Intro to Entomology
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Economic reasons to study insects
Insects affect human economies by destroying crops, contaminating stored food, and infesting livestock and structures; examples include locust swarms, grain weevils, and termites.
Medical reasons to study insects
Many insects transmit human and animal diseases—fleas spread plague, mosquitoes transmit malaria and yellow fever, and flies spread filariasis and other pathogens.
Biological abundance and diversity of insects
Insects make up over half of all known species, with an immense variety in form, habitat, and function; their total biomass surpasses that of all vertebrates combined.
Food-web dynamics
Insects serve as herbivores, decomposers, predators, and prey, recycling nutrients and sustaining ecosystems; birds, reptiles, and fish depend heavily on them as food sources.
Insect products and pollination
Humans use insect products like honey, silk, shellac, and dyes; pollinating insects such as bees are vital for fruit and crop reproduction.
Scientific importance of insects
Insects are key model organisms for research in genetics, physiology, ecology, and evolution because of their diversity and short life cycles.
Aesthetic value of insects
Butterflies, beetles, and fireflies provide beauty and inspiration in art, culture, and conservation.
Tagma
The main body divisions of insects: head, thorax, and abdomen, each specialized for different functions such as sensing, locomotion, and reproduction.

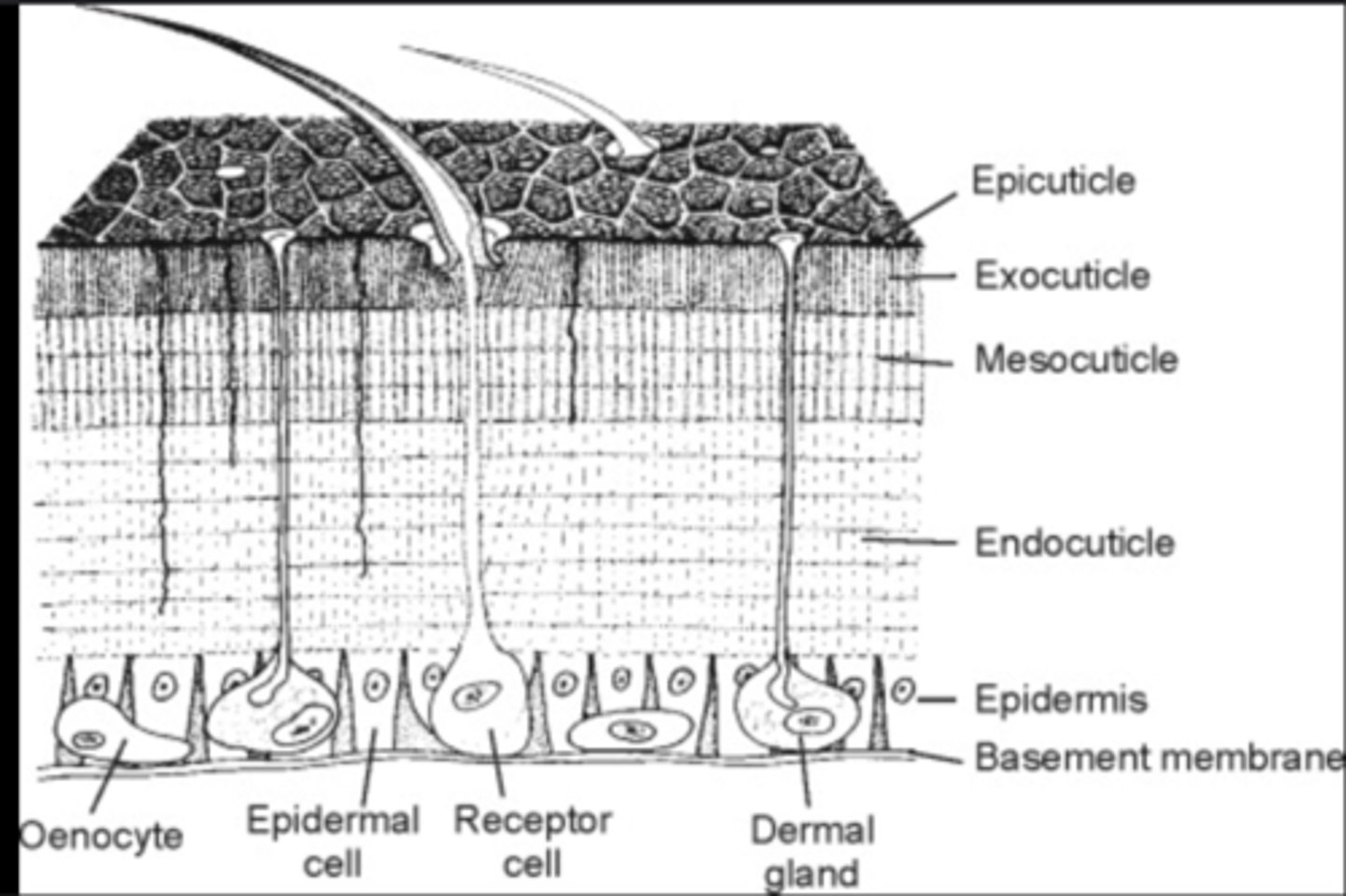
Exoskeleton
A rigid external covering made of chitin and proteins that protects the insect, prevents desiccation, and provides muscle attachment; must be molted for growth.
Integument
The entire body covering, including the living epidermis and the non-living cuticle layers above it.
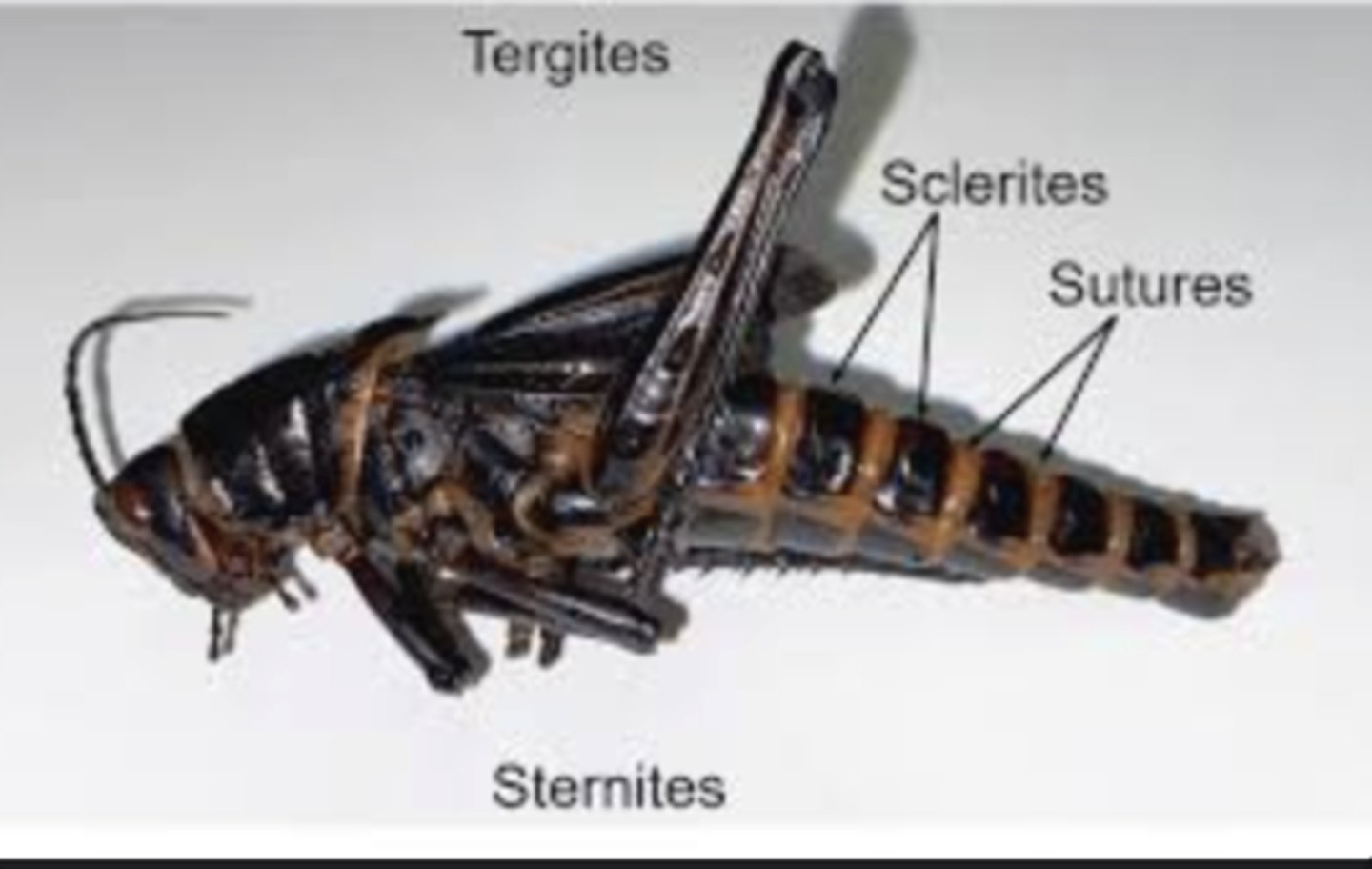
Sclerites
Hardened plates of the exoskeleton that give structural strength; joined by flexible membranes for movement.
Basement membrane
Thin layer beneath the epidermis separating it from internal tissues and serving as a foundation for secretion of new cuticle.
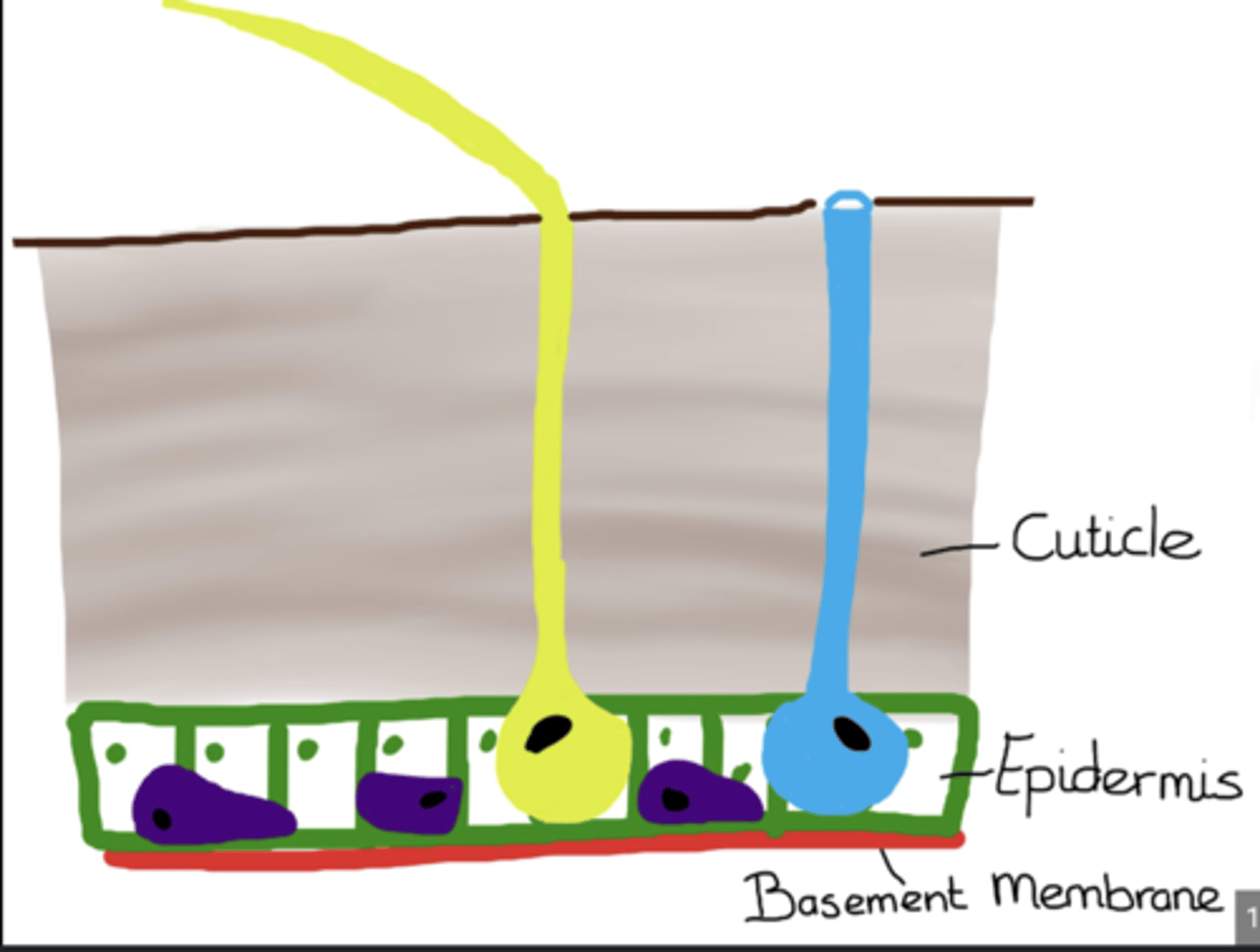
Epidermis
Single layer of living cells that secretes and repairs the insect's cuticle; plays a role in molting.
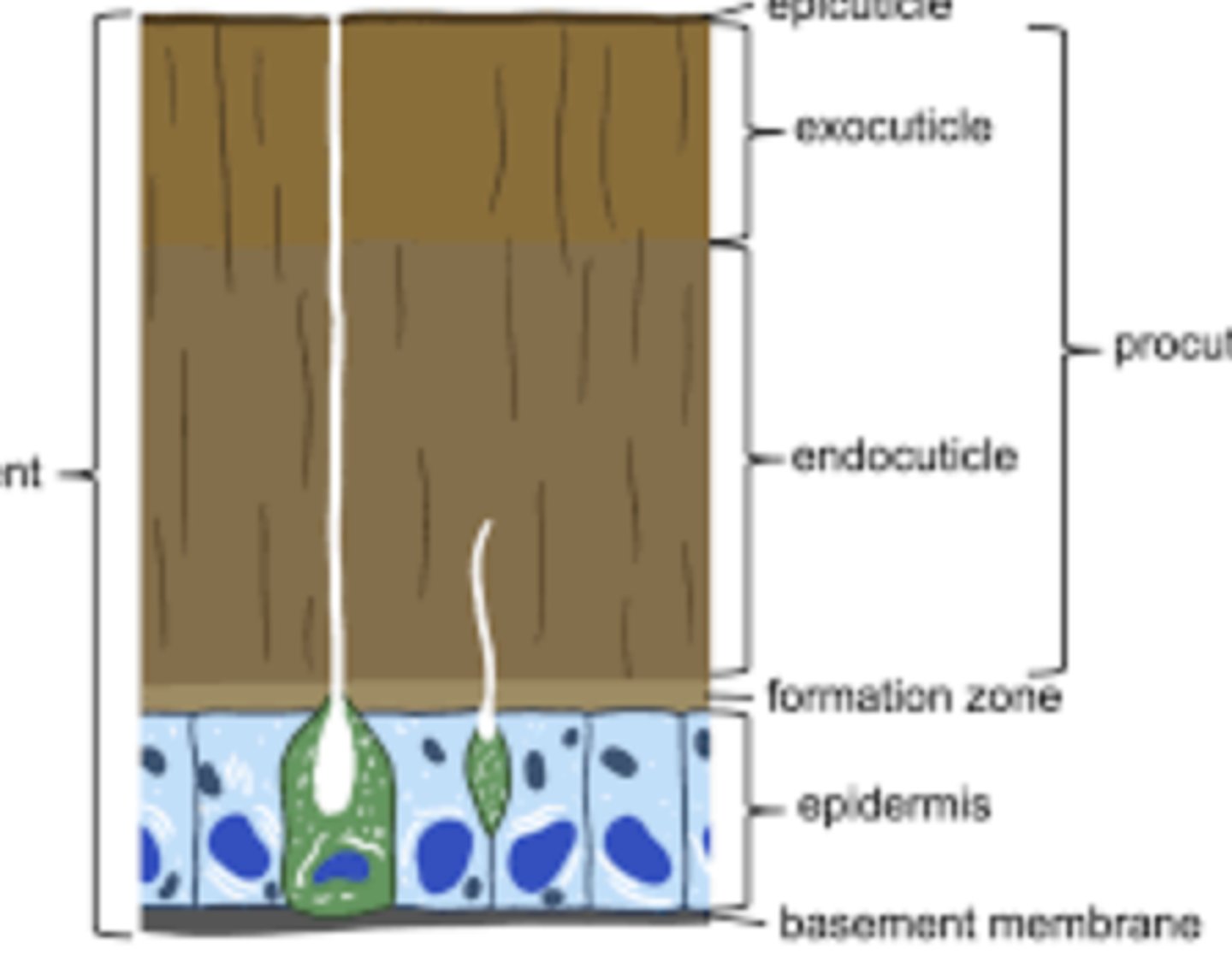
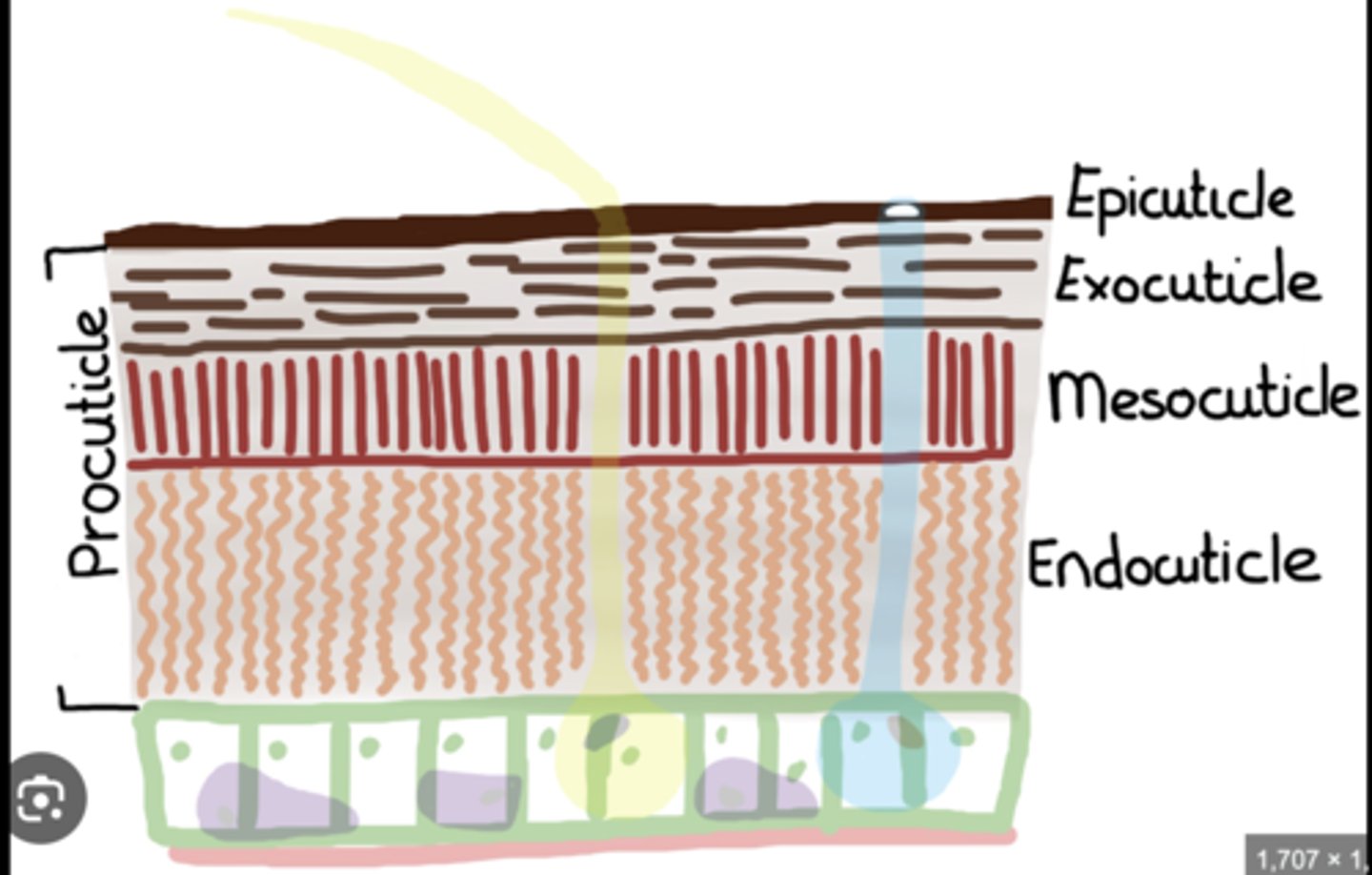
Cuticle
Non-cellular outer layer secreted by the epidermis; includes the waxy epicuticle and the supportive procuticle.
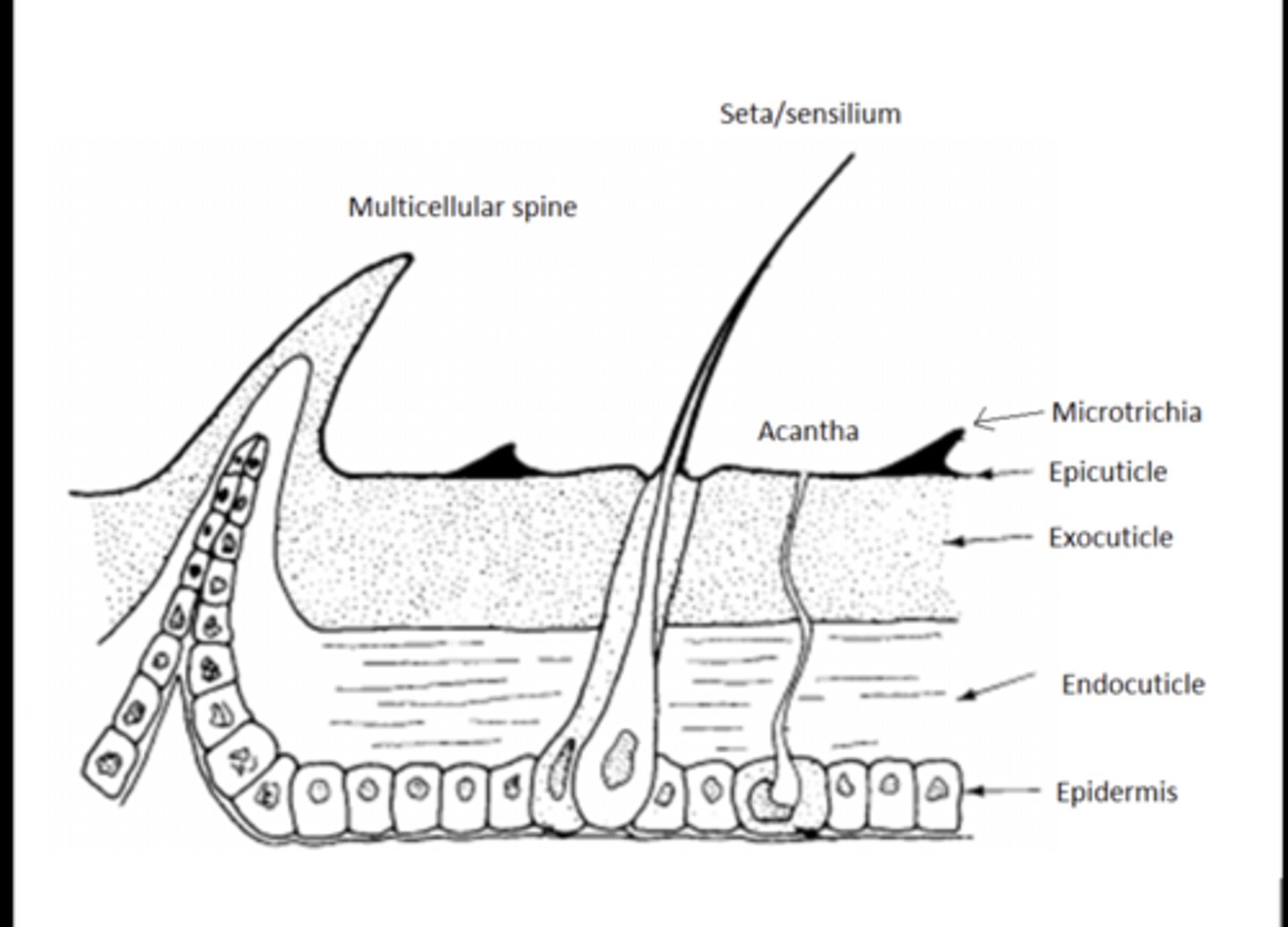
Epicuticle
Thin, outermost waterproof layer that prevents dehydration and protects against chemicals.
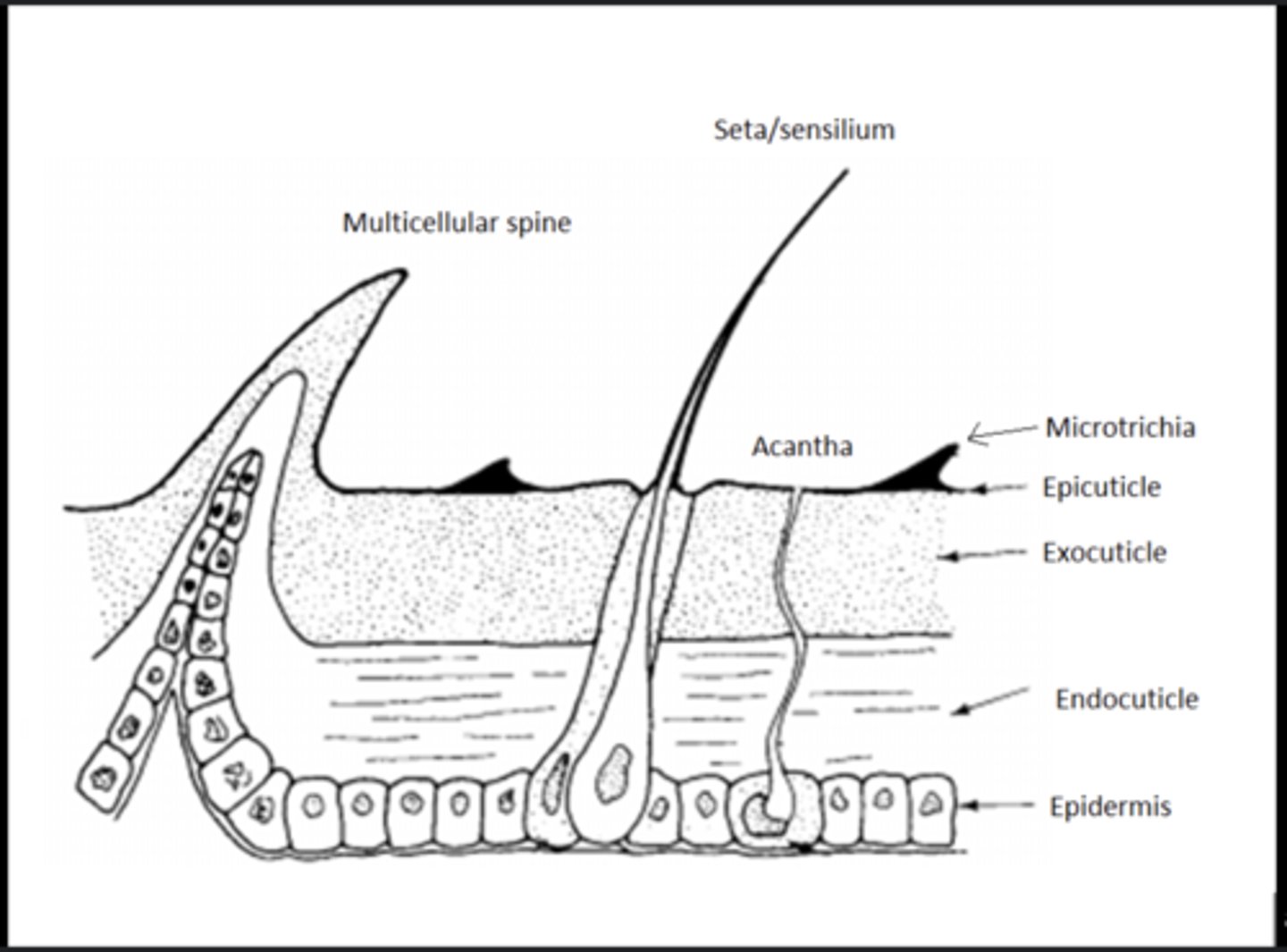
Procuticle
Thicker inner portion of the cuticle made of chitin and proteins that provide strength and flexibility.
Chitin
Long-chain polysaccharide forming the framework of the exoskeleton, similar in structure to cellulose but with nitrogen groups.
Sclerotin / Sclerotization
Proteins and the chemical process that harden the cuticle through cross-linking, increasing durability and color.
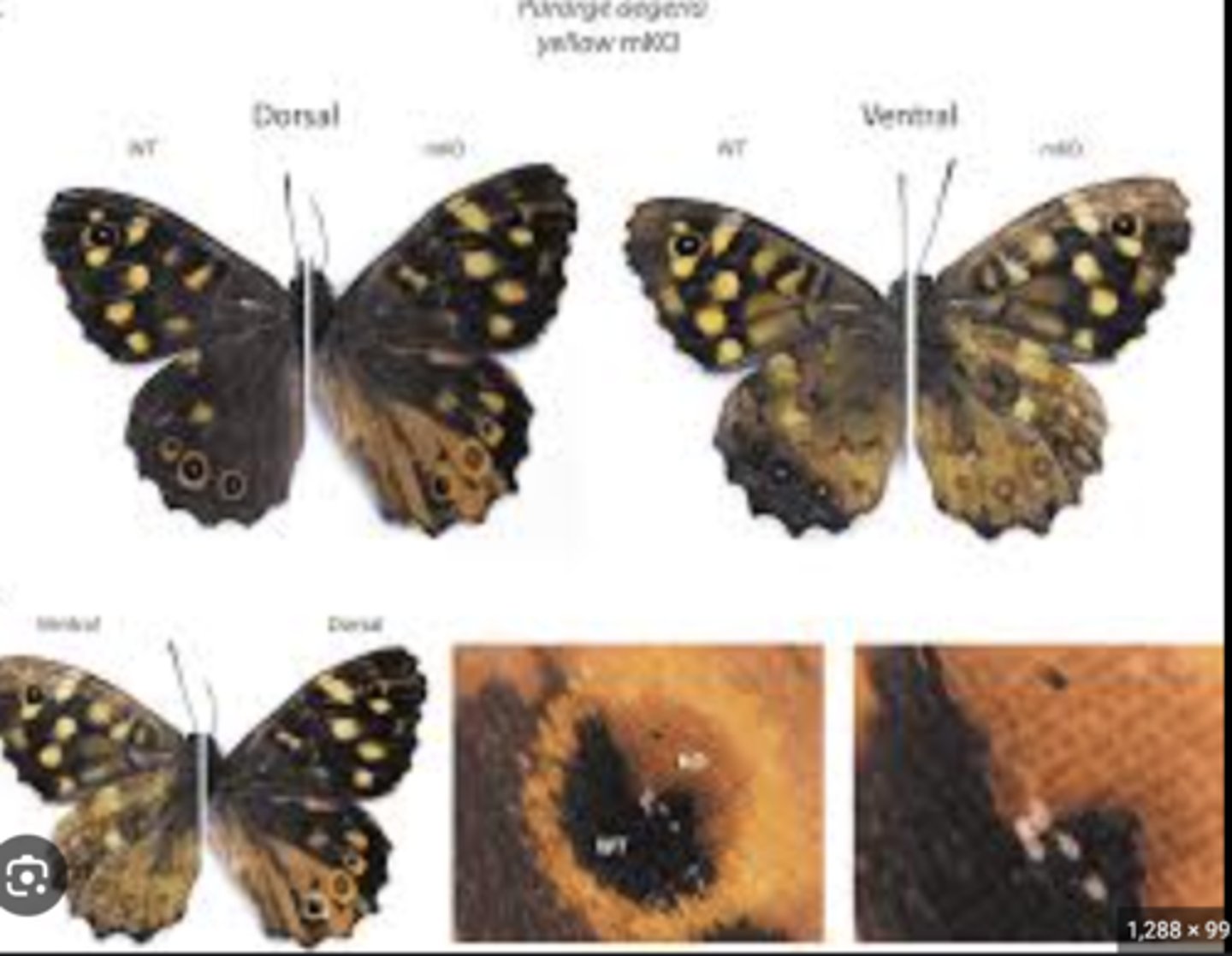
Consequences of exoskeleton
Allows strength and protection but restricts growth, requiring periodic molting and limiting body size.
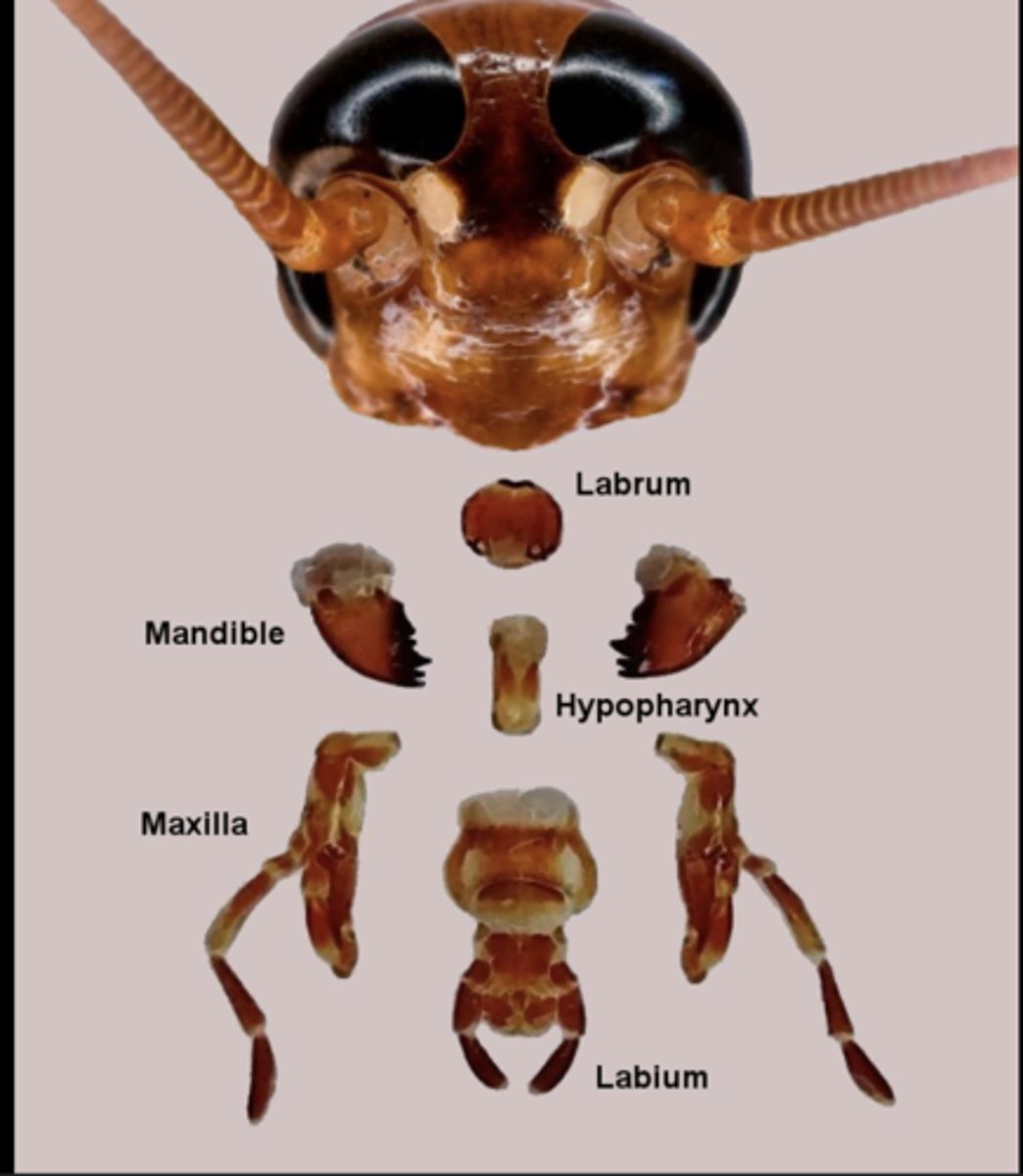
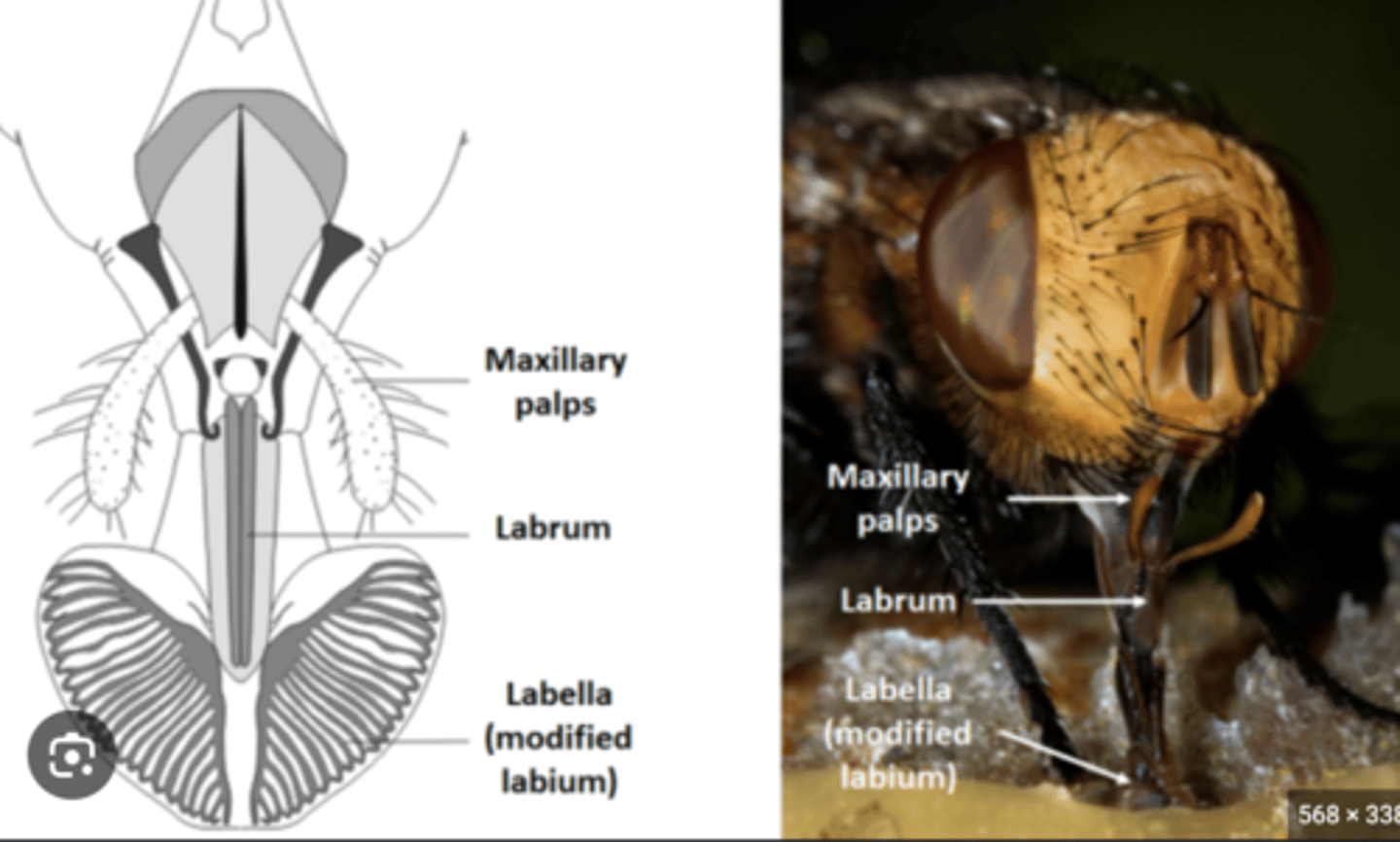
Labrum
Upper lip that helps hold and manipulate food during feeding.
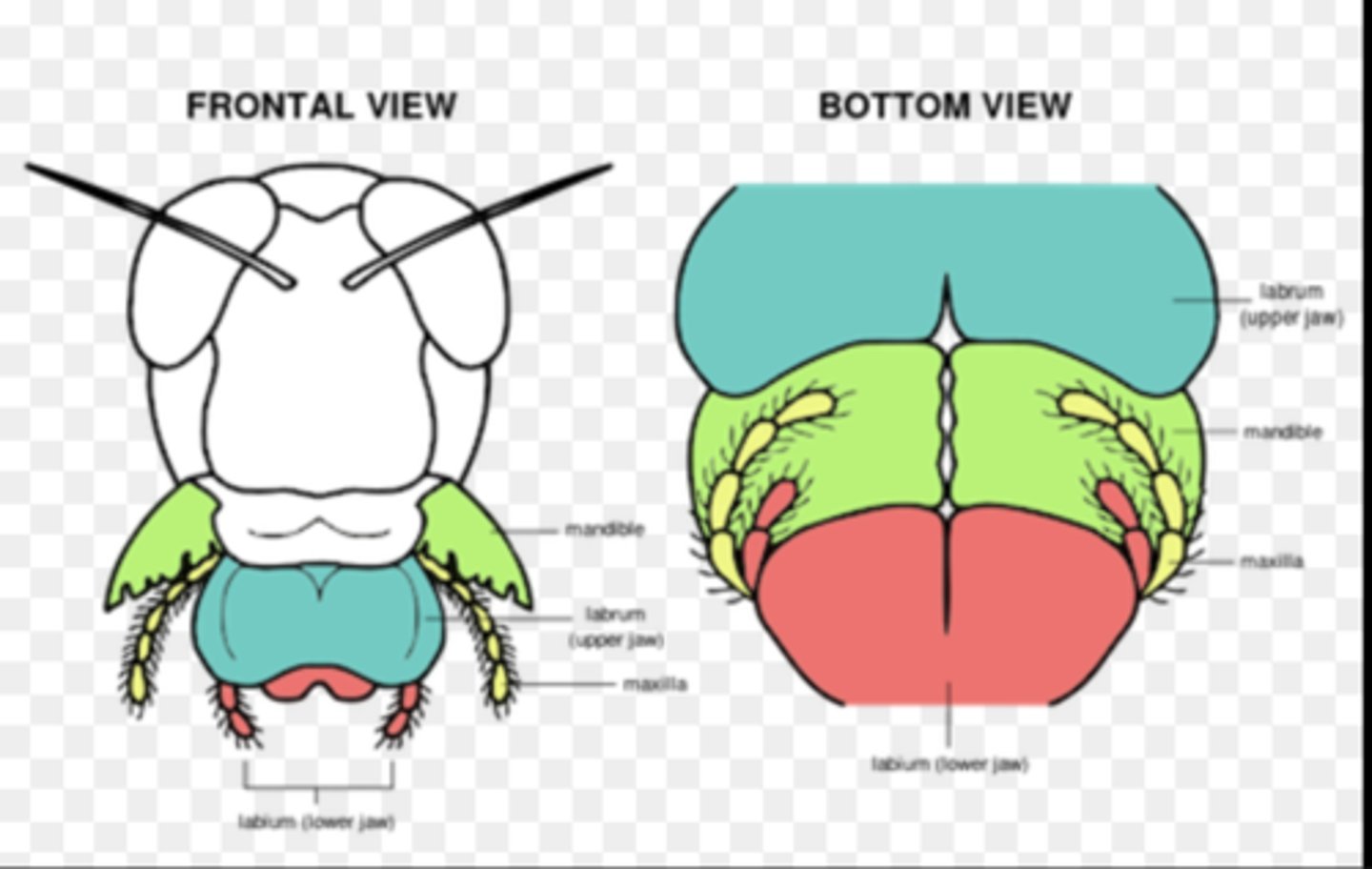
Mandibles
Paired, jaw-like mouthparts used for biting, chewing, and cutting solid food.
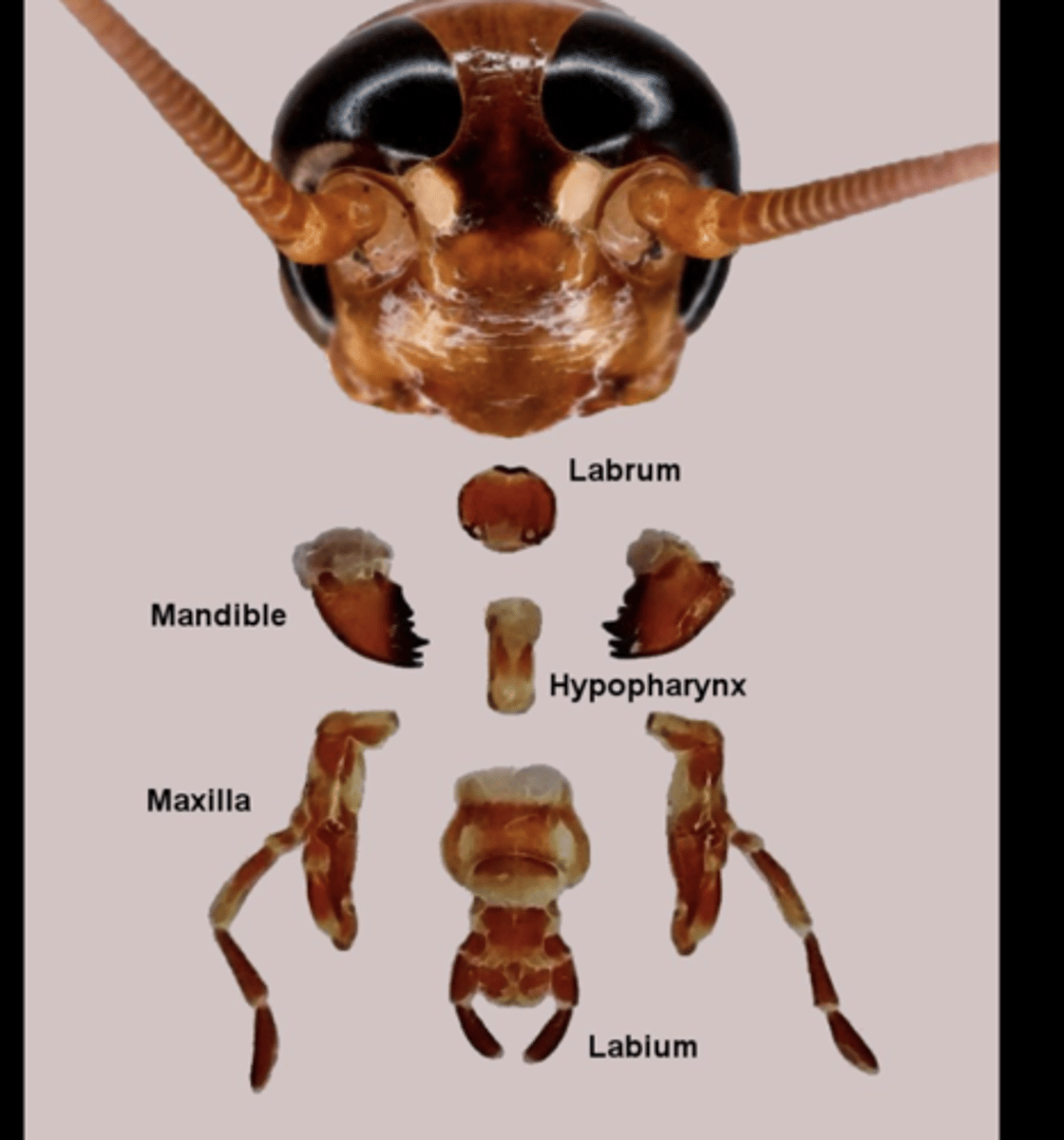
Maxillae
Paired mouthparts that manipulate food and assist mandibles; each bears a sensory palp.
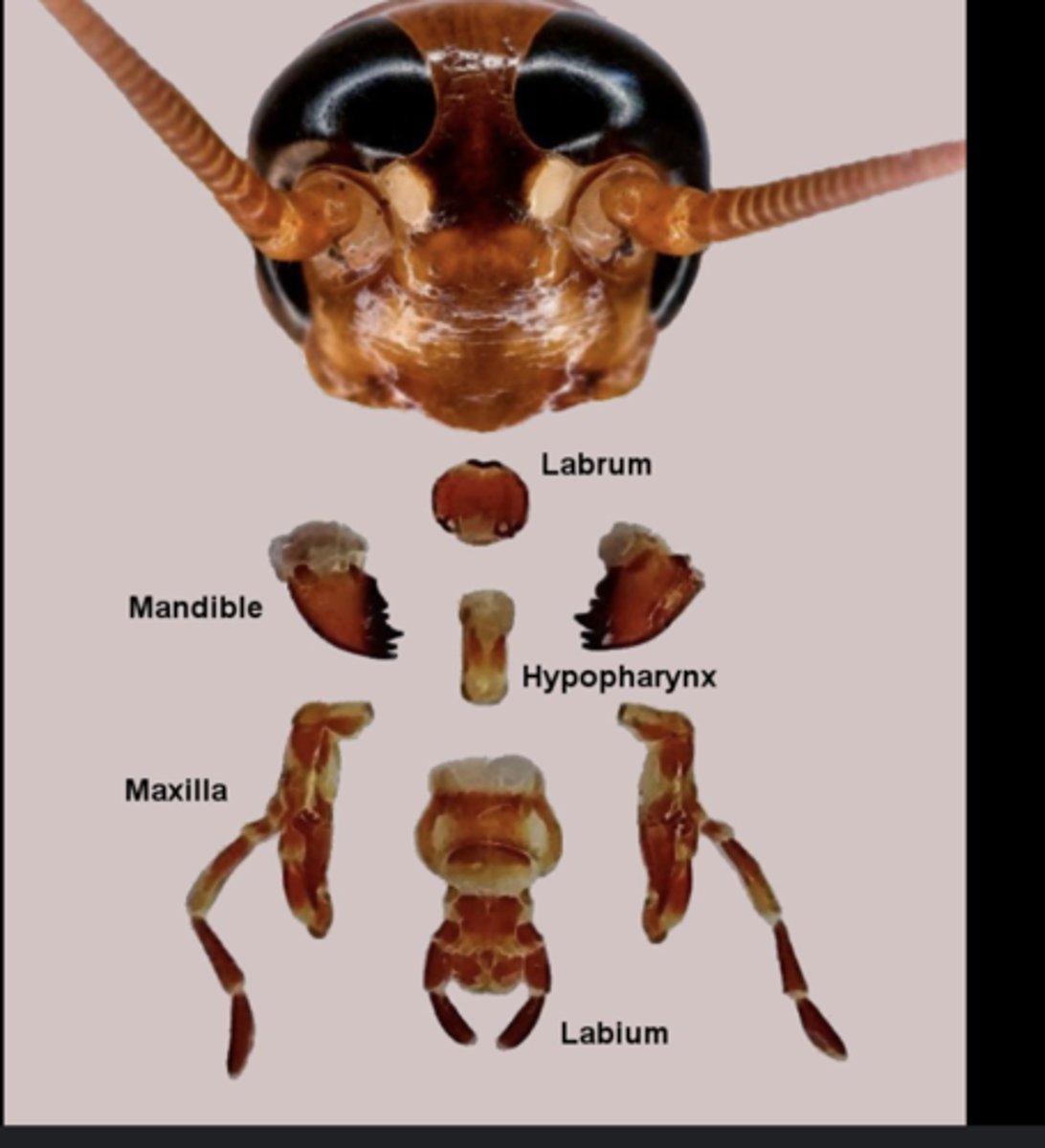
Labium
Lower lip structure that assists food handling and supports palps.

Palps
Sensory appendages on maxillae or labium that detect taste and texture.
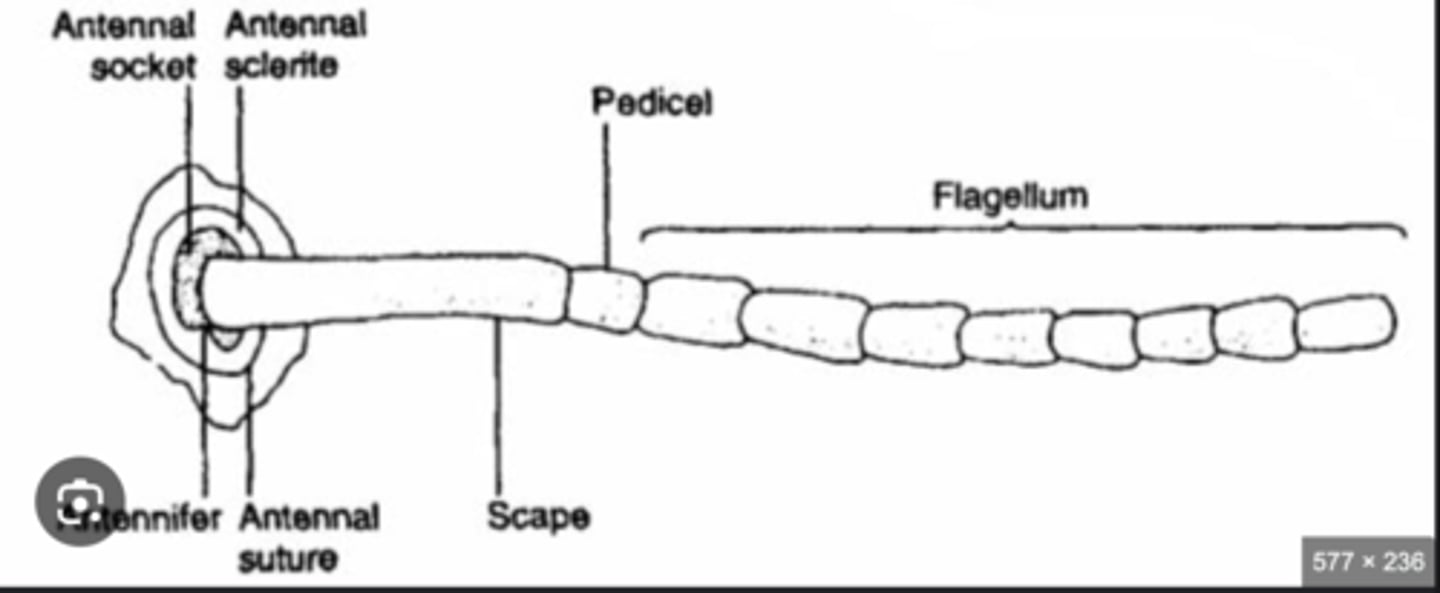
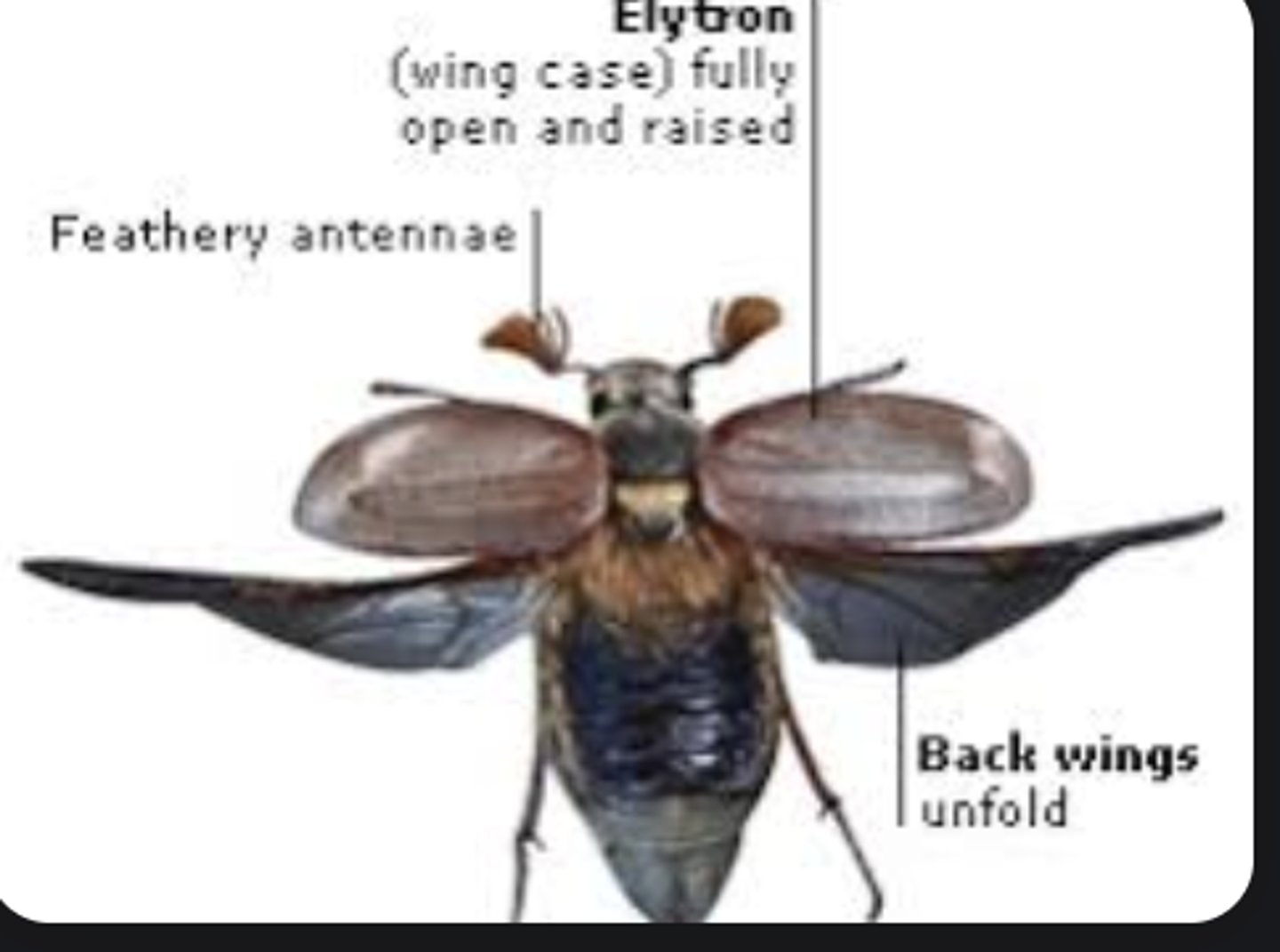
Antennae
Paired sensory appendages detecting chemical cues (smell), movement, humidity, and sometimes sound.
Scape, Pedicel, Flagellum
Three main antenna segments—scape (base), pedicel (middle, often with sensory organs), flagellum (distal section, may have many subsegments).
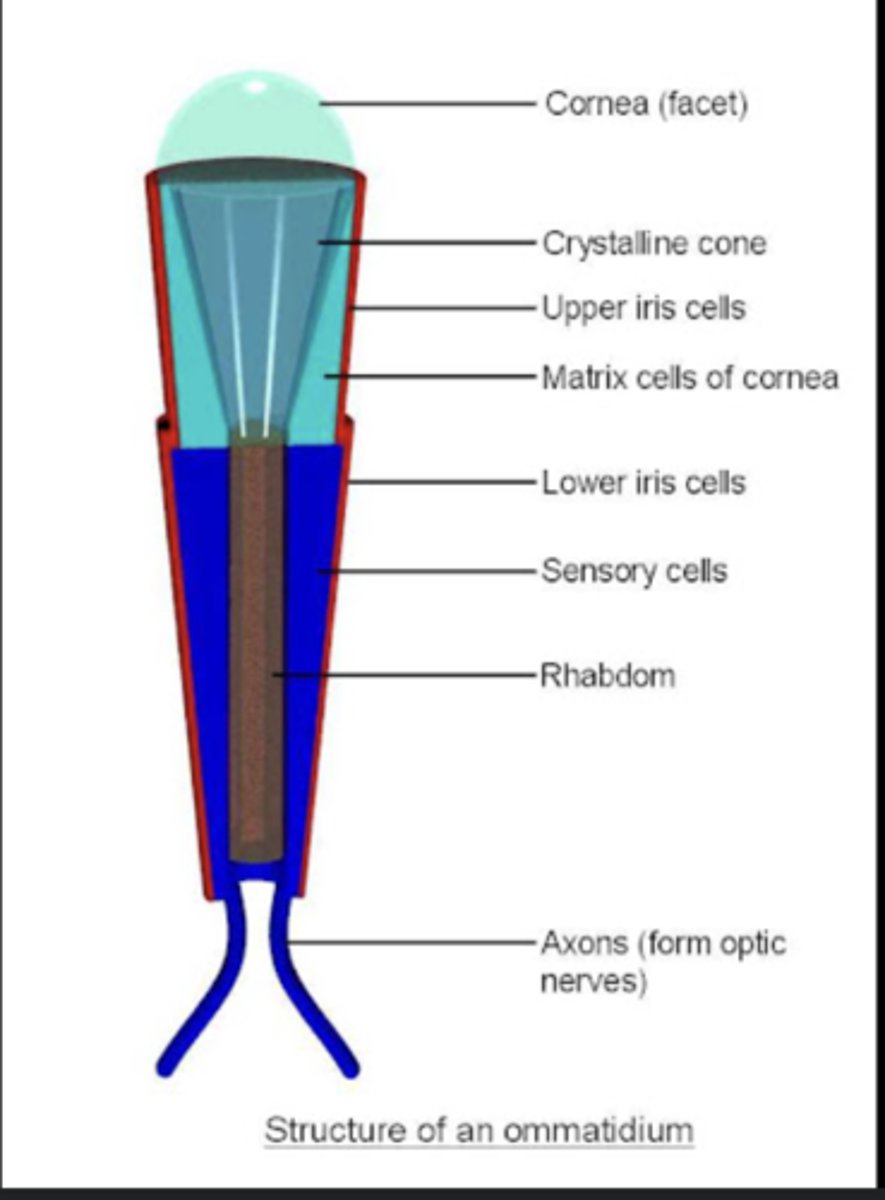
Compound eyes
Large eyes made of many ommatidia providing wide field vision and motion detection; capable of perceiving color and ultraviolet light.
Ommatidium
A single visual unit in a compound eye, containing a lens, photoreceptor cells, and pigment cells.
Ocelli
Simple eyes that detect light intensity and aid in maintaining equilibrium; not image-forming.
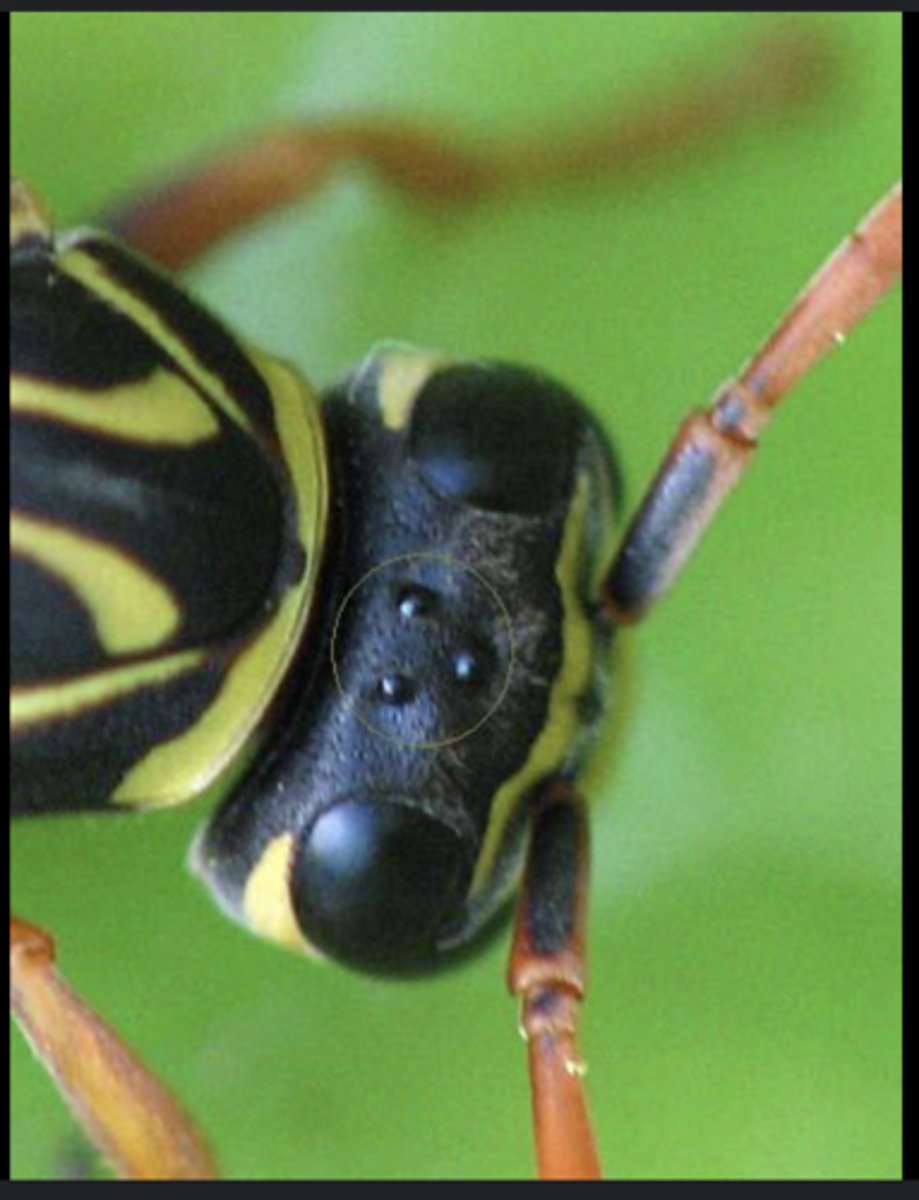

Stemmata
Simple larval eyes capable of basic image formation; used by holometabolous larvae.

Thorax
Middle body region composed of three segments (pro-, meso-, metathorax) bearing legs and wings.
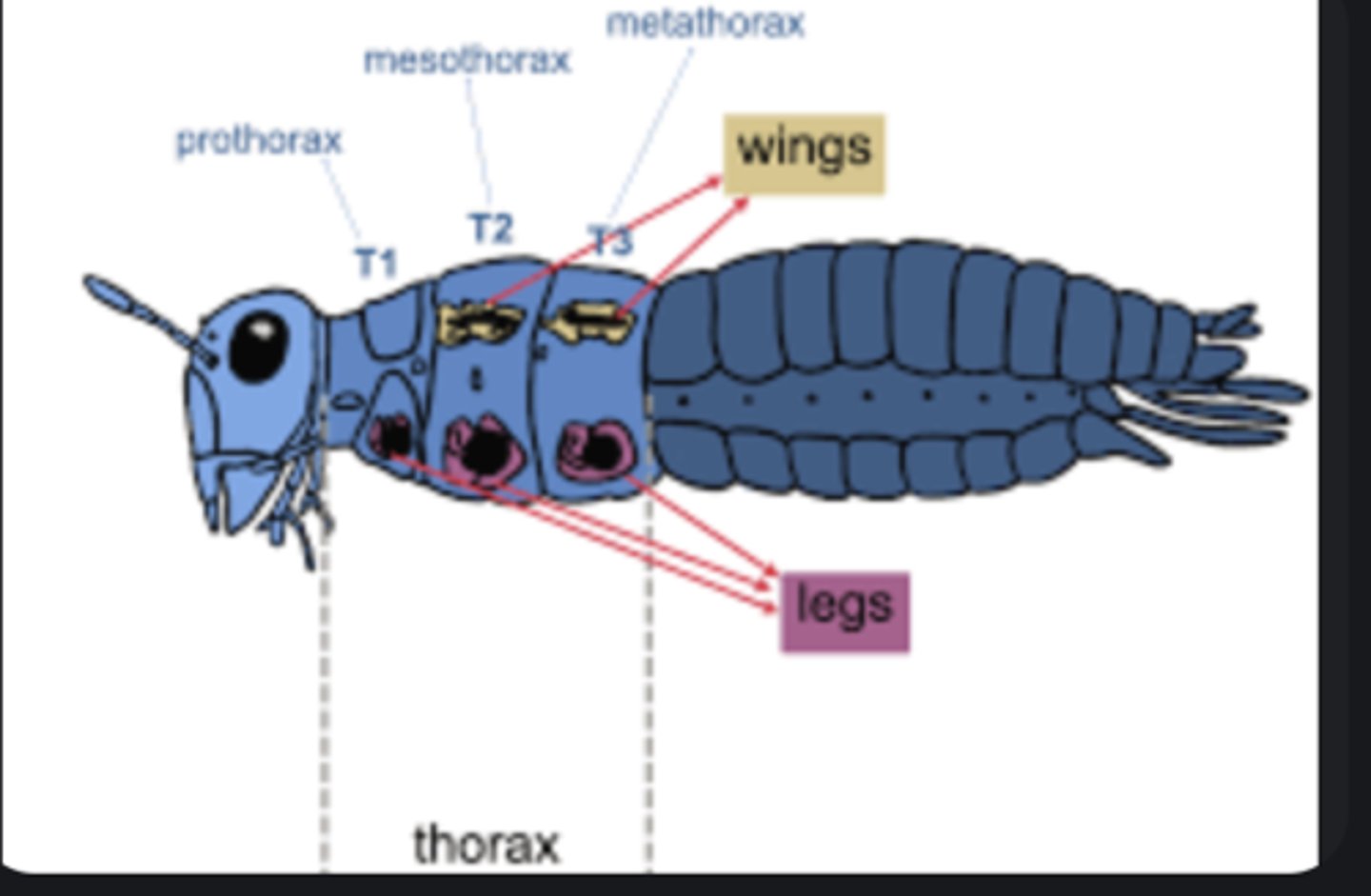
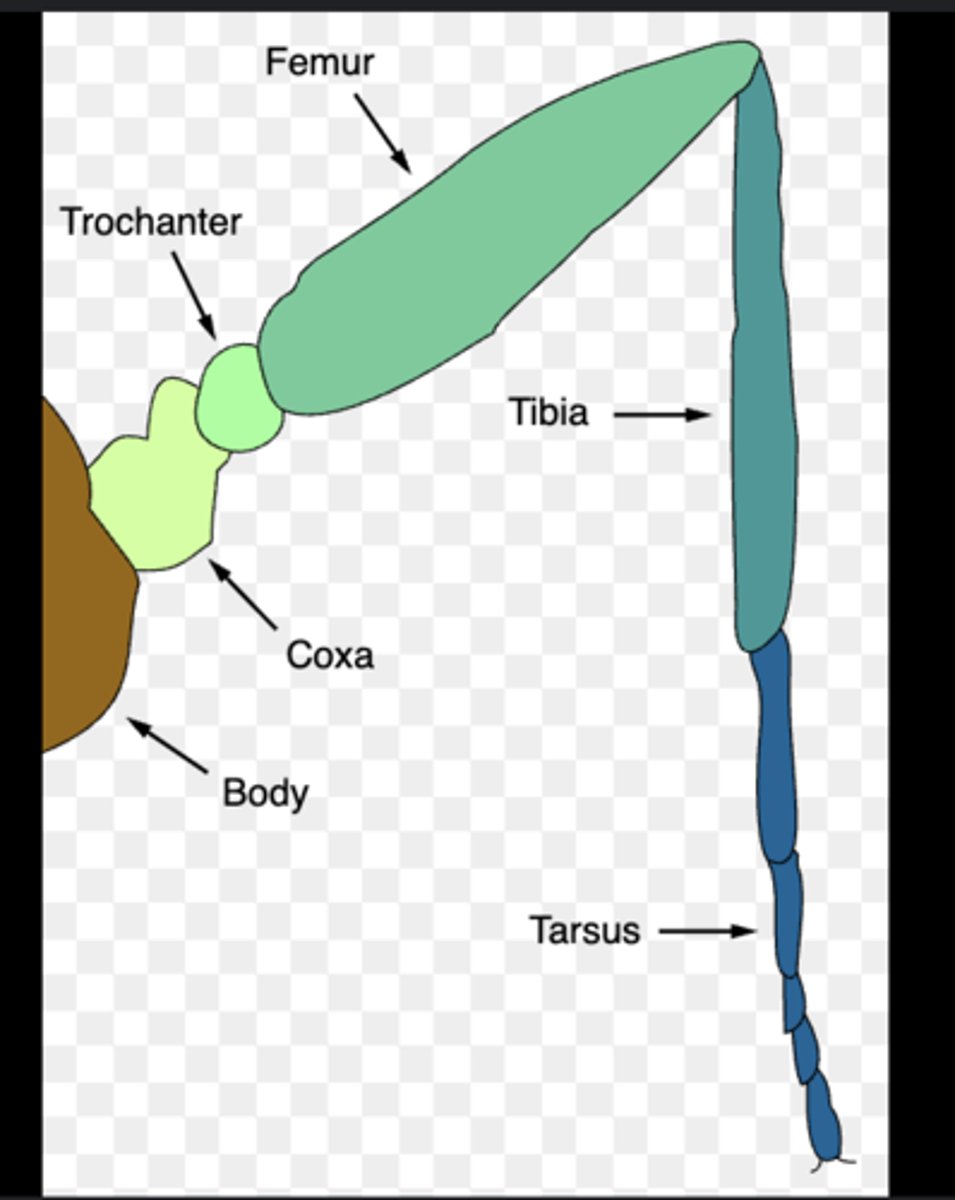
Leg segments
Five parts: coxa (base), trochanter, femur, tibia, and tarsus (foot).
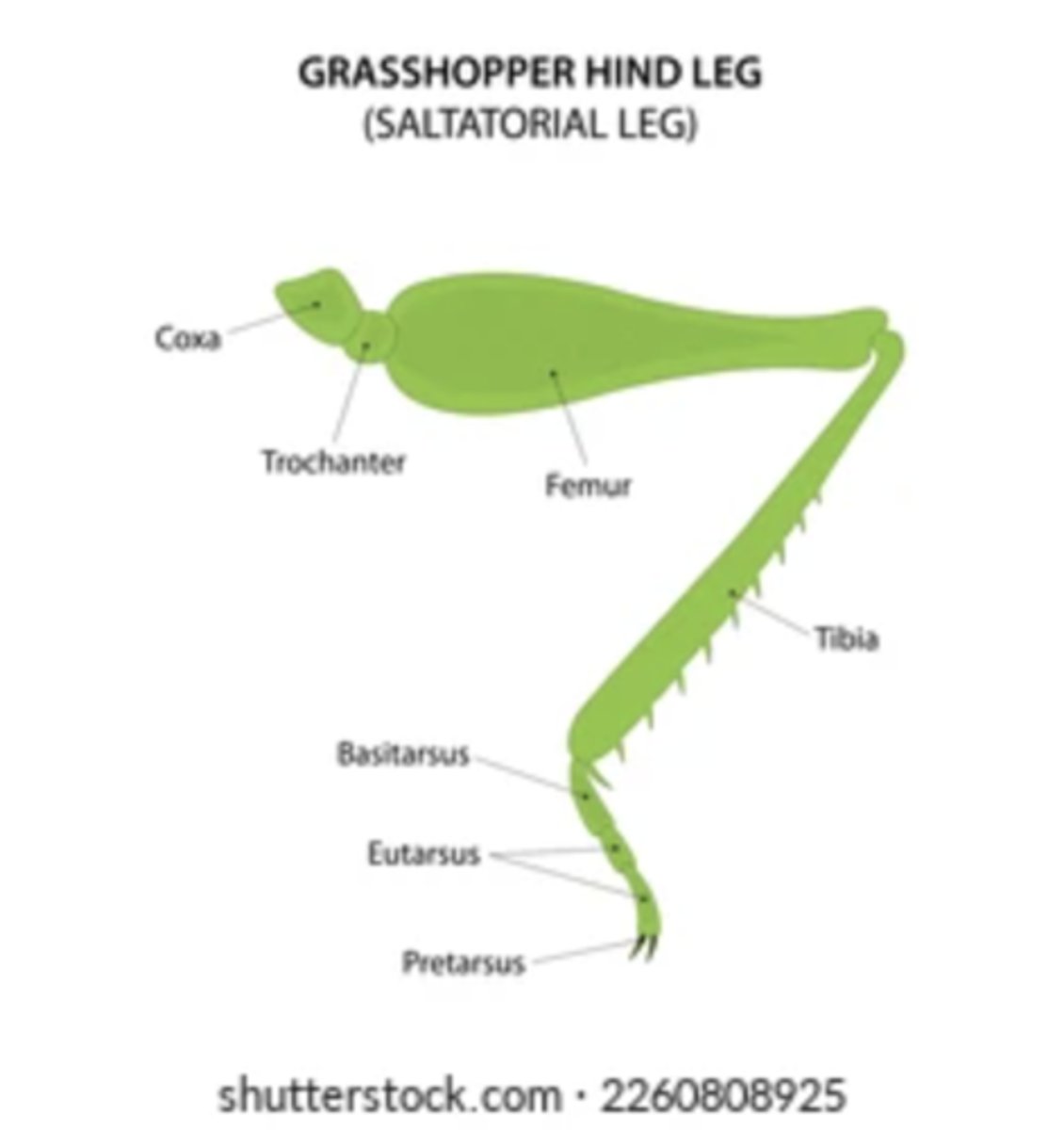
Saltatorial legs
Adapted for jumping; characterized by enlarged femurs (e.g., grasshoppers).
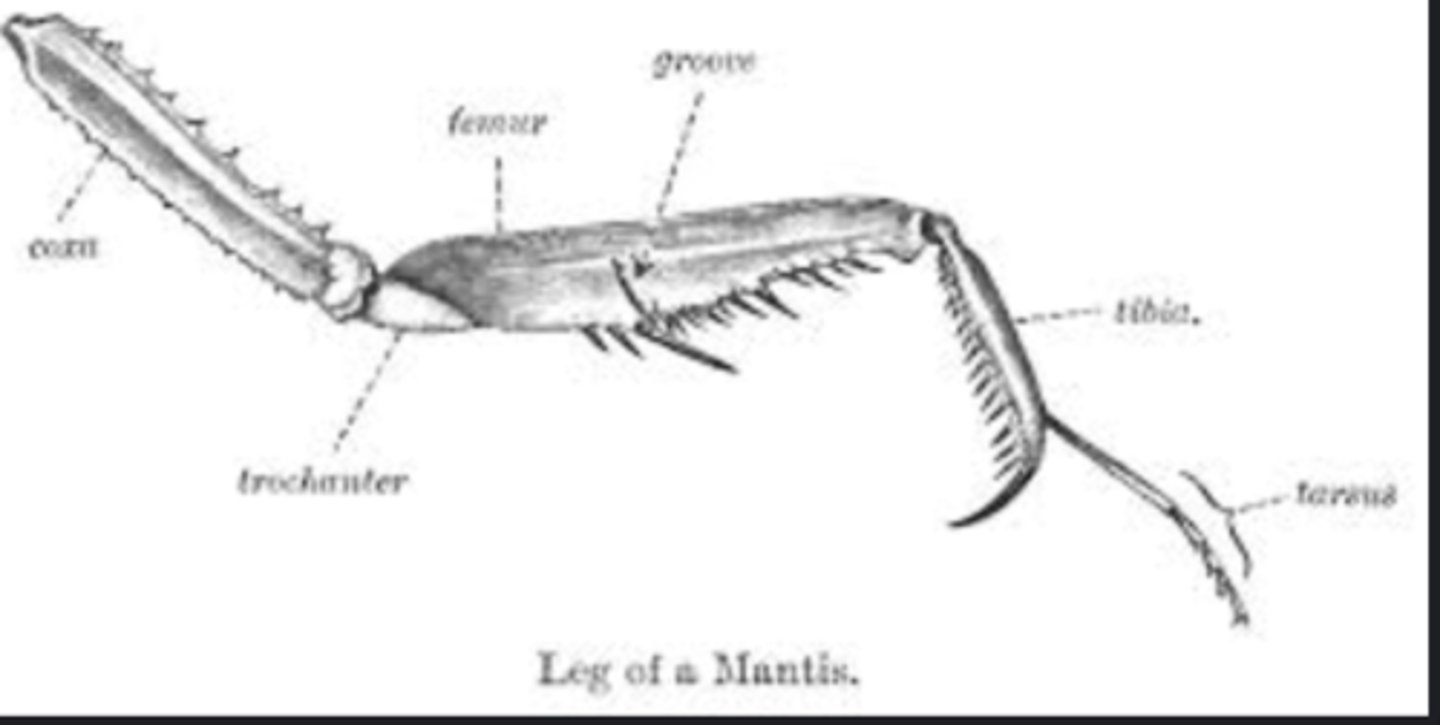
Raptorial legs
Modified for grasping prey (e.g., praying mantis).
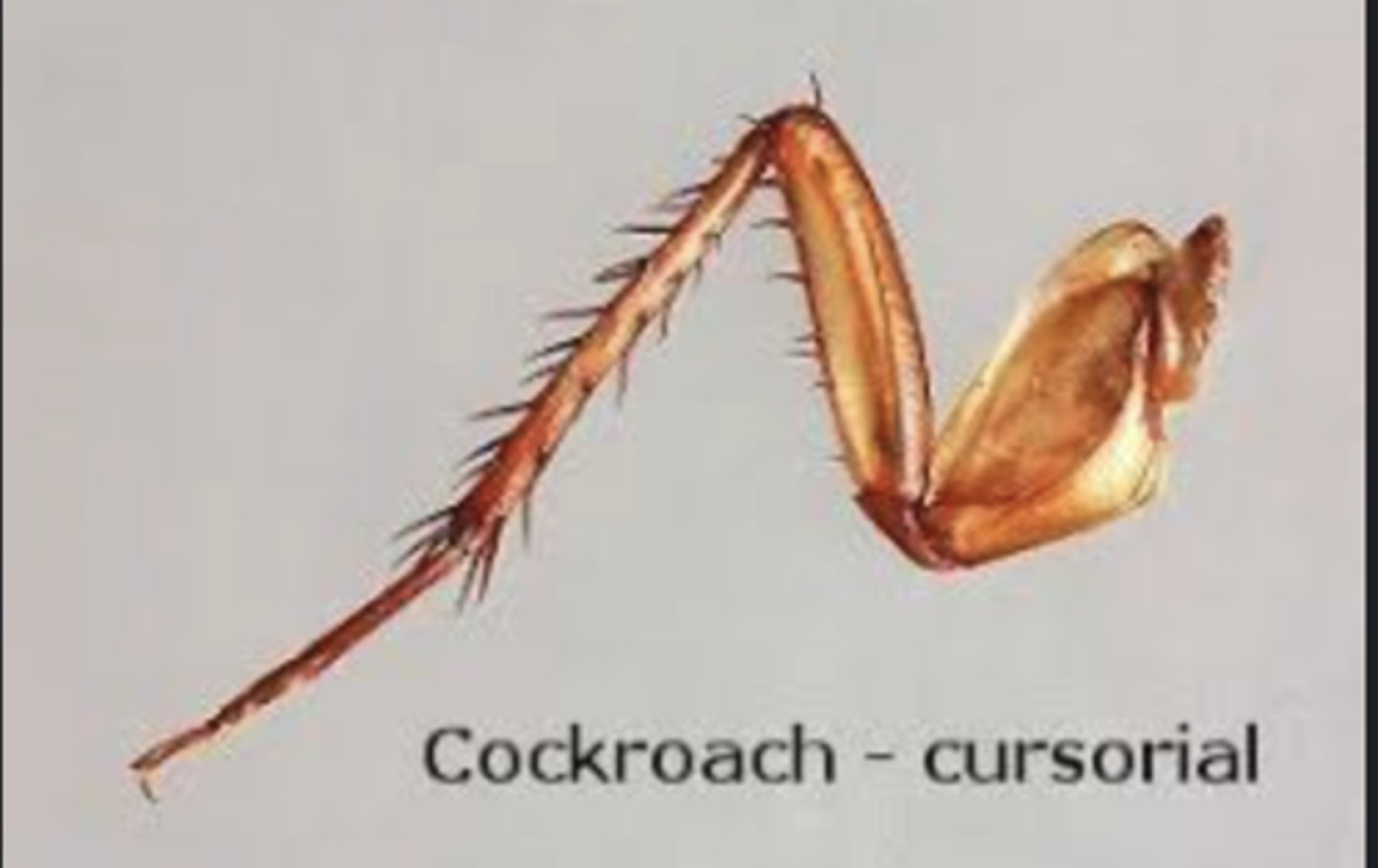
Cursorial legs
Adapted for running (e.g., cockroaches).

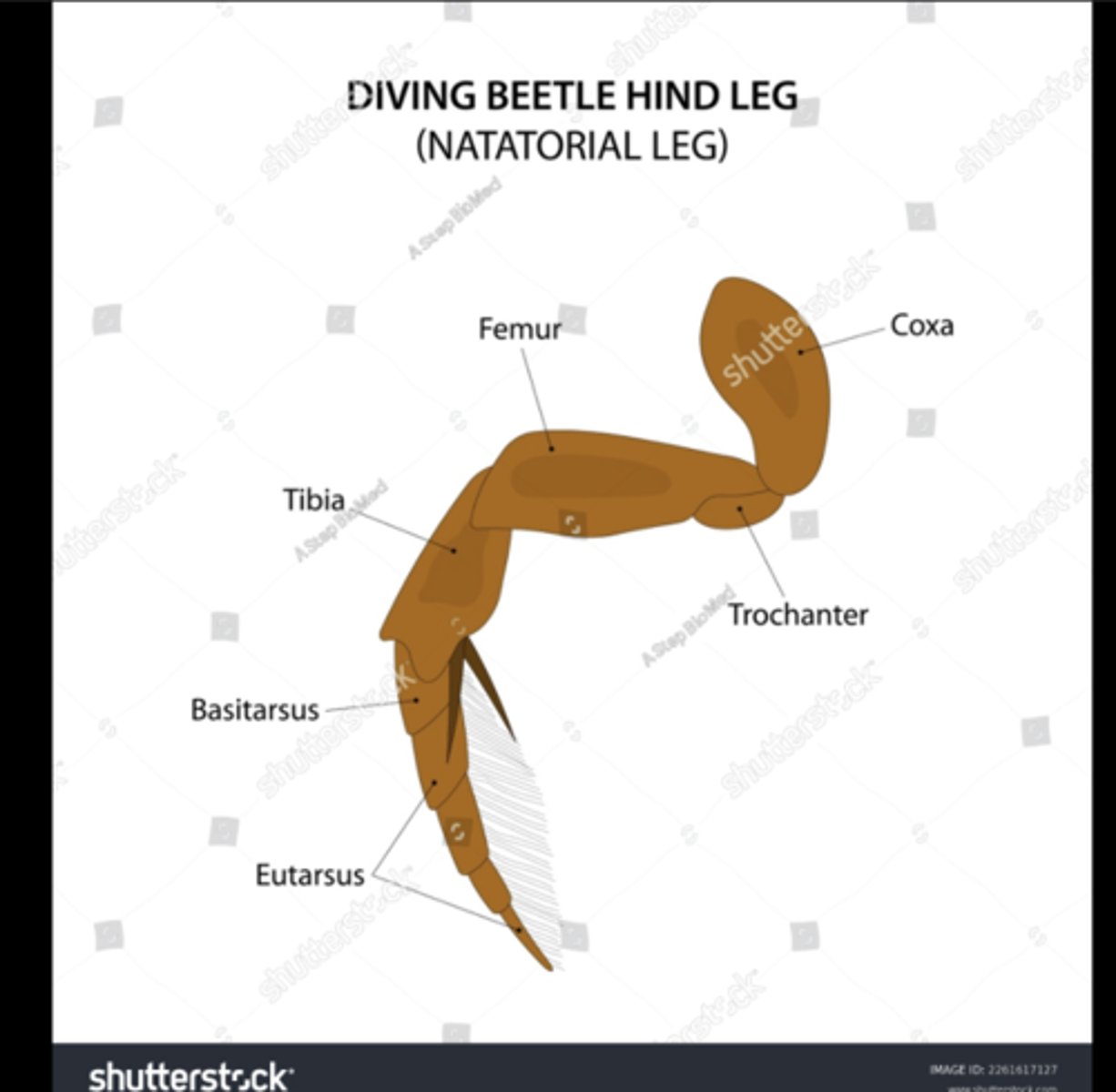
Natatorial legs
Modified for swimming with flattened tibiae or tarsi (e.g., diving beetles).
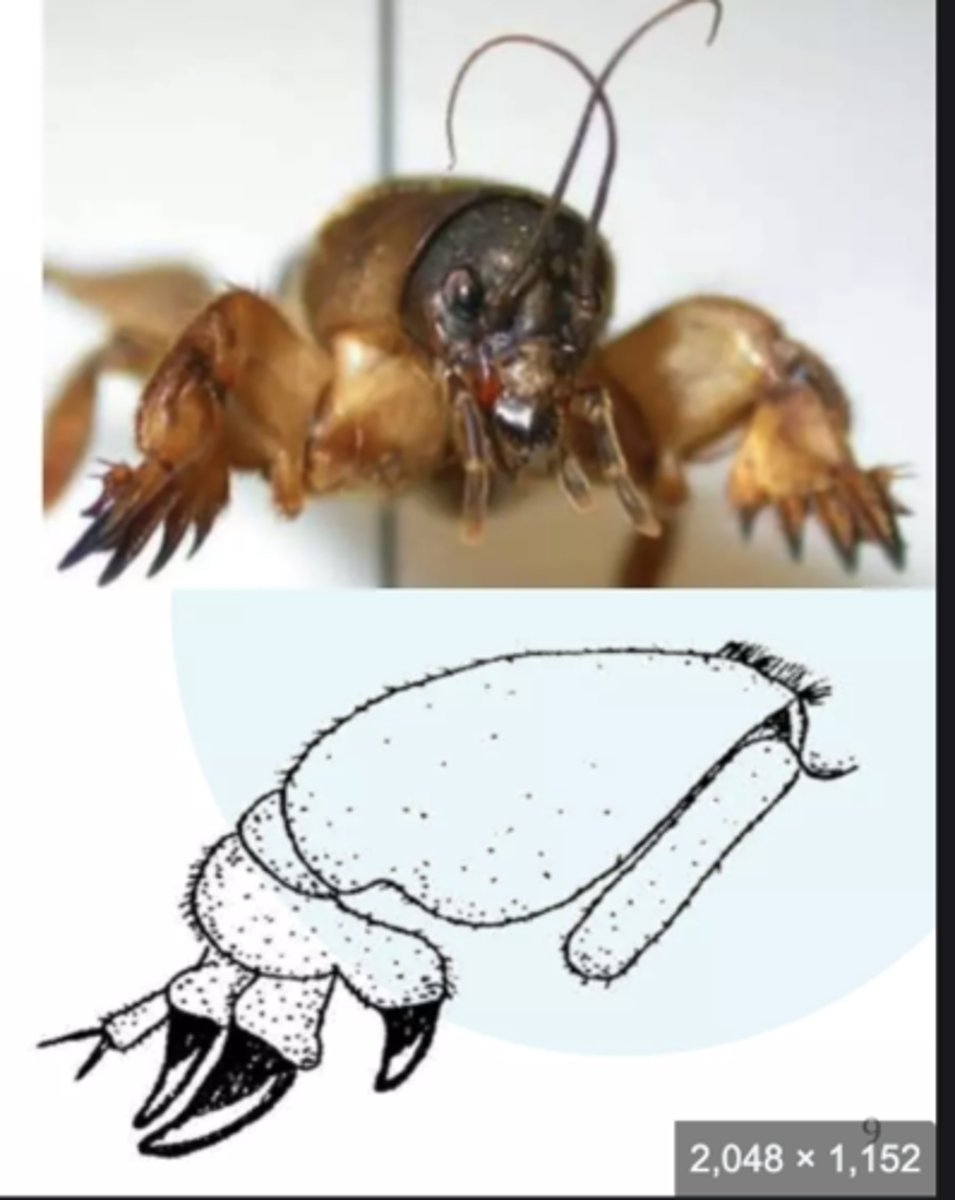
Fossorial legs
Adapted for digging with broad, spade-like segments (e.g., mole crickets).

Wings
Cuticular extensions used for flight; supported by a network of veins carrying nerves and hemolymph.
Apterygota
Primitive wingless insects that never possessed wings.
Pterygota
Winged insects or their descendants, representing most modern species.
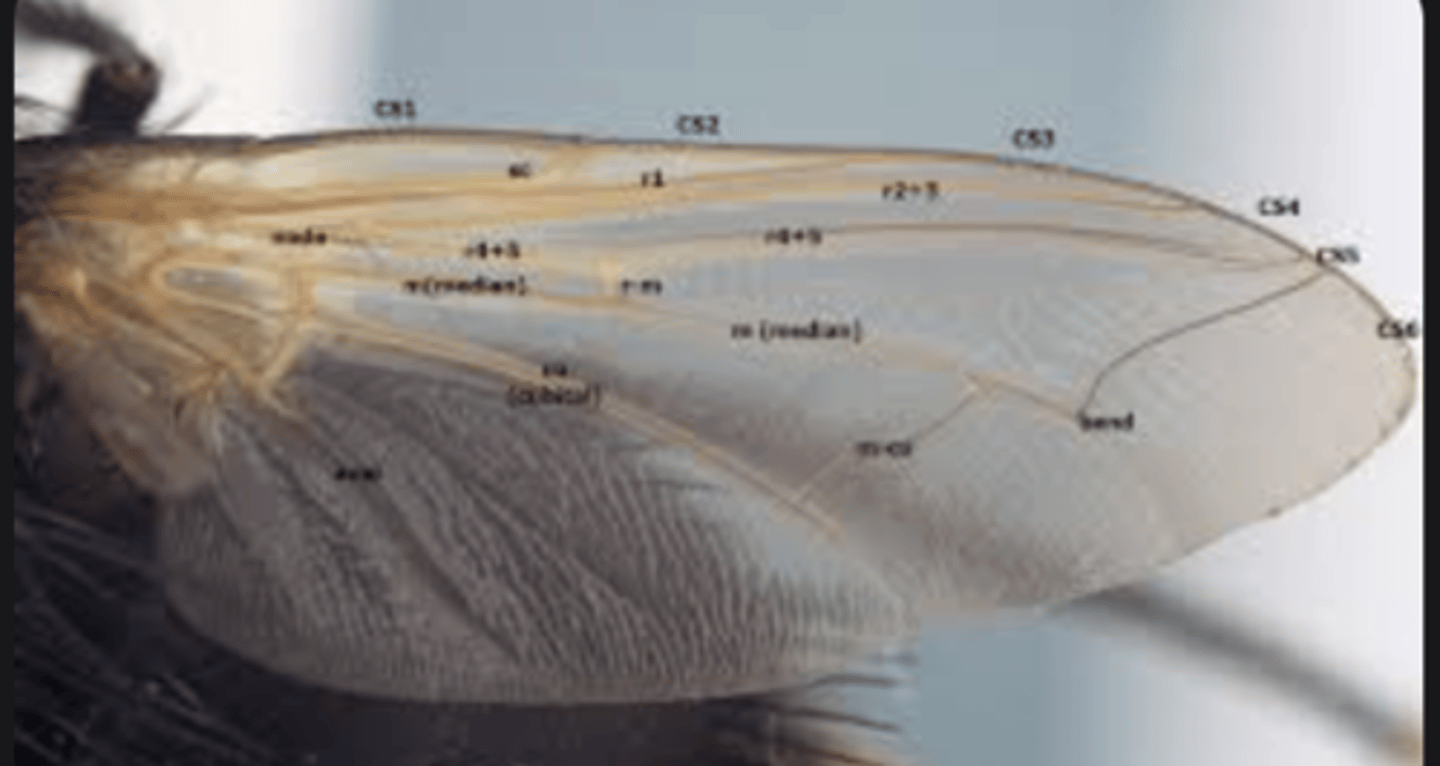
Wing veins
Reinforcing tubes within wings that support structure and distribute hemolymph.

Halteres
Small, club-shaped hindwings in flies acting as gyroscopic balance organs.
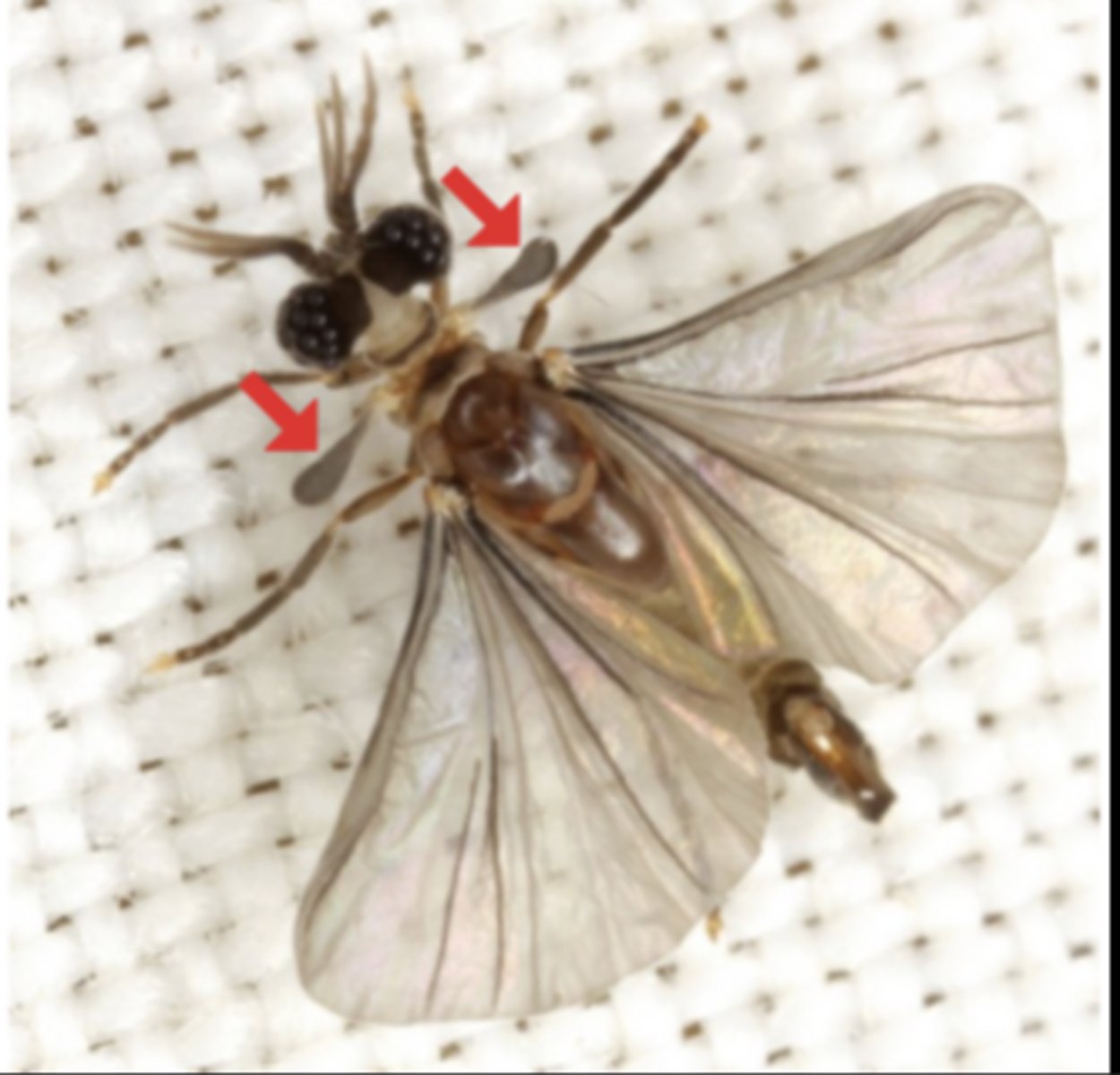

Elytra
Hardened forewings that protect the membranous hindwings (beetles).

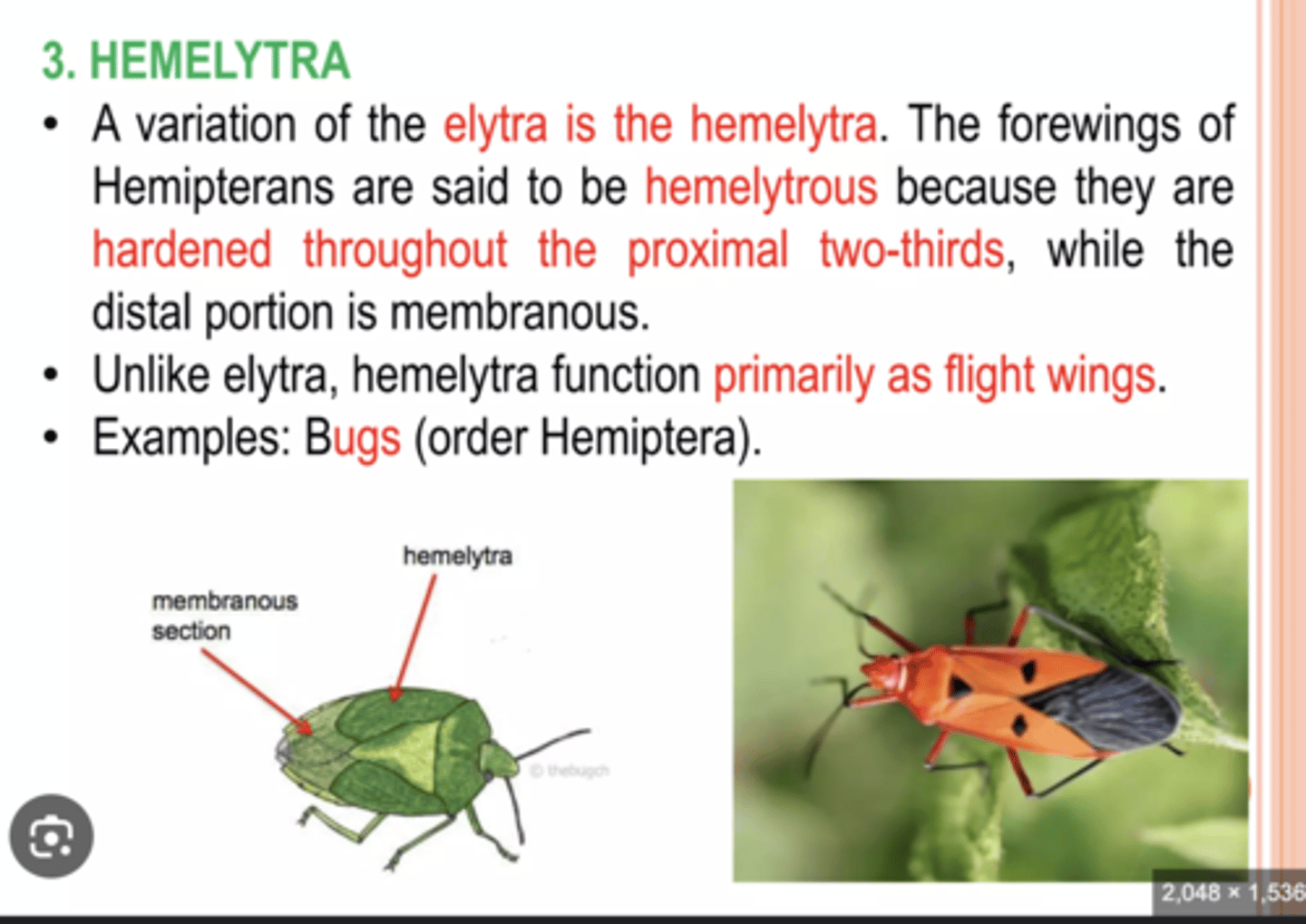
Hemielytra
Forewings partly hardened at the base and membranous at the tip (true bugs).
Tegmina
Leathery forewings providing protection but limited flight aid (grasshoppers, roaches).

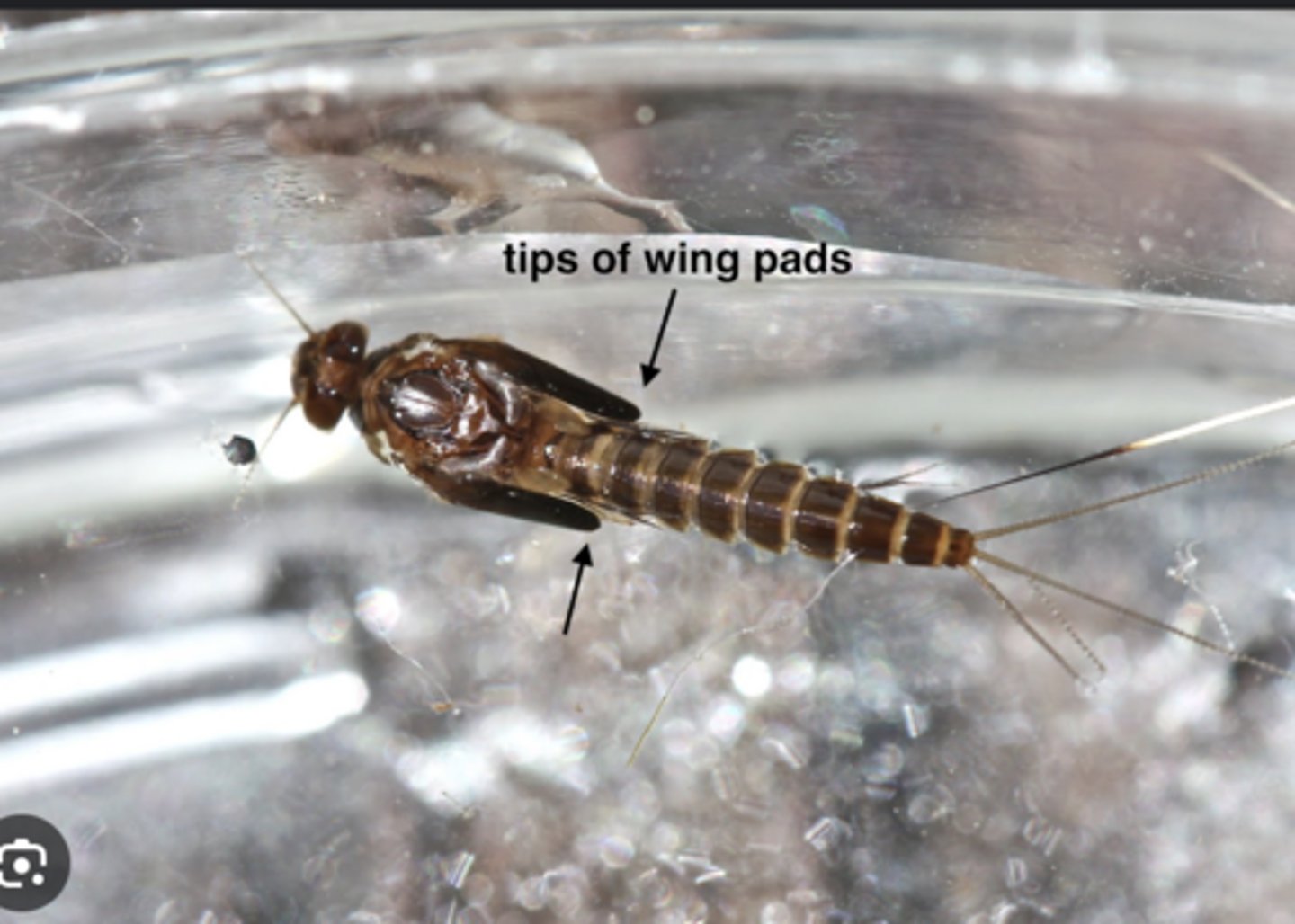
Wing pads
Developing wings of immature nymphs in hemimetabolous insects.

Abdomen
Posterior body region containing digestive, excretory, and reproductive organs.
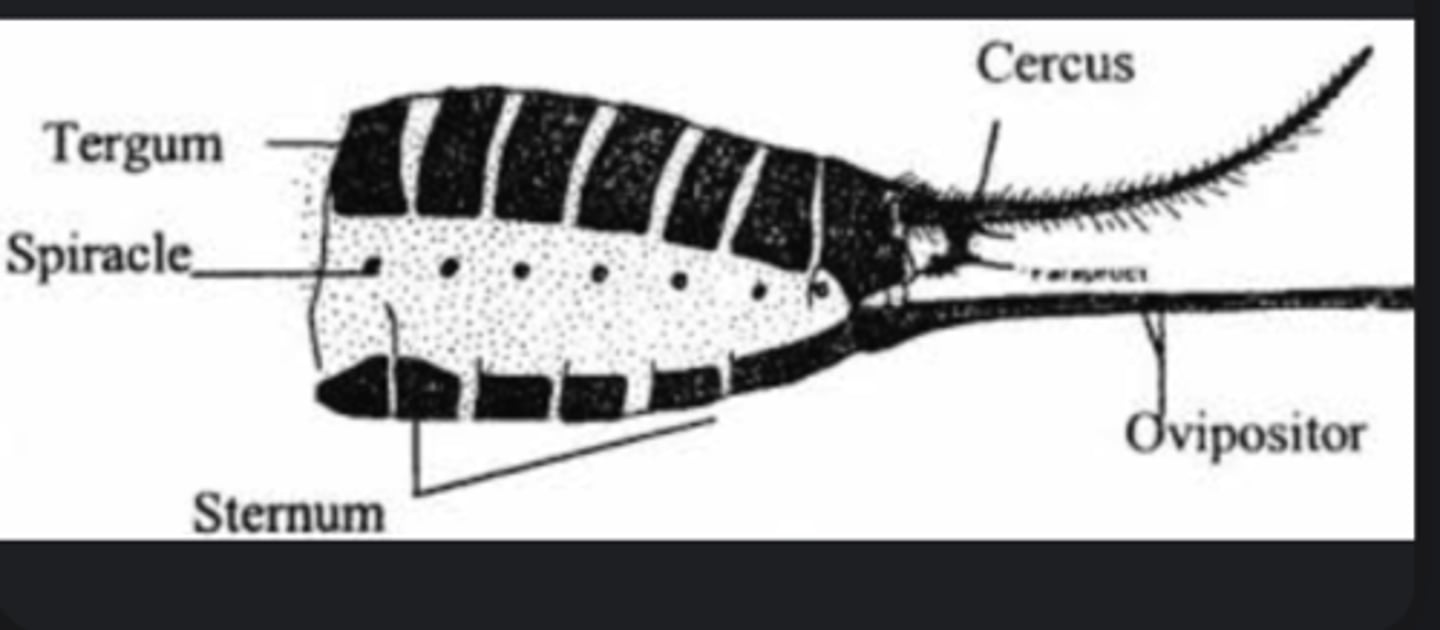
Cerci
Paired sensory appendages at abdomen tip that detect air currents or serve as pincers.

Aedeagus
Male copulatory organ for transferring sperm to female.
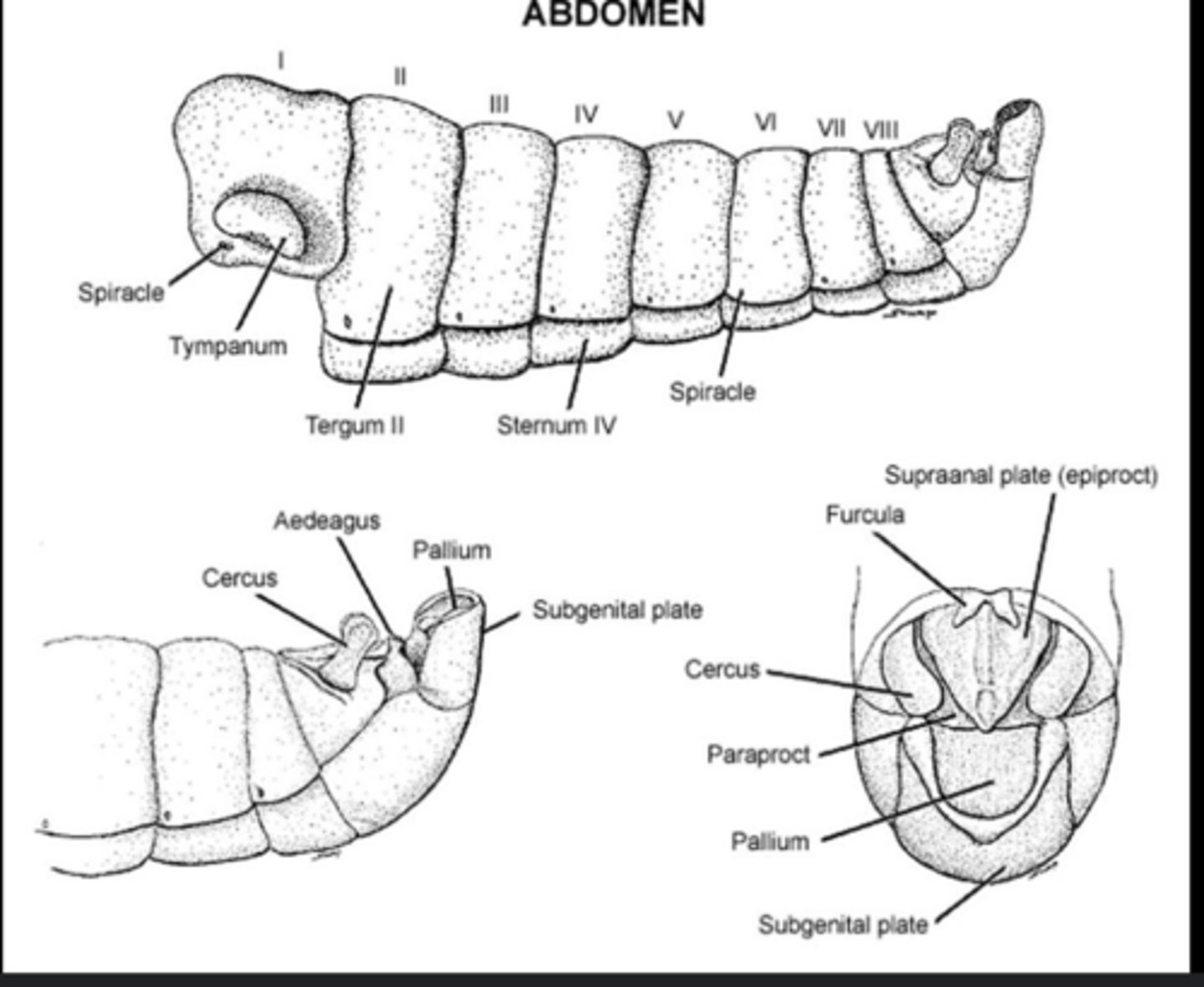
Ovipositor
Female organ used for laying eggs or modified into a sting (wasps, bees).
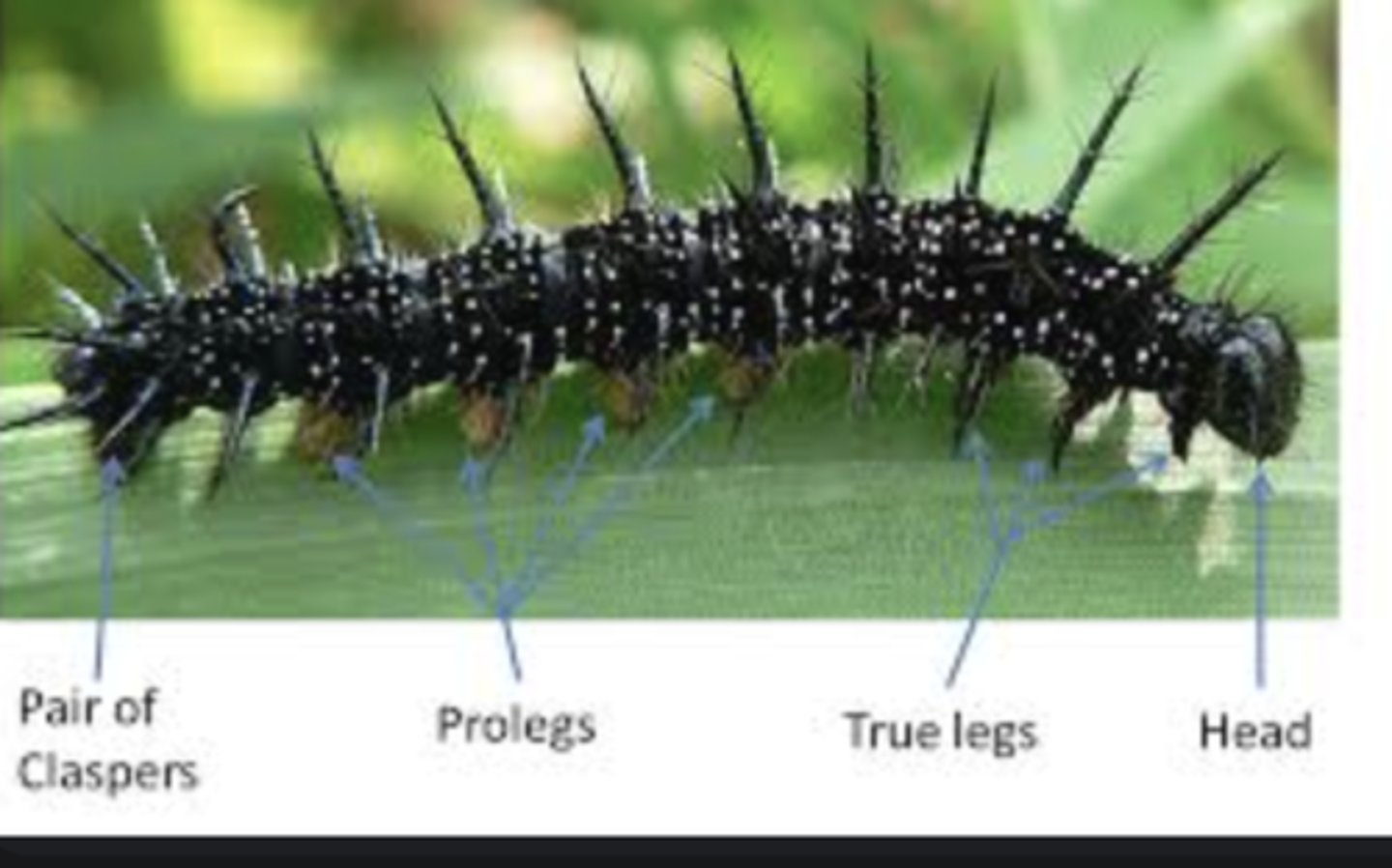
Prolegs
Fleshy, unsegmented legs found on caterpillars and larvae for gripping surfaces.

Rectal gills
Aquatic adaptations in larvae allowing gas exchange in the rectal area.
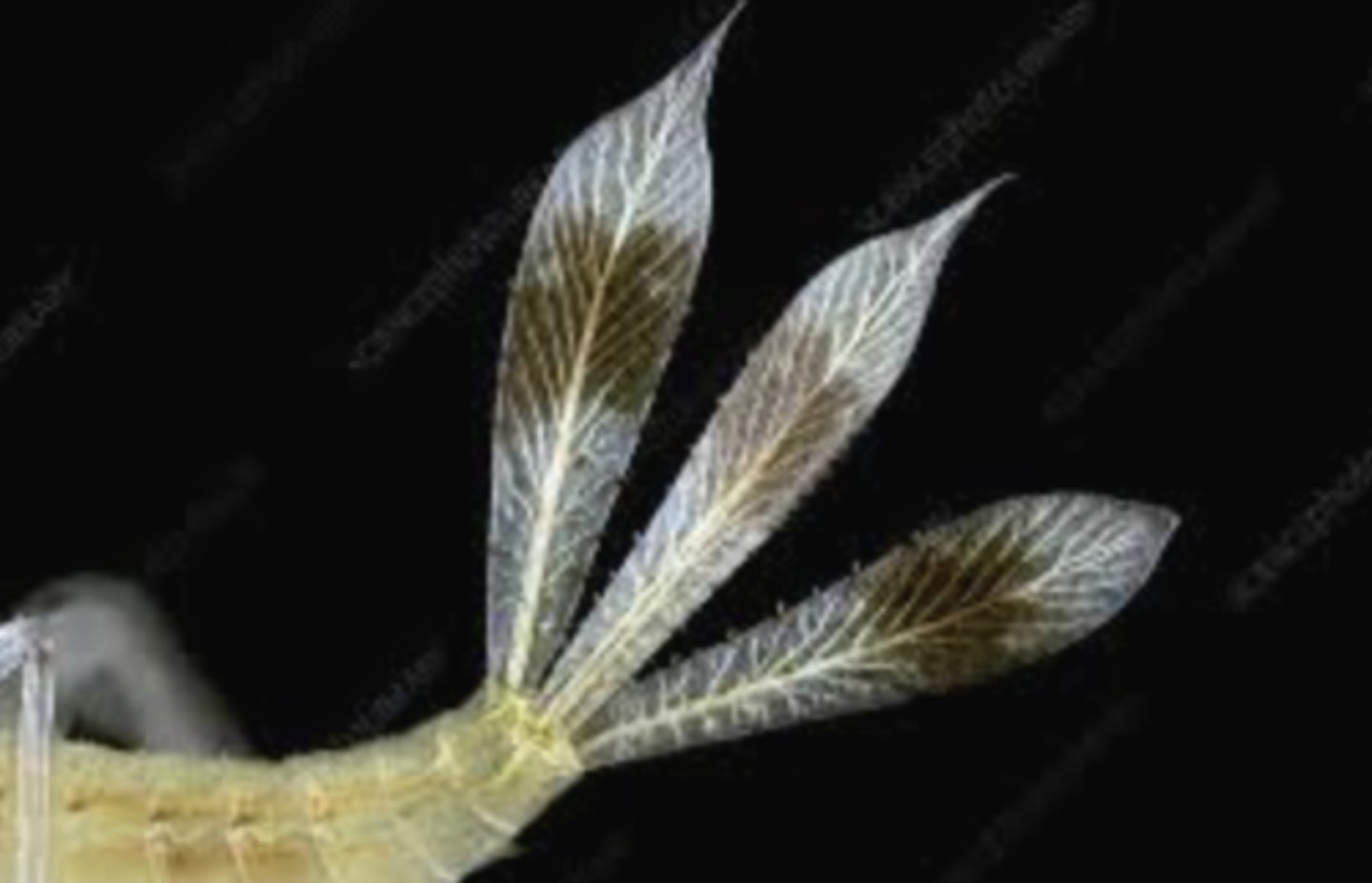

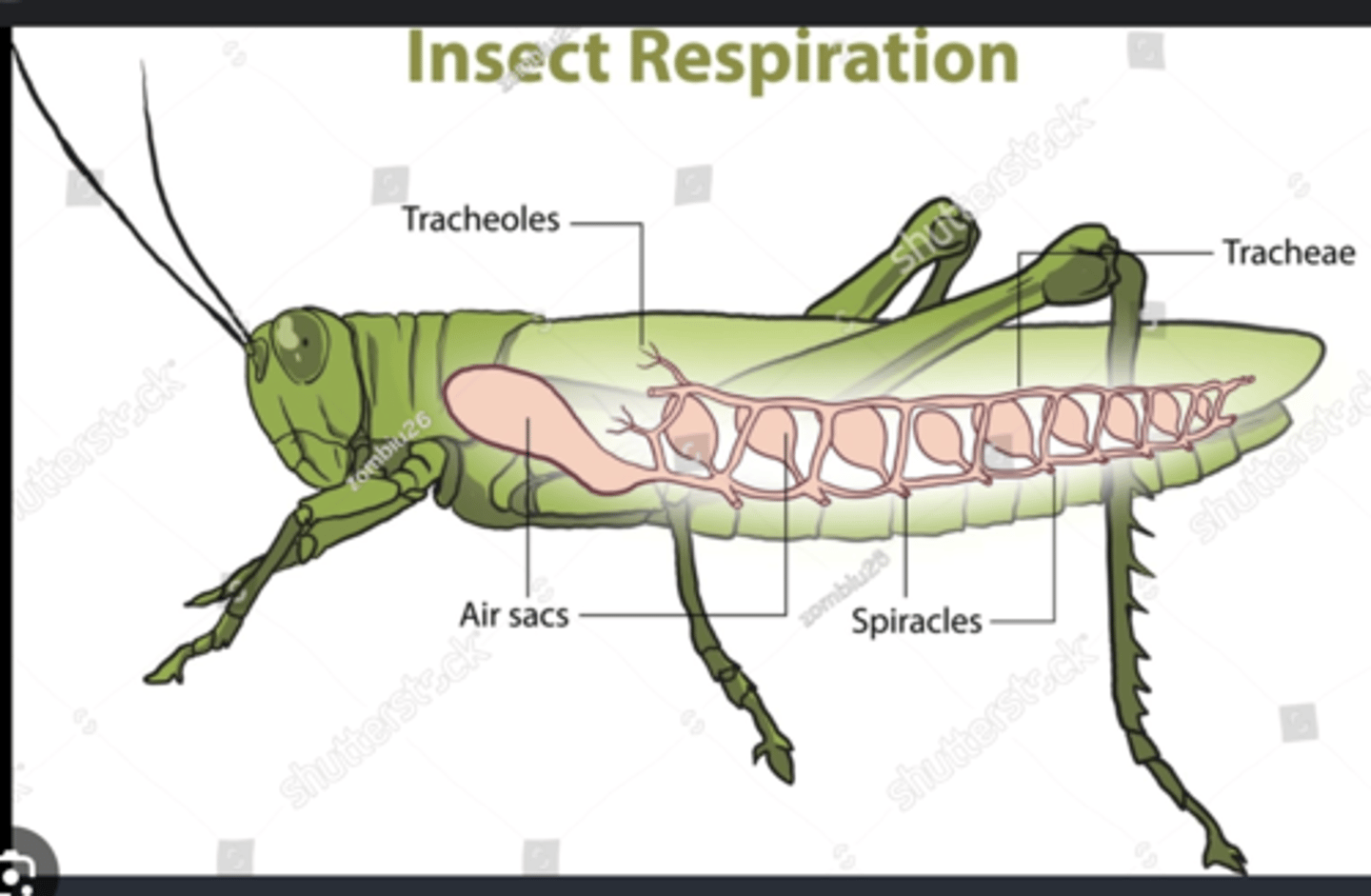
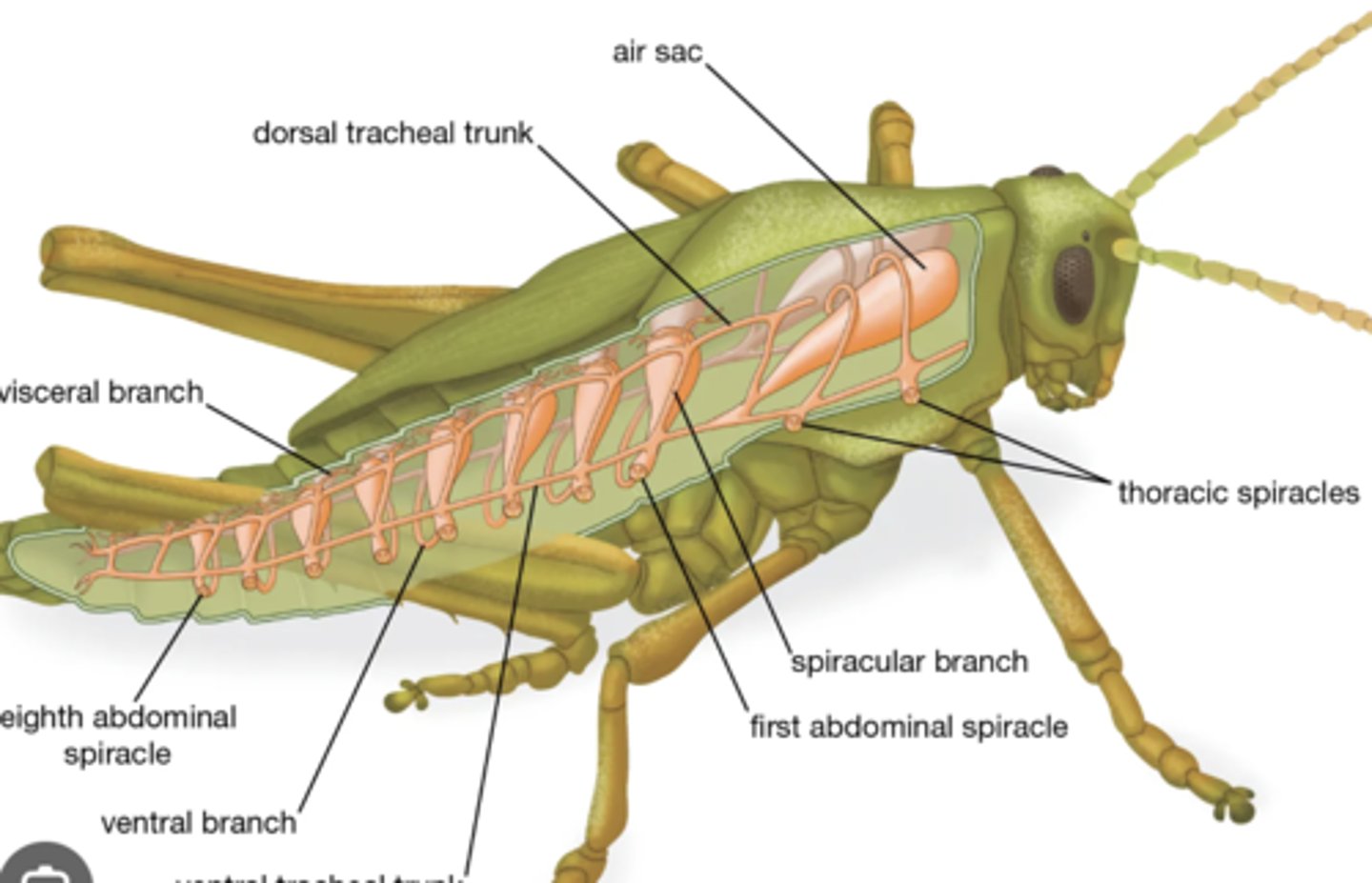
Spiracles
External openings that connect to the tracheal system for gas exchange.
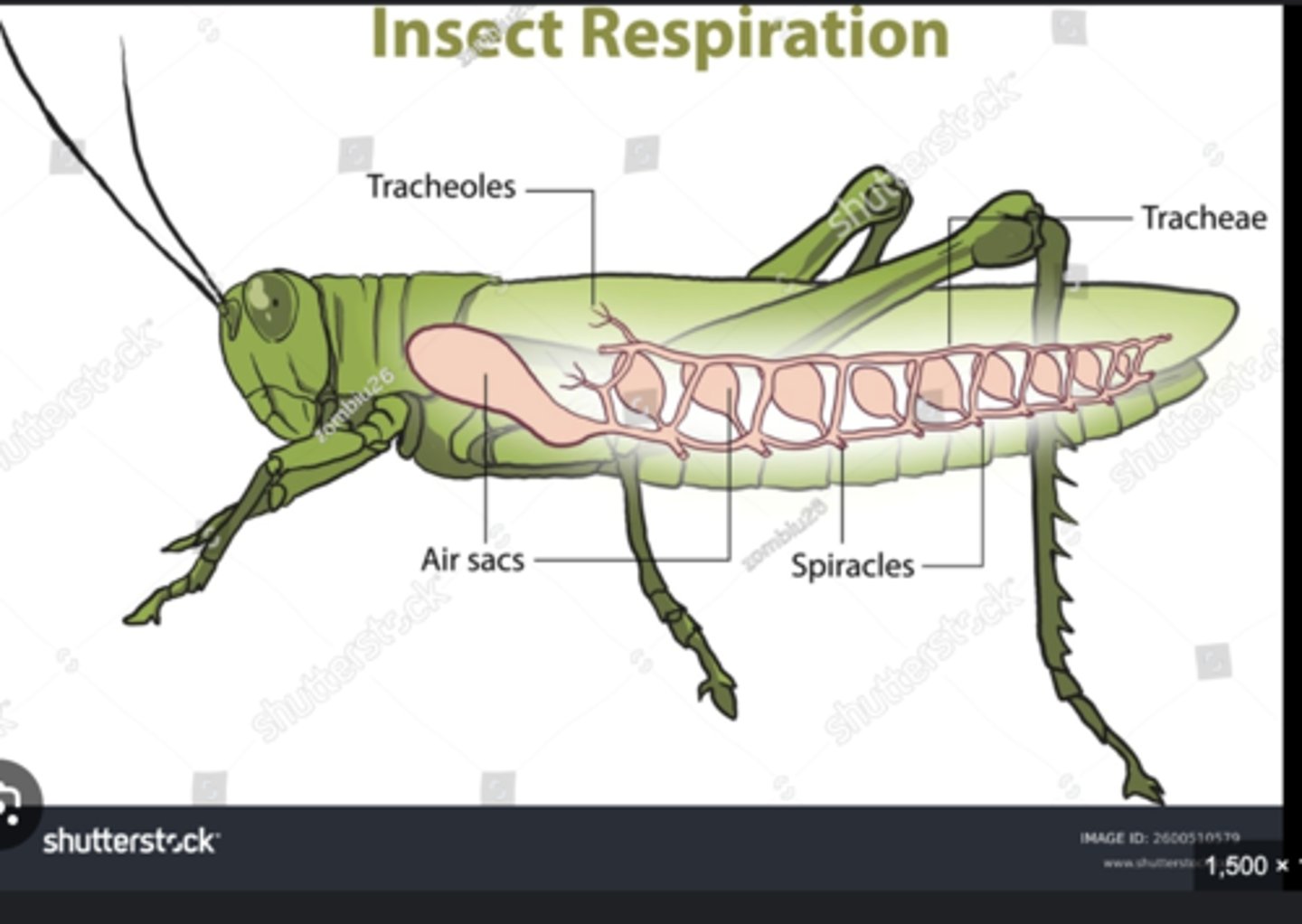
Tracheae
Branching air tubes delivering oxygen directly from spiracles to tissues; bypass circulatory system.
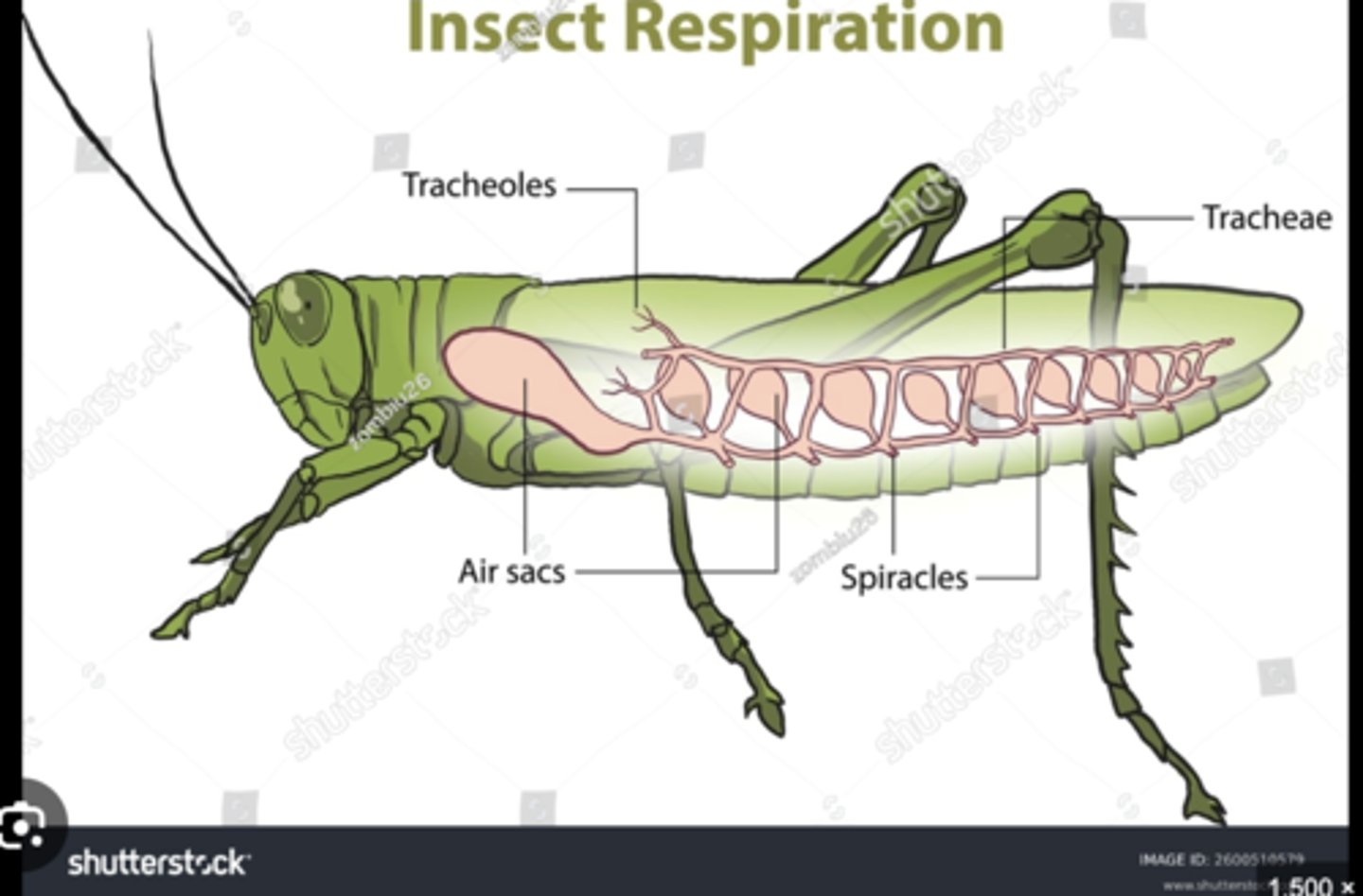
Tracheoles
Microscopic tubes delivering oxygen to individual cells for efficient respiration.
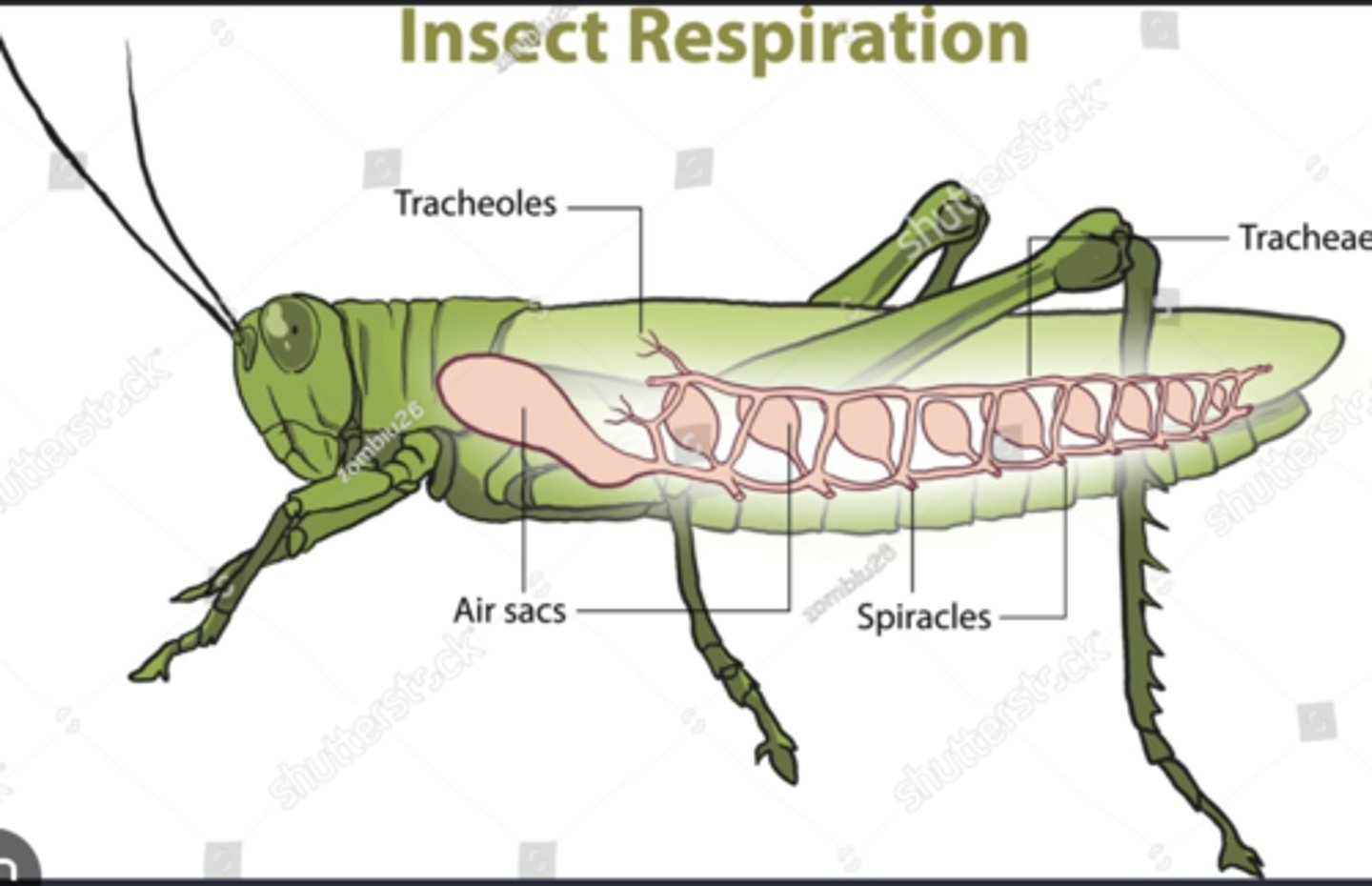
Air sacs
Enlarged tracheae that store air and facilitate ventilation during flight.
Passive ventilation
Diffusion of gases through tracheae without muscular movement.
Active ventilation
Body muscle contractions that push air through tracheae, common in flying insects.
Hemolymph
Insect 'blood' circulating in open system; transports nutrients, hormones, wastes, and immune cells.
Hemocoel
Main internal body cavity where hemolymph bathes organs directly.
Hemocytes
Cells in hemolymph that provide immunity, phagocytosis, wound repair, and encapsulation of parasites.
Open circulatory system
Circulatory system without closed vessels; hemolymph flows freely around organs.
Phagocytosis
Process where hemocytes engulf bacteria or debris as immune defense.
Encapsulation
Immune response where large parasites are surrounded by hemocytes and sealed off.
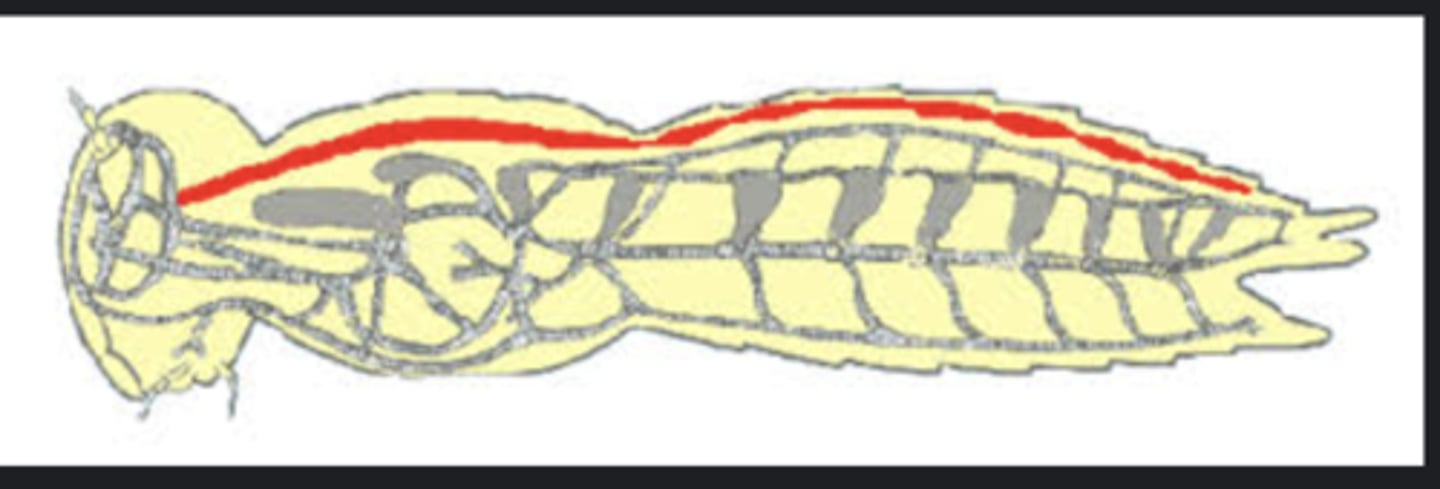
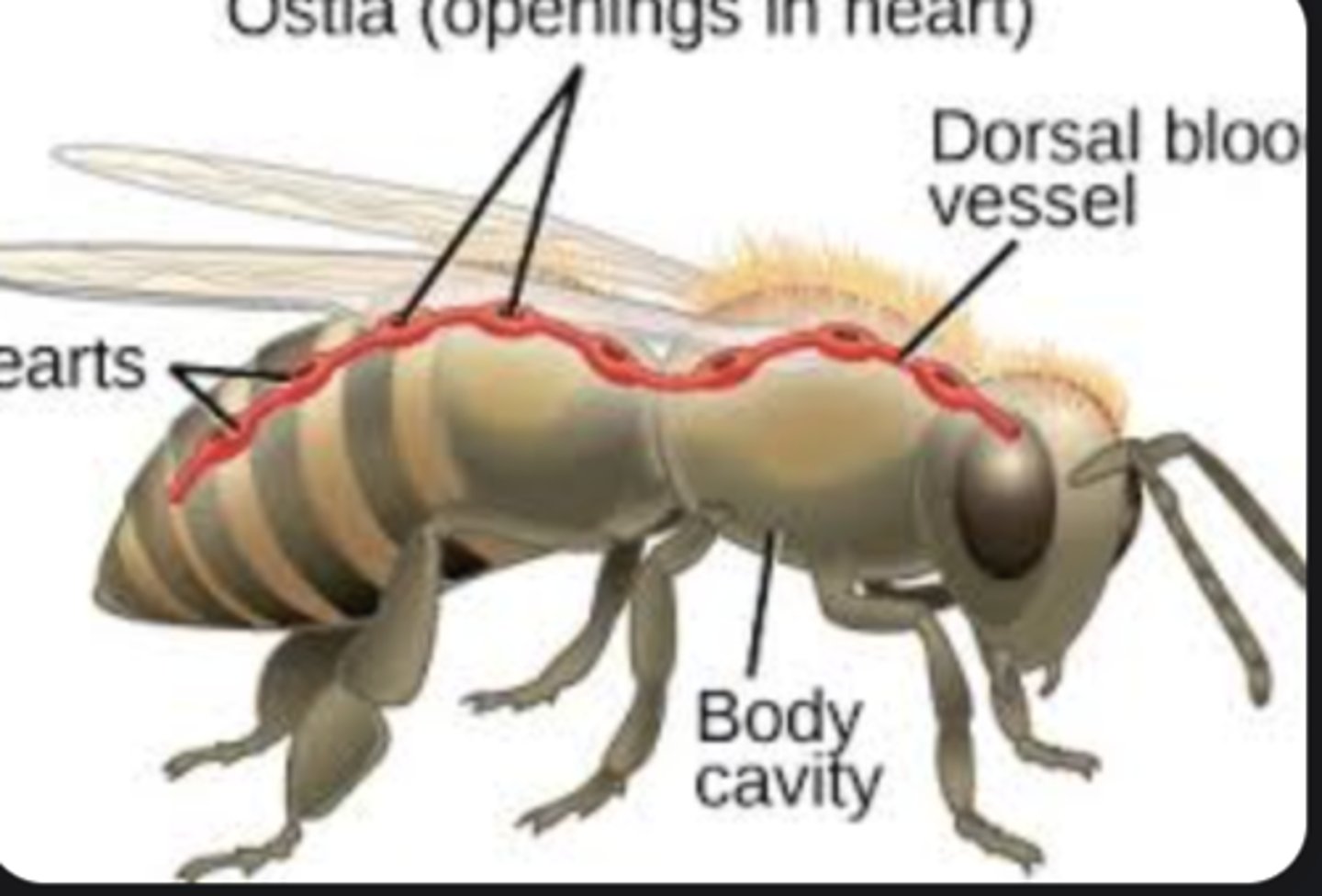
Dorsal vessel
Primary circulatory organ running along back; includes heart (pulsatile) and aorta (non-pulsatile).
Ostia
Valved openings through which hemolymph enters the heart chambers.
Fat body
Tissue that stores energy reserves, detoxifies, and aids metabolism; comparable to vertebrate liver and fat.

Luminescence
Light production via chemical reactions (e.g., luciferin-luciferase system in fireflies).
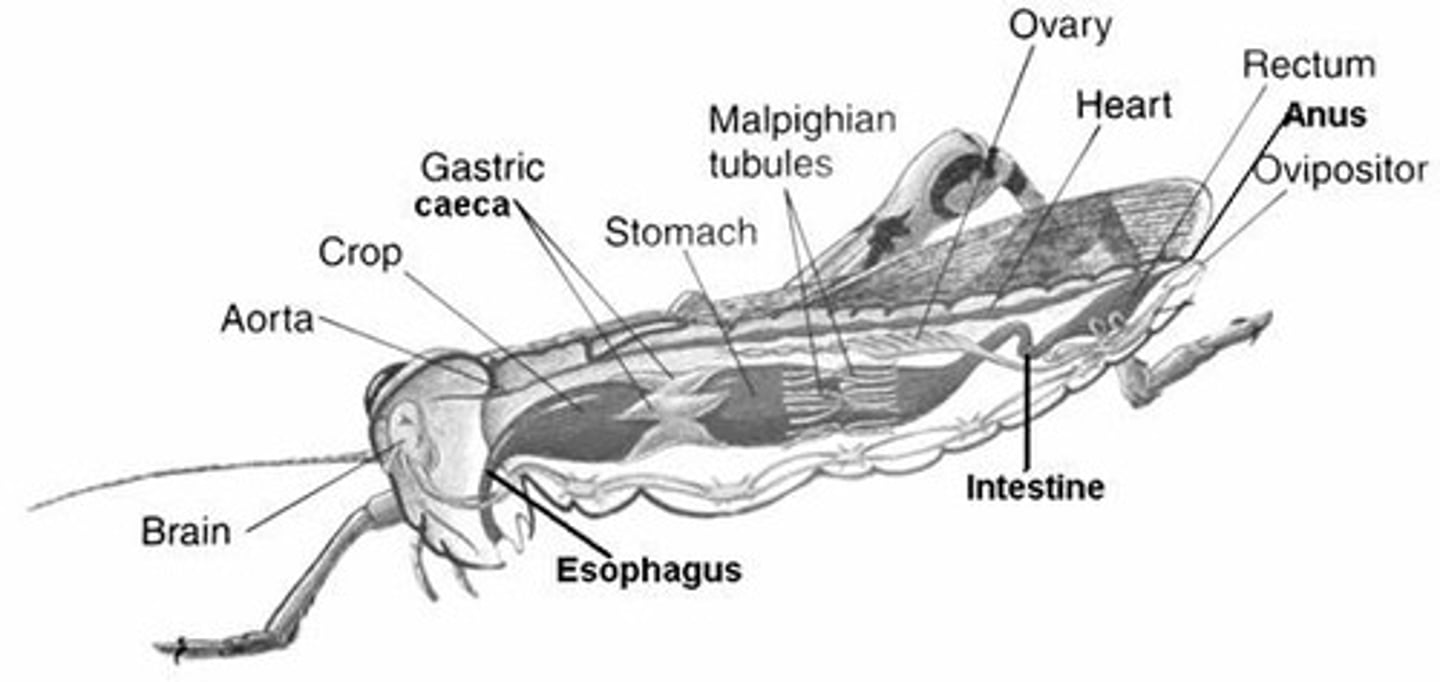
Alimentary canal
Digestive tract from mouth to anus; divided into foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
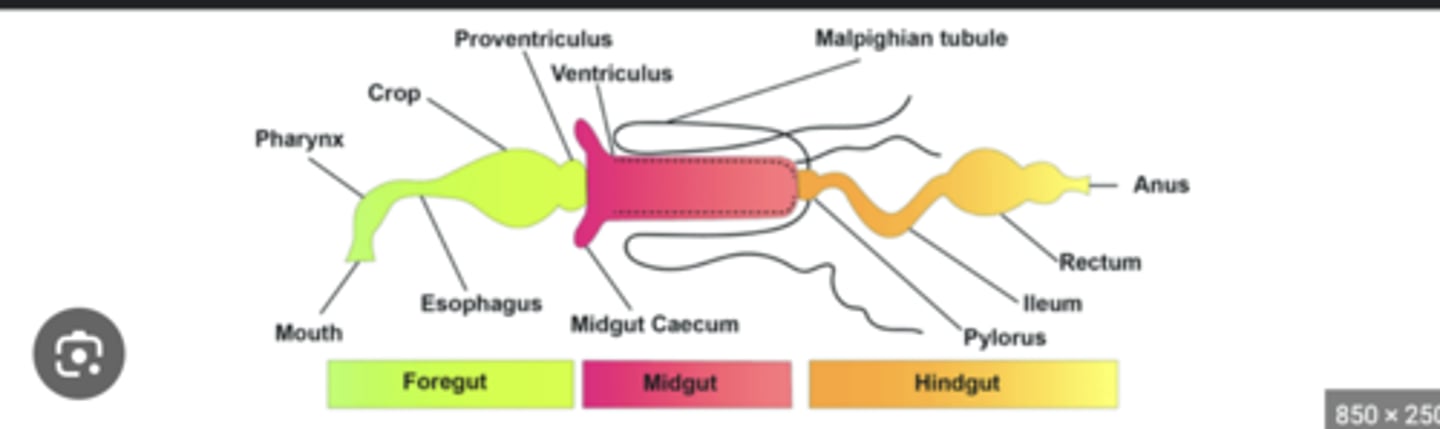
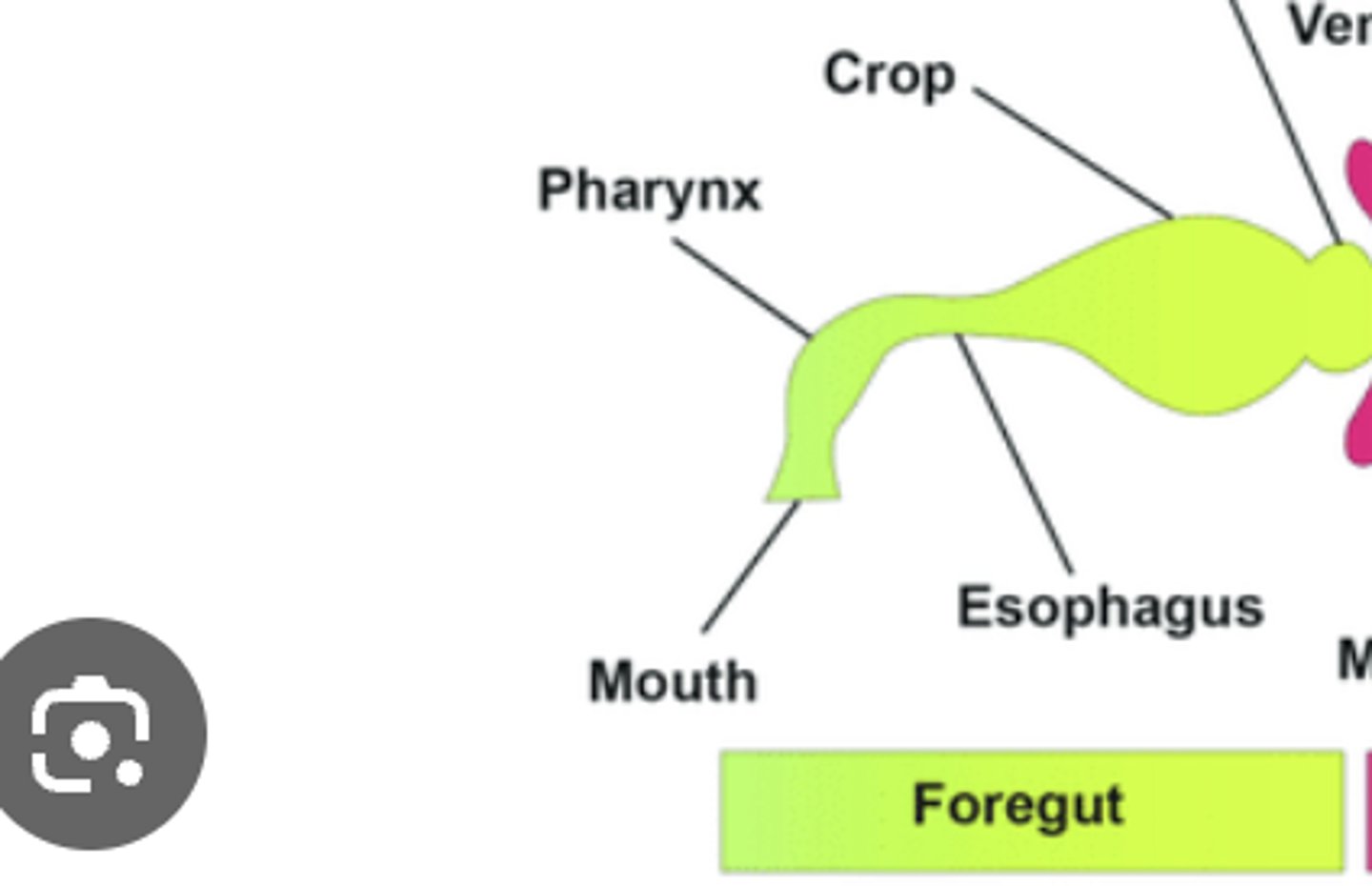
Foregut
Region for ingestion, food storage, and initial digestion; includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and crop.
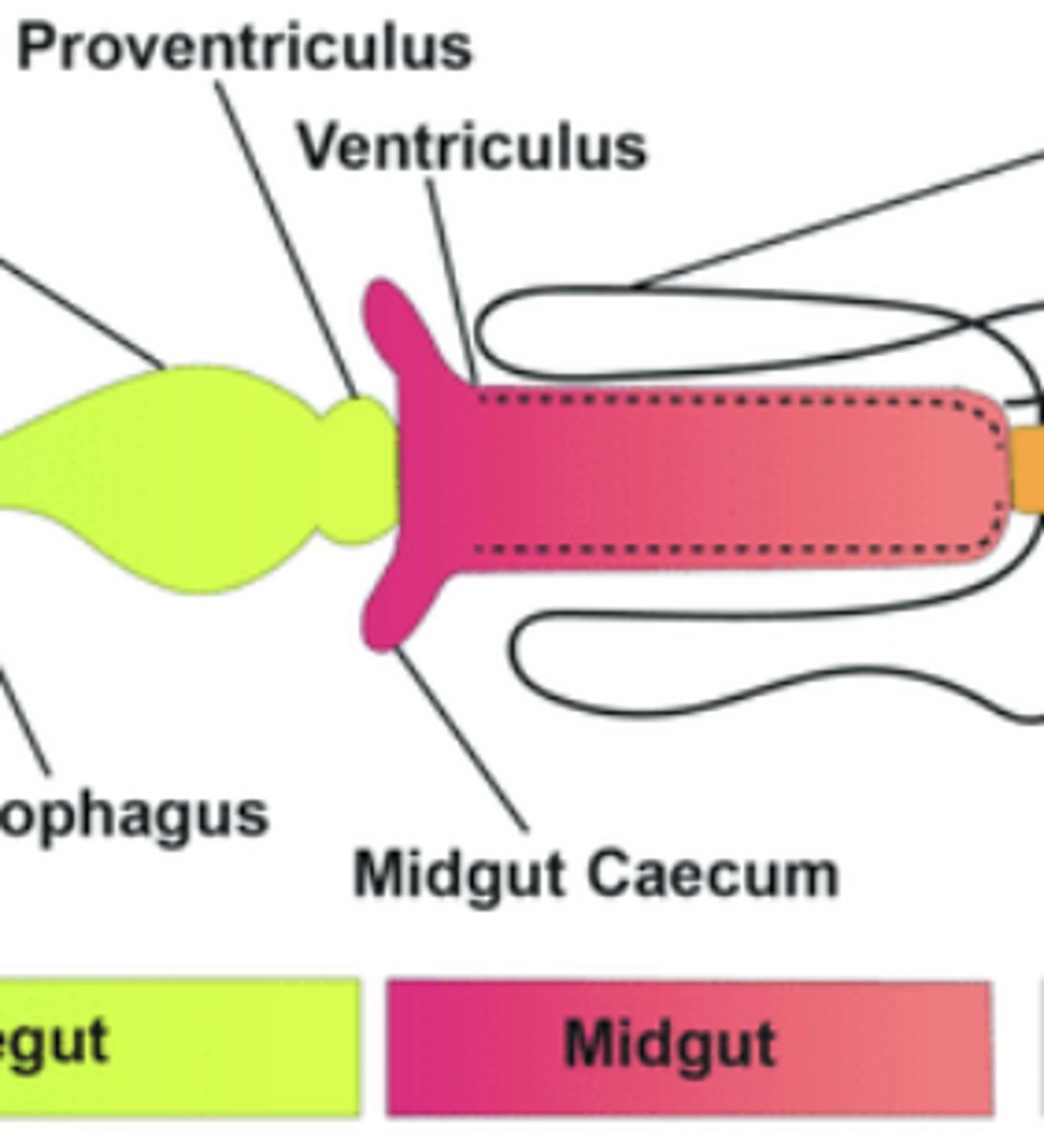
Midgut
Main site of enzymatic digestion and nutrient absorption.
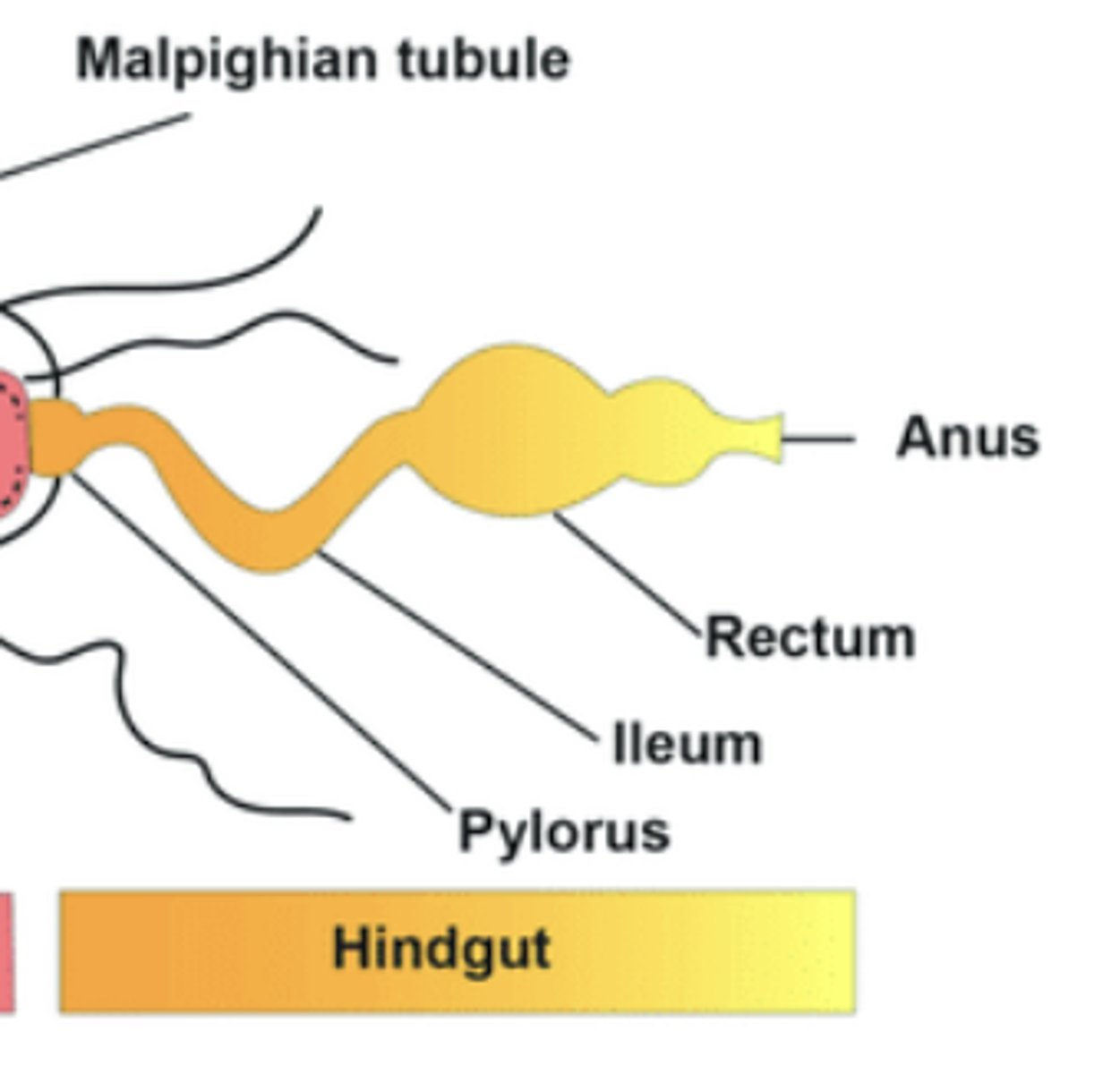
Hindgut
Area for water and salt reabsorption and fecal formation.
Gastric caeca
Blind-ended pouches in midgut that secrete digestive enzymes and increase surface area.
Symbionts
Mutualistic microbes living in gut that aid digestion or synthesize nutrients.
Malpighian tubules
Excretory organs filtering hemolymph and excreting nitrogen waste into gut for elimination.
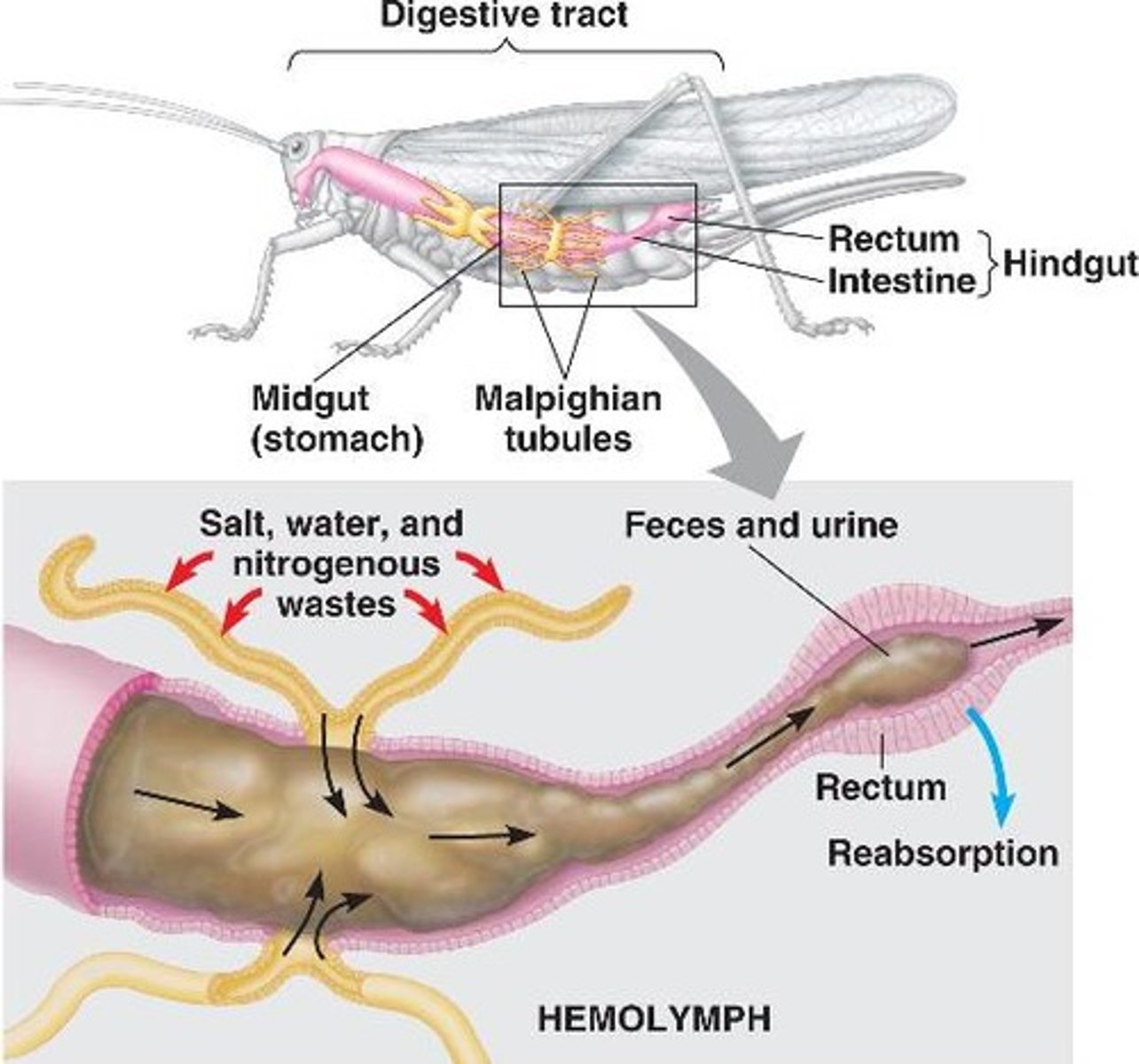
Ammonia, Urea, Uric acid
Nitrogenous waste products; uric acid conserves water and is common in terrestrial insects.
Parthenogenesis
Reproduction without fertilization; offspring are genetically identical to the mother, allowing rapid population growth but low genetic variation.
Bisexual reproduction
Involves both male and female parents, promoting genetic diversity through sexual recombination.
Testis
Male reproductive organ that produces and stores sperm.
Male accessory glands
Produce seminal fluid and proteins that nourish sperm and influence female physiology after mating.
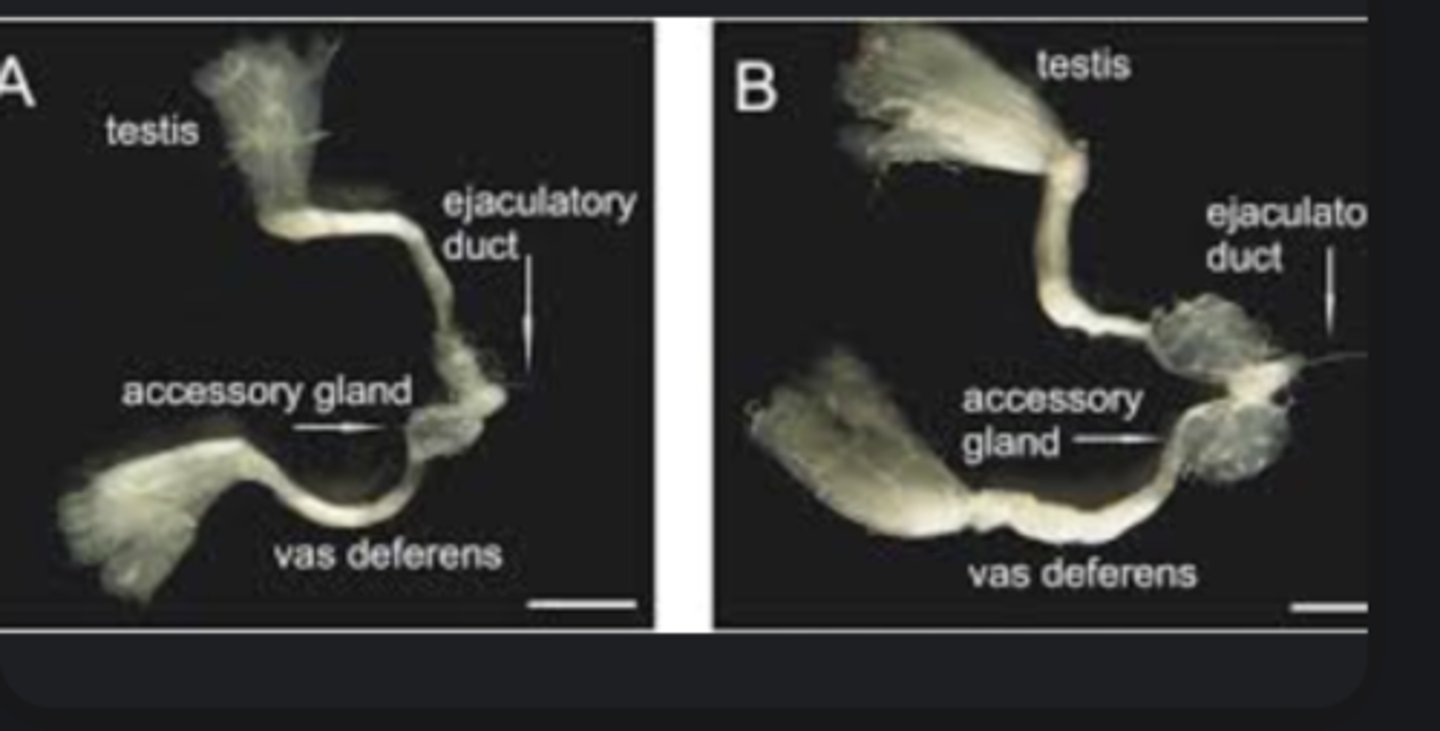
Spermatophore
Package of sperm (and sometimes nutrients) transferred from male to female.

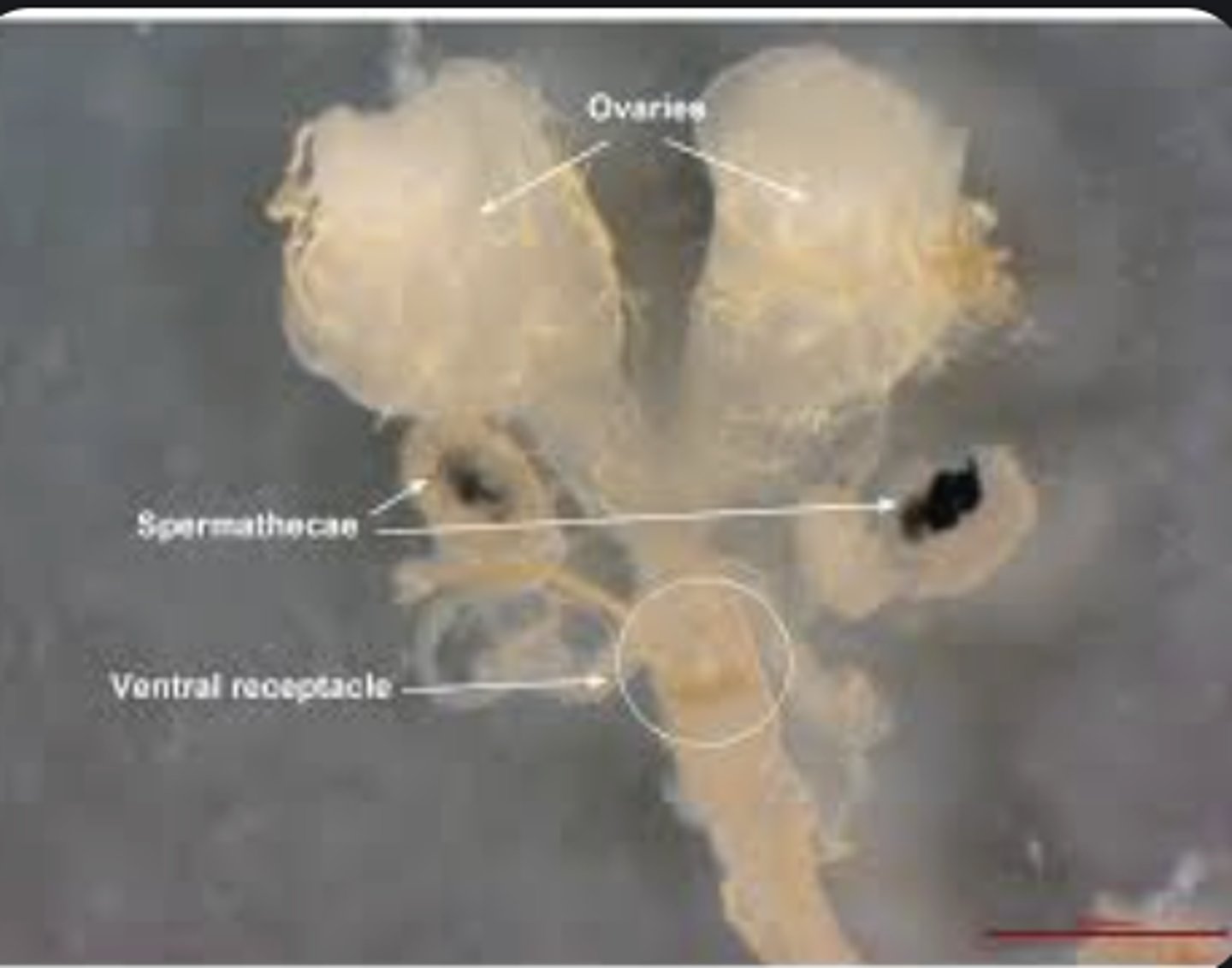
Ovary
Female organ producing ova (eggs).
Oviduct
Tube carrying eggs from ovaries to outside the body.
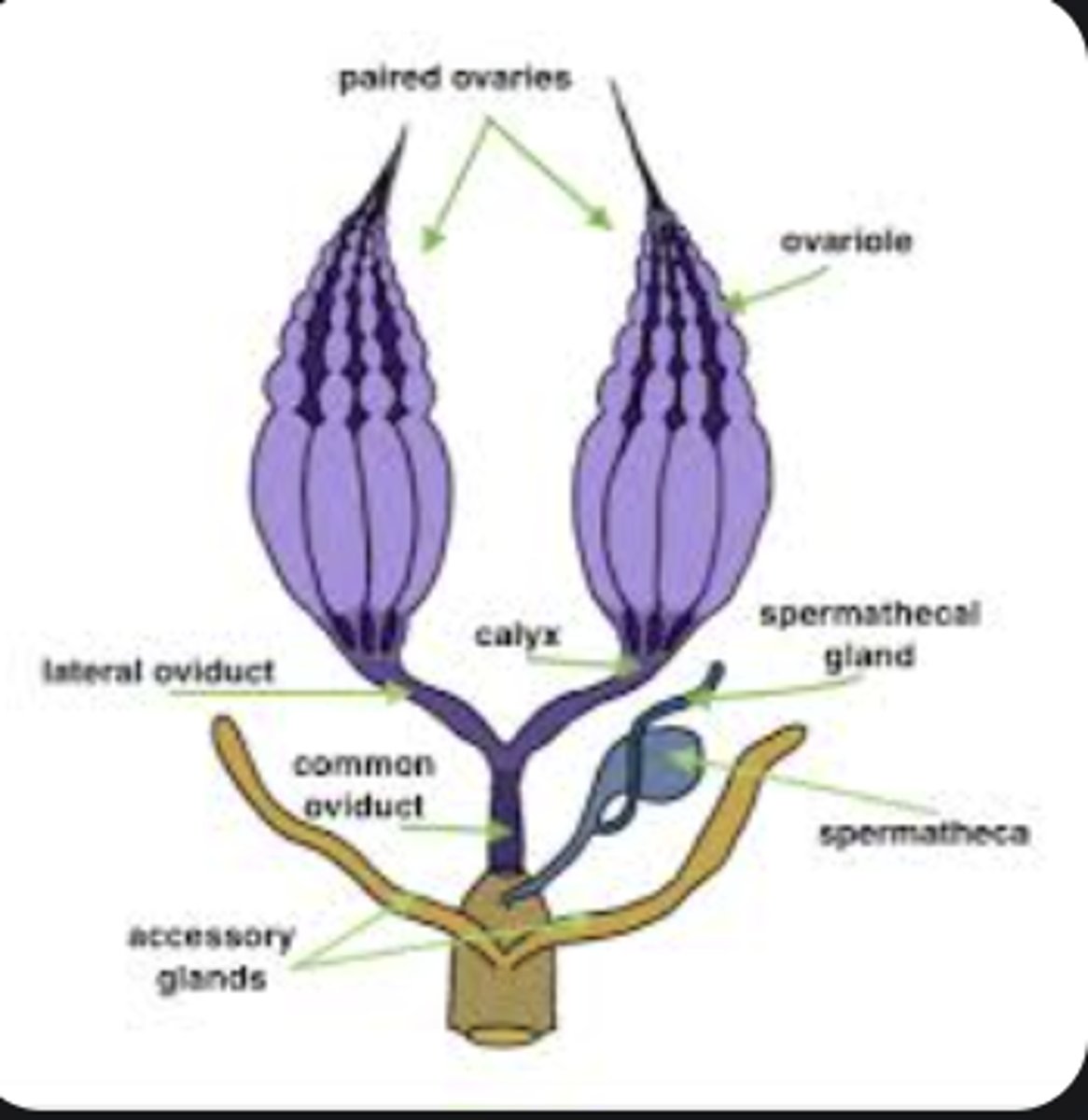
Spermatheca
Storage sac in female reproductive tract that holds sperm for later fertilization.
Egg
Female reproductive cell containing yolk and protective layers for embryonic development.
Yolk
Nutrient supply for developing embryo.
Chorion
Protective outer eggshell layer.
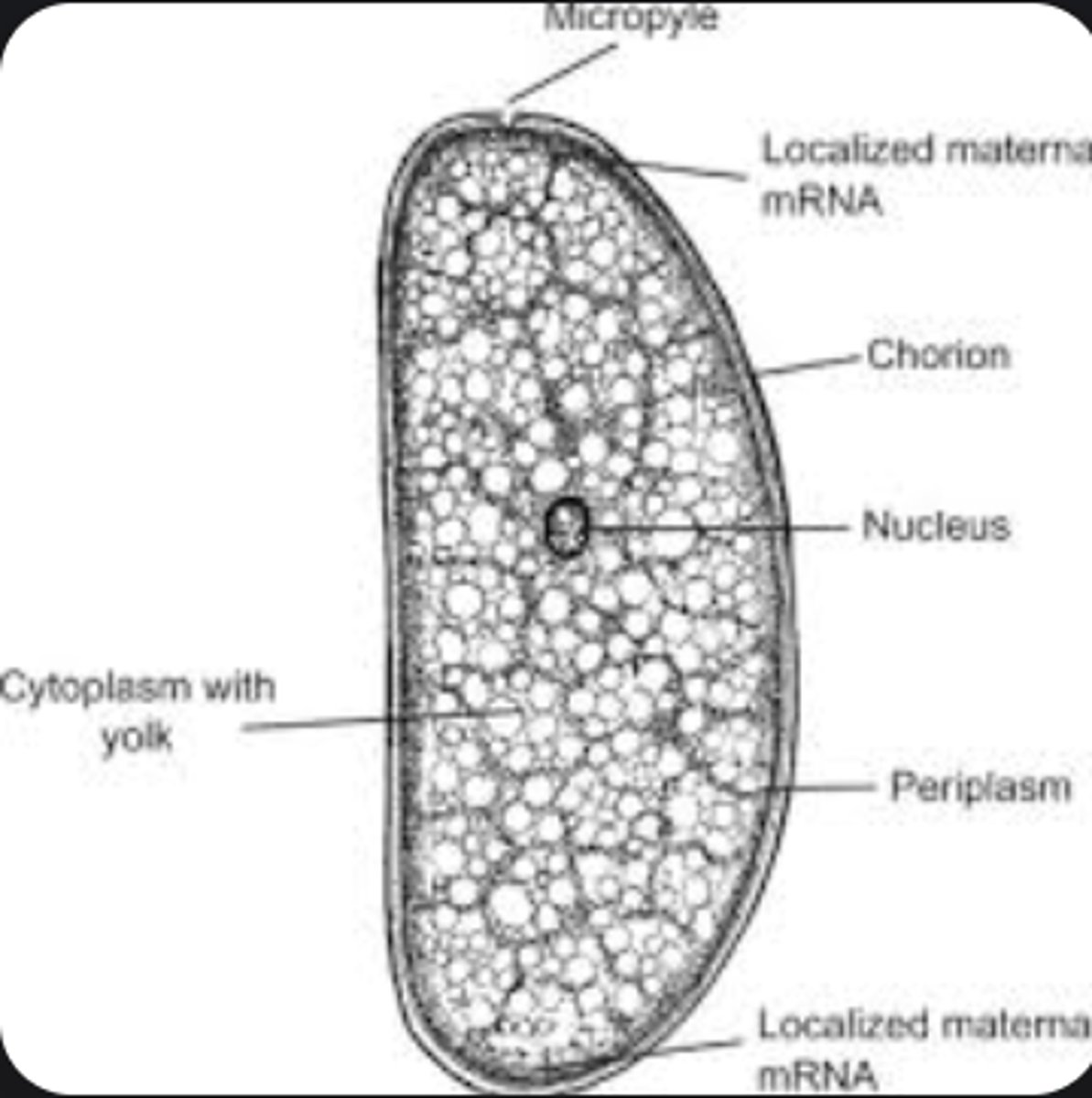
Micropyle
Tiny opening in egg allowing sperm entry for fertilization.
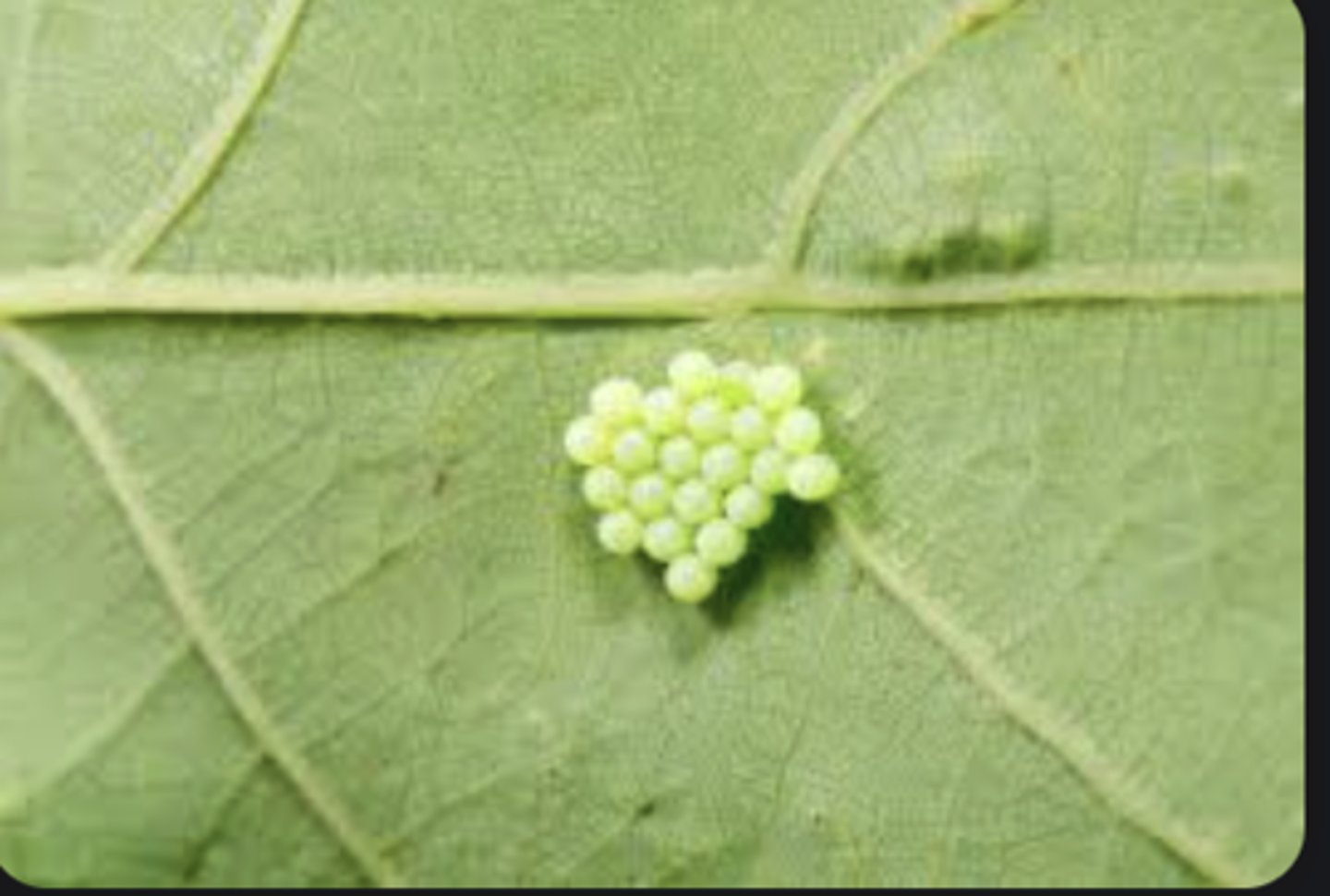
Oviparous
Eggs laid externally; embryo develops outside female body.

Viviparous
Embryo develops inside female; live young are born.

Ovoviviparous
Eggs develop and hatch inside female, producing live young.

Neuron
Basic nerve cell transmitting electrical impulses; composed of soma, dendrites, and axon.
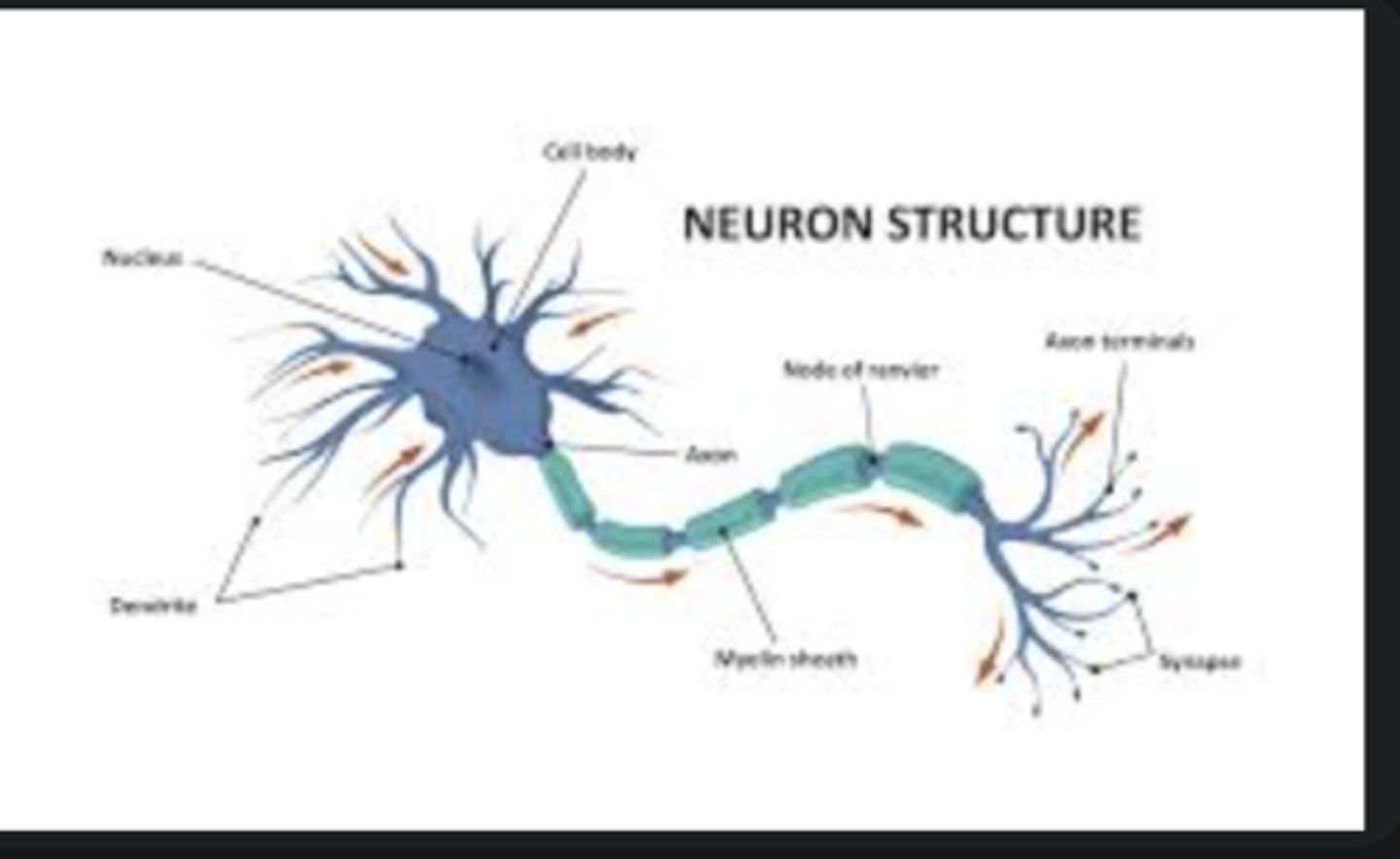
Axon
Long fiber that conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body.
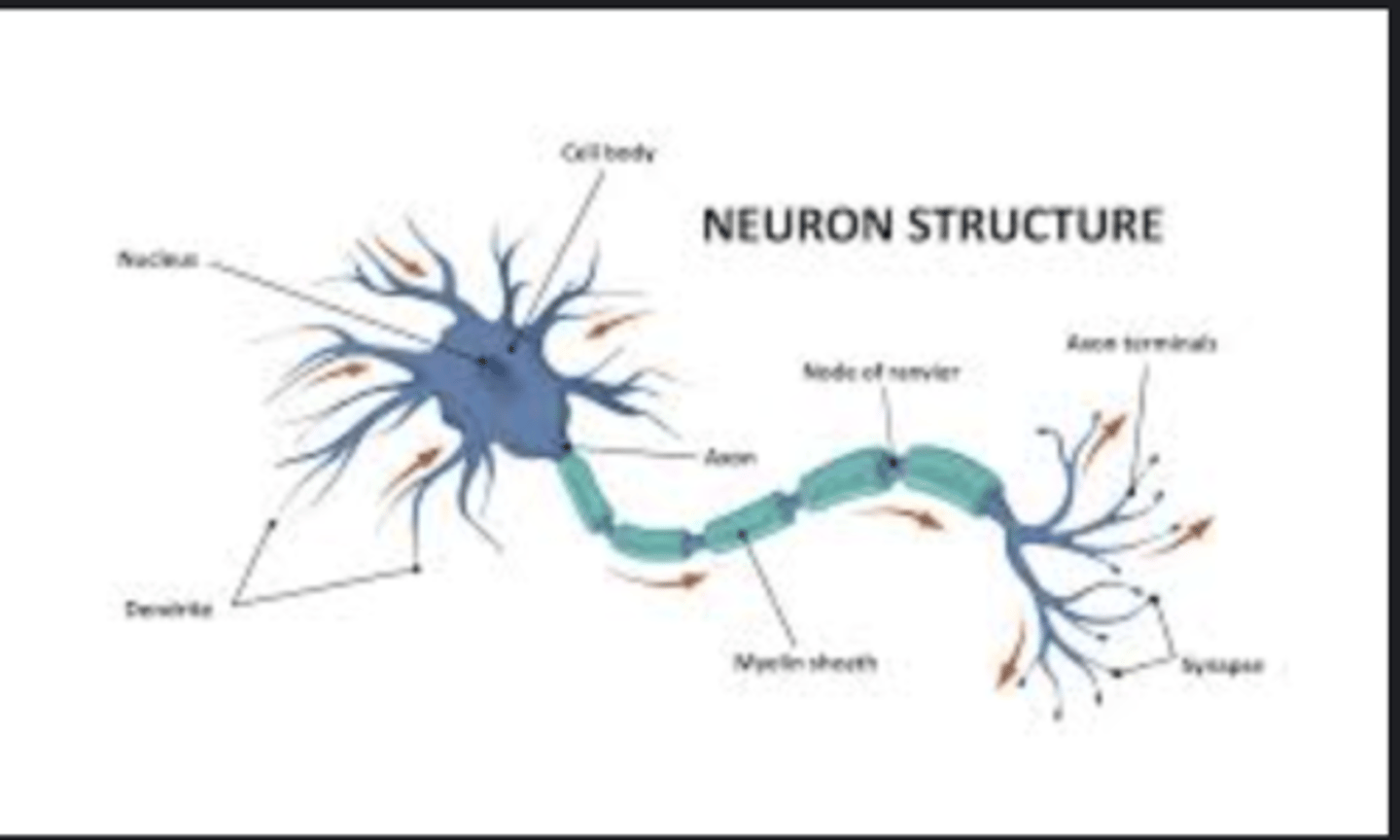
Dendrites
Branching structures receiving signals from other neurons.
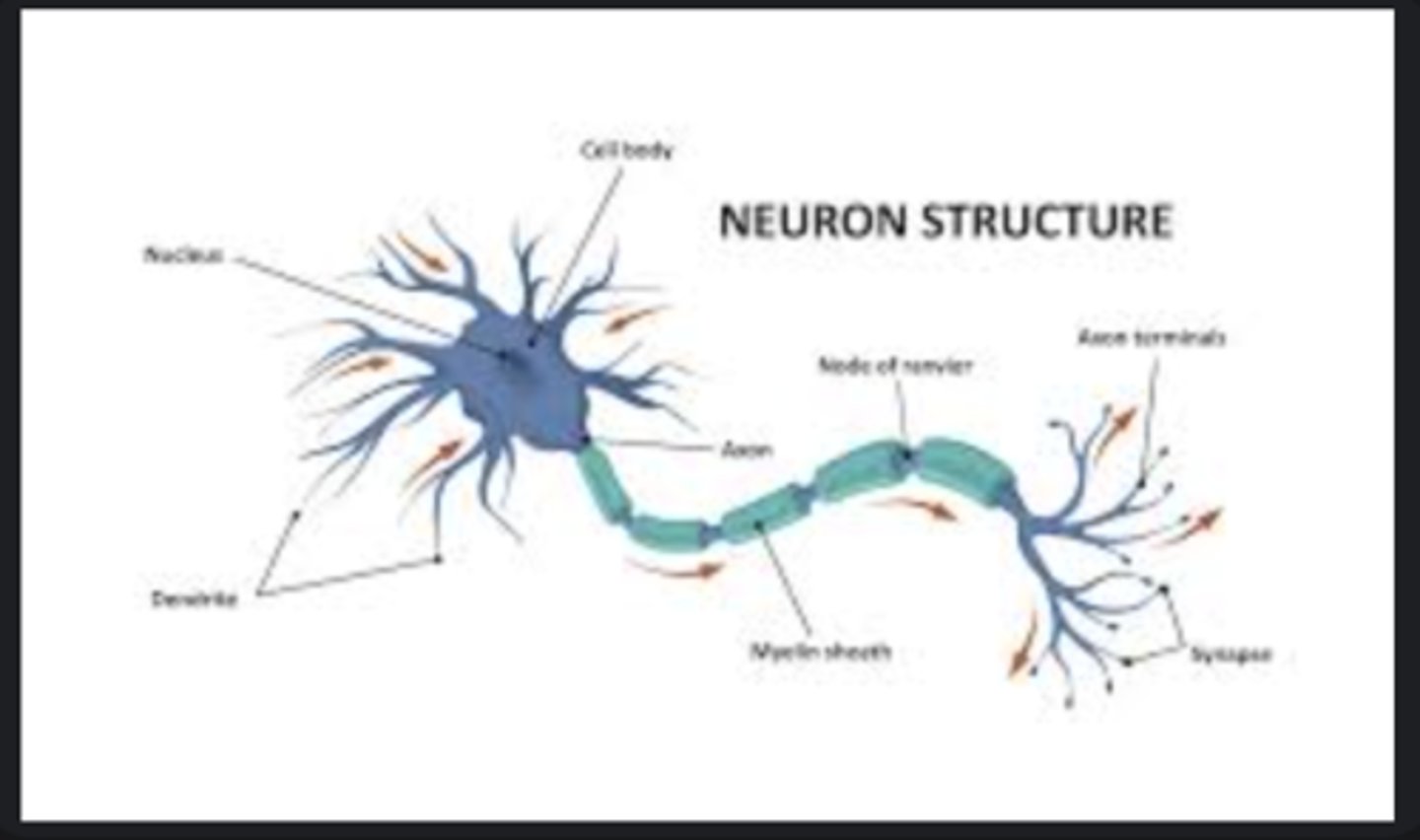
Synapse
Junction where nerve impulses pass between neurons using neurotransmitters.
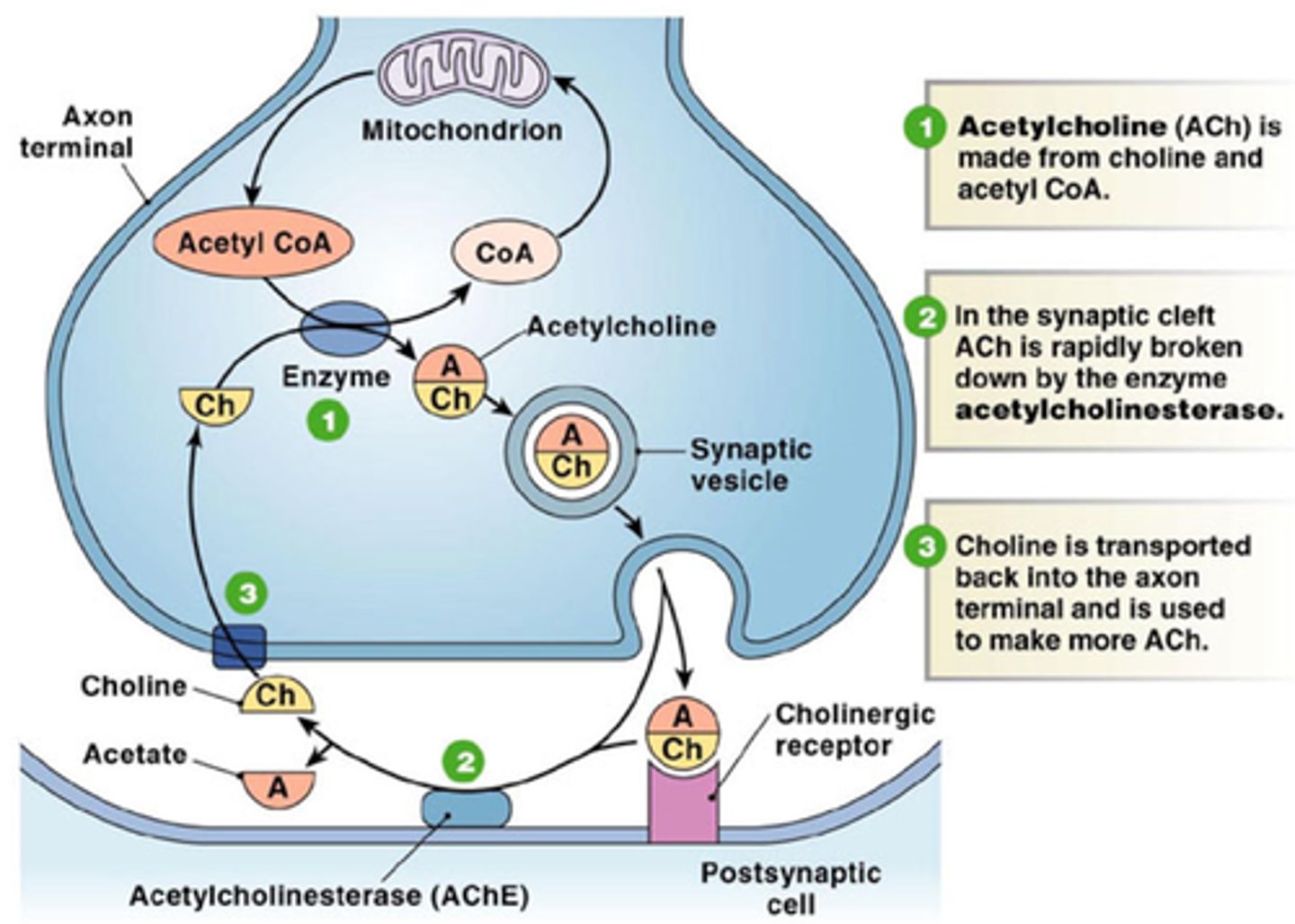
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Primary neurotransmitter in insects; transmits nerve impulses across synapses.
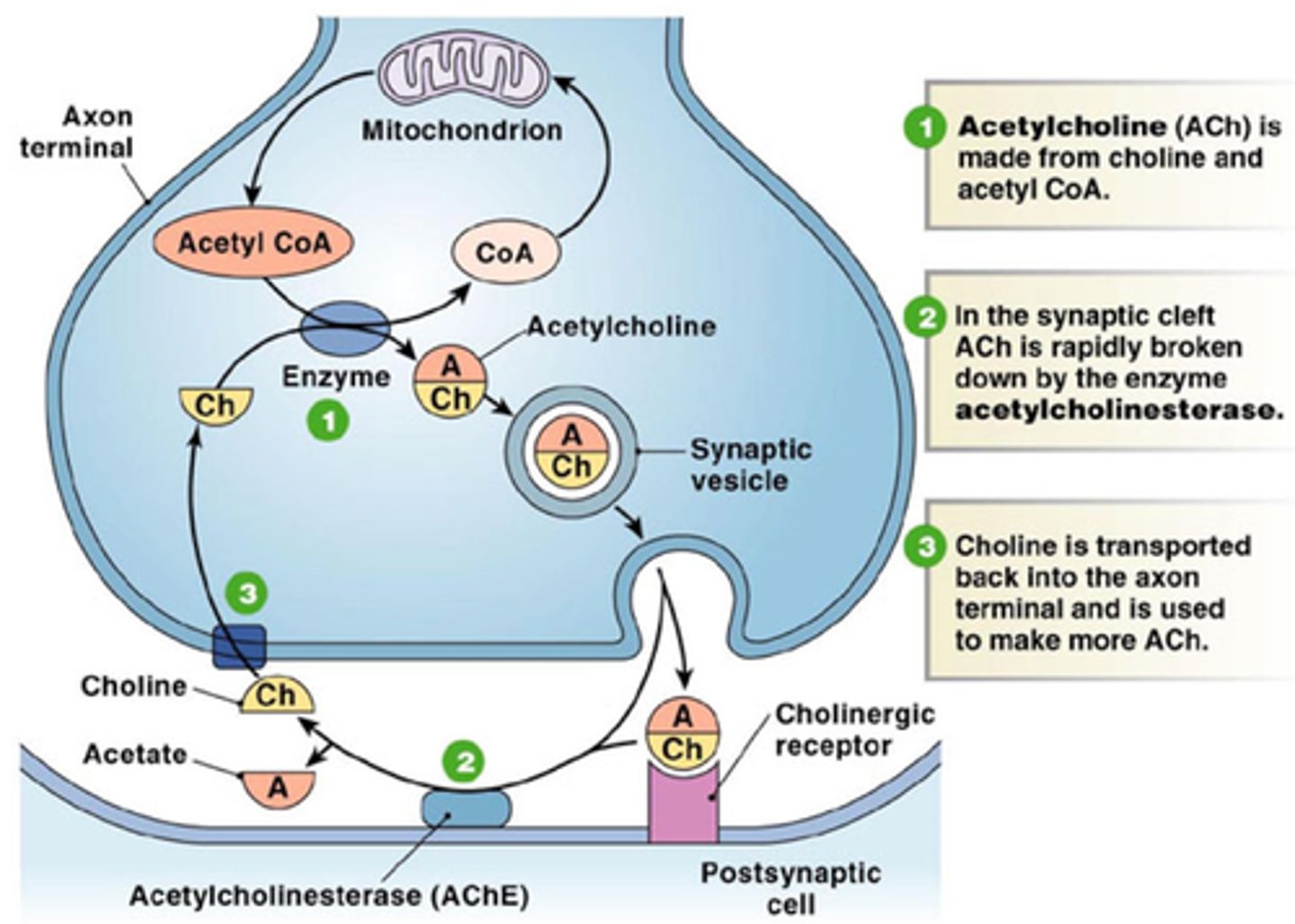
Acetylcholinesterase
Enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine to stop signal transmission; target of many insecticides.
Ganglia
Clusters of nerve cell bodies controlling body segments independently.
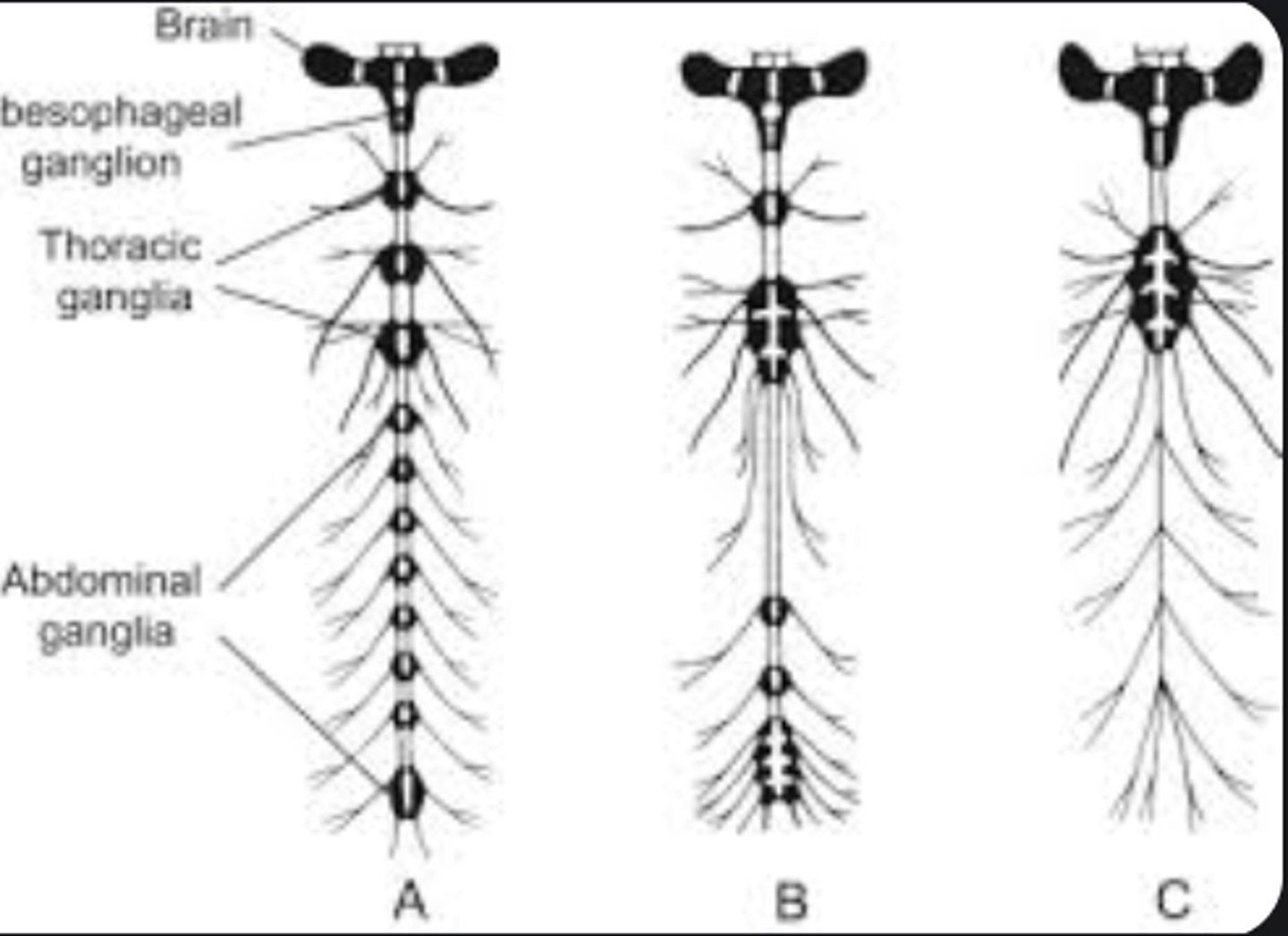
Brain
Central processing center consisting of protocerebrum (vision), deutocerebrum (antennae), tritocerebrum (mouthparts).
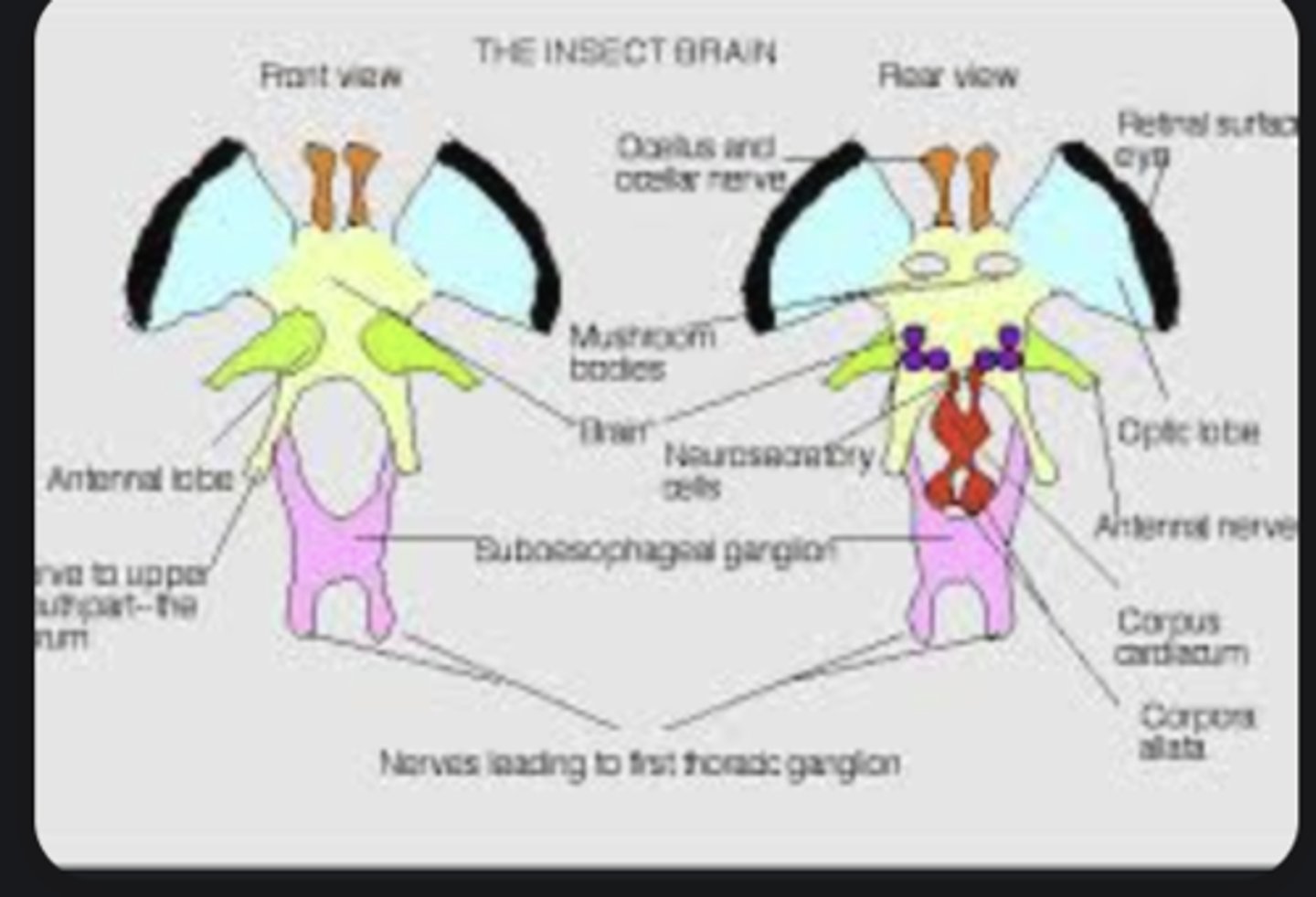
Ventral nerve cord
Main longitudinal nerve structure with paired ganglia along the insect's underside.