PHYS GEOL metamorphism and metamorphic rocks
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Metamorphism
transformation (change) of rocks without melting, usually beneath earth’s surface
» results in heat, pressure, and fluid activity
» changes rocks’ mineral composition and texture
Protolith
rock before metamorphism (proto = before | lith = rock)
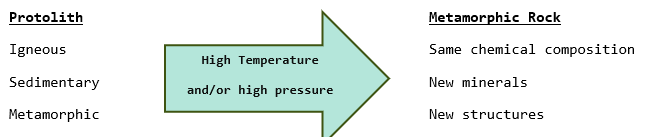
Heat (agent of metamorphism)
increases the rate of reactions
» sources of heat include lava, magma, and deep burial
» temperature increases with depth; geothermal gradient averages 25C/km in crust (closer to core & radioactive elements)
Pressure (agent of metamorphism)
increasing pressure squeezes the atoms together to eliminate unoccupied volume in the crystal
» high pressure minerals are denser than low pressure minerals
Lithostatic (confining) pressure [agent of metamorphism pressure]
caused by weight of overlying and surrounding rock
» equal in all directions (like hydrostatic pressure you feel in swimming pool)
Differential pressure (agent of metamorphism pressure)
directed pressure (not equal in all directions)
» caused by mountain building (found at convergent boundaries) → ←
» influences the development of metamorphic structures and textures
Fluids (agent of metamorphism)
fluids in sedimentary rocks or coming from magmas can accelerate chemical changes, which occur during metamorphic and can cause new minerals to form
» common metamorphic fluids are water & CO2
Types of Metamorphism
results largely depend on which of the three agents was dominant, the timescale, and the location
» contact
» dynamic
» regional
» meteorite impact
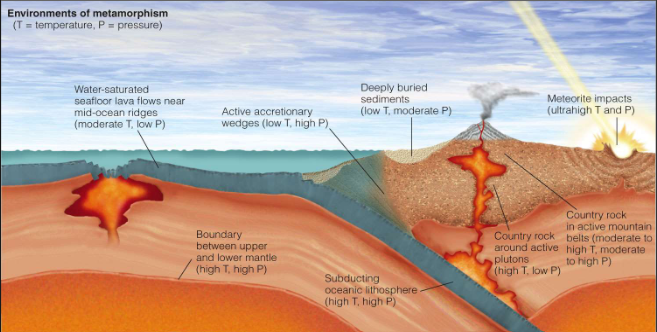
Contact (type of metamorphism)
magmas or lavas come into contact with existing rock, baking it
» metamorphic “baked zone” is called aureole
» high temperature
» low pressure
» long (intrusive) or short (extrusive) timescales
» localized area
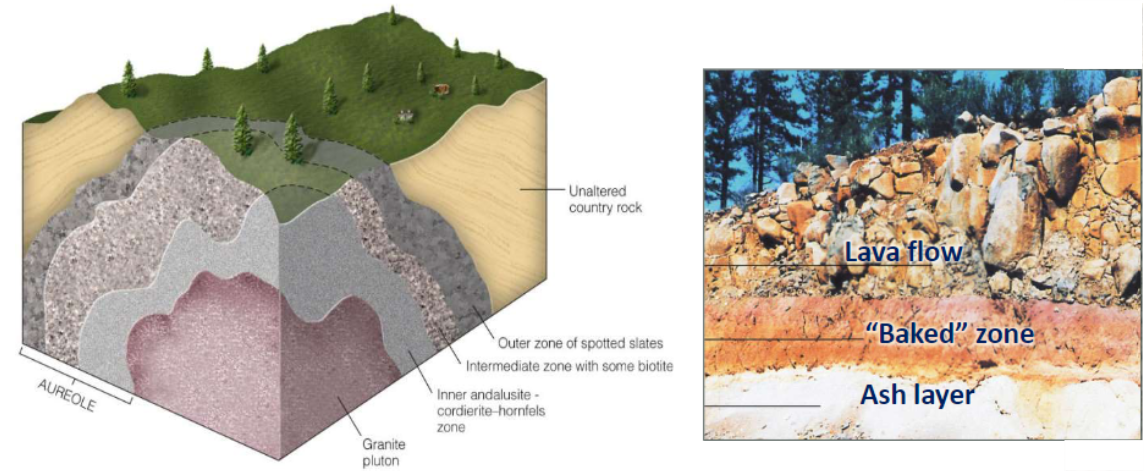
Aureole size depends on:
» size of the intrusion
» temperature of intrusion mafic magmas tend to be hotter than felsic magmas, so they bake more of the surrounding rock
» amount of water and other fluids
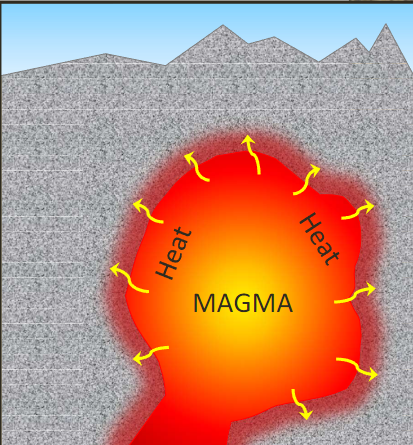
Dynamic (type of metamorphism)
occurs when rocks are ground up and crushed along faults, like at convergent or transform plate boundaries
» high pressure
» low temperature
» long timescales
» Mylonite = fine-grained rocks in faults that result from grinding and crushing during fault movements (earthquakes)
Regional (type of metamorphism)
most common type of metamorphism
» found at convergent plate boundaries
» broad range
» long timescales
» high temperature and pressure both as as driving forces for metamorphic reactions
Meteorite impact (type of metamorphism)
» ultrahigh temperature
» short timescale
» ultrahigh pressure
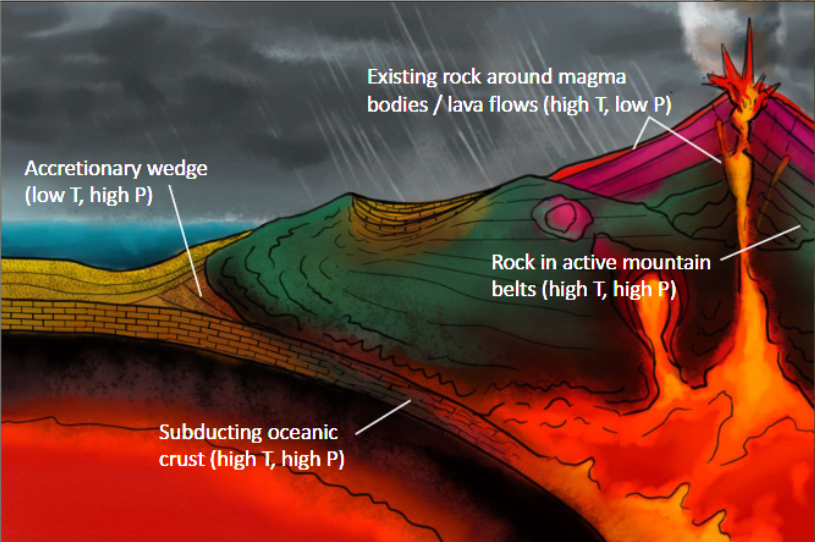
Plate tectonics and metamorphism
can happen at all plate boundaries but is most common and extensive at convergent boundaries
» two plates smashing together produces tremendous amounts of heat and pressure
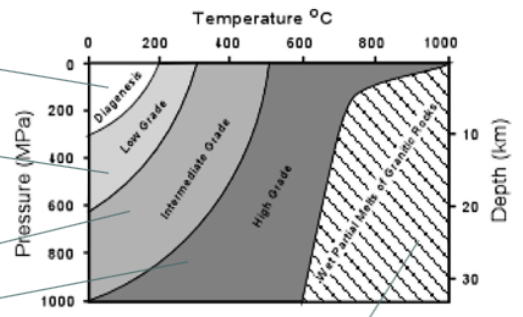
Metamorphic grade
degree of metamorphic change a rock has undergone, usually listed as low, intermediate, or high
» diagenesis = unmodified
» low grade = small amount of change
» intermediate = medium amount of change
» high = large amount of change
» partially melting = magma creation (moving from metamorphic to igneous)
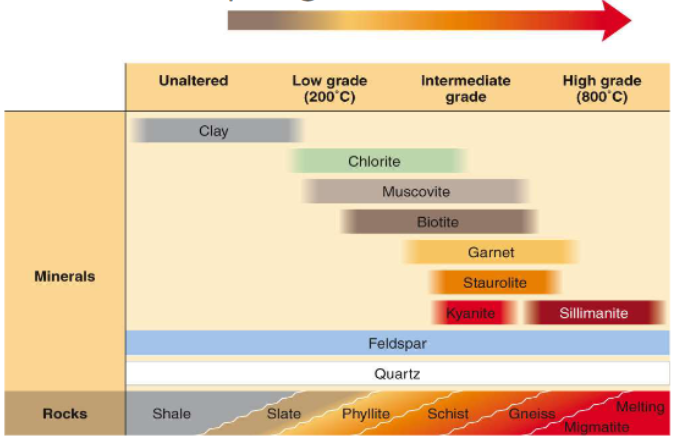
Index minerals
certain minerals form under specific ranges of temperatures and pressures. They can be used to determine the metamorphic grade of a rock
Foliate (metamorphic texture)
produced by the preferred orientation of platy minerals, such as Muscovite, because of pressure (occurs at convergent plate boundary)
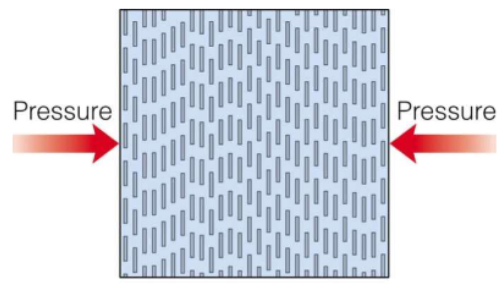
Schistosity (foliate metamorphic texture)
wavy layers, at least some coarse grains

Gneissic banding (foliate metamorphic texture)
mafic and felsic minerals segregate into alternating bands of dark and light minerals

Amphibolite (foliate metamorphic texture)
composed mainly of amphibole (can be foliated or non-foliated)

Migmatite (foliate metamorphic texture)
actually mixed igneous and metamorphic rock
» contains streak of granite from partial melting - felsic minerals melt at lower temperature than mafic, so the felsic minerals form an igneous rock mixed in with the unmelted metamorphic mafic minerals

Non-foliated metamorphic rocks
» marble
» quartzite
» anthracite
» hornfels
Marble (non-foliated metamorphic rock)
metamorphosed limestones and dolostones

Quartzites (non-foliated metamorphic rock)
metamorphosed quartz sandstones

Anthracite (non-foliated metamorphic rock)
metamorphic coal

Hornfels (non-foliated metamorphic rock)
fine-grained metamorphic rocks formed contact metamorphism

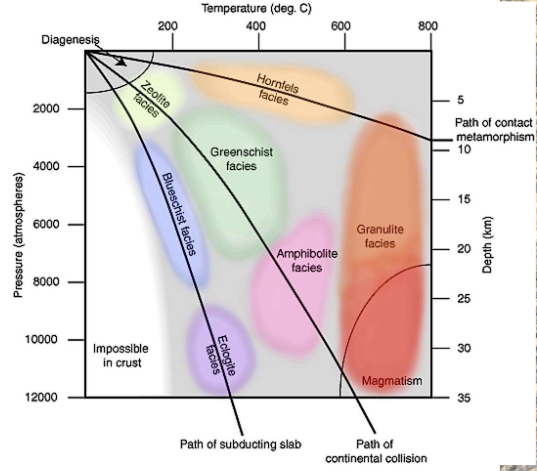
Metamorphic facies
group of rocks containing a distinctive mineral assemblage formed under similar conditions of temperature and pressure
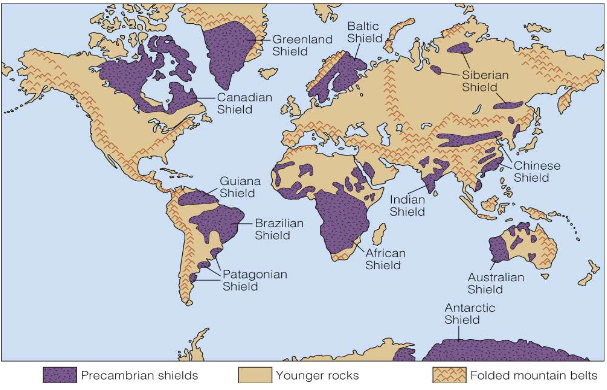
Shields
oldest part of the continental crust (cores of large mountain ranges)
» where metamorphic rocks are found

Sandstone —>
Quartzite


Limestone/Dolostone —>
Marble


Basalt —>
Greenstone


Lignite/Bituminous Coal —>
Anthracite
