Weekly Check-Ins - EXAM ONE
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biochemistry - Chapters 1 & 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Which is the major feature that distinguishes eukaryotes from Bacteria and Archaea?
a. DNA
b. Photosynthetic Capability
c. Plasma Membrane
d. Ribosomes
e. The Nucleus
e. The Nucleus
What functional groups are present on this molecule?
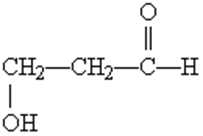
a. Ether and aldehyde
b. Hydroxyl and aldehyde
c. Hydroxyl and carboxylic acid
d. Hydroxyl and ester
e. Hydroxyl and ketone
b. Hydroxyl and aldehyde
Chlorine (Cl) is: _________.
a. Not found in living organisms
b. Considered an essential ion
c. Used by one specific enzyme to complete one specific action
d. Is one of the 5 elements that makes up 97% of living organisms by mass
b. Considered an essential ion
If the free-energy change ΔG for a reaction is -46.11 kJ/mol, the reaction is:
a. At equilibrium
b. Endergonic
c. Endothermic
d. Exergonic
e. Exothermic
d. Exergonic
1) For the reaction below which is the correct equation for the equilibrium constant?
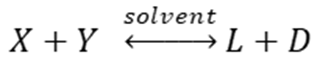
A.
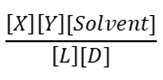
B.
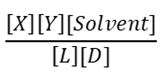
C.
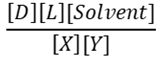
D.
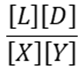
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
e. It depends on which direction is favored at equilibrium
d. D
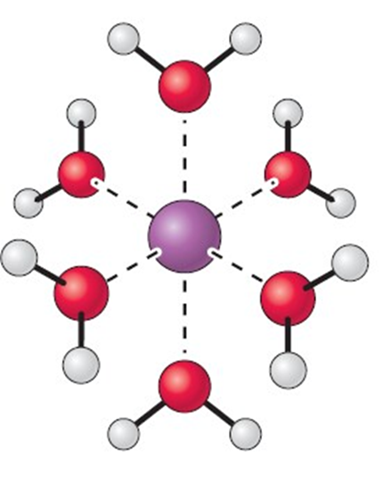
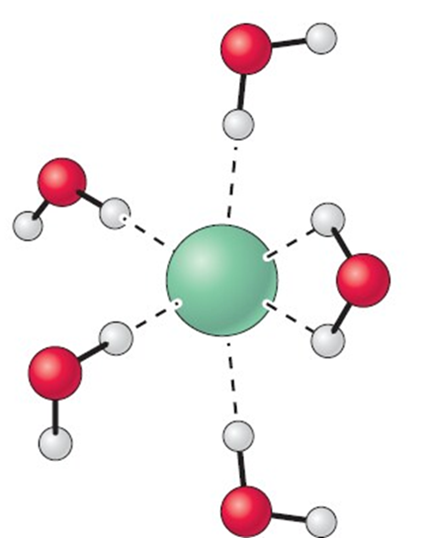
Which of the following picture depicts water solvating a cation and why?
I)
II)
Because
III) The partial negative is found on oxygen (red) and is attracted to the formal positive charge on the cation (purple/green)
IV) The partial negative is found on the hydrogen (white) and is attracted to the formal positive charge on the cation (purple/green)
a. I, IV
b. II, IV
c. II, III
d. I, III
d. I, III
The pH of a sample of blood is 7.4, while gastric juice is pH 1.4. The blood sample has ___________ lower [H+] than the gastric juice.
a. 6,000,000 times lower
b. One million times lower
c. 0.189 times lower
d. 5.29 times lower
e. 6 times lower
b. One million times lower
Which process would NOT disrupt the weak interactions between two biomolecules in solution?
a. Lowering the pH of the solution
b. Heating the solution
c. Increasing the ionic strength of the solution
d. All of the answer choices would disrupt interactions between biomolecules
e. Cooling the solution
e. Cooling the solution
Which diagram illustrates an amphipathic molecule?
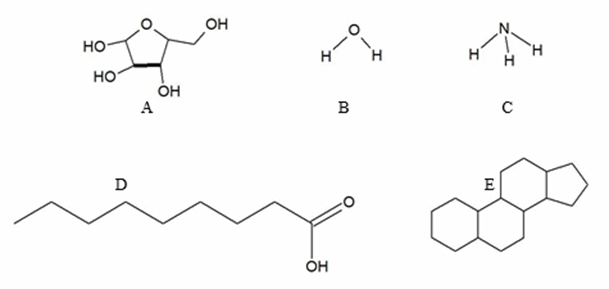
a. E
b. D
c. C
d. A
e. B
d. A
In an acidic solution, _______.
a. [H3O+]<[OH-]
b. [H3O+]= 0 M
c. [H3O+]>[OH-]
d. [OH-]> 7.00 M
e. [H3O+]=[OH-]
c. [H3O+]>[OH-]
1) Rank the following intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest.
Strongest –
2nd Strongest –
3rd Strongest –
3rd Weakest –
2nd Weakest –
Weakest –
a. Ion-Ion, Ion-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole, Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole
b. Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, Ion-Dipole, Ion-Ion
c. Ion-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, Ion-Ion, Dipole-Dipole, Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole.
d. Hydrogen Bonding, Ion-Ion, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole, Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole
a. Ion-Ion, Ion-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole, Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole
Distilled white vinegar has a pH of 2.4. What is the [H+] of distilled white vinegar?
a. 3.98 x 10^-6 M
b. 2.5 x 10^-12 M
c. 2.5 x 10^-3 M
d. 2.4 M
e. 3.98 x 10^-3 M
e. 3.98 x 10^-3 M
The pH of a sample of blood is 7.4, while gastric juice is pH 1.4. The blood sample has ________________ [H+] than the gastric juice.
a. 6,000 times lower
b. One million times lower
c. 0.189 times lower
d. 5.29 times lower
e. 6 times lower
b. One million times lower
List the acids in increasing order of strength (weakest to strongest): nitrous acid (Ka = 4.0x10-4), carbonic acid (Ka = 4.4x10-7), acetic acid (Ka = 1.7x10-5), phosphoric acid (Ka = 7.3x10-3).
a. Carbonic acid, Phosphoric acid, Nitrous acid, Acetic acid
b. Carbonic acid, Acetic acid, Nitrous acid, Phosphoric acid
c. Phosphoric acid, Nitrous acid, Acetic acid, Carbonic acid
d. Acetic acid, Carbonic acid, Nitrous acid, Phosphoric acid
e. Acetic acid, Nitrous acid, Carbonic acid, Phosphoric acid
b. Carbonic acid, Acetic acid, Nitrous acid, Phosphoric acid
If the Ka of an acid is 1.38 x 10-7, what is the pKa?
a. 10.7
b. 1.38
c. 4.37
d. 7.14
e. 6.86
e. 6.86
According to the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, when is the pH equal to the pKa?
a. None of the answers are correct
b. When the concentration of the conjugate base is equal to the ionization constant for water
c. When the concentration of acid is close to zero
d. When the pH approaches 7
e. When the concentration of the conjugate base is equal to the concentration of the acid
e. When the concentration of the conjugate base is equal to the concentration of the acid
Consider an acetate buffer, initially at the same pH as its pKa (4.76). When sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is mixed with this buffer, the:
a. pH rises more than if the same amount of NaOH is added to an acetate buffer initially at pH 6.76
b. Sodium acetate formed precipitates because it is less soluble than acetic acid
c. pH rises more than if the same amount of NaOH is added to unbuffered water at pH 4.76
d. pH remains constant
e. Ratio of acetic acid to acetate ion in the buffer decreases
e. Ratio of acetic acid to acetate ion in the buffer decreases
According to the titration curve shown, what is the approximate pKa of acid A?
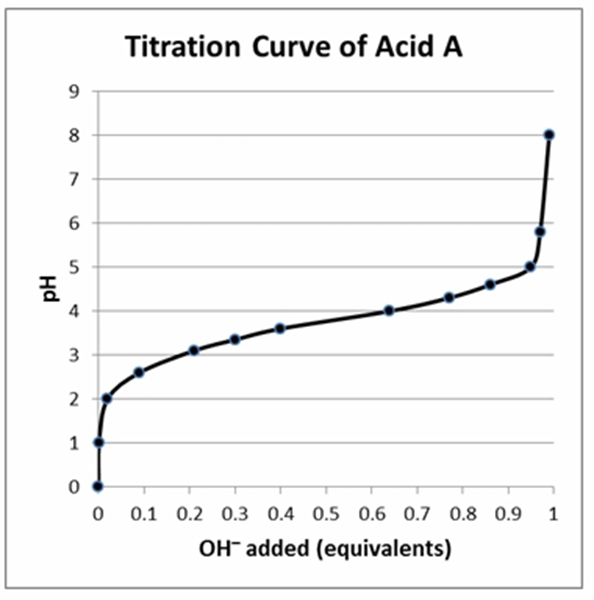
a. 3.8
b. 3.2
c. 0.5
d. 4.8
e. 0.2
a. 3.8
If a person is suffering from mild acidosis, which treatment/action would help counteract the acidosis the most?
a. All of these treatments/actions could be used to counteract acidosis
b. Deep Breathing
c. Vigorous Exercise
d. Breathing into a paper bag
e. Intravenous administration of glucose
b. Deep Breathing
Which statement about buffers is true?
a. At pH values lower than the pKa, the conjugate base concentration is higher than that of the conjugate acid
b. The pH of a buffered solution remains constant no matter how much acid or base is added to the solution
c. A buffer composed of a weak acid of pKa = 5 has a greater buffering capacity at pH 4 than at pH 6
d. When pH = pKa, the weak acid and conjugate base concentrations in the buffer are equal
e. The best buffers are those composed of strong acids and strong bases
d. When pH = pKa, the weak acid and conjugate base concentrations in the buffer are equal
The objective is to maintain pH = 7.0 for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction that will produce hydrogen ions along with the desired product. At equal concentrations, which weak acid, if any, will serve s the better buffer for the reaction: acid A with pKa = 6.5 or acid B with pKa = 7.5?
a. Both are equally effective
b. Water is as good as either of the acids available
c. Acid A
d. Acid B
c. Acid A
What is the conjugate base of H2PO4-1?
a. H3PO4
b. HPO4 2-
c. PO4 3-
d. H2PO4 2-
e. HPO4 3-
b. HPO4 2-
Milk of magnesia has a pH of 10.2. What is the [OH-] of milk of magnesia?
a. 6.31 x 10-11 M
b. 6.31 x 10-4 M
c. 1.58 x 10-5+ M
d.1.02 x 10-3 M
e. 1.58 x 10-4 M
e. 1.58 x 10-4 M
Three buffers are made by combining a 1M solution of acetic acid with a 1M solution of sodium acetate in the ratios shown.
Buffer | 1 M Acetic Acid | 1 M Sodium Acetate |
Buffer 1 | 10 mL | 90 mL |
Buffer 2 | 50 mL | 50 mL |
Buffer 3 | 90 mL | 10 mL |
Which is true of the resulting buffers?
a. pH of buffer 1 < pH of buffer 2 < pH of buffer 3
b. pH of buffer 1 > pH of buffer 2 > pH of buffer 3
c. the problem cannot be solved without knowing the pKa of acetic acid
d. pH of buffer 1 = pH of buffer 2 = pH of buffer 3
e. None of these statements are true
b. pH of buffer 1 > pH of buffer 2 > pH of buffer 3
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
a. Relates the pH of a solution to the pKa and the concentrations of acid and conjugate base
b. Does not explain the behavior of di- or tribasic weak acids
c. Employs the same value for pKa for all weak acids
d. Allows the graphical determination of the molecular weight of a weak acid from its pH alone
e. Is equally useful with solutions of acetic acid and hydrochloric acid
a. Relates the pH of a solution to the pKa and the concentrations of acid and conjugate base