12. Cartilage tissue
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What type of tissue is cartilage?
-semi-rigid connective tissue with abundant extracellular matrix
-rich in GAGs, proteoglycans, collagen, and elastic fibers.
Is cartilage vascularized or innervated?
No. It is avascular and lacks innervation
What are the main functions of cartilage?
Support, cushioning, low friction for joints, and structural role in embryo and respiratory system.
Where is cartilage found in the body?
Joints, nose, ear, intervertebral discs
What are the main cell types of cartilage?
Chondrogenic cells, chondroblasts, and chondrocytes.
What is the perichondrium?
dense irregular connective tissue surrounding most cartilage
What are the layers of the perichondrium?
Inner cellular layer (chondroblasts, progenitor cells) and outer fibrous layer (type I collagen, fibroblasts).
What are the functions of the perichondrium?
Nutrition, oxygen supply, and source of progenitor cells.
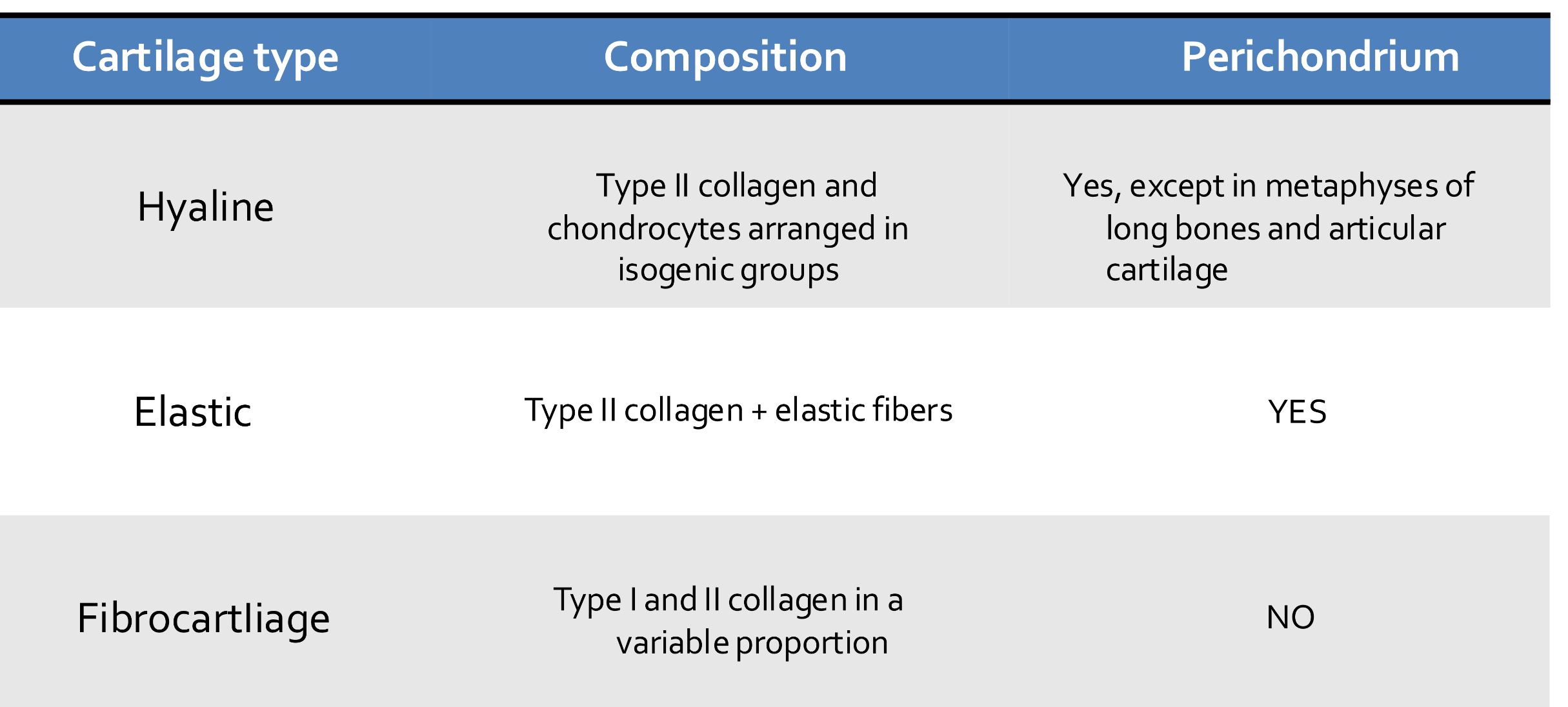
Which are the three main types of cartilage?
-Hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
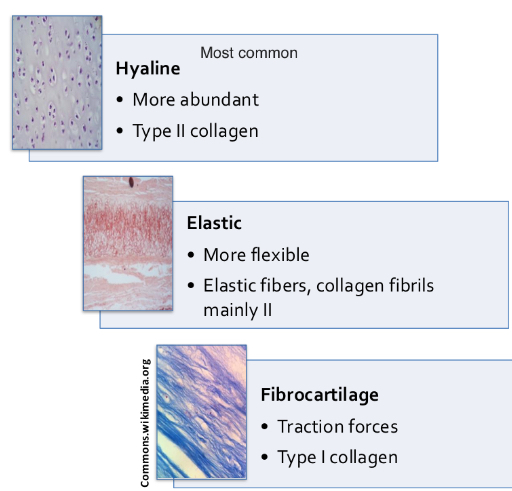
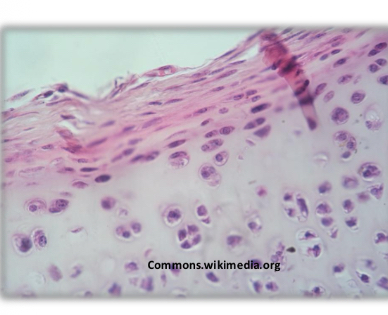
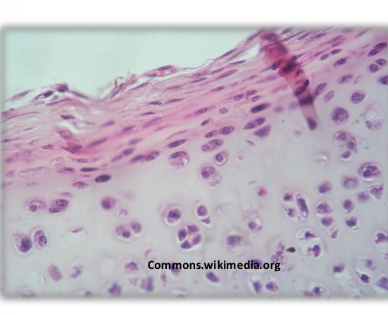
Hyaline cartilage
-most abundant and common
-chondrocytes form isotonic groups
-mostly type 2 collagen
-nasal septum
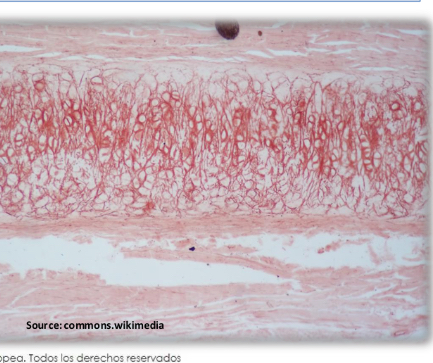
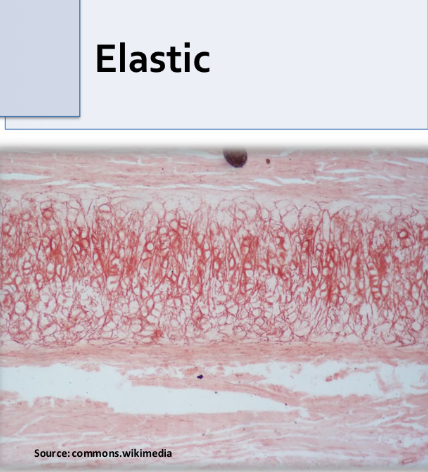
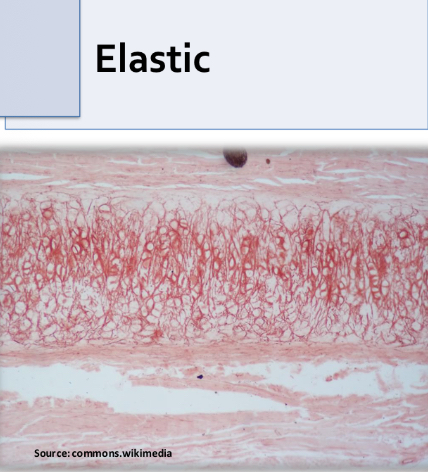
Elastic cartilage
-chondrocytes form isotonic groups
-type 2 collagen Fiber
-abundant elastic fibers
-in external ear
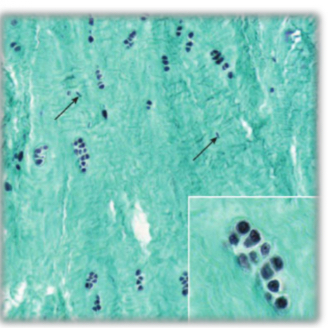
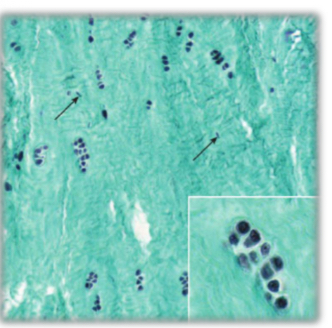
Fibrocartilage
-type 1 & 2 collagen
-no perichondrium
-intervertebral discs
What is chondrogenesis?
Process where mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondroblasts that secrete ECM and form cartilage.
What are the two types of cartilage growth?
Interstitial (from within) and appositional (from perichondrium surface).
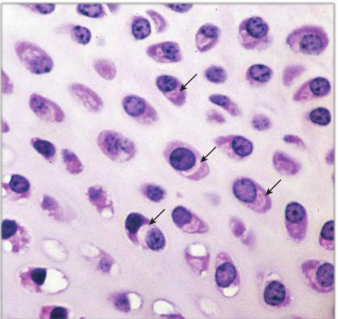
What is interstitial growth?
Mitotic division of chondrocytes forming isogenic groups inside matrix.
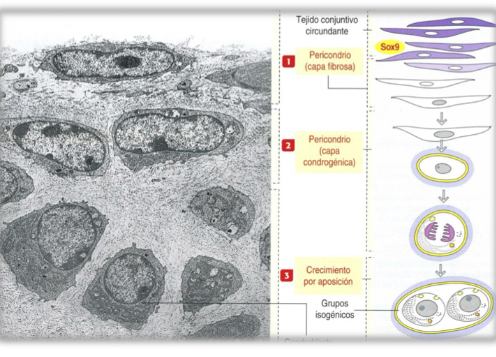
What is appositional growth?
Differentiation of chondroblasts in perichondrium into chondrocytes on the surface.
Why does cartilage heal poorly?
Because it is avascular; nutrients and repair factors reach cells only by diffusion.
What happens in case of major cartilage injury?
Scar tissue of dense connective tissue forms instead of new cartilage.
Summary