Genetic Mutations and Mechanisms
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is a mutation and how does it differ from a polymorphism?
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can lead to genetic disorders, whereas a polymorphism is a common, non-pathogenic genetic variation in the population.
What is a point mutation?
A point mutation involves a change in a single nucleotide base pair in DNA, potentially leading to missense, nonsense, or silent mutations.
What is a missense mutation?
A missense mutation changes a single nucleotide, resulting in a different amino acid in the protein, which may affect its function (e.g., sickle cell anemia).
What is a nonsense mutation?
A nonsense mutation converts a codon to a stop codon, terminating protein synthesis prematurely and often resulting in a nonfunctional protein.
What is a frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutation involves the insertion or deletion of nucleotides, altering the reading frame of the gene and potentially producing a nonfunctional protein.
What is a deletion mutation?
A deletion mutation involves the loss of a DNA segment, potentially removing essential genetic information and causing disorders like Cri-du-chat syndrome.
What is a translocation in genetics?
A translocation is the rearrangement of genetic material between non-homologous chromosomes, which can disrupt gene function and cause genetic disorders.
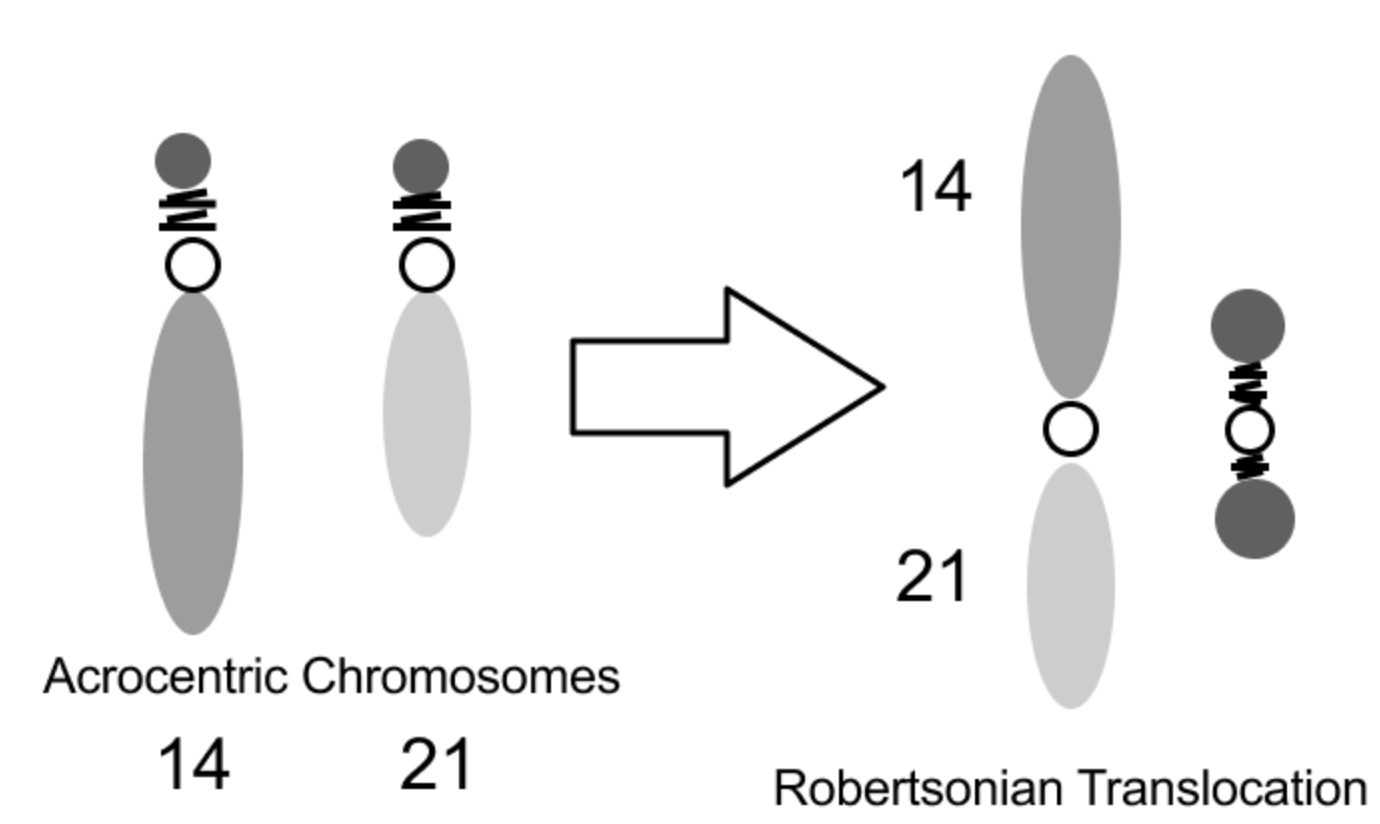
What is a Robertsonian translocation?
A Robertsonian translocation involves the fusion of two acrocentric chromosomes, leading to potential genetic imbalances.
What is non-disjunction and associated disorders?
Non-disjunction is the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis, leading to aneuploidies like trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) and Turner syndrome.
What is a trinucleotide repeat expansion?
A trinucleotide repeat expansion involves the abnormal increase in three-nucleotide sequences, causing disorders like Huntington’s disease and Fragile X syndrome.