Fluid and Electrolyte Balance in Human Nutrition: Chapter 7
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What are fluids composed of?
Substances composed of freely moving molecules that can conform to the shape of their container.
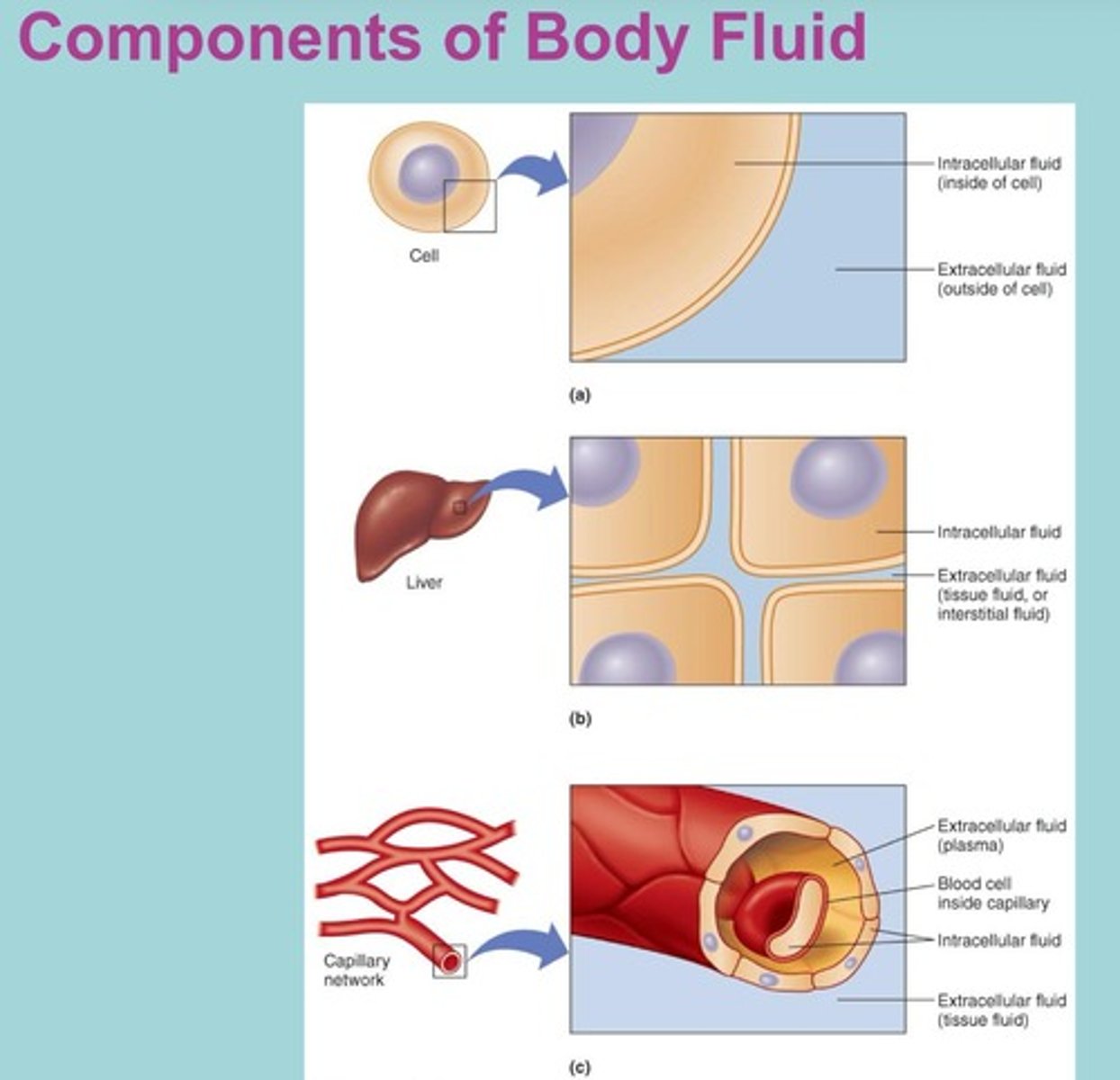
What percentage of the body's fluid is intracellular fluid?
Two-thirds of the body's fluid.
What are the two main types of extracellular fluid?
Tissue fluid and plasma.
What is tissue fluid?
Fluid found between the cells within tissues and organs.
What is plasma?
The fluid portion of blood that carries blood cells.
How does tissue type affect body fluid composition?
Lean tissues have a higher fluid content than fat tissues.
How does gender influence body fluid composition?
Males have more lean tissue and therefore more body fluid.
What effect does aging have on body fluid?
Lean tissue is lost with age, resulting in a loss of body fluid.
What are the predominant electrolytes in intracellular fluid?
Potassium and phosphorus.
What are the predominant electrolytes in extracellular fluid?
Sodium and chloride.
What is the function of fluids in the body?
Fluids dissolve and transport substances, account for blood volume, help maintain body temperature, and protect and lubricate tissues.
How do fluids help maintain blood volume?
Increased blood volume can raise blood pressure, while decreased blood volume can lower it.
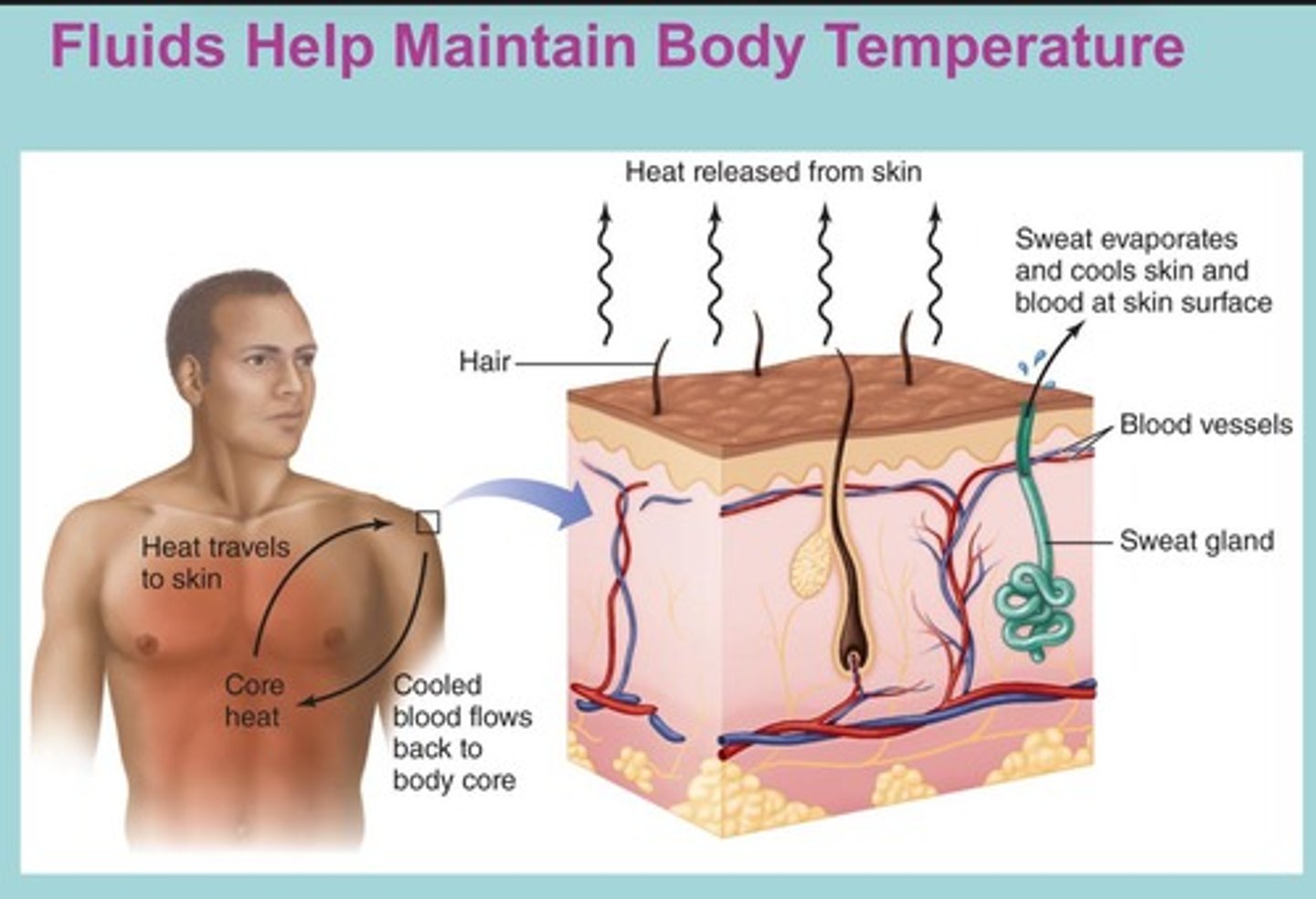
What is the role of water in temperature regulation?
Water has a high heat capacity, keeping body fluids stable and allowing sweating to cool the body.
What is cerebrospinal fluid's function?
It protects the brain and spinal column.
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
A mechanism that maintains charge across cell membranes by moving sodium and potassium ions.
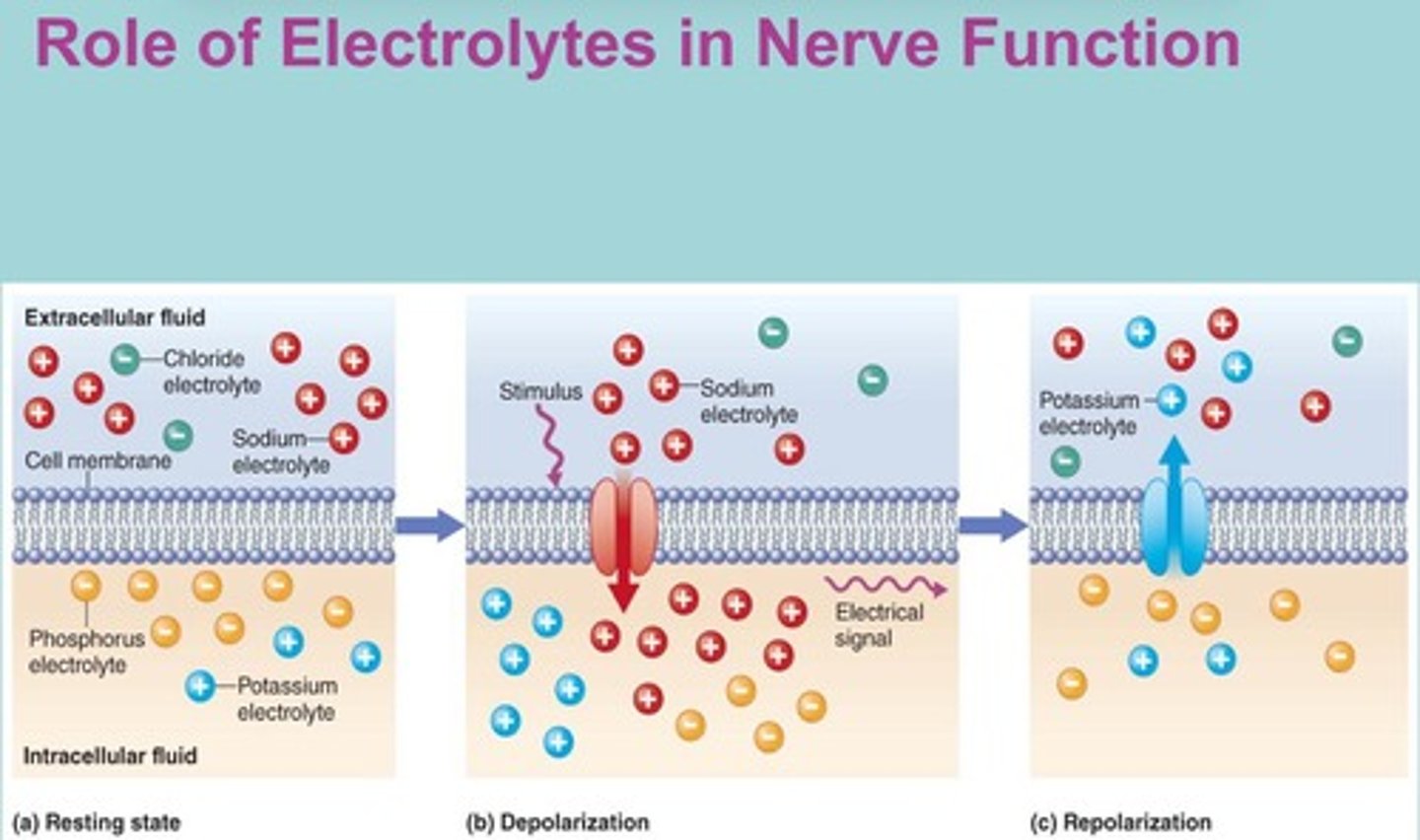
How do electrolytes enable nerve function?
Movement of sodium and potassium changes the electrical charge across cell membranes, carrying nerve impulses.
What stimulates muscle contraction in response to electrolytes?
The movement of calcium into muscle cells stimulates contraction.
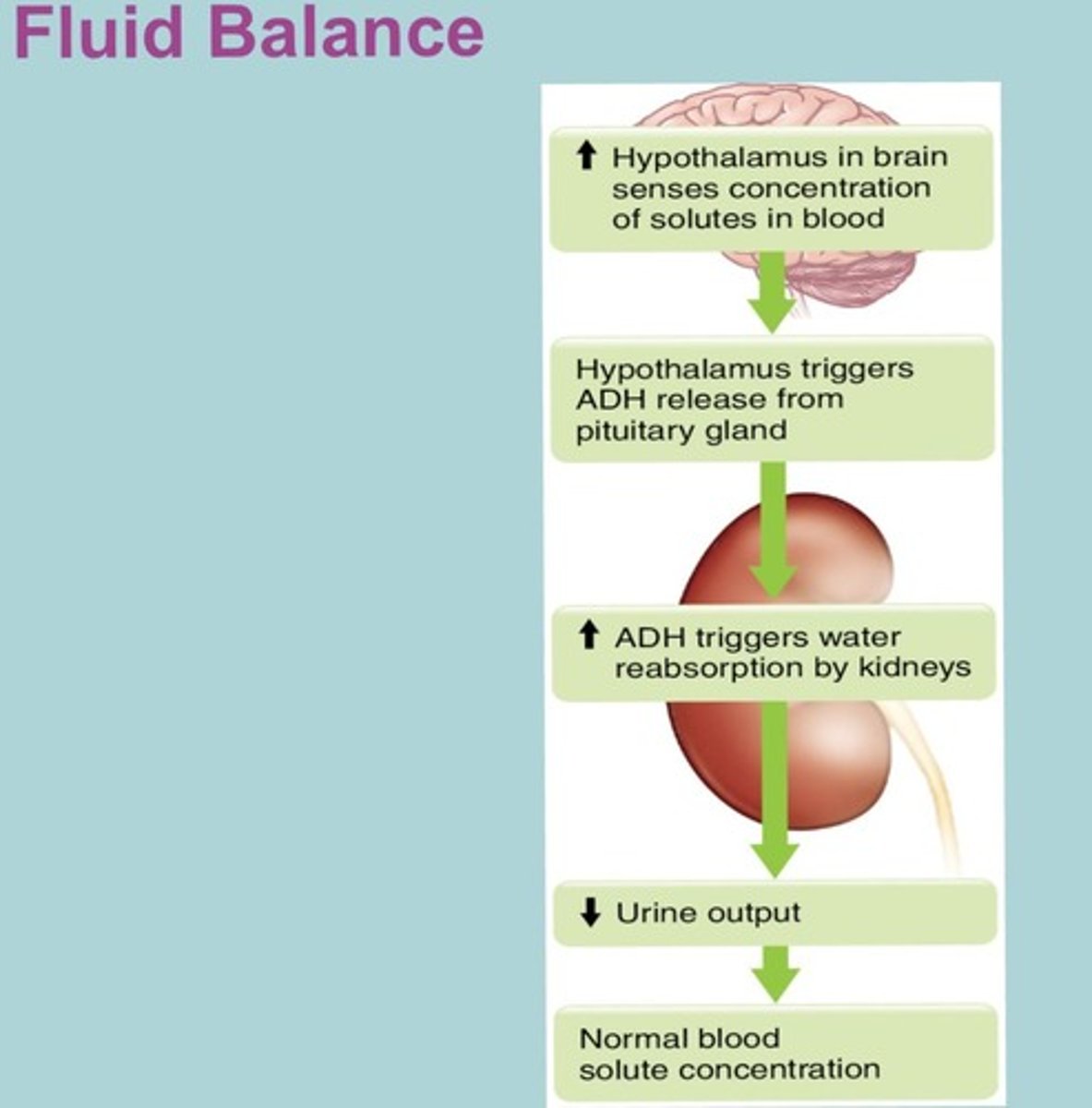
What regulates fluid balance in the body?
Several mechanisms, including the thirst mechanism controlled by nerve cells.
What are some ways the body loses water?
Urine, sweat, evaporation, exhalation, and feces.
What are some ways the body gains water?
Beverages, food, and metabolic water.
What is the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
ADH helps regulate water retention in the body.
What are the potential effects of drinking too much water?
Overhydration can lead to dilution of sodium (hyponatremia).
What happens if you don't drink enough water?
Insufficient water intake can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Who are especially vulnerable to dehydration?
Infants and the elderly
What are the potential health risks of energy drinks?
High caffeine levels can cause a dramatic rise in blood pressure and heart rate.
What is the recommended daily intake of sodium?
1.5 g/day is required; no more than 2.3 g/day is recommended.
What condition results from excessive sodium intake?
Hypernatremia: abnormally high blood sodium concentration.
What can cause hyponatremia?
Prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive water intake without sodium replacement.
What is the recommended daily intake of potassium?
4.7 g/day (4,700 mg/day).
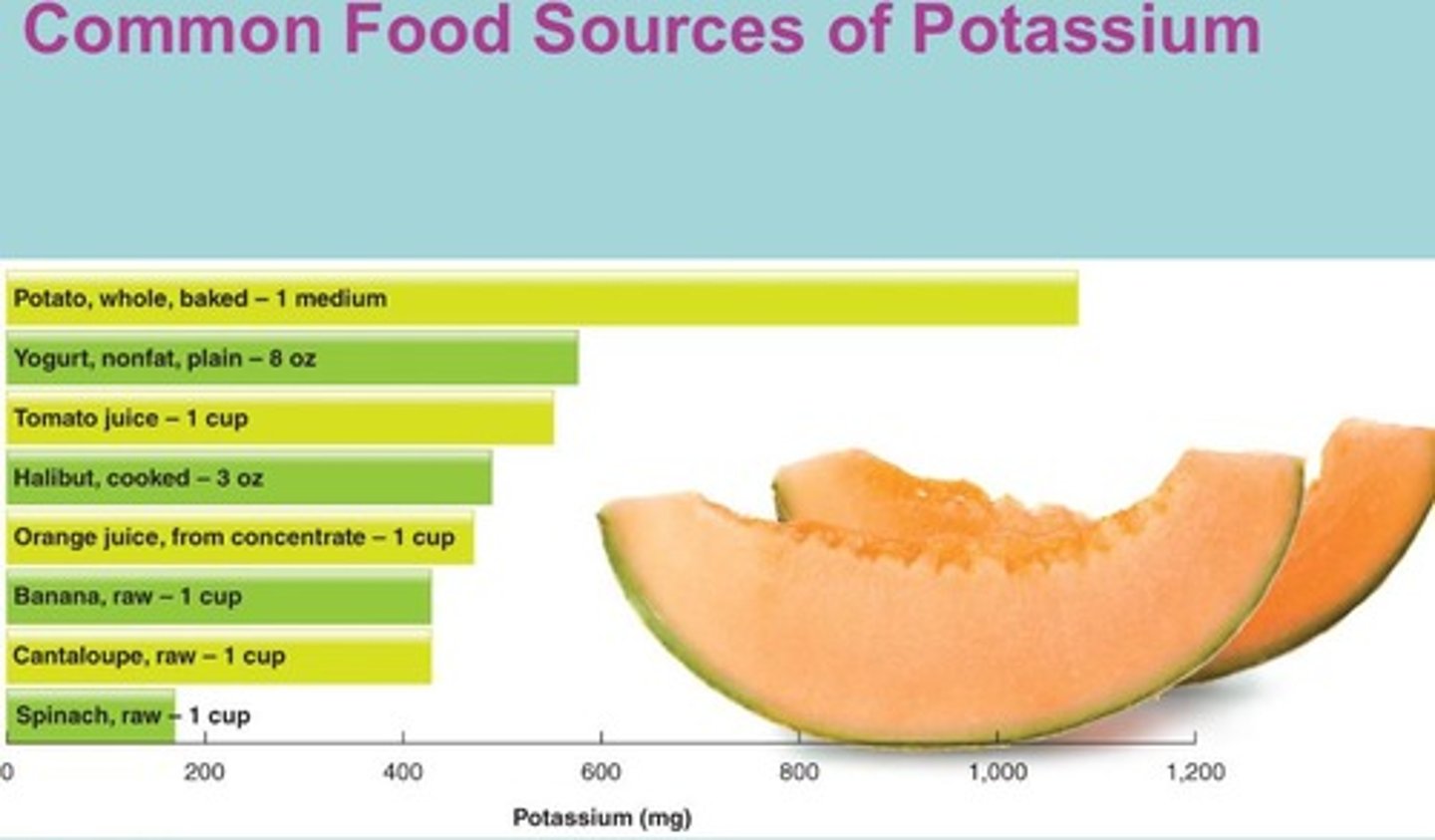
What are the functions of potassium?
Fluid and electrolyte balance, muscle contractions, and nerve impulse transmission.
What condition can result from excessive potassium intake?
Hyperkalemia: a high blood potassium level that can alter heart rhythm.
What is the minimum recommended intake of chloride?
2.3 g/day (2,300 mg/day).
What is phosphorus's role in the body?
Fluid balance, bone formation, and regulating biochemical pathways.

What can happen if you consume too much phosphorus?
High blood levels can occur with kidney disease or excessive vitamin D, causing muscle spasms and convulsions.
What are the common causes of dehydration?
Diarrhea, vomiting, fever, burns, poorly controlled diabetes, and diuretic abuse.
What are the three common types of heat illnesses linked to dehydration?
Heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke.
What are the symptoms of heat cramps?
Painful muscle cramps in the abdomen, arms, or legs during vigorous activity in heat.
What are the symptoms of heat exhaustion?
Cramps, weakness, vomiting, dizziness, and elevated blood pressure and pulse.
What occurs during heatstroke?
Body temperature regulation fails, leading to rapid pulse, hot and dry skin, and high body temperature.
What is the primary function of sodium in the body?
Fluid and electrolyte balance, blood pressure regulation, and nerve impulse transmission.
What foods are typically high in sodium?
Processed foods and restaurant foods.
What is the role of chloride in the body?
Maintaining fluid balance, assisting the immune system, and being a component of HCl in the stomach.
What can happen if you don't consume enough sodium?
Hyponatremia: an abnormally low blood sodium level.
What are the symptoms of hyponatremia?
Headaches, dizziness, fatigue, nausea/vomiting, and muscle cramps.
What are common sources of potassium?
Fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
What can excessive water intake without sodium lead to in athletes?
Hyponatremia, especially in marathon runners.