1 - Elements and the Periodic Table
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Complete past exam questions after you have gone through these cards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Mixture
Two or more substances mingled together but not chemically combined
Compound
Two or more elements chemically combined
Molecule
Two or more atoms chemically combined
Element
Substance that cannot be broken down into anything simpler by chemical means
What was a triad of elements according to Dobereiner?
Give an example
Elements that have similar chemical properties //
atomic mass of middle element is average of the other two
e.g. Li, Na, K
What contribution did Newlands make to the systematic arrangement of the elements?
Arranged in increasing relative atomic mass / octaves
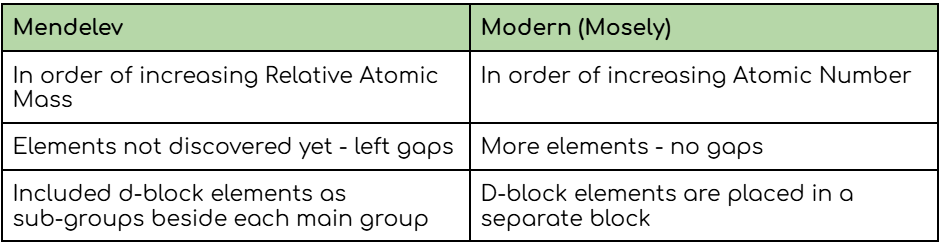
How did Mendelev arrange the elements to form his periodic table?
Elements listed in order of increasing atomic mass //
Elements with similar chemical properties were listed in columns //
left gaps
Suggest a reason why Mendelev did not suspect the existence of argon
Noble gases were unknown (undiscovered) /
inertness of argon (noble gases) /
no gap for argon
Comment on the positioning of tellurium (Te) and iodine (I) in the 1869 table.
listed correctly according to chemical properties /
chemical properties matched better when order reversed
Give an advantage of arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic number
more fundamental property of element /
no need to reverse order to force elements into correct groups /
tellurium (Te) and iodine (I) in correct groups /
indicates undiscovered elements
Explain why all the elements of Group 18 in the periodic table are chemically inert
Stable arrangement of electrons / do not lose or gain electrons / satisfy octet rule
Explain how and why the reactivity of the halogens changes down Group 17
How: less reactive down group / less likely to gain an electron down group
Why: increasing atomic radius / more shells / nucleus farther from outer electrons / increasing screening / more difficult to achieve full outer sub-level / decreasing electronegativity
In the periodic table, identify an element
i) in the same period as magnesium but with larger atoms,
ii) in the same group as magnesium but with smaller atoms
i) Sodium (Na) //
ii) Beryllium (Be)
Mendelev predicted the properties of the elements gallium and germanium years before either of them was discovered. Explain the basis for his predictions
Having arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight /
where elements with similar properties were arranged in columns /
left gaps for elements with certain properties yet to be discovered
Explain why
i) the alkali metals are all reactive
ii) the reactivity of the alkali metals increases down the group
i) Readily lose single electron / low first ionisation energy
ii) Increase in atomic radius / atoms getting bigger / decrease in first ionisation energy / outer electron more easily lost
State two differences between Mendelev’s periodic table and the modern periodic table of the elements