Price determination in a competitive market
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
What is a market?
A voluntary meeting of buyers and sellers
If violence or threat is used then it is no longer classed as a market
What is a competitive market?
a market in which the large number of buyers and sellers possess good market information and can easily enter or leave the market
What is perfect competition model?
Assumptions including:
products are homogenous(identical)
consumers have perfect knowledge of the market
there is a large number of businesses operating in the market
easy entry and exit for businesses from the market
price takers-the price is decided by the market
Define equilibrium price
the price at which planned demand for a good or service exactly equals the planned supply
Define demand
the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at given prices in a given period of time
What is effective demand?
the desire for a good or service backed by the ability to pay
What is market demand?
the quantity of a good or service that all the consumers in a market are willing and able to buy at different market prices
What is individual demand?
the quantity of a good or service that a particular individual would like to buy
What is speculative demand?
the desire to hold money for investment or other profitable purposes rather than for transactions like trade or consumption
What is the ‘law’ of demand?
that there is an inverse relationship between the price asked and the quantity demand of a good assuming ceteris paribus
What is ceteris paribus?
the idea that all other factors remain unchanged
What illustrates the ‘law’ of demand?
The demand curve
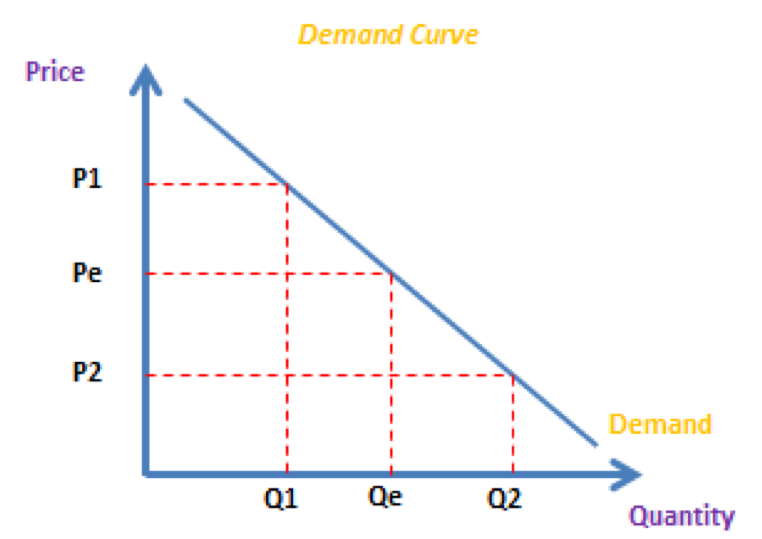
What causes movement along a demand curve?
a change in price
What way is the demand curve sloping?
downwards
What is an extension of demand?
when a fall in price results in more of a good being demanded
What is contraction of demand?
when a rise in press leads to less of a good being demanded
What else does demand depend on?
incomes and substitutes
What are the conditions of demand?
the prices of substitute goods
the prices of complementary goods
personal income
tastes and preferences
population size
What causes a shift in the demand curve?
If any of the conditions of demand change
What way does the demand curve shift when there is an increase in demand?
rightwards (out)
What way does the demand curve shift when there is an decrease in demand?
leftwards (in)
What is a normal good?
a good for which demand increases as income rises and demand decreases as income falls
What is an inferior good?
a good for which demand decreases as income rises and demand increases as income falls
What defines whether a good is normal or inferior?
people’s tastes and income
What are veblen goods?
those where the high price is part of the attraction e.g Rolex watches
What are quantity signalling goods?
those where consumers use price as a proxy for quality - hence thinking a higher price is a higher quality
What are giffen goods?
a product that people buy more of even when the price increases e.g rice
Define total revenue
the total money earned from all sales
How do you calculate total revenue?
total revenue = price x quantity
Define supply
the quantity of a good or service that firms are willing and able to sell at given prices in a given period of time
What is the supply curve?
a graph that shows the quantity supplied at any given price
What is the ‘law’ of supply?
that as the price of the good rises, so does the supply
What way does the supply curve slope?
upwards
Why does the supply curve slope upwards?
the profit motive - a rational firm will always aim to maximise profits
production and costs - output expanding means production costs tend to rise so a higher price is needed to cover this
new entrants coming into the market - higher prices gives an incentive for businesses to enter the market
What is profit?
the difference between the total sales revenue and total costs of production
What is the profit motive?
We assume that a rational firm will always aim to maximise profits
If the market price rises following an increase in demand, it becomes more profitable for businesses to increase their output
What are some of the assumptions of supply?
firms don’t set their own price
firms wish to maximise their profits
production becomes more difficult as a business tries to supply more
when firms see a price increase, they believe that this is because there is more demand
What causes movement along the supply curve?
a change in price
What are the conditions of supply?
costs of production (e.g raw material costs, wage costs, borrowing costs etc)
technological progress
natural conditions
indirect tax e.g VAT
subsidies granted by the government
What way does the supply curve shift when there is an increase in supply?
rightward
What way does the supply curve shift when there is an decrease in supply?
leftward
What is fixed supply?
when supply is limited to a certain output. It is shown by a vertical supply curve
What is elasticity?
the measurement of how responsive one economic variable is to a change in another
What is price elasticity of demand (PED)?
a measurement of how responsive demand is to a change in price
What is the PED equation?
%change in quantity demanded / %change in price
What way does the PED graph slope?
downwards
What does it mean if a good is elastic?
it is very responsive to a change in price, the change in price leads to an even bigger change in demand
What is the PED of an elastic good?
PED>1
What does it mean if a good is inelastic?
that it is relatively unresponsive to a change in price, the buyer’s demand does not change as much as the goods change in price
What is the PED of an inelastic good?
PED<1
What does it mean if a good is unitary elastic?
when the change in demand of a product is equal to the change in price
What is the PED of a unitary elastic good?
PED=1
What is a perfectly inelastic good?
one where no matter the change in price, demand remains unresponsive
What is the PED of a perfectly inelastic good?
PED=0
What is a perfectly elastic good?
a good which the demand falls to 0 when the price changes, buyers are prepared to buy all that they can at some prices but none at all at higher prices
What is the PED of a perfectly elastic good?
PED=infinity
What are the factors affecting PED?
substitutability
percentage of income
necessities or luxuries
width of market definition
time
addictive properties/habit forming
How does substitutability affect PED?
When very close substitutes for a product are available, demand for the product is highly elastic as consumers respond to a price change by buying the substitute good instead
How does percentage of income affect PED?
if a good only takes up a small proportion of income (e.g magazine) , demand is likely to be inelastic compared to a good that takes up a lot of income (e.g car), which is likely to be elastic
How does whether if something is a necessity or luxury affect PED?
a necessary good (e.g bread) will have a relatively inelastic demand. Luxury goods (e.g holidays) are more elastic, if the price of a flight increases then demand will decrease
How does the ‘width’ of market definition affect PED?
a broader market definition means a higher PED as it implies more available substitutes, while a narrower market definition decreases PED due to fewer substitutes
How does time affect PED?
for many goods, demand is more elastic in the long run than in the short run because it takes time to respond to a price change
How does addictive properties/habit forming affect PED?
if a good is addictive it is likely to be in demand regardless of changes in price of the good, therefore the good is relatively price inelastic
If consumer expenditure increases in response to a price fall then what is demand?
elastic
If consumer expenditure decreases in response to a price fall then what is demand?
inelastic
What is income elasticity of demand (YED)?
it measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income
What is the formula for income elasticity of demand?
YED = %change in quantity demanded / %change in income
What does income elasticity of demand depend on?
whether the good is a normal good or inferior good
What YED do normal goods have and why?
positive
quantity demanded of a normal good rises with income
What is the YED of luxury goods?
YED>+1
they are income elastic
What is the YED of necessities/basic goods?
YED lies between 0 and +1
they are income elastic
What are luxury goods and basic goods classed as?
normal goods
What YED do inferior goods have and why?
negative
quantity demanded of an inferior good falls as income rises
What are the factors affect YED?
whether the good is a necessity or a luxury
the level of income of a consumer
What is cross elasticity of demand (XED)?
the responsiveness of a change in demand of one good, X, to a change in price of a related good, Y
What is the equation for cross elasticity of demand?
XED= %change in quantity demanded for good X / %change in price of good Y
What are the possibilities of the relationship of goods for XED?
complementary goods (or joint demand)
substitutes (or competing demand)
an absence of any demand relationship
Substitutes and XED
with these, an increase in the price of one good will lead to an increase in demand for a rival product
value of XED for two substitutes is always positive
Complements and XED
a fall in price of one product causes an increase in demand for the complementary product
value of XED for two complements is always negative
What does it mean if close substitutes have a strongly positive XED?
that a small change in relative price causes a big switch in consumer demand
What does a strong complementary relationship between products mean?
a highly negative XED, if one good becomes more expensive, the quantity demanded for both goods will fall
Close complements graph
a small fall in price of good X leads to a large increase in quantity demanded of Y
Weak complements graph
a large fall in price of good X leads to only a small increase in quantity demanded of good Y
Close substitutes graph
a small increase in price of good X leads to a large increase in quantity demanded of Y
Weak substitutes graph
a large increase in the price of good X leads to a smaller increase in quantity demanded of Y
What is the XED of unrelated products
XED=0
Why are firms interested in XED?
as it allows them to see how many competitors they have
What is price elasticity of supply (PES)?
it measures the extent to which the supply of a good changes in response to a change in the price of that good
What equation is used to calculate price elasticity of supply?
PES= %change in quantity supplied / %change in price
What does it mean if the PES>1?
It indicates that supply is elastic, meaning a small change in price leads to a relatively large change in the quantity supplied. Suppliers can increase supply quickly at little cost
What does it mean if the PES<1?
It indicates that supply is inelastic, meaning a significant change in price leads to a relatively small change in the quantity supplied
What does it mean if the PES=1?
it means supply is unitary elastic, if the price of a good changes by a certain percentage, the quantity supplied will change by the same percentage
What does it mean if the PES=infinity?
It means supply is perfectly inelastic, indicating that any quantity demanded can be met without changing price
What are some of the factors affecting PES?
length of production period
spare capacity
level of stocks
how substitutable factors are
barriers to entry to the market
time
How does the length of the production period affect PES?
a shorter production period usually results in a more elastic supply, as firms can easily adjust the amount supplied in comparison to the price
How does the availability of spare capacity affect PES?
If the firm is operating at full capacity, there is no space left to increase supply. If there are spare resources, supply can be increased quickly.
How does the ease of accumulating stocks affect PES?
If goods can be stored, such as CDs, firms can stock them and increase market supply easily. If the goods are perishable, such as apples, firms cannot stock them for long so supply is more inelastic.
How do substitutable factors affect PES?
The availability of substitute inputs allows firms to switch quickly between resources, making supply more elastic when prices change.
How do barriers and entry to the market affect PES?
Higher barriers to entry means supply is more price inelastic, because it is difficult for new firms to enter and supply the market.
How does time affect PES?
In the short run, supply is more price inelastic, because producers cannot quickly increase supply. In the long run, supply becomes more price elastic.