Biology chapter 1 and 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:32 PM on 10/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
1
New cards
inference
A logical interpretation based on prior knowledge and experience/what scientist already know.
2
New cards
Hypothesis
A testable prediction; suggested explanation
3
New cards
Steps of an experiment
Scientific Question, Hypothesis, Design Experiment, Results, Conclusion
4
New cards
Independent Variable (Manipulated Variable)
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable that you change. (x - axis)
5
New cards
Dependent Variable (Responding Variable)
the variable that is observed and that changes in response to the independent variable. What you measure. (y-axis)
6
New cards
controlled variable (constant)
A variable that is not changed
7
New cards
qualitative data
descriptive data, described with words
8
New cards
quanatative data
uses numbers to describe something
9
New cards
Casual Theory
hunch or prediction based on intuition, not facts
10
New cards
scientific theory
a well-tested concept that is supported by repeated testing and facts
11
New cards
scientific law
a rule that describes a pattern in nature/a natural phenomenon. Often mathematical.
12
New cards
cells
The smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive - smallest unit of life.
13
New cards
sexual reproduction
type of reproduction in which cells from two parents unite to form the first cell of a new organism
14
New cards
asexual reproduction
process of reproduction involving a single parent that results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
15
New cards
DNA
A molecule/universal genetic code that determines the inherited traits of every organism on earth.
16
New cards
Metabolism
the combination of chemical reactions as it carries out its life processes. (Need to eat, excrete waste, exchange gases - humans)
17
New cards
Stimulus
a signal to which an organism responds
18
New cards
external stimuli
environment outside
19
New cards
internal stimuli
within an organism
20
New cards
Homostasis
the relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions that organisms maintain
21
New cards
Response to stimuli
Living things adjust and respond to changes in their internal and external environments.
22
New cards
Characteristics of life
1. Made of cells
2. Ability to reproduce
3. DNA,
4. Growth & development
5. Responds to stimuli
6. Homeostasis
7. Metabolize
8. Evolve
2. Ability to reproduce
3. DNA,
4. Growth & development
5. Responds to stimuli
6. Homeostasis
7. Metabolize
8. Evolve
23
New cards
evolve
To change over time; change based on environmental pressure
24
New cards
Grow and develop
To grow and mature, to be able to reproduce
25
New cards
atom
The basic unit of matter
26
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
27
New cards
Protons
Positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom
28
New cards
Nuetrons
Neutral subatomic particles that don't have a charge and located in an atoms nucleus
29
New cards
Electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus - in the (shell/orbit/level)
30
New cards
Elements
One or more atoms but are the same type of atoms ; cannot be broken into simpler units by chemical reactions. ( example H2)
31
New cards
Compounds
2 or more different types of atoms chemically combined / bound together (example H2O)
32
New cards
Molecules
two or more atoms bound together, can be the same or different atom (example H2O & H2)
33
New cards
Ions
positively and negatively charged atoms
34
New cards
Anions
negatively charged ions
35
New cards
Cations
positively charged ions
36
New cards
valence shell
outermost shell of an atom
37
New cards
valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell
38
New cards
Neutral atoms have
same number of protons and electrons
39
New cards
covelant bond
bond formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms
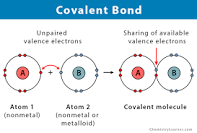
40
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
Weaker than Ionic and covalent bonds; Caused by the bonding of a partial positive charged hydrogen atom to a partial negative charged atom. Hydrogen bonds have the ability to attach and detach.
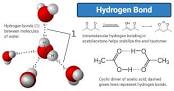
41
New cards
hydrogen bonds affect on water?
Since water is polar it can form many hydrogen bonds. hydrogen bonds are also responsible for water's cohesion and ability to dissolve many other substances. Since water expands upon freezing, it makes ice more dense than liquid water.
42
New cards
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
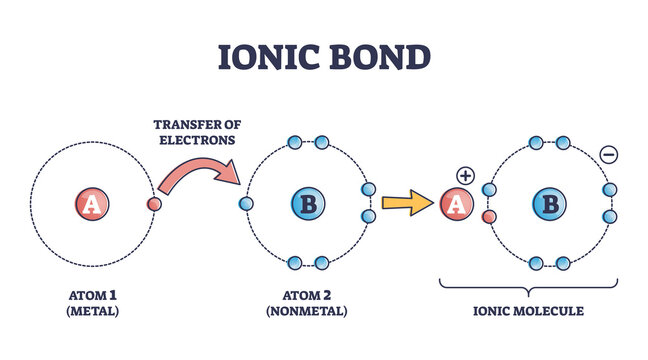
43
New cards
ionic compound
A compound that consists of positive and negative ions
44
New cards
Water is -----
polar
45
New cards
polar
A molecule that has negative and positive sides
46
New cards
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
47
New cards
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
48
New cards
water is a _____ bond
covalent
49
New cards
water has the highest _____
heat capacity
50
New cards
heat capacity
amount of energy needed to raise a substances temperature by making it's molecules move faster.
51
New cards
universal solvent
Water- due to its polarity and ability to dissolve many different solutes
52
New cards
Buffers
Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. They help maintain a given pH even after the addition of an acid or a base; help maintain homeostasis in organism
53
New cards
Marcomolecules
large organic molecules found in living things
54
New cards
monomers
small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers
55
New cards
polymers
chains of monomers
56
New cards
monomers hook together using
dehydration synthesis (releasing water)
57
New cards
monomers unhook using
hydrolysis (taking in water)
58
New cards
Name the 4 macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
59
New cards
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars found in foods
60
New cards
Lipids
fats and oils; large, varied group of macromolecules that aren't generally soluble in water.
61
New cards
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA genetic codes
62
New cards
Protien
a class of nutrients that builds body tissues and supplies energy.
63
New cards
monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccharides (ex: glucose and fructose)
64
New cards
monomer of lipids
glycerol and fatty acids
65
New cards
monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides made of 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
66
New cards
monomer of proteins
amino acids
67
New cards
polymer of carbohydrates
polysaccharide (ex: starch, cellulose, glycogen)
68
New cards
polymer of lipids
triglyceride and diglyceride
69
New cards
polymer of nucleic acids
polynucleotide (nucleic acid)
70
New cards
polymer of protein
polypeptide
71
New cards
function of carbohydrates
provide energy for all living things and for structural purposes.
72
New cards
function of lipids
long term energy storage; Important for the biological membrane and water proof coverings.
73
New cards
function of nucleic acids
store and transmit genetic or hereditary information
74
New cards
function of proteins
To control the rate of chemical reactions and regulates cell procedures. Important for structure and transporting cells to help fight diseases.
75
New cards
A protein is one or more ____________
folded polypeptide
76
New cards
Carbohydrates are made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
77
New cards
Lipids are made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
78
New cards
nucleic acids are made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
79
New cards
Proteins are made of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
80
New cards
polyunsaturated fats
fat molecules that have more than one unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond in the molecule.
81
New cards
chemical reaction
a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals.
82
New cards
reactant
a chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction.
83
New cards
product
element/compound produced as a result of a chemical reaction
84
New cards
catalyst
a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction; works by lowering reactions activation energy.
85
New cards
enzyme
A protein that acts as a biological catalyst - speeds up chemical reactions, lowers activation energy.
86
New cards
What property of the enzyme makes it specific to the substrate?
Enzymes are specific to substrates as they have an active site which only allow certain substrates to bind to the active site. This is due to the shape of the active site and any other substrates cannot bind to the active site.
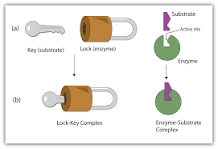
87
New cards
How are saturated fats different from unsaturated fats?
Saturated fatty acids lack double bonds between the individual carbon atoms, while in unsaturated fatty acids there is at least one double bond in the fatty acid chain.
88
New cards
radioactive isotopes
isotopes with unstable nuclei and break down at a constant rate over time; Dangerous; can be used to detect cancer, kill bad bacteria in food, and can also be used as labels/tracers to follow the movements of substances within organisms.