A levels chemistry: Acid-Base Equilibria
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what is a strong acid
undergoes complete dissociation in aqueous solution to produce H+
eg [H+] = initial [HCl]
degree of dissociation, α=1
what is a weak acid
undergoes partial dissociation in aqueous solution to produce H+
eg [H+] < initial [CH3COOH]
degree of dissociation, 0 < α < 1
what is a strong base
undergoes complete dissociation in aqueous solution to produce OH-
eg [OH-] = initial [NaOH]
degree of dissociation, α=1
what is a weak
undergoes partial dissociation in aqueous solution to produce OH-
eg [OH-] < initial [NH3]
degree of dissociation, 0 < α < 1
what is an arrhenius acid
an acid releases H+ ions in aqueous solution
eg HCl (aq) —> H+ + Cl-
what is an arrhenius base
a base releases OH- ions in aqueous solution
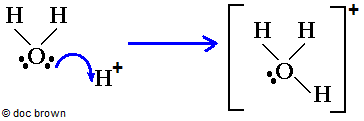
characteristics of proton, H+
high charge density
attracts any molecule with unshared electrons such as H2O
in aqueous solution, a water molecule forms a dative covalent bond to the H+ ion to produce the hydronium ion
what is a bronsted-lowry acid and base
acid: a proton donor
base: a proton acceptor
an acid-base reaction involves the transfer of a proton from the acid to the base
an acid is only an acid in the presence of a base, and a base is only a base in the presence of an acid
what does it mean by Water is amphiprotic
Water is amphiprotic
can either donate or accept a proton
thus can act as both an acid and a base
HCl(aq) + H2O (l) —> Cl- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
HCl is the acid, H2O is the base
CO3 2- (aq) + H2O (l) —> HCO3- (aq) + OH- (aq)
CO3 2- is the base, H2O is the acid
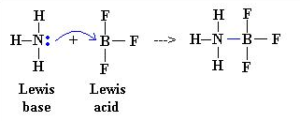
what is a lewis acid
an electron pair acceptor
accept a pair of electrons from a base to form a dative covalent bond
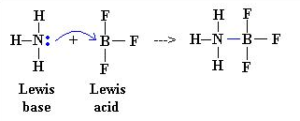
what is a lewis base
an electron pair donor
donate a pair of electrons to an acid to form a dative covalent bond
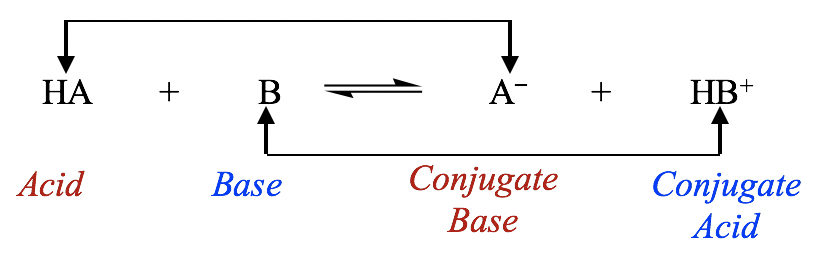
what is an acid and its conjugate base
in each conjugate pair, the acid and base differ from each other by a proton, H+
Conjugate acid-base pairs
HA and A-
HB+ and B
In the forward reaction
HA is an acid as it donates a proton to B
B is a base as it accepts a proton from HA
In the backward reaction
HB+ is an acid as it donates a proton to A-
A- is a base since it accepts a proton from HB+
what is pH of solution defined as
pH = -lg[H+]
how to find [H+] from pH
[H+] = 10−pH
relation between [H+] and pH
the higher the [H+] in a solution, the lower the pH of the solution
methods of measuring pH of a solution
using universal indicator paper or solution for an approximate pH value
using a pH meter for an accurate pH determination
what is pOH
pOH = -lg[OH-]
how to find [OH-] from pOH
[OH-] = 10-pOH
relationship between [OH-] and pOH
the higher the [OH-] in a solution, the lower the pOH of the solution
what is the ionic product of water
Kw = [OH-][H+]
units: mol2 dm-6
the exact value of Kw depends on the temperature
at 25°C, Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10⁻¹⁴
since Kw is a constant, the concentrations of H+ and OH- are limited by this value
what is the pH and pOH of a neutral aqueous solution
For a neutral aqueous solution, [H+] = [OH-]
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10⁻¹⁴
[H+]² = 1.0 x 10⁻¹⁴
[H+] = √1.0 x 10⁻¹⁴ = 1.0 x 10⁻⁷ mol dm⁻³
pH = -lg[H+] = -lg (1.0 × 10⁻⁷) = 7
[OH-] = [H+] = 1.0 x 10⁻⁷ mol dm⁻³
pOH = -lg[OH-] = -lg (1.0 × 10⁻⁷) = 7
how does the value of Kw vary with temperature
the value of Kw increases with temperature
this is because the self-ionisation of water is an endothermic process
As temperature is increased, the equilibrium position of the above reaction shifts to the right to absorb the heat added. This is in accordance with LCP
with the forward endothermic reaction favoured as temperature increases, there will be higher concentrations of H+ and OH- ions
what is pKw
pKw = -lg Kw
express pKw in terms of pH and pOH
pKw = pH + pOH
At 25°C, pKw = pH + pOH = 14