A&P II Exam 3
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
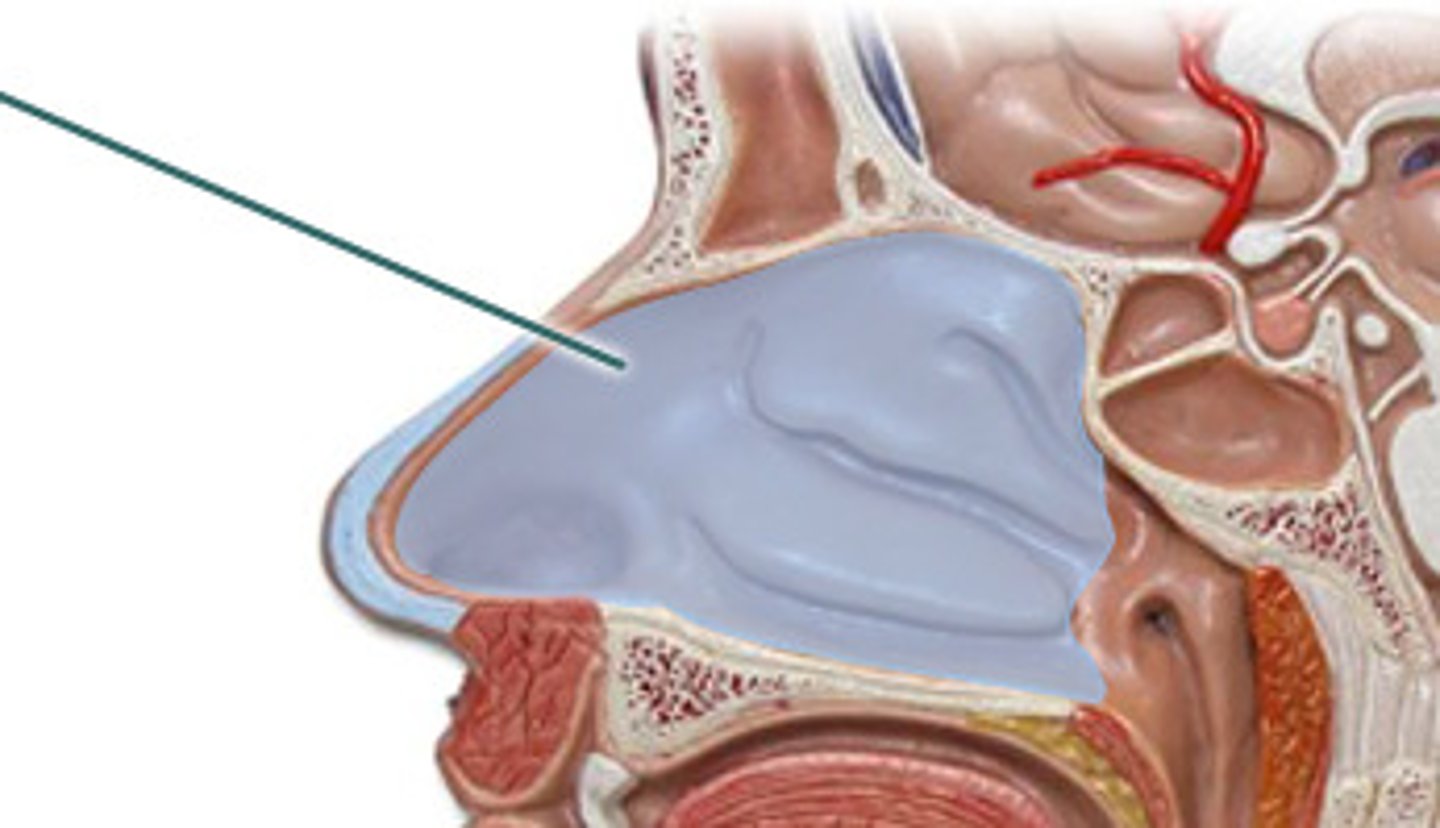
Nasal cavity
The hollow space inside of the nose, containing structures such as the conchae.
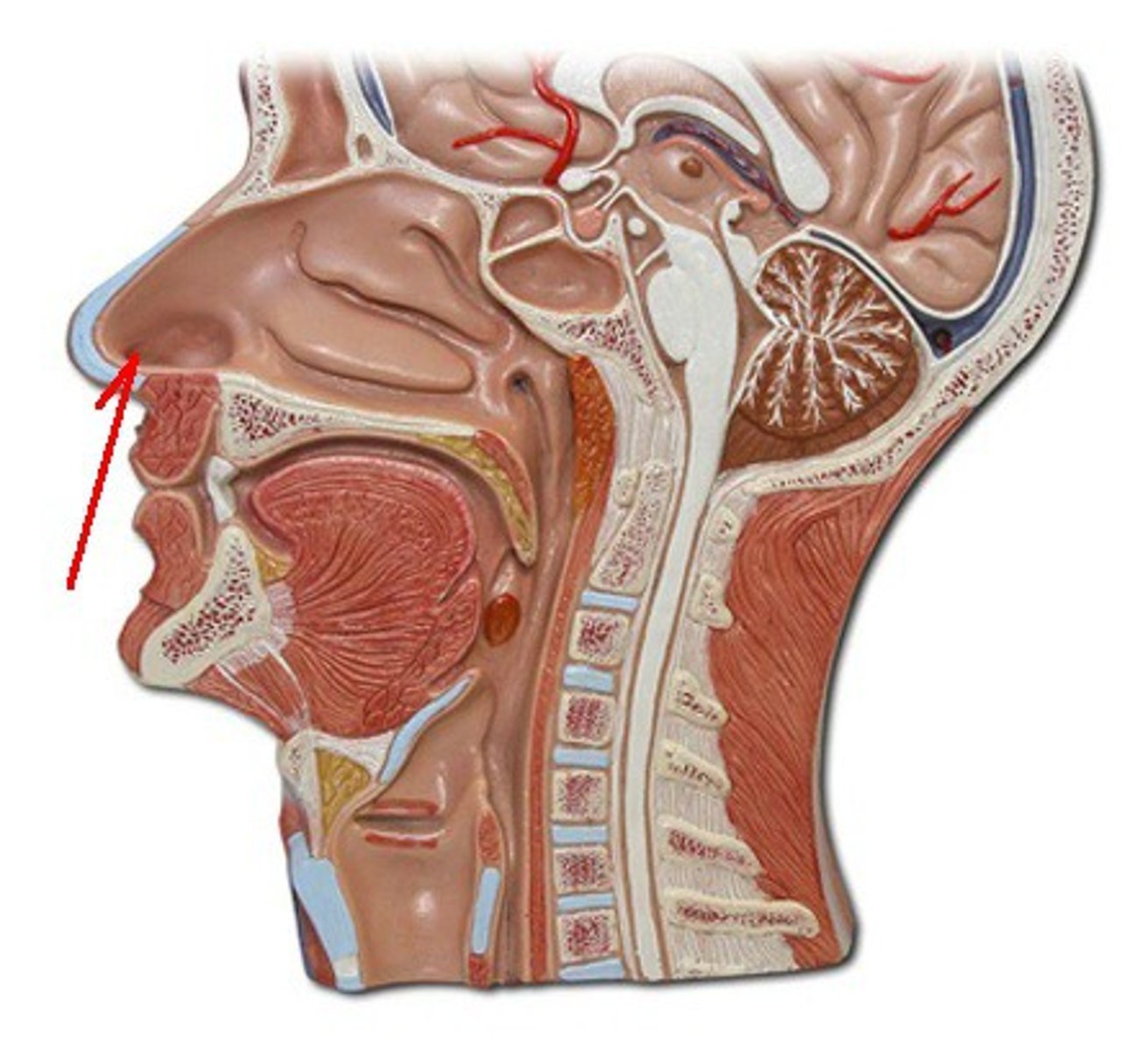
External nares
2 openings which open into the nasal cavity; where air enters the respiratory system.
Nasal septum
a wall of cartilage that divides the nose into two equal sections, spans the length of the entire nasal cavity
Inferior conchae
the thin, scroll-like bones that form part of the interior of the nose, functions to create turbulence within the nasal cavity and helps keep air in there longer to help clean and humidify air.
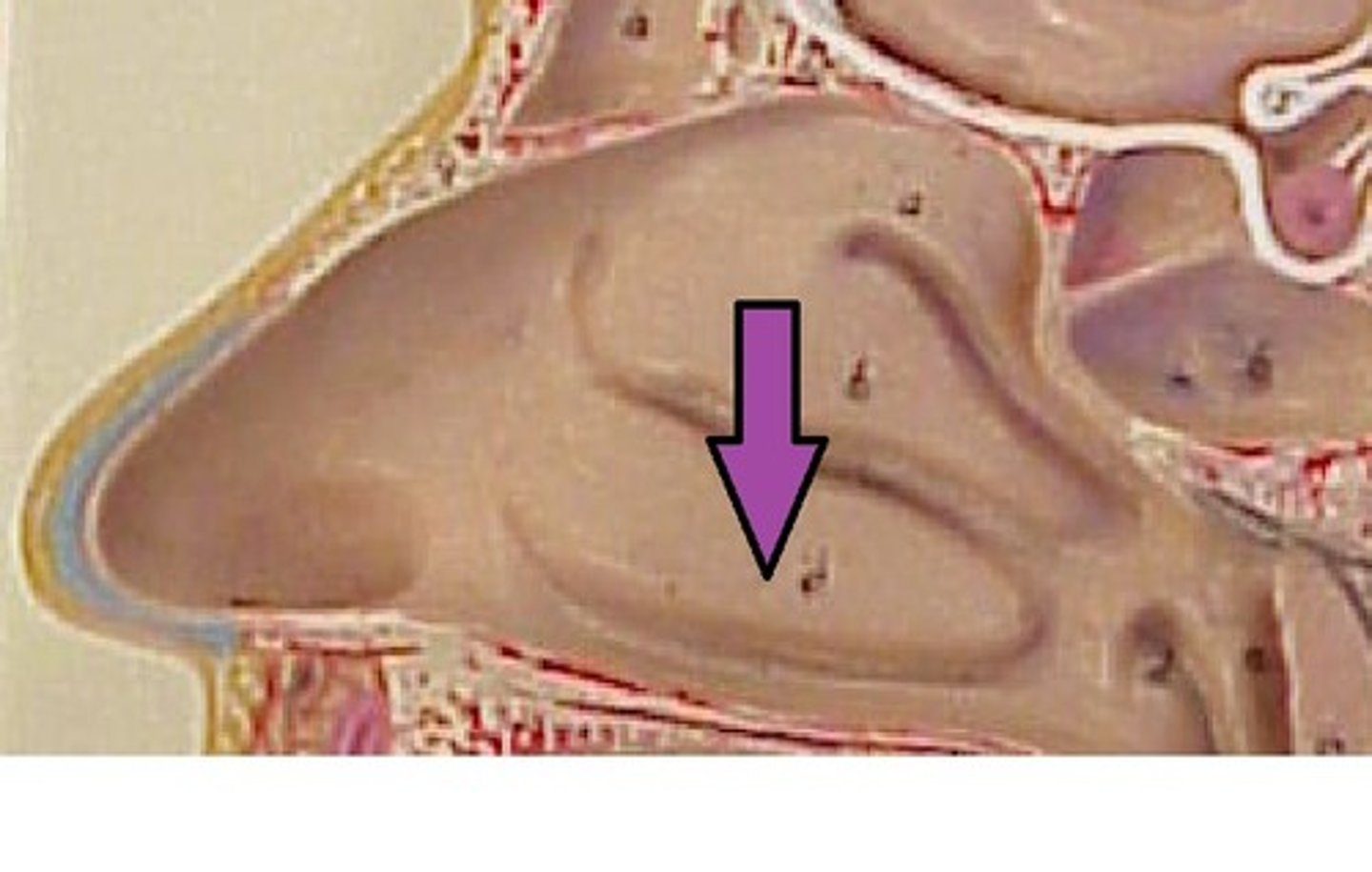
middle conchae
part of the ethmoid bone.
-on lateral walls.
-increase surface area of mucus membrane (moistens air).
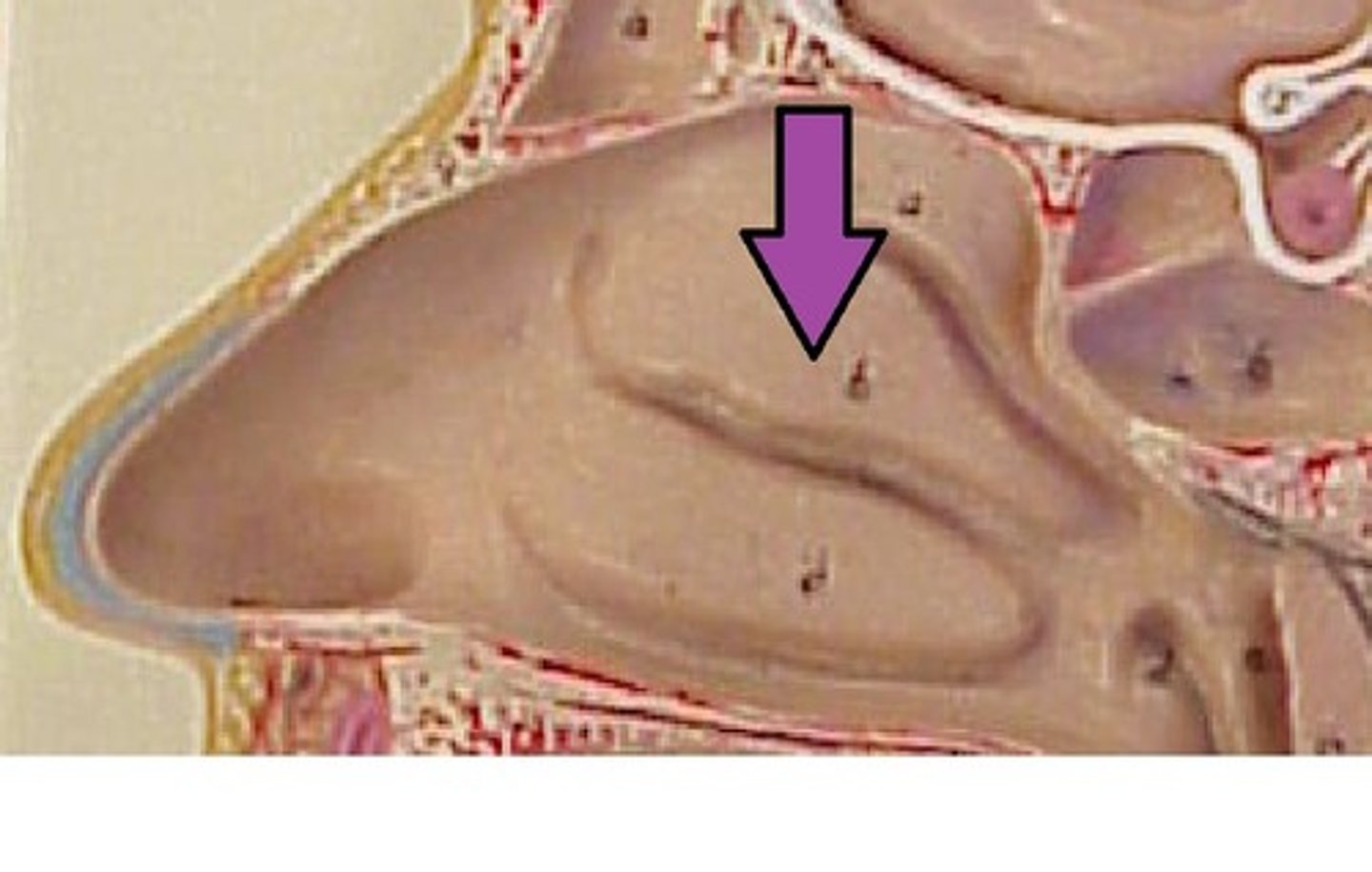
superior conchae
small, curved bony plates located in the nasal cavity, forming part of the ethmoid bone and playing a crucial role in filtering, warming, and moistening inhaled air
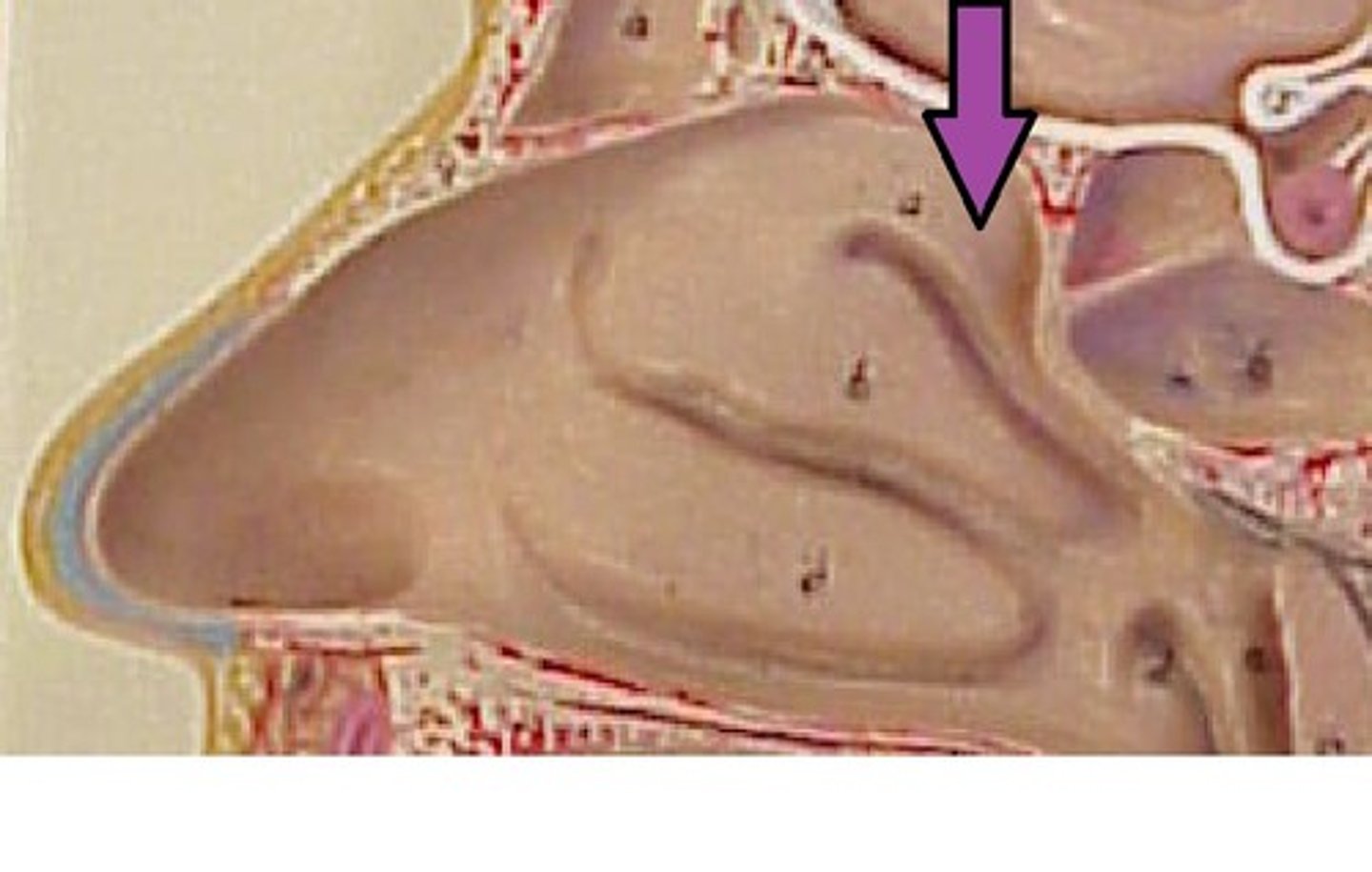
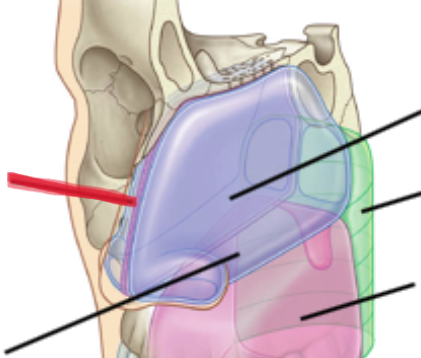
Pharynx
commonly referred to as the throat, a passage way in the head and neck that is part of both the digestive system and respiratory system
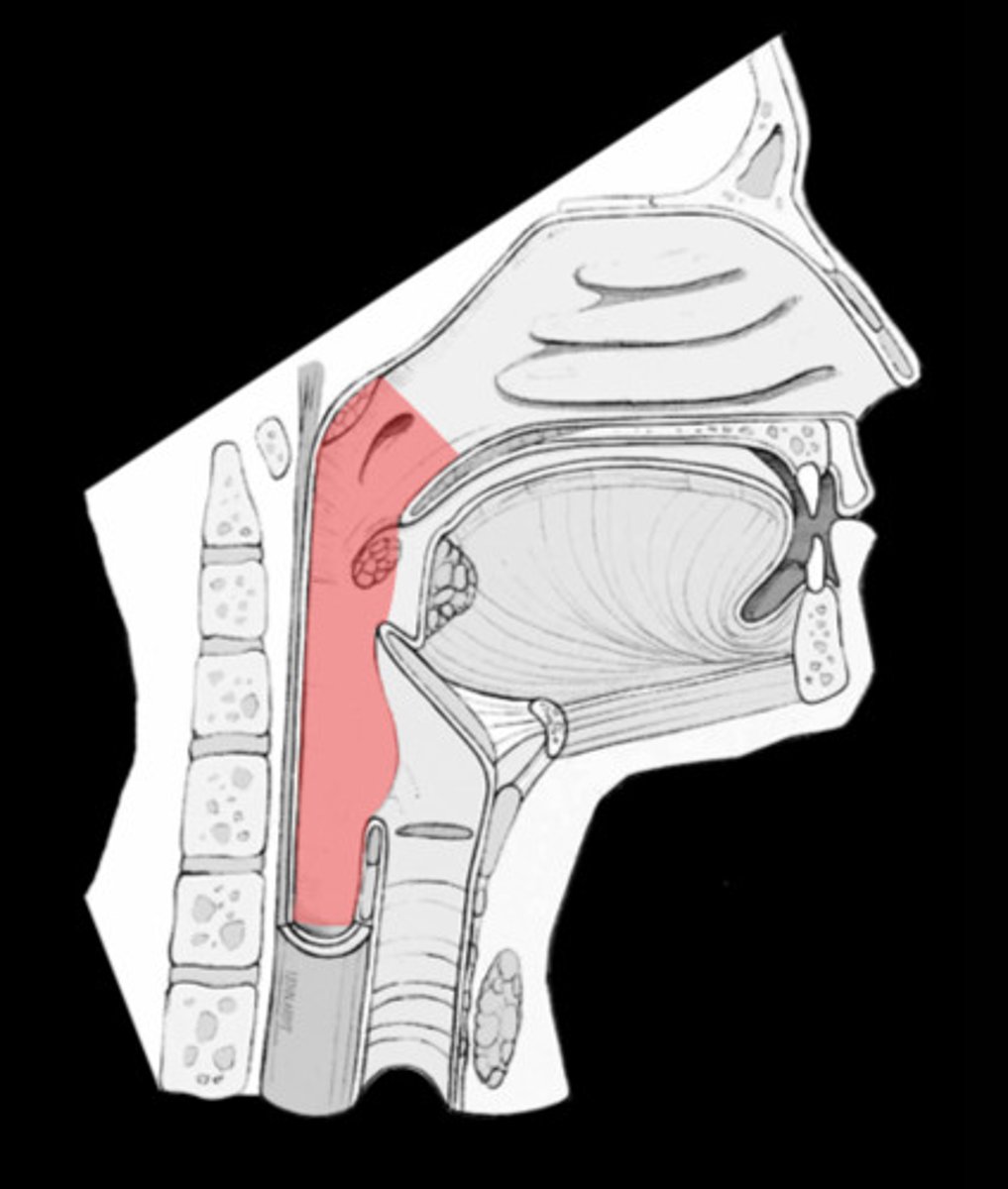
nasopharynx
region of the pharynx at the back of the nose and above the soft palate, starts from the top of the nasal cavity and ends towards the soft palate (uvula)
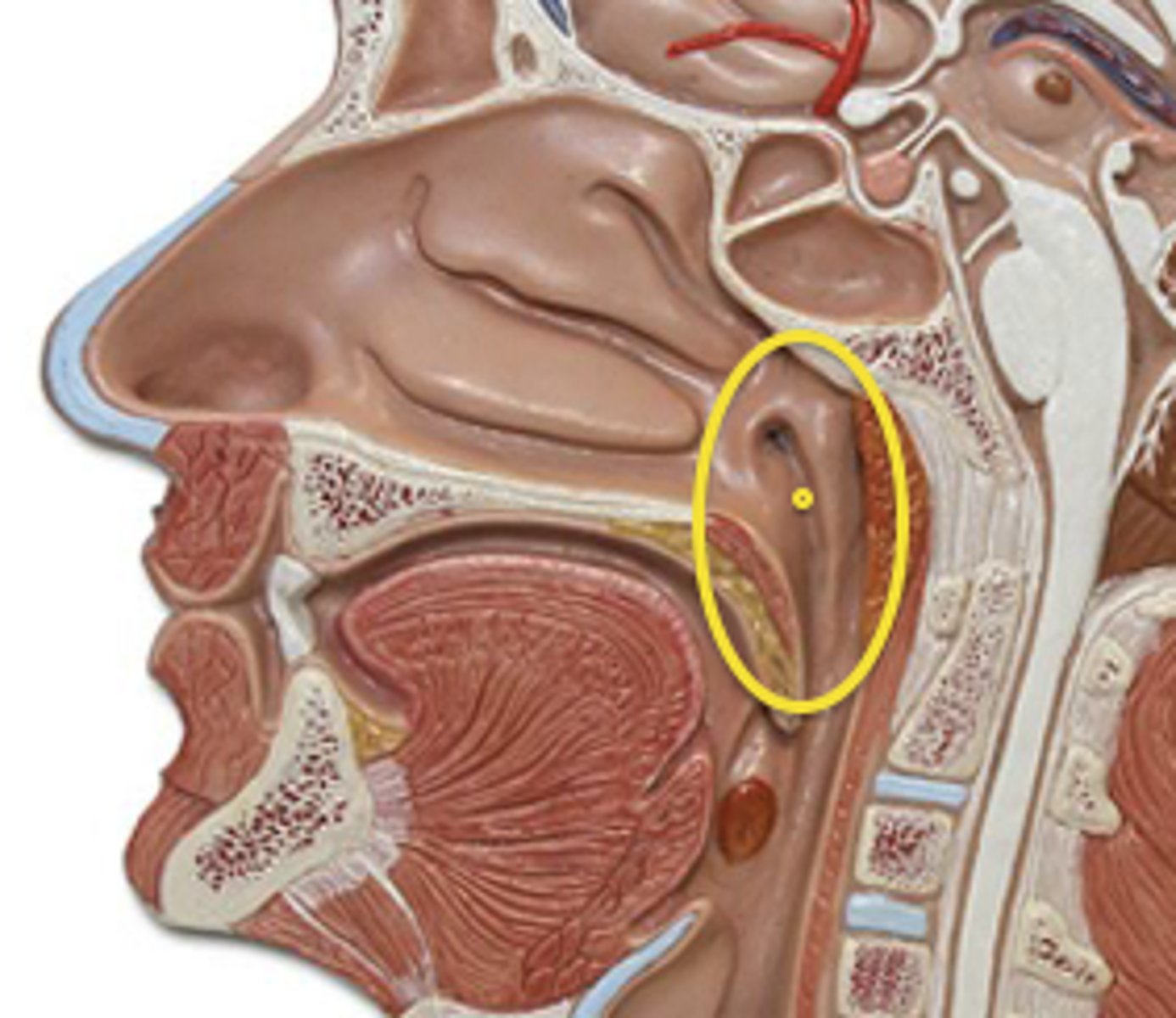
oropharynx
central portion of the pharynx between the roof of the mouth and the upper edge of the epiglottis.
Starts from the uvula down to the epiglottis, located between the naso and laryngopharynx
laryngopharynx
lower part of the pharynx, just below the oropharyngeal opening into the larynx and esophagus
Larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
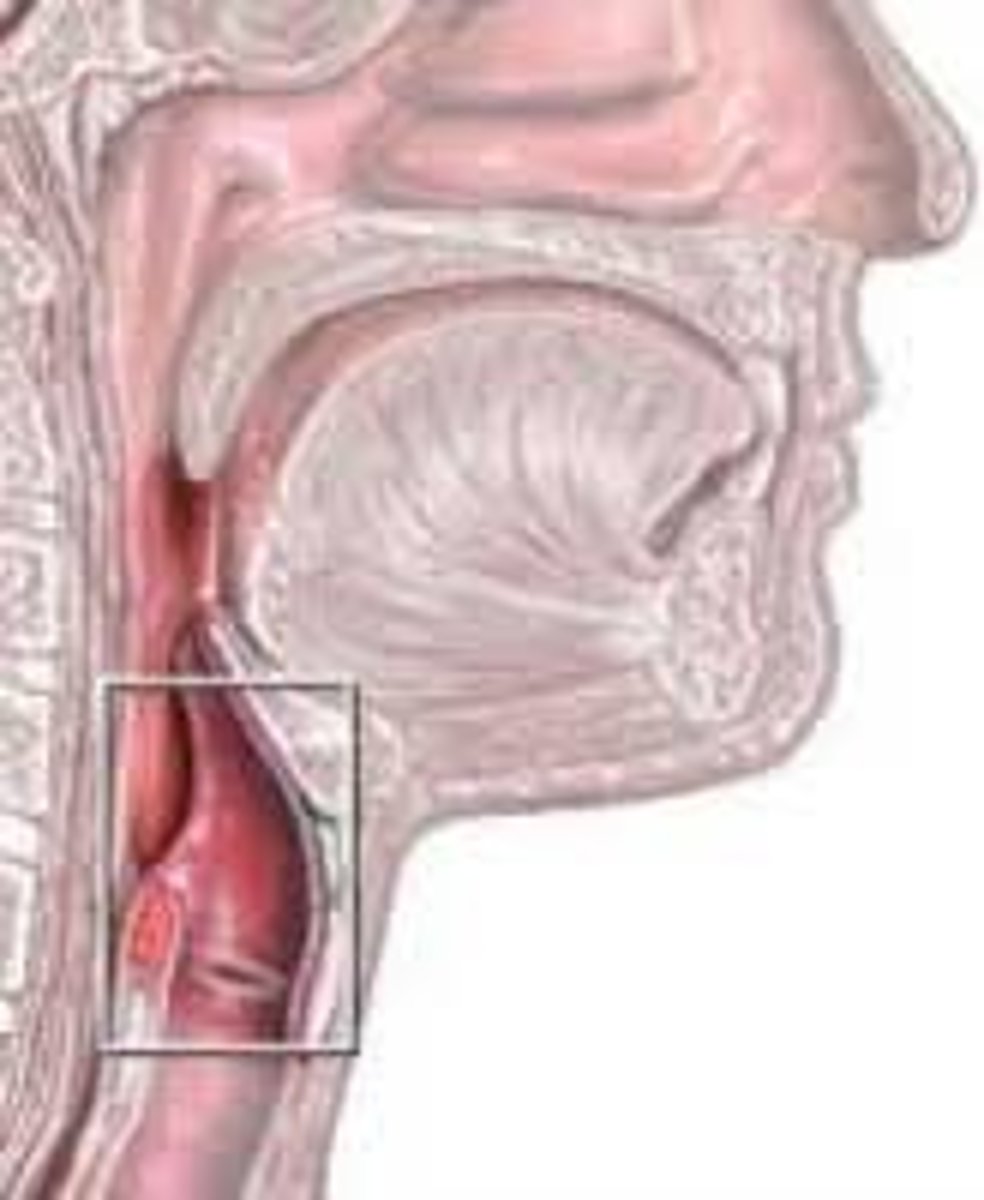
Epiglottis
a flap of cartilage at the root of the tongue, which is depressed during swallowing to cover the opening of the windpipe.
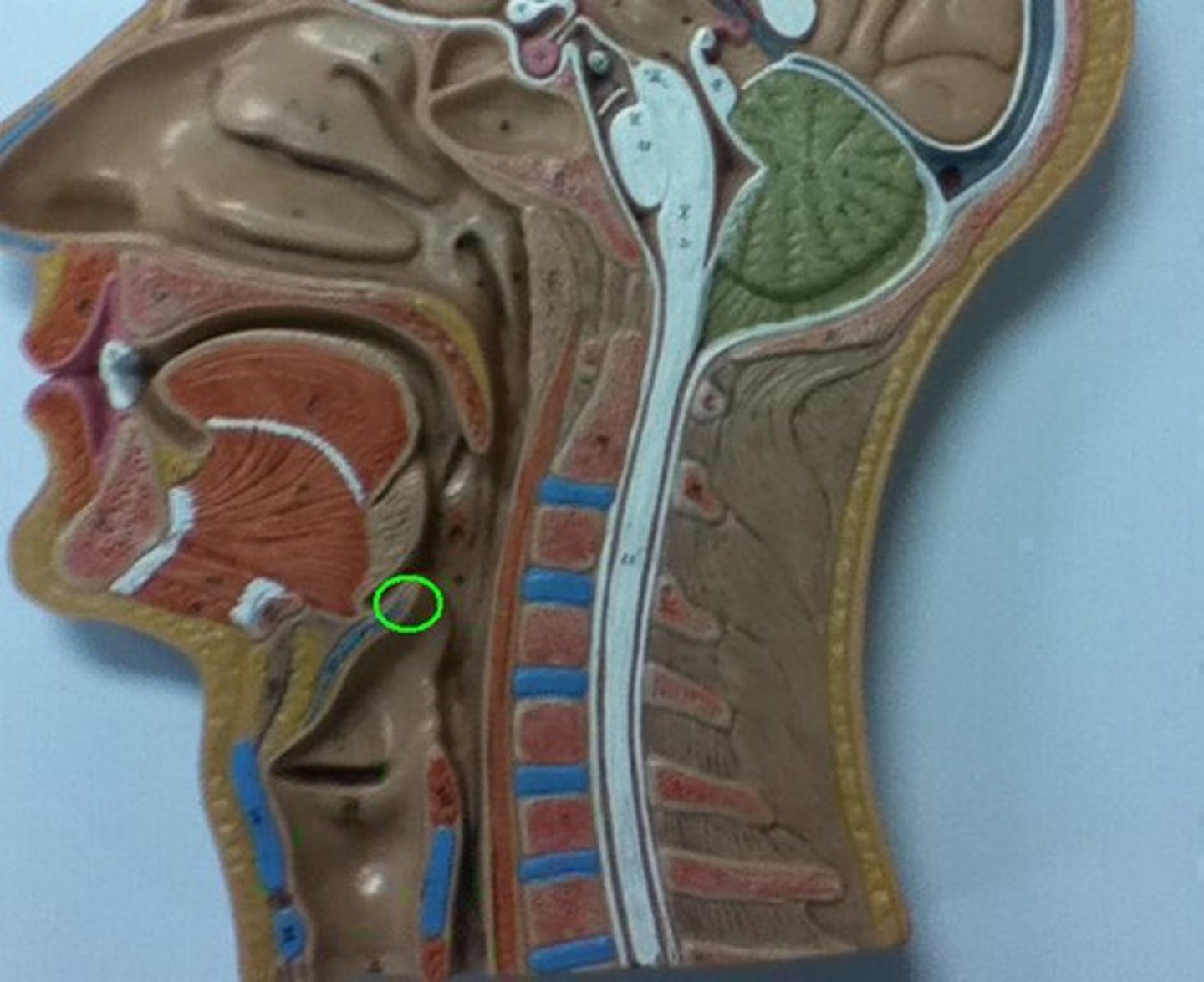
thyroid cartilage
The shield-shaped plate of cartilage that sits anterior to the larynx and forms the Adam's apple.
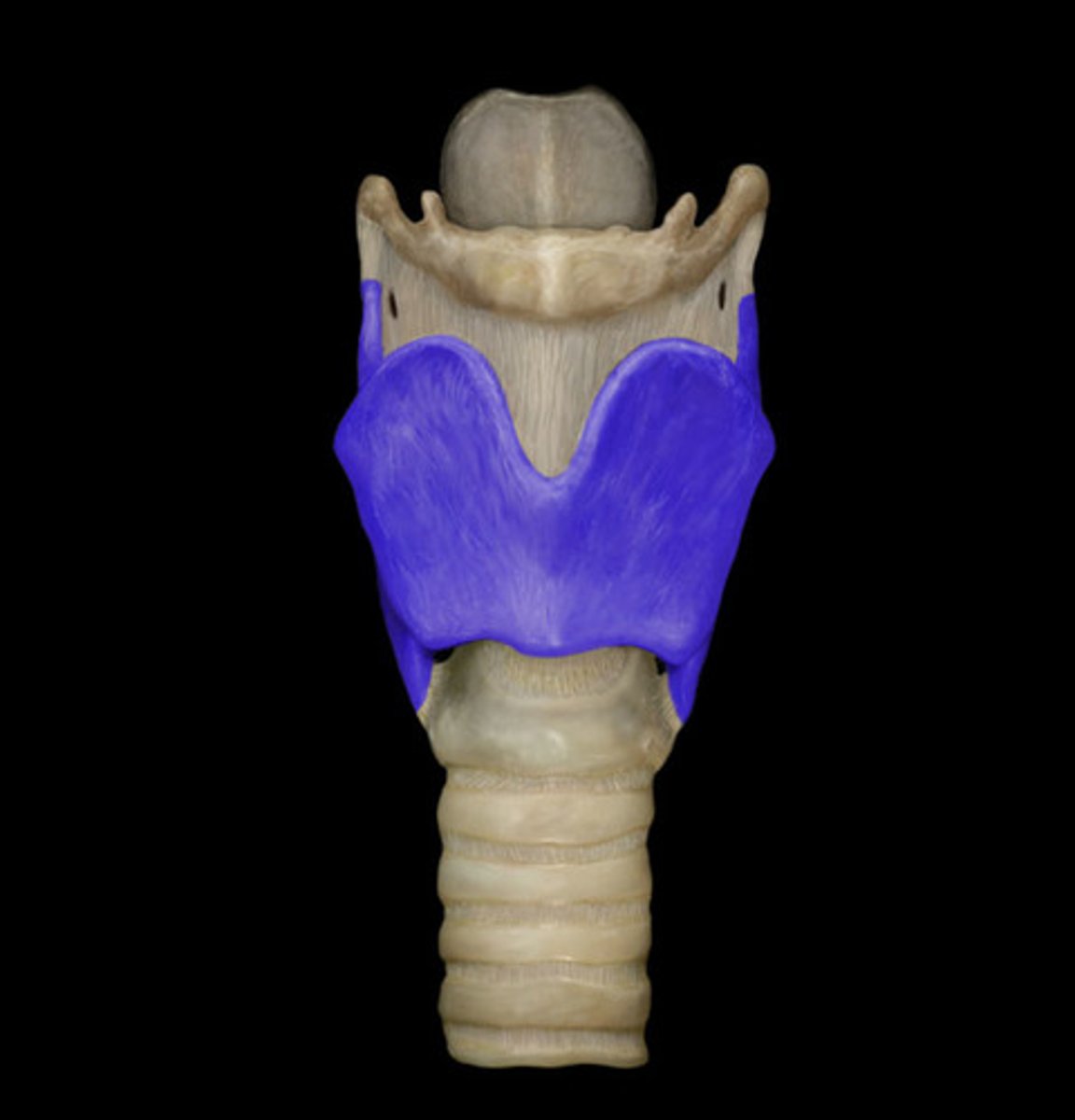
cricothyroid membrane
A thin sheet of fascia that connects the thyroid and cricoid cartilages that make up the larynx.
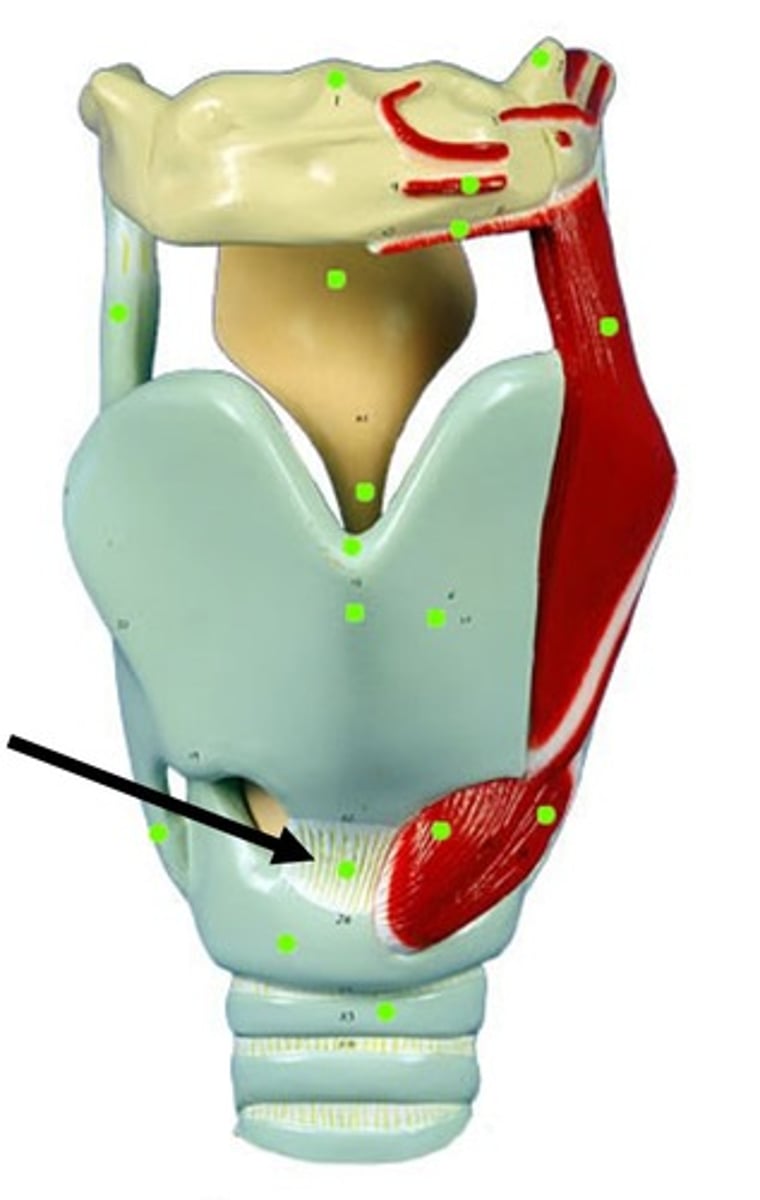
cricoid cartilage
A firm ring shaped ridge of cartilage that forms the lower part of the larynx.
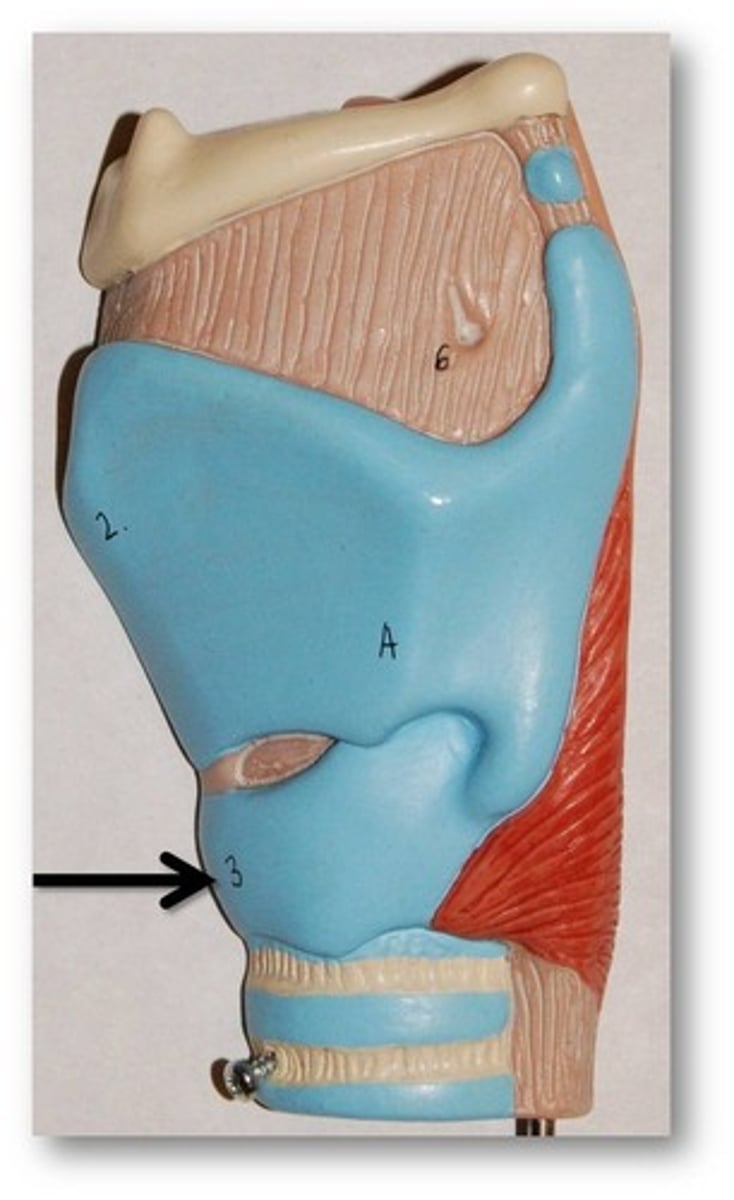
Arytenoid cartilage
Two small cartilages in the larynx, the movements of which abduct and adduct the vocal folds.
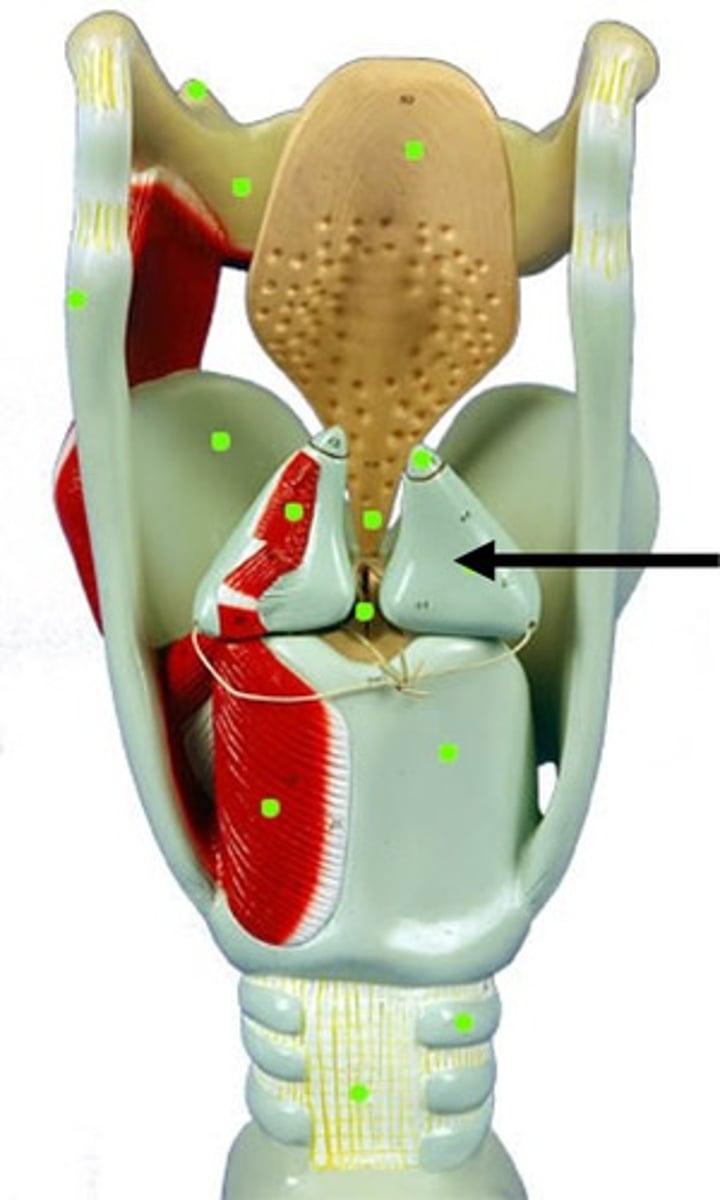
Vestibular folds (false folds)
Located superior to the glottis and true folds, this structure functions to close off the larynx during swallowing.
Glottis
The opening between the vocal cords at the upper part of the larynx. functions and aids in respiration, voice production, protecting the airway, and modulating (controlling) airflow.
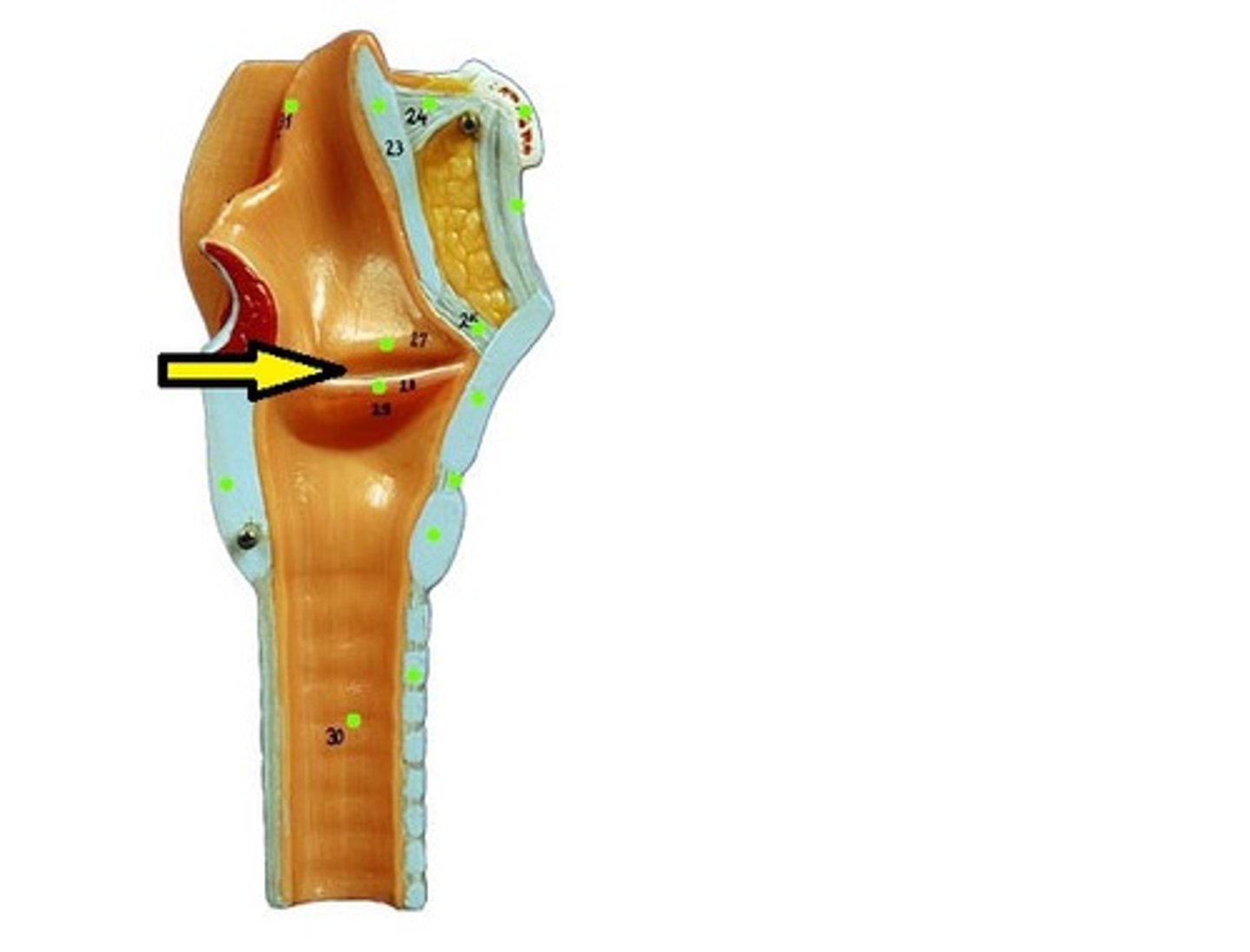
Vocal folds (true folds)
found inferior to the glottis, responsible for sound production through vibration when air passes through them, and they also act as a laryngeal sphincter to protect the airway
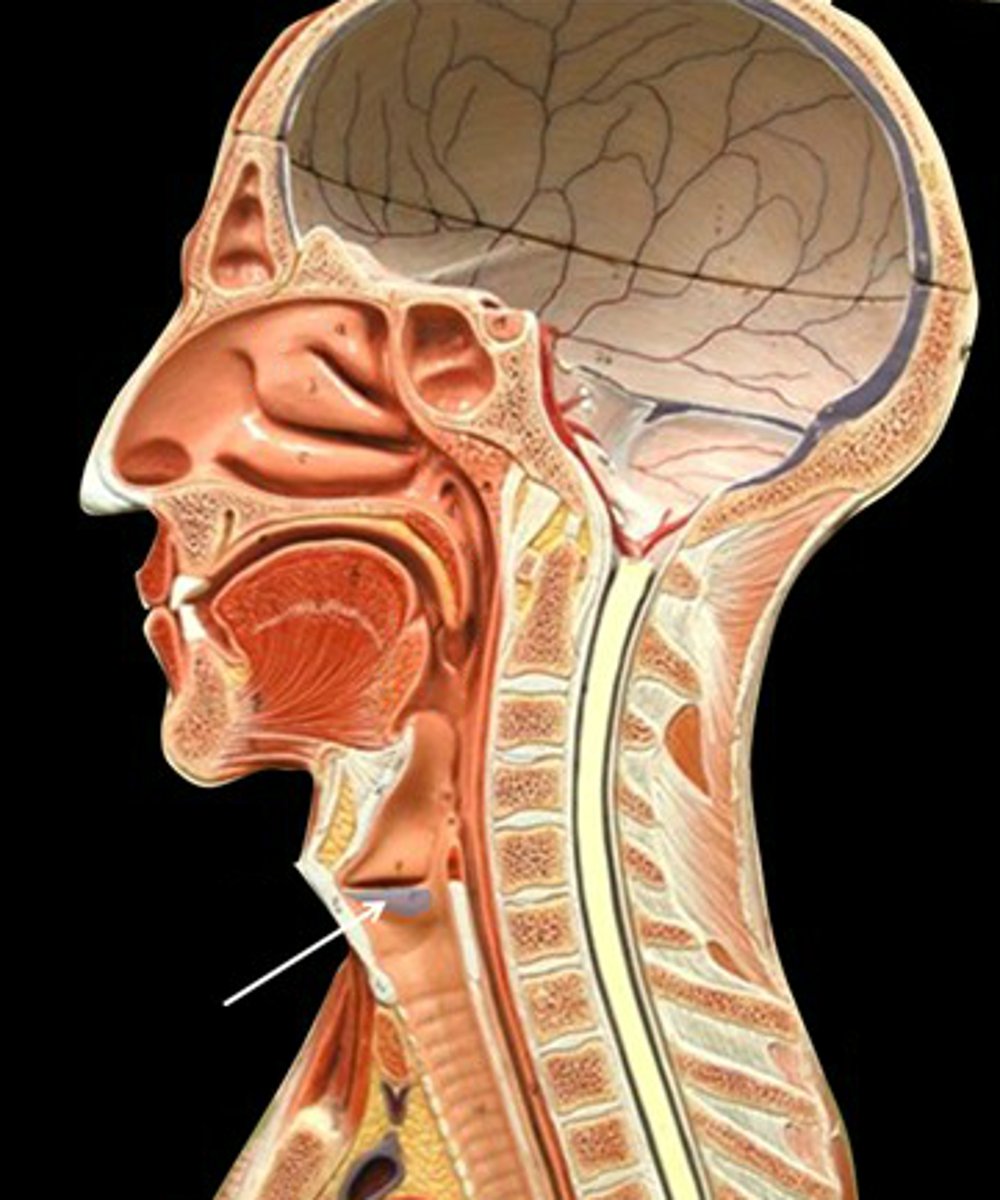
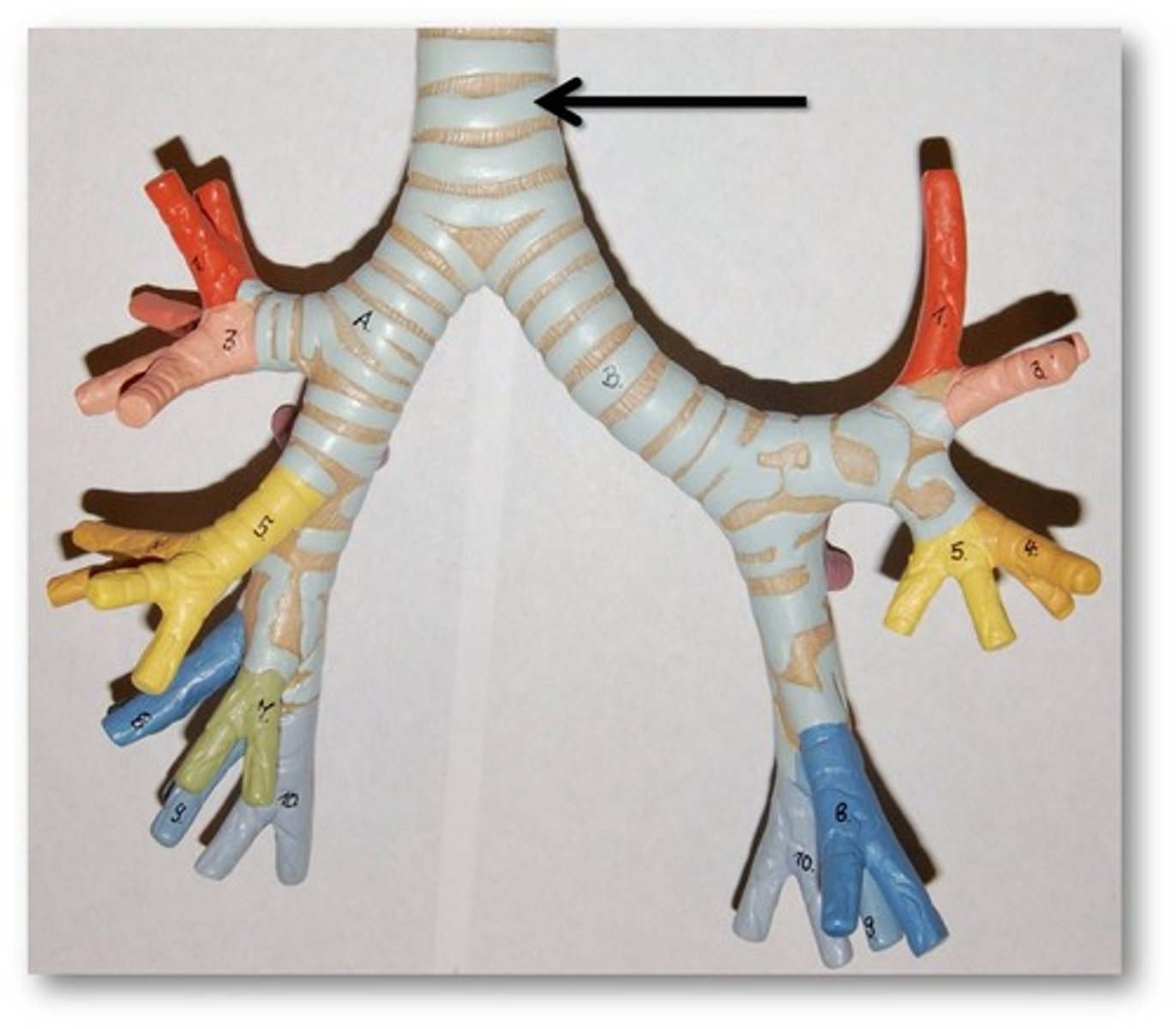
Trachea
commonly known as the windpipe, found inferior to the larynx, part of the lower respiratory tract and the conducting zone.
Lined by C shaped cartilage in the front and towards the back its is a concaved shape lined by the trachealis muscle.
Primary Bronchus
a pair of branches of the trachea that lead to the right and left lung; consist of incomplete rings of cartilage and are lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
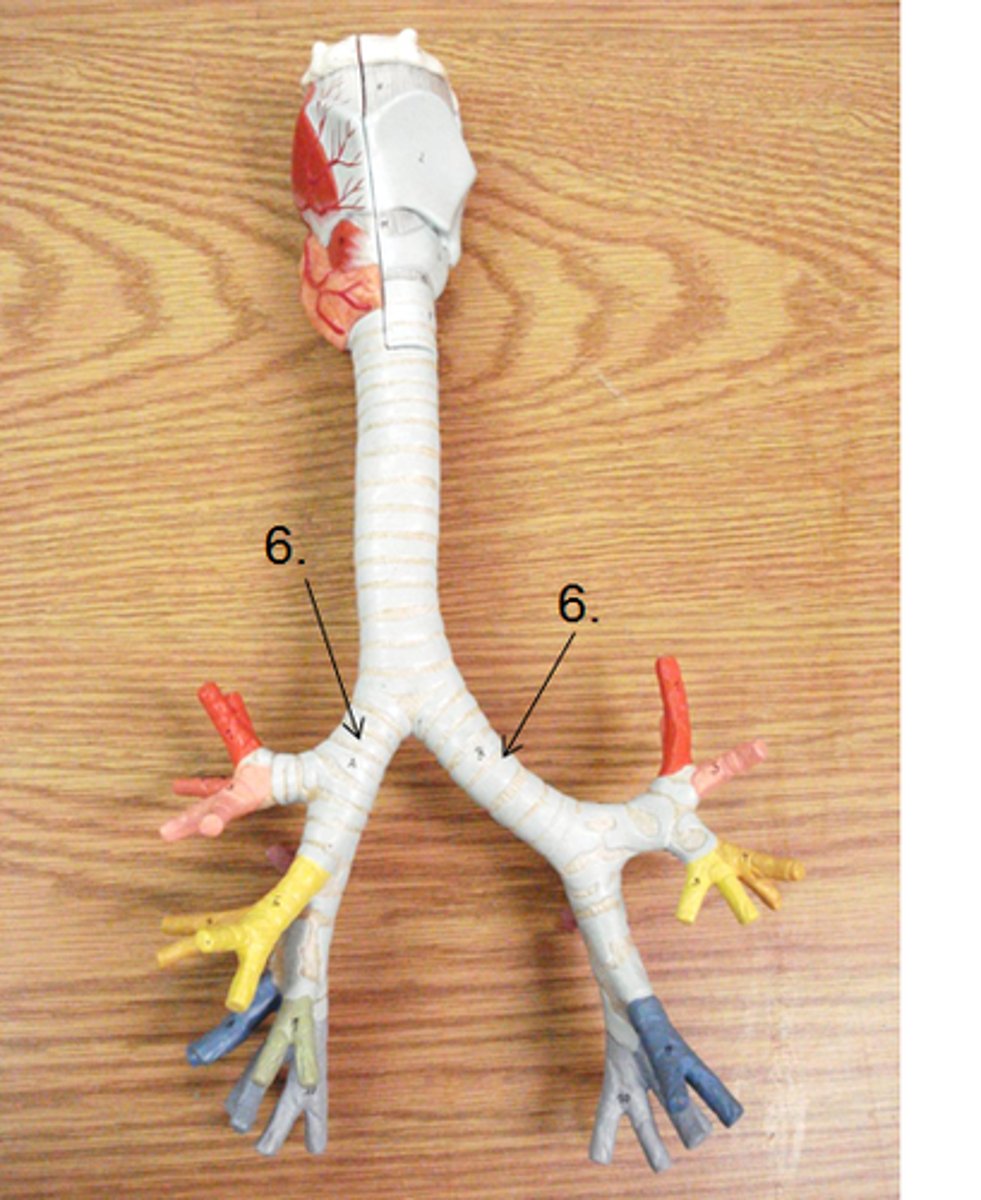
Secondary bronchus
branches of the primary bronchi which supply each lobe of lung; there are 2 in the left lung and 3 in the right lung
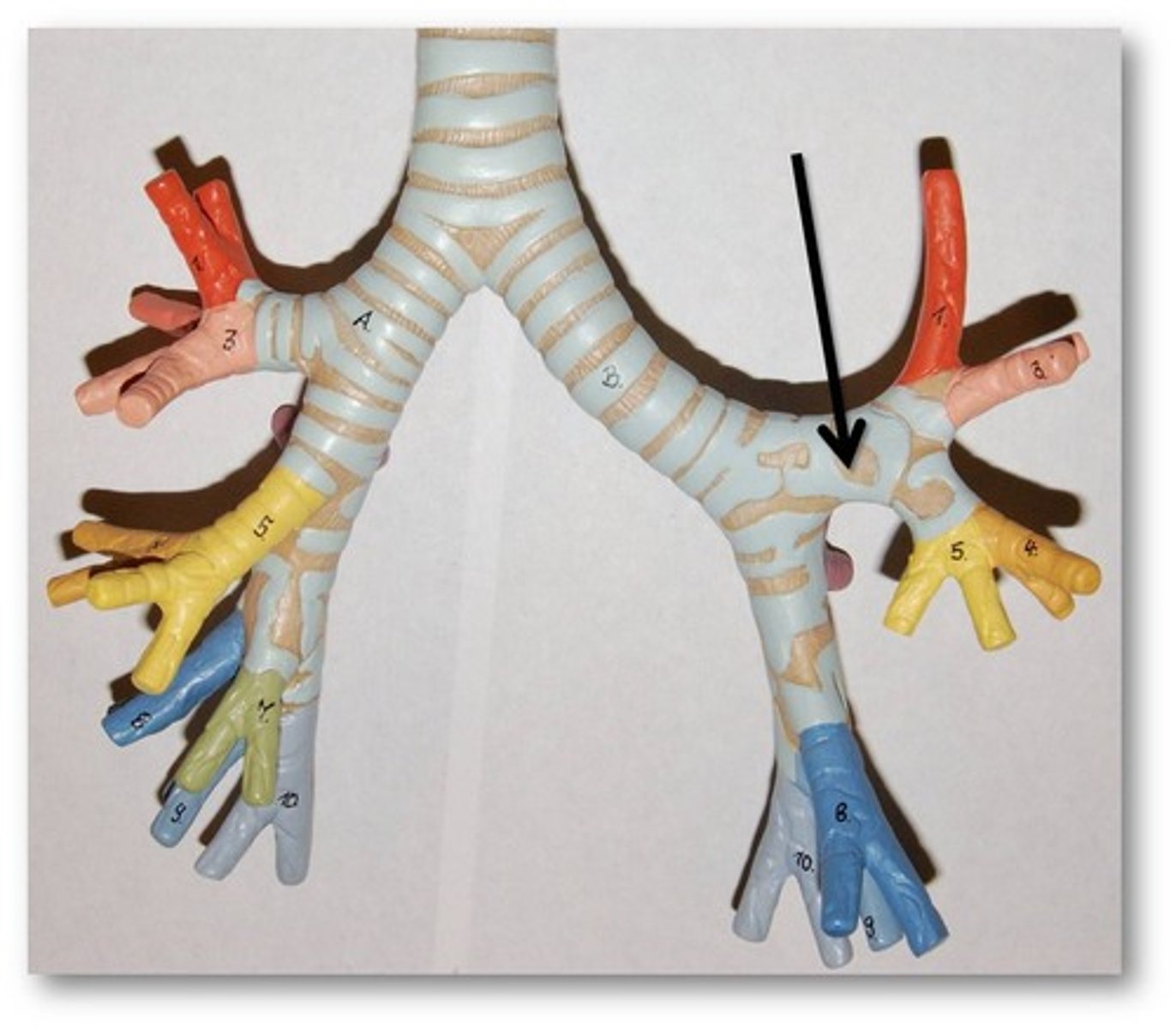
Tertiary bronchus
Extends from the secondary bronchus and conducts air to each lobule of the lungs.
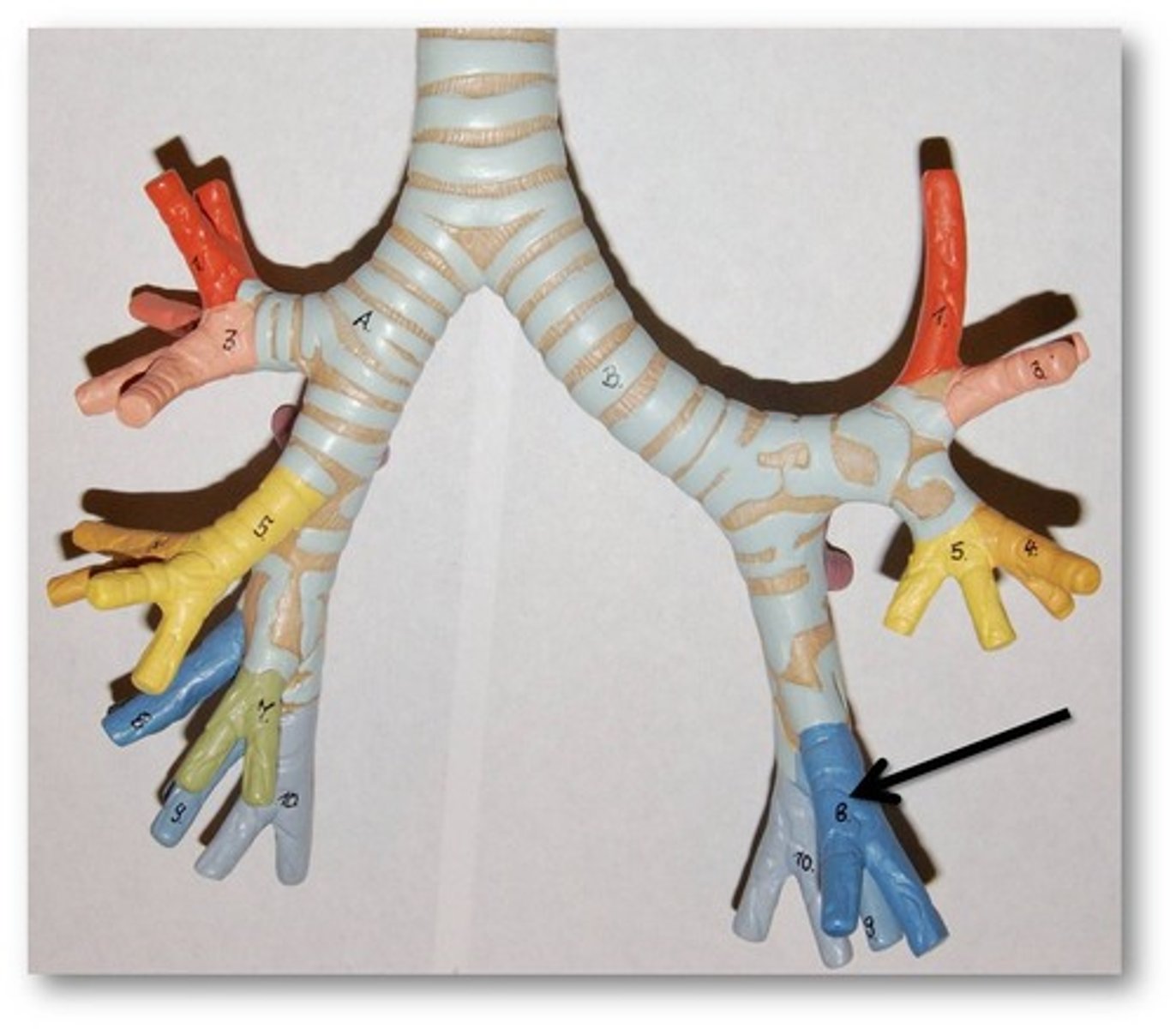
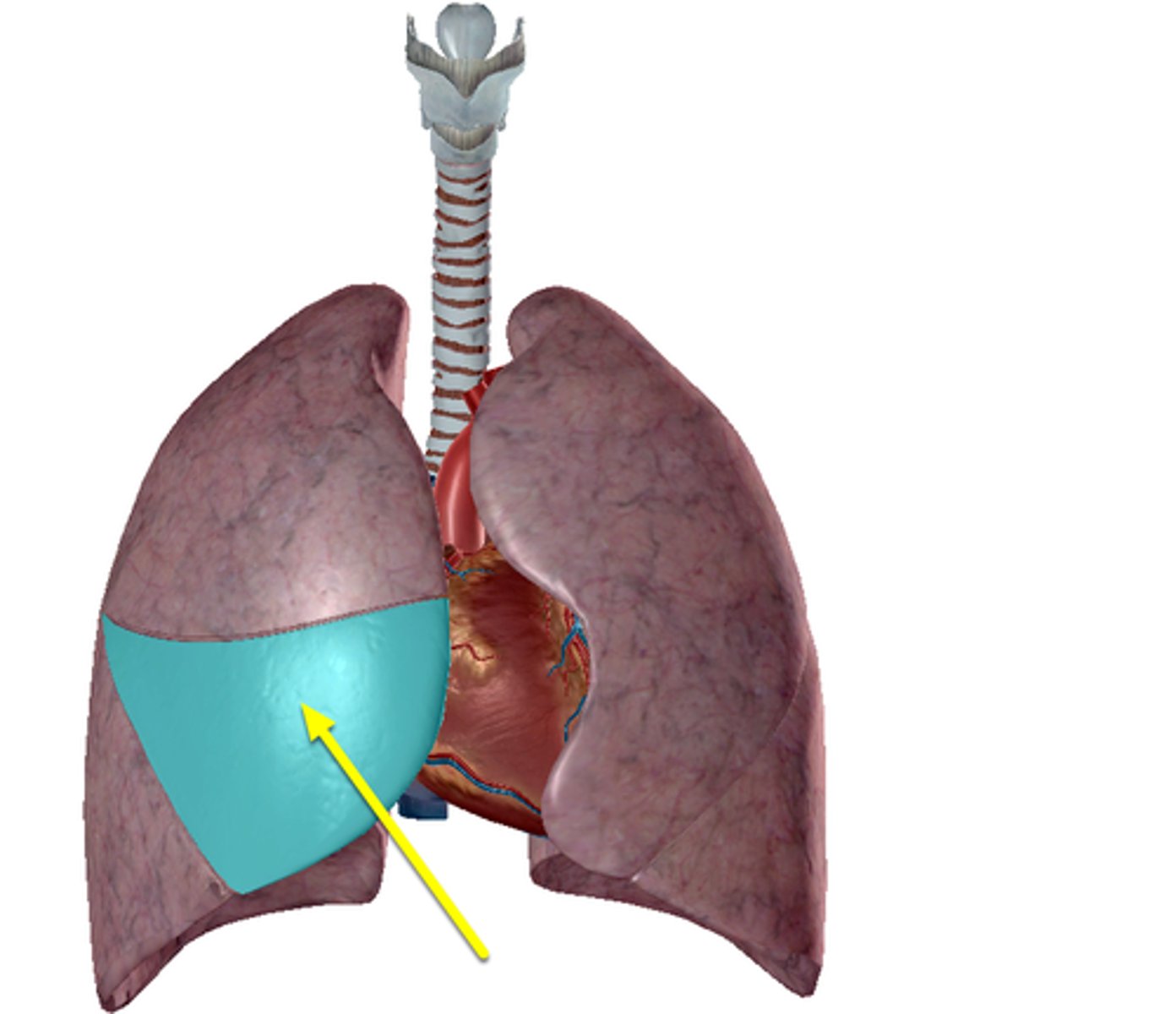
Right lung
contains 3 lobes (superior, middle, and inferior), and known as the largest of the 2 lungs, also contains 2 fissures (horizontal and oblique)
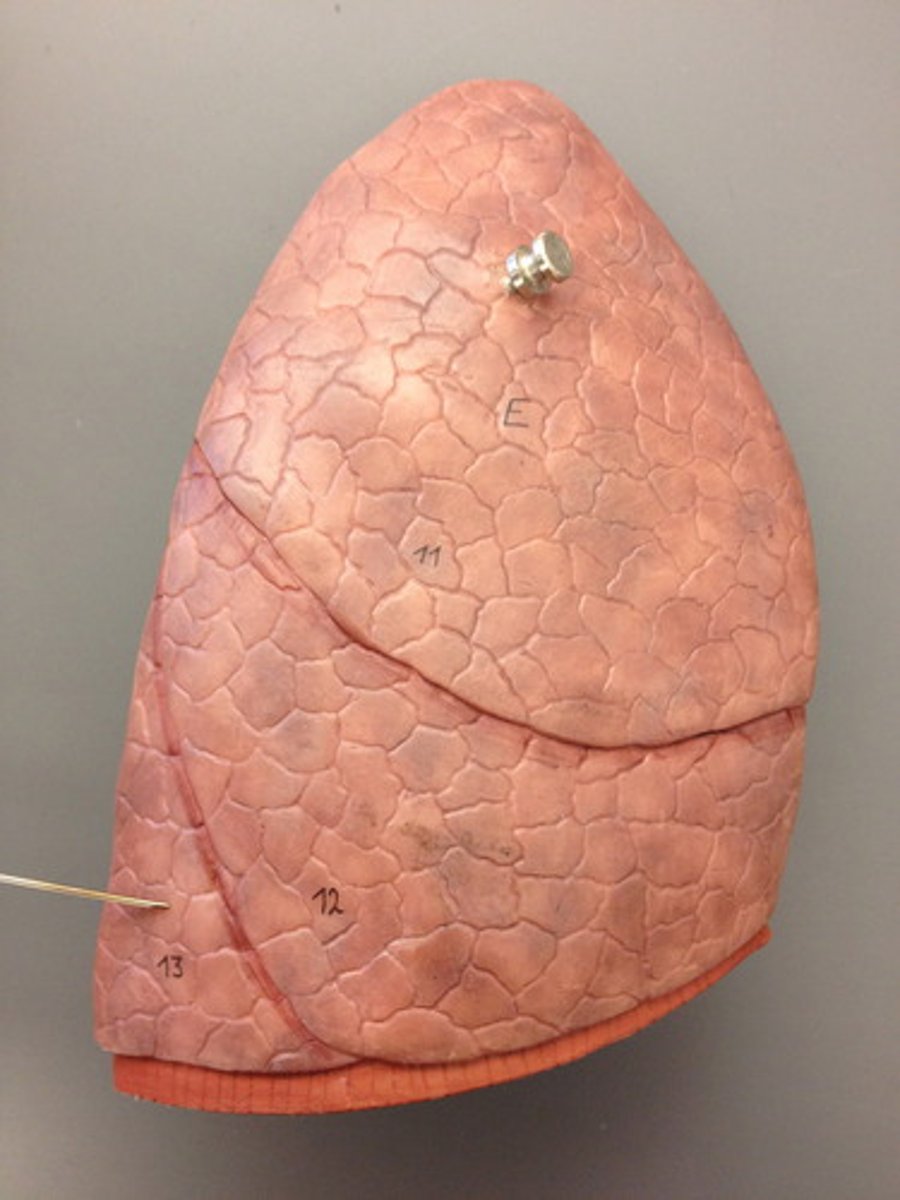
superior lobe of right lung
Separated from middle lobe by horizontal fissure: receives secondary bronchus
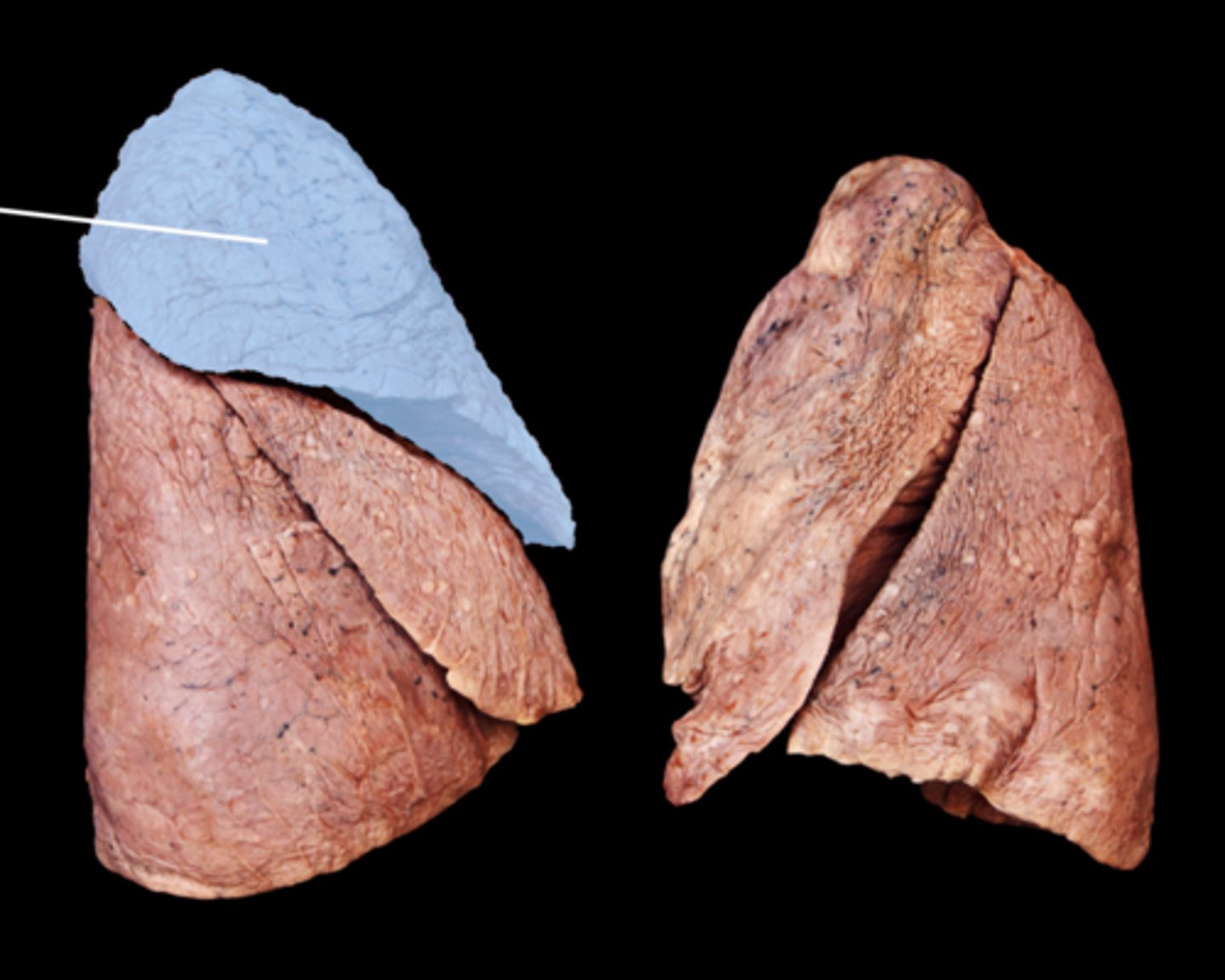

middle lobe of right lung
Separated from superior lobe by horizontal fissure, and lower lobe by oblique fissure: receives secondary bronchus
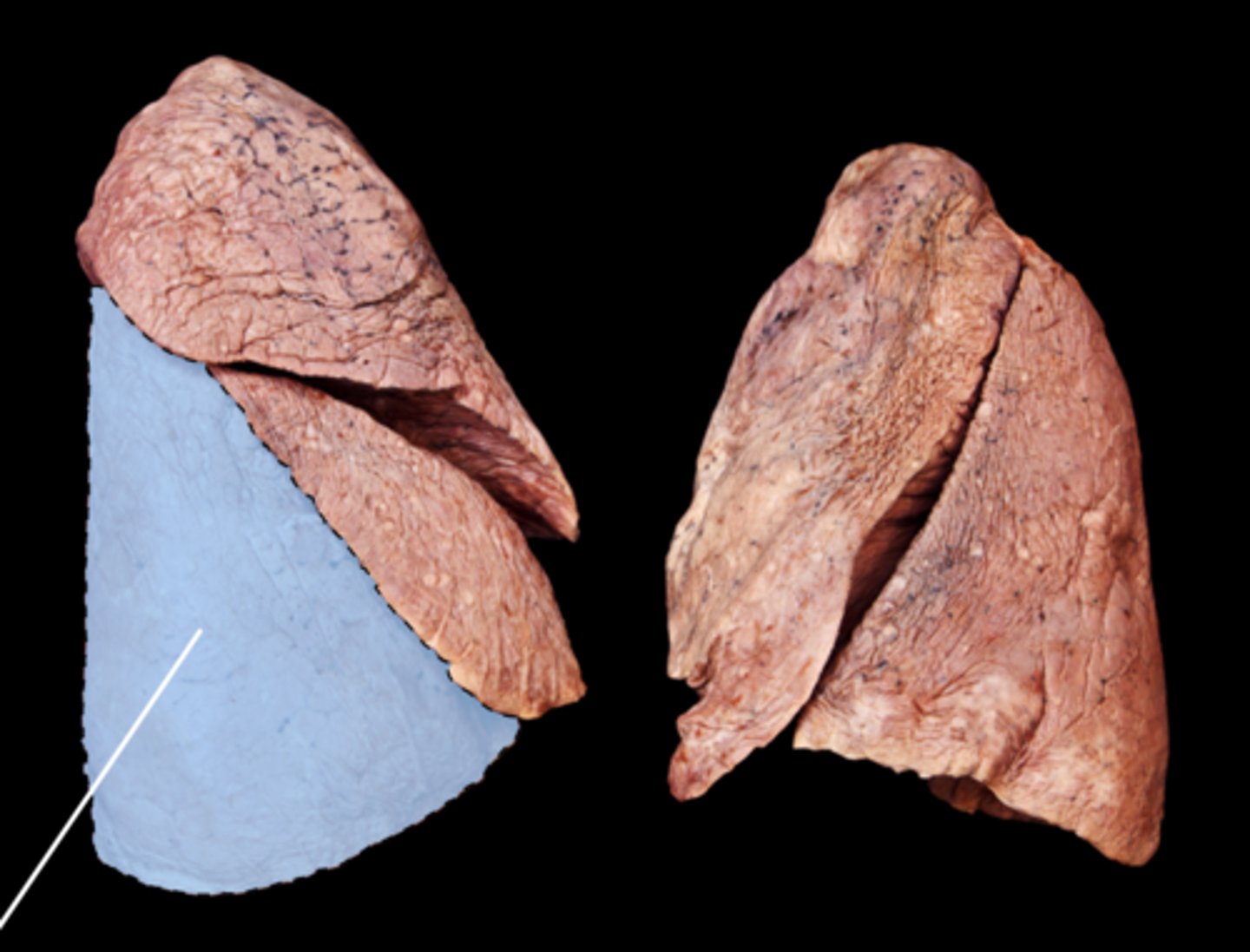
inferior lobe of right lung
Separated from middle lobe by oblique fissure: receives secondary bronchus

horizontal fissure of right lung
Separates upper and middle lobes, joins oblique fissure laterally
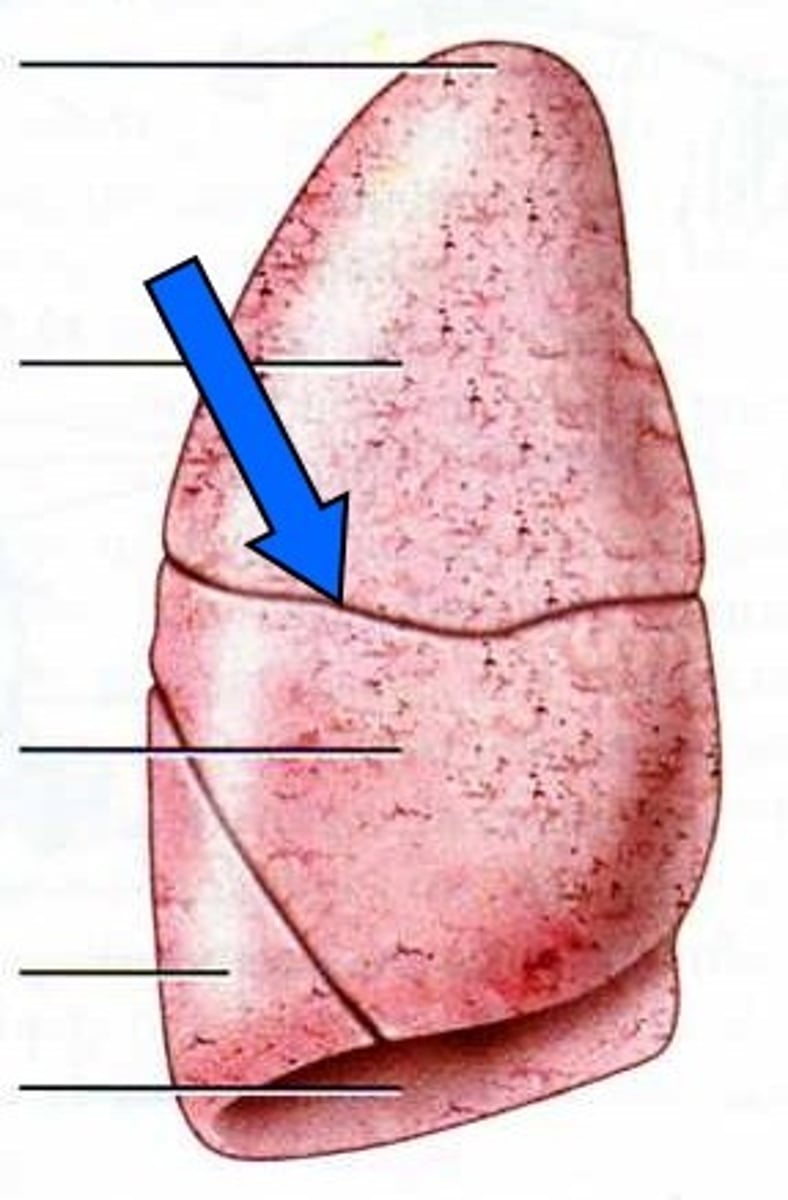
oblique fissure of right lung
separates the middle lobe from the inferior lobe
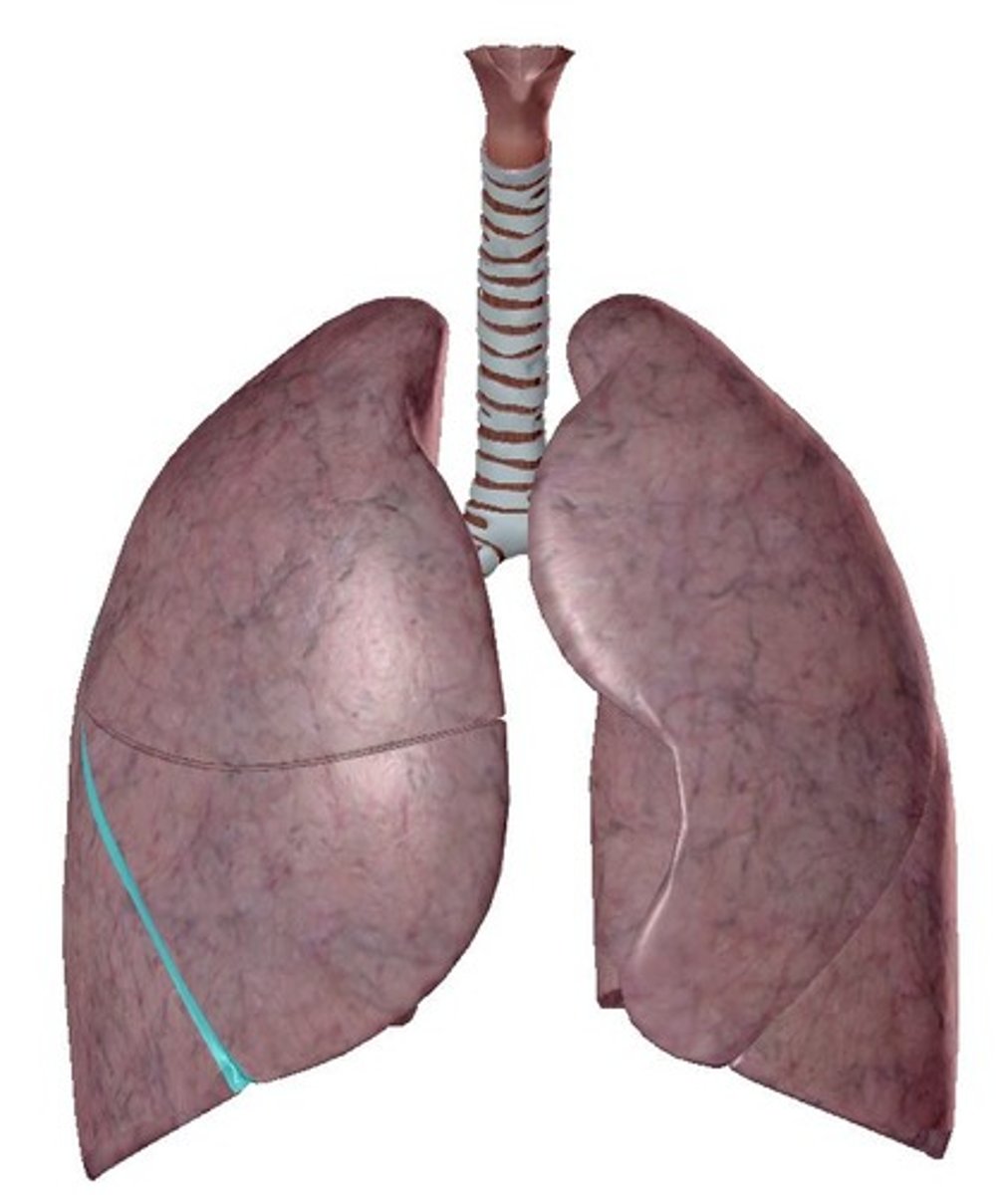
superior lobe of left lung
the upper portion of the left lung, situated above the oblique fissure
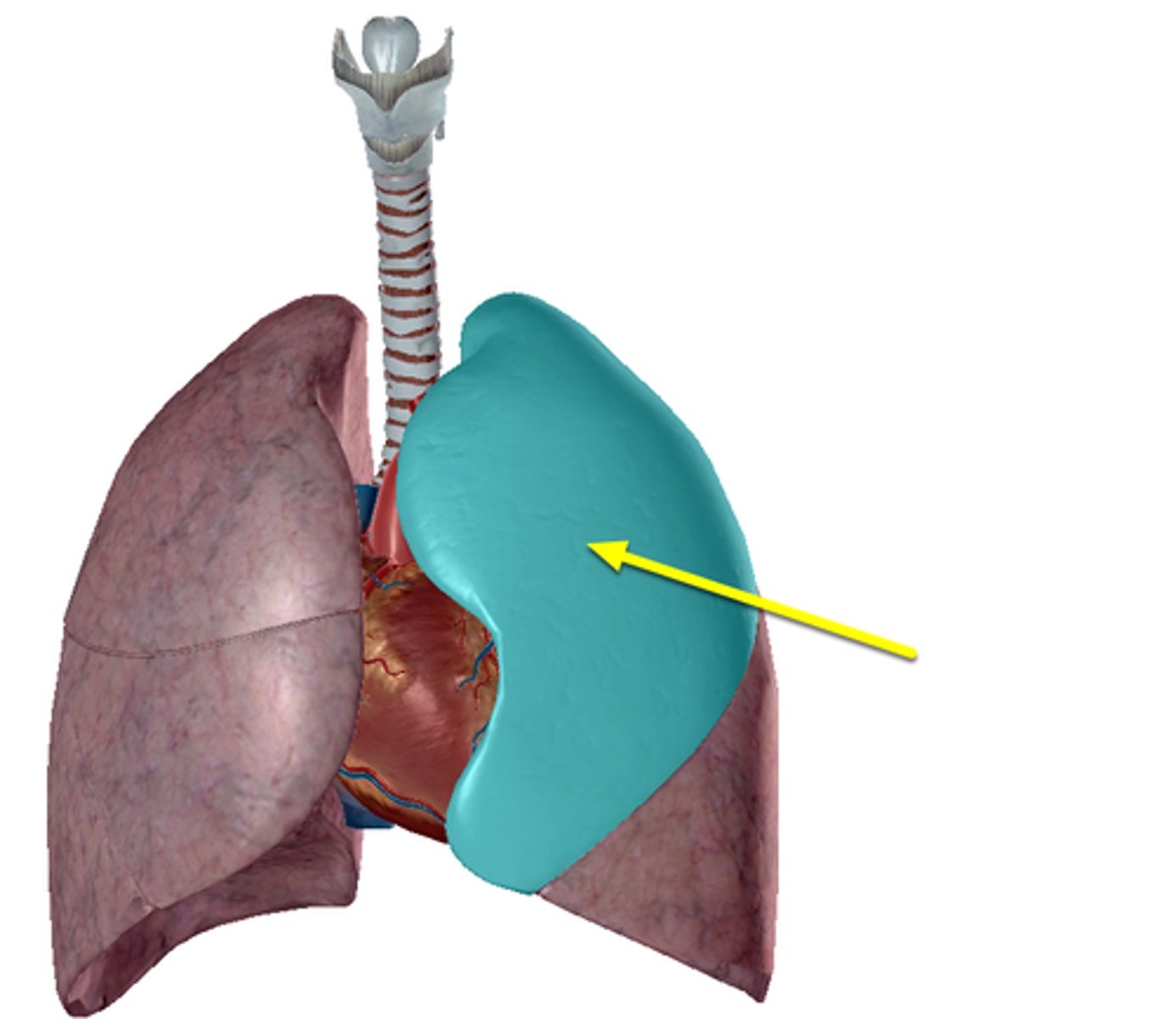
inferior lobe of left lung
Rests on diaphragm, separated from upper by oblique fissure: receives secondary bronchus
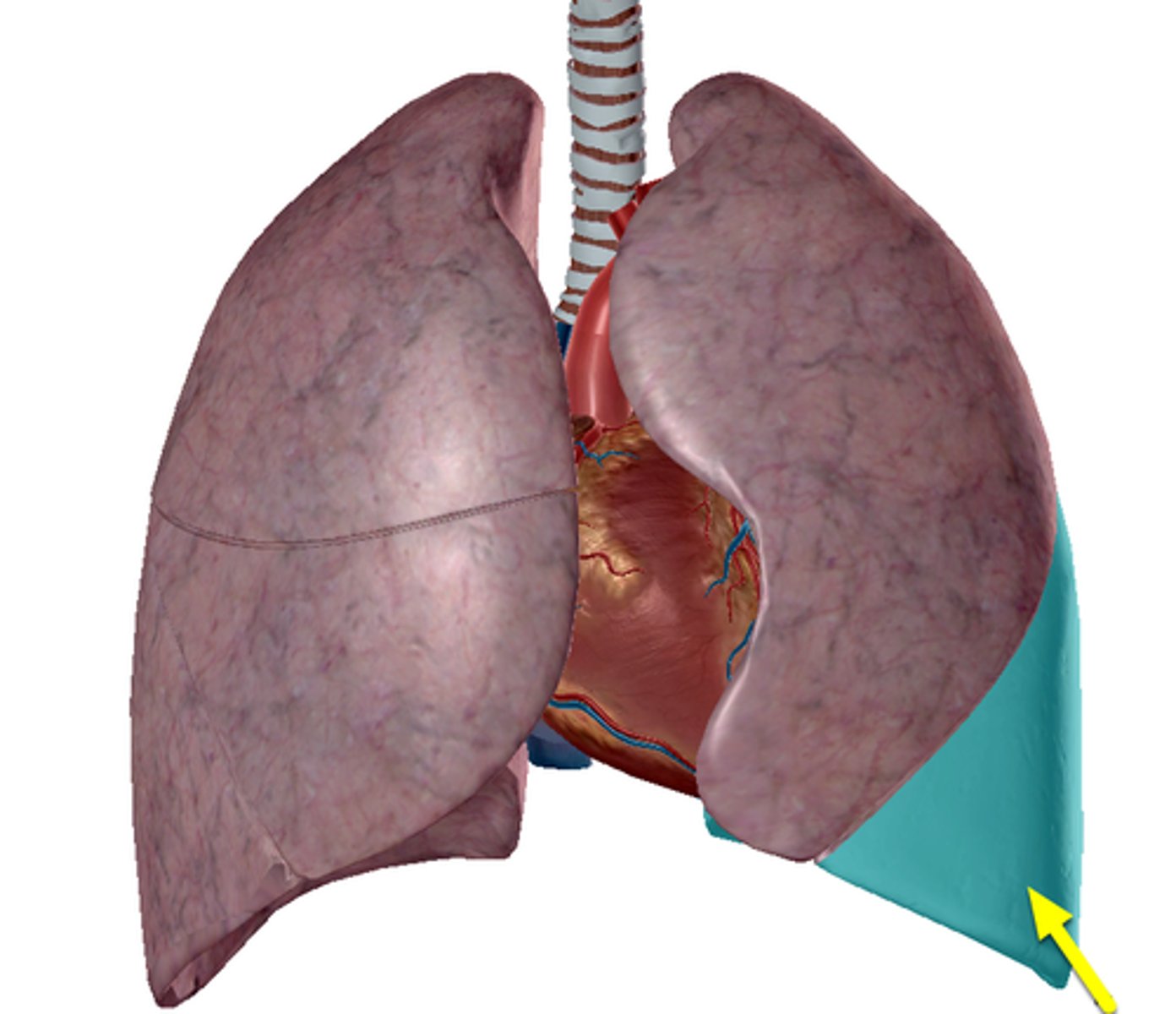
oblique fissure of left lung
Located on the left lung, it separates the superior and inferior lobes
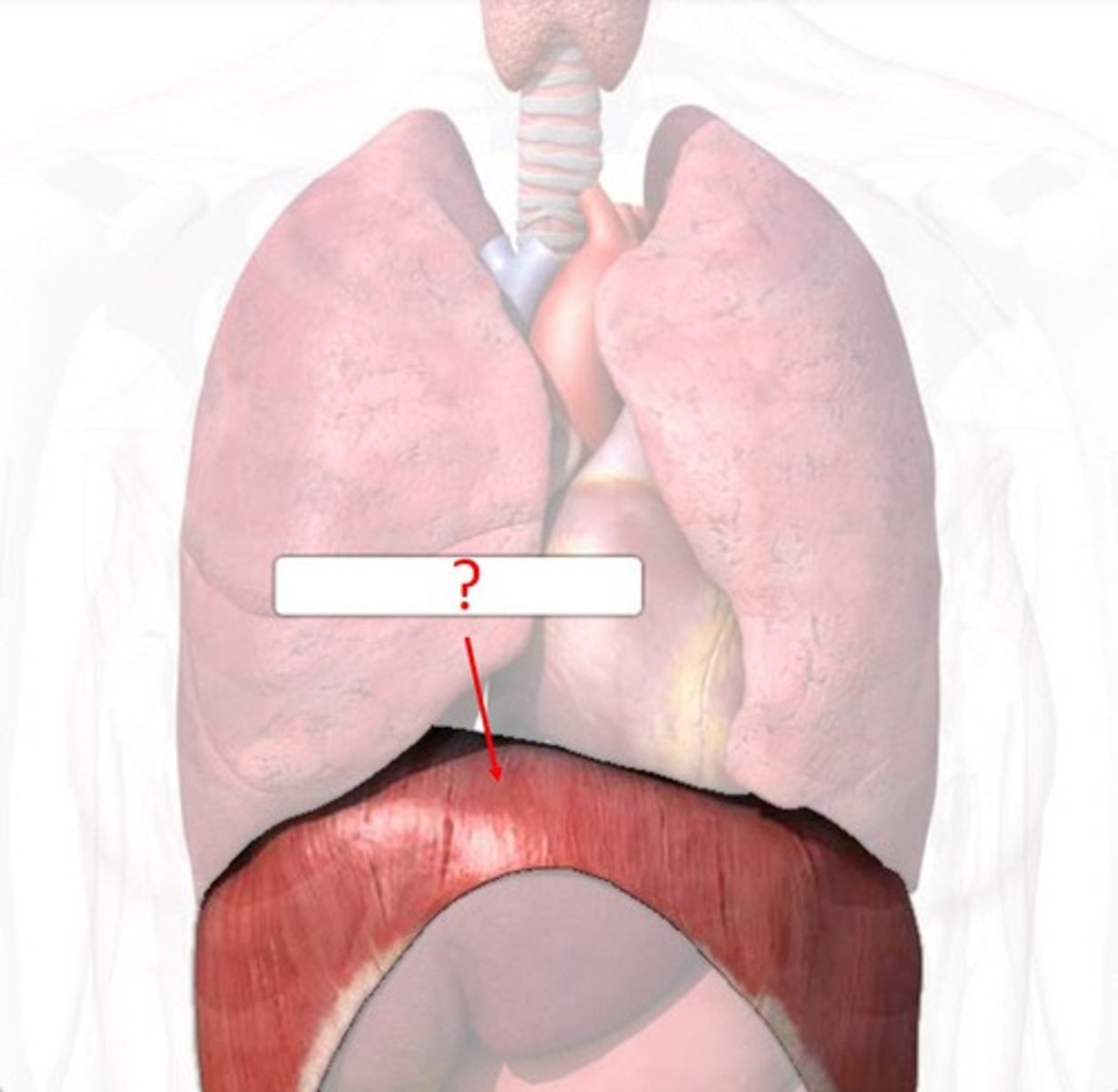
Diaphragm
a dome-shaped, muscular partition separating the thorax from the abdomen in mammals. It plays a major role in breathing, as its contraction increases the volume of the thorax and allows the lungs to inflate.
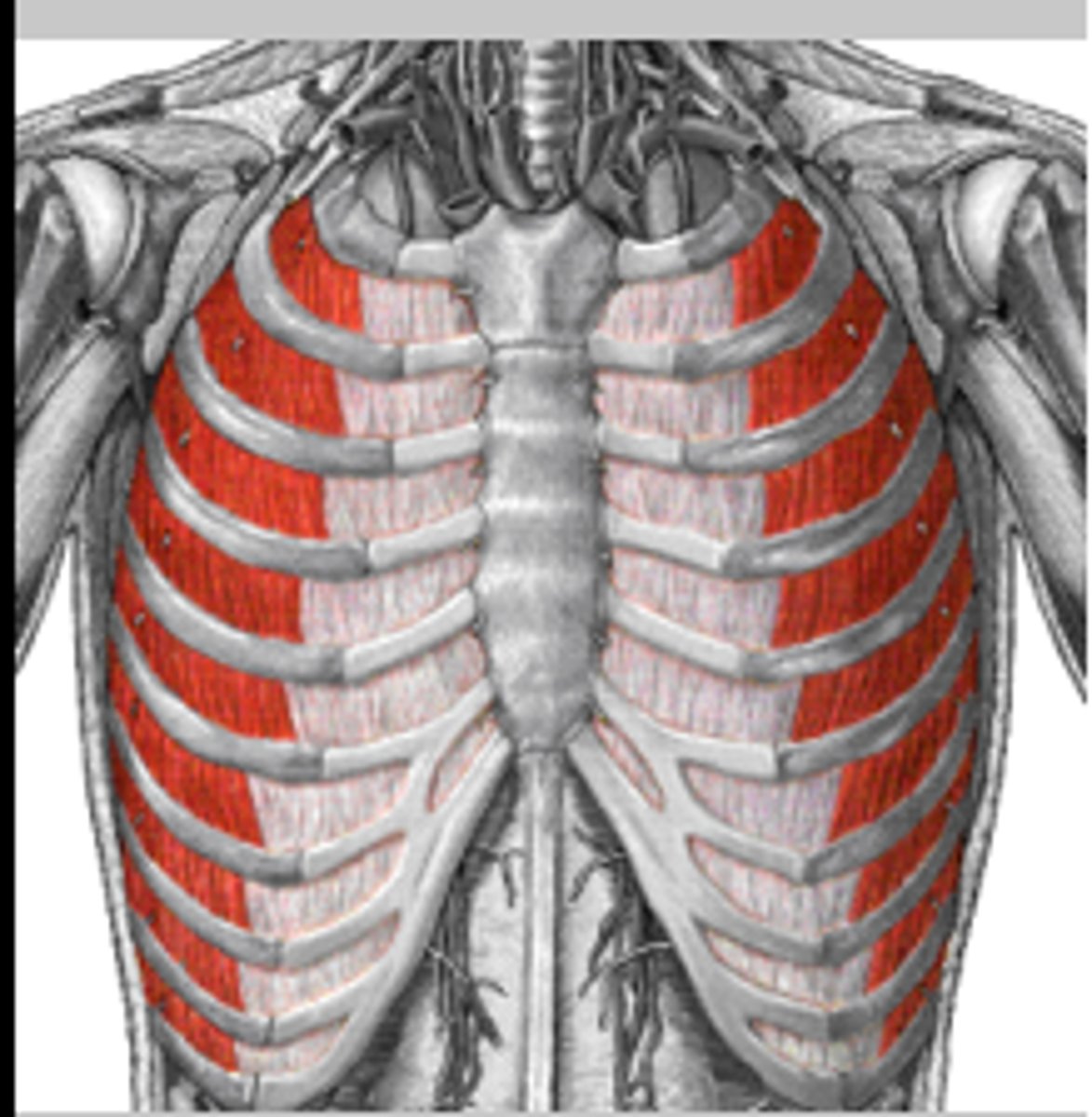
internal intercostal muscles
muscles responsible in lowering the rib cage during forced expiration
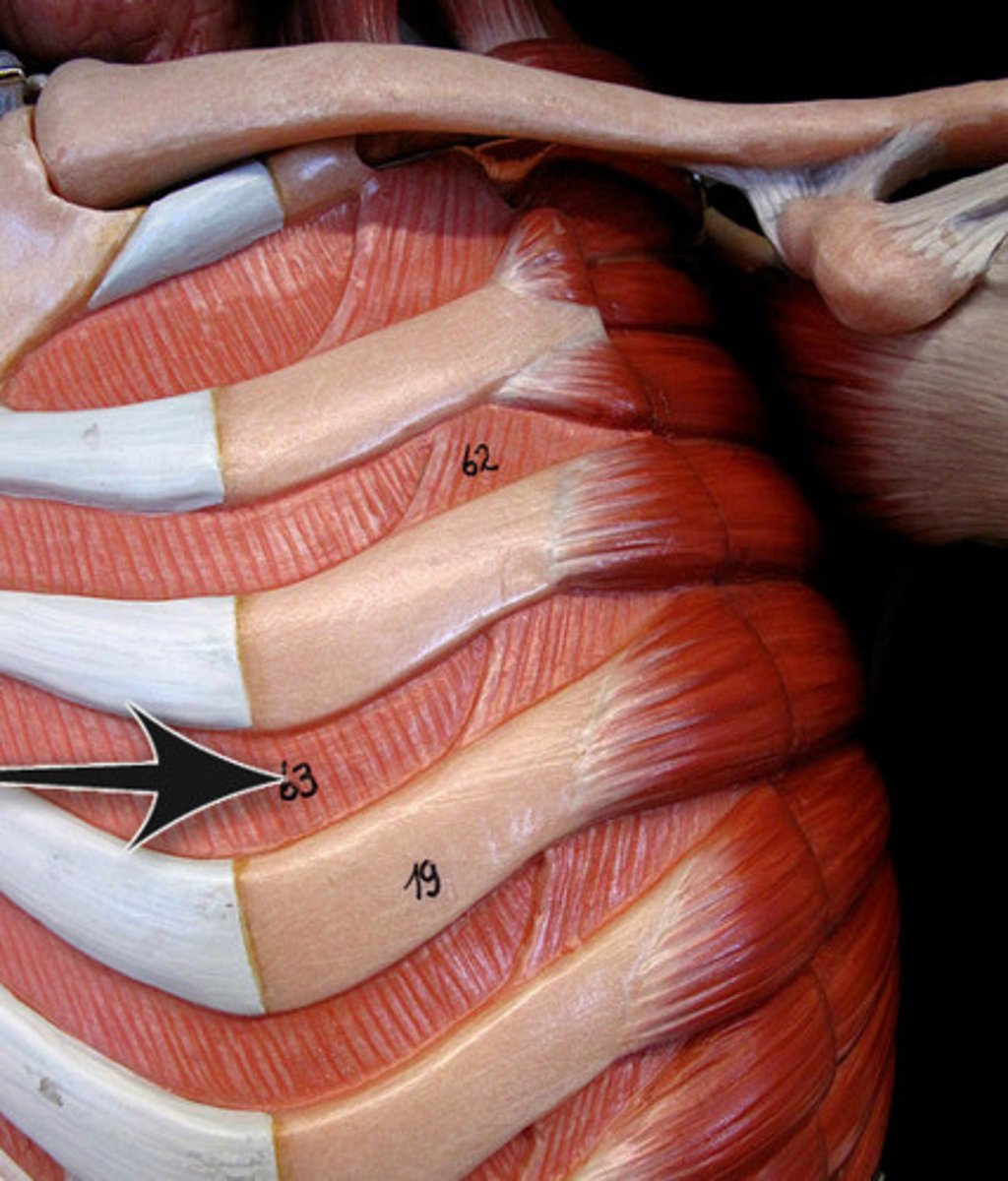
external intercoastal muscles
Muscles assist with breathing by moving the ribs up and outward to increase the total volume in the thoracic cavity.
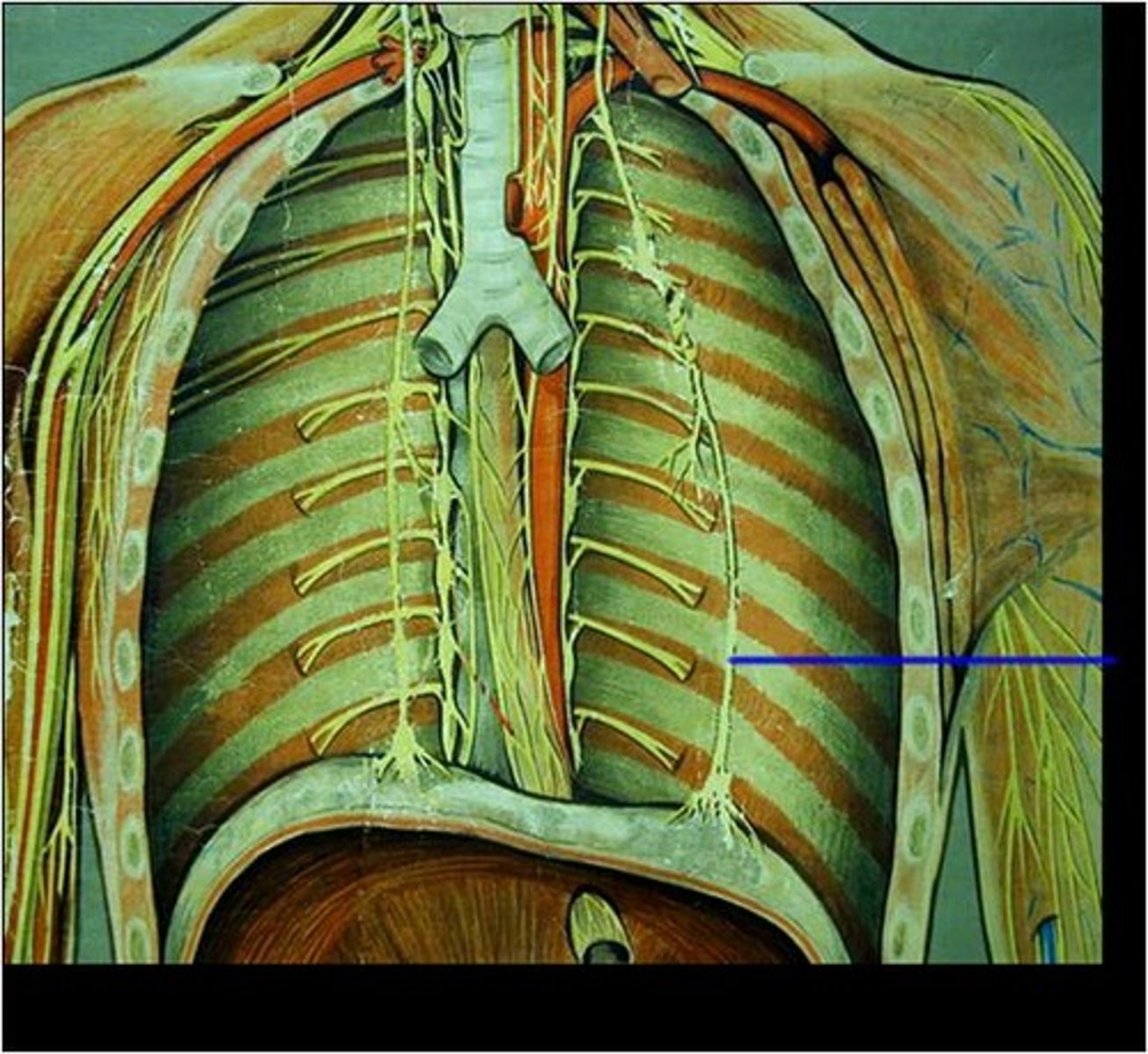
Phrenic Nerve
located on both right and left sides this nerve directly innervates the diaphragm. Helps to provide motor function to the diaphragm. Tells the diaphragm to contract and relax.
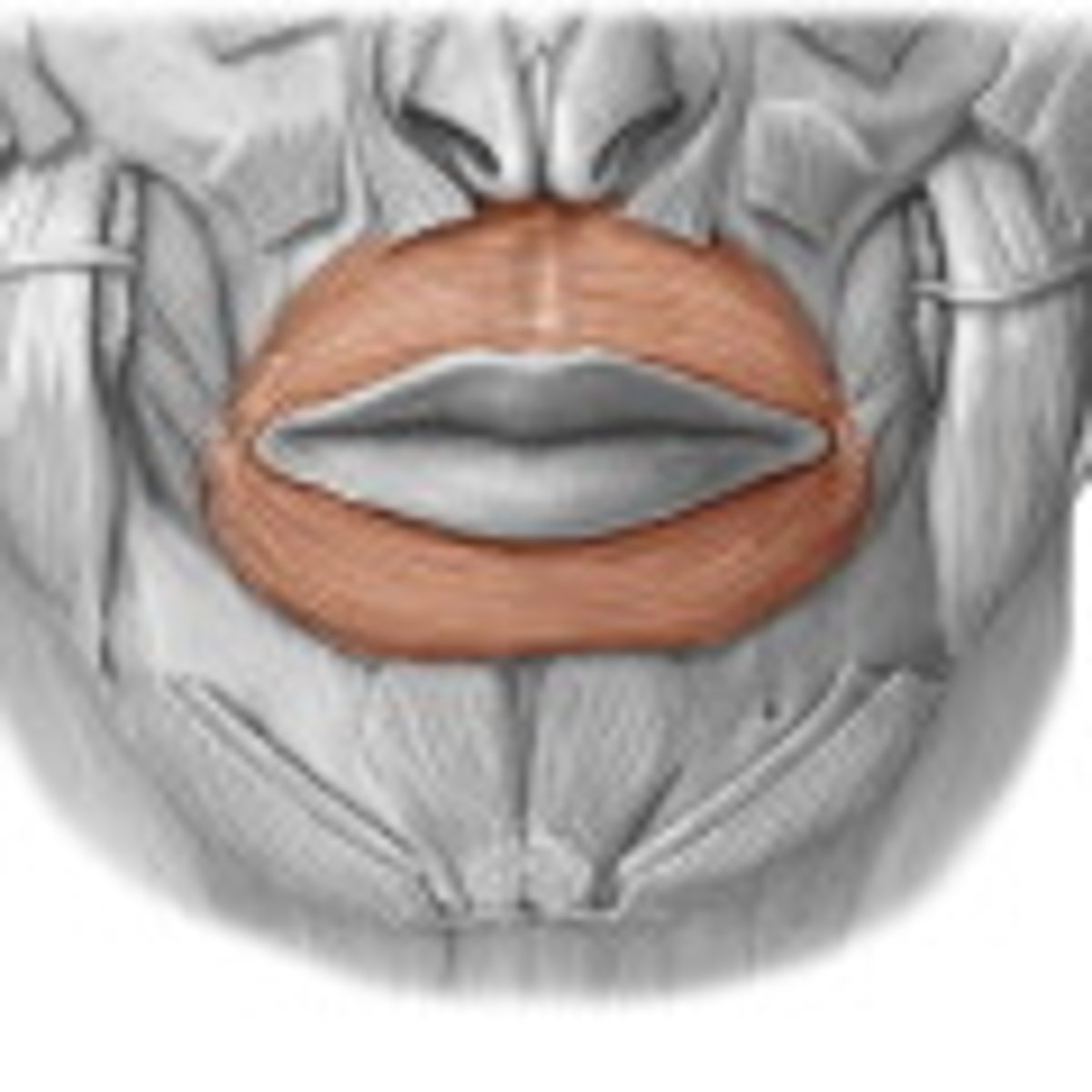
Orbicularis Oris
round shaped muscle that surrounds the lips,
closes the lips, purses, and protrudes lips,
Innervated by Facial nerve
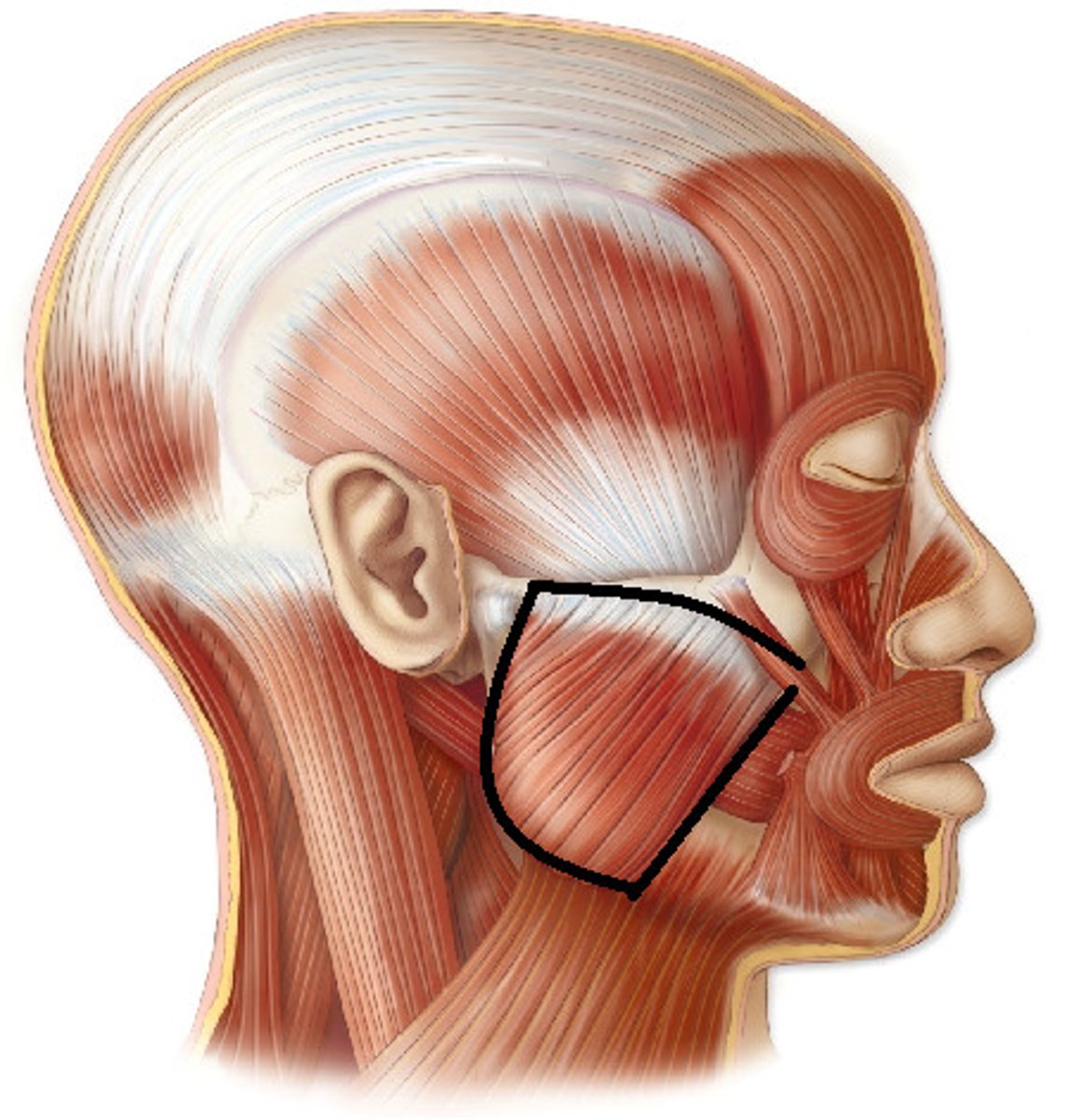
Buccinator
Muscle responsible for compressing the cheeks,
innervated by Facial nerve
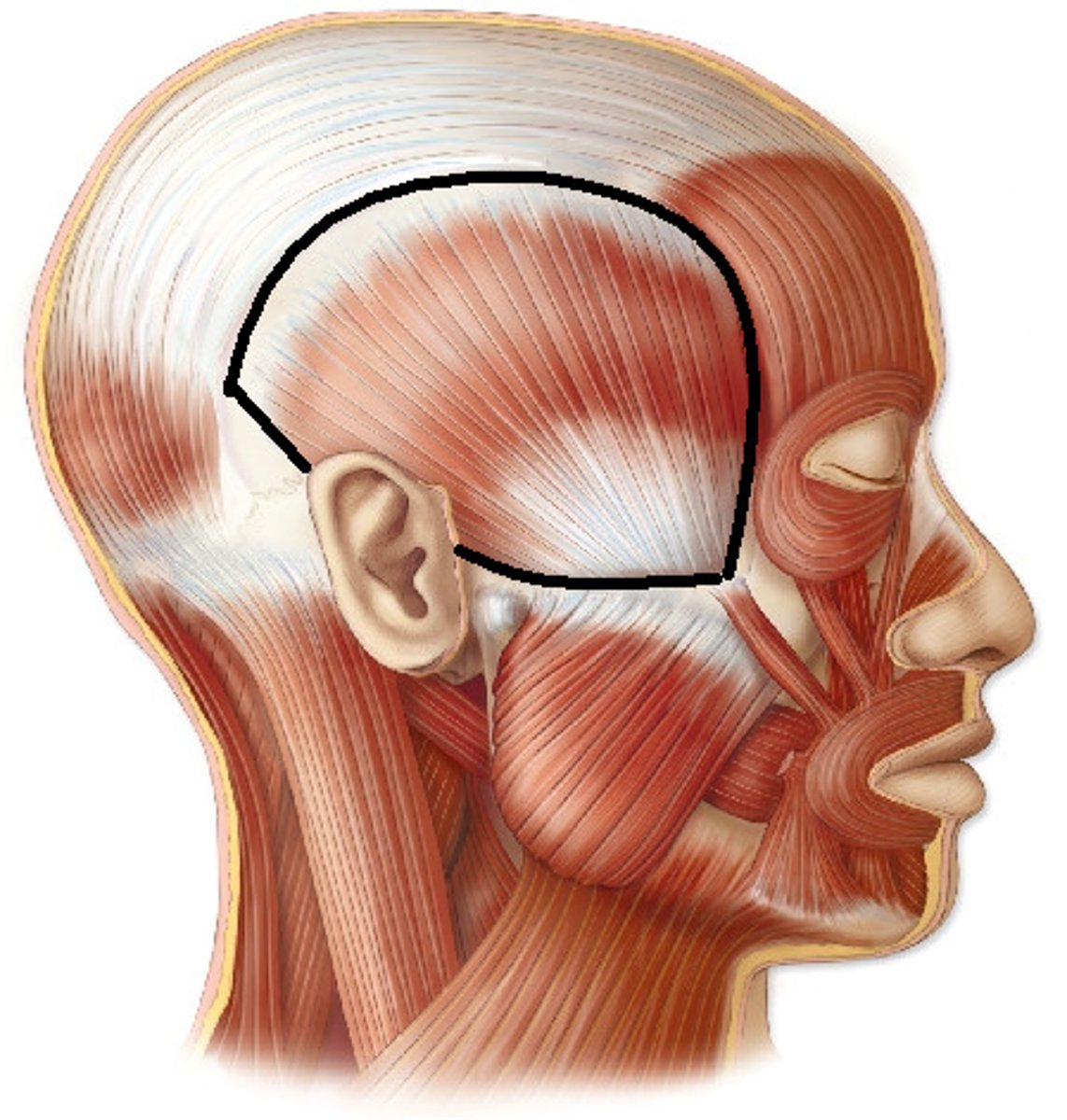
Temporalis
large muscle found along the temporal bone,
responsible for closing the jaw
innervated by the Trigeminal nerve
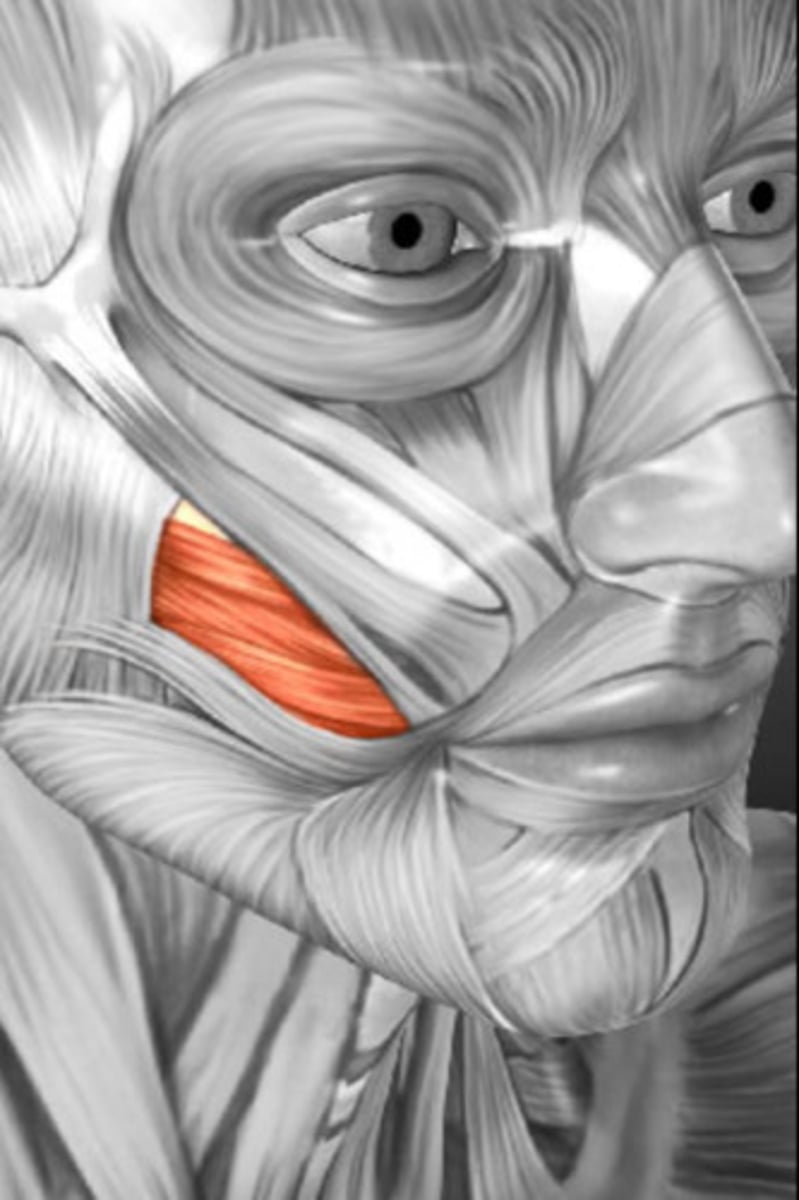
Masseter
One of the strongest muscles in the body,
Prime mover of jaw closure, elevates mandible,
Innervated by the Trigeminal nerve
Central incisor
the first tooth starting from the midline; used to cut or bite the food that is ingested
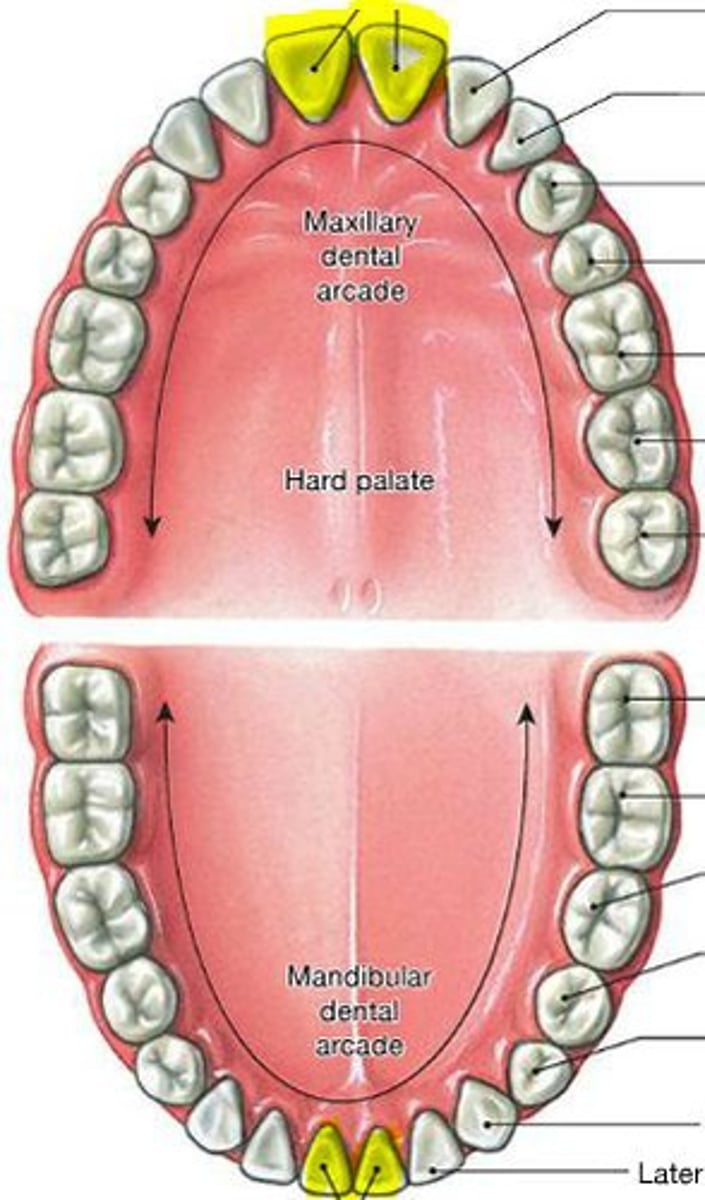
Lateral inscisors
the two teeth located to the right and left sides of the central incisors, Function to shear or cut food during mastication
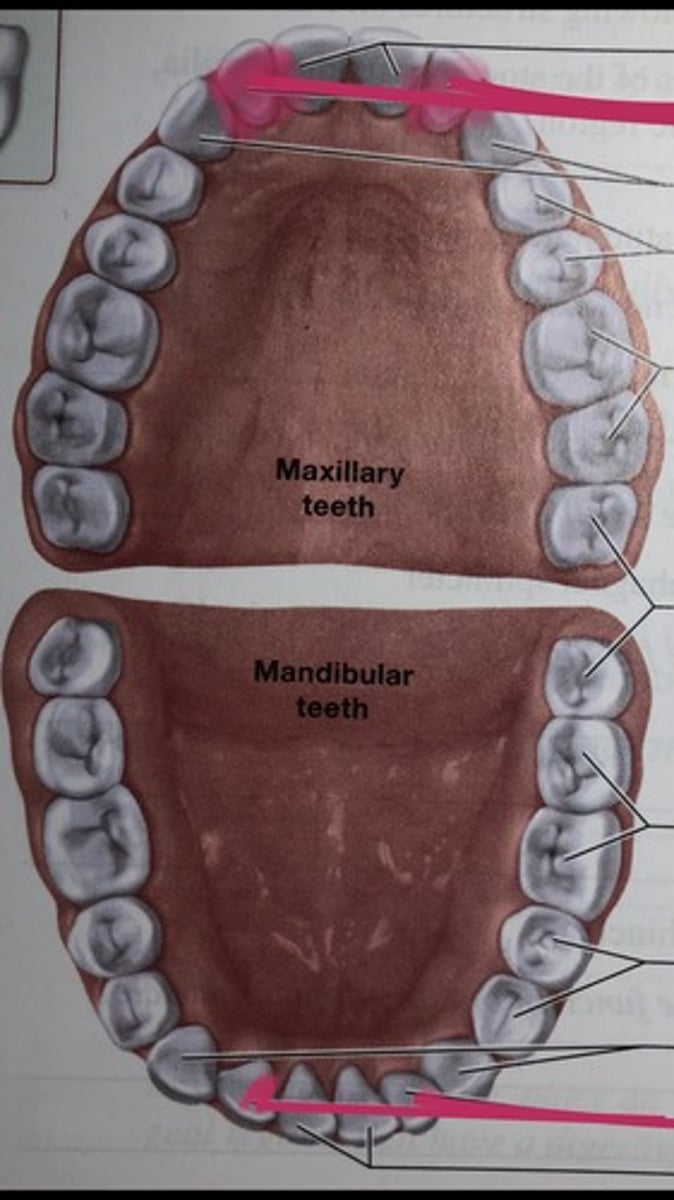
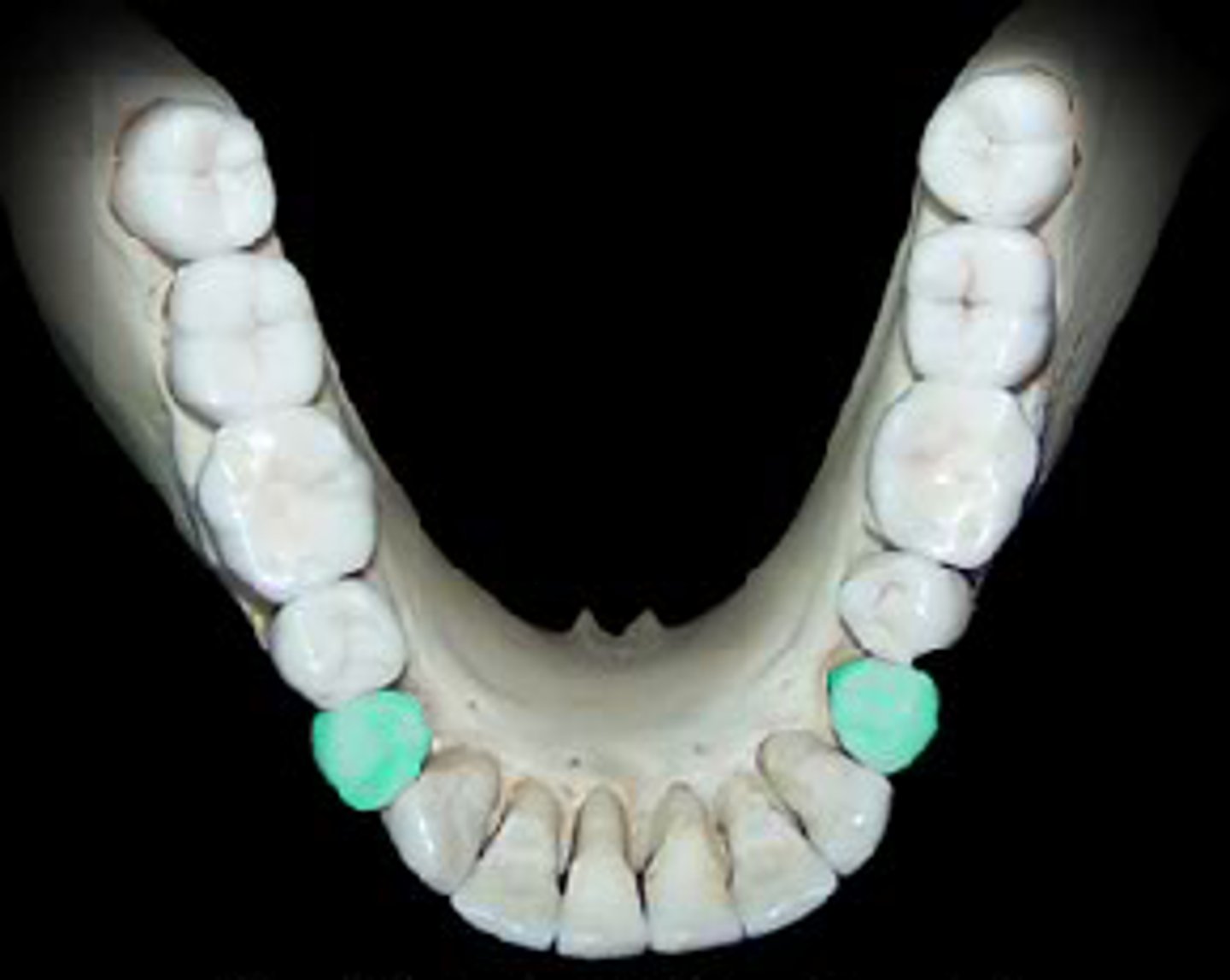
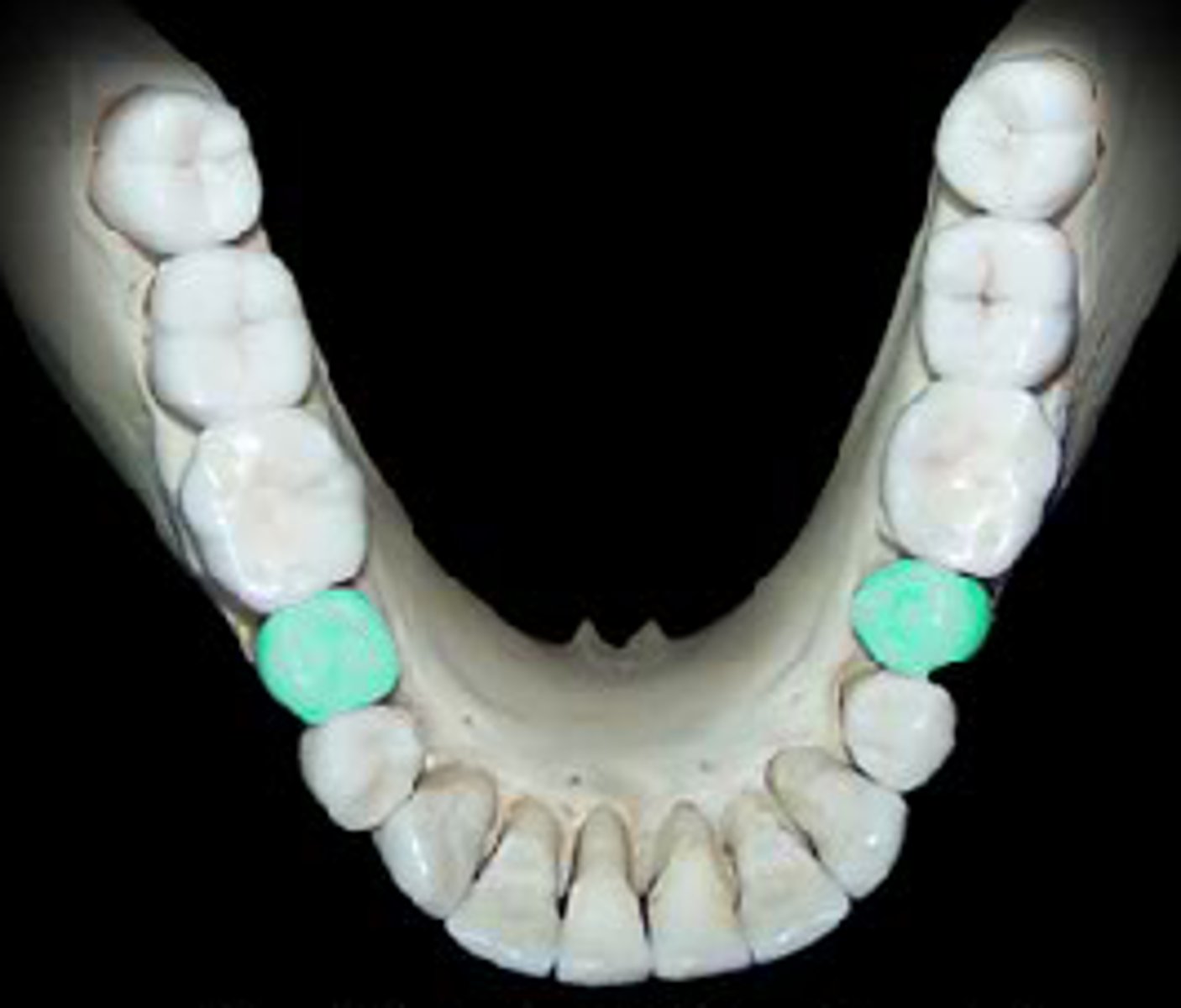
Canines
Fanglike teeth in front of the premolars that rip and tear food.
First premolars
one of two transitional teeth (also called bicuspids) located between the canine and molar teeth
Second premolars
known as a bicuspid, is a tooth located between the first premolar and the first molar in the upper and lower jaws
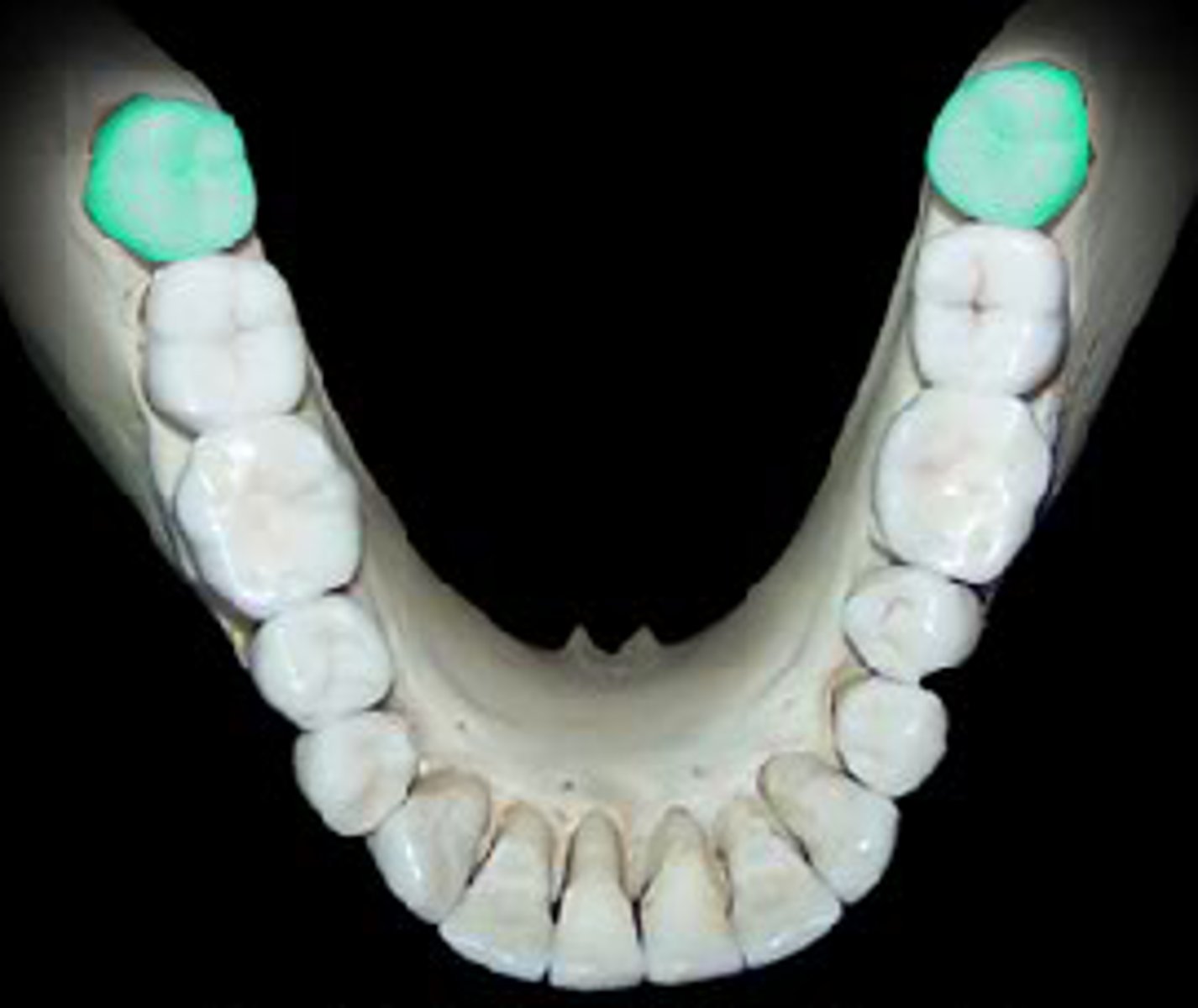
First molars
the first permanent teeth to erupt in the mouth, function to grind down food into small pieces
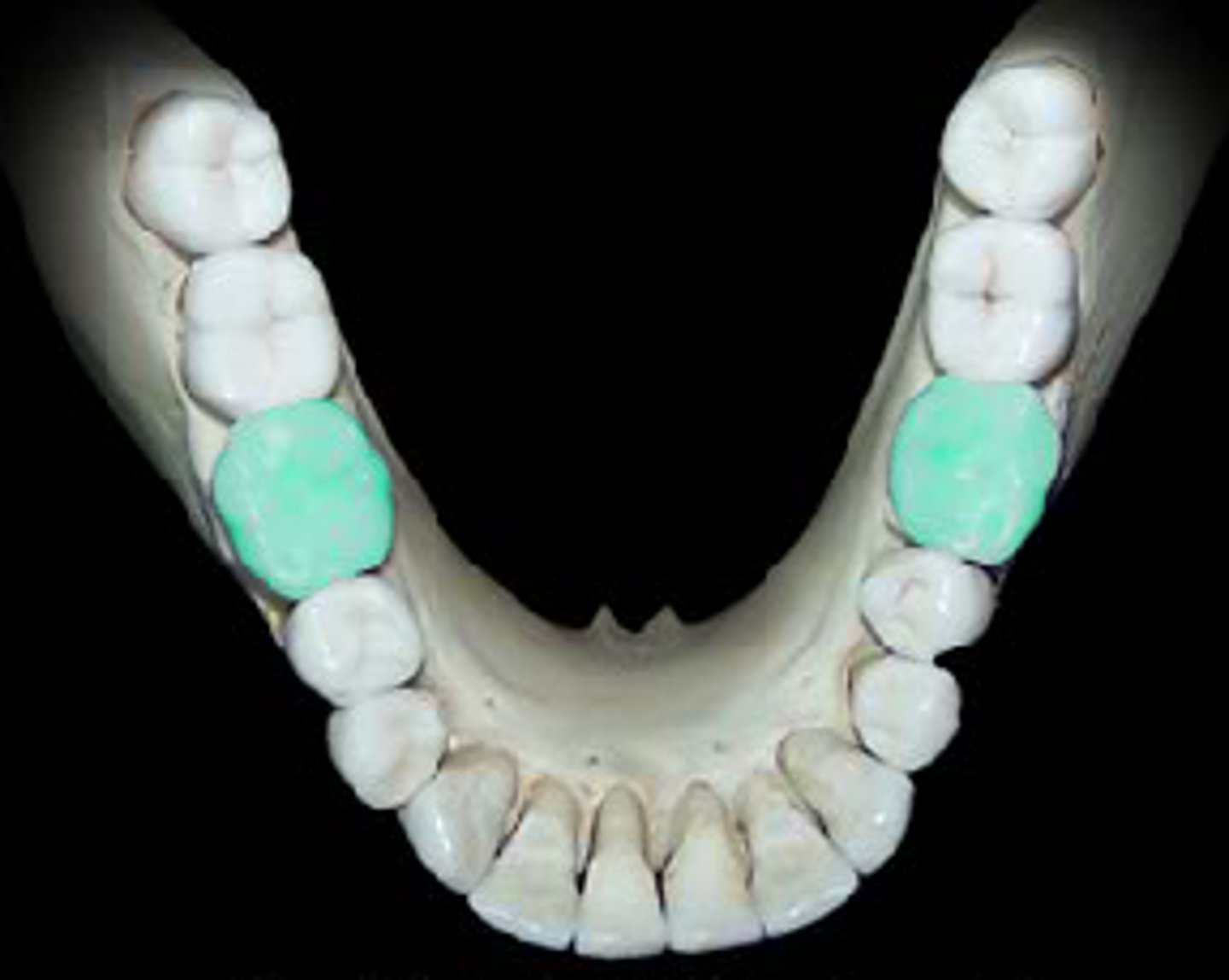
Second molars
sandwhiched between the 1st molar and the wisdom teeth
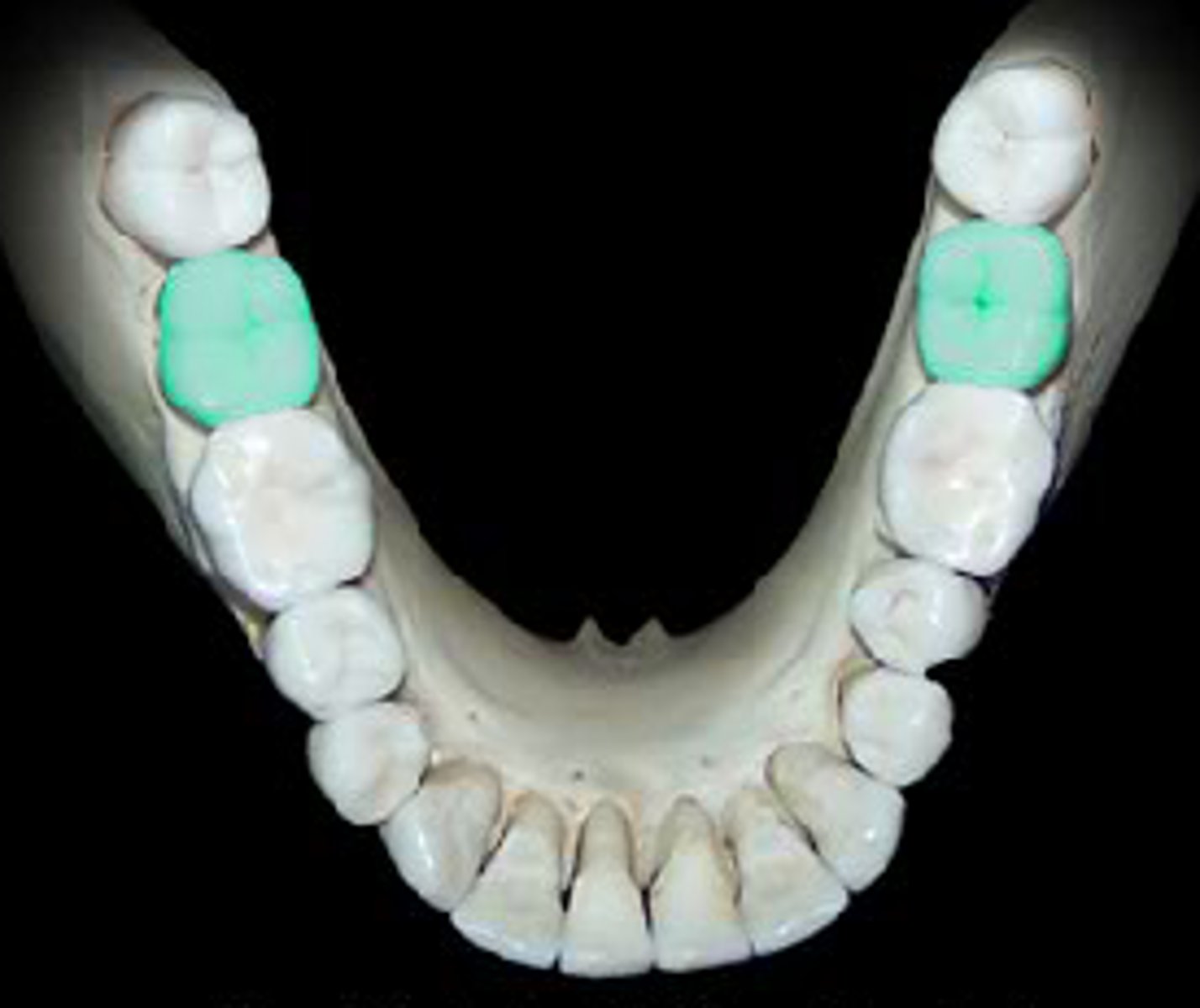
Third molars
Known as the wisdom teeth, the last row of your molars
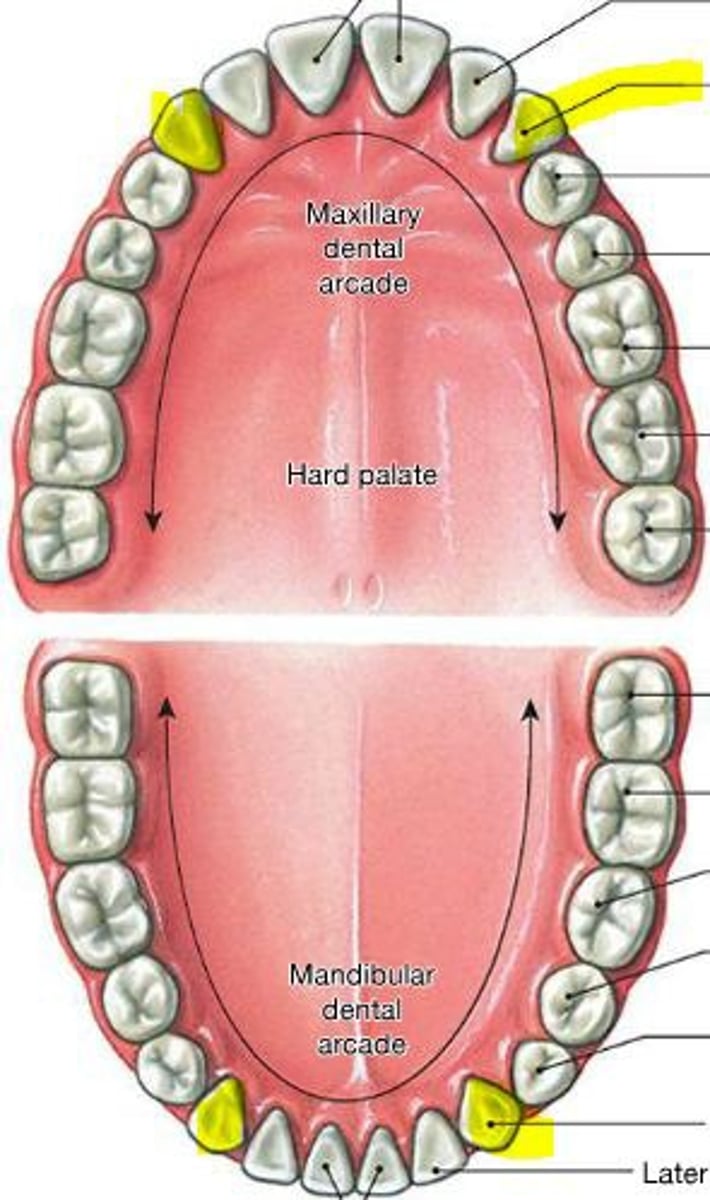
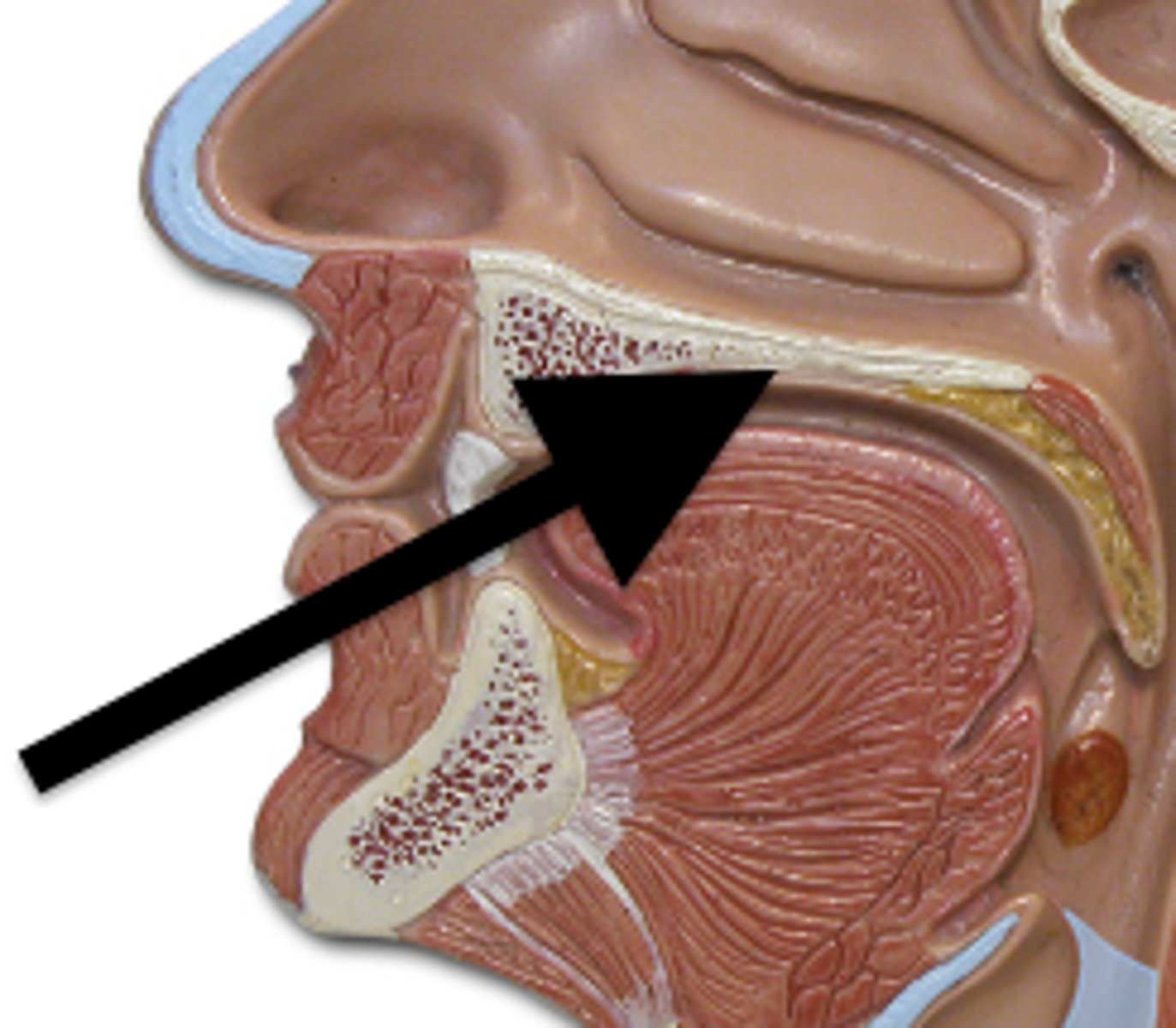
Hard palate
Bony part of the mouth also known as the roof of the mouth.
Separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
Comprised of the palatine bone and the maxilla.
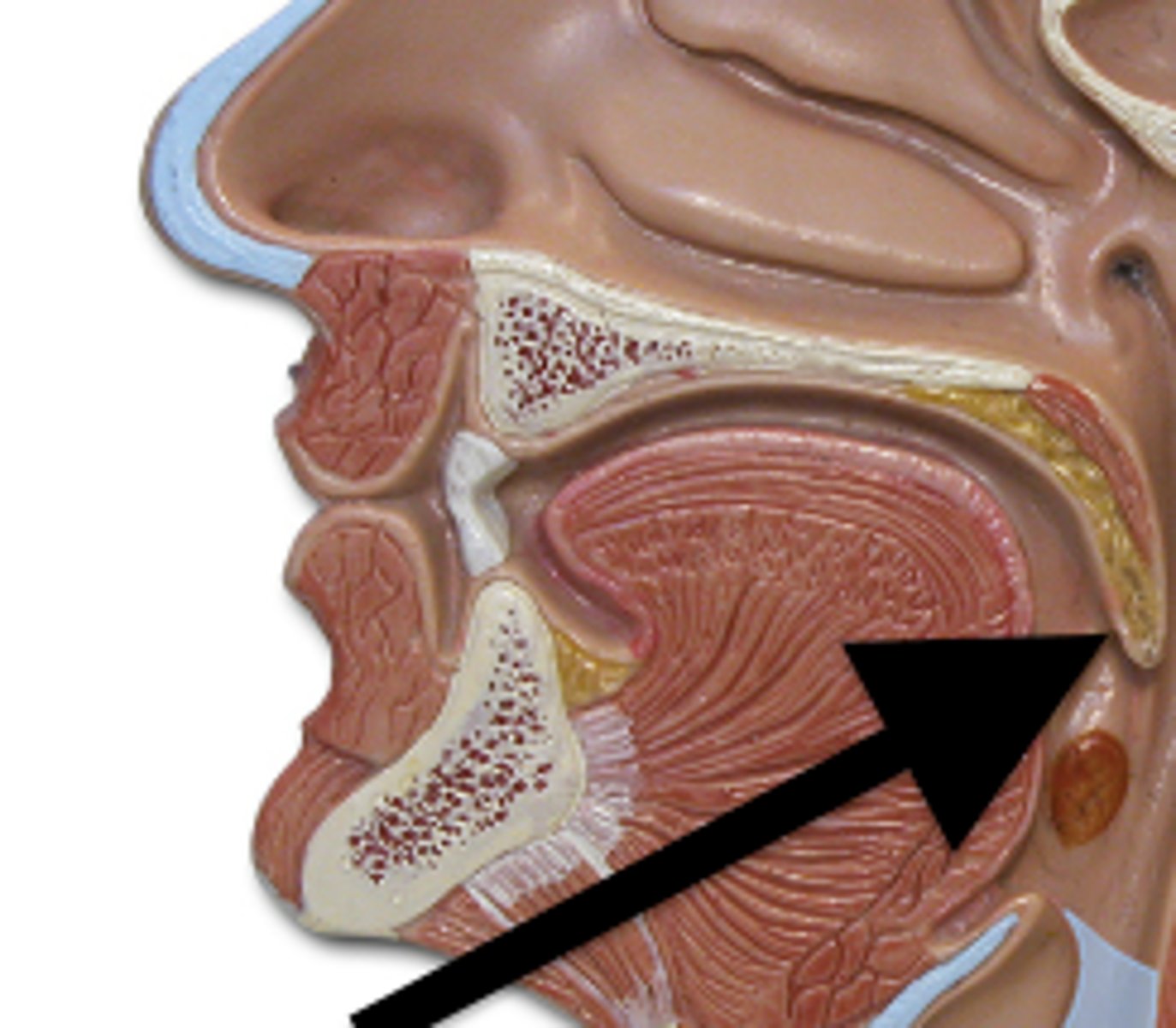
Soft palate
the fleshy, flexible part toward the back of the roof of the mouth. functions to separate the oral and nasal cavities, playing a crucial role in feeding, breathing, swallowing, and speech.
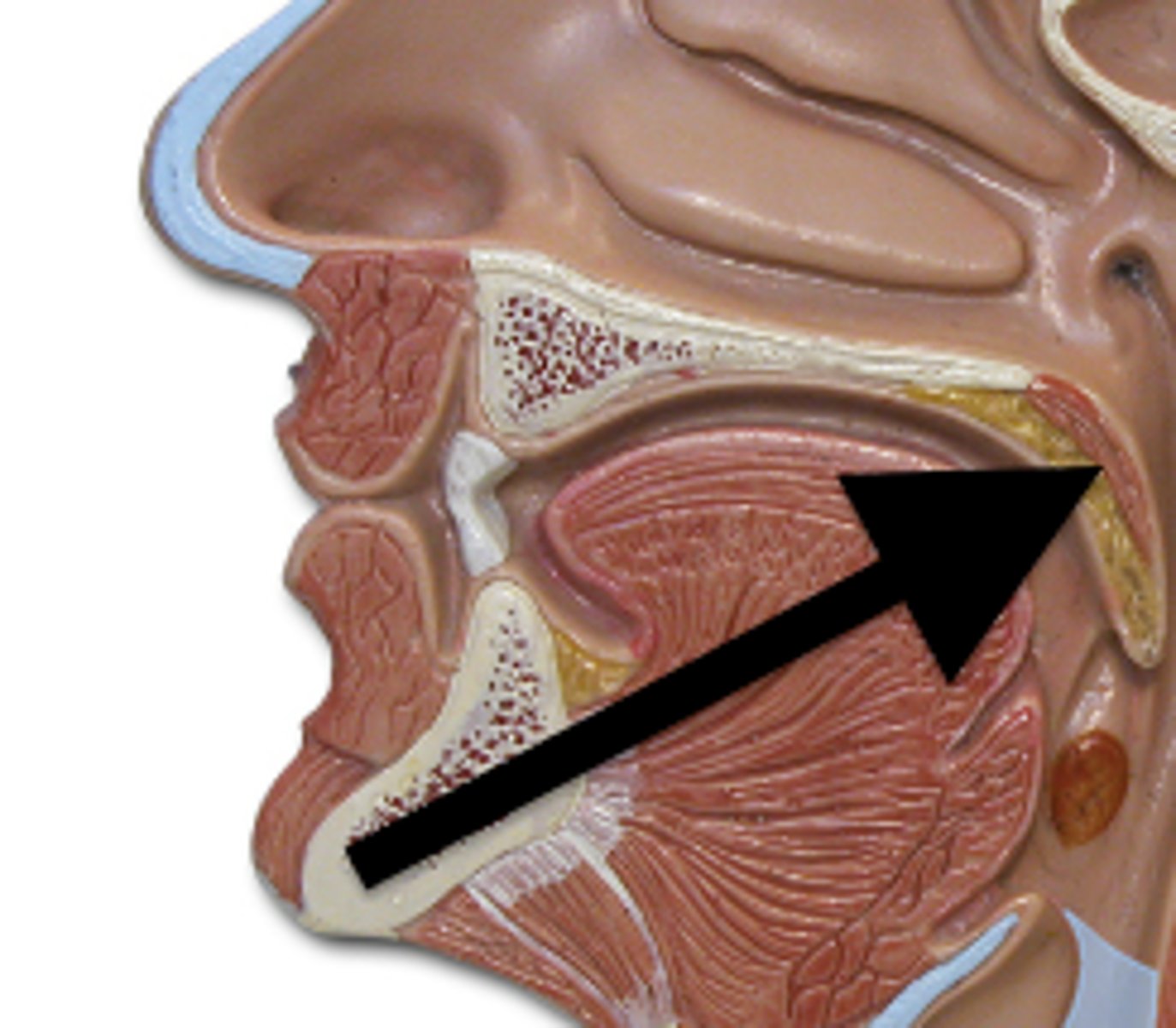
Uvula
small projection hanging from the back middle edge of the soft palate. Functions to prevent food or drink from entering the nasal cavity
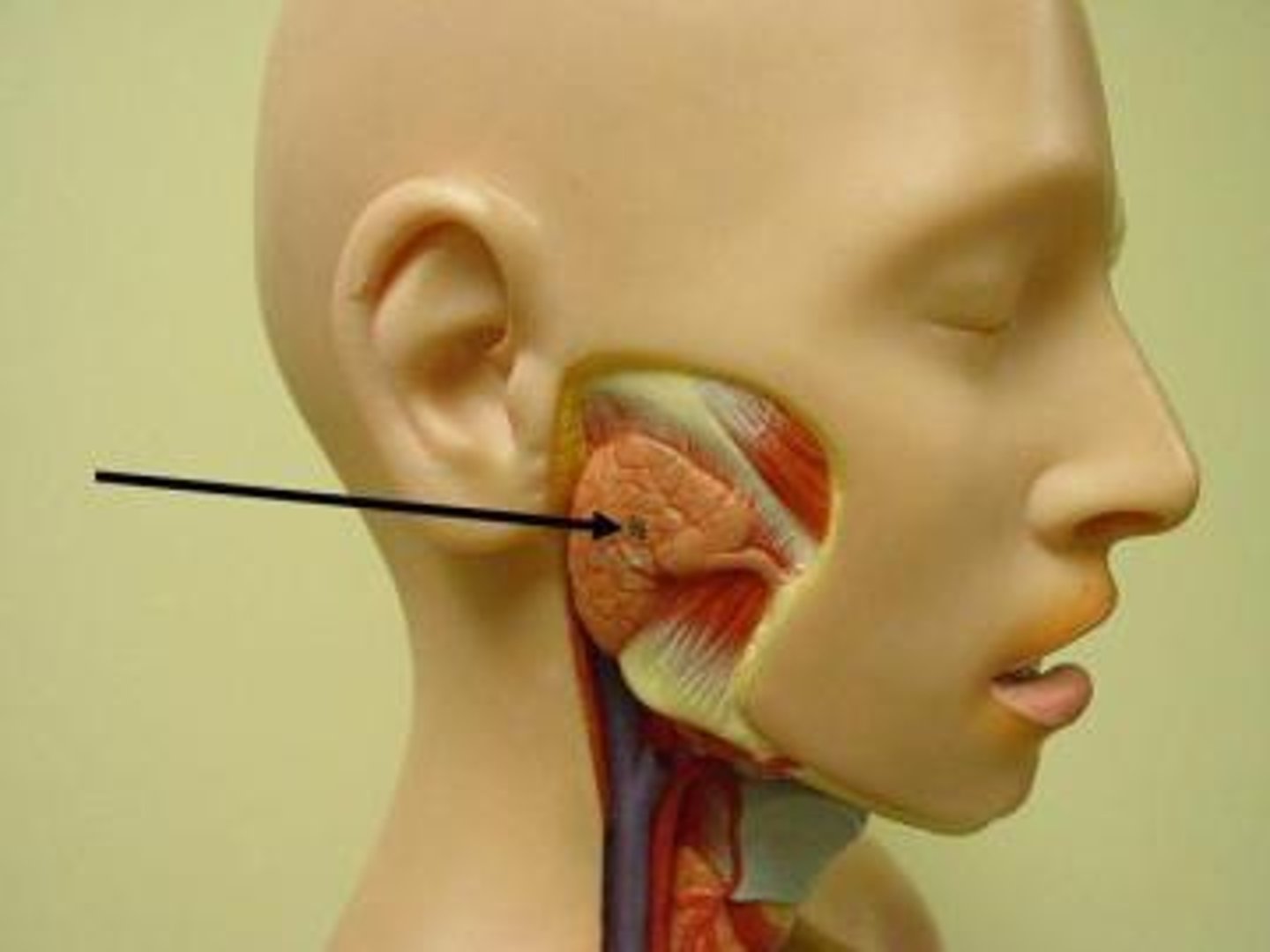
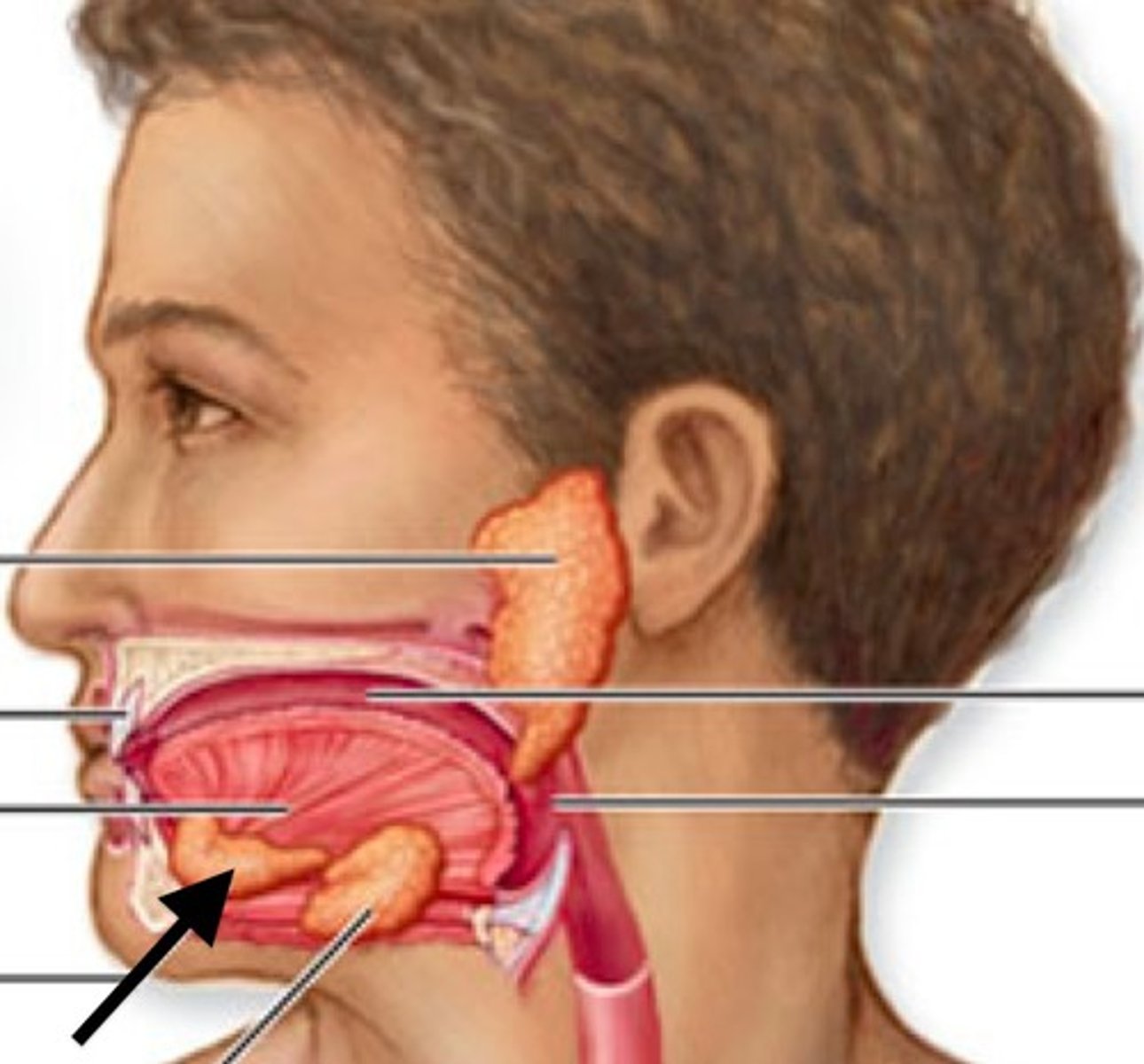
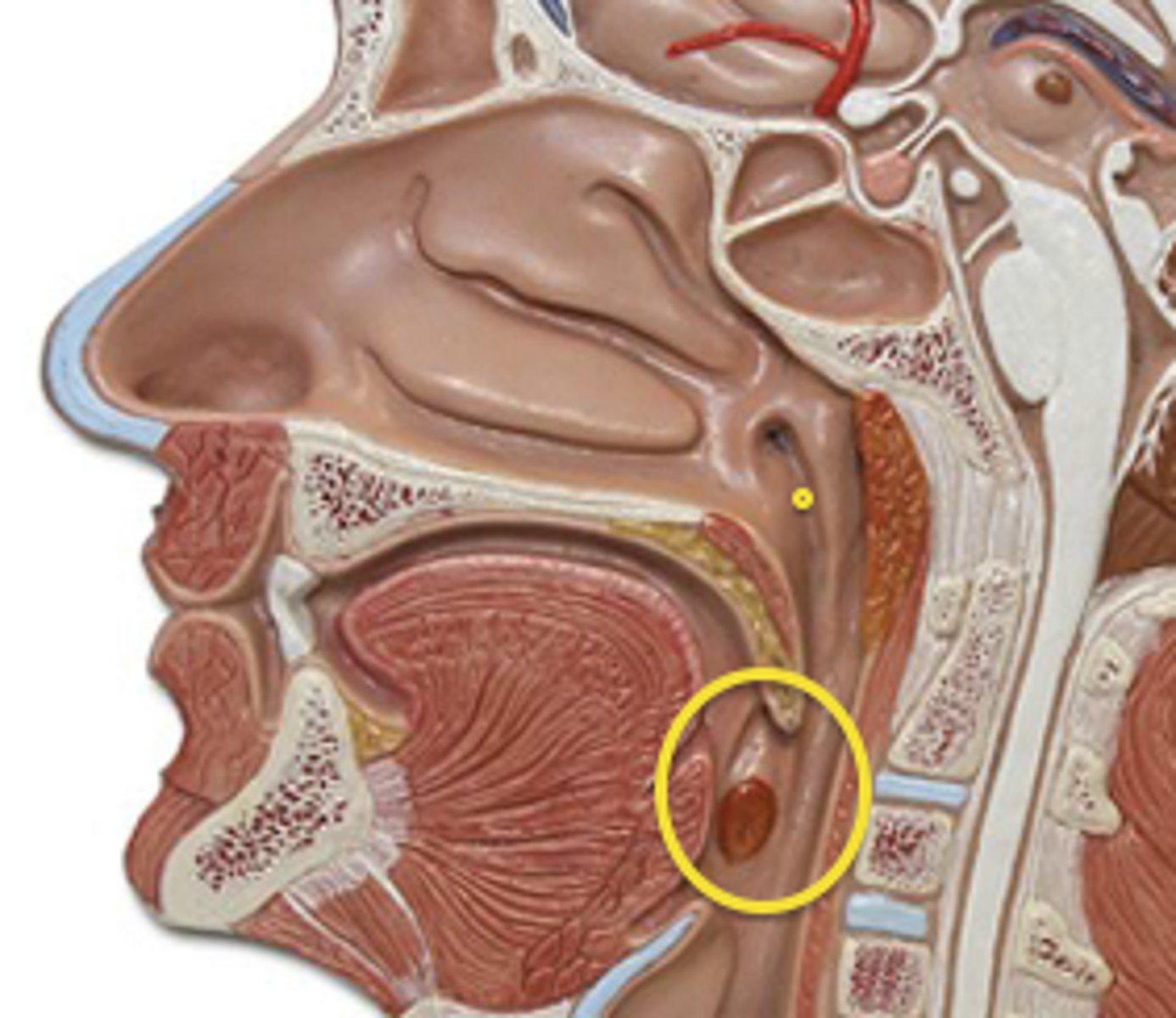
Parotid gland
paired salivary glands that sit just in front of the ears. Functions to produce/ secrete saliva, also helps to lubricate the mouth. Secretes amylase to help breakdown starches and carbohydrates.
Submandibular gland
a salivary gland found below the lower jaw on either side that produces most of the nocturnal saliva, secretes amylase to help breakdown starches and carbohydrates.
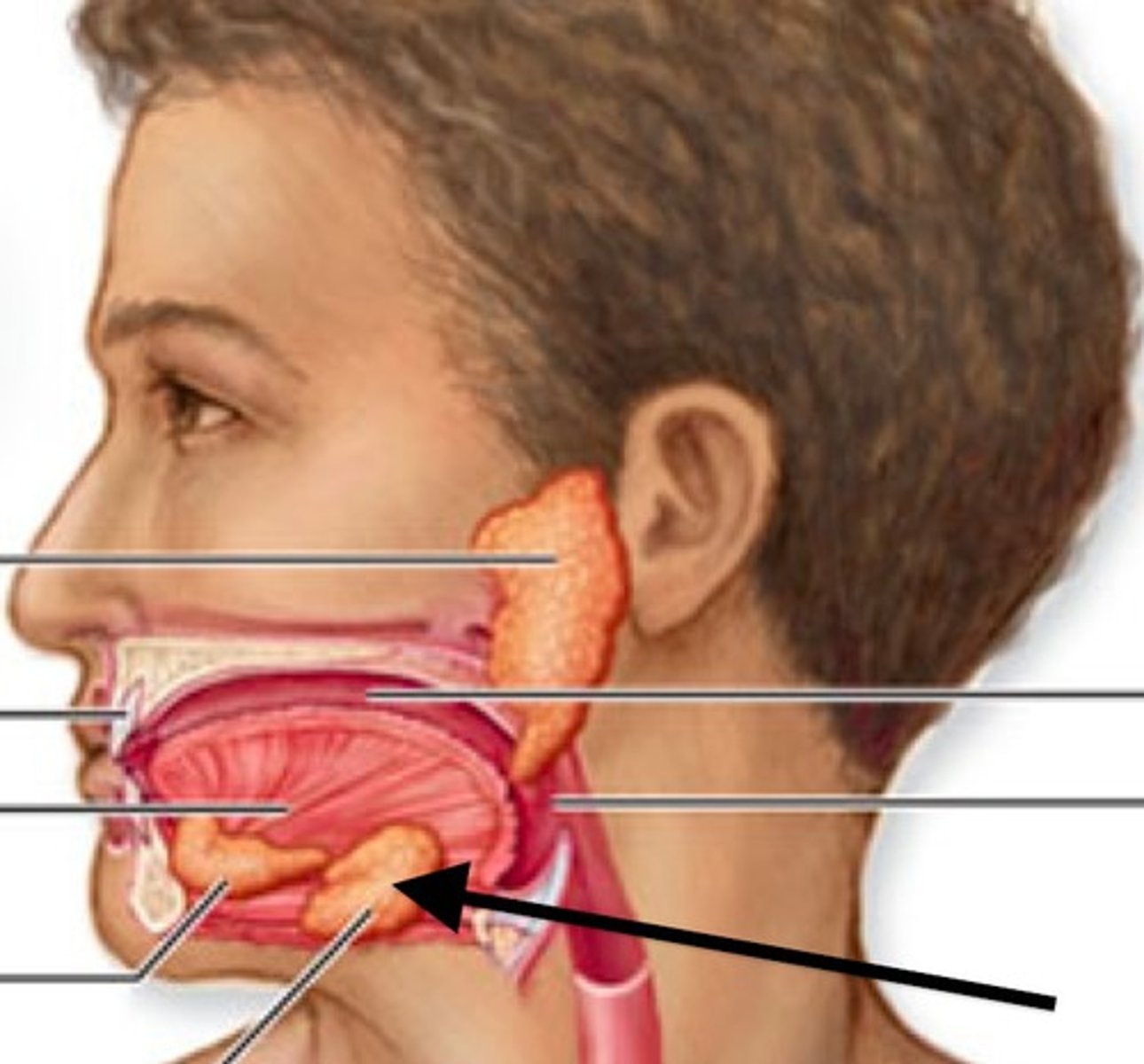
Sublingual gland
smallest salivary gland found under the tongue, primarily secretes mucins, and a minimal amount of saliva and amylase
Nasopharynx
region of the pharynx at the back of the nose and above the soft palate
Oropharynx
central portion of the pharynx between the roof of the mouth and the upper edge of the epiglottis
Laryngopharynx
the third division of the pharynx, is shared by both the respiratory and digestive systems
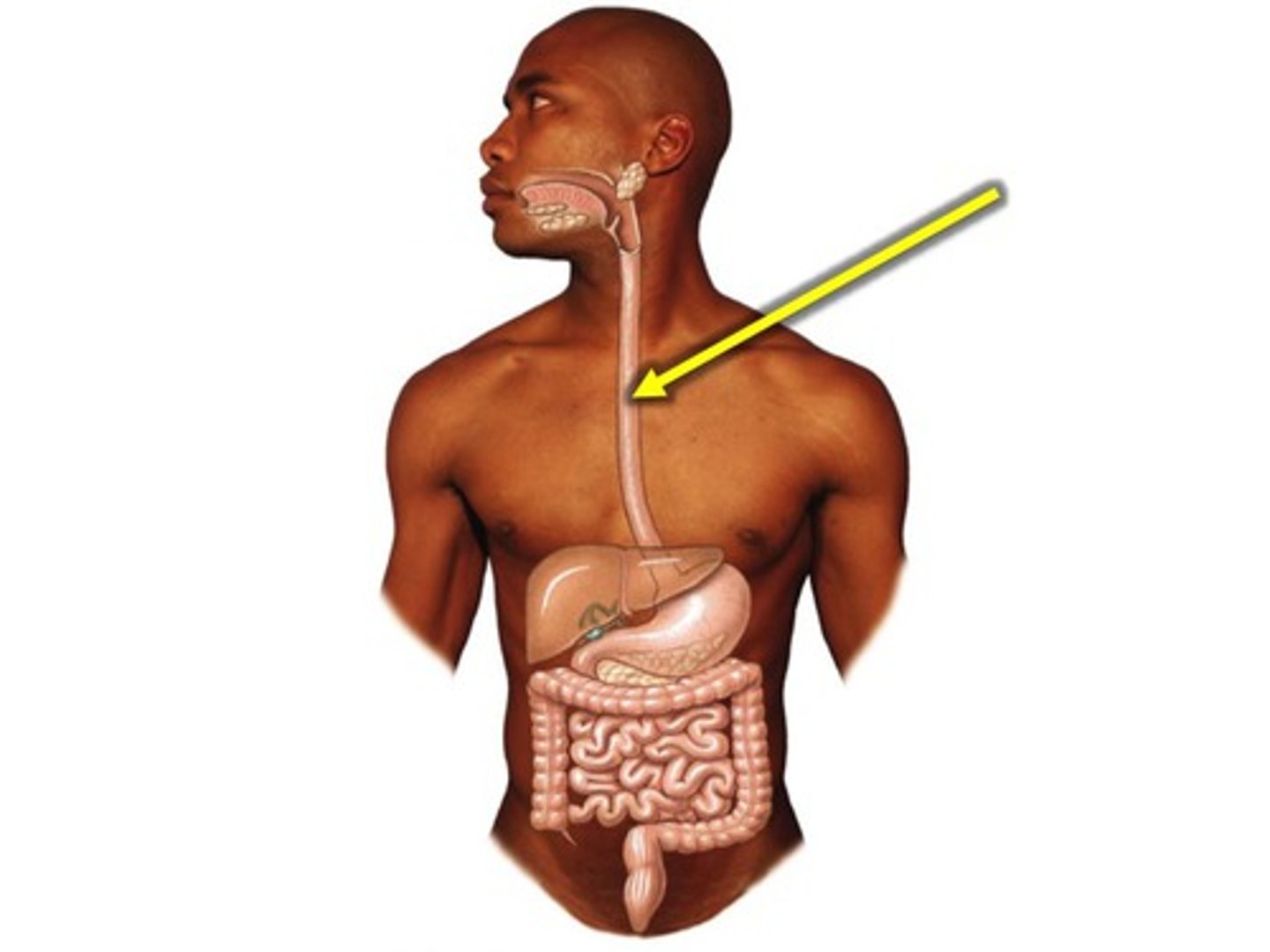
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. consists of 4 layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, and adventitia
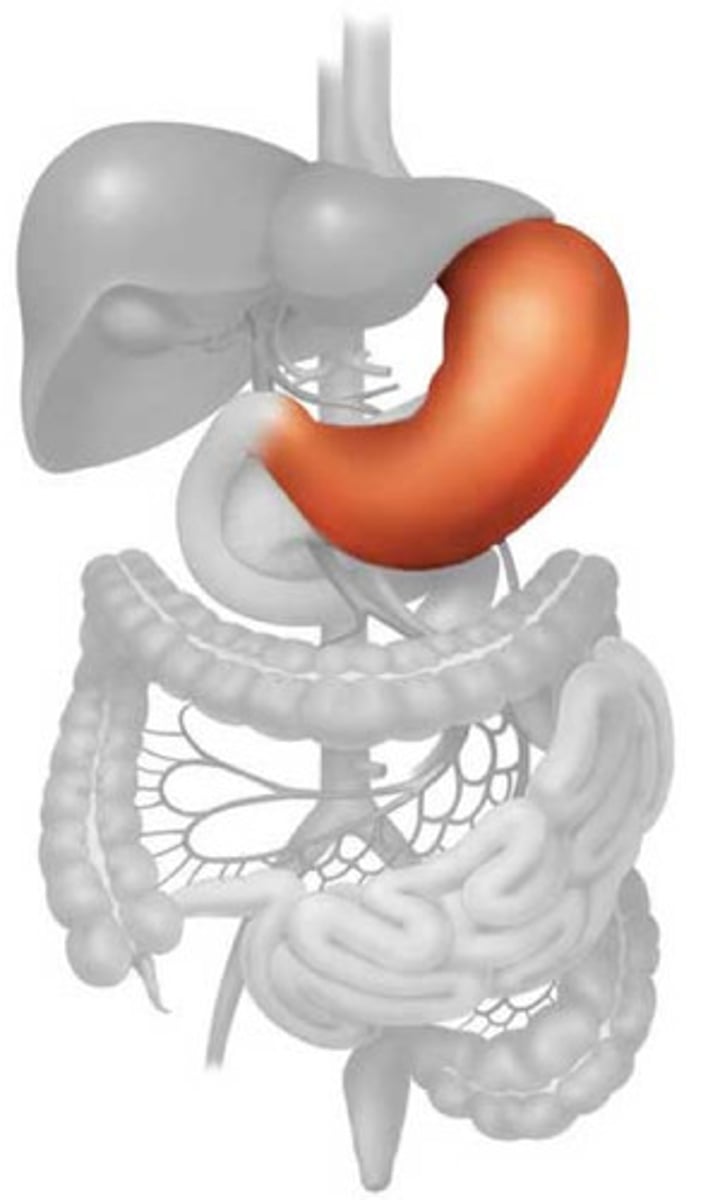
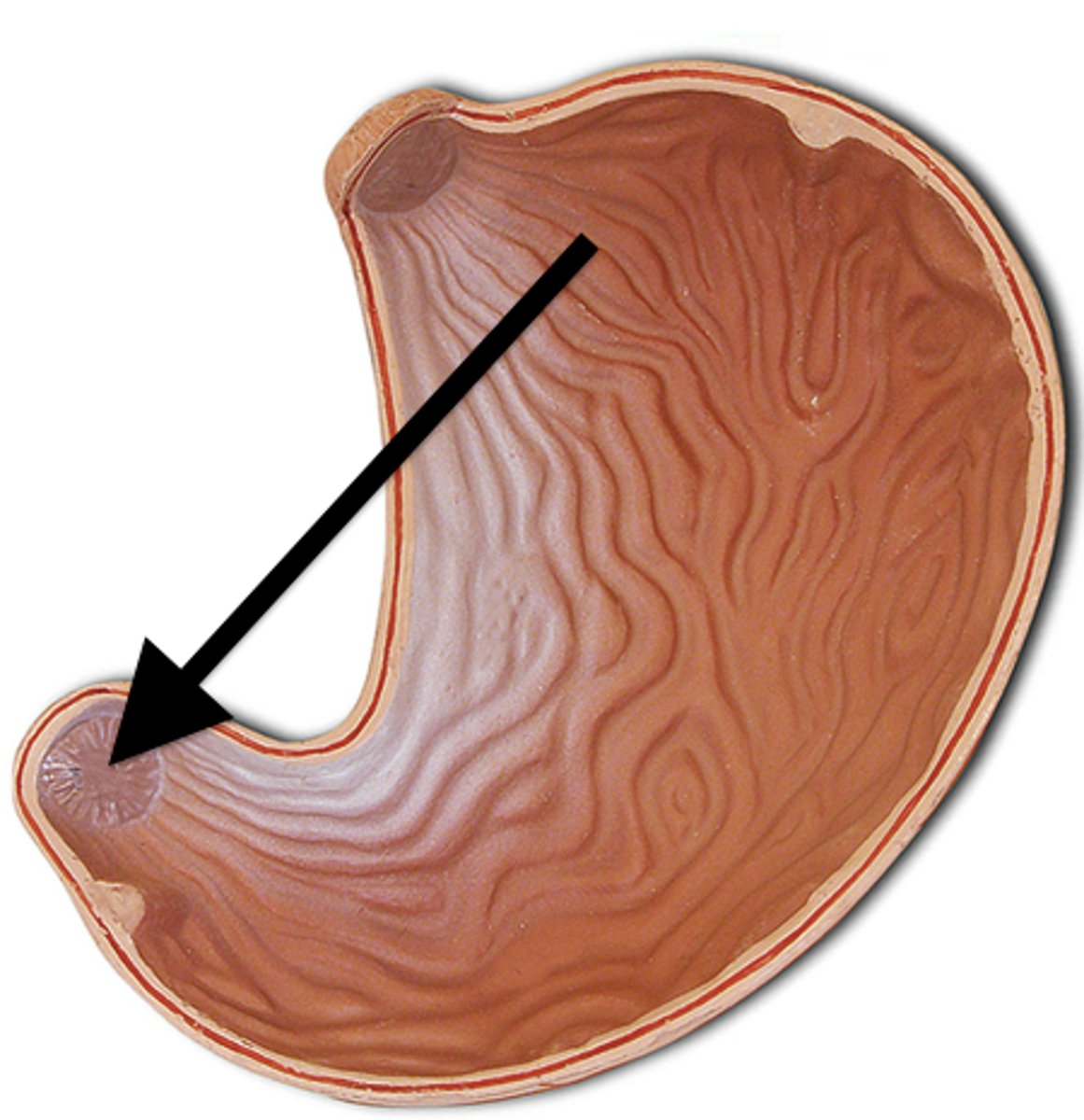
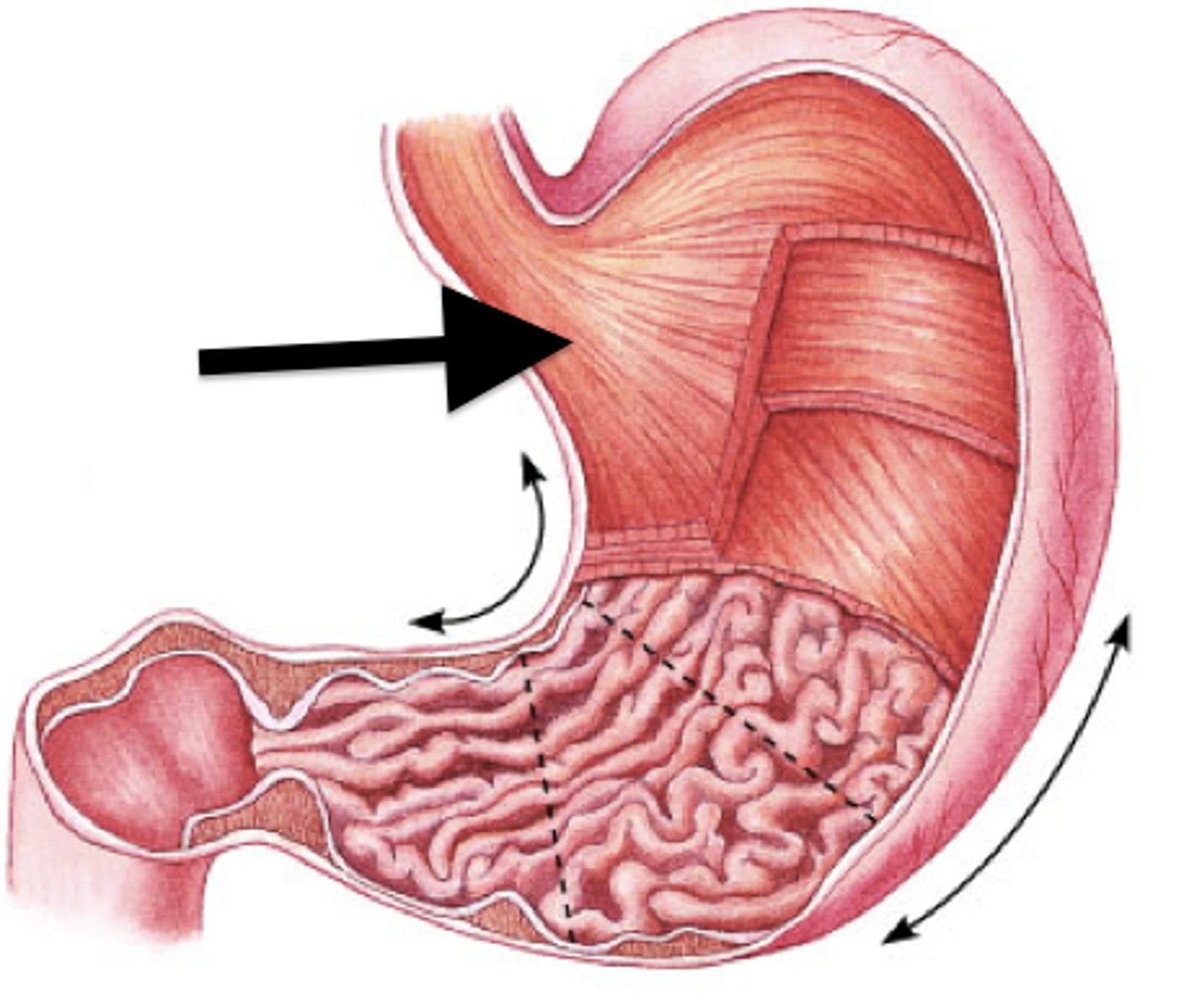
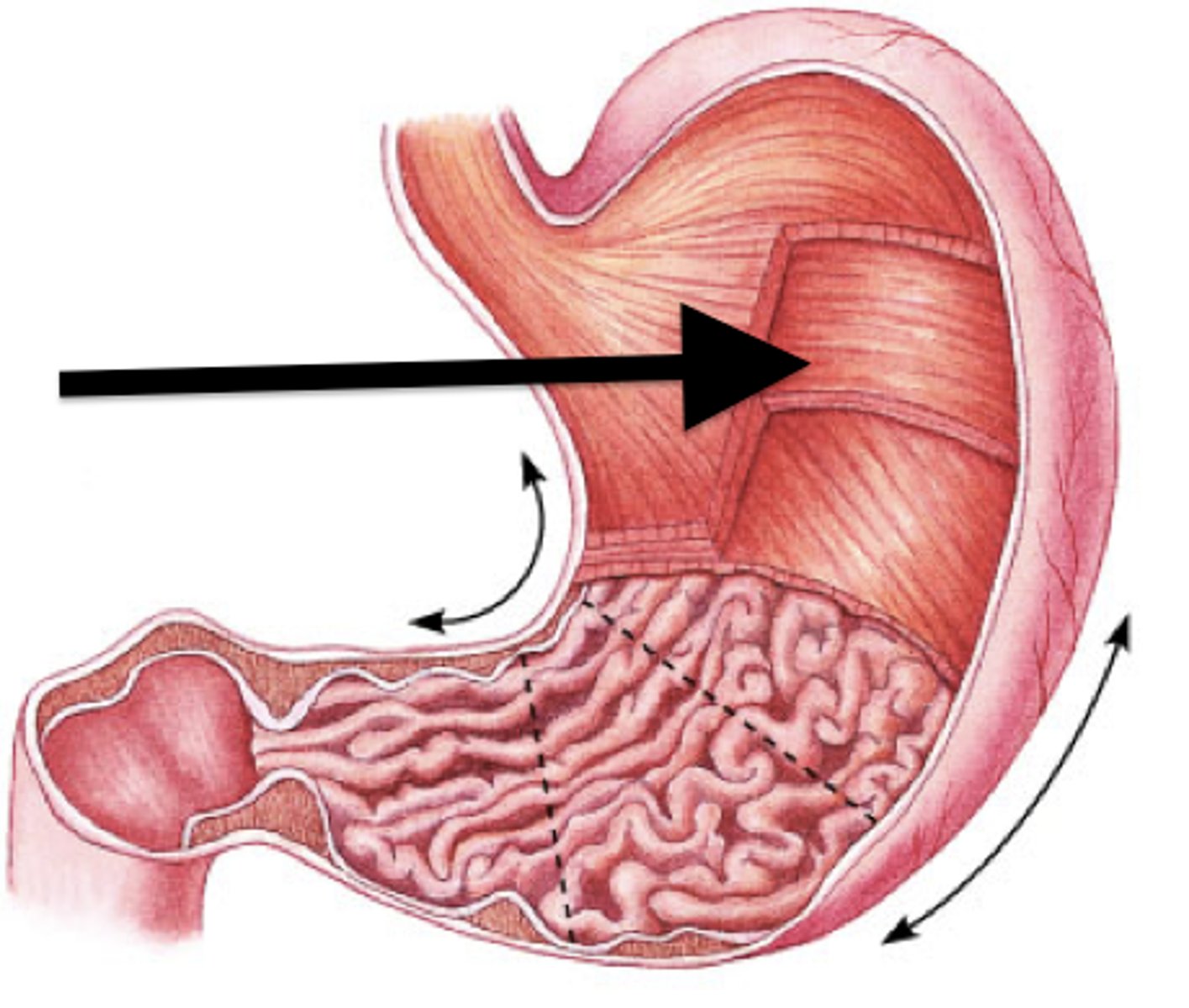
Stomach
A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat. Consists of mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa
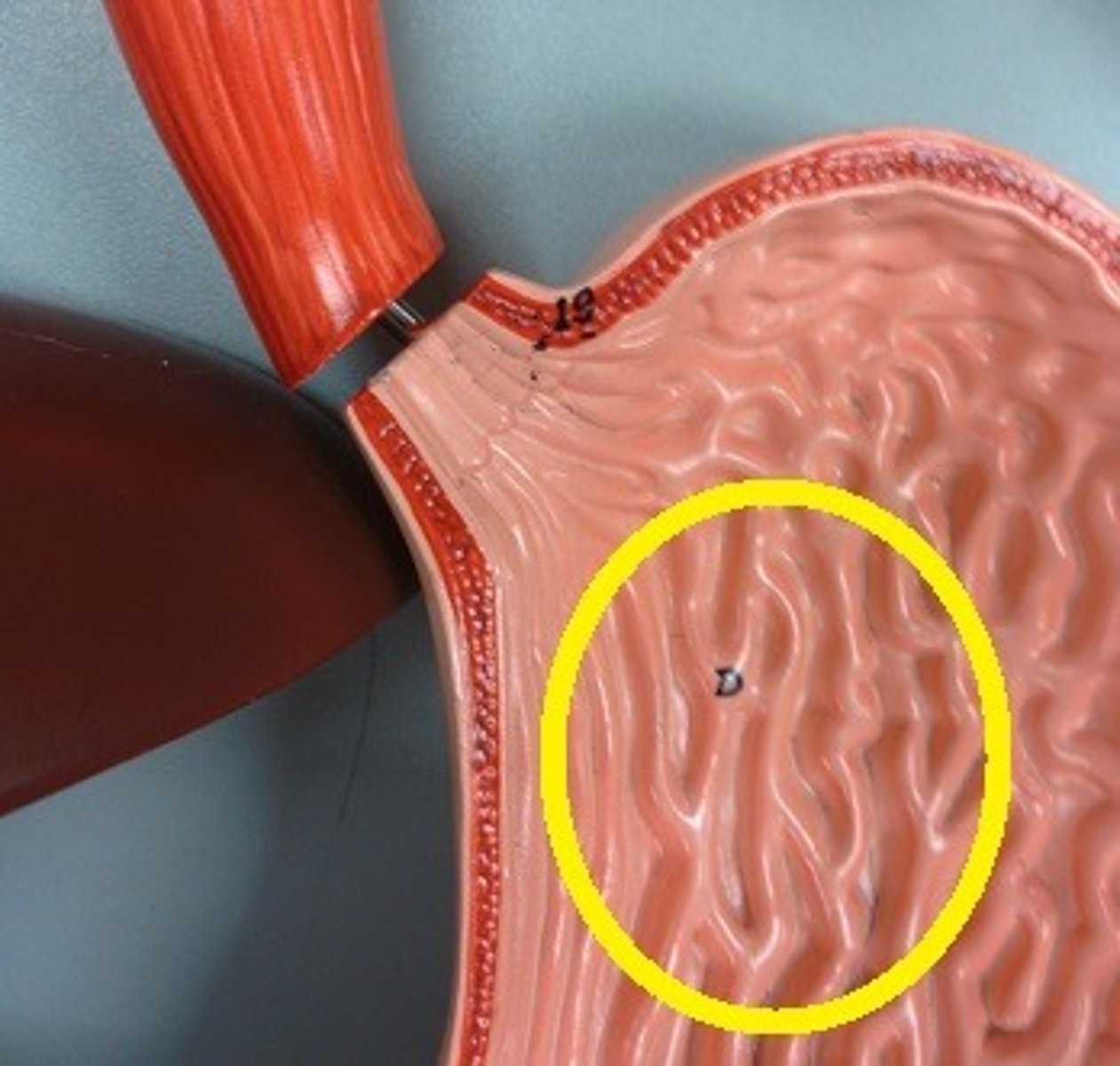
Rugae
the folds in the mucosa lining the stomach
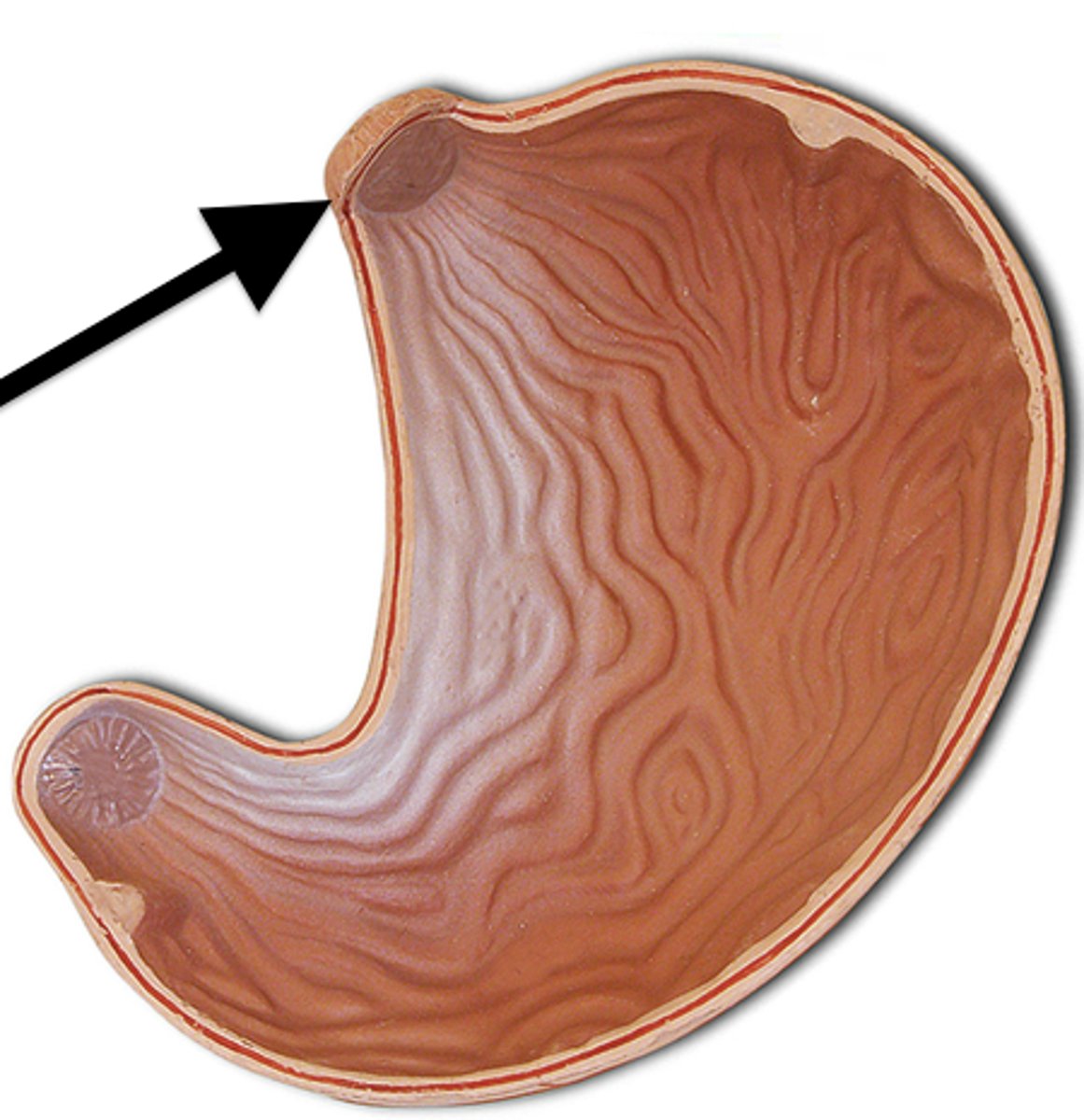
Cardiac sphincter
circular muscle located at the base of the esophagus and functions to prevent food materials from entering or leaving the esophagus from the stomach
Pyloric sphincter
ring of muscle that guards the opening between the stomach and the duodenum
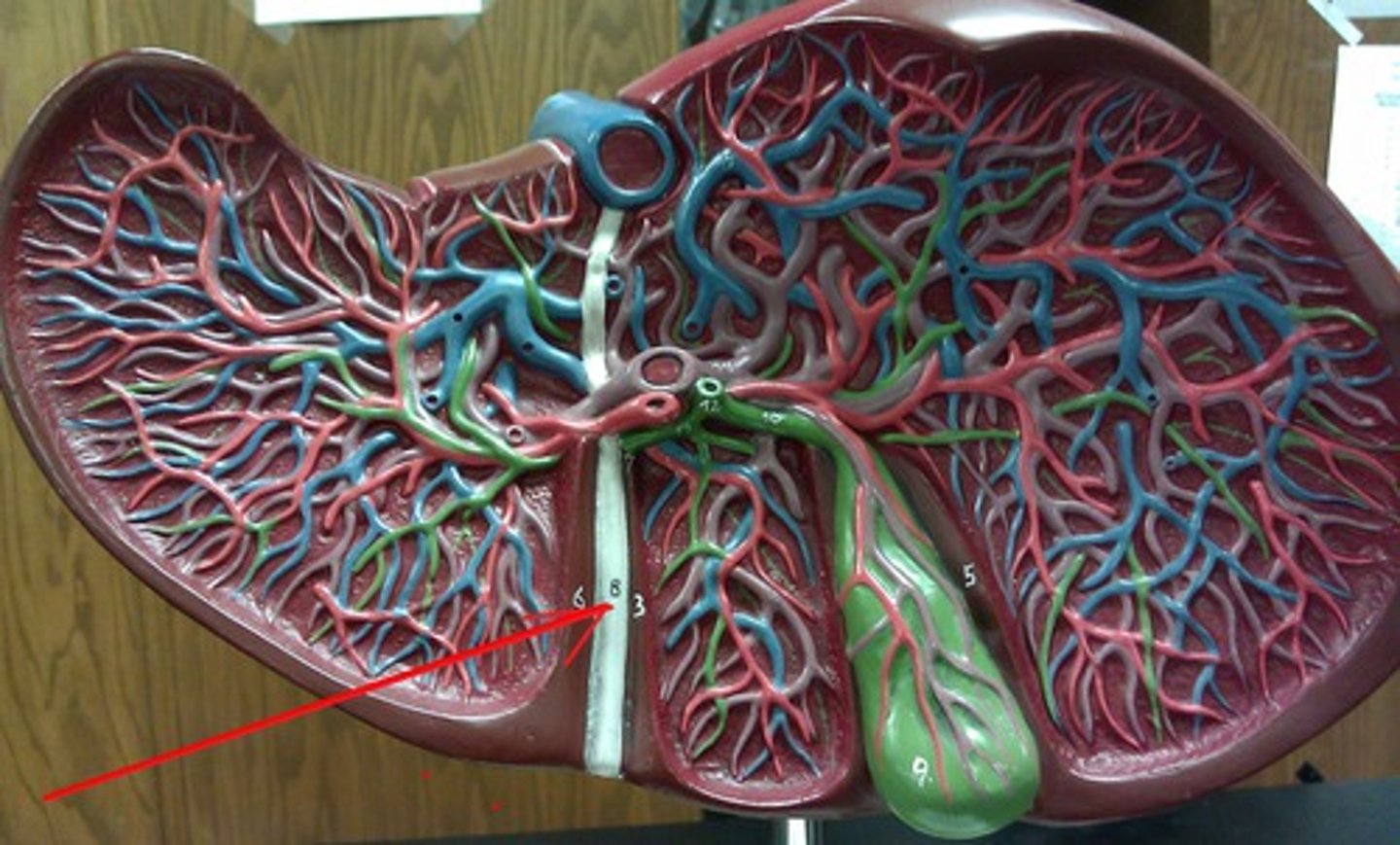
Liver
A large organ located in the upper abdomen (RUQ), this organ has 4 major lobes, and functions to filter blood, metabolize drugs, stores nutrients such as vitamins and minerals and glucose in the form of glycogen, produces Bile, and synthesizes proteins, process hemoglobin, regulates blood sugar levels, immune functions.
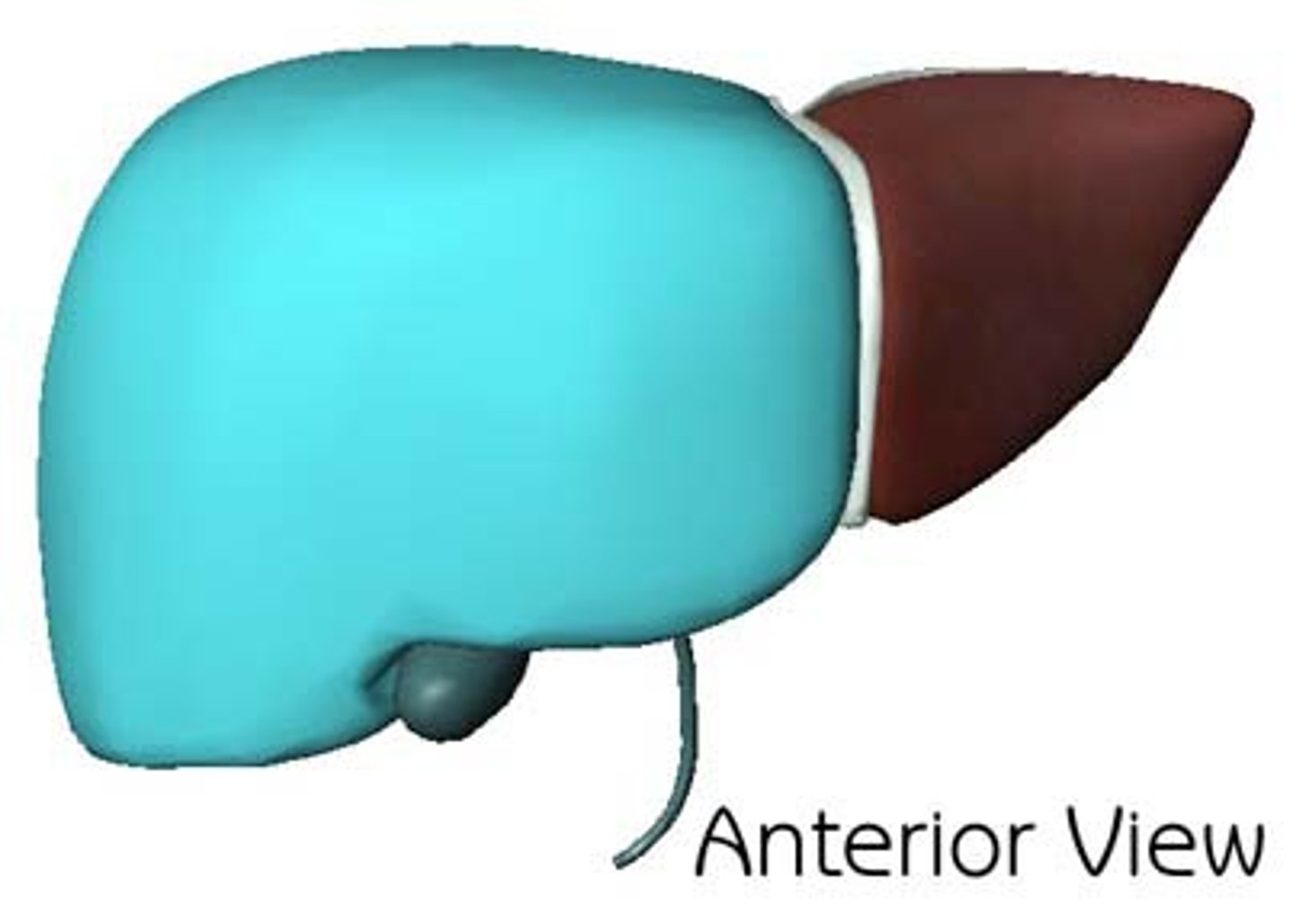
Right lobe
The largest lobe of the liver, separated from the left lobe above and in front by the falciform ligament, and separated from the caudate and quadrate lobes by the sulcus for the vena cava and by the fossa for the gallbladder.
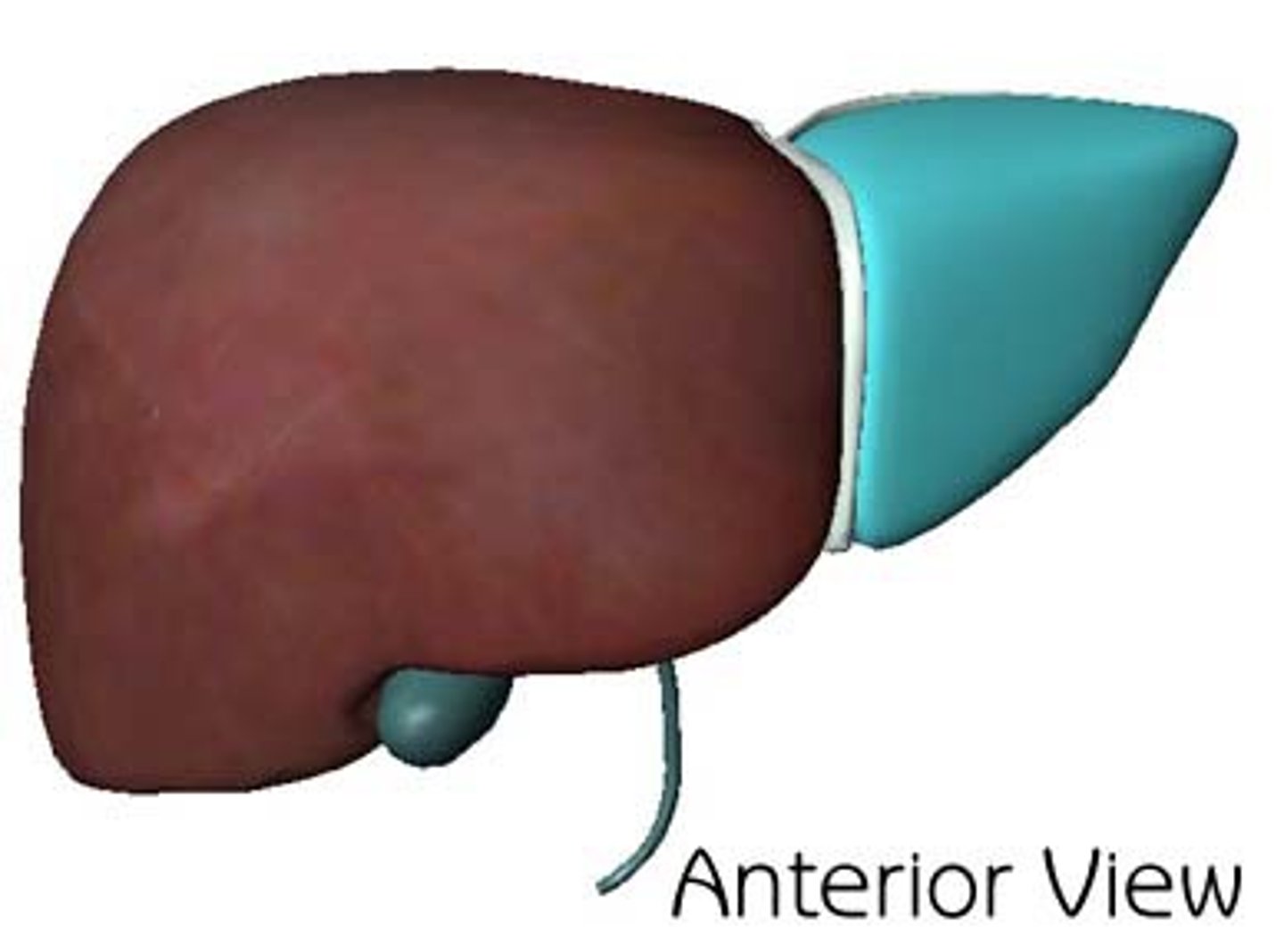
Left lobe
smaller lobe of liver
Caudate lobe
smallest lobe of the liver situated on the posterosuperior surface of the left lobe; the ligamentum venosum is the anterior border (located posteriorly to the quadrate lobe)
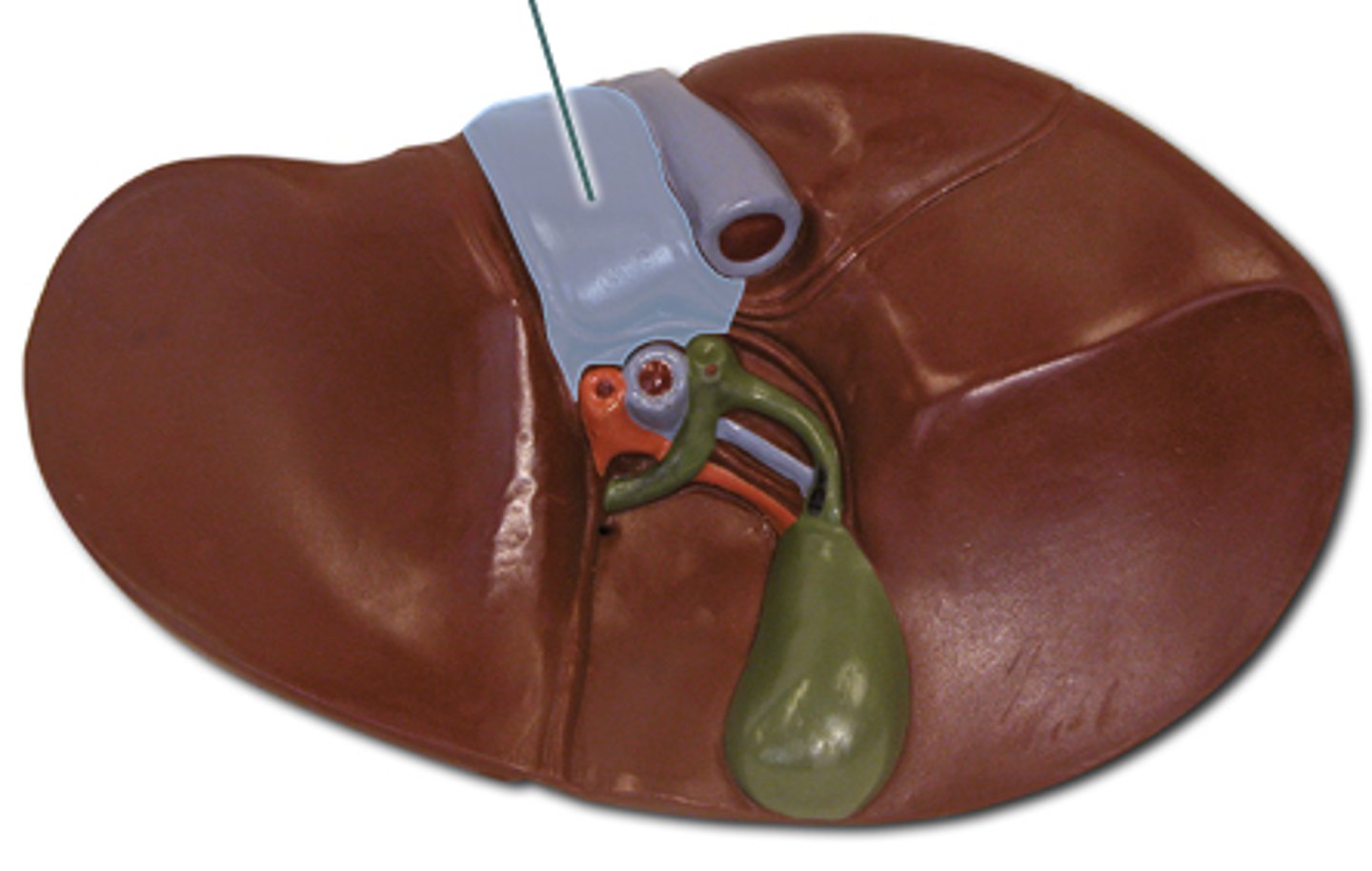

Quadrate lobe
square like lobe located in between the gallbladder and left lobe.
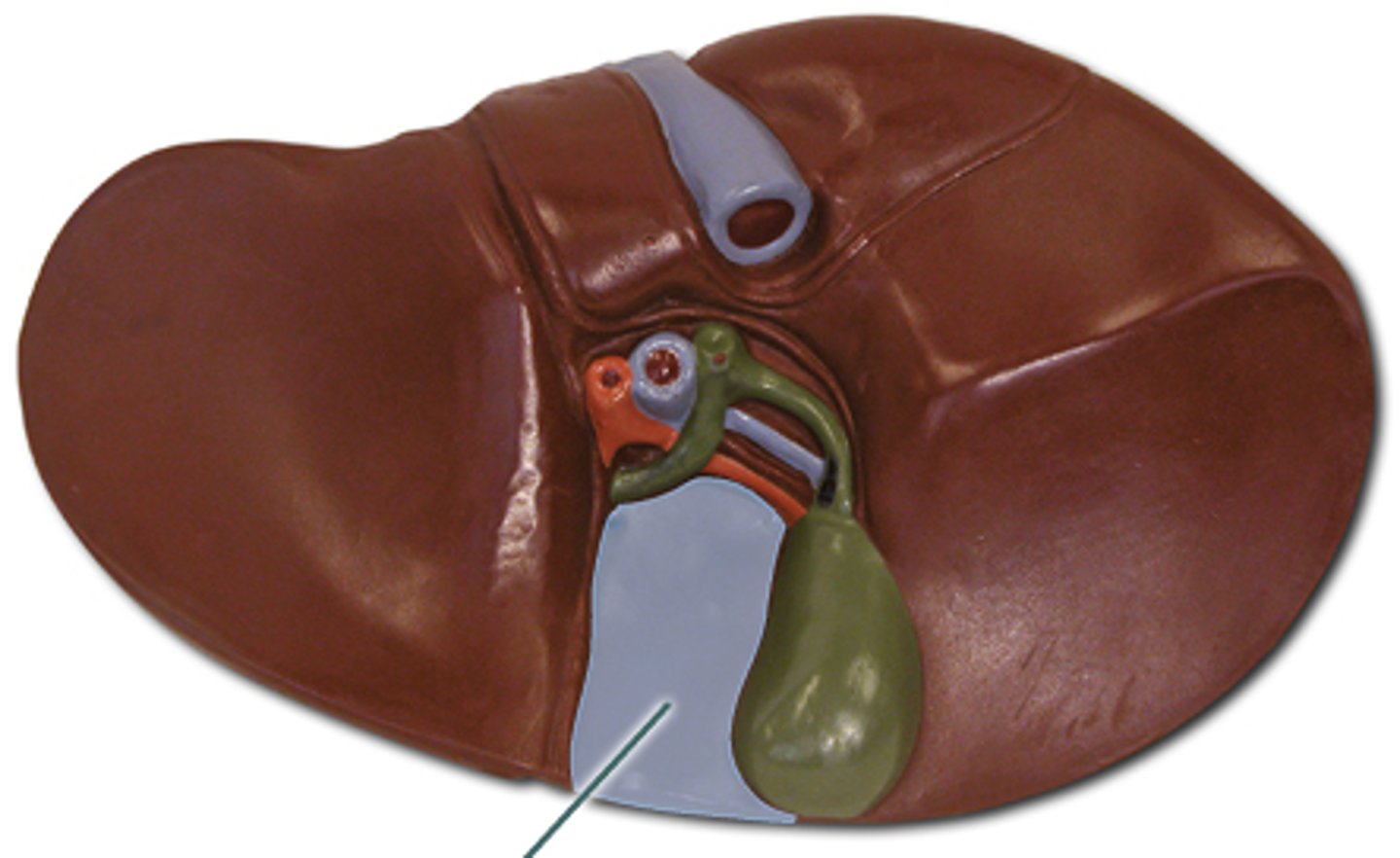
Round ligament/ligamentum teres
A ligament that forms part of the free edge of the falciform ligament of the liver. It connects the liver to the umbilicus. It is the remnant of the left umbilical vein. located on the inferior side of the liver in-between the left and quadrate lobe
Portal Triad
Comprised of the hepatic portal vein, proper hepatic artery, and common bile duct
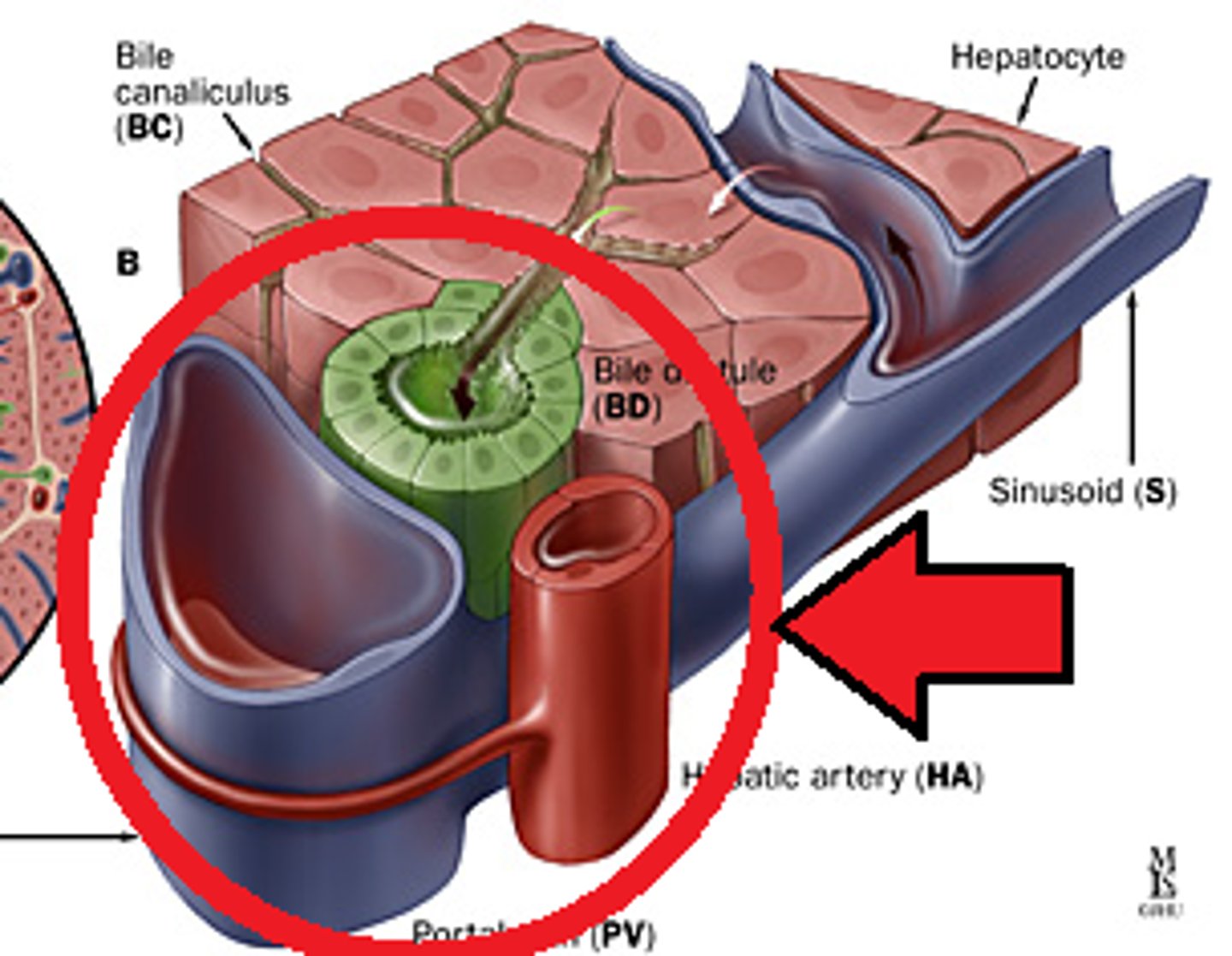
Hepatic portal vein
the vein that collects blood from the GI tract and conducts it to the liver
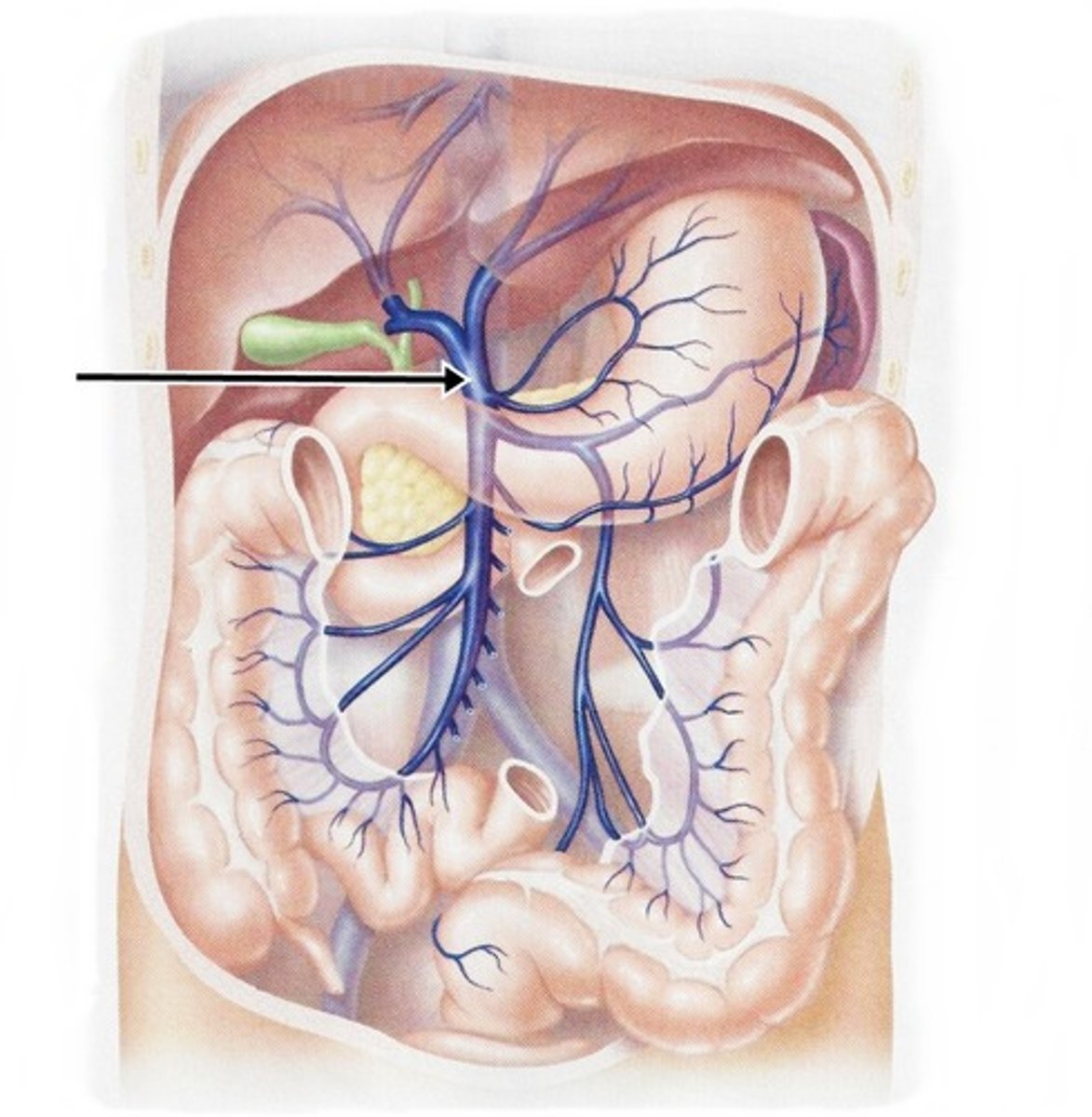
Proper Hepatic Artery (PHA)
Artery that supplies nutrients to the liver and gallbladder, branches off of the the common hepatic artery
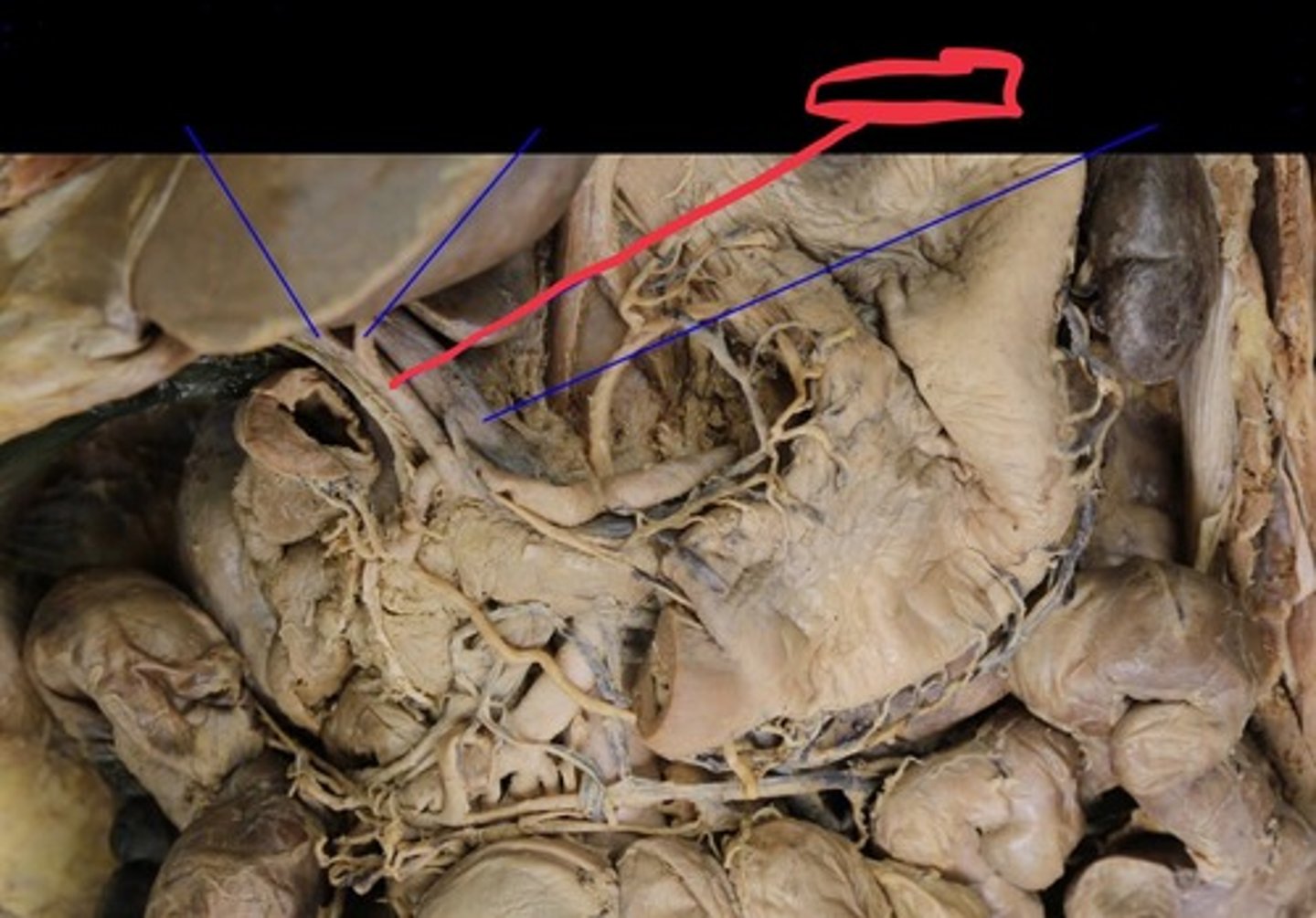
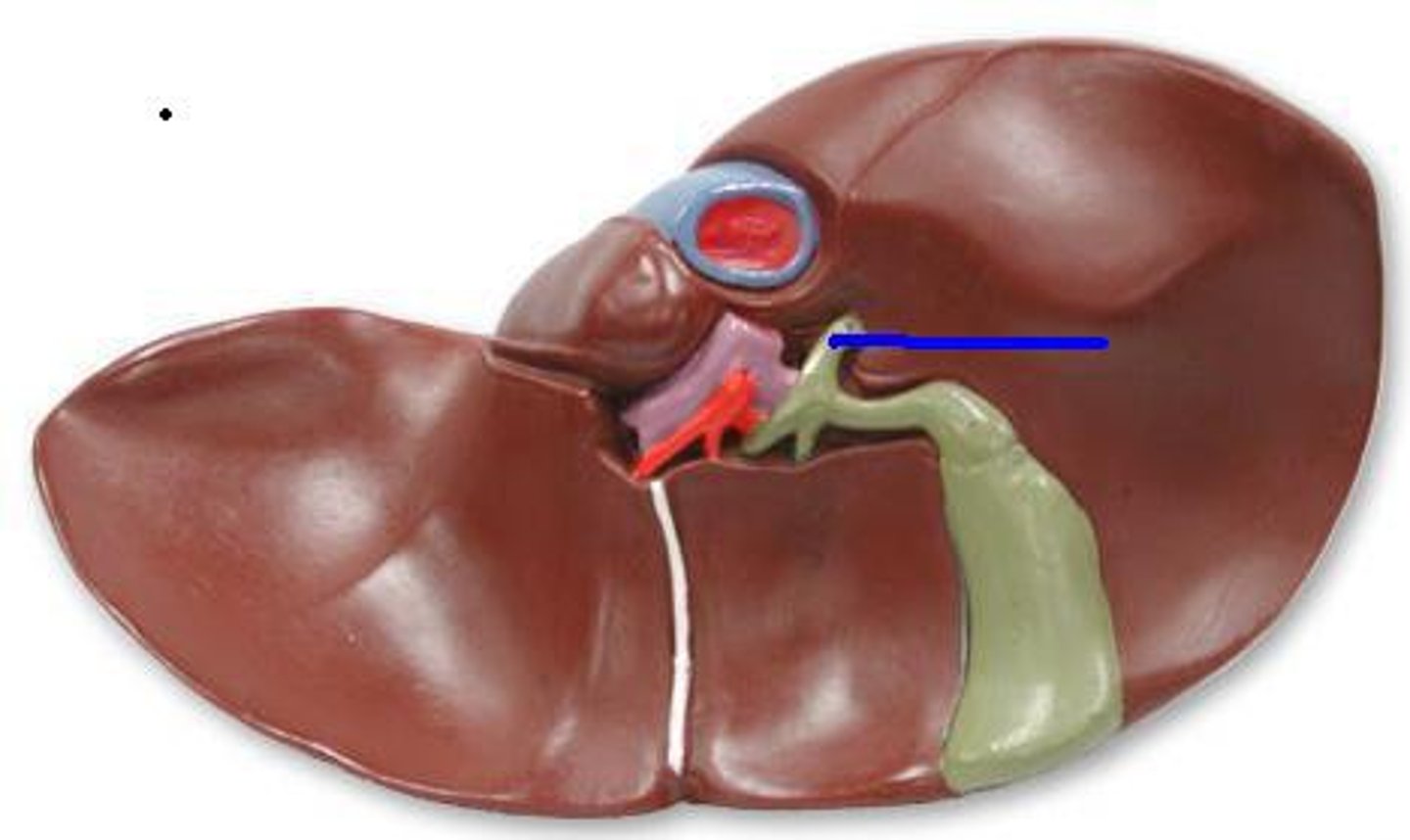
Common bile duct
Carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum. Also called the choledochus.
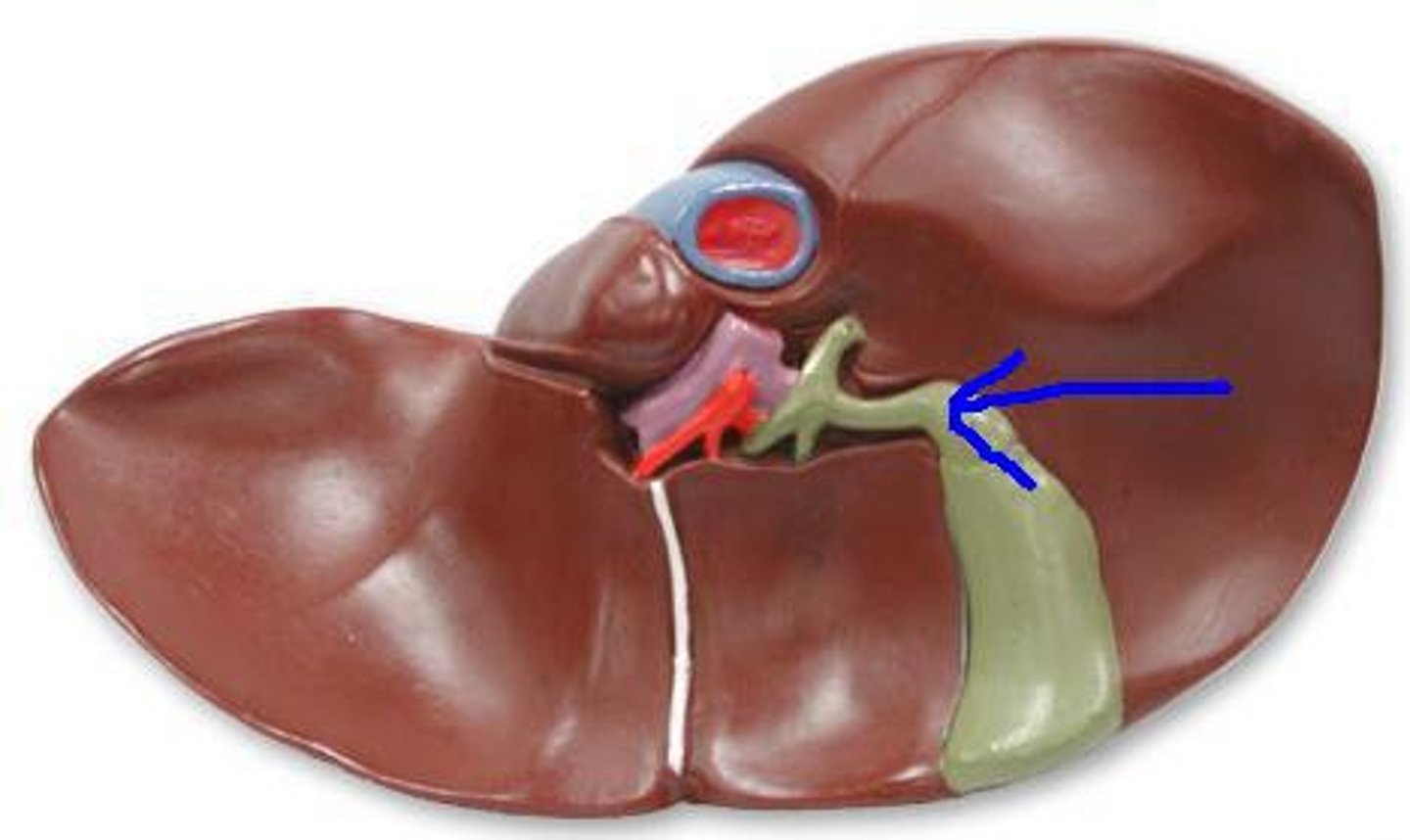
Cystic duct
a duct draining bile from the gallbladder; merges with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct
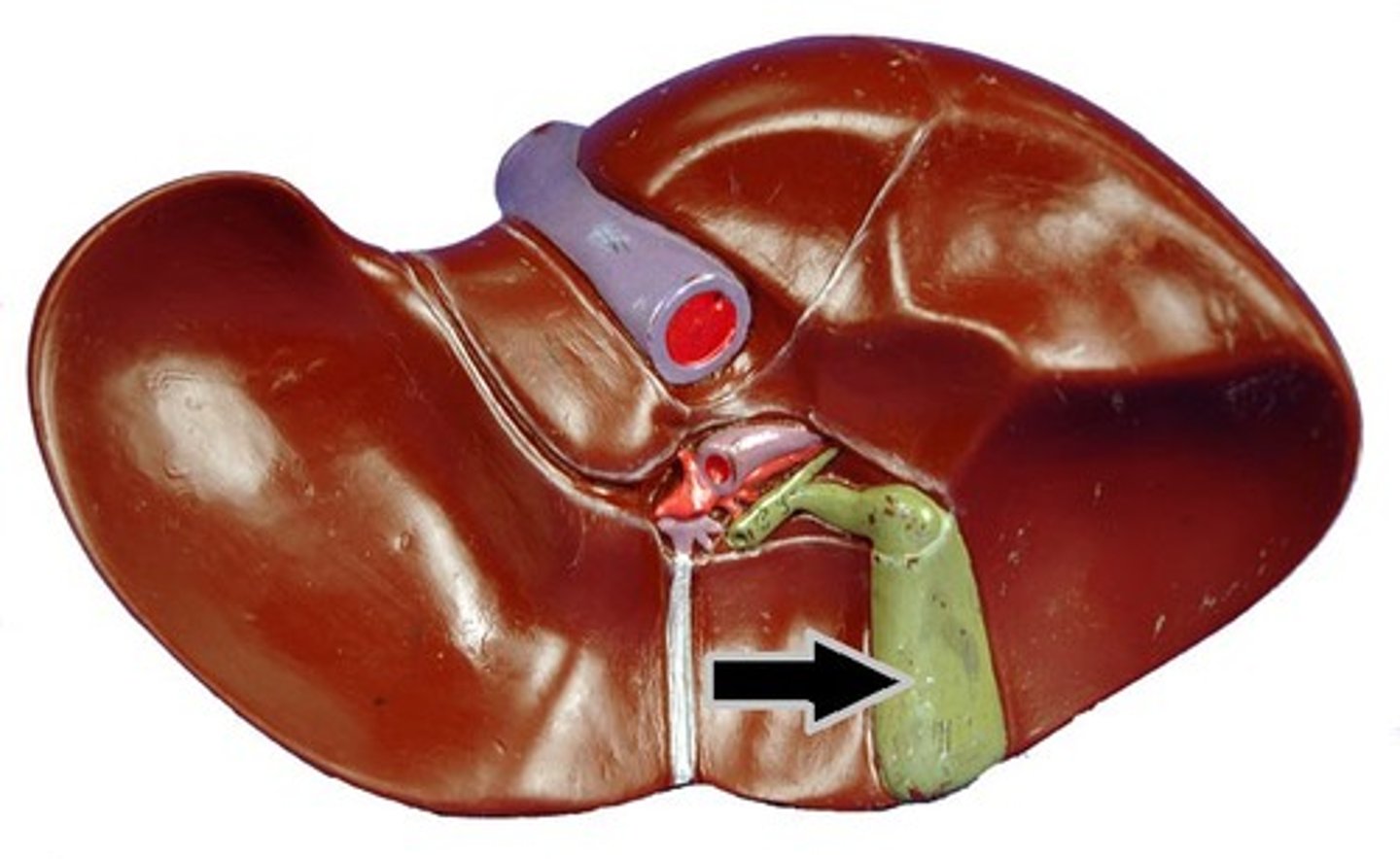
Common hepatic duct
large bile duct leading from liver; joins with the cystic duct to form the common bile duct
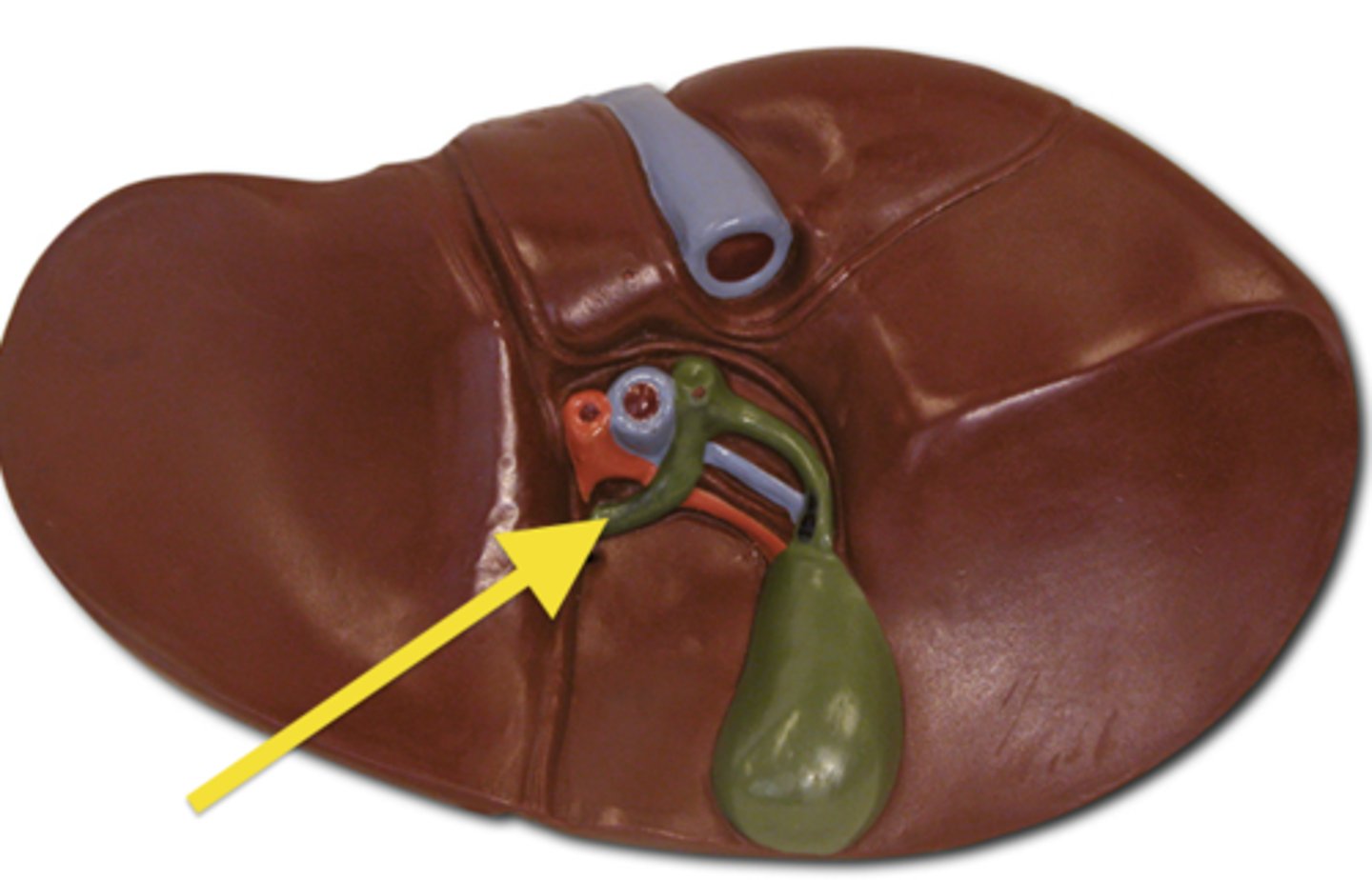

Gallbladder
A muscular sac attached to the liver that secretes bile and stores it until needed for digestion
Pancreas
An organs in the abdominal cavity with two roles. The first is an exocrine role: to produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are delivered to the small intestine via the pancreatic duct. The second is an endocrine role: to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
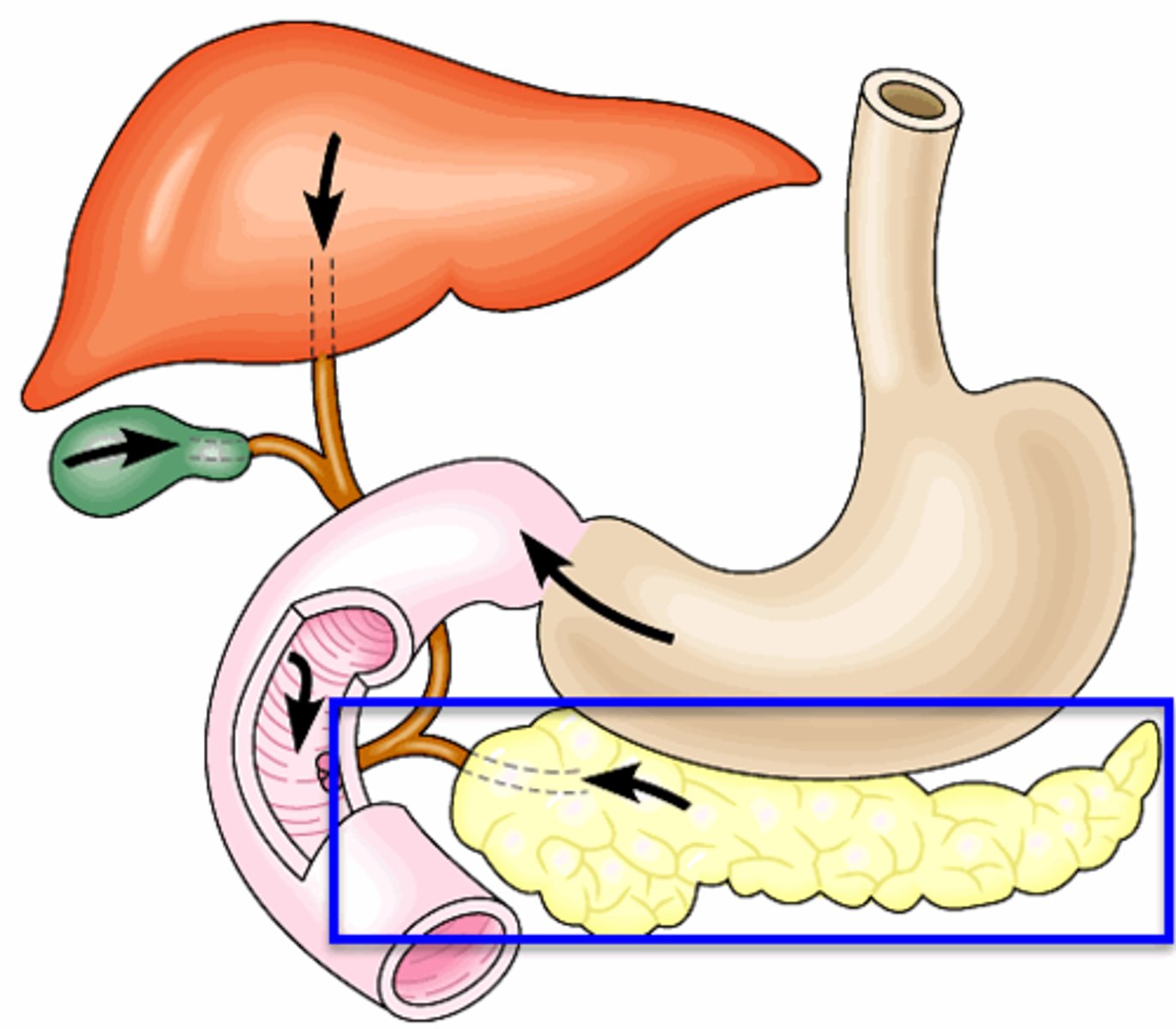
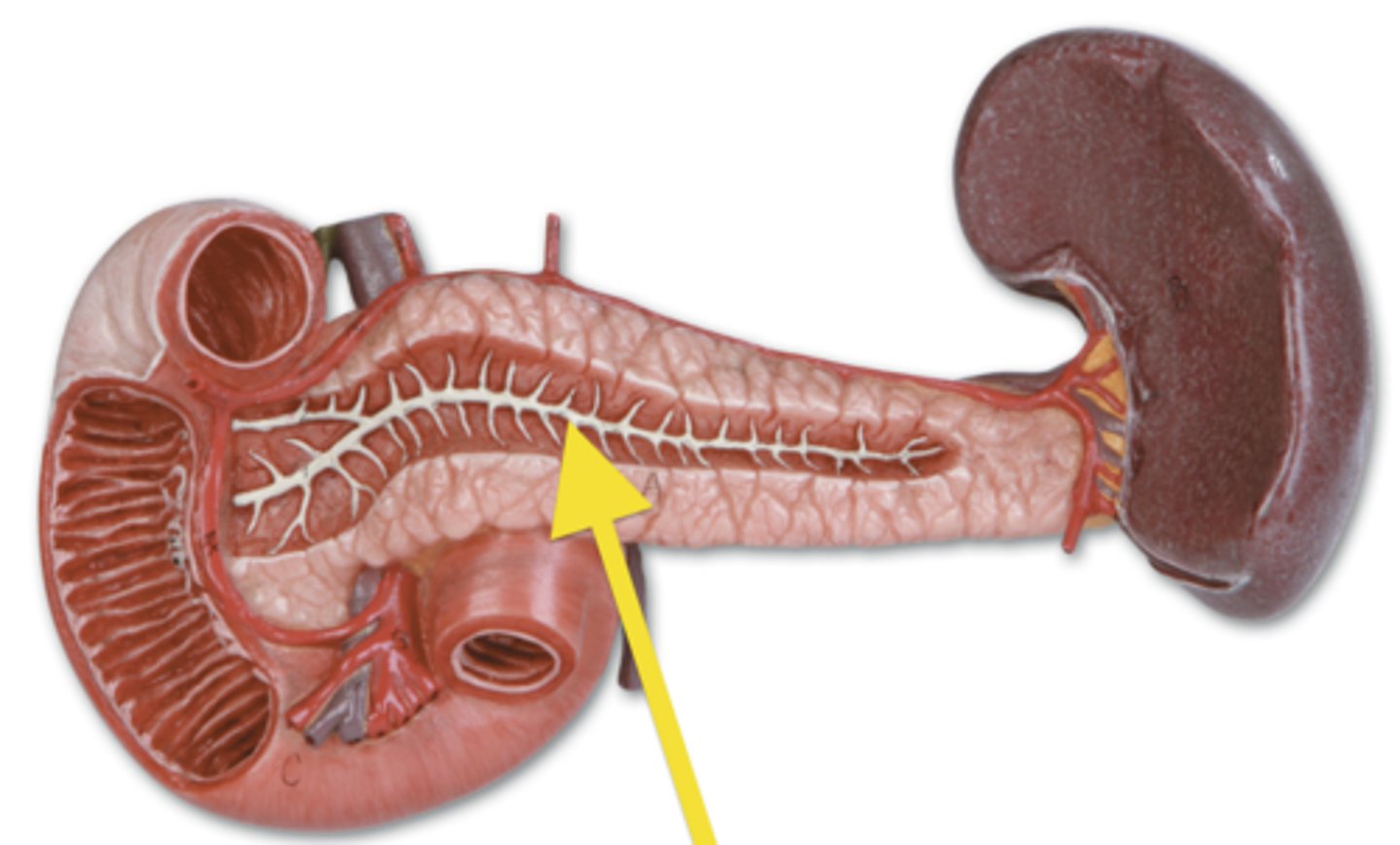
Pancreatic duct
The main duct of the pancreas. The pancreatic duct carries the exocrine secretions of the pancreas (enzymes and bicarbonate) to the small intestine (dueodenum).
Greater/Major duodenal papilla
a rounded projection in the duodenum into which the common bile duct and pancreatic duct drain
Small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place, has 3 distinct regions called the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Known as the longest intestine.
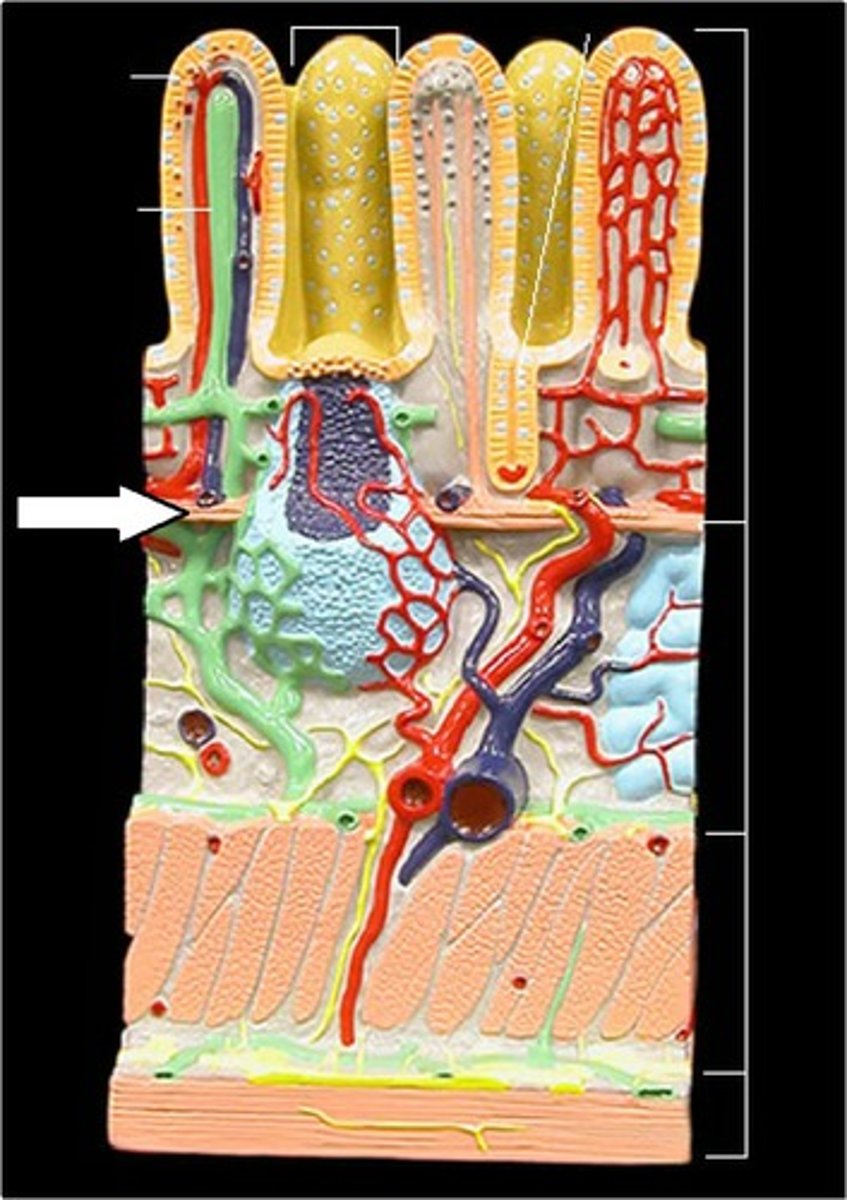
Villi
Fingerlike extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption
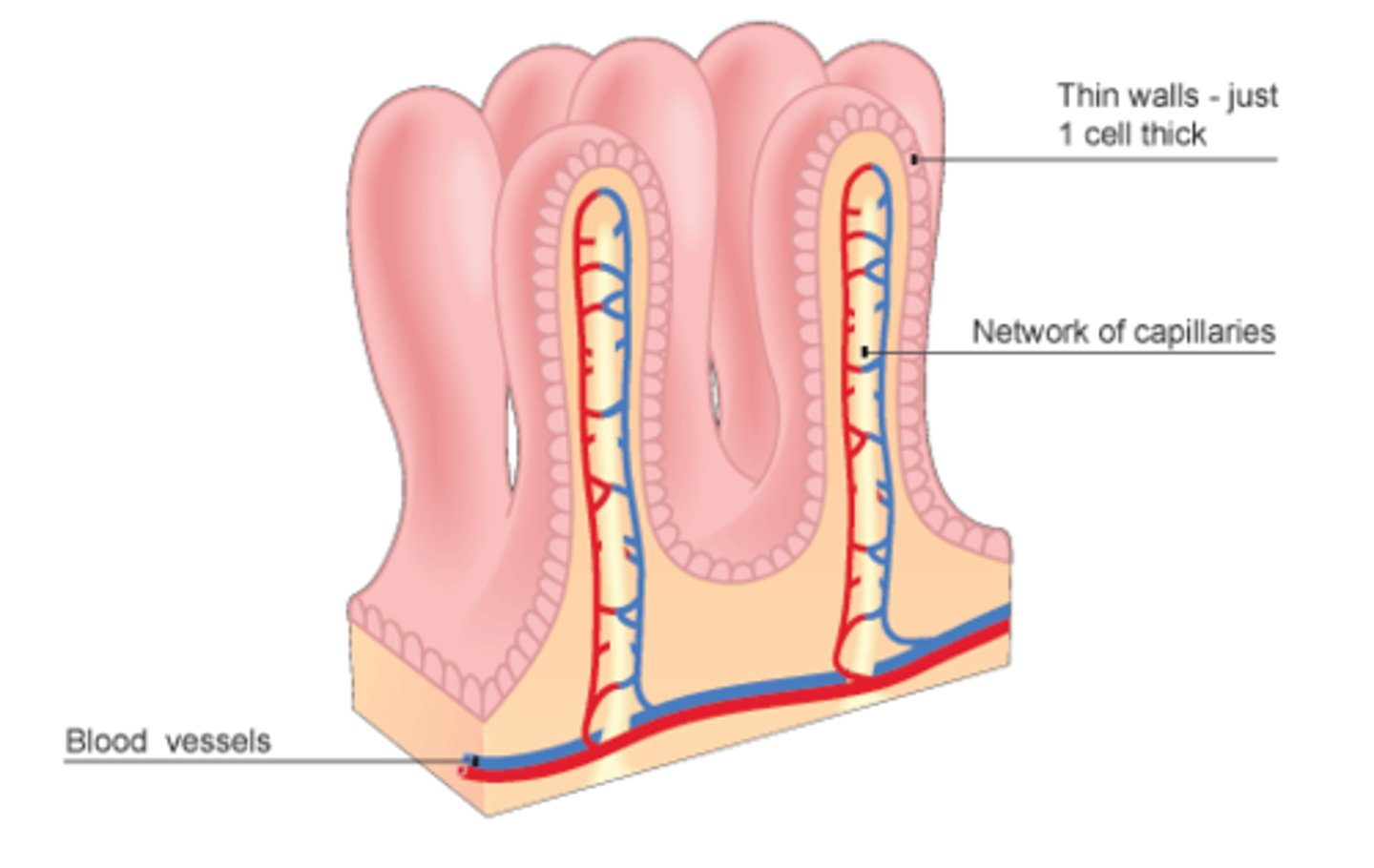
Lymphatic duct (small intestine)
lacteals in the small intestine's villi, play a crucial role in absorbing dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins

Intestinal Crypt/Crypts of Lieberkühn
invaginations in the intestinal lining between villi, containing stem cells and specialized cells that regenerate and maintain the intestinal epithelium
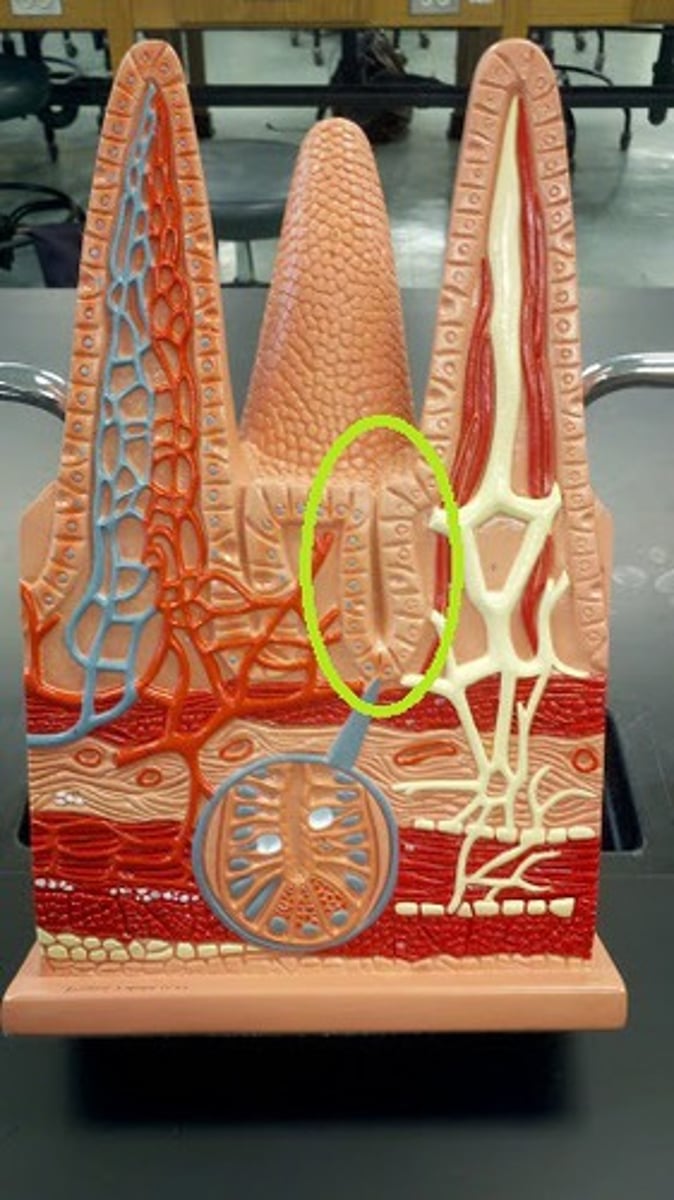

Longitudinal layer muscle
outer layer of smooth muscle that helps propel food through the gut
Circular layer muscle
inner layer which orients around the circumference of the canal
Muscularis mucosa
thin layer of smooth muscle,
tenses mucosa creating grooves and ridges that enhance surface area and contact with food,
improves efficiency of digestion and nutrient absorption
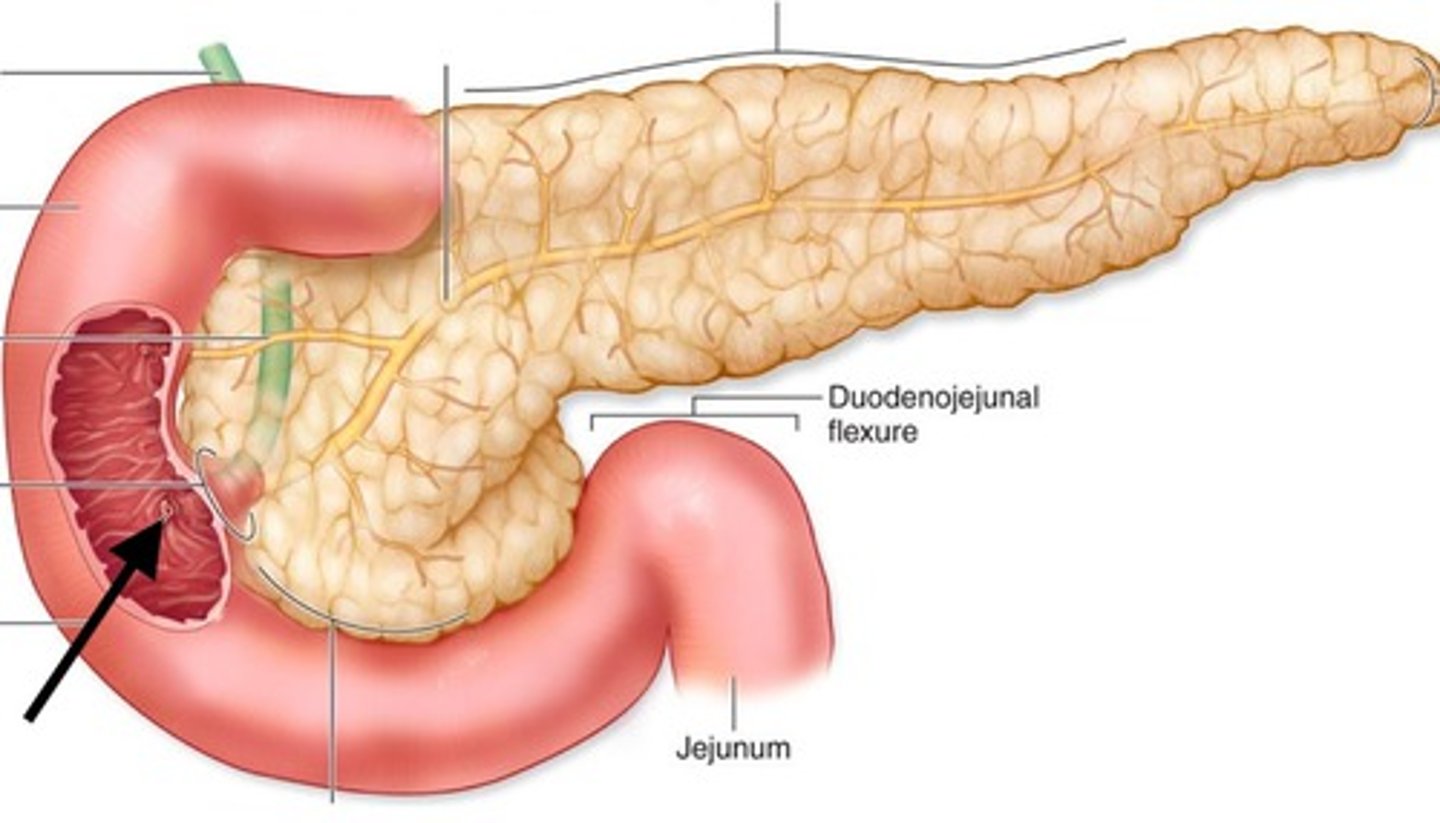
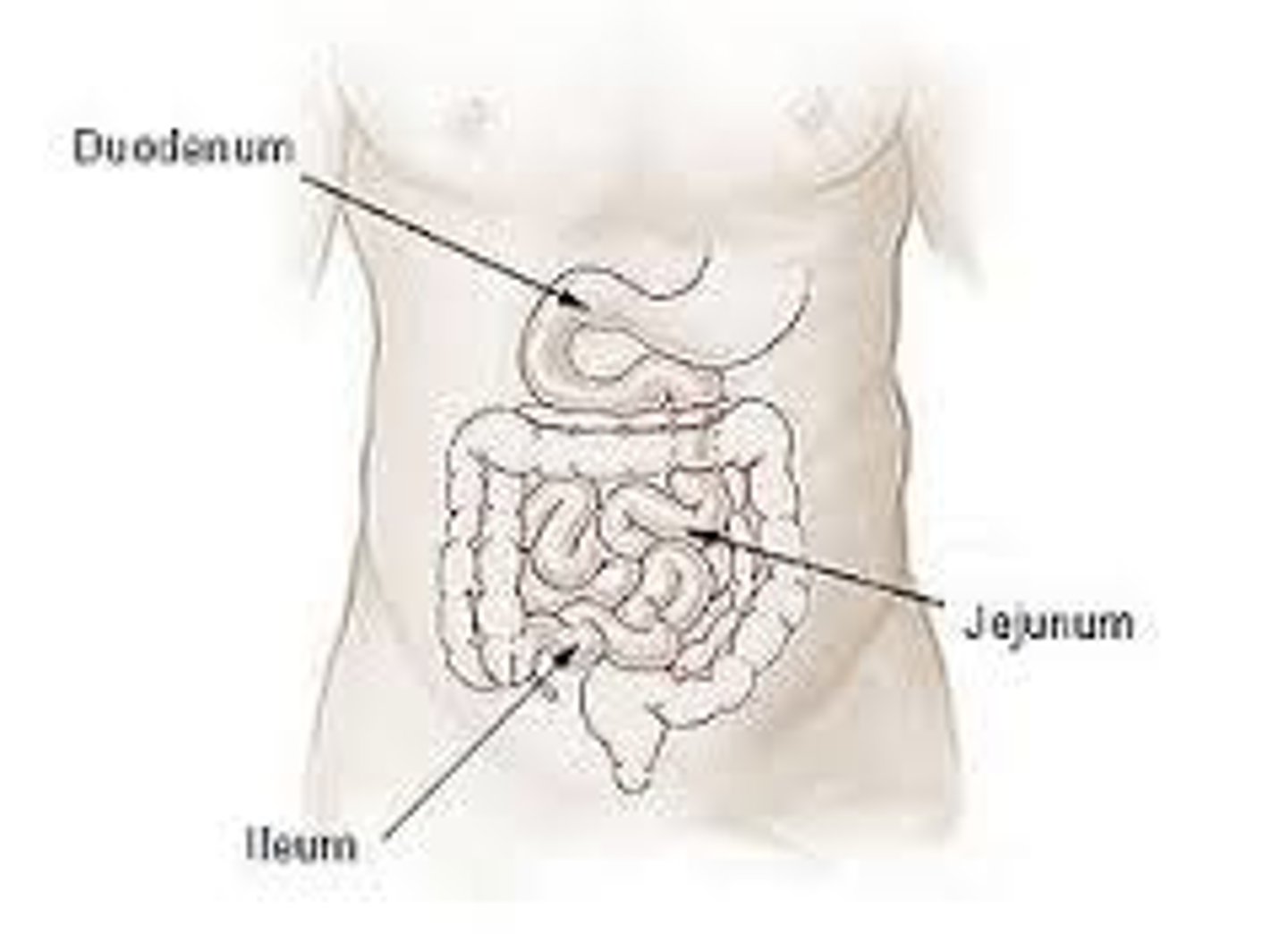
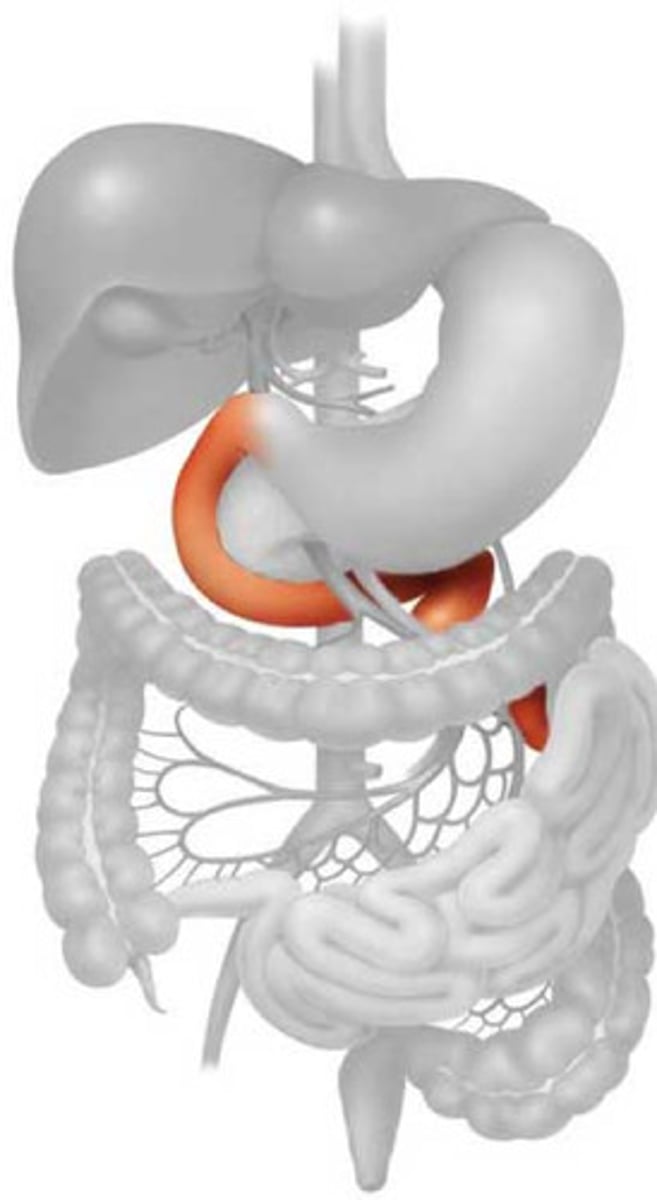
Duodenum
first portion of the small intestine
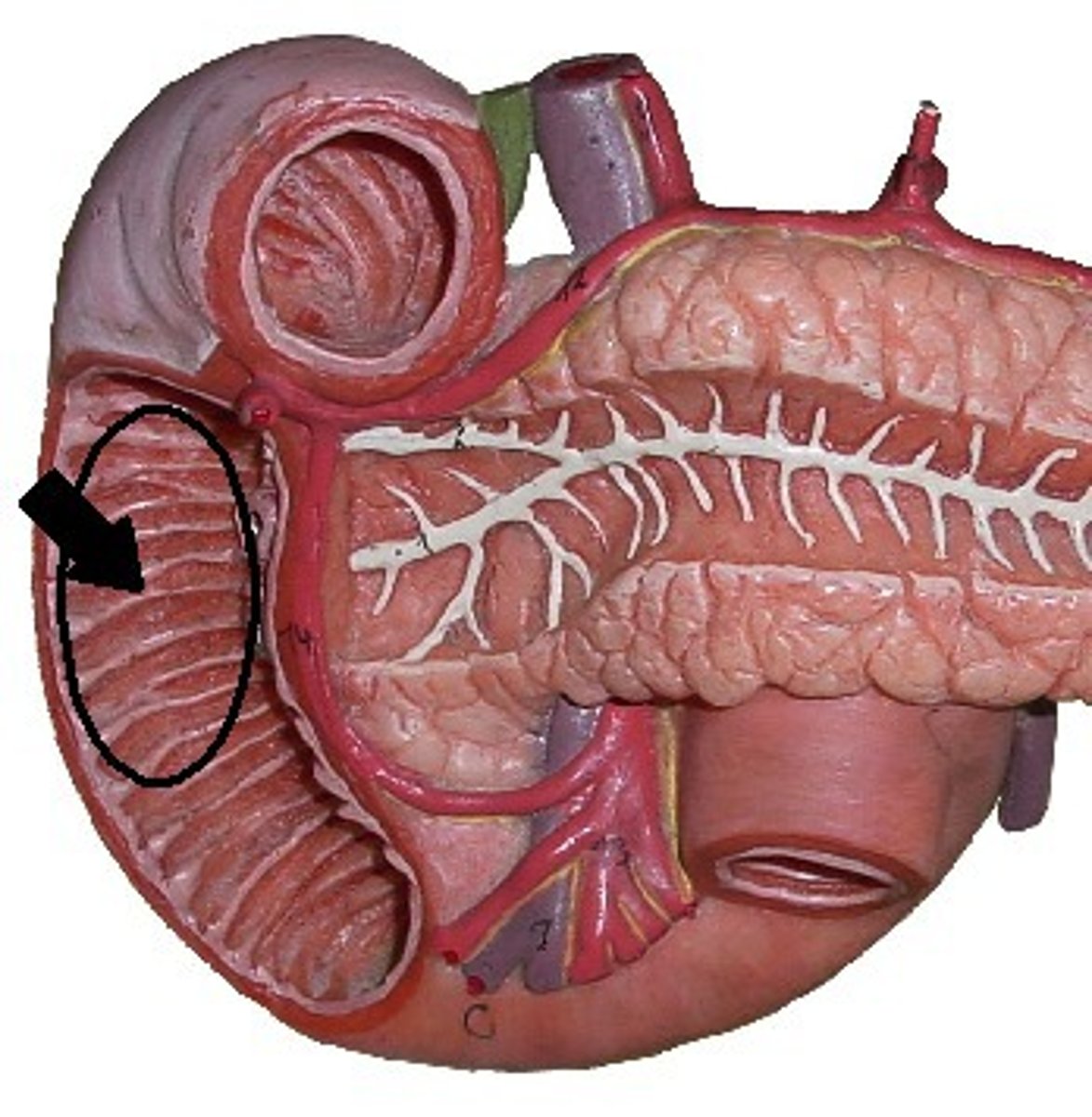
Plicae circulares
circular folds in small intestine
Jejunum
second part/ region of the small intestine (B)
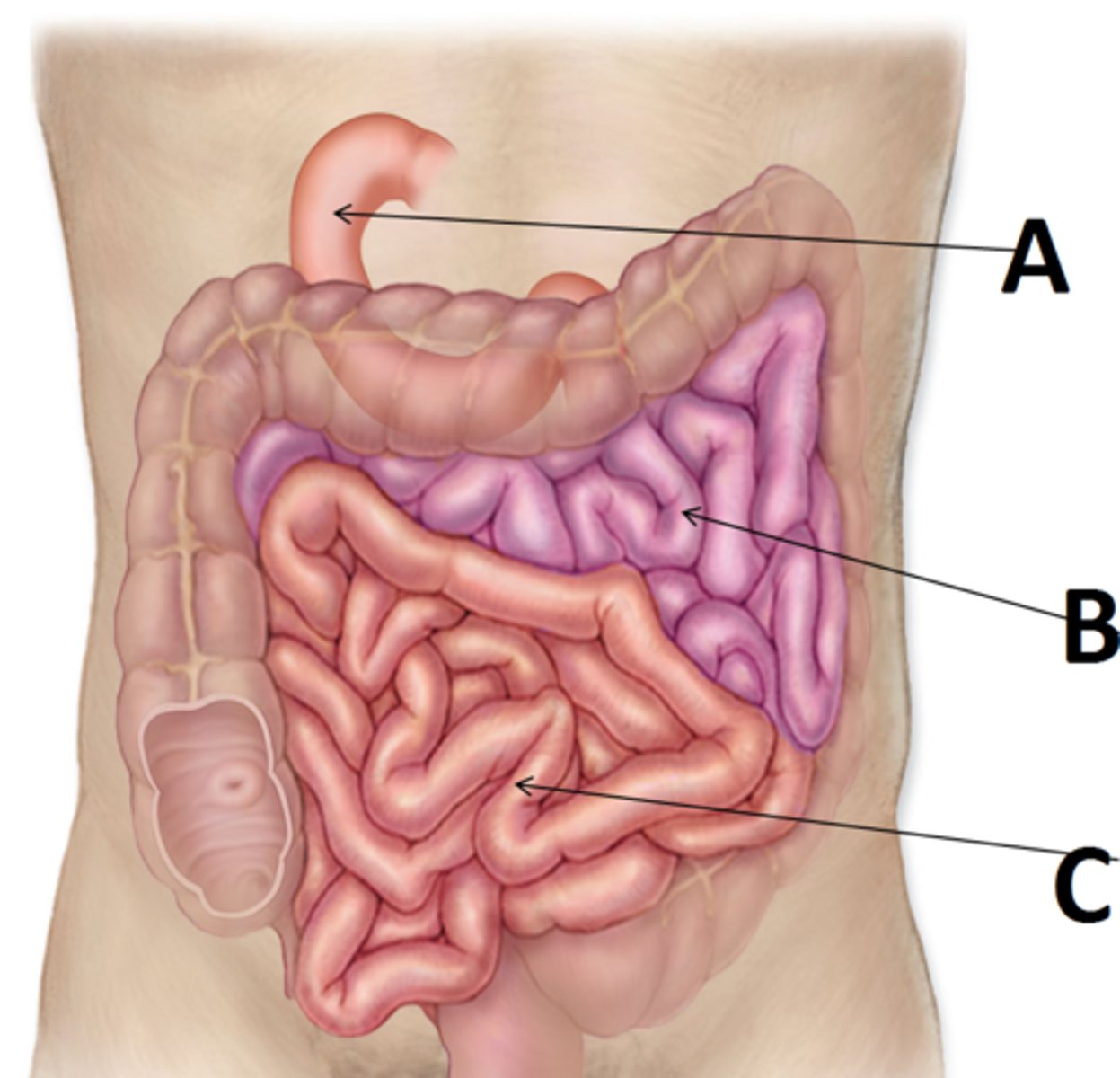
Ileum
the last and longest portion of the small intestine (C)
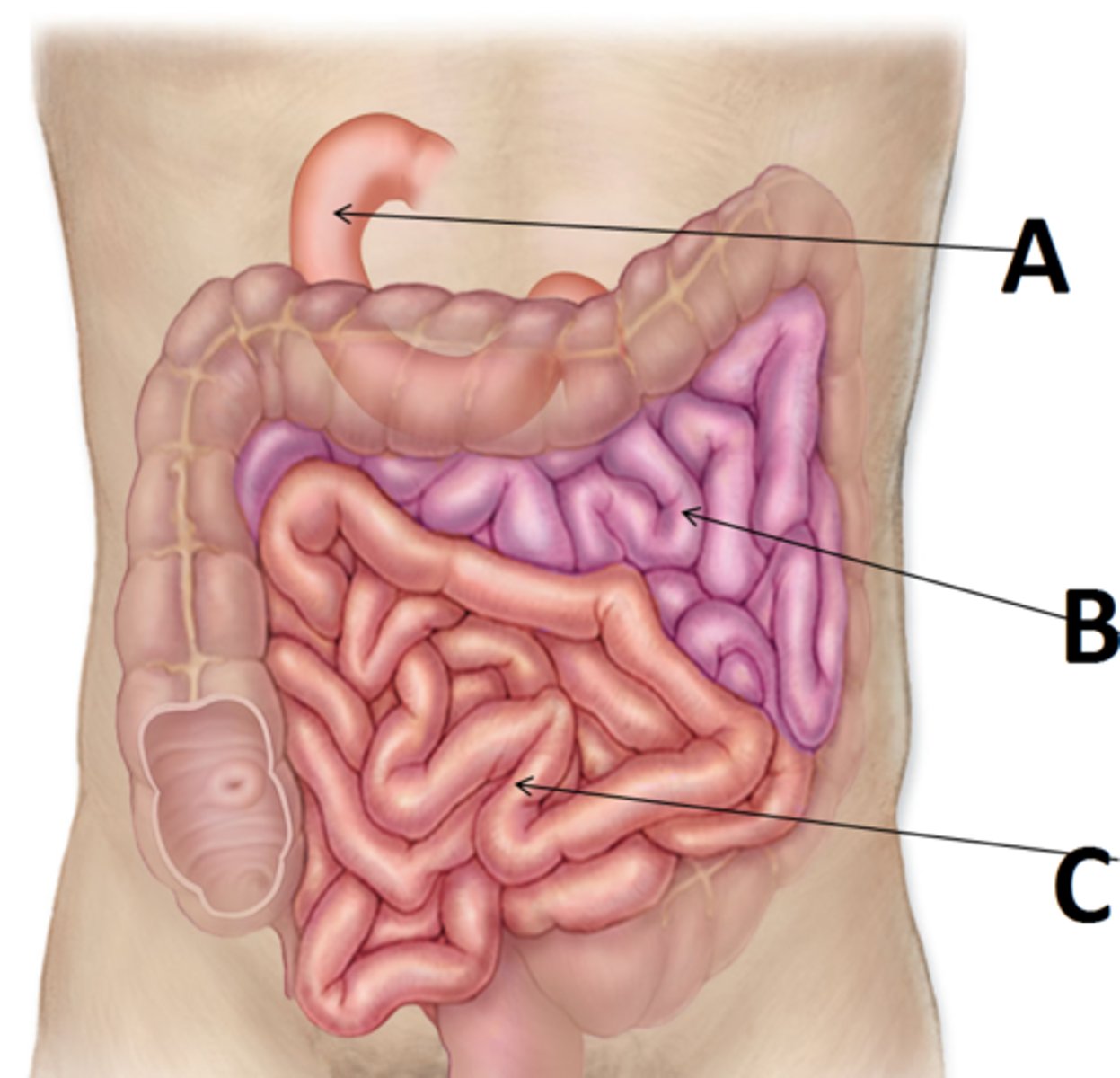
Ileocecal junction
the end of the small intestine where the ileum joins the cecum of the large intestine
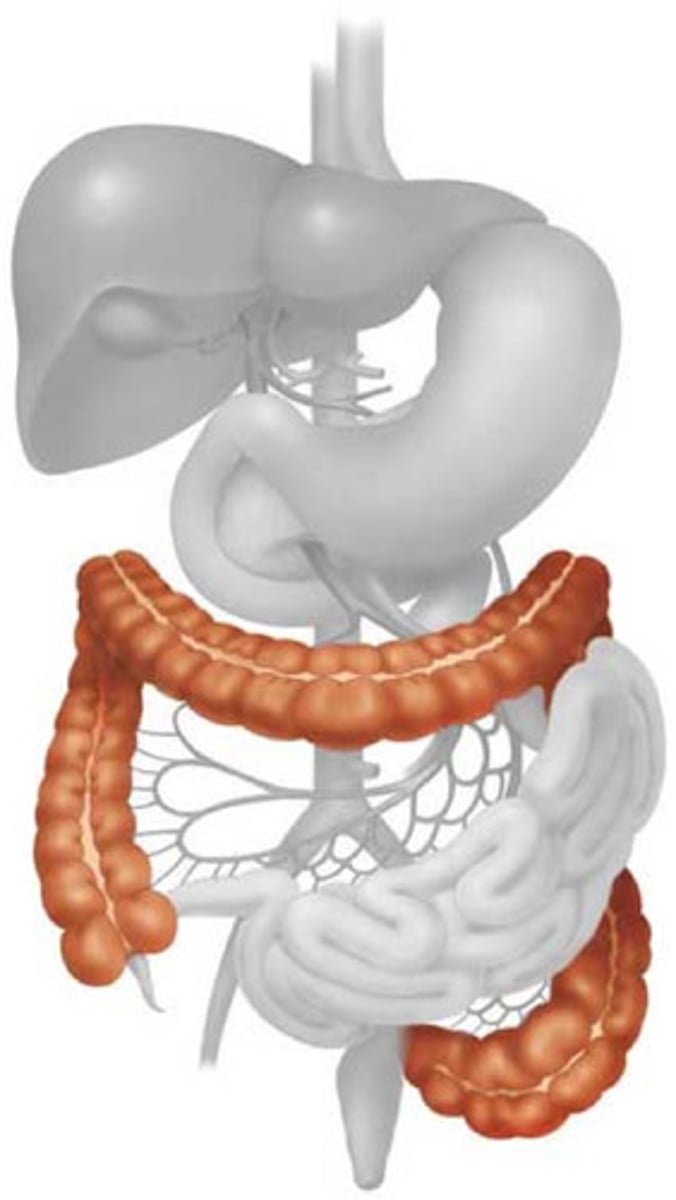
Large intestine/Colon
The long, tube-like organ that is connected to the small intestine at one end and the anus at the other. absorbing water and electrolytes, producing and absorbing vitamins, and forming and propelling feces toward the rectum for elimination.
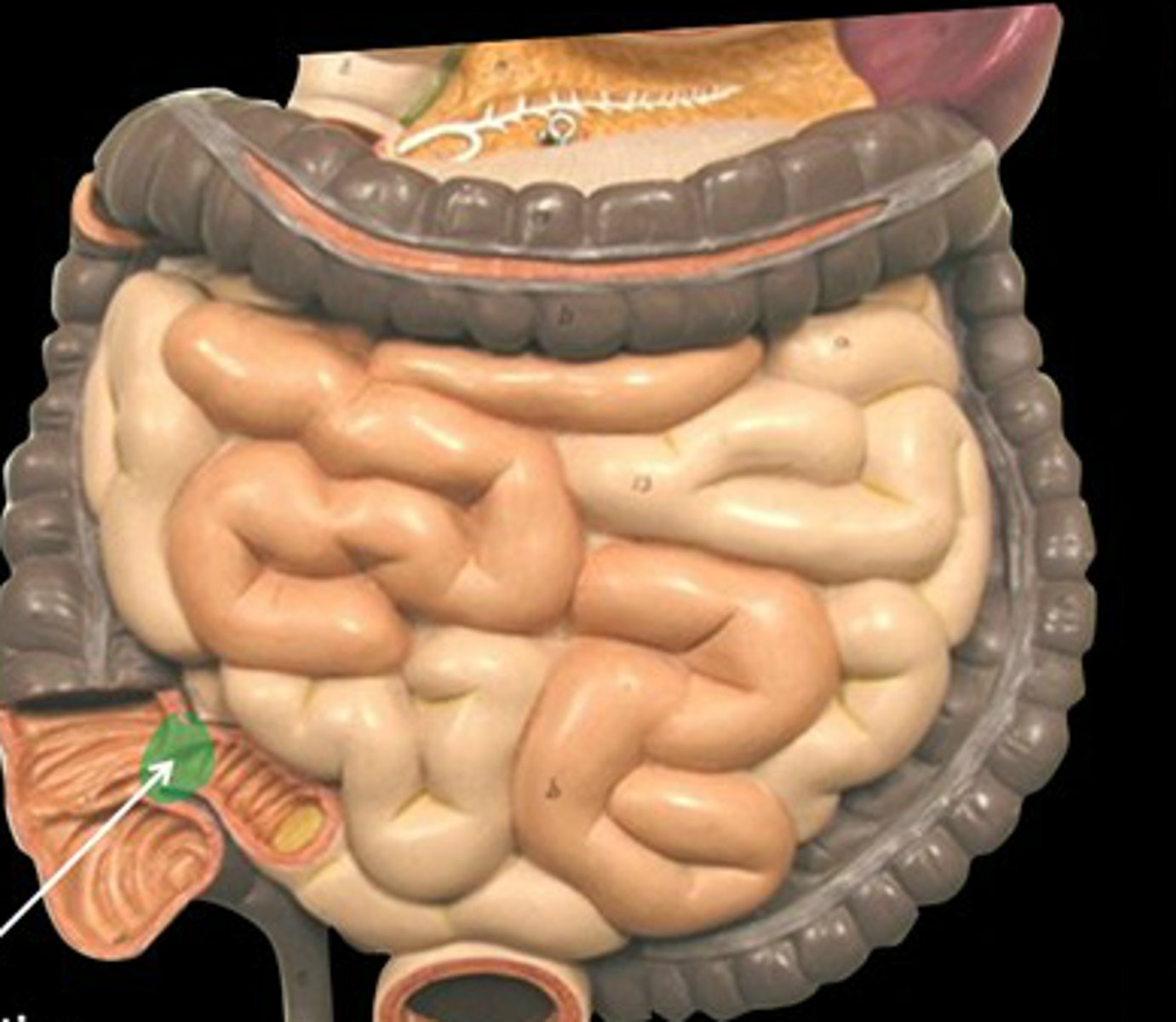
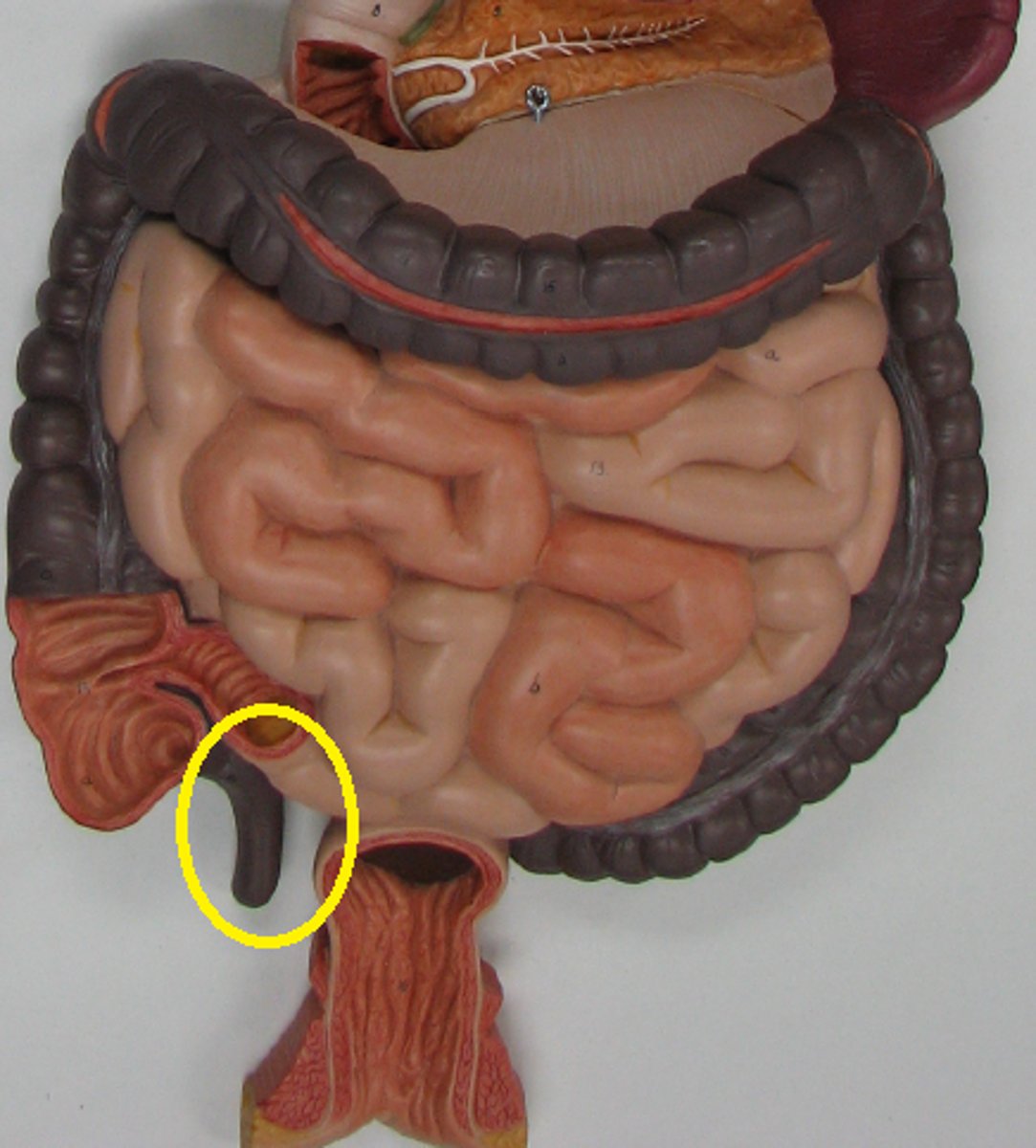
Cecum
a pouch connected to the junction of the small and large intestines. receives undigested food from the small intestine, absorbs water and salts, and lubricates the waste material with mucus, ultimately contributing to the formation of feces
Vermiform appendix
a vestigial process that extends from the lower end of the cecum and that resembles a small pouch, houses bacteria.
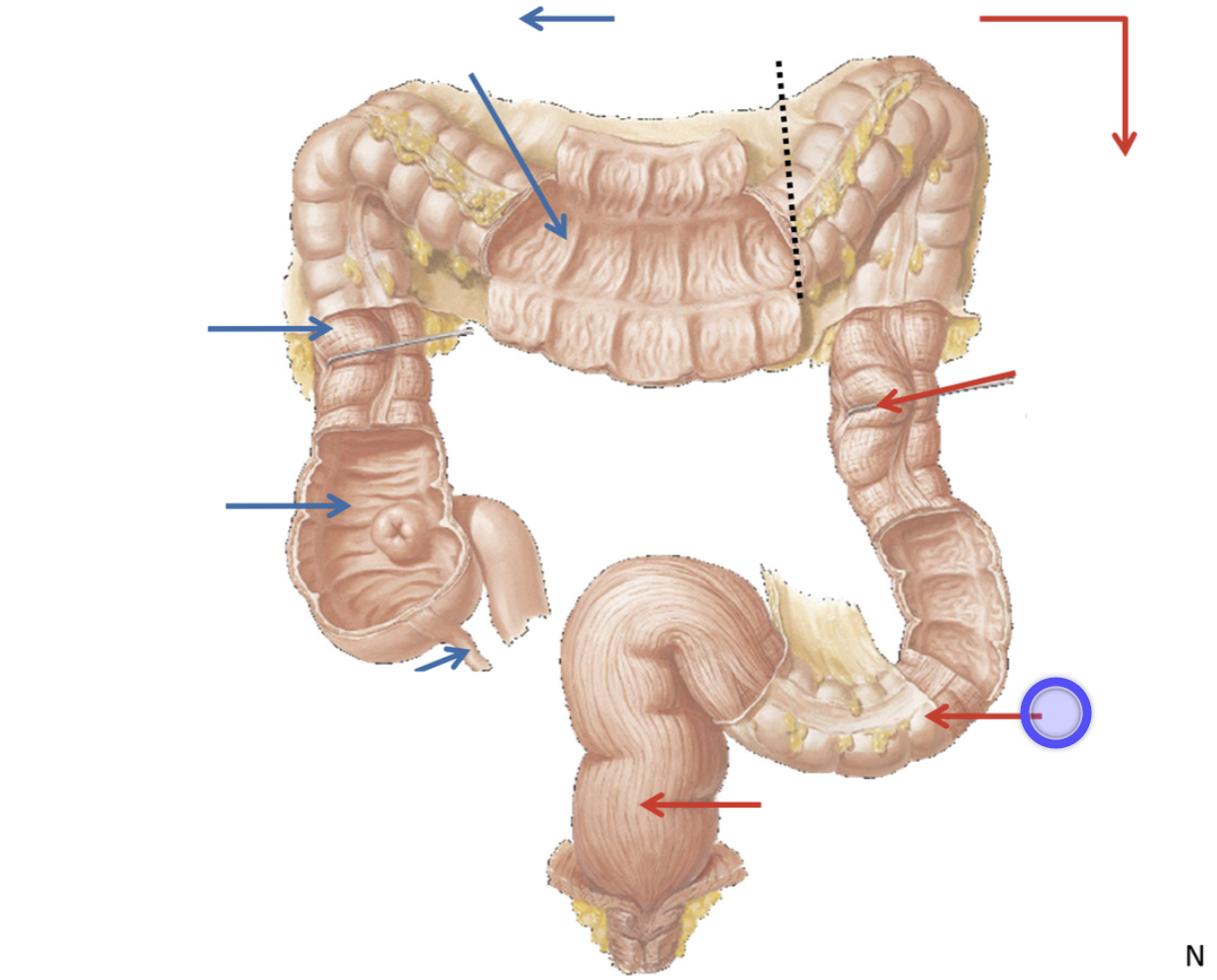
Ascending colon
Part of the large intestine that travels upward from the cecum to the undersurface of the liver
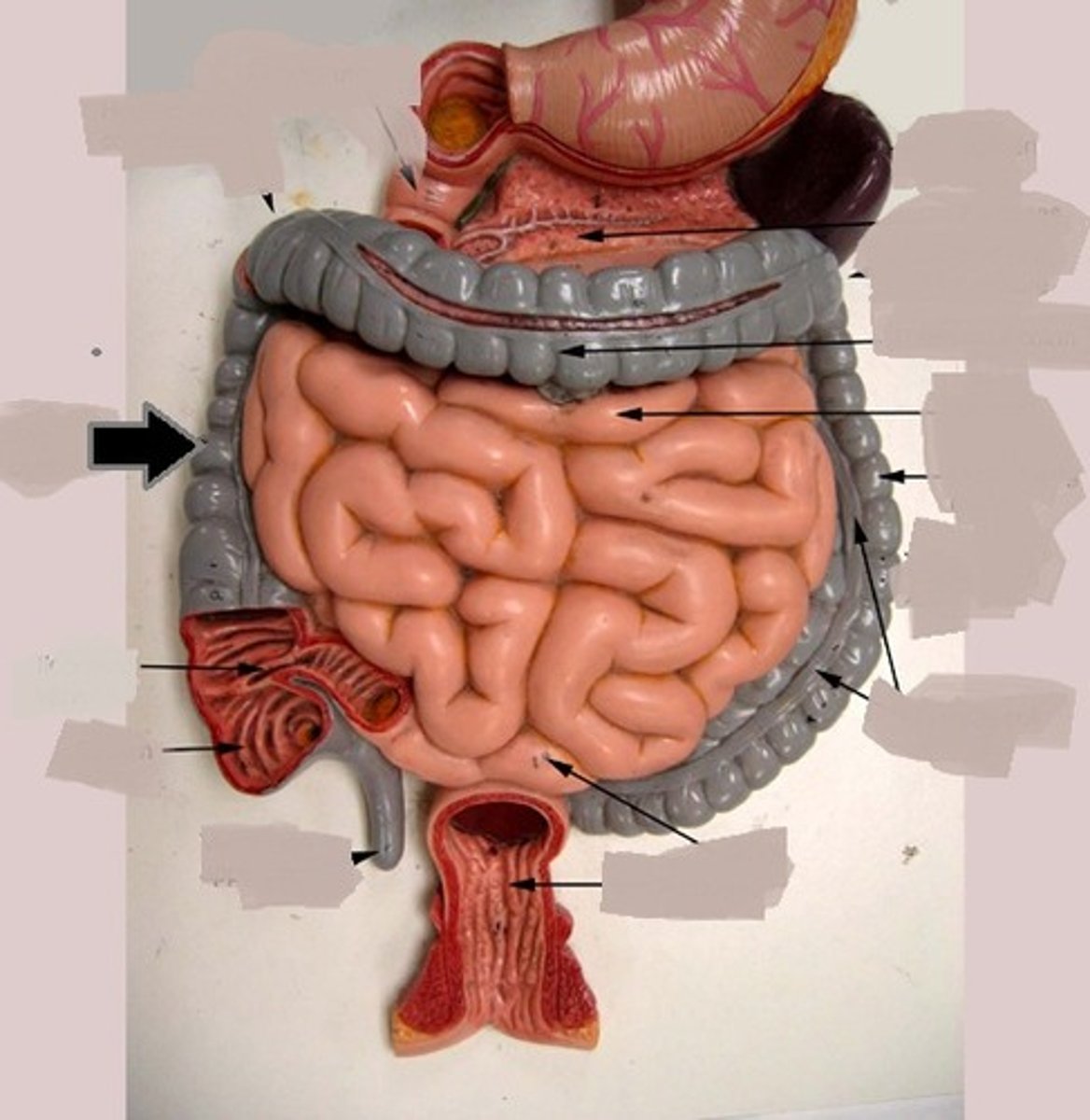
Transverse colon
the middle part of the large intestine, passing across the abdomen from right to left below the stomach.
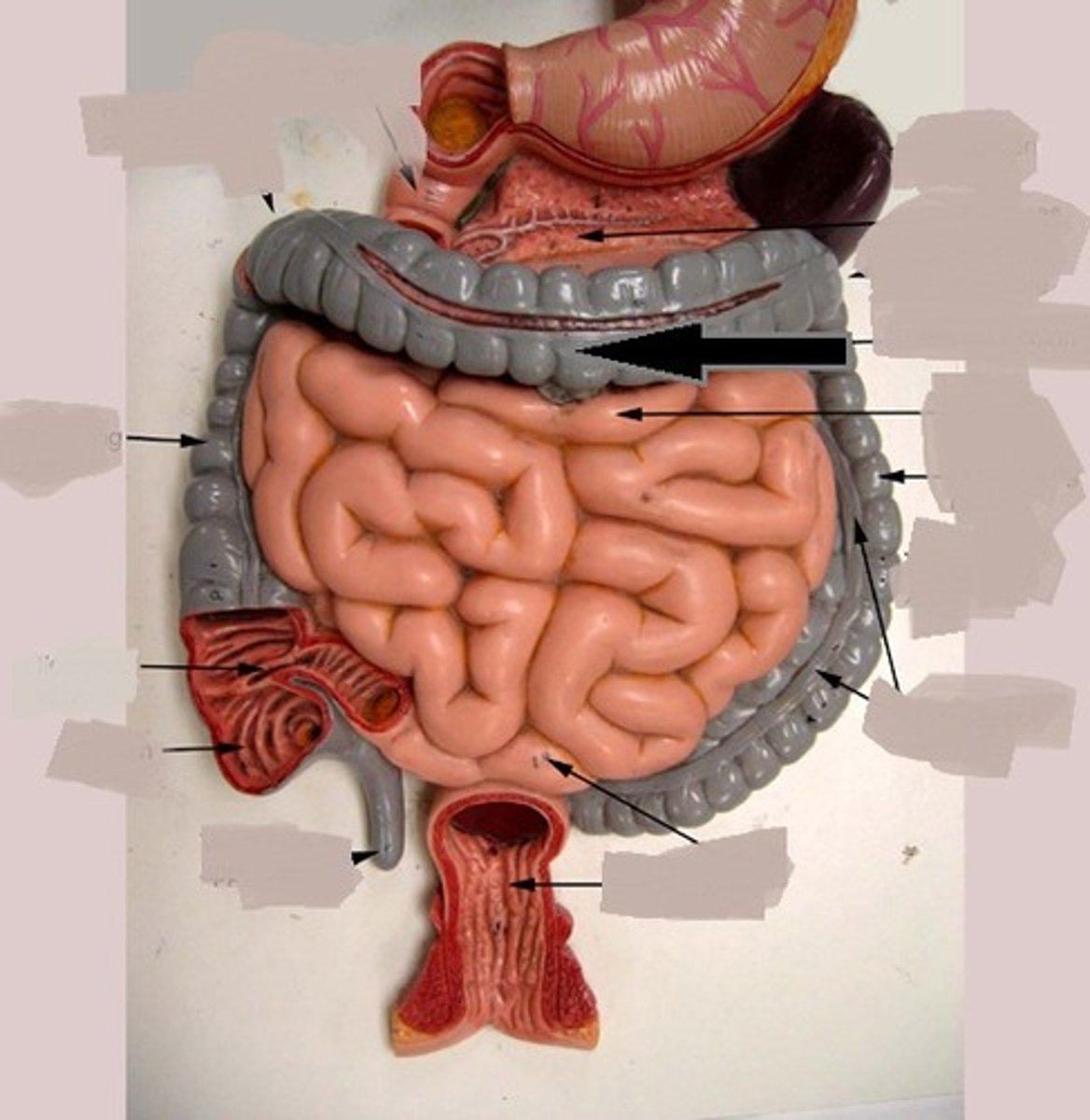
Descending colon
the part of the large intestine that passes downward on the left side of the abdomen toward the rectum.
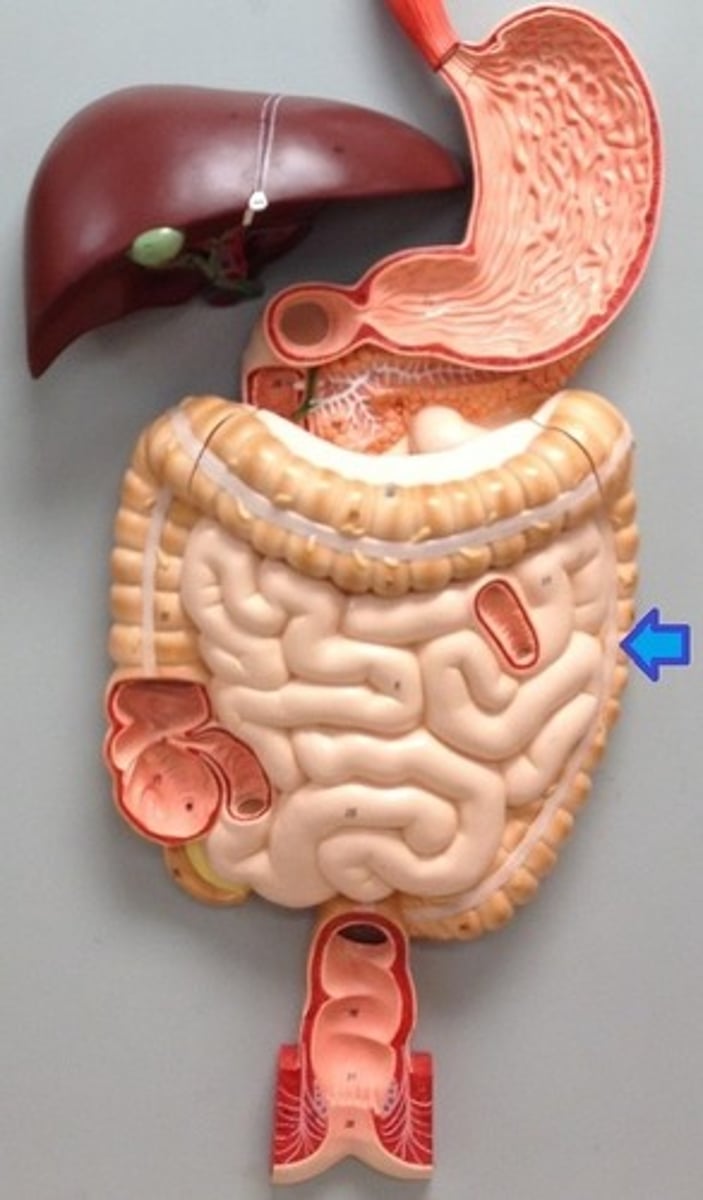
Sigmoid colon
fourth and last, S-shaped segment of the colon, just before the rectum; empties into the rectum
Rectum
A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated
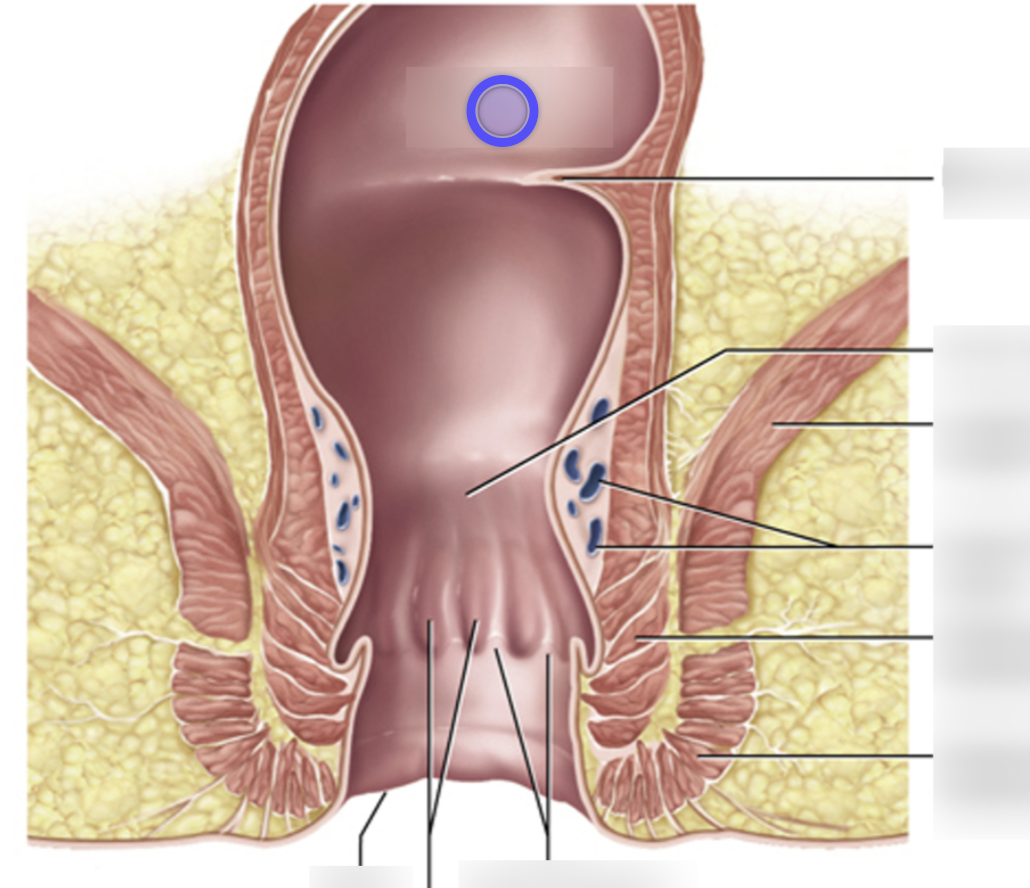
Anal canal
the terminal region of the digestive tract, containing two sphincters, through which feces are expelled from the body
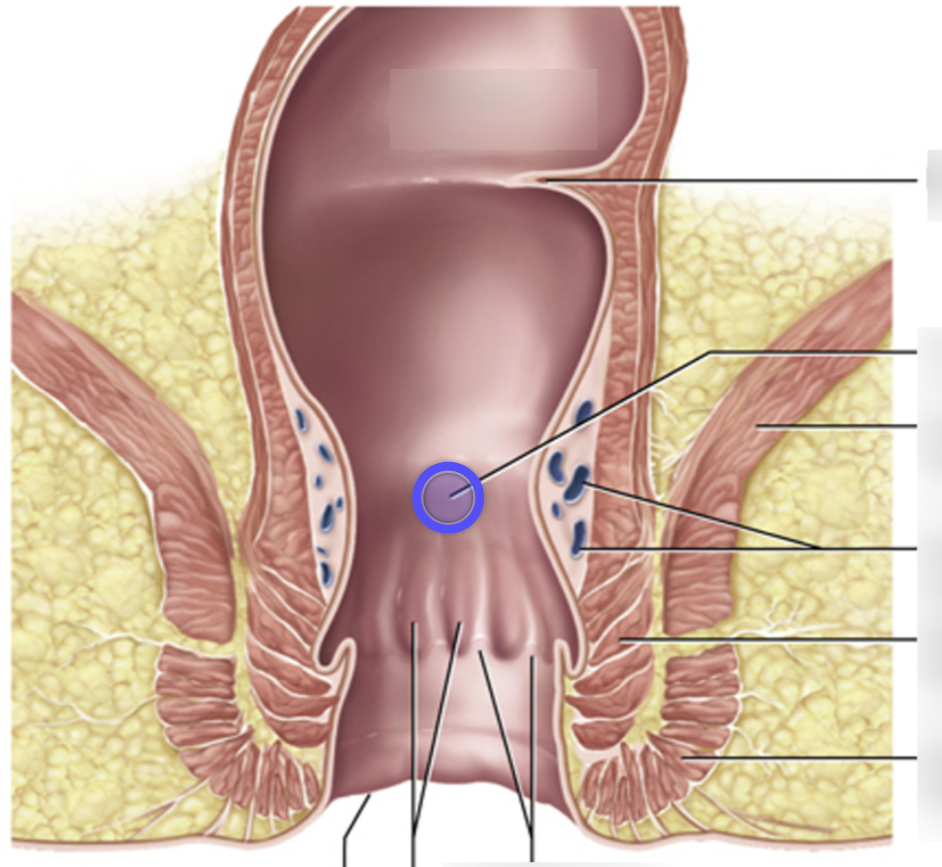
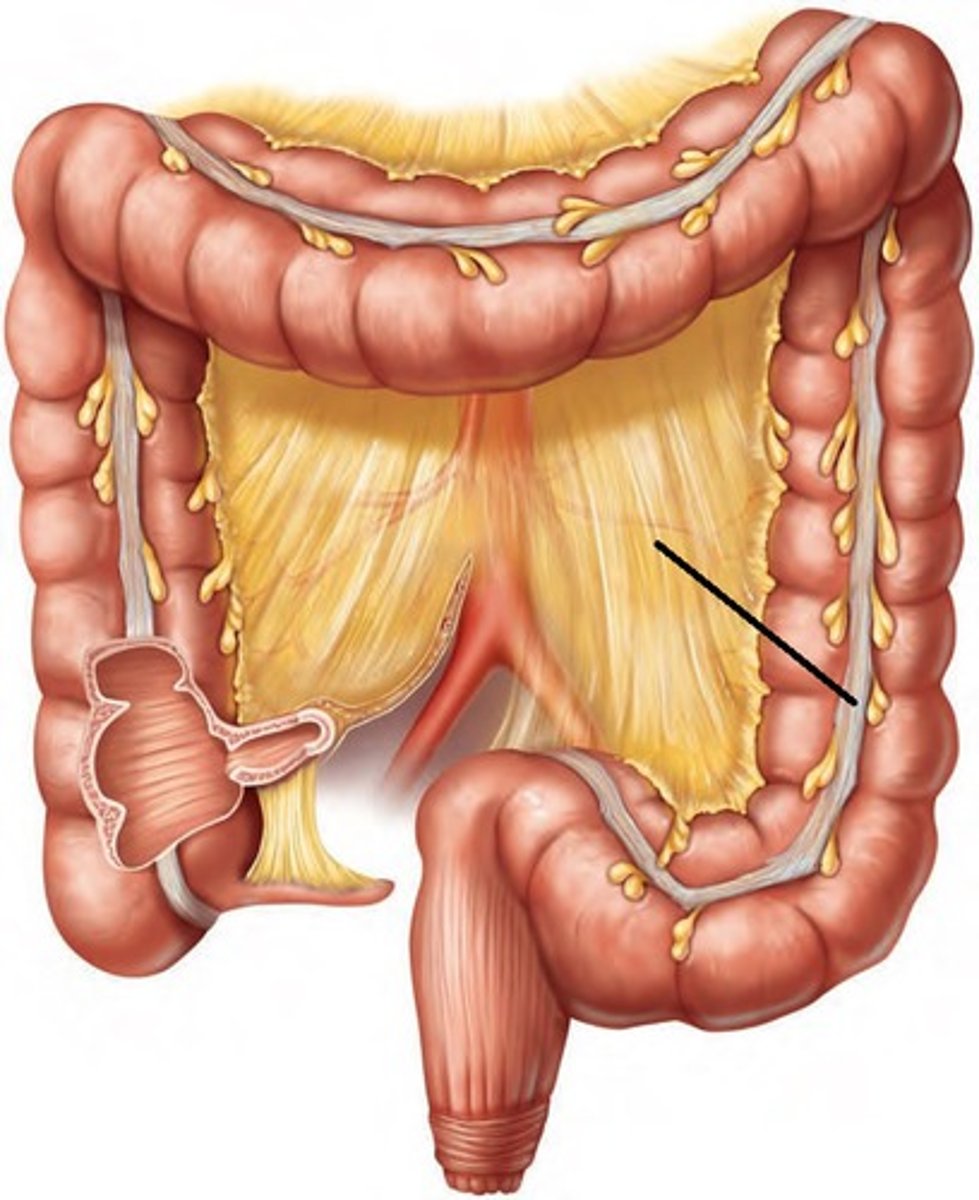
Teniae coli
3 tiny shiny bands that spans the length of the colon (large intestine), comprised of smooth muscle functions to contract and shorten the colon, allowing for the formation of haustra and facilitating the movement of fecal matter through the large intestine.