Contraception
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
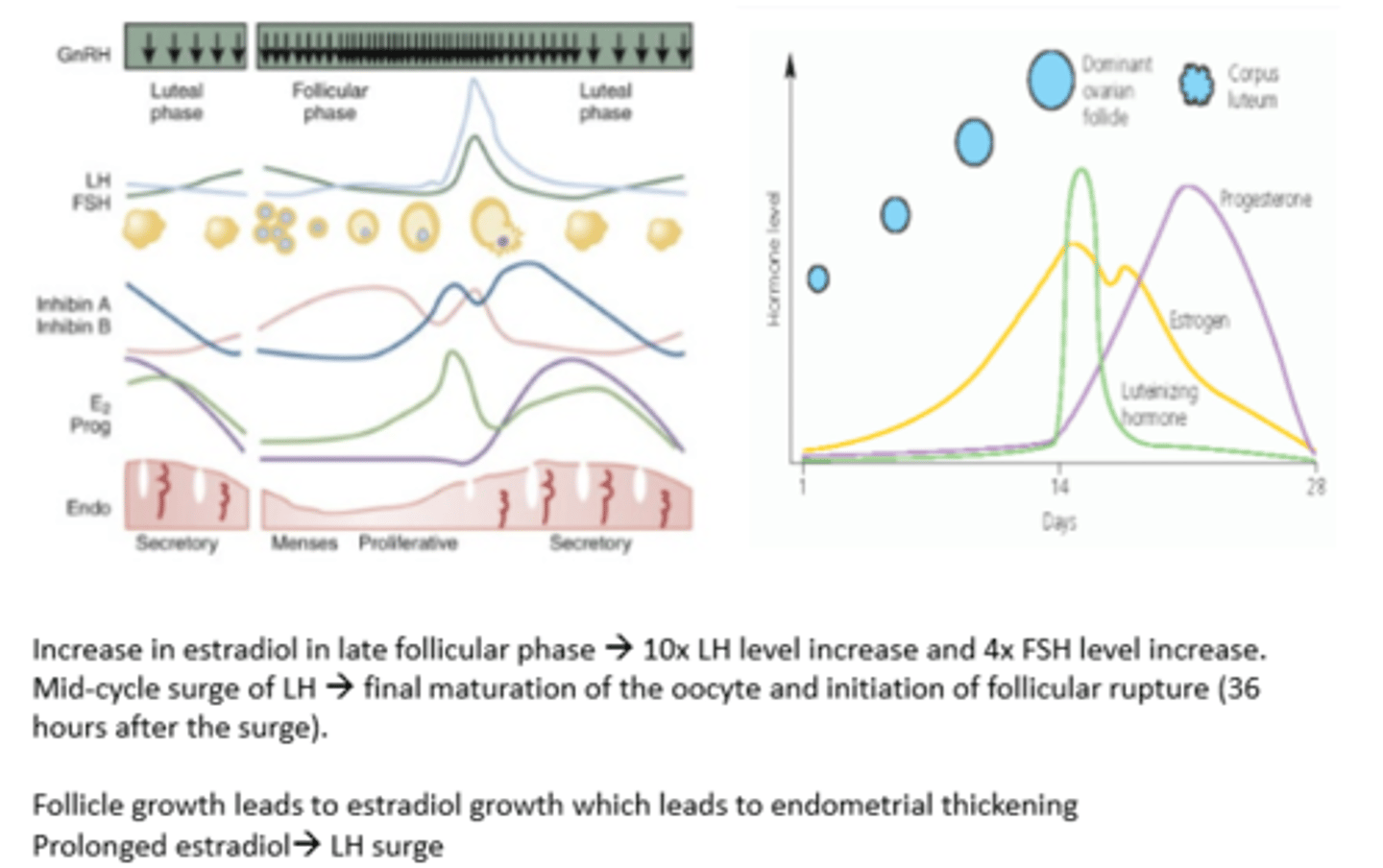
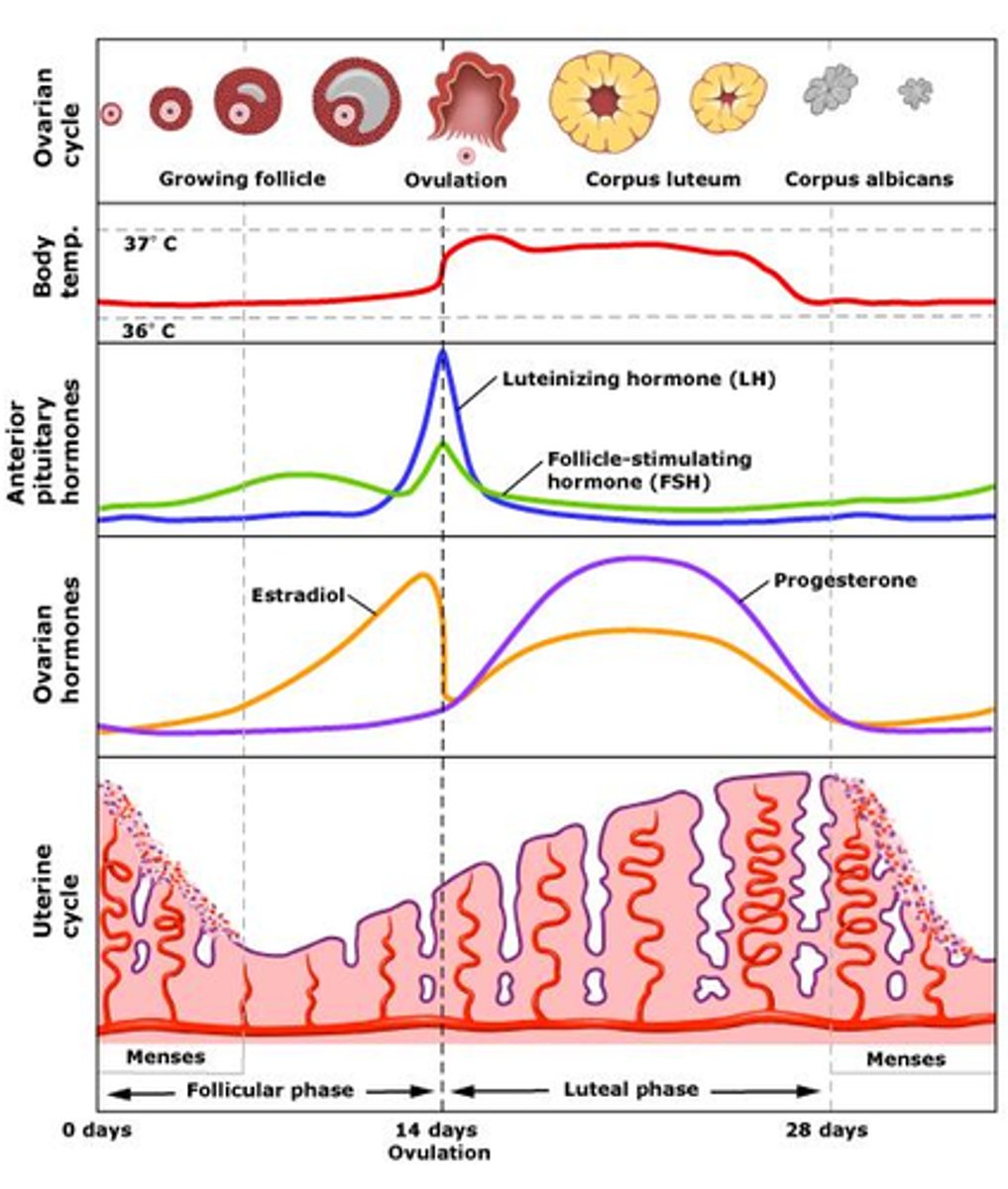
Hypothalamic pituitary feedback system
Hypothalamus releases GnRH -->
Stimulates anterior pituitary to release LH and FSH -->
Stimulates oestrogen (E) and progesterone (P) release
What is GnRH?
Gonadotropin releasing hormone
Stimulates release of LH and FSH
What is LH?
Stimulates the release of the egg (ovulation) and progesterone
When oestrogen peaks, LH surges to trigger ovulation
What is FSH?
Stimulates growth and maturation of ovarian follicle and oestrogen
Role of oestrogen
When oestrogen peaks, LH surges triggering ovulation
Thickens uterine lining (endometrium)
Role of progesterone
Thickens cervical mucus
Menstrual cycle: phases
Menstrual (day 1-5)
Follicular (day 1-14)
Ovulation (day 14)
Luteal (day 15-28)
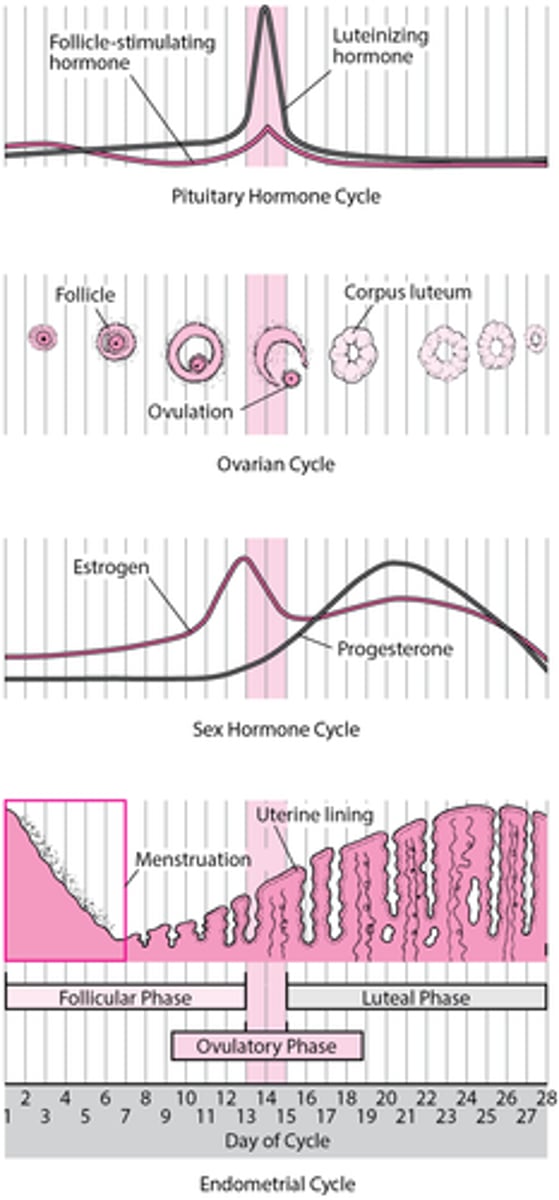
Menstrual phase
Marks the beginning of the cycle
Shedding of endometrium through vaginal bleeding
Bleeding lasts for 3-7 days
Oestrogen and progesterone levels are LOW
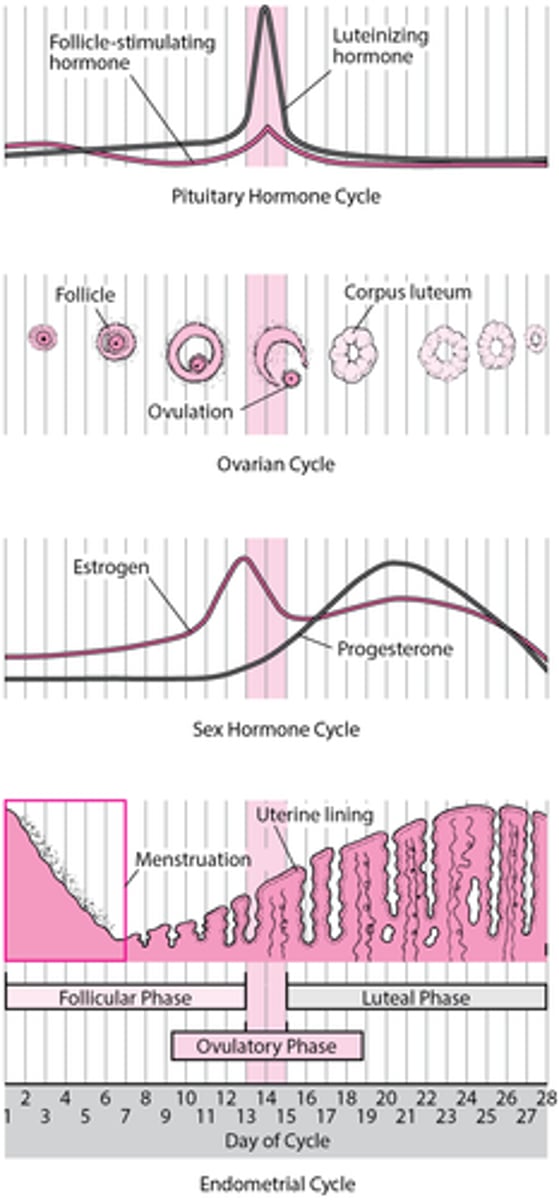
Follicular phase
Begins on first day of menstruation and lasts until ovulation
Development and maturation of ovarian follicle
FSH is released and oestrogen slowly increases
Progesterone remains LOW
Ovulation phase
Release of mature egg from ovary
Occurs around midpoint of cycle
Triggered by surge of LH due to increased oestrogen levels
Oestrogen is HIGH
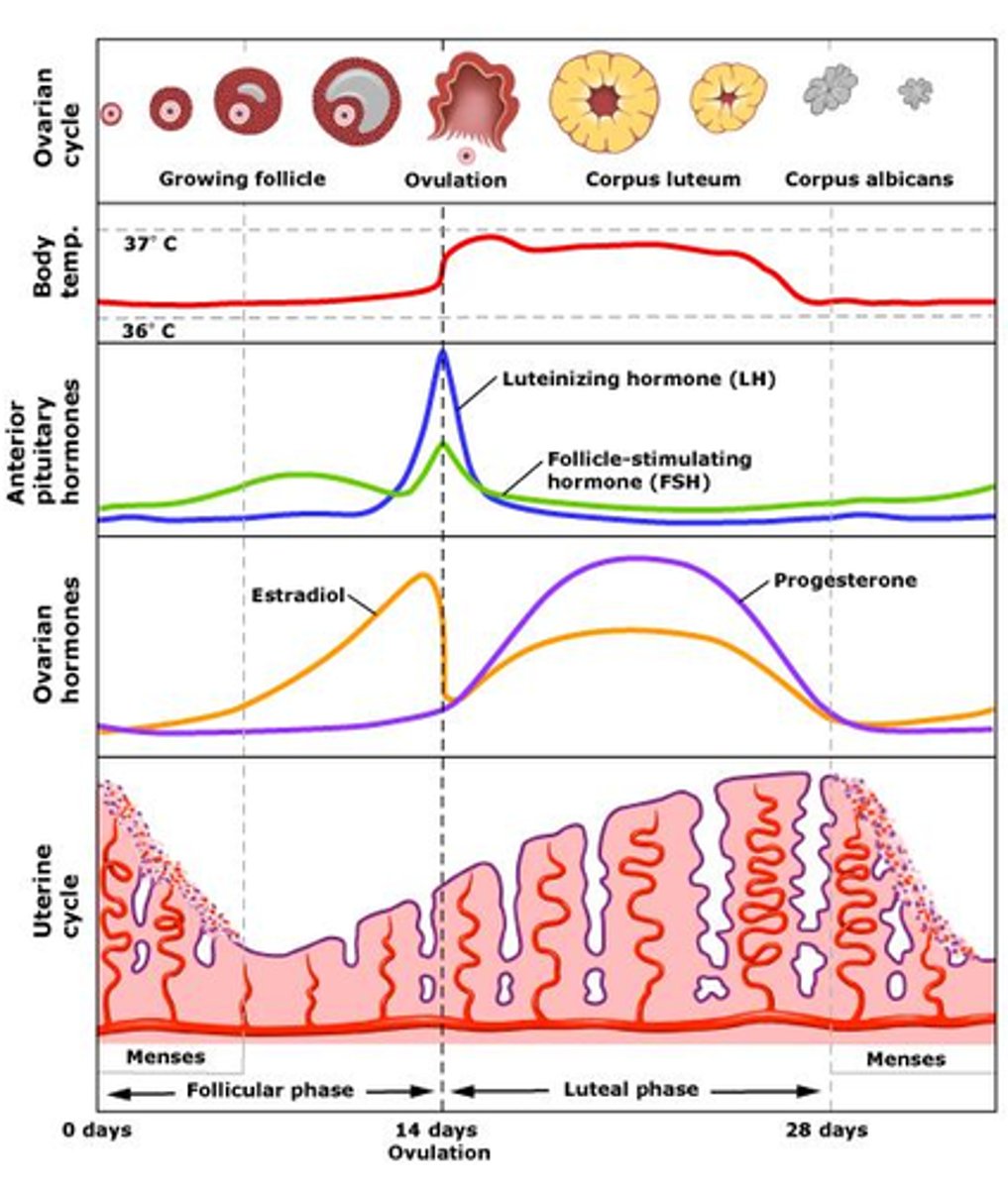
Luteal phase
Begins after ovulation and lasts until the start of the next menstrual period
Ruptured follicle transforms into corpus luteum which produces progesterone
Progesterone prepares endometrium for potential implantation
If implantation does not occur, corpus luteum breaks down
Progesterone and oestrogen levels RISE
What are current contraception options?
Fertility awareness methods
Withdrawal method
Male and female
- barrier method
- permanent method
Hormonal method
- combined methods
- progesterone only
Intrauterine methods
Emergency contraception
Hormonal contraceptive options
Contraceptive pills
- COCP
- POP
Vaginal rings
Depot injections
Long acting reversible contraceptives
- implants
- IUDs
Which contraception is the most effective?
Implant
IUD
Male sterilisation
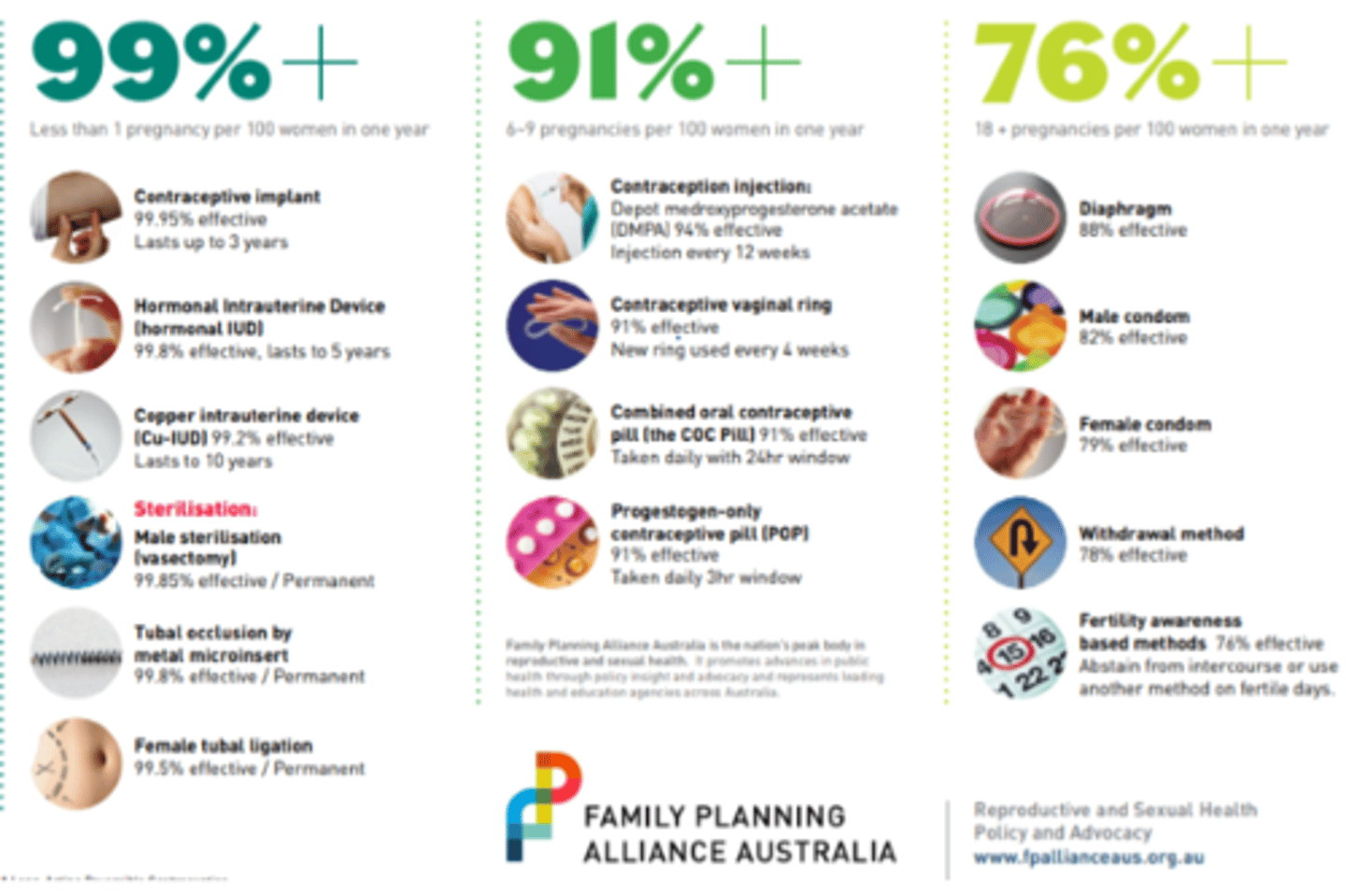
Contraceptive failure rates
70% of women of reproductive age use contraceptive method
>50% women have had an unplanned pregnancy
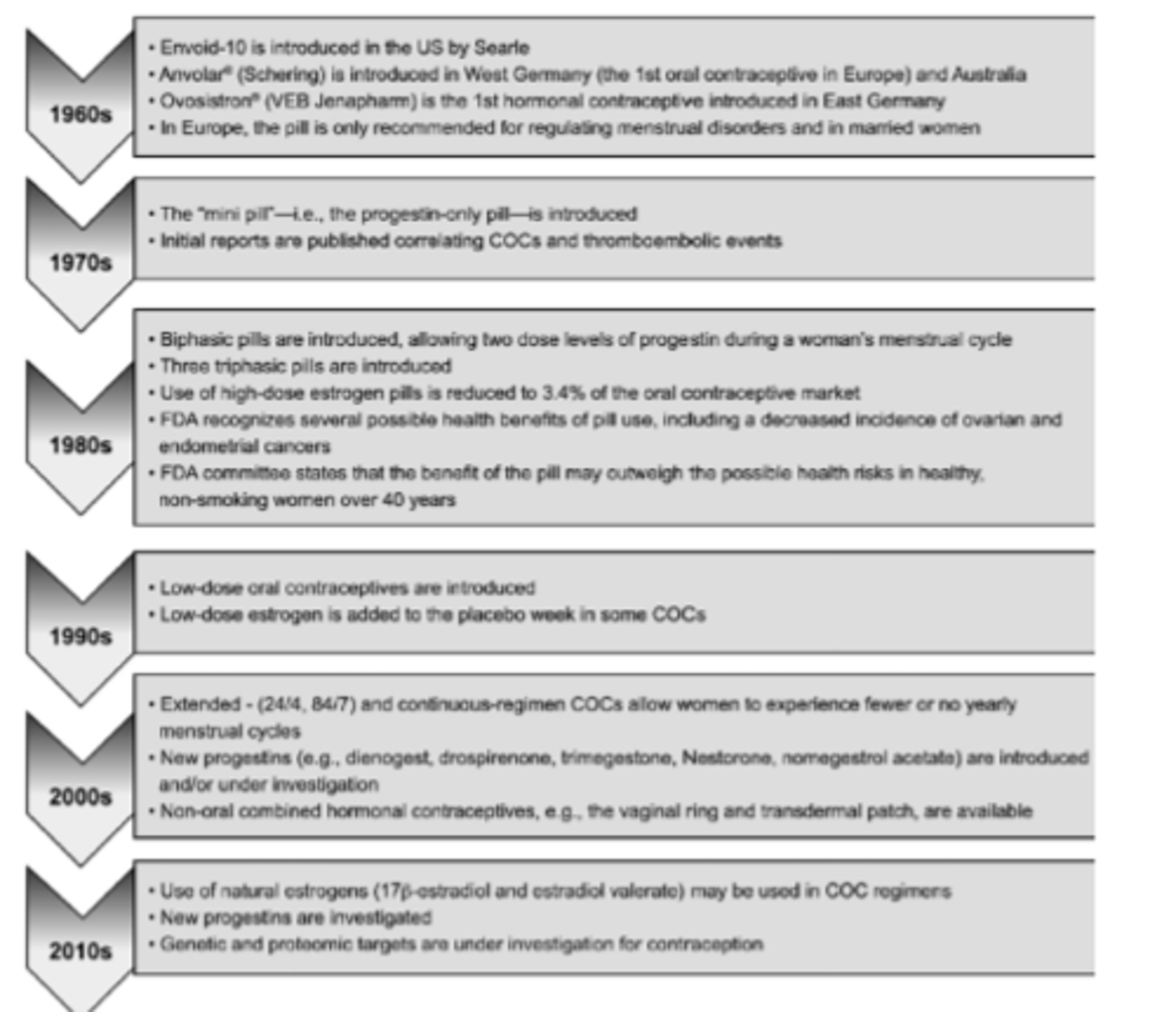
History of contraceptive pill
70s
- progesterone only pill was introduced
- concerns about COCP and thromboembolic events
80s
- biphasic and triphasic pills introduced
- high-dose oestrogen pills reduced
90s
- low dose pills introduced
2000s
- new progestins introduced
- non-oral combined hormonal contraceptives introduced
2010s
- use of natural estrogens introduced
What is the most common form of contraceptive pill?
COCP
COCP: administration
Taken daily for 21 or 28 days depending on formulation
Withdrawal bleed will normally occur during pill free/placebo days of the 28 days
COCP: first line
Any formulation with
- 30-35 mcg ethinyloestradiol OR 50 mcg mestranol
- levonorgestrel or norethisterone
COCP: multiphasic
Triphasic
- varying E/P across 21 days
- 7 inactive pills
New multiphasic (Qlaira)
- varying E/P across 26 days
- 2 inactive pills
COCP: components
Progestogen
Estrogen
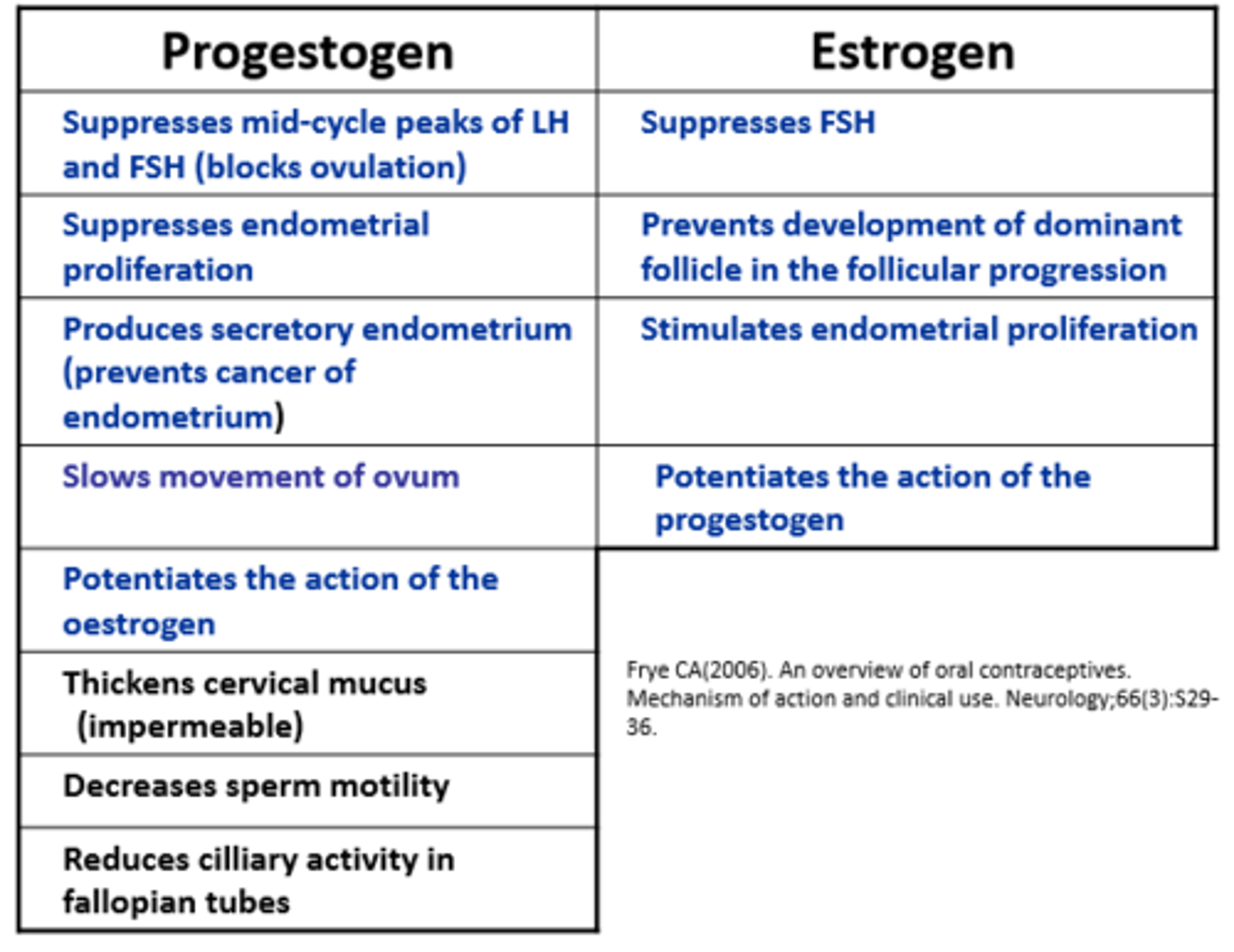
What are progestogens?
Synthetic forms of progesterone
Progestogens suppresses...
Mid-cycle peaks of LH and FSH = blocks ovulation
Endometrial proliferation
Progestogens produce...
secretory endometrium
- prevents cancer of endometrium
Which component of the COCP slows the movement of the ovum?
Progestogen slows movement of ovum
Does progestogen and oestrogen potentiate the action of each other?
Yes
Progestogen does what to the cervical mucus?
Thickens cervical mucus which makes it impermeable to the sperm
What effect does progestogen have on the sperm?
Decreases sperm motility
What effect does progestogen have on cilliary activity?
Reduces cilliary activity on fallopian tubes
Which hormone suppresses FSH?
Both progestogen and oestrogen
Oestrogen _______ development of dominant follicle in follicular progression
prevents
___________ stimulates endometrial proliferation
Oestrogen
Oestrogen: metabolic and side effects
Side effects
- nausea, vomiting
- breast tenderness
- fluid retention
- change in libido
Metabolic effects
- increased HDL, VLDL, TGs
- decreased LDL and bone resorption
- increased coagulation factors (dose-related)

Oestrogen: examples
Ethinyloestradiol
Mestranol
Estradiol
Oestrogen: ethinyloestradiol
Most common due to high oral bioavailability
Oestrogen: estradiol
Rapid inactivation by liver or short half life
Combined with synthetic ester (estradiol valerate) improved bioavailability + half-life
May have more favourable impact on lipid + carbohydrate metabolism
Which formulation of oestrogen has a favourable impact on lipid + carb metabolism?
Estradiol
Which formulation of oestrogen is combined with an ester to improve bioavailability and half-life?
Estradiol --> estradiol valerate
Oestrogen: contraindications
Thromboembolic disorder
Uterine bleeding
Liver disease
Cerebrovascular artery
Coronary artery disease
Breast cancer
Progestogen: side and metabolic effects
Side effects
- menstrual irregularity
- nausea, bloating
- weight gain
- breast tenderness
- changes in libido
- acne, mood changes
Metabolic effects
- decreased HDL, LDL
- increased VLDL
Progestogen: contraindications
Vaginal bleeding
Arteriopathy
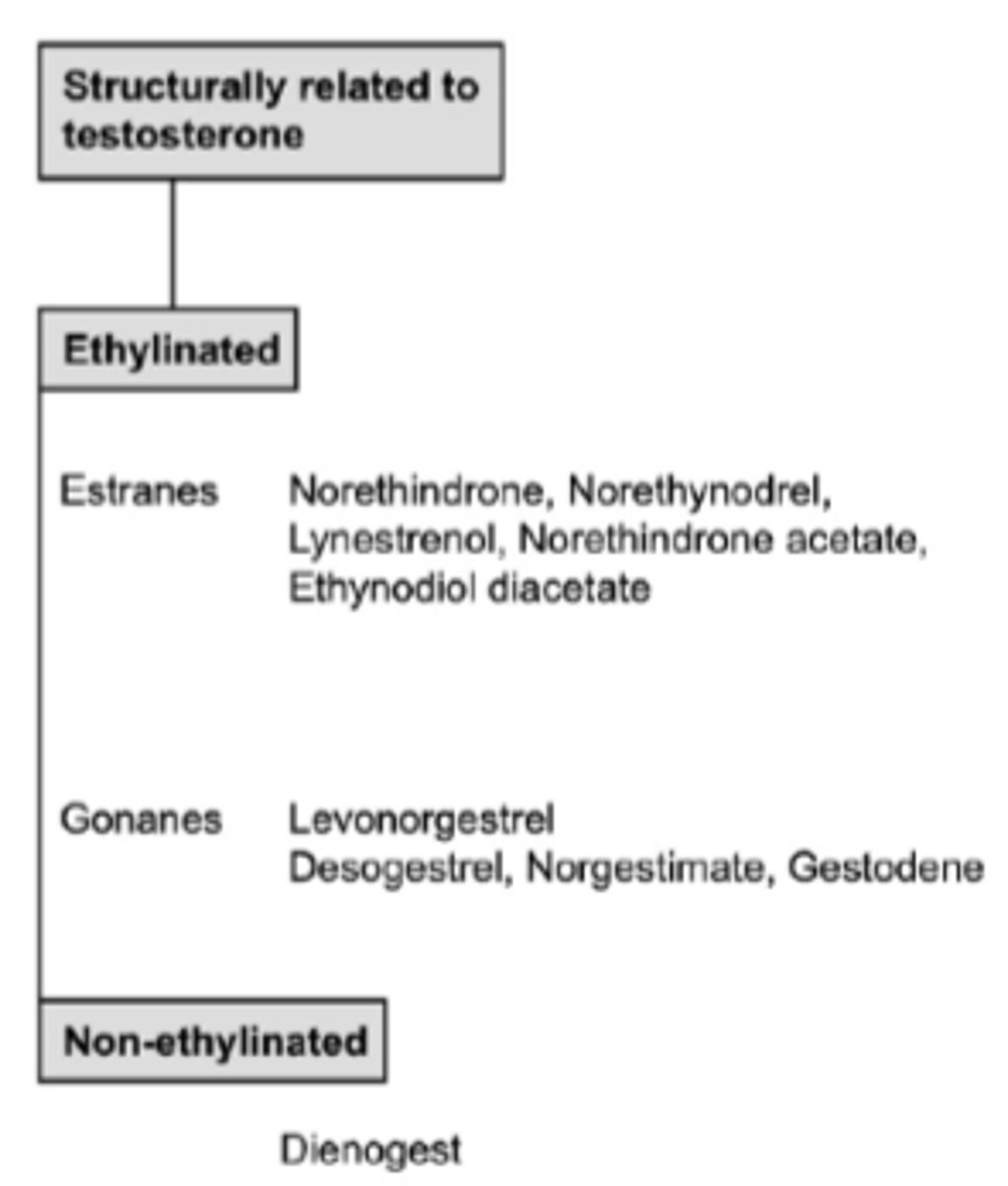
Which progestogen is structurally related to testosterone?
Estranes
- norethindrone
Gonanes
- levonergestrel
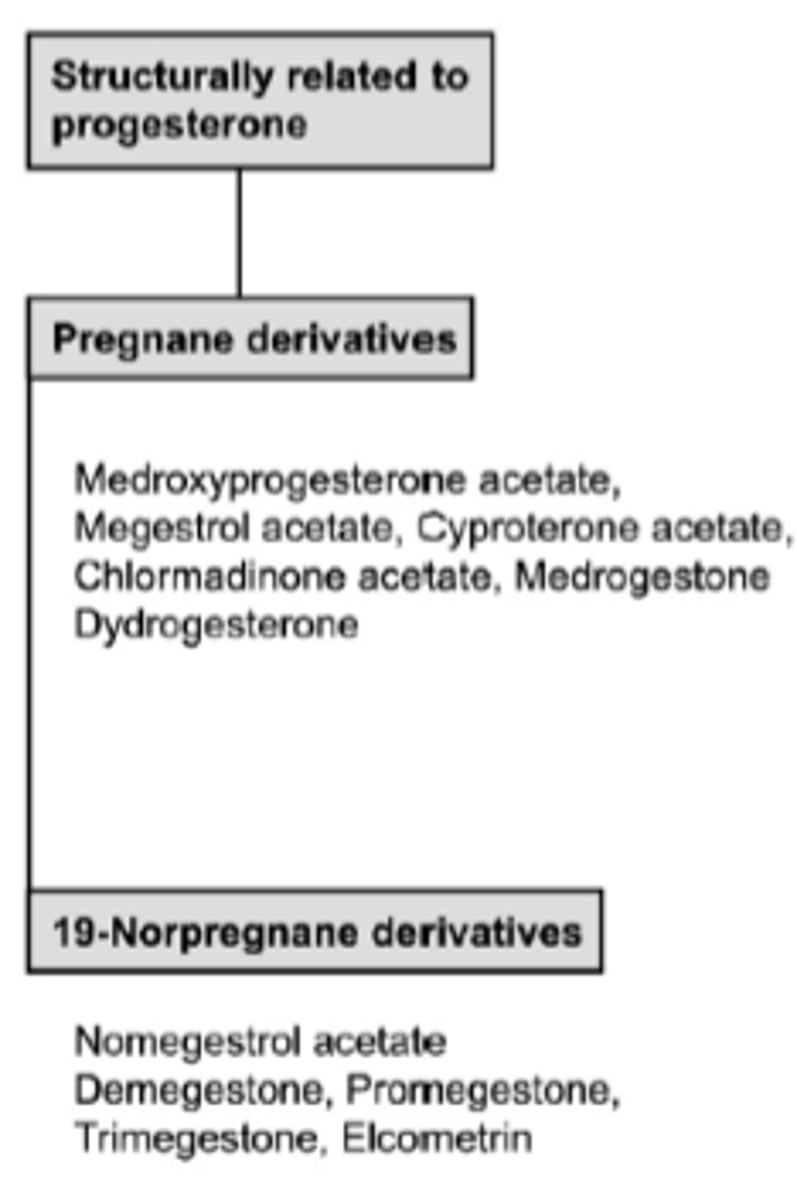
Which progestogen is structurally related to progesterone?
Pregnane derivatives
- medroxyprogesterone acetate
- cyproterone acetate
19-norpregnane derivatives
- nomegestrol acetate
Which progestogen is structurally related to sprinolactone?
Drosperinone
COCP: main action
Inhibits ovulation
COCP: role of oestrogen
Suppresses the development of ovarian follicles by FSH suppression
Stabilises endometrium to reduce unwanted breakthrough bleeding + irregular shedding
Potentiates action of progestogen by increasing concentration of intracellular progestational receptors
COCP: role of progestogen
Inhibits LH surge which is necessary for ovulation
Produces a non-receptive endometrium
Thick mucus impervious to sperm
COCP: other actions
Hostile cervical mucus and atrophic endometrium --> sperm transport and implantation may be impaired
Monophasic COCP contain how much oestrogen and progestogen?
The same amount throughout each of the 21 active tablets - fixed dose
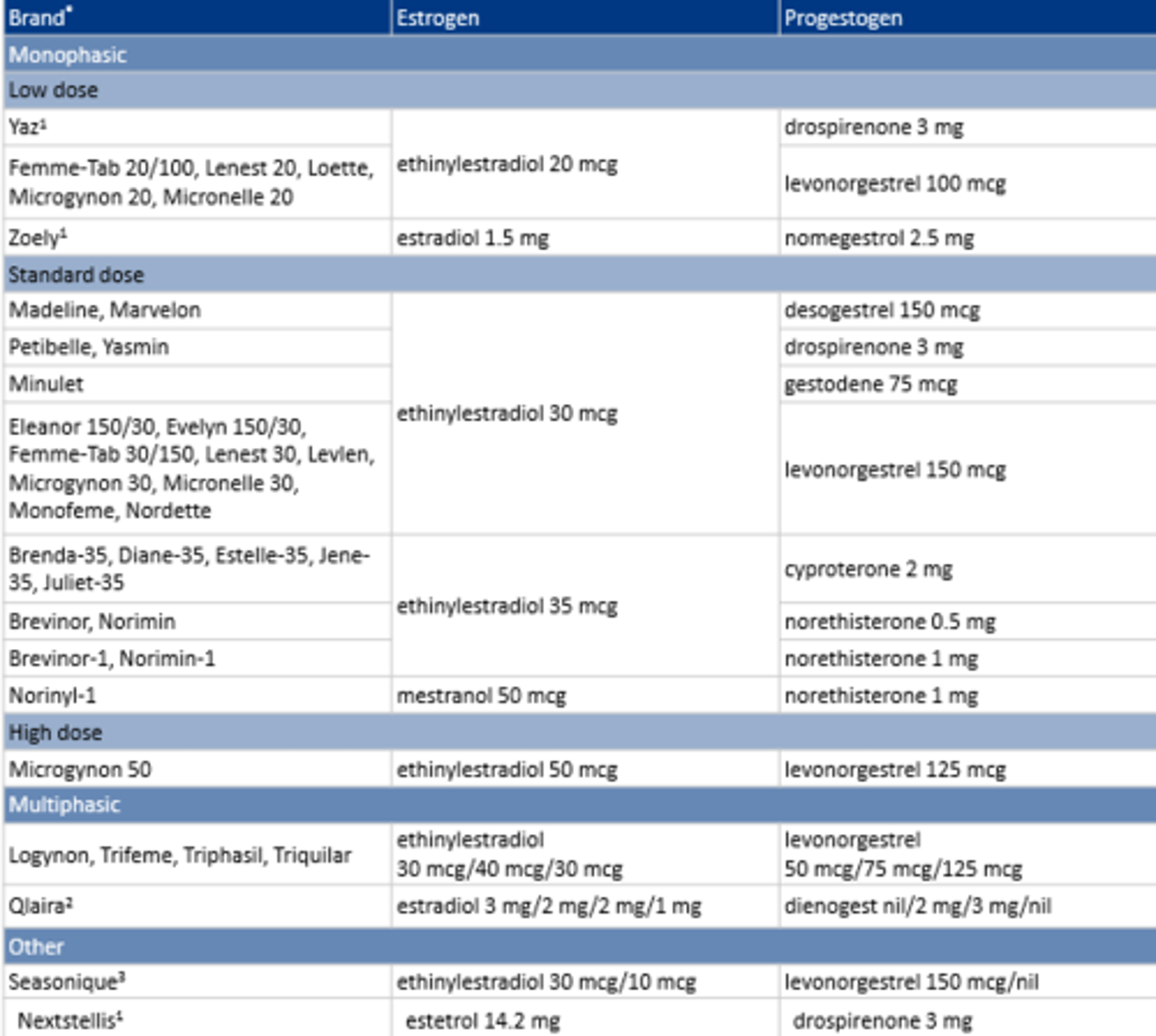
COCP: examples
See image
Can you change the time of menstruation with monophasic COCP? Why do some women do this?
Yes by carrying on with the next pack of active tablets
You don't take the 7 inactive pills
Some women prefer to have withdrawal bleed only once every three months
- tricycling or extended cycling
What happens if you shorten the hormone free interval?
May reduce incidence of hormone withdrawal symptoms
May increase contraceptive effectiveness
Monophasic COCP options
Zoely (nomegestrol with estradiol)
- 24 active, 4 inactive
- common to have no withdrawal bleed
Yaz (drosperinone with ethinylestradiol)
- 24 active, 4 inactive
- shorter pill free break --> increases contraceptive effectiveness
Seasonique (levonorgestrel with ethinylestradiol)
- extended regimen, taken continuously for 91 days
- no pill free break
- 84 tabs of 150 mcg levonorgestrel + 30 mcg ethinylestradiol
- 7 tabs 10 mcg ethinylestradiol
Nextstellis (drosperinone with esterol)
- esterol (E4) is synthetic analogue of oestrogen
- better effects on CV risk - need more evidence

What is E4?
Estetrol is a synthetic analogue of human oestrogen
It has high selectivity for oestrogen receptors
Binds to both alpha and beta receptors
Which monophasic COCP has no pill free break?
Seasonique
It just has a lower dose of ethinylestradiol during the 7 days
Multiphasic COCP mimics...
normal hormonal cycle
What happens to oestrogen and progestogen in multiphasic COCPs
Oestrogen increased mid cycle to reduce risk of breakthrough bleeding
Progestogen increased incrementally throughout cycle
Why are multiphasic COCPs used sometimes? What are the drawbacks?
Because it provides better cycle control
But,
More complex and more difficult to change the timing of the withdrawal bleed
Multiphasic COCP: side and metabolic effects
Side effects
- cyclical symptoms
- fluid retention
- PMS
Metabolic effects
- low metabolic effects
- less effect on carbohydrates and lipids
Is there any evidence for choosing multiphasic over monophasic?
No
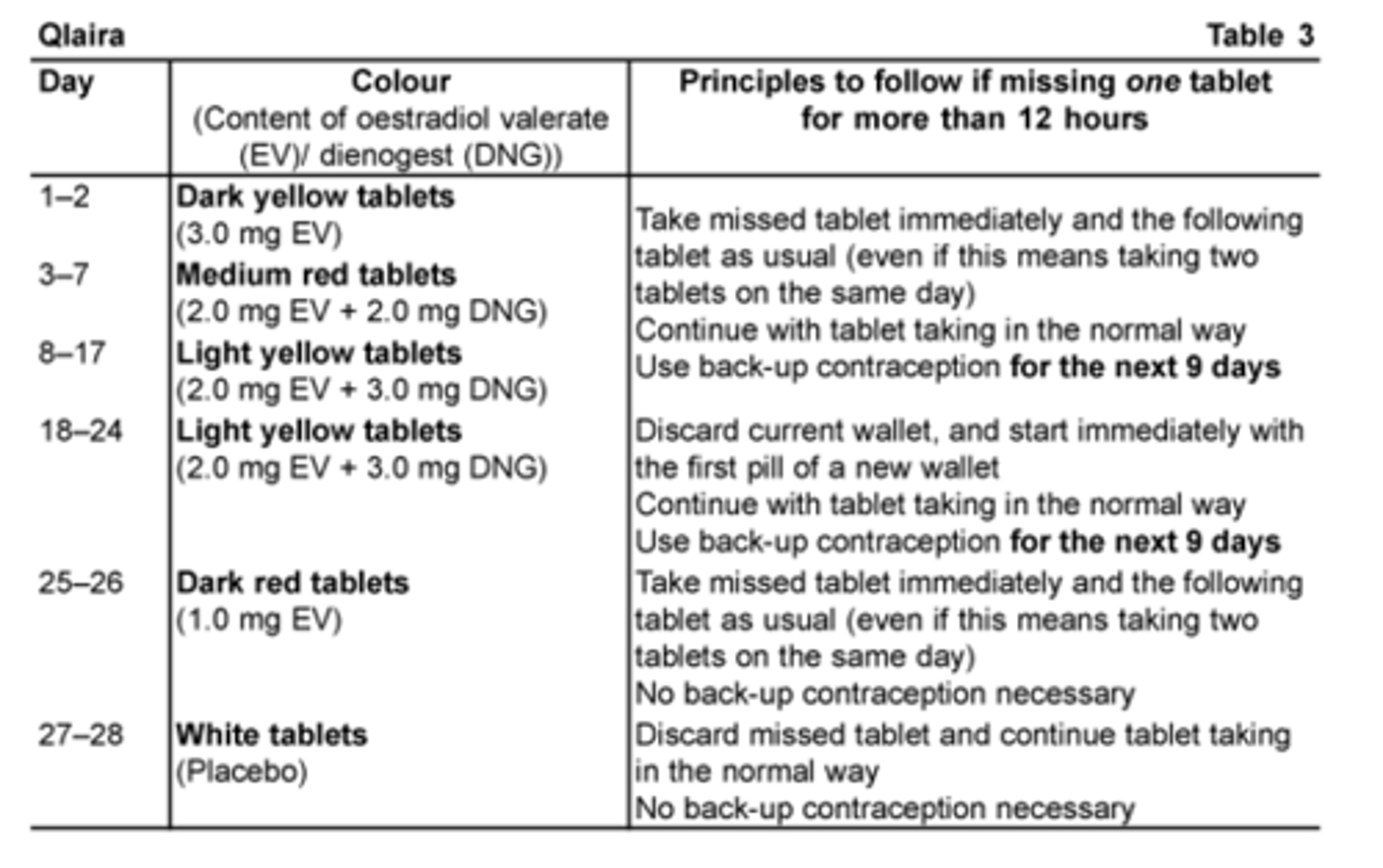
Multiphasic COCP (Qlaira)
Very complicated for user
Combined contraceptive (vaginal ring)
Nuvaring (etonogestrel with ethinylestradiol)
- 3 weekly use + 1 week free
- better adherence + convenient
- localised concentration + steady drug release
- avoid first pass effect + GI absorption
- less ADRs
- same DDIs

Even though the NuvaRing is used locally, it is ____________ absorbed
systemically
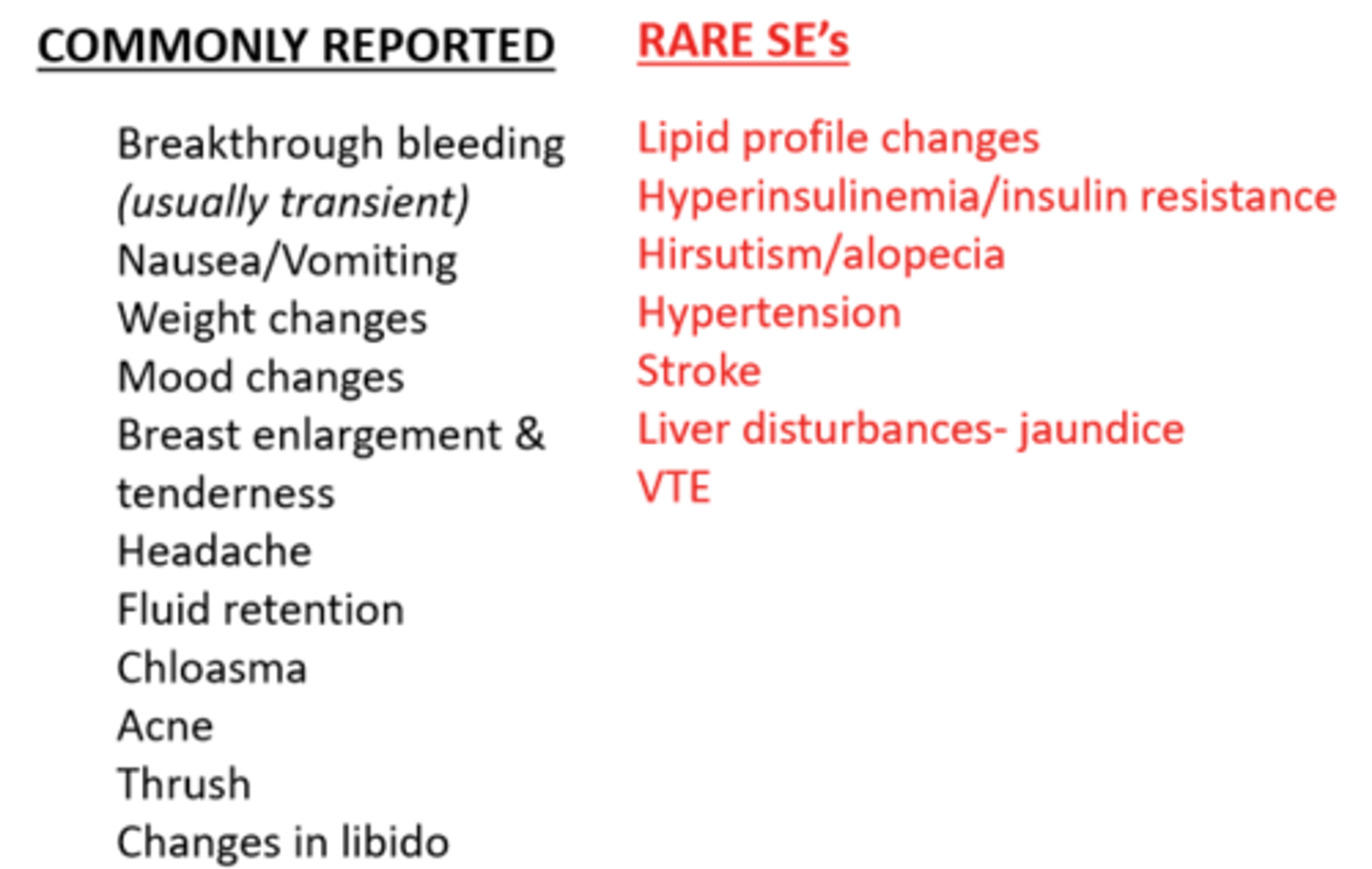
COCP: adverse effects
Varies according to
- dose
- combination
- patient
Commonly reported
- breakthrough bleeding (transient)
- nausea/vomiting
- mood changes
- thrust
Rare
- lipid profile changes
- hypertension
- VTE
- stroke
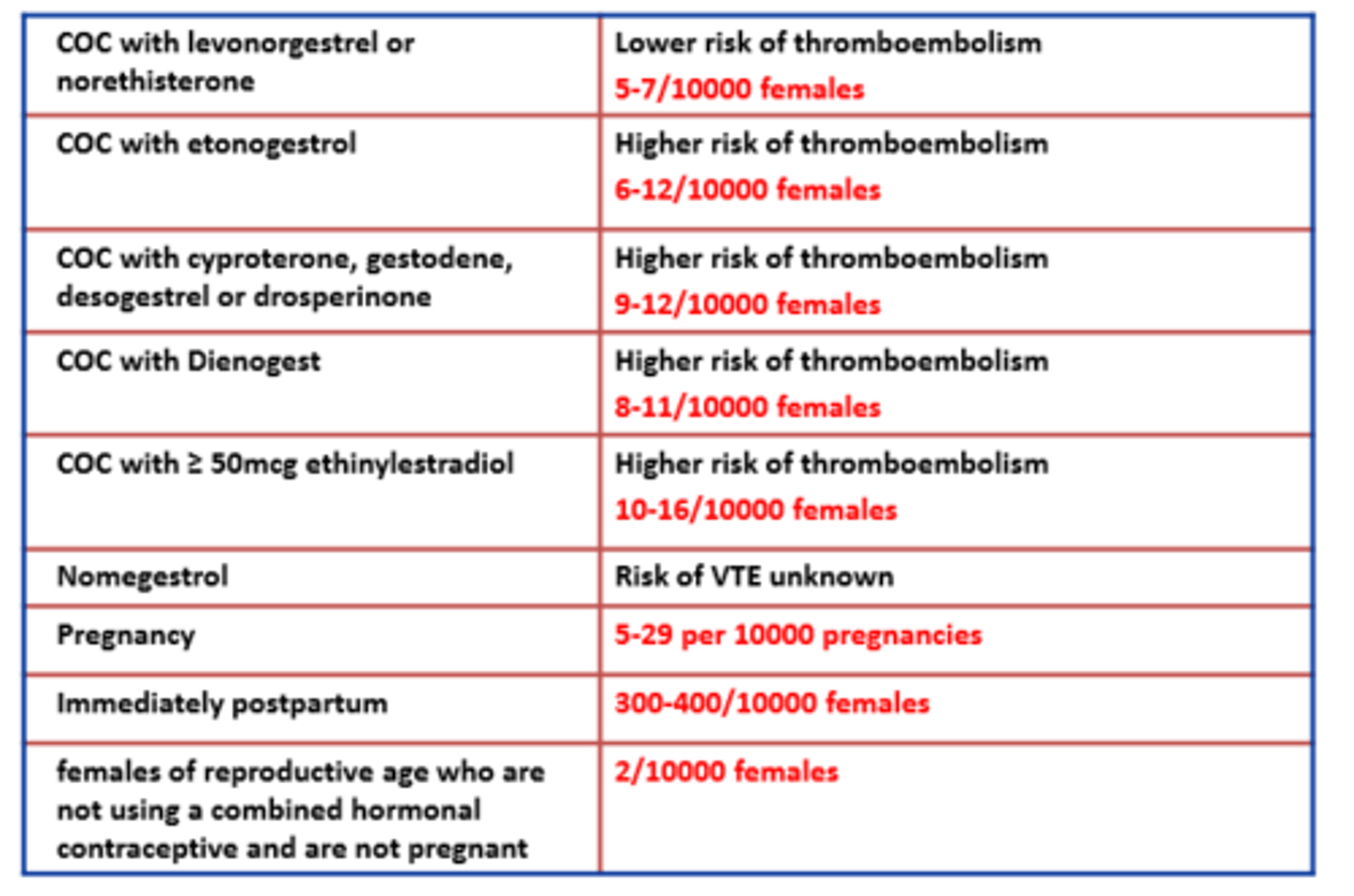
COCP: VTE (risk and CI)
All COCP increase risk of VTE but absolute risk is still low
Risk of VTE depends on
- dose of oestrogen/progestogen
- other risk factors
CI
- family history of VTE
- obese
- prolonged immobilisation
- <21 days post-partum
Progestogens + VTE
The higher the progestogen the higher the risk of VTE
Post-partum is riskiest time for VTE
Medical eligibility criteria for hormonal contraceptives
UKMEC
1 or 2
- safe to use
3
- require expert clinical judgement or referral
4
- absolute contraindications

COCP: UKMEC 3
BMI >35 kg/m2
Diabetes with
- nephropathy
- retinopathy
- neuropathy
History of
- migraine with aura (but not within last 5 years)
- VTE in family
CVD risk factors
Between
- 0-3 weeks postpartum
- 3-6 weeks postpartum
* COCP CI until 6 weeks

COCP: UKMEC 4
Current breast cancer
History of
- migraine with aura (within last 5 years)
- heart disease, stroke
- smoking
- high BP
- VTE
First
- 6 weeks postpartum
- 3 weeks postpartum

Choice of COCP
Lowest dose pill should be used wherever possible
- available as low, standard and high dose
- generally start with low or standard dose
- high dose used with anti-epileptics
Tricycling with monophasic pills useful for patients with menstruation problems
What dose of COCP should patients start on?
Low dose
A high dose of COCP should be used when patients are on what medication?
Anti-epileptics
Tricycling with monophasic pills are useful for patients with?
Menstruation related problems
COCP: managing side effects
Main action is to reduce oestrogen dose for
- headache
- nausea
- breast tenderness
- bloating/fluid retention
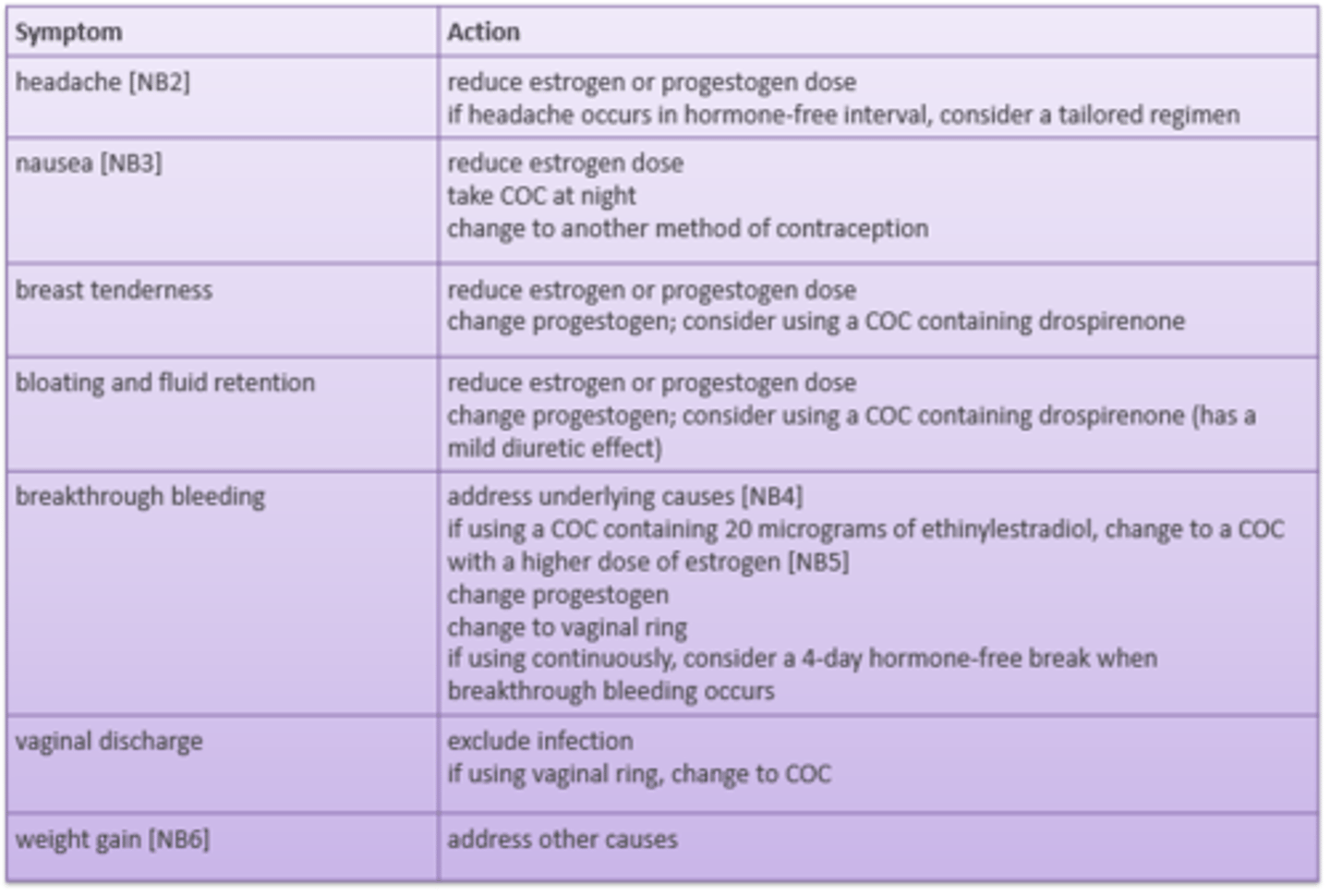
If a patient has breakthrough bleeding, they need to increase _________ dose or change __________ dose
oestrogen, progestogen
COCP: counselling
Starting, changing, stopping
After childbirth
Missed pill
Breakthrough bleeding
Skipping a period

If new to OC they start in the...
active tablets on day 1-2 of their menstrual cycle
- first day of bleeding
- no additional contraception required
If new to OC and they're not on their period, they can start...
with active tablets any other time BUT they will not have contraceptive cover until AFTER 7 days
When should the woman get her period while taking COCP?
The period should start 2-3 days after the last 'active' pill is taken
If patient is switching COC when do they start taking the active pills? Do they need additional contraceptive cover?
Start taking active pills the day after you stop your old pill (on any day of your cycle)
Additional contraception is not required
If switching from POP when do they start taking active pills? Do they need additional contraceptive cover?
Start taking active pills without any interval
Use additional contraceptive methods until you have taken active pills for 7 days
If you vomit <2 h of taking an active pill, you should?
Take another active pill ASAP
If you miss a pill <24 h of due time, you should?
Take the missed pill ASAP
PLUS
Take the next active pill when it is due
No additional measures necessary
If you miss a pill and its >24 h late, you should?
Take one active pill when you remember
PLUS
Take the next active pill when it is due
PLUS
Use additional contraception (e.g. condoms) for 7 days of active pills
Which pills are the most dangerous to miss?
Those pills at the beginning or end of the active pill cycle
If the 7 day additional cover extends into the inactive pill week, you should?
Skip the inactive tablets and start the new pack right away
So you will have no withdrawal bleed (period)
If the missed pills occurs 7 days after the inactive pill week, you should?
Seek emergency contraception
Up to how many missed pills can you take?
Only two
NuvaRing: contains? for how long?
Contains:
- 0.015 mg ethinylestradiol
- 0.12 mg etonogestrel
- per day, vaginally
Remains within the vagina for
- 3 of 4 weeks
Nuvaring: if not taking any other form of OCP you should?
Insert the ring vaginally during the first 5 days of the cycle
Nuvaring: if changing from COCP, you should?
Insert the ring immediately or at least within 7 days of the last active pill
Nuvaring: if changing from POP, you should?
Insert the ring the same day as the last active pill is taken
Nuvaring: if ring is expelled within 3 weeks, you should? What about protection?
Re-insert the ring
<3 hours
- protected
<3 hours
- may not be protected
- need additional contraceptive cover till the ring is in place for 7 days
Nuvaring: if the ring is left in for too long, you should?
= 4 weeks
- insert new ring after 1 week free
>4 weeks
- protection is lost
- check pregnancy status
- insert new ring ASAP
- additional contraceptive cover till ring is in place for 7 days
Nuvaring: if the ring breaks, you should?
Remove and discard it
Insert a new ring ASAP
Nuvaring: if the interval >1 week
Check for pregnancy
Insert new ring ASAP
Use additional contraceptive cover till the ring is in place for 7 days
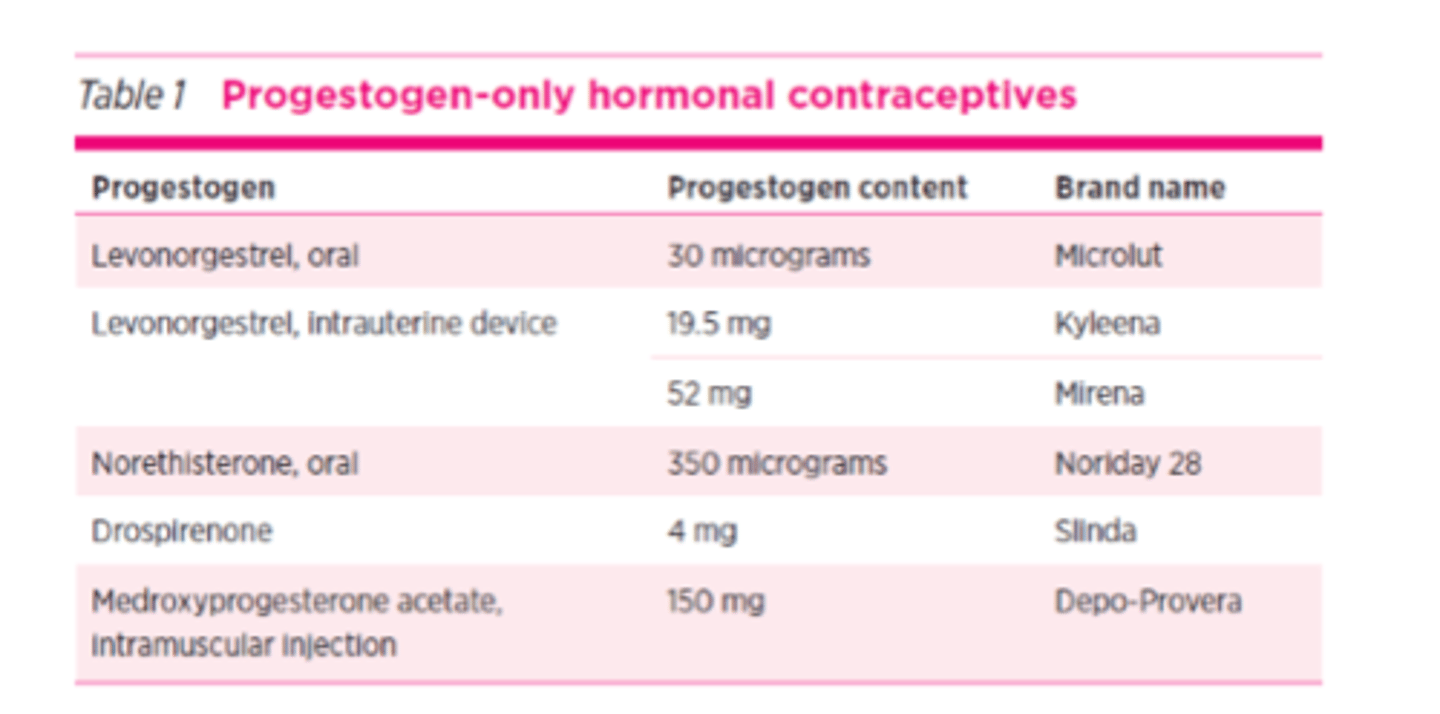
Examples of progestogen only formulations
Levonorgestrel
- oral
- IUD
Norethisterone
Drosperinone
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
- IM
POP: main points
Mini pill
Less effective than COCP
Taken continuously (no inactive pills)
- regular withdrawal bleed may not occur
Useful if oestrogen to be avoided
Less progesterone than COC
Effective within 48 h
e.g.
- levonorgestrel
- norethisterone
POP is useful if __________ is to be avoided
oestrogen
POP protects against pregnancy by...
- thickens cervical mucus thus hindering sperm motility
- making endometrium inhospitable ot fertilised eggs
- slow ovum transport through fallopian tubes
- suppressing ovulation