Unit 2: Nucleic Acids
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
the closest living relative to humans is
chimpanzees
we share 99.5% of our genome with them
epigenetics involves
covalent modifications to DNA to alter gene expression
DNA function
to store genetic information
gets transcribed by forming mRNA
replication translation, transcription
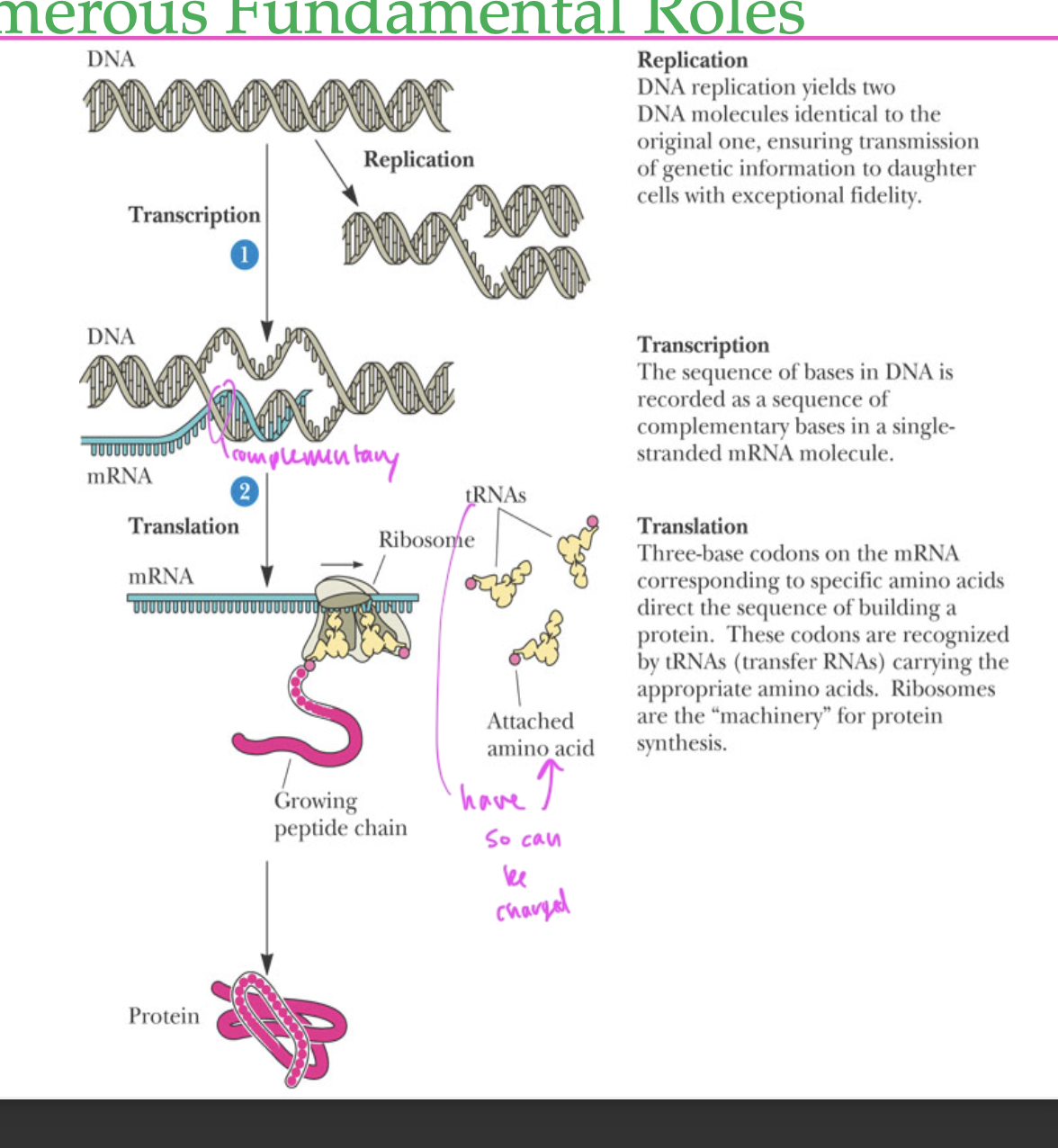
there are many types of
RNAs
miRNA, tRNA, rRNA, mRNA, etc
tRNAs have ____ attached to them
AAs, so can be charged
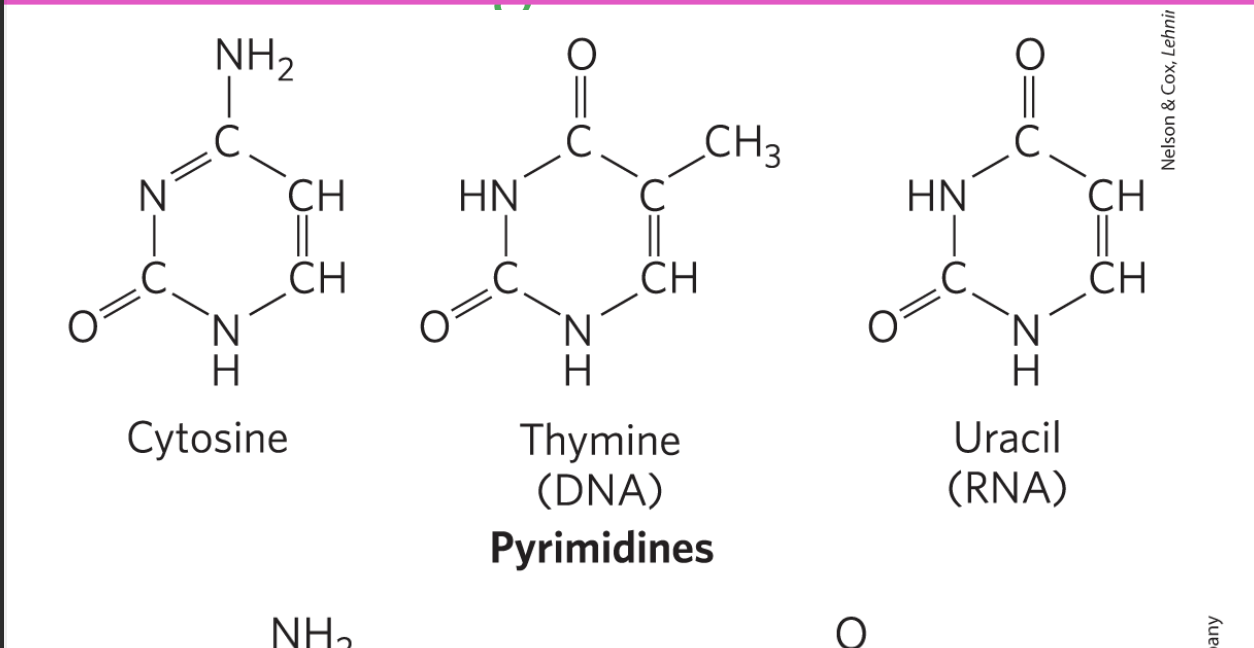
nucleobases in RNA
cytosine
guanine
adenine
uracil
C,A,G,U
nucelobases in DNA
cytosine
guanine
adenine
thymine
C,G,A,T
pyrimidines
have only one ring
includes C, U, T
purines
have two rings
includes A, G
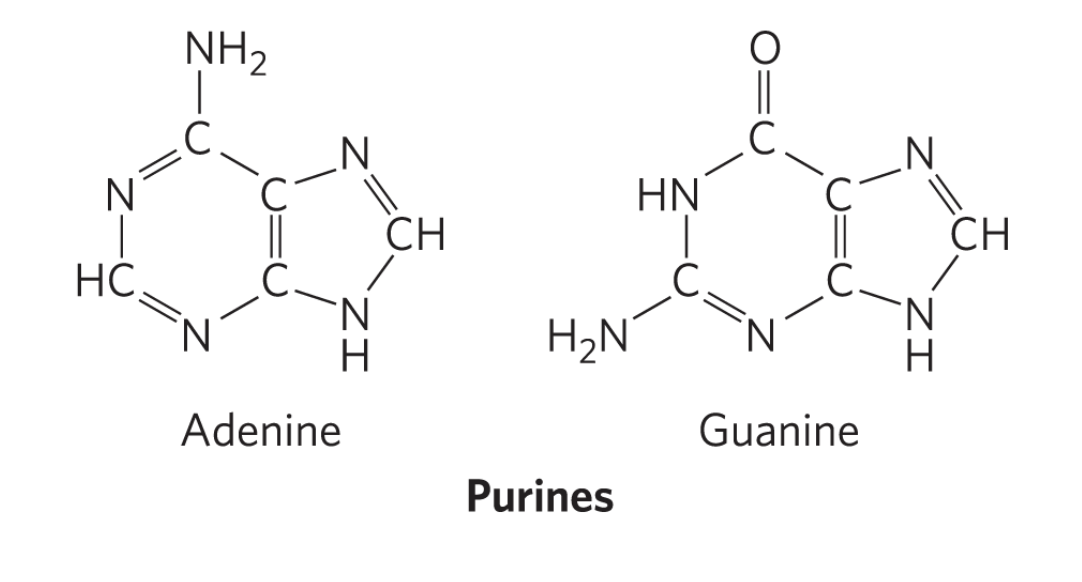
RECOGNIZE structures of all nucelobases
nitrogenous bases
nucelobases
CUTAG
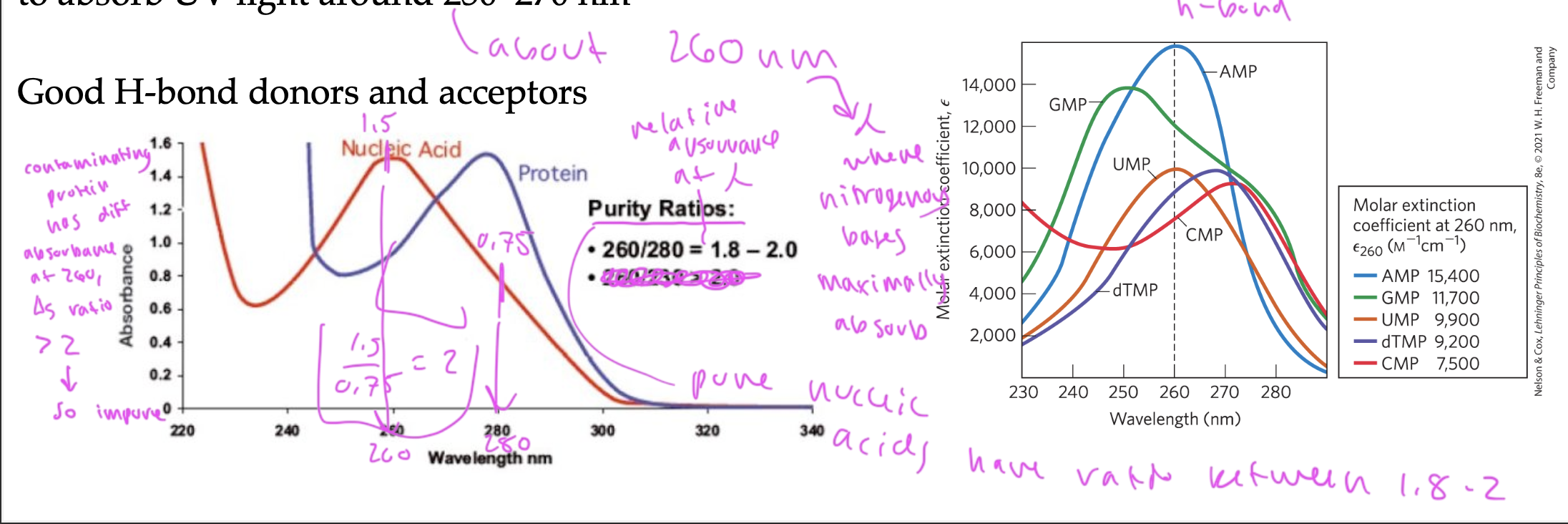
nitrogenous bases absorb
nitrogen-containing heterocyclic aromatic amines
are mostly planar due to much sp2
absorb UV light around 250-270nm due to the resonance in their aromatic rings
so they are good H-bond acceptors and donors
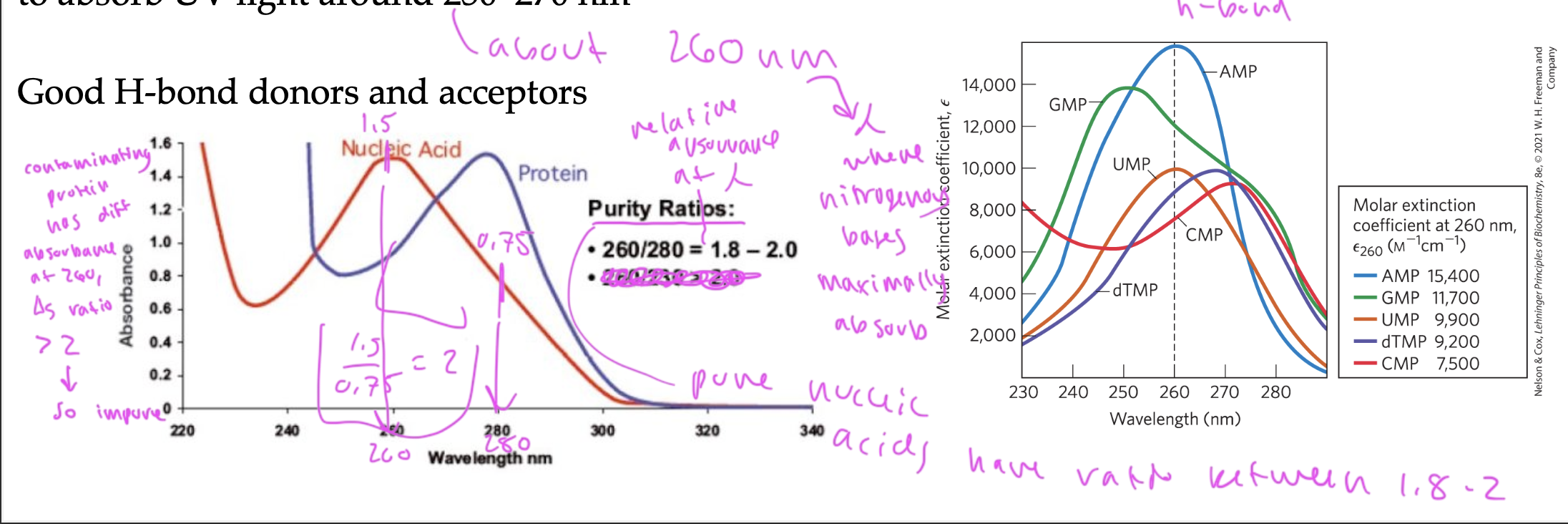
nitrogenous bases maximally absorb UV light at 260nm
how nitrogenous bases absorb UV
have purity ratios between 1.8-2 if pure
if there is protein contaminating the sample, the purity ratio would be greater than 2
look at the absorbance when wavelength equals 260 and 280. If values of absorbance (260 absorbance/280 absorbance) is 1.8-2, it shows purity
nucleobases
aka nitrogenous bases
nucleosides
contain
the nitrogenous base
pentose sugar
nucleotides
contain
nitrogenous base
pentose sugar
phosphate (at least 1)
nucleotide structure
phosphate is off the 5’ carbon of the pentose sugar
the alpha carbon is in the nitrogenous base
the 1’ carbon is in the pentose sugar
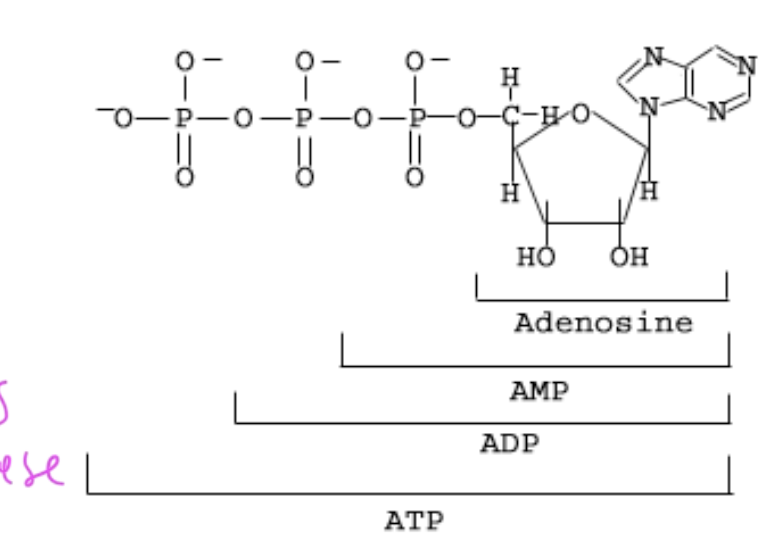
ATP full name
adenosine triphosphate
Nucleoside name of adenine
adenosine deoxyadenosine
nucleoside name of guanine
guanosine deoxyguanosine
nucleoside name of cytosine
cytidine deoxycytidine
nucleoside name of thymine
thymidine OR deoxythymidine
nucleoside name of uracil
uridine
ribose
has a 2’ OH
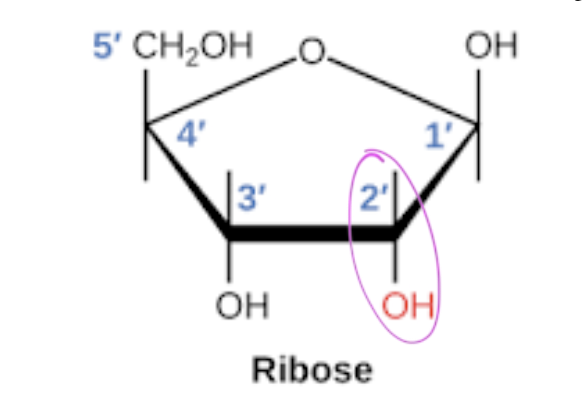
ribonucleic acids
polymers of ribose
deoxyribose
has a 2’ H
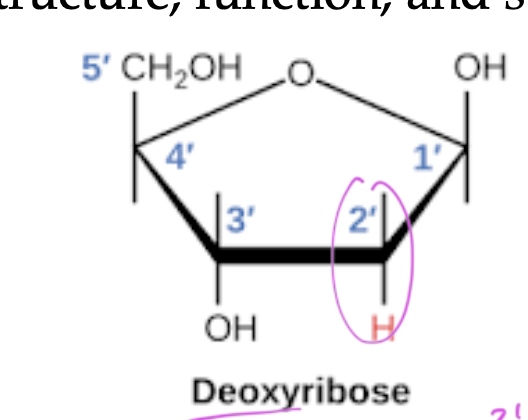
deoxyribonucleic acids
polymers of deoxyribose
nucelic acid functions
store genetic info in DNA
transmit genetic info using RNA
synthesize proteins (using tRNA and rRNA)
process pre-mRNA (using small nuclear RNA)
parts of ATP
ATP has 3 Ps
ADP has 2 Ps
AMP has 1 P
adenosine has no Ps
nucleotide functions
energy for metabolism (ATP)
enzyme coenzymes (like NAD+)
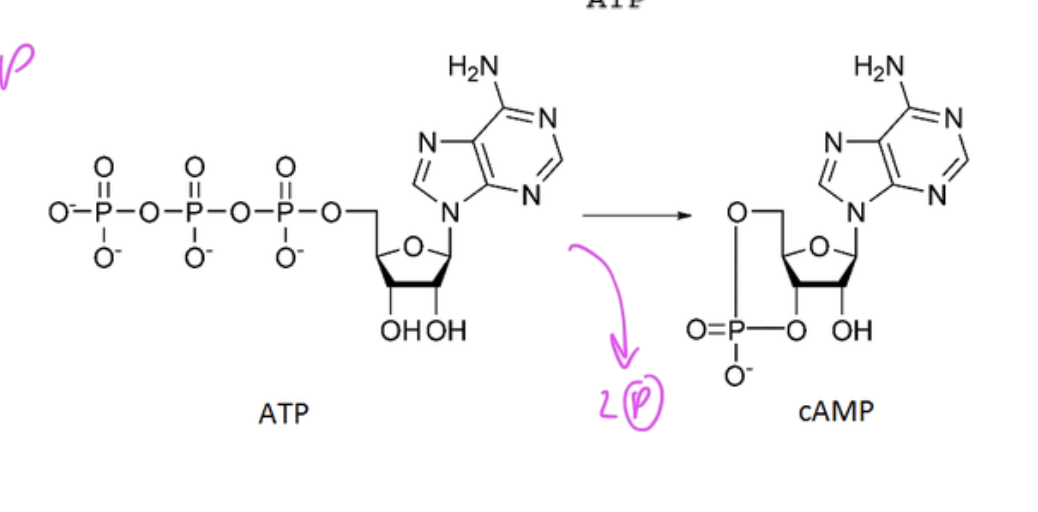
signal transduction (cAMP)
cAMP is made from
ATP
it is ATP with two less Ps (so only 1 P)
NAD+ is
two nucleotides joined together
glycosidic bond
between a sugar and nitrogenous base of a nucleotide
is sterically hindered in nitrogenous bases
can be syn or anti conformation
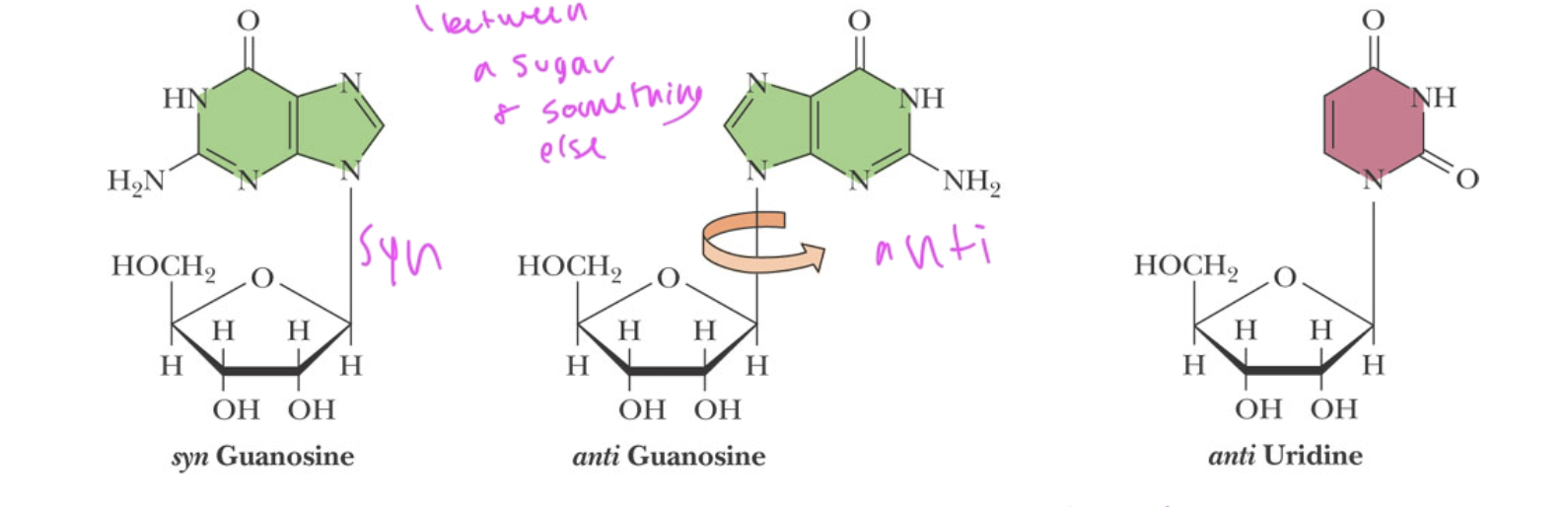
what conformation of glycosidic bonds is favorable in normal DNA?
anti
helps form the DNA double helix
what conformation of glycosidic bonds is favorable in RNA
both syn and anti since RNA is single stranded and therefore more flexible
nucleic acid backbone uses what connections
phosphodiester bonds
between the 3’ OH of a deoxyribose and the 5’ of the phosphate group of another nitrogenous base
new nucleotides are added onto the 3’ hydroxyl end
two phosphates leave to drive the condensation of two nucleotides (so a water molecule is released as a result)
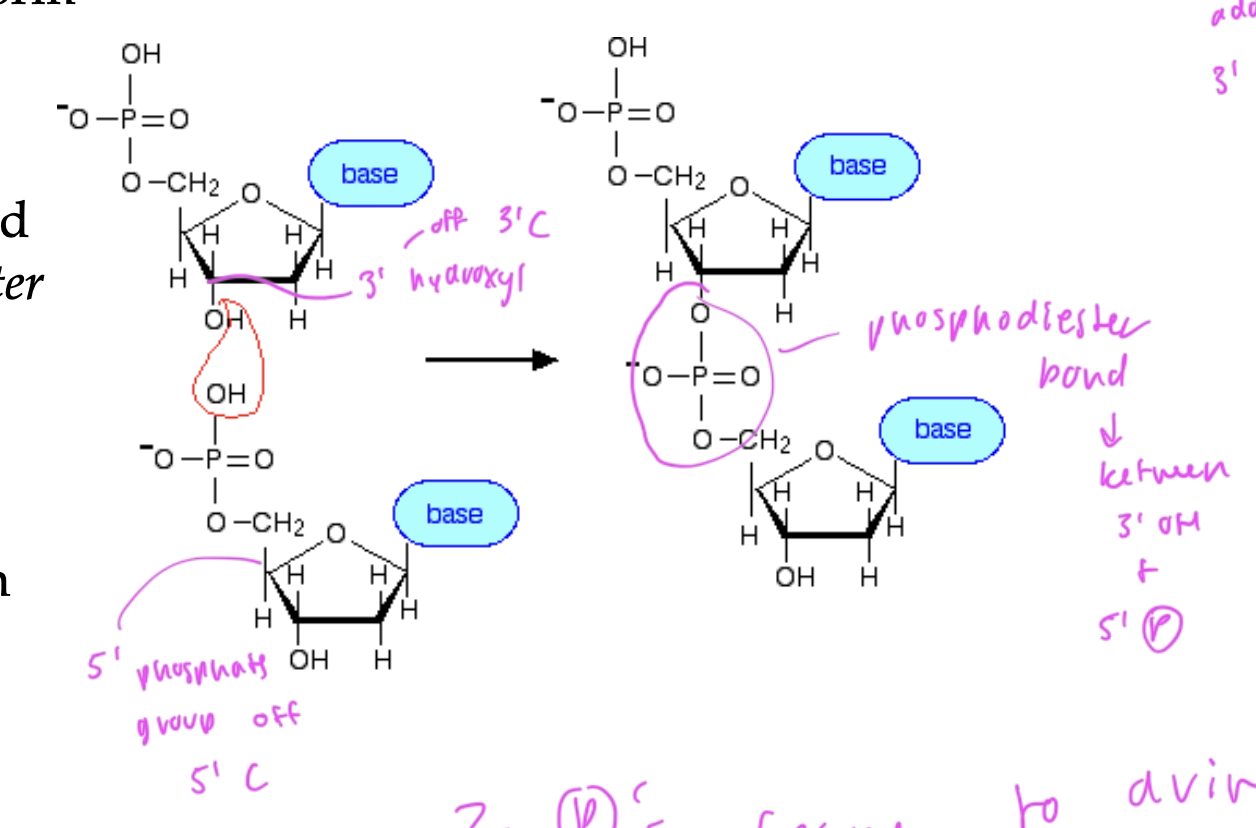
the nucleic acid backbone is _____ charged
negatively
due to the neg phosphates
the nucleic acid backbone is read
5’—>3’ (N—>C)
and made 3’—>5’. (C—>N)
RNA folding
secondary folding like hairpin loops all go together to form the finally completed tertiary structure
the secondary structures are held together by hydrogen-bonds between A and U, G and C, and sometimes G and U
so between complementary bases
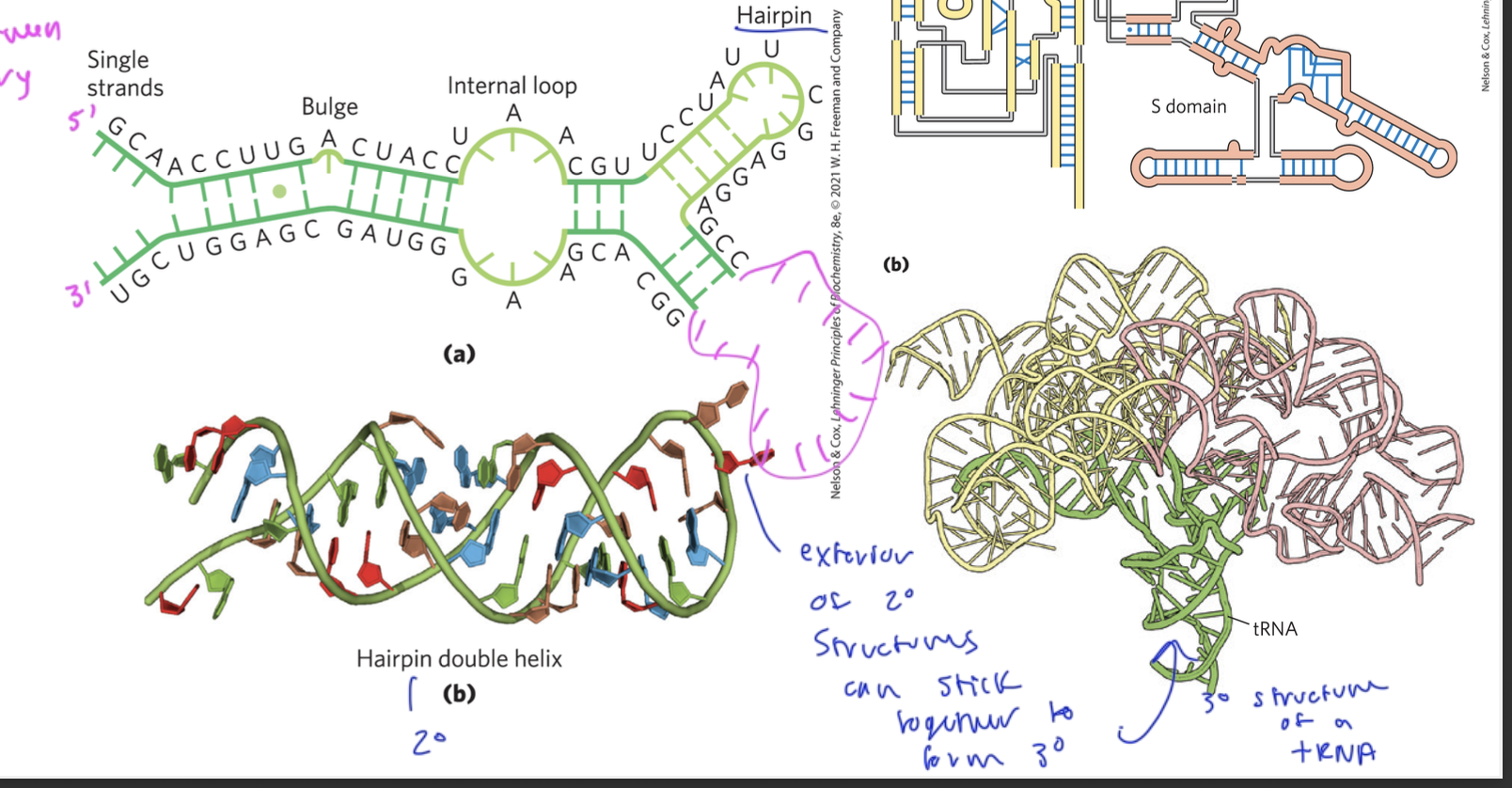
tertiary structure of RNA
see fully folded up in bottom right
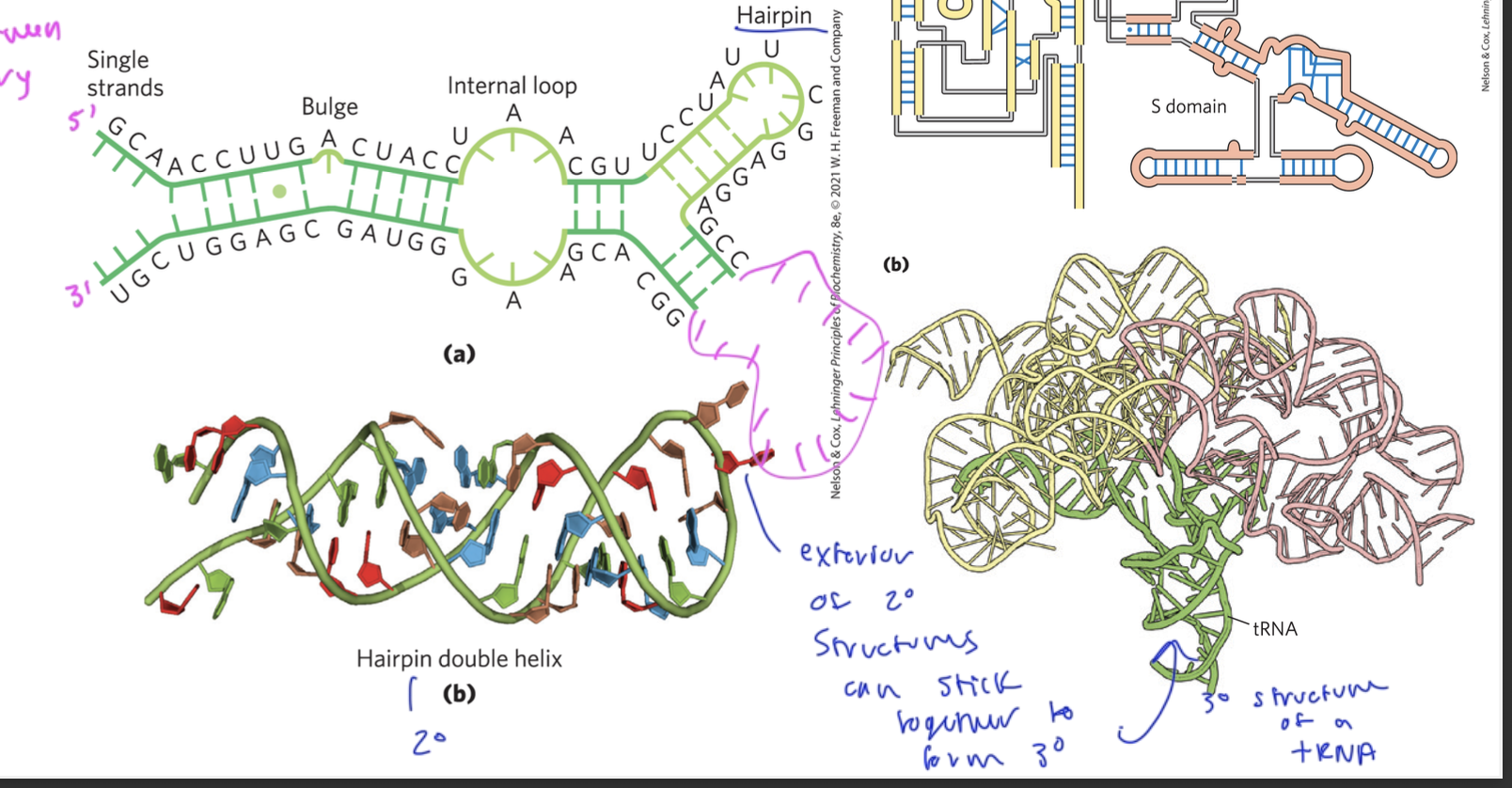
primary structure of RNA
the single strand
hydrogen bonds between _____ form the secondary structures in nucleic acids
A and U
G and C
sometimes G and U
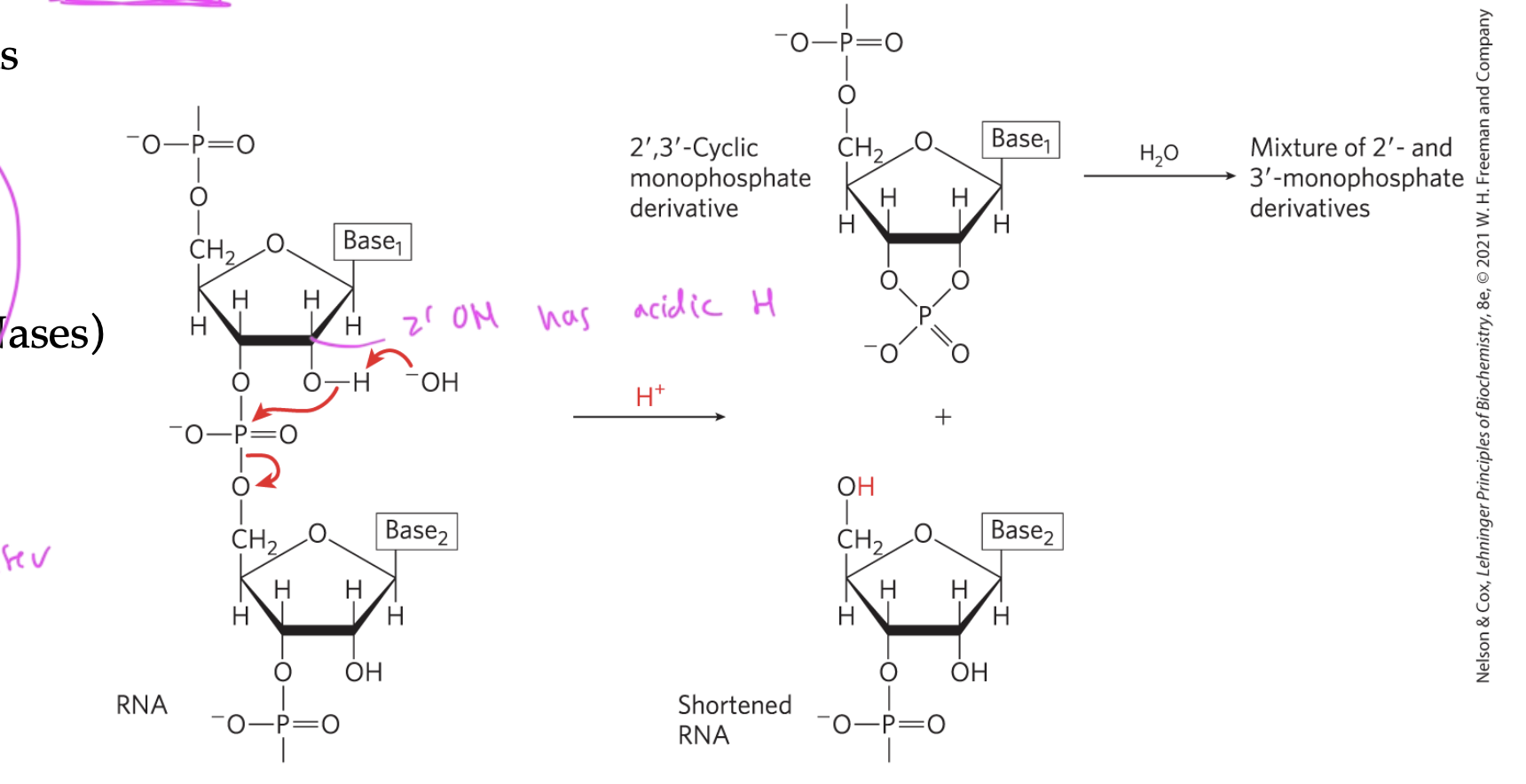
what can cause RNA to undergo hydrolysis/breaking apart?
alkaline (basic conditions)
enzymes (RNases)
both cause the acidic H of the 2’ OH to be removed, so it attacks the adjacent phosphate group
this causes the phospodiester bond to break, so the two nucleotides split
DNA is less susceptible to hydrolysis
strands in DNA run
antiparallel
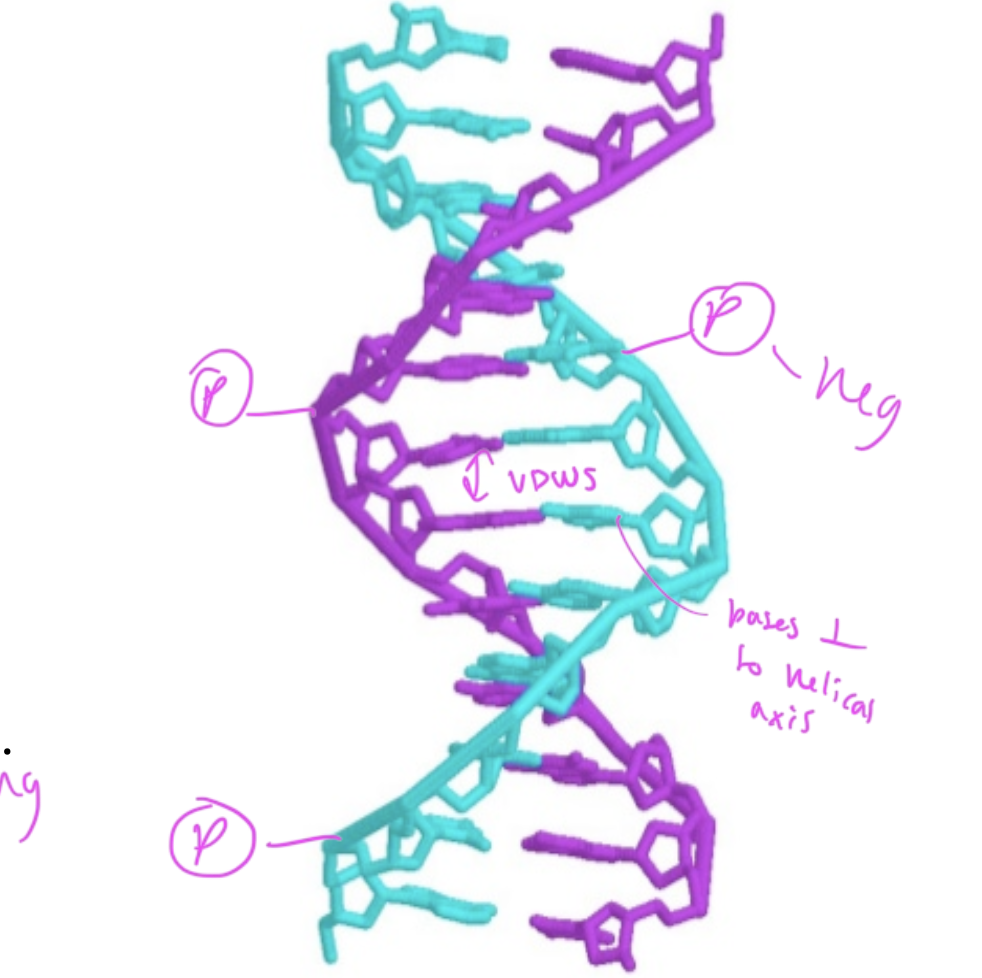
where are phosphate groups in regards to the dsDNA
they are in the exterior, pointing out
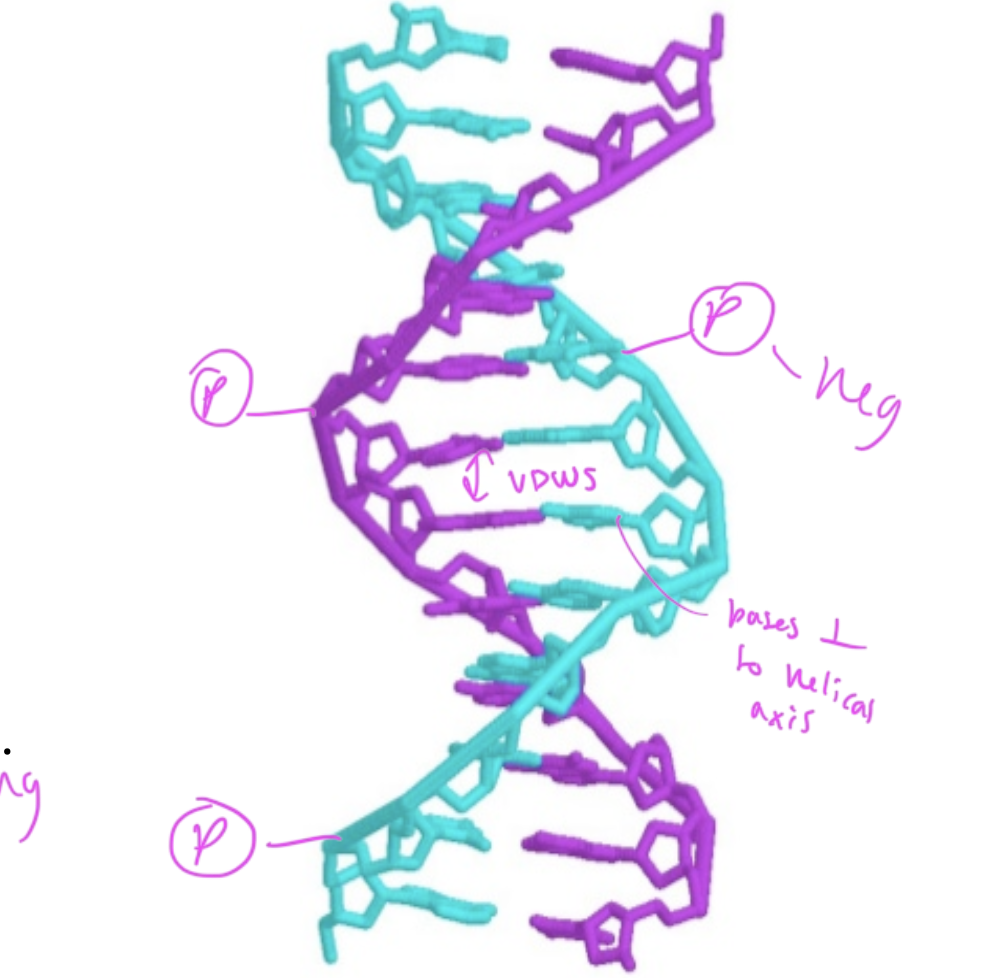
nucleobases in the middle of dsDNA are ____ to the helical axis
perpendicular
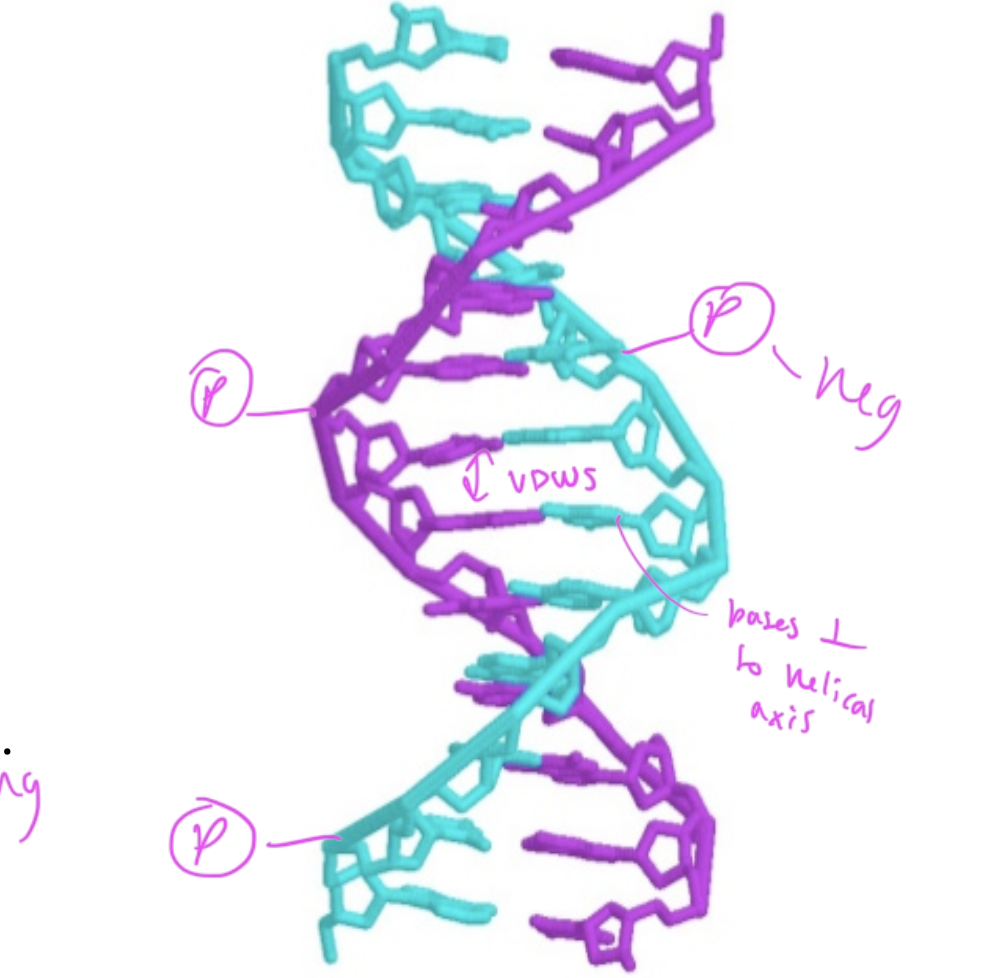
interactions within dsDNA
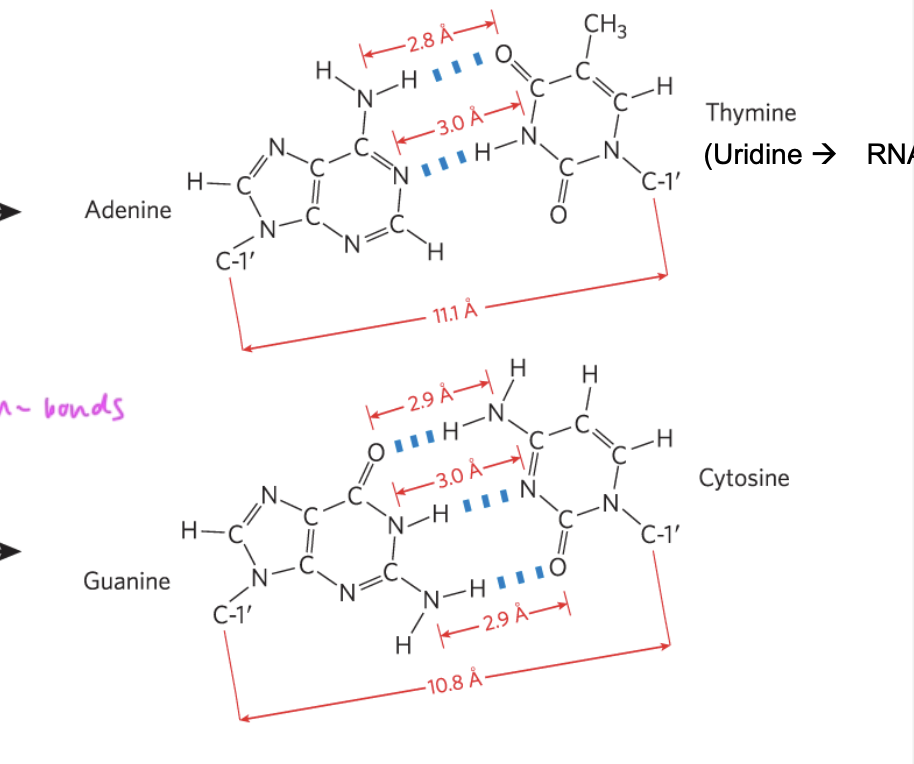
hydrogen bonds between C and G (3 h-bonds) and A and T (2 h-bonds)
VDWs forces between the hydrophobic nucleobases
the number of adenosine residues in dsDNA equals
the number of thymidine residues
and number C equals number G
so number purines=number pyrimidines
the double helix of DNA is a _____ structure
secondary
and the final structure of DNA (that we will cover)
base pairs within DNA ___
hydrogen-bond to their complementary counterpart
see where between two nucleotides h-bonds actually occur
major and minor grooves and what binds
major: base pairs are more exposed, so proteins that regulate gene expression bind here
minor: hard for things to reach the bases inside the dsDNA, so proteins that help package up DNA bind here
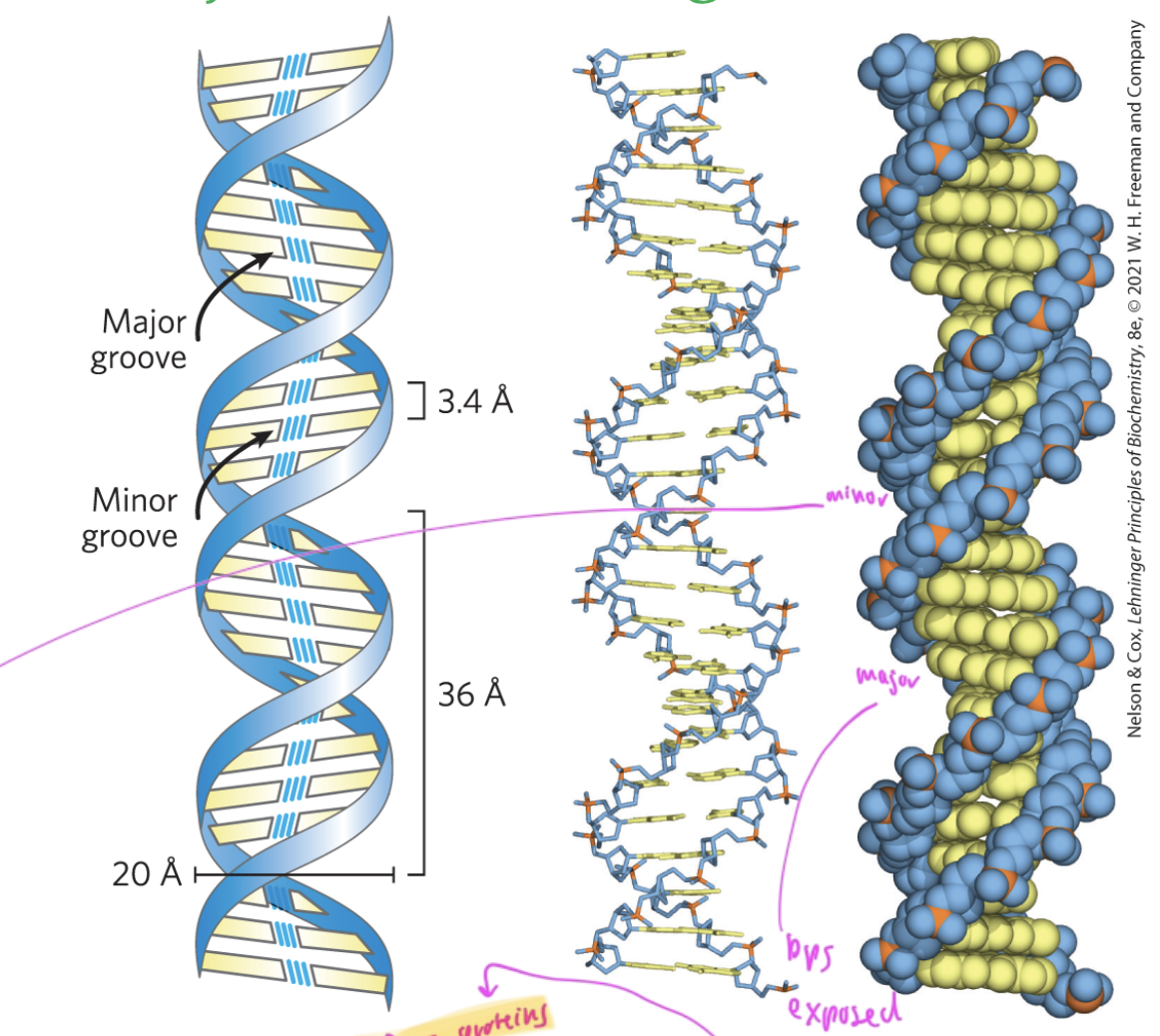
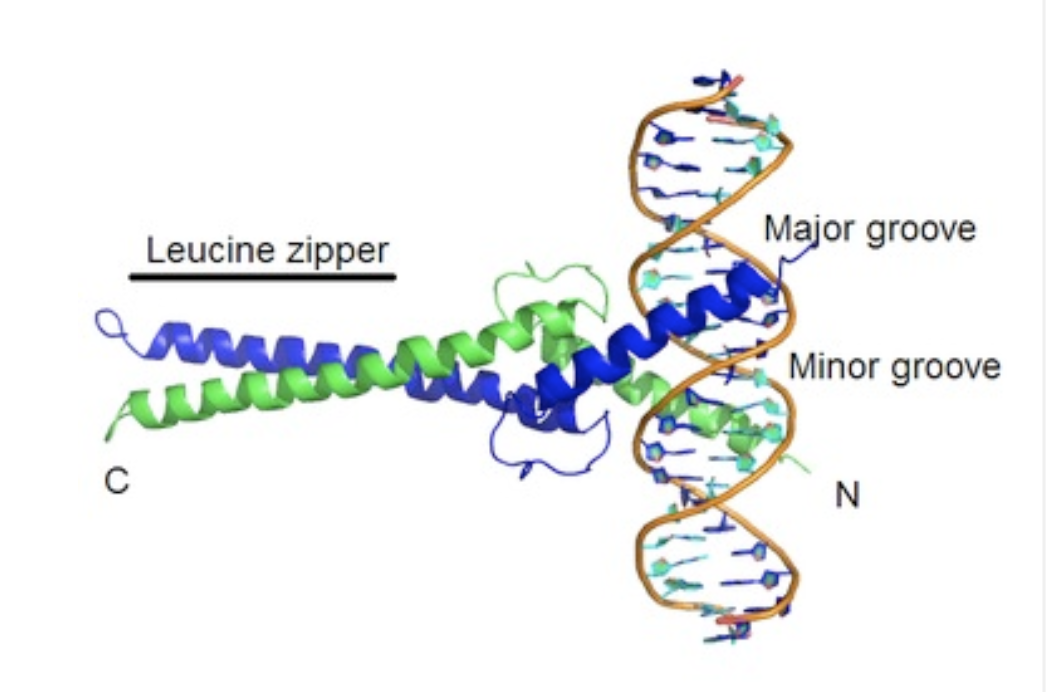
the major groove of DNA is large enough for _____ to bind
an alpha helix of a protein
so regulatory proteins/transciption factors can bind here to recognize the pattern of nucleobases
how tightly DNA is bound in chromatin, for example, regulates
gene expression
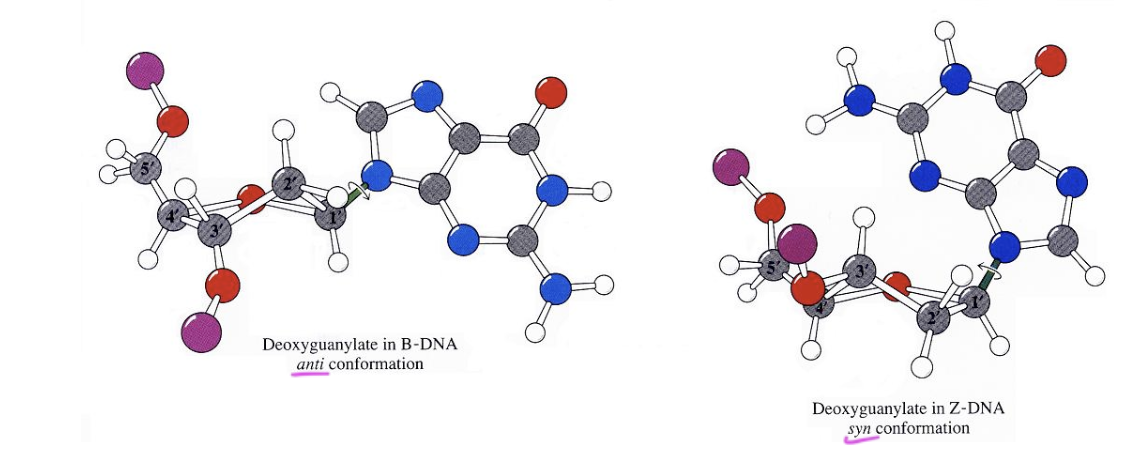
3 types of DNA strands
A form
B form (standard)
Z form
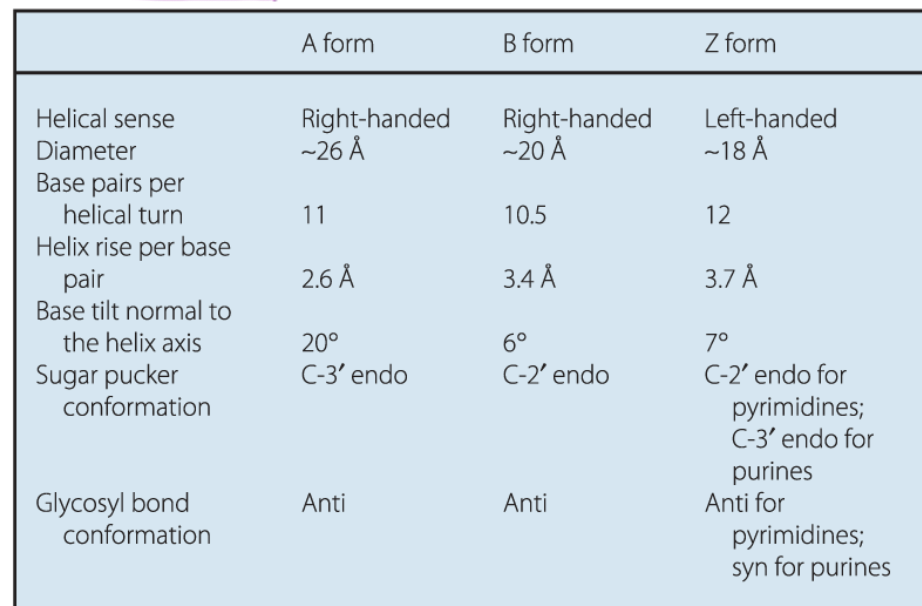
A form of DNA
RHH
has a larger opening in the middle
occurs when you put DNA in a solution than let it dry
has nucleobases tilted a bit, but still has major and minor grooves
B form of DNA
RHH
standard form
bases are perpendicular to the helical axis
has normal major/minor grooves
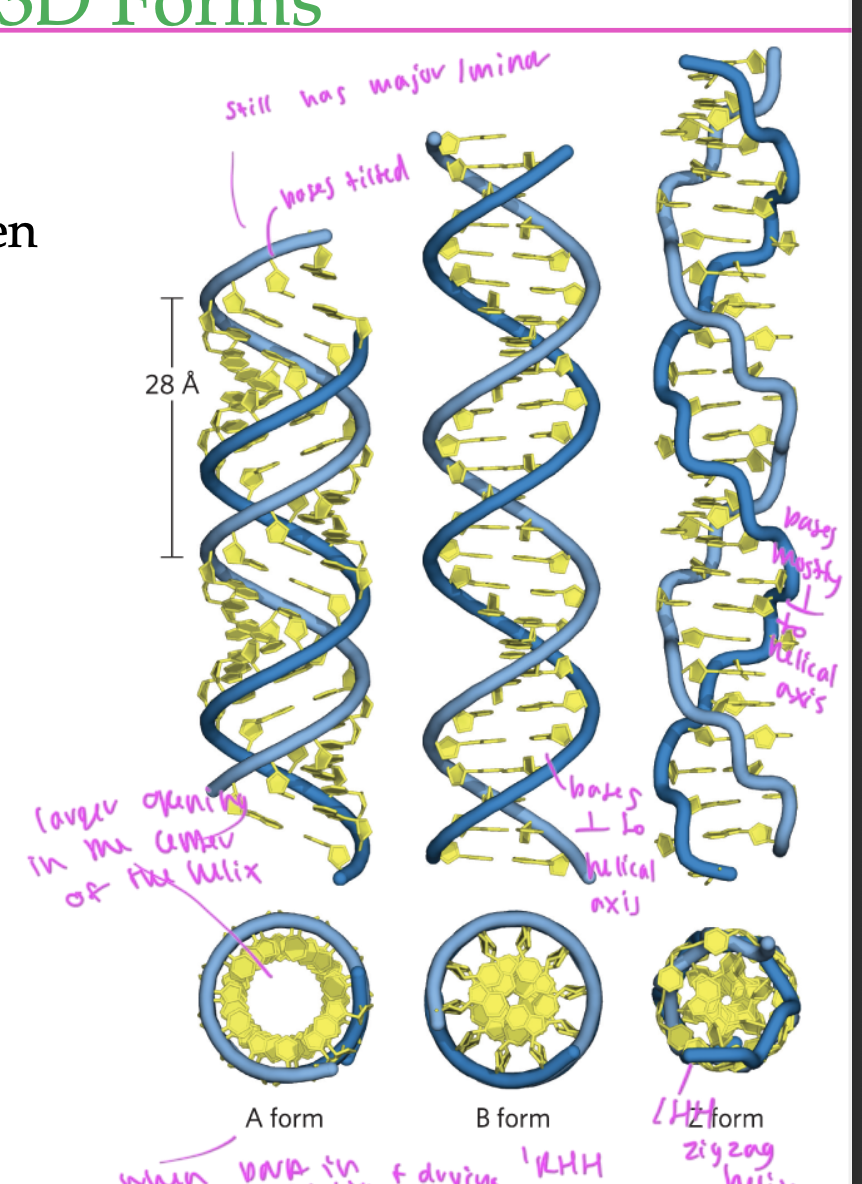
Z form of DNA
LHH
zigzagged helix
bases are mostly perpendicular to the helical axis
what form of DNA is the major conformation
B
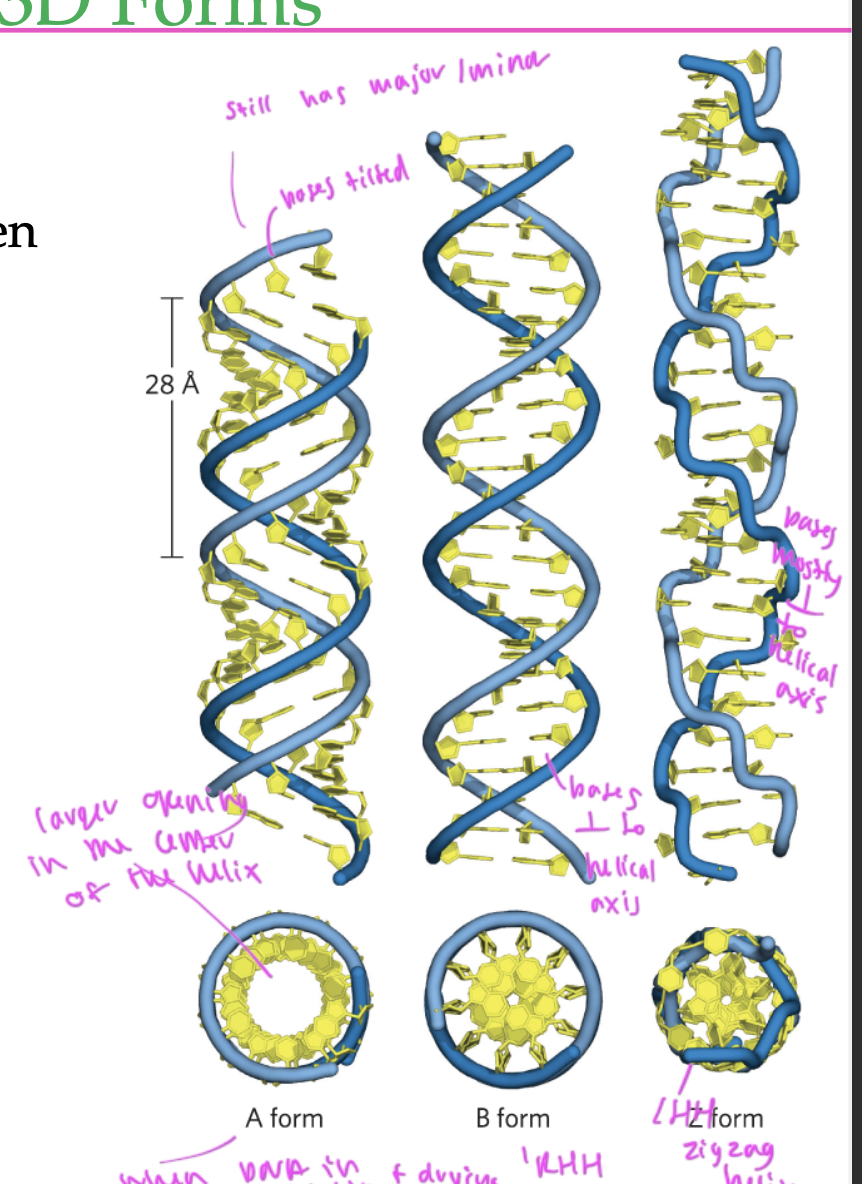
denaturation of DNA
causes dsDNA to turn ss
can be caused by temp, pH, or ionic strength
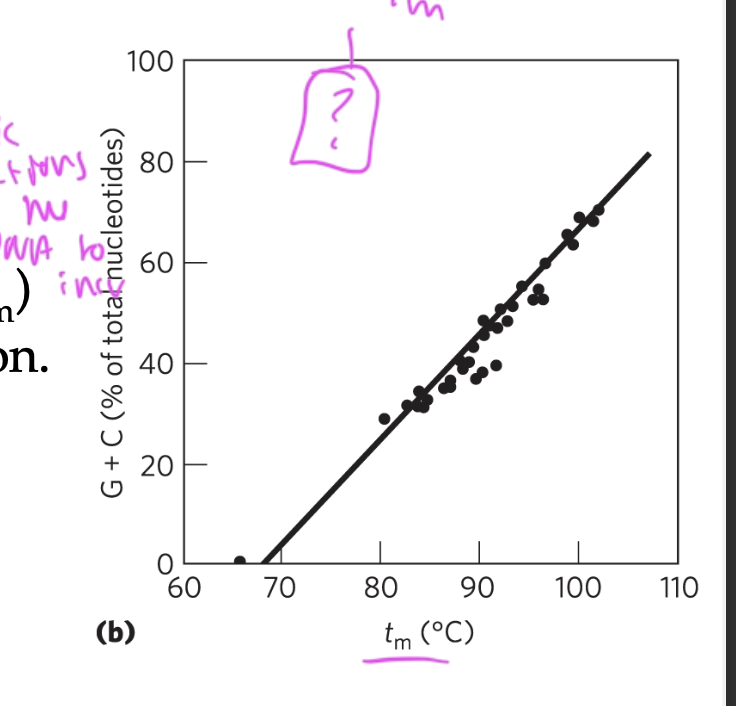
incr ionic strength (salt conc) or G/C content (since they have 3 not 2 h-bonds) causes the melting temp of the DNA to incr
its easier to anneal ____ regions of DNA
shorter
since less room for error
what can cause DNA to anneal back to dsDNA?
normal temp/pH
annealing takes a while
denaturation of DNA is
quick
can be caused by
high temp
low salt conc
low pH
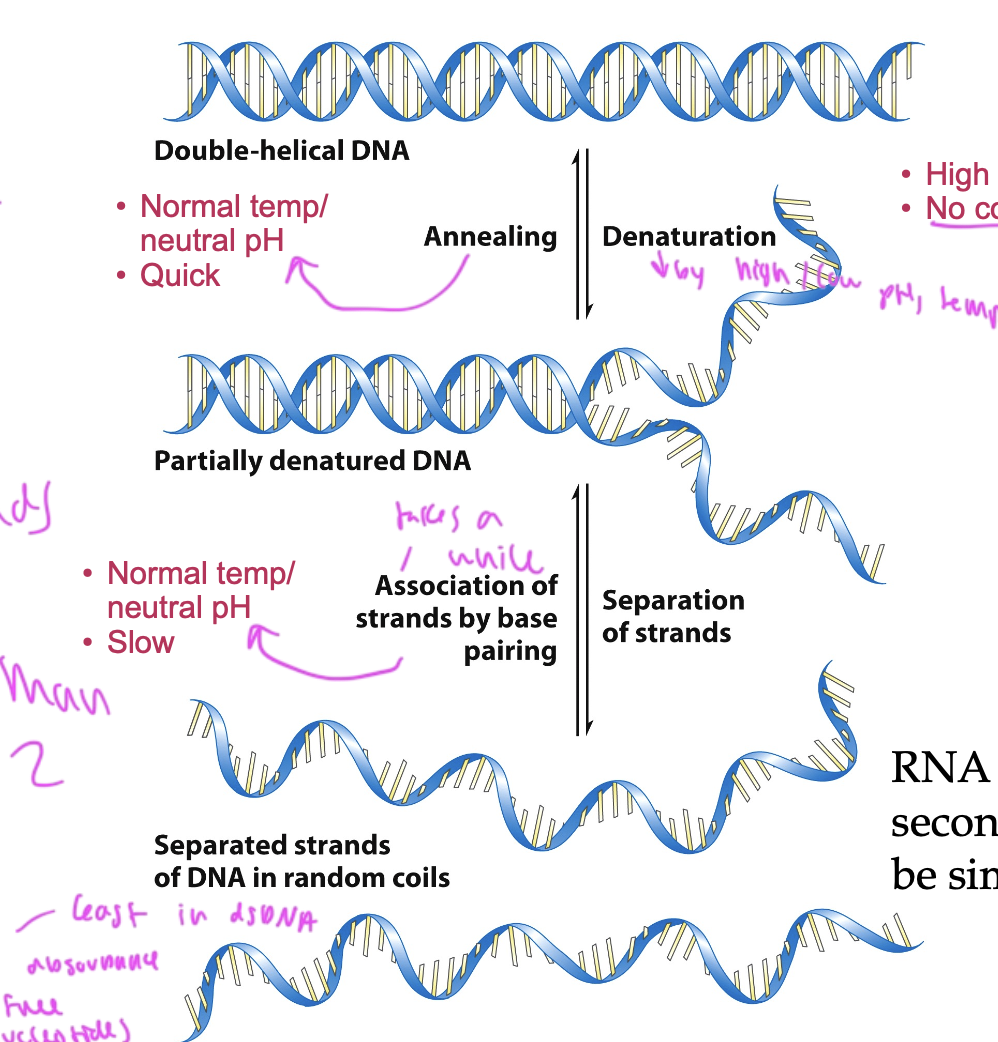
hyperchromic effect
a decr in the absorbance at 260nm (A260)
seen when DNA/RNA is denatured since free nucleotides absorb more than ds or ss dNA
since stacked bps in dsDNA absorb less light since they are covered up more
when DNA is heated, its UV absorbance…
incr
since denaturation causes there to be more free nucleotides, and therefore absorbs more UV light (by 30-40%)
Tm
the temp at which half of nucleotides are in dsDNA and half are in ssDNA
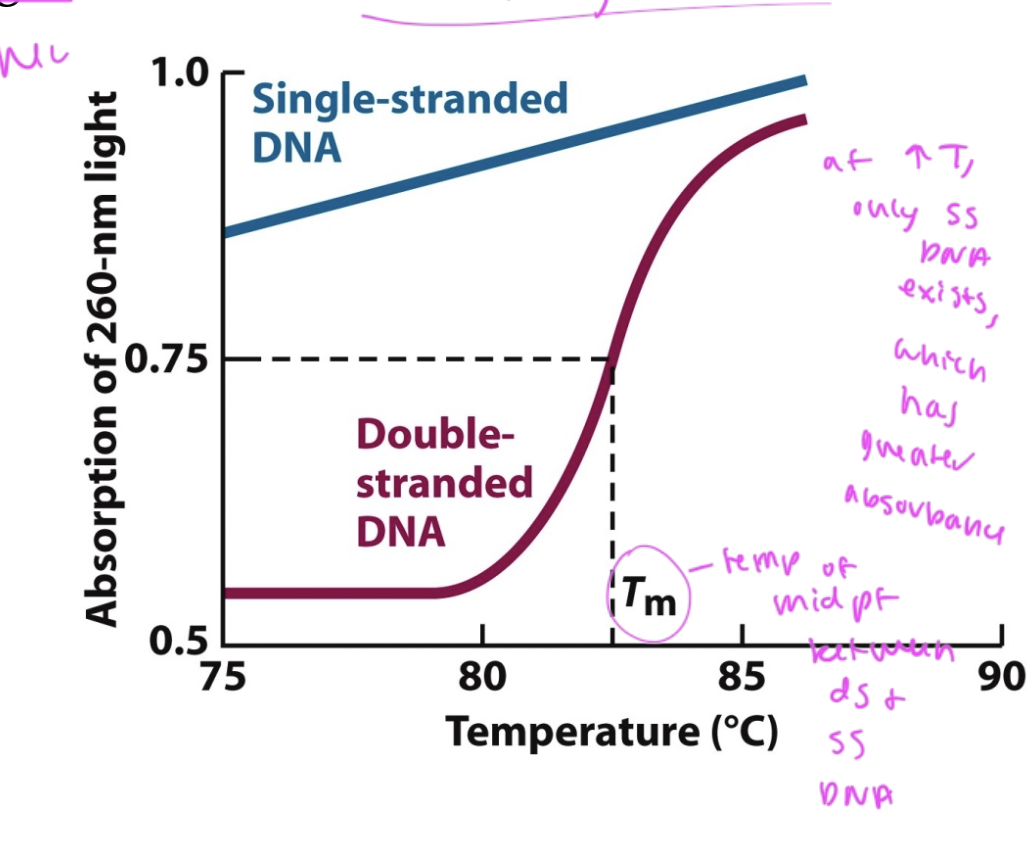
if temp lowers, absorbance ___
drops
shows that dsDNA formed again after denaturation
melting curve of DNA
shows that there is most in ssDNA at high temp (and it has the highest UV absorbance here)
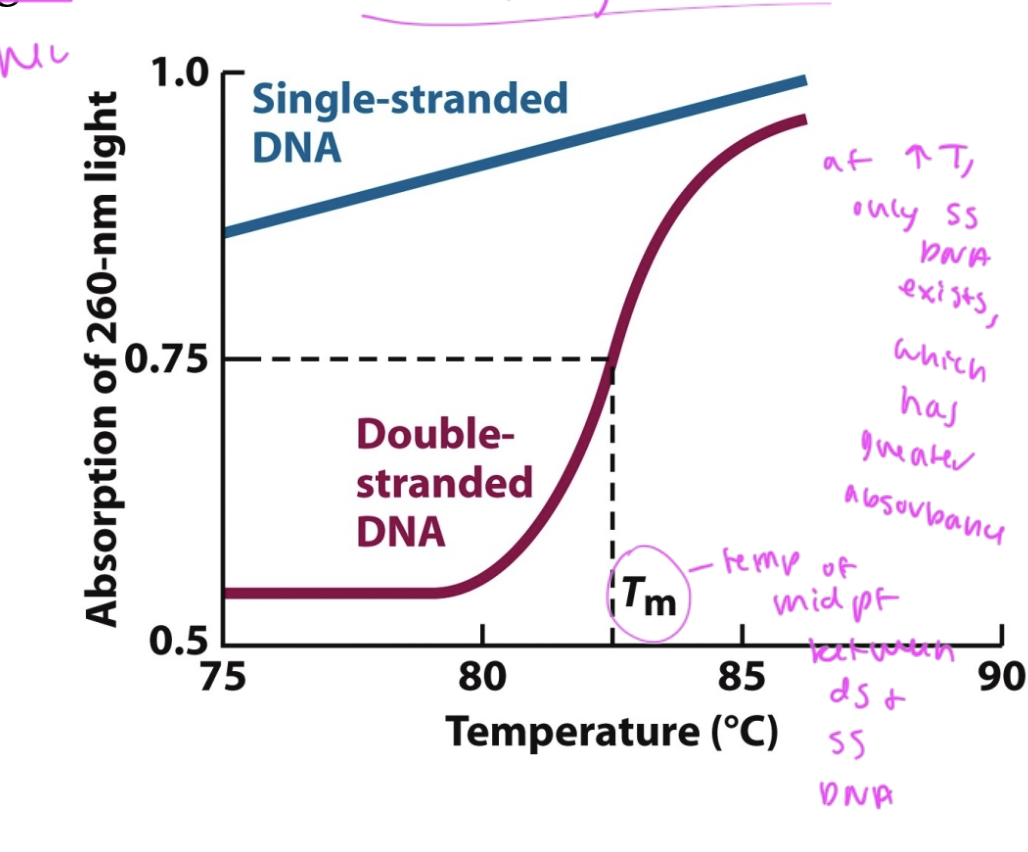
longer DNA has ___ Tm
higher
since there is a higher temp at which half of its in ssDNA
Tm depends on
pH and ionic strength, and base composition
high salt conc: causes hydrophobic interactions within the dsDNA to solidify/incr (so Tm incr)
pH: too high or low pH affects Tm
base pair composition: high C-G bonds (triple h-bonds) causes Tm to incr
since it takes more energy to break