PSYC 311 Exam 1
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
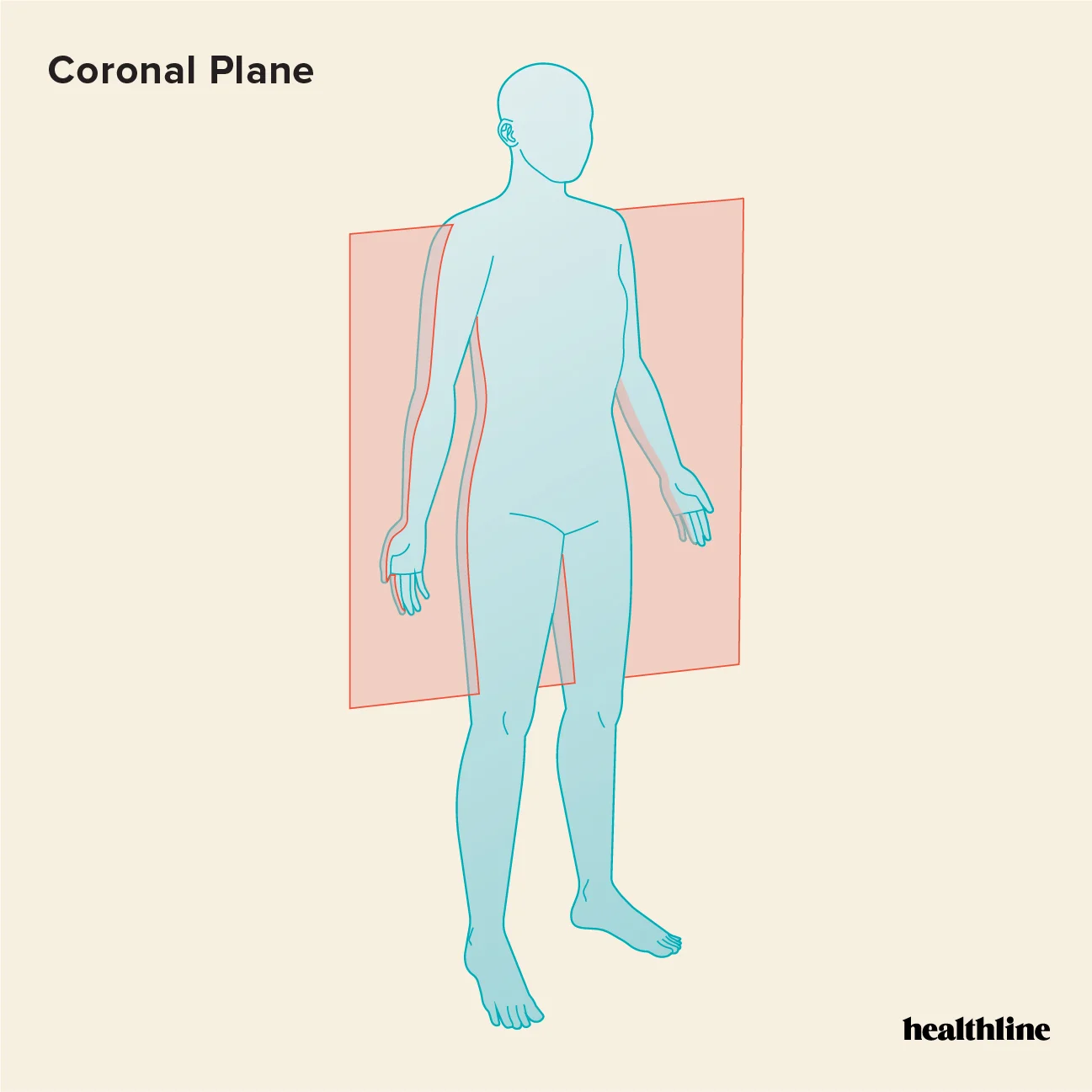
Frontal or Coronal Plane
a cut dividing anterior and posterior portions
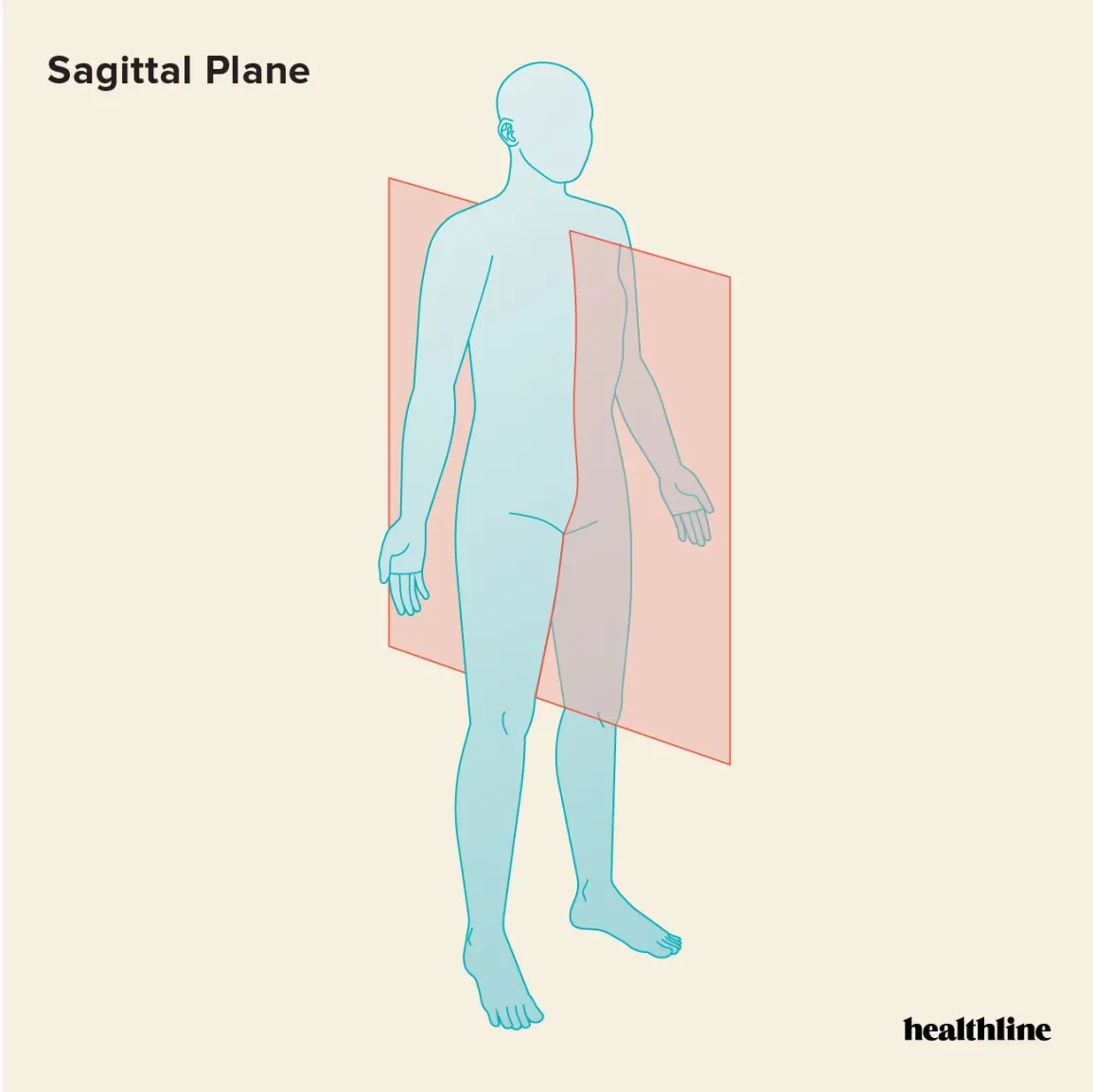
Sagittal Plane
cut running anterior to posterior dividing left and right sections
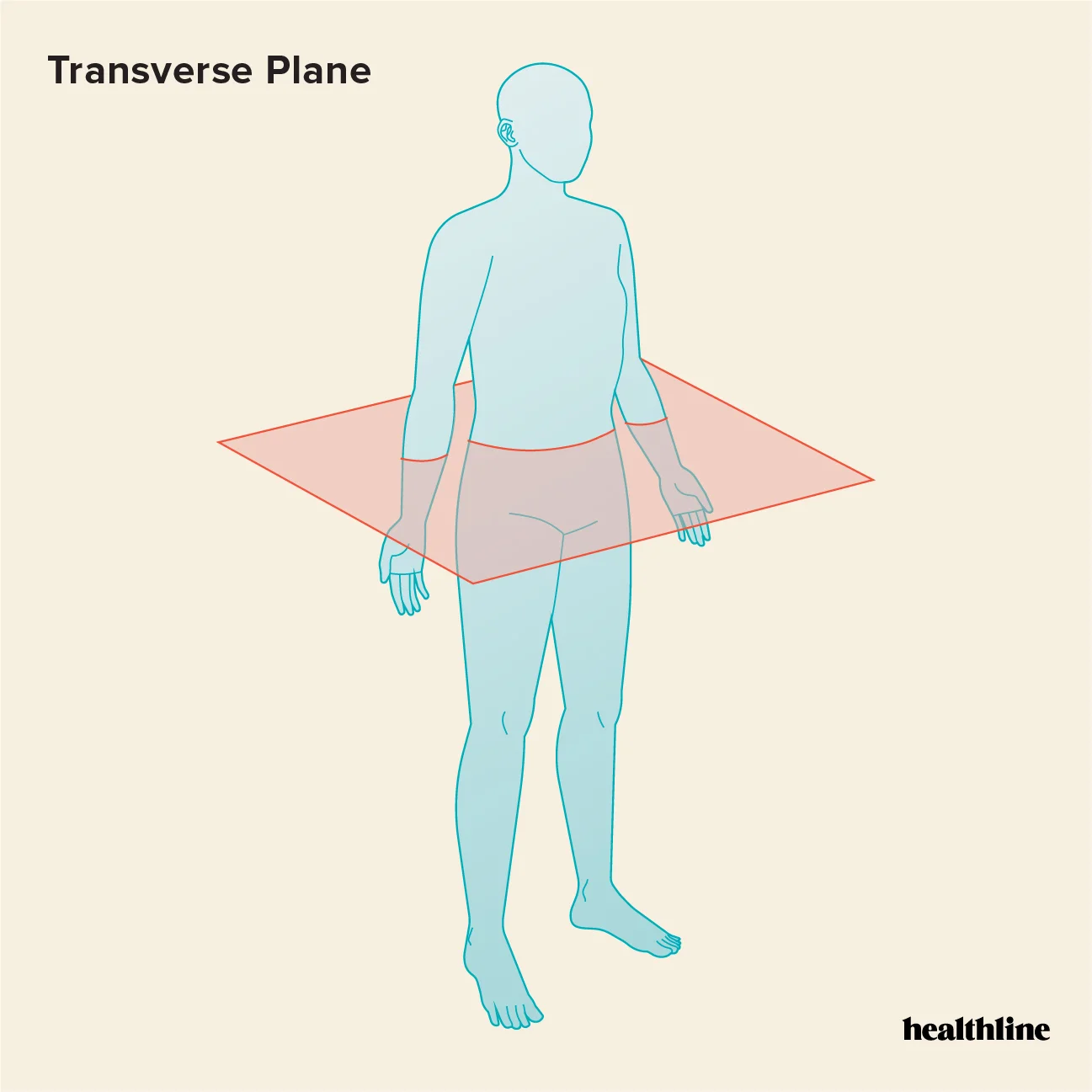
Horizontal or Transverse Plane
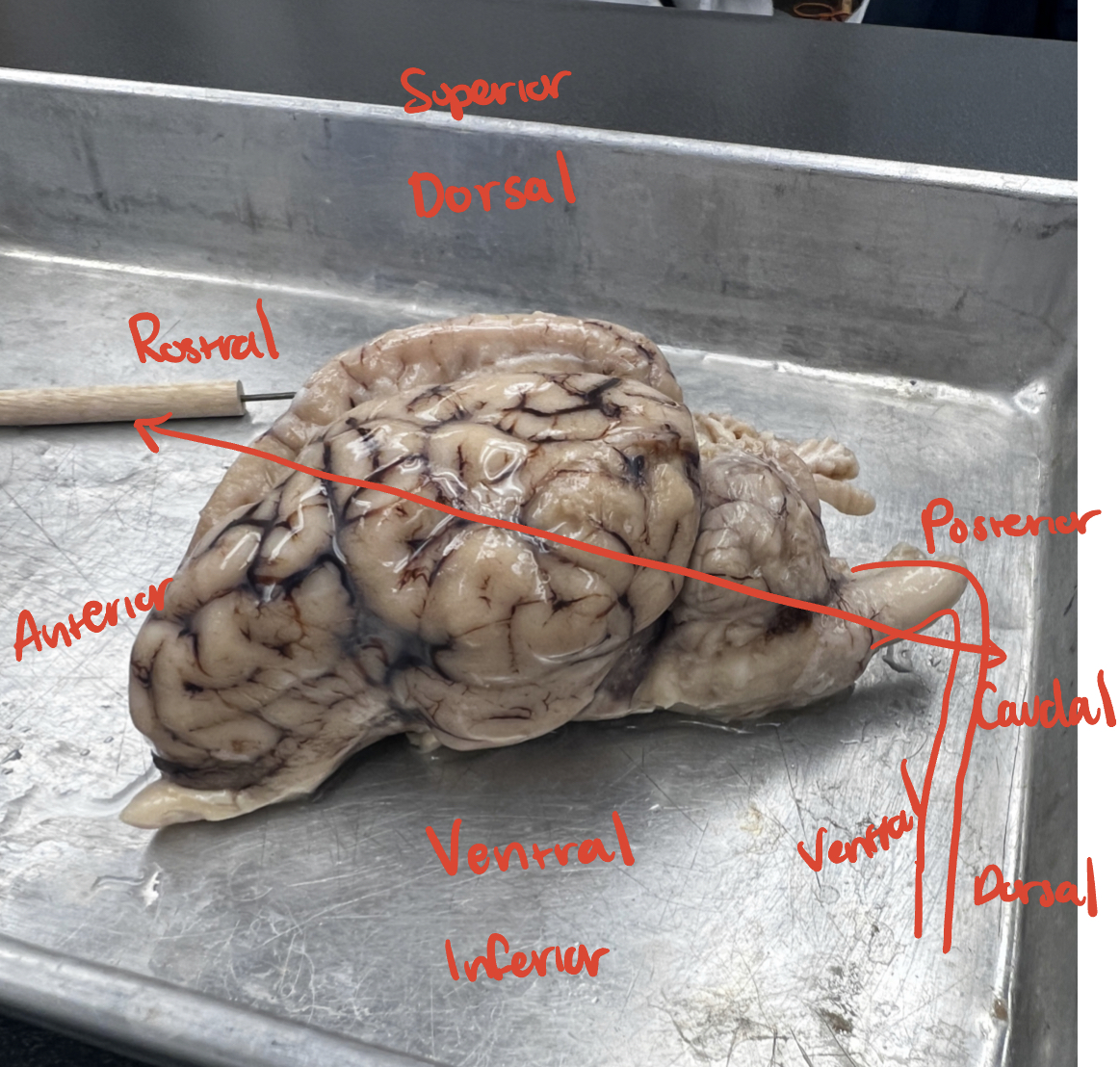
Anatomical Directions
IACUC
Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
Ensures compliance with humane care of animals in research. Must review research facilities’ once every 6 months
Positive findings bias
studies in which some independent variable is
shown to have a significant effect on the dependent variable tend to be more
readily published and appear in higher-impact journals.
Variables
any characteristics that can take on different values, such as weight, age, temperature, or maybe...yawning times.
reliability vs validity
reliability- consistent results
validity- how well the test measures
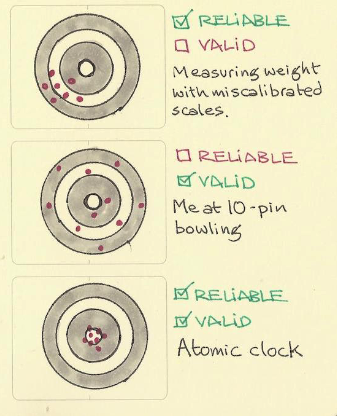
internal validity vs external validity
internal - the extent to which any effects on the dependent variable can be attributed to the independent variable (only the study)
external - the extent to which the results of a study can be applied outside of that specific context (bigger picture)
Within subject design vs between subject design
within - the same participants tests all conditions corresponding to a variable ; repeated measures
between - different participants are assigned different conditions corresponding to a variable ; independent measures
confound
an independent variable that is conceptually distinct but empirically inseparable from one or more other independent variables
Ex. In a study on the effect of sleep on memory, if the amount of caffeine consumed by participants is not controlled, caffeine becomes a confound.
caveat
warning of specific stipulations, conditions, or limitations.
Ex. If a study on memory improvement was conducted exclusively on male rodent
Caveats plague science: only recently did the NIH require that both sexes are tested.
Categorical variables vs Quantitative variables
categorical - names or labels (eye color, gender, breed, etc)
quantitative - numeric
null hypothesis vs alternative hypothesis
null - a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables. H0- male yawns = female yawns
alternative - your research prediction of an effect or relationship. Ha- male yawns > female yawns
P value
The probability that, given the null hypothesis
is true, a result could occur.
if the p-value is below your threshold of significance (typically p < 0.05), then you can reject the null hypothesis
data cleaning
is the process of fixing or
removing incorrect, incomplete data
within a dataset
T test vs ANOVA
T test - Compares 2 means; Determines significant difference of means
ANOVA - Analysis of variance– how do 2 or more
groups vary? Determines significant difference in variance from the mean
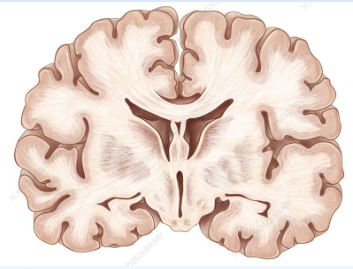
coronal/frontal section
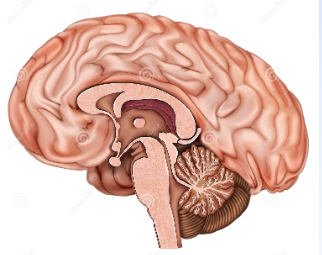
sagittal/medial section
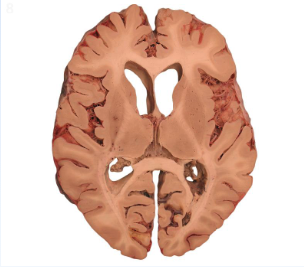
horizontal/transverse
CNS
Brain and spinal cord
PNS
Nerves and sensory organs, ganglia
- Nerves: bundles of axons within the PNS
- Sensory organs: eyes, ears, nose, tongue, skin
- Ganglia: bundles of neuronal bodies within the
PNS
Frontal lobe
CNS ; Working memory
• Executive functions (focus, planning,
impulse control, etc.)
• Motor cortex
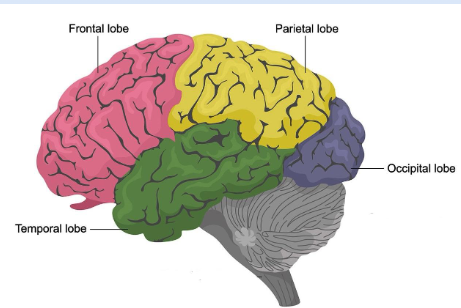
Parietal Lobe
Somatosensory cortex (touch, pain, body
position etc.)
Temporal Lobe
Language production and perception
• Auditory cortex
Occipital Lobe
Visual cortex
Cerebellum
Incredibly densely packed with neurons
Functions : Balance and muscle memory
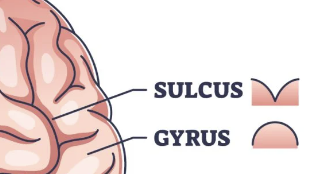
Gyri and Sulci
Gyrencephalic vs Lissencephalic
Gyrencephalic: having cerebral hemispheres marked by gyri and sluci (primates, sheep, large mammals) These folds allow for greater surface area
Lissencephalic: smooth brain (rodents, small animals, less time to produce)
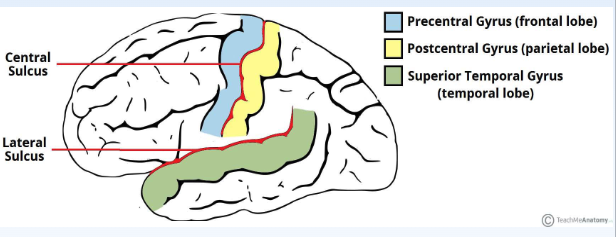
Lateral Sulcus (Sylvian Fissure)
• Separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
• Superior temporal gyrus (sound reception and processing)
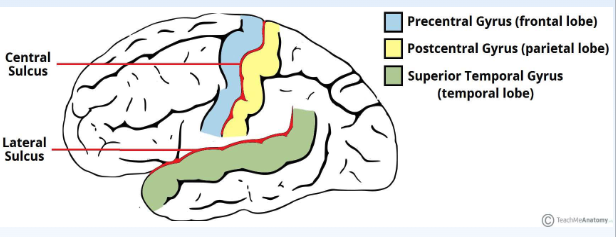
Central Sulcus
Separates the frontal lobe from
the parietal lobe
• Precentral gyrus (motor cortex)
• Postcentral gyrus
(somatosensory cortex)
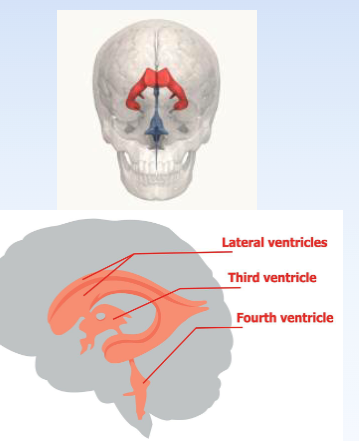
Ventricles
Four interconnected channels filled
with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to protect the brain, clear waste, and provide nutrients and ions
used in neural transmission.
• Ventricles I and II: lateral ventricles
• Ventricle III: surrounds the thalamus
• Ventricle IV: between the cerebellum and
brainstem
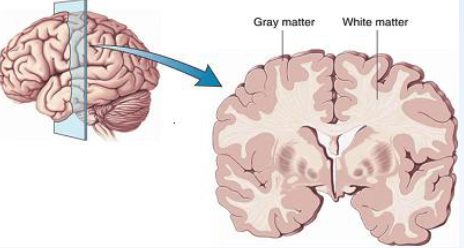
Grey vs White Matter
Grey Matter: Somas (cell bodies) and Dendrites
White Matter: Myelinated axons
Why use animals?
- It enables ethical exploration of invasive experiments that cannot be performed on humans.
- Good for testing neurological diseases, like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Rodents and other animals share significant genetic and biological similarities with humans,
95% of animal research is rats and mice
Examples of animal studies
Pavlov dog, Non-human primates, Throndike’s cat
Why rodents?
• Social
• Curious and smart
• Short (but not too short) lifespans
• Can be modified through breeding or
genetic editing to possess a number of
traits/phenotypes
• Easy to house and handle
• Tools for observing the rodent brain are
readily available.
• Extensively studied. Tons of data
available!
Rodent Ethology
Social Structures: individuals form complex social hierarchies and engage in grooming and bonding behaviors.
Nocturnal Behavior: Rodents are primarily
nocturnal, showing increased activity during the
night and resting during the day.
Burrowing: Rodents create elaborate
underground tunnel systems that serve as nests,
foraging areas, and protection from predators.
Foraging Behavior: Rats exhibit scavenging
behavior, often exploring urban environments to
find and exploit diverse food sources.
rat v mice
Rats - more complex behavior, more suitable for cognitive tasks and social interactions ; Tend to have superior spatial memory and learning
capabilities, more suitable for task experiments ; Exhibit more pronounced social structures and interactions, which are useful for studying social behavior and hierarchy.
Mice - used for more straightforward behavioral assays ; often used in genetic studies related to learning and memory due to their well characterized genome ; Display social behaviors but are less complex compared to rats
Rotarod test
The Rotarod is a device used in animal research to assess motor coordination and balance by
measuring how long a rodent can stay on a rotating rod
Hot plate test
Tests Sensory ability - The hot plate test is used in rodent studies to measure pain sensitivity and analgesic effects by assessing the time it takes for a rodent to respond to a heated surface.
- At what point does the rat respond as if the hot plate is painful?
• Can test analgesic drugs.
• Ethics are important here, we want to see mild
discomfort in the rat, not an extreme pain response
Open field test
Tests navigation - An open space that allows rodents to freely explore
Elevated plus maze
Tests anxiety - uses natural rat fears
Forced swim test
Tests depression - used to evaluate
depressive-like behavior in rodents by measuring
how long they persist in attempting to escape from a confined, inescapable water tank.
Tube test
used to assess social dominance and
aggressive behavior in rodents by observing their interactions when confined in a narrow tube.
• The test observes which animal is able to push the other out of the tube, indicating dominance.
Visual burrow system
Studies group behaviors - open arena and a series of tunnels and burrows
Patch-leaving
Studies foraging to assess decision making by measuring how rodents leave one patch of food to explore and exploit new patches in search of additional rewards
Operant conditioning
The operant chamber is a controlled environment used to study animal behavior by
measuring responses to stimuli, such as pressing levers or pecking keys, to obtain
rewards or avoid punishments ex. push lever to get food or punishment to decrease behavior
radial arm maze
Working and Reference Memory
• Remember which arms they’ve
already collected rewards from
on that day. (working)
• Remember which arms contain
rewards from previous
experiences on the maze (reference)
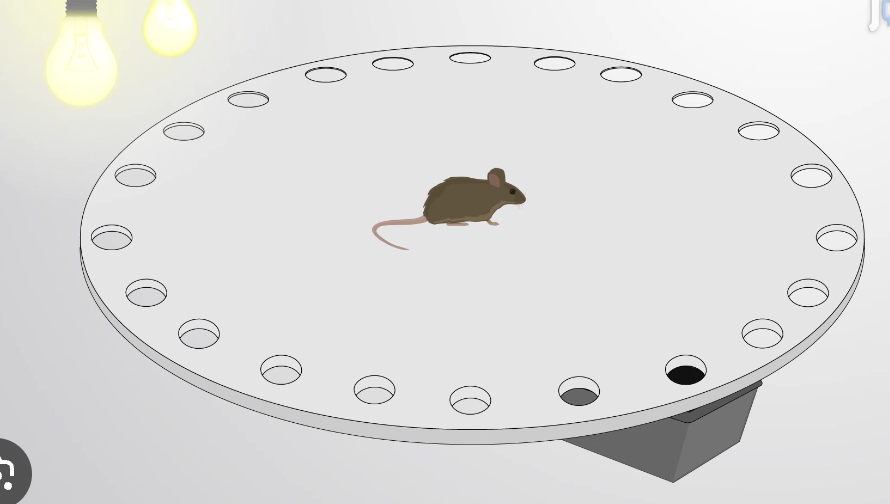
barnes maze
Learn and remember the location of a
target zone using distal cues.
• Intrinsic inclination of the rodents to escape
from an aversive environment

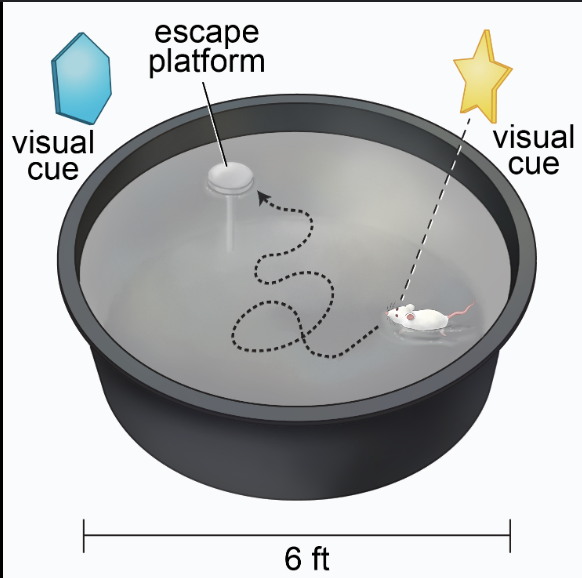
morris water maze
Learn and remember the location of a hidden
platform using distal cues.
• Dislike of water
Silico vs Vitro vs Vivo
silico - experiments using computer simulations or models ; best for brain function models, study neurodisorders
In Vitro - Experiment outside of a living organism. Ex. Patch clamp - tool that can measure electrical currents flowing through ion channels in cells
In Vivo - Experiment in a whole, living organism. Ex. lesion studies (not done on humans unless patient HM who had temporal lobe surgery to cure epilepsy but ended up damaging ability to form new memories)
Invasive stereotaxic surgery
A stereotaxic device uses three coordinates to pin the location of brain sections where probes can be placed to deliver drugs, monitor neural activity, monitor neurotransmitter levels, induce lesions
Lesion techniques
Chemical injection - Kainic acid is injected to kill cells in hippocampus
Radiofrequency - wire electrodes passes radiofrequency to heat the tissue and kill axons and somas
temporary control techniques
Chemical inactivation: using chemicals to temporarily block or inhibit the activity of neurotransmitter receptors, allowing research of the effects of reduced neural activity on behavior and neural processes
chemogenetics: uses viruses to alter gene expression, to control the activity of specific neurons in order to investigate the relationship between neural activity and behavior
optogenetics: uses light to control genetically modified neurons, allowing researchers to manipulate neural activity to study behavior and brain function
Single unit electrophysiology
Using a microelectrode to record electrical activity in a neuron, which can detect the rate and patterns of firing neurons to tell us about neural functions (direct, invasive, high spatial and temporal resolution)
calcium imaging
measures calcium ion status in brain cells (high spatial and temporal resolution, invasive, indirect signal)
CT
imaging technique that uses xrays and computer processing to create images, showing internal structures and abnormalities
MRI
powerful magnets produce a magnetic field to force protons in the body to produce 3d images
Histology
study of microscopic structure of tissues using cutting and staining techniques
Nissl Staining
Can differentiate DNA and RNA (negatively charged molecules) by staining the soma (cell body) used for counting cell number and trace a structure for volume
Golgi Staining
used to examine dendritic branding and number of spines
Immuno Staining
immunohistochemistry (IHC) selects for specific proteins within the cells of a tissue section
Uses antibodies to target specific proteins
Used to count proteins, study their morphology, and pinpoint location
Microscopy
Allows us to view cells
c-FOS
gene expression; action potential triggers translation of cFOS protein to indirectly measure recent neural activity
tract tracing
labels somas and axons tracts
connectomics- understanding the architecture of the nervous system and the patterns of synaptic connectivity that are thought to underlie functional properties of neural circuits
anterograde tracing - traces from origin to termination (soma to terminal)
retrograde tracing - traces from termination to origin
transgenic
animals who have been genetically altered
knock out models
mutate a gene to the point that it is non-functional
knock in models
adding in genes or variants of genes
microdialysis
cells release neurotransmitter in during an action potential
probe placed into region of interest and it samples and collects neurotransmitters and other substances
grey matter
made up of cell bodies
white matter
made up of axons, usually a tract or pathway
sulcus/fissure
grooves or crevices in the cerebral cortex (brain’s most outer layer)
gyrus vs sulcus
gyrus - ridges of the cerebral cortex
sulcus - grooves or crevices
tract
a group of axon fibers connecting different areas of the brain
nerve
same as a tract but outside the central nervous system
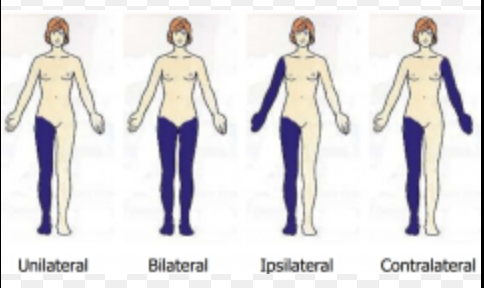
contralateral vs ipsilateral
contralateral - opposite side
ipsilateral - same side
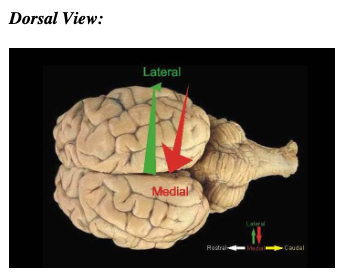
dorsal view
dorsal = back
ventral view
belly or abdomen
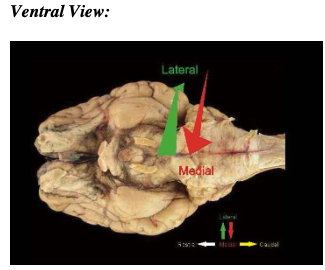
lateral vs medial
lateral - away from the midline
medial - toward the midline
dura mater
grayish membrane that is the outer most layer of the meninges, membranes that keep spinal fluid
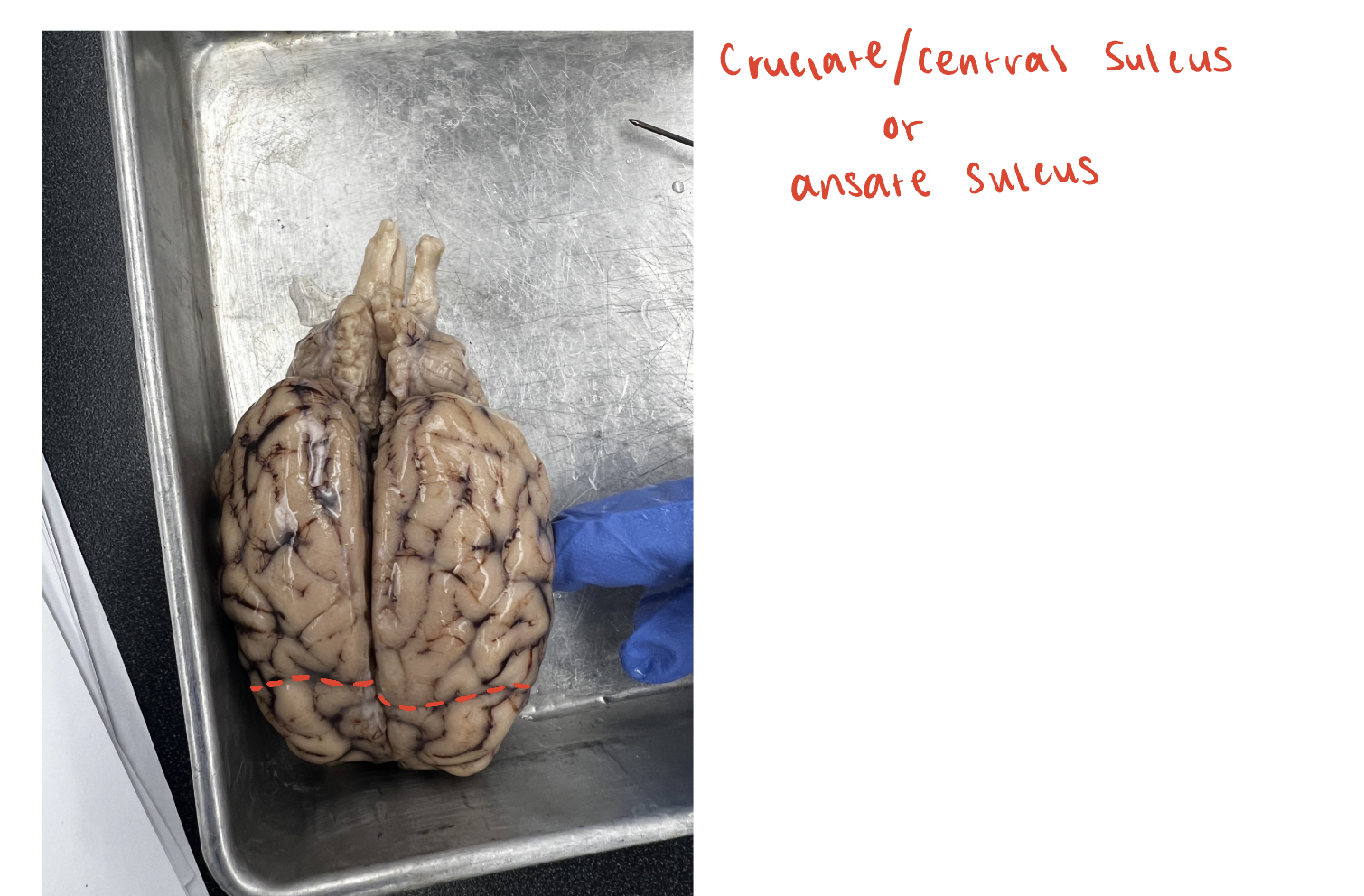
cruciate/central sulcus
(O) or ansate sulcus; divides frontal lobe and parietal lobe
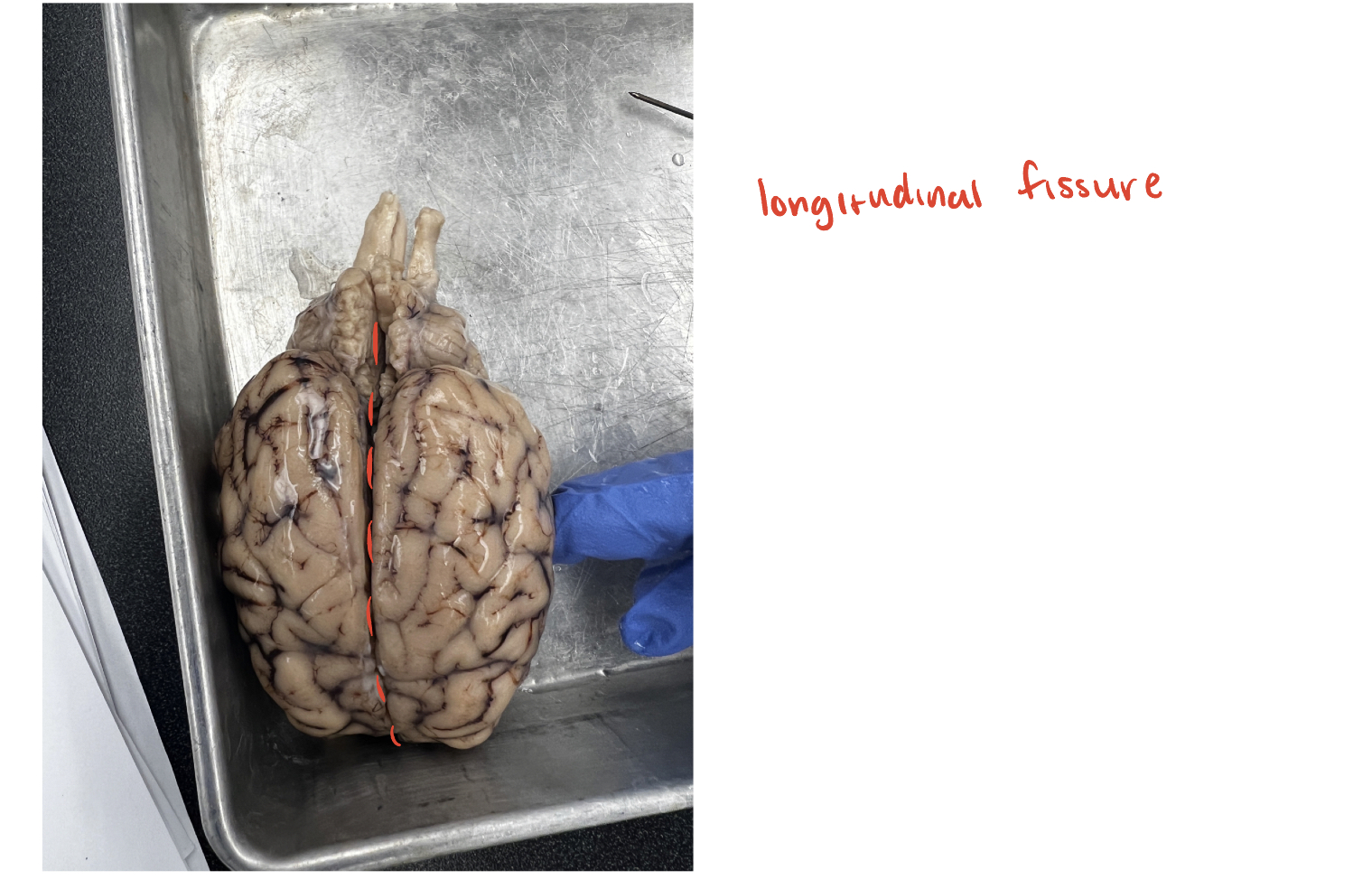
longitudinal fissure
(O) This is the major fissure that runs along the midline of the brain, separating the brain into two hemispheres
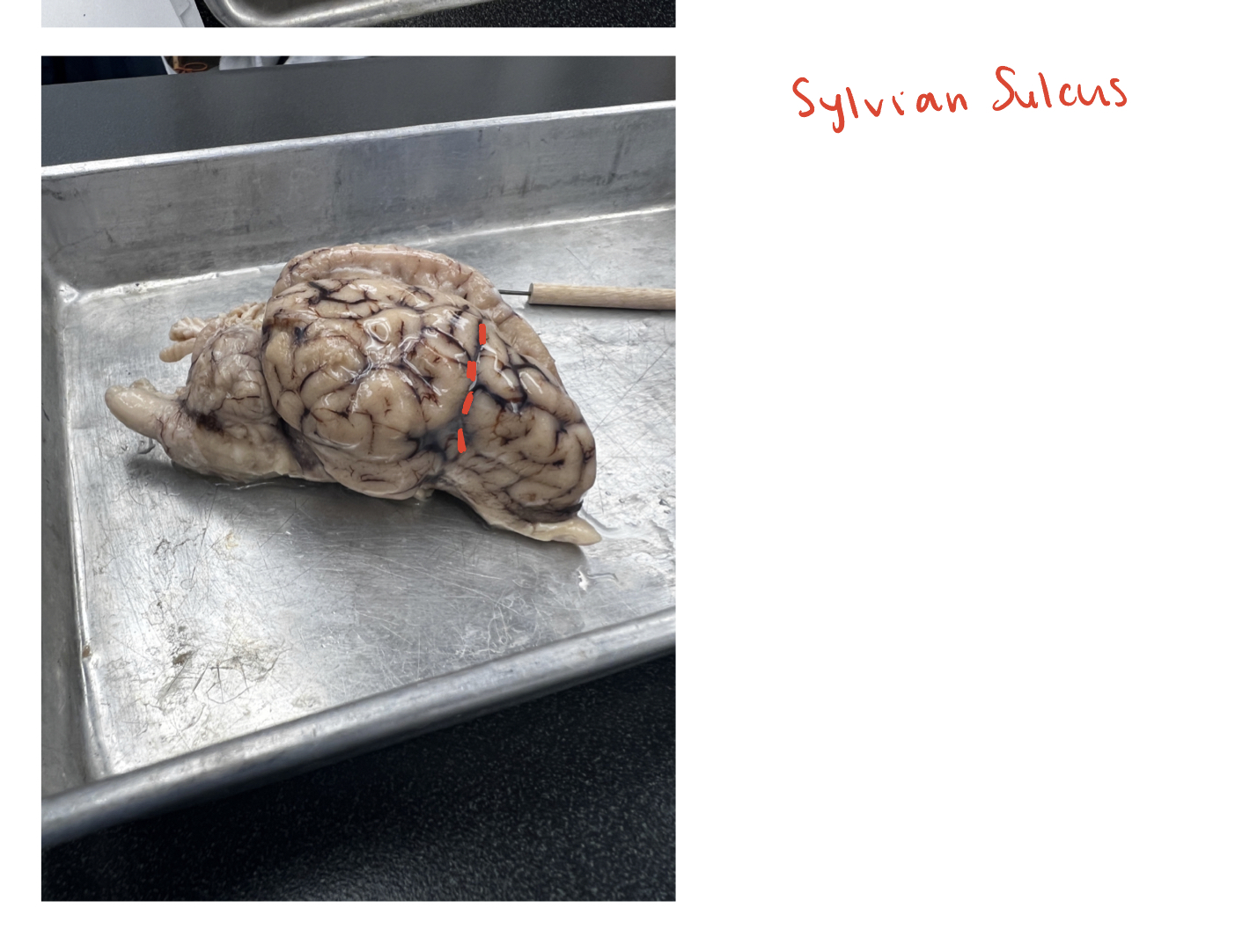
sylvian sulcus
(O) This is the sulcus running vertically towards the cruciate/central sulcus.
This forms the frontal boundary for the temporal lobe and is shown in the lateral view of the brain

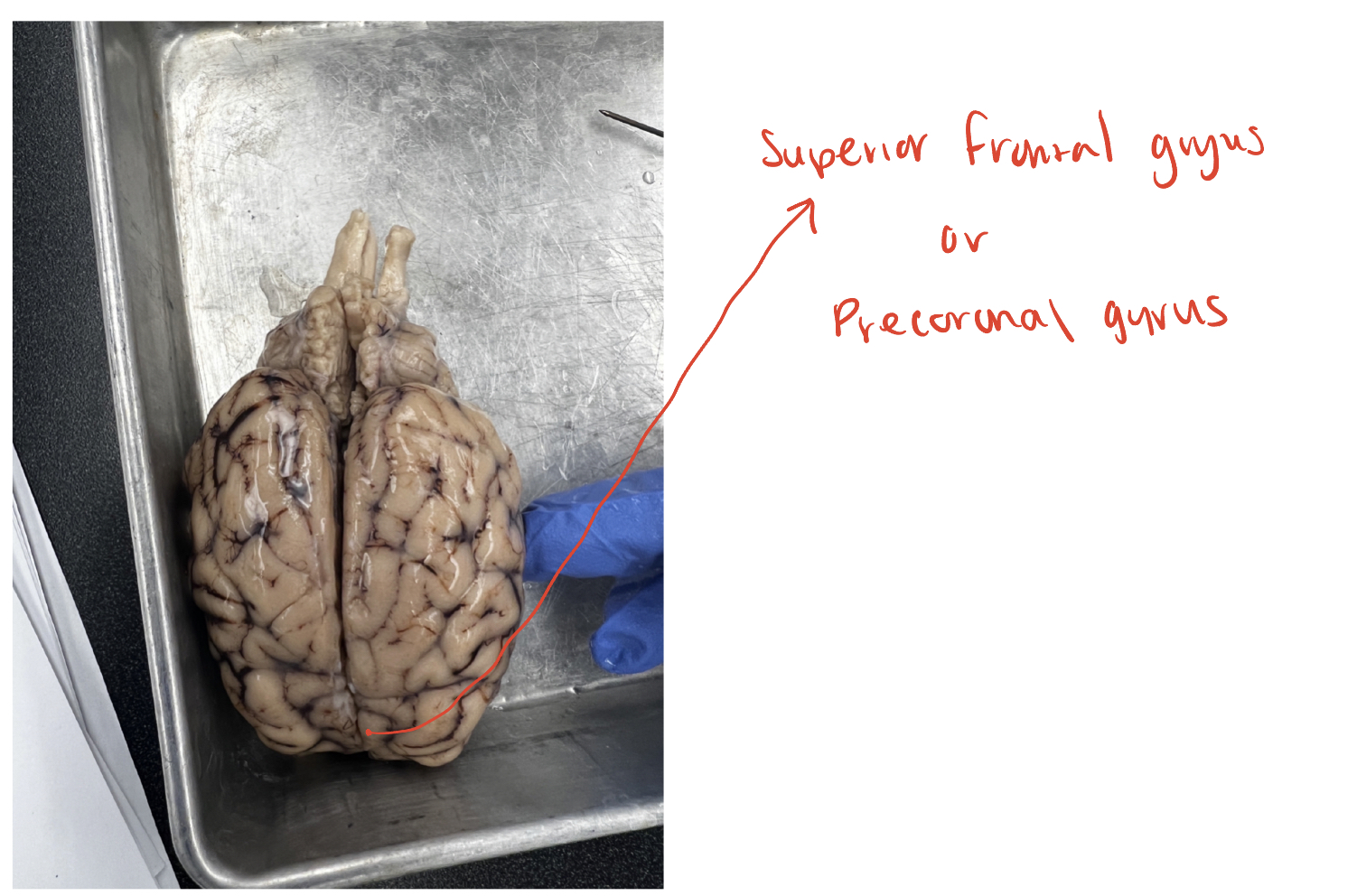
superior frontal gyrus
(O) Also known as the precoronal gyrus, this is the question mark shaped
gyrus in the frontal lobe that lies anterior to the cruciate/central sulcus.
This is the primary motor cortex for the sheep
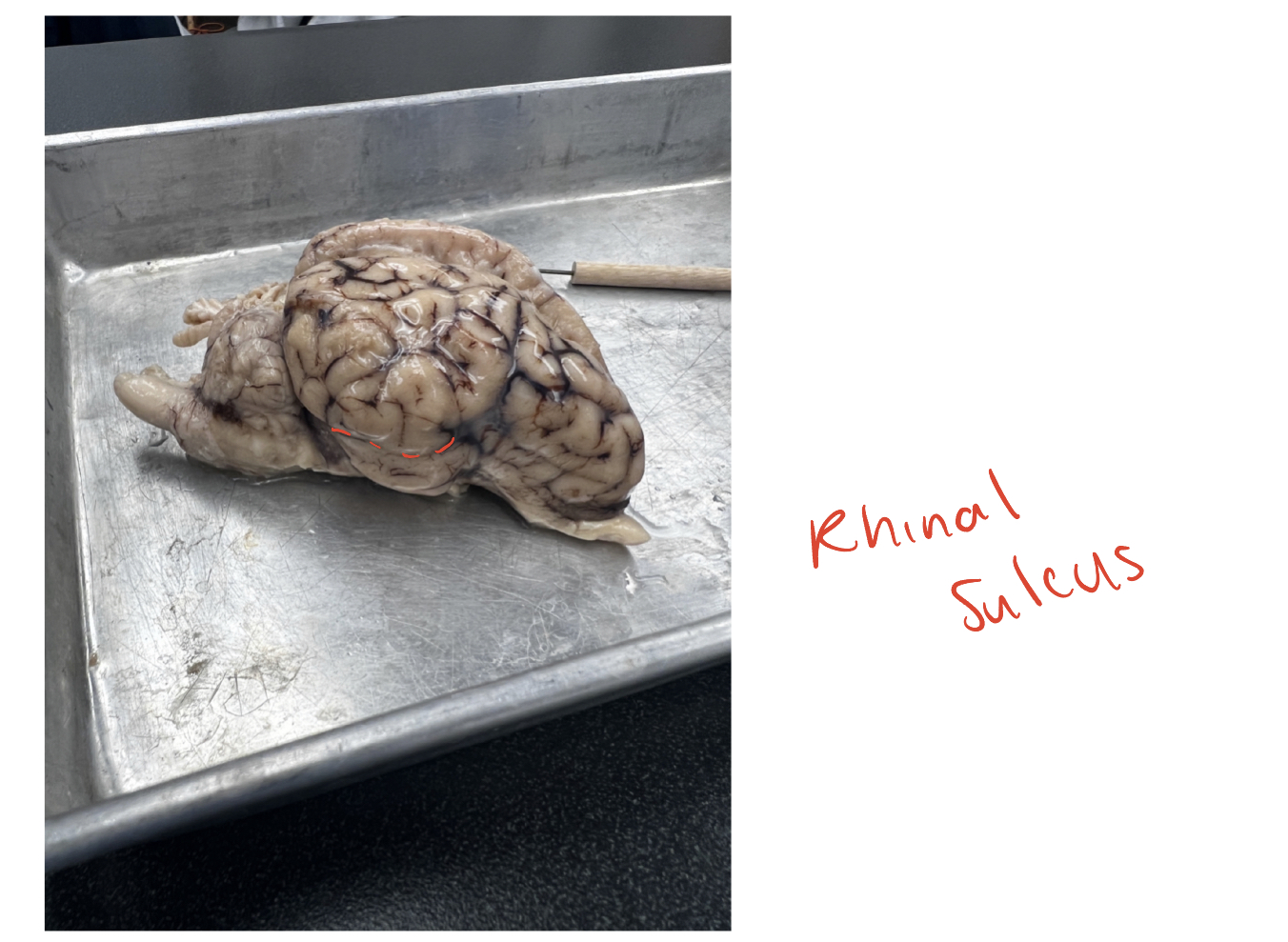
rhinal sulcus
(O) The well-defined sulcus easily seen from the lateral or ventral view of
the brain. This sulcus forms the superior boundary for the pyriform lobe
frontal lobe
(O) this is the lobe lying anterior to the cruciate/central sulcus. where motor cortex is located and is also associated with complex cognitive functions and personality
temporal lobe
(O) contains auditory cortex and is used for higher level visual processing as well as language. most easily seen in lateral view
occipital lobe
(O) most posterior; visual cortex is here
parietal lobe
(O) lobe responsible for processing sensory information and contains somatosensory cortex.
pyriform lobe
(O) contains the entorhinal cortex and parahippocampal gyrus. involved in olfactory perception (smell)
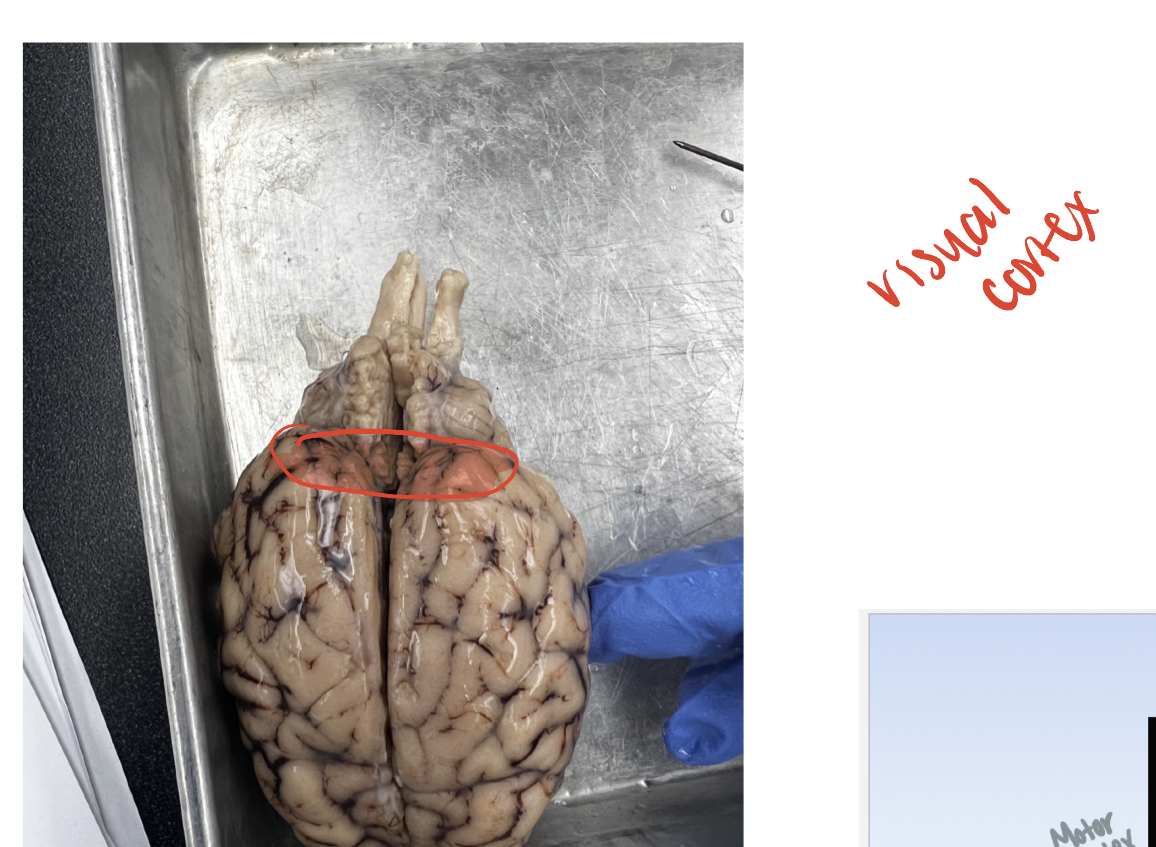
Visual cortex
(G) in occipital lobe, the most posterior portion. complex visual processing
motor cortex
(G) bounded by the cruciate sulcus at the posterior border, the motor cortex is within the precoronal gyrus or superior frontal gyrus
somatosensory cortex
(G) region of the cortext where incoming somatosensory info is processed. It is located in the gyrus posterior to the cruciate sulcus
auditory cortex
(G) bounded at the front by the sylvian sulcus; part of the temporal lobe. home of auditory processing
entorhinal cortex
(G) posterior part of pyriform lobe, immediately inferior to the rhinal fissure. hippocampus is located just below the entorhinal cortex
optic nerve
(W) primary projection axons leaving the eye
optic tract
(W) after the optic chiasm. these are white matter axons projecting to the lateral geniculate nucleus
optic chiasm
(W) intersection of the optic nerve from each eye. The incoming axons decussate here, and project out as the optic tracts
olfactory bulb
(O) primary sensory organ for olfaction. Receives inputs from the nasal cavity and send information to the pyriform lobe for further processing
lateral olfactory tract
(W) The band of axons that connect the olfactory bulb with the pyriform
lobe. This is the main band of axons that carry olfactory information into
the brain to be processed.