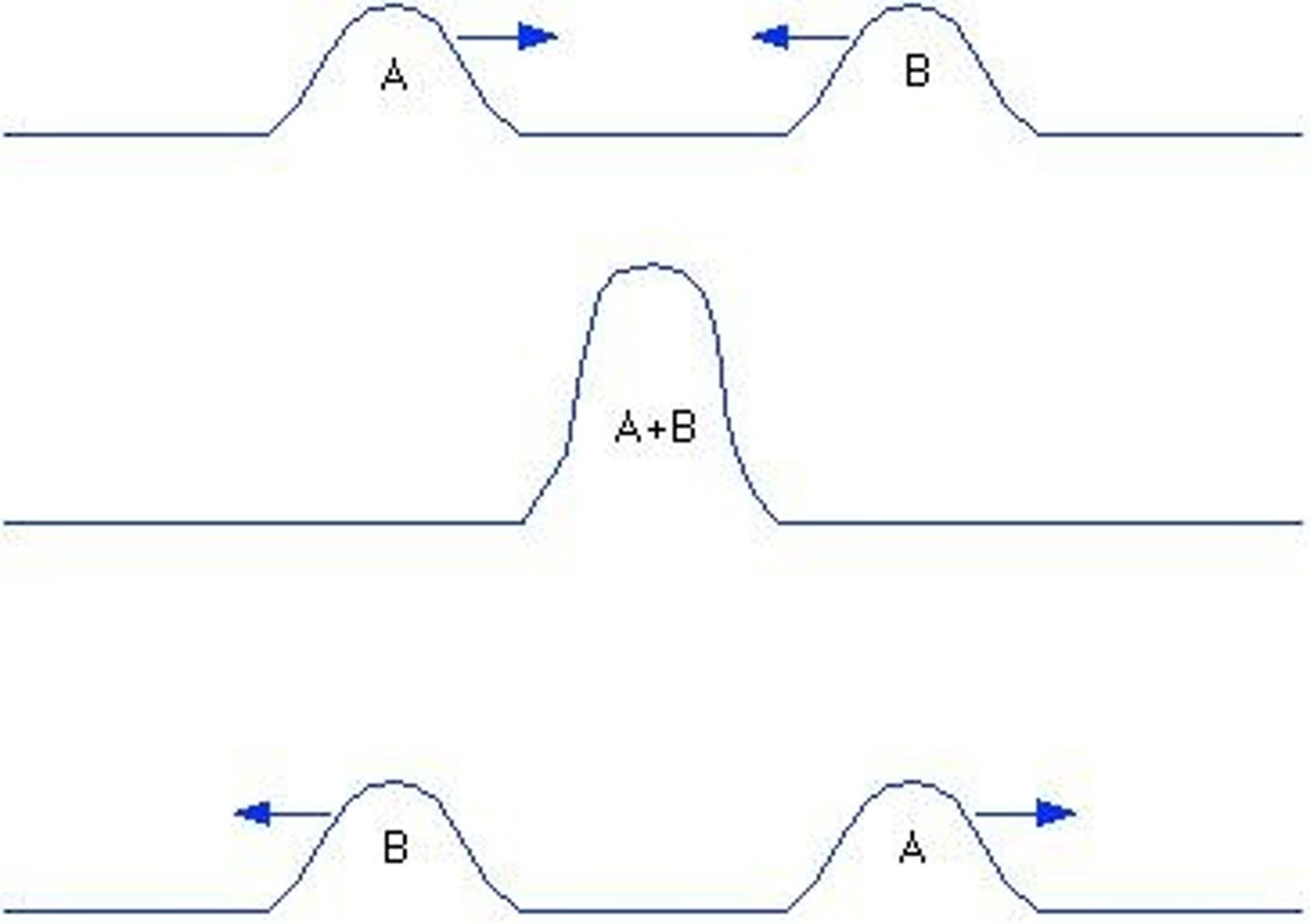
Interference
the process of generating a new wave when two or more waves meet
Constructive Interference
the process of forming a wave with a larger amplitude when two or more waves combine
Destructive Interference
the process of forming a wave with a smaller amplitude when two or more waves combine
Principle of Superposition
at any point the amplitude of two interfering waves is the sum of the amplitudes of the individual waves
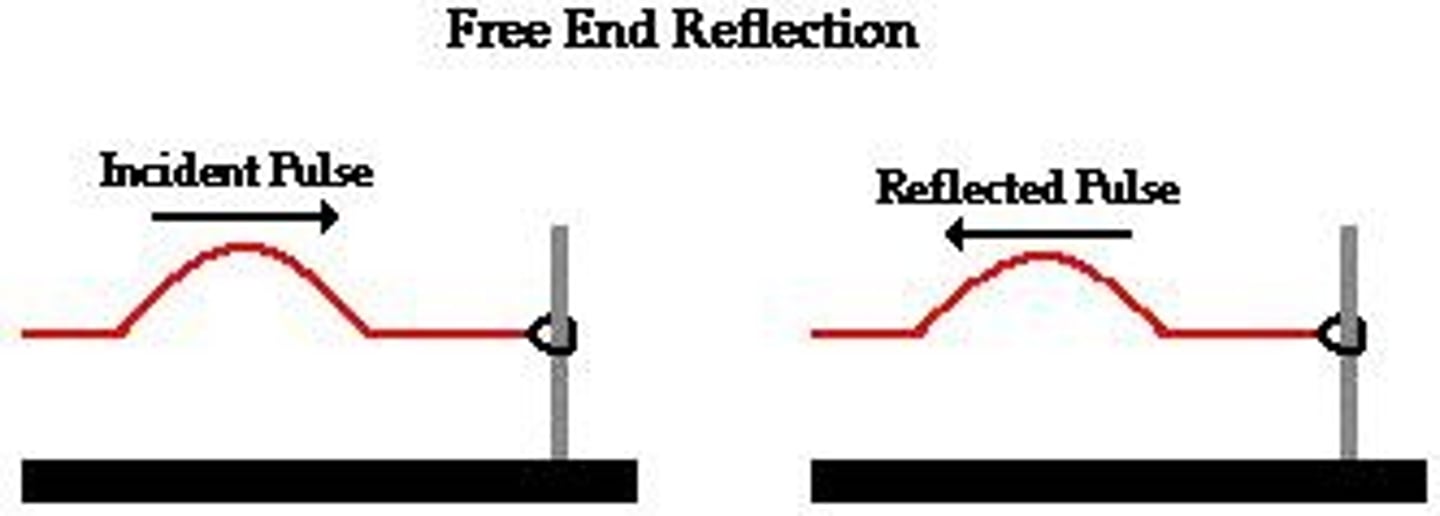
Free-End Reflection
a reflection that occurs at a media boundary where the second medium is less dense than the first medium; reflections have an amplitude with the same orientation as the original wave
Fixed-End Reflection
a reflection that occurs at a media boundary where one end of the medium is unable to vibrate; reflections are inverted
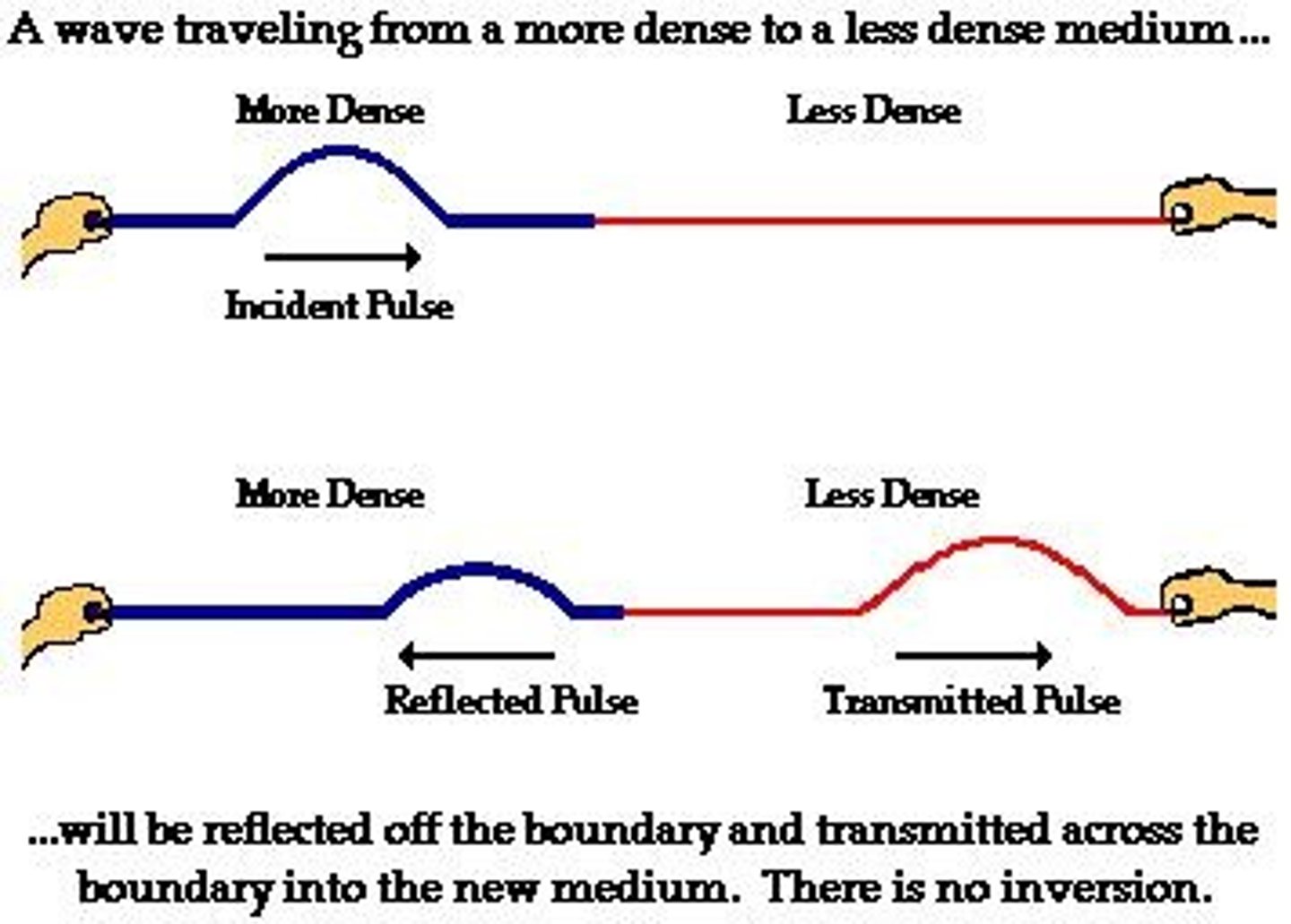
Wave Transmission
When waves travel from one medium into another, some of the energy will transmit through, while some will be reflected
Standing Wave
an interference pattern produced when incoming and reflected waves interfere with each other; the effect is a wave that appears to be stationary
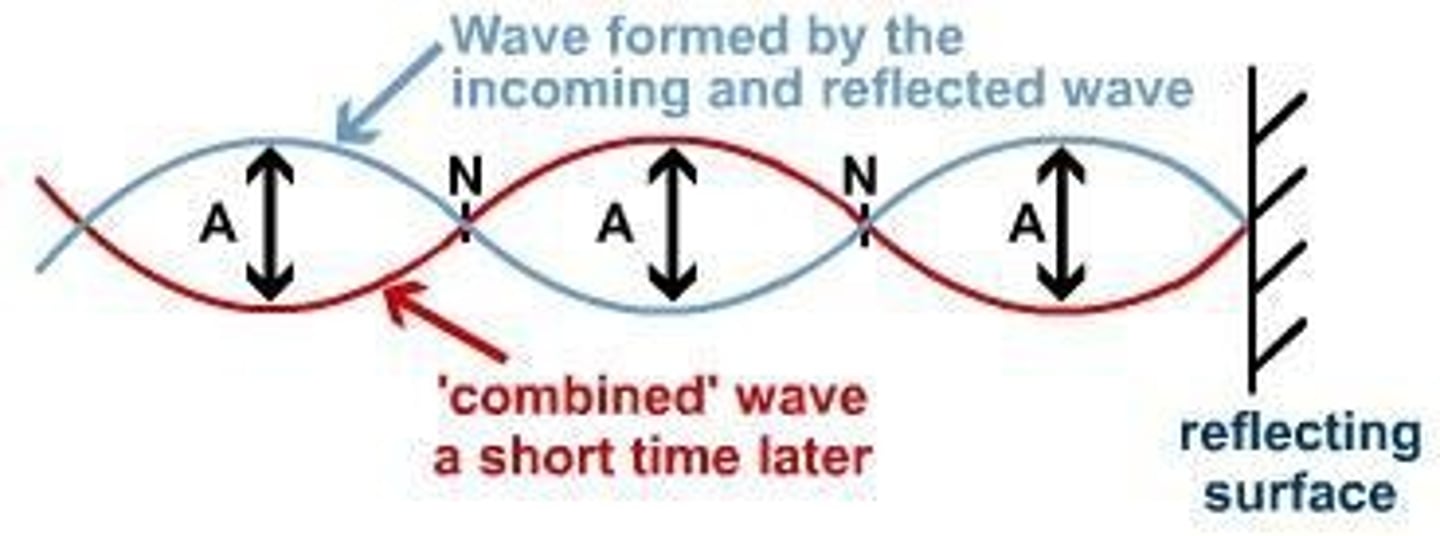
Nodes
in a standing wave, the location where the particles of the medium are at rest - constant total destructive interference
Antinodes
in a standing wave, the location where the particles of the medium are moving with the greatest speed; the amplitude will be twice the amplitude of the original wave
Fundamental frequency
the lowest frequency that can produce a standing wave in a given medium
Harmonics
whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency

Overtone
a sound resulting from a string that vibrates with more than one frequency
Standing Waves in Fixed Ends
To produce standing waves in media with two fixed ends or two free ends, the length of the medium, L, is equal to the number of the harmonic, n, times half the standing wave's wavelength, λ/2.
Standing Waves in Fixed-Free Ends
To produce standing waves in media with one fixed end and one free end, the shortest possible length is λ/4. The next possible length is λ/2 more than this.
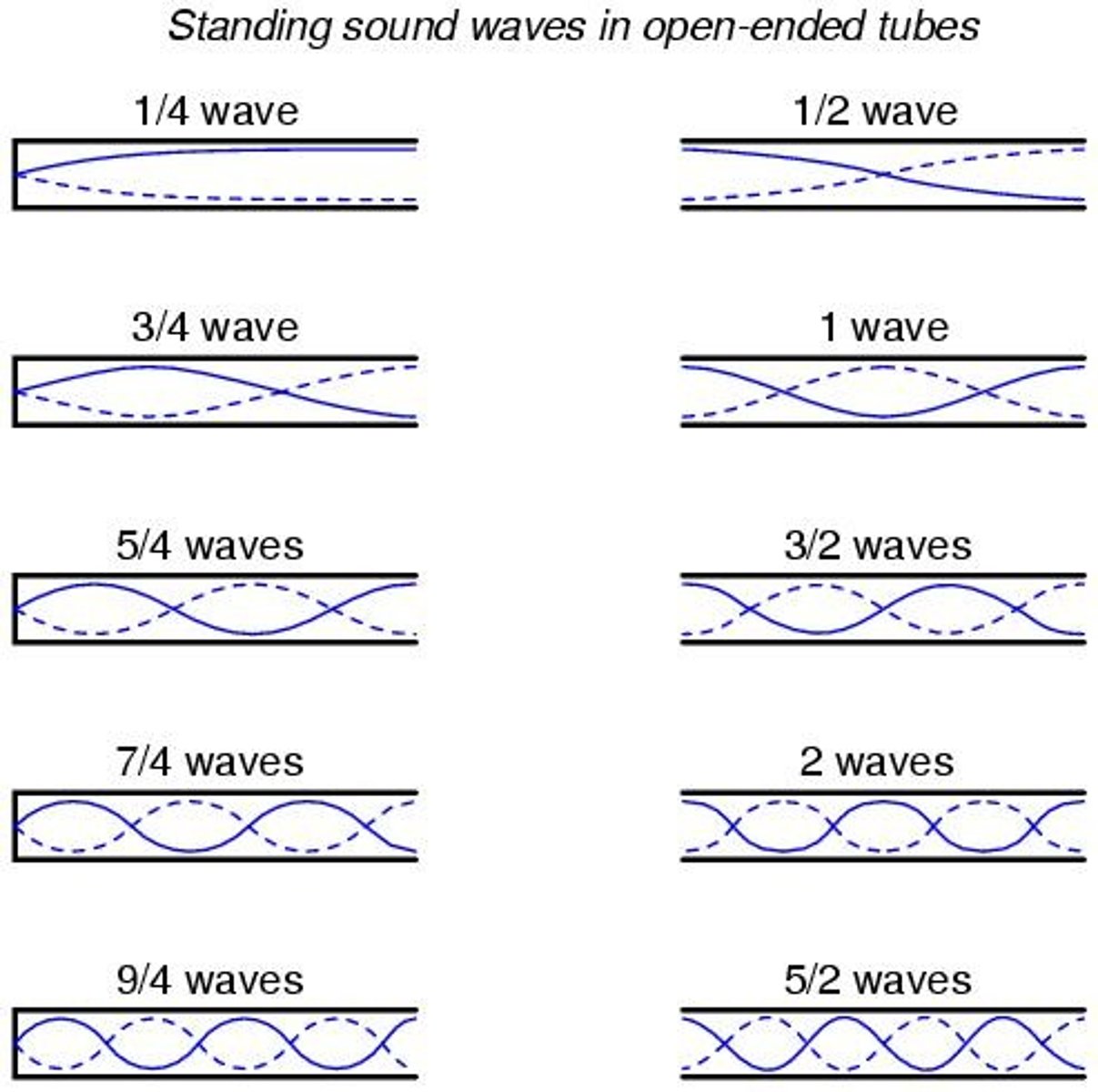
Resonance Tube Activity
Using the resonance tube, calculate the temperature of the air in the room.
Frequency of tuning fork
Data point for resonance tube activity.
Length of air column
Data point for resonance tube activity.
Wavelength
Data point for resonance tube activity.
Temperature
Data point for resonance tube activity.