05.J BIO, HN The Kreb's Cycle (PART J)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
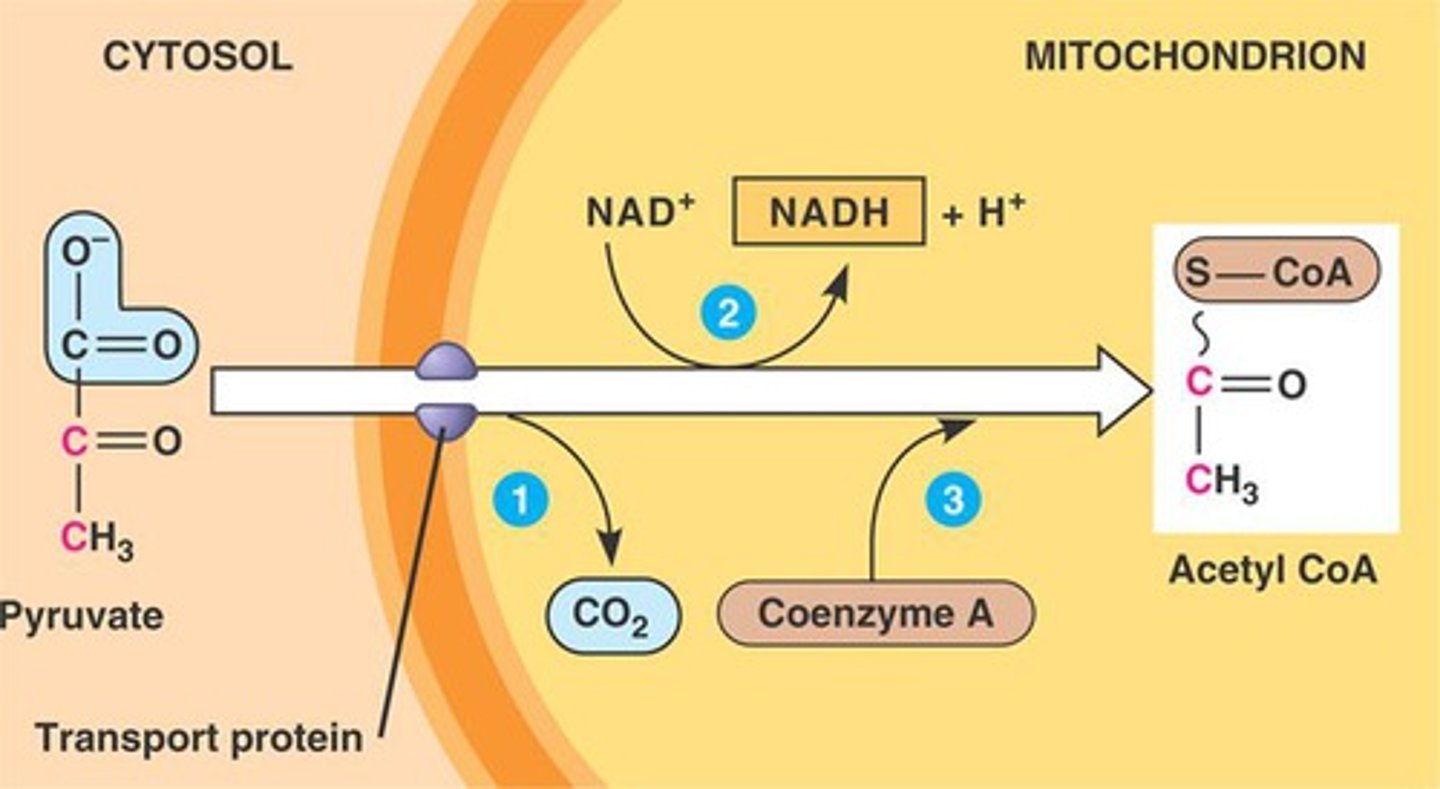
Formation of Acetyl CoA (Description)
An aerobic process that occurs when pyruvic acid (3-carbon compound) enters the mitochondrial matrix and combines with Coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA (2-carbon compound). During the process a CO2 is released and NAD+ is reduced NAD+ to produce NADH that will enter the ETC
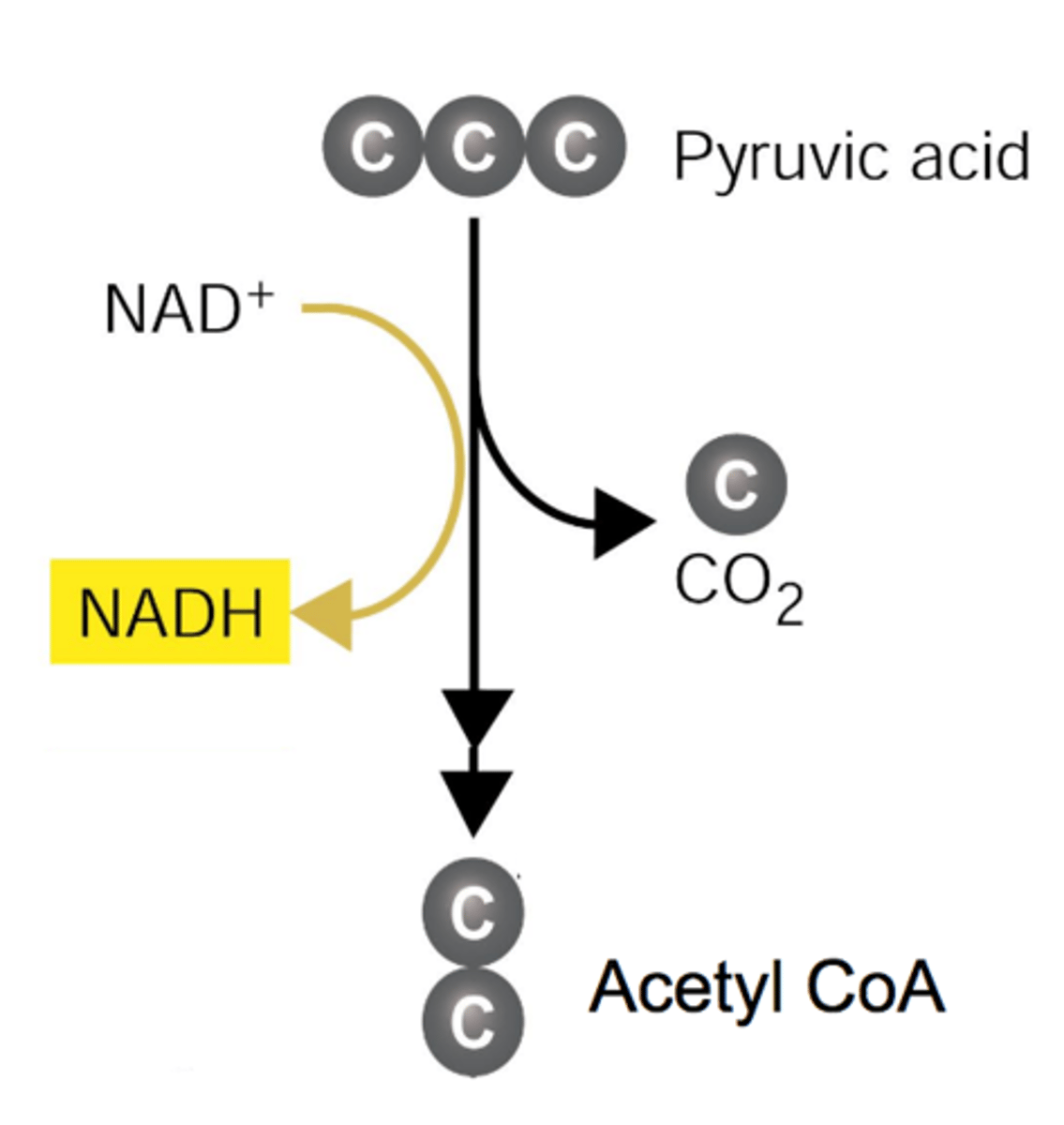
Formation of Acetyl CoA (Location)
Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix to produce acetyl CoA
Formation of Acetyl CoA (Reactants)
2 Pyruvic acid
2 NAD+
Formation of Acetyl CoA (Products)
2 Acetyl CoA
2 NADH
2 CO2
Kreb's cycle (Description)
A process in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions that produces ATP, NADH and FADH2
Also known as the citric acid cycle
Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria
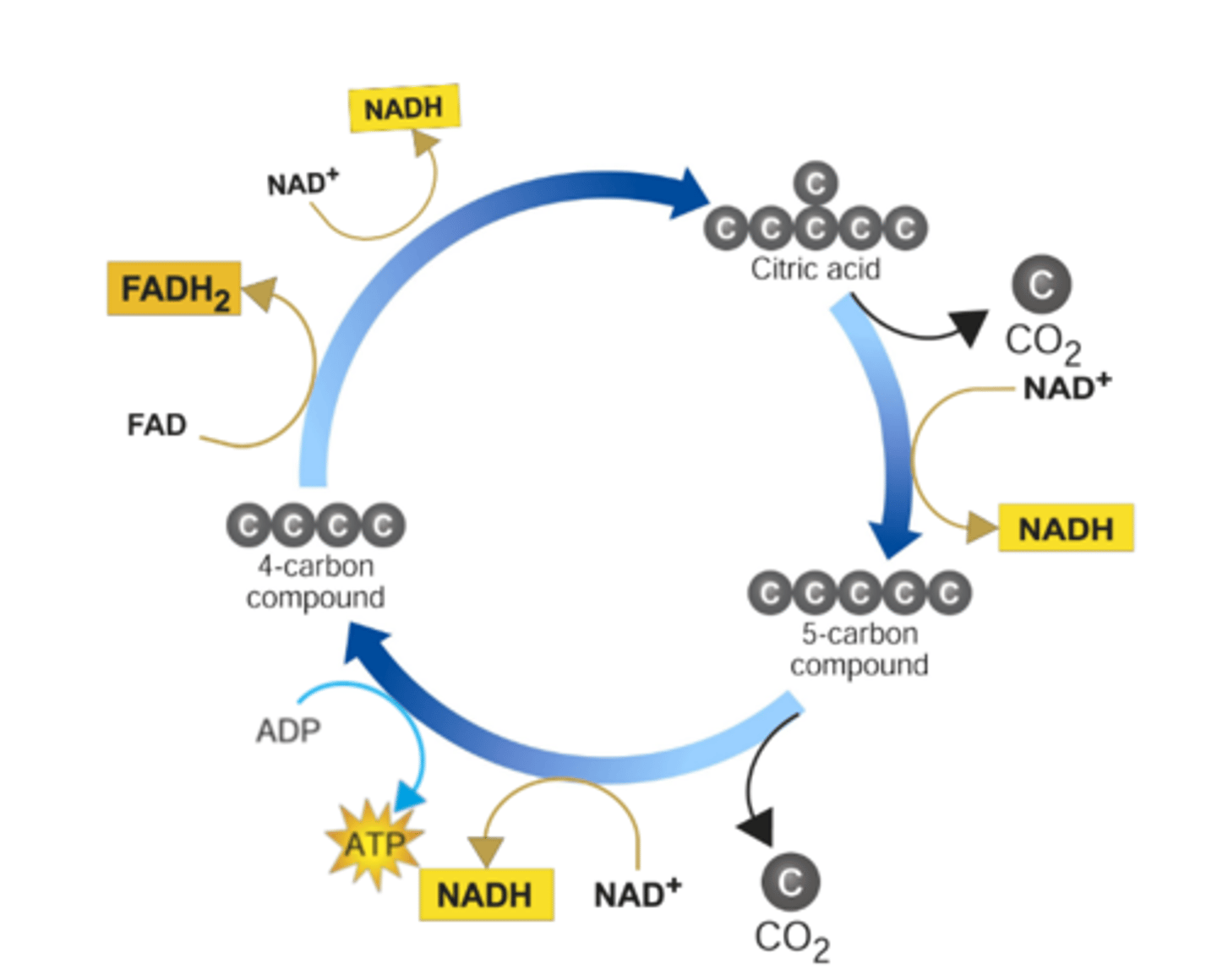
Kreb's cycle (Location)
Occurs in the fluid-filled matrix of the mitochondria
Kreb's cycle (Reactants)
2 Acetyl CoA
2 4-carbon molecules
2 ADP + 2Pi
6 NAD+
2 FAD
Kreb's cycle (Products)
Citric acid regenerates 4-C molecule
2 ATP
6 NADH
2 FADH2
Acetyl CoA
A 2-carbon compound that results when pyruvate acid is broken down in the presence of oxygen
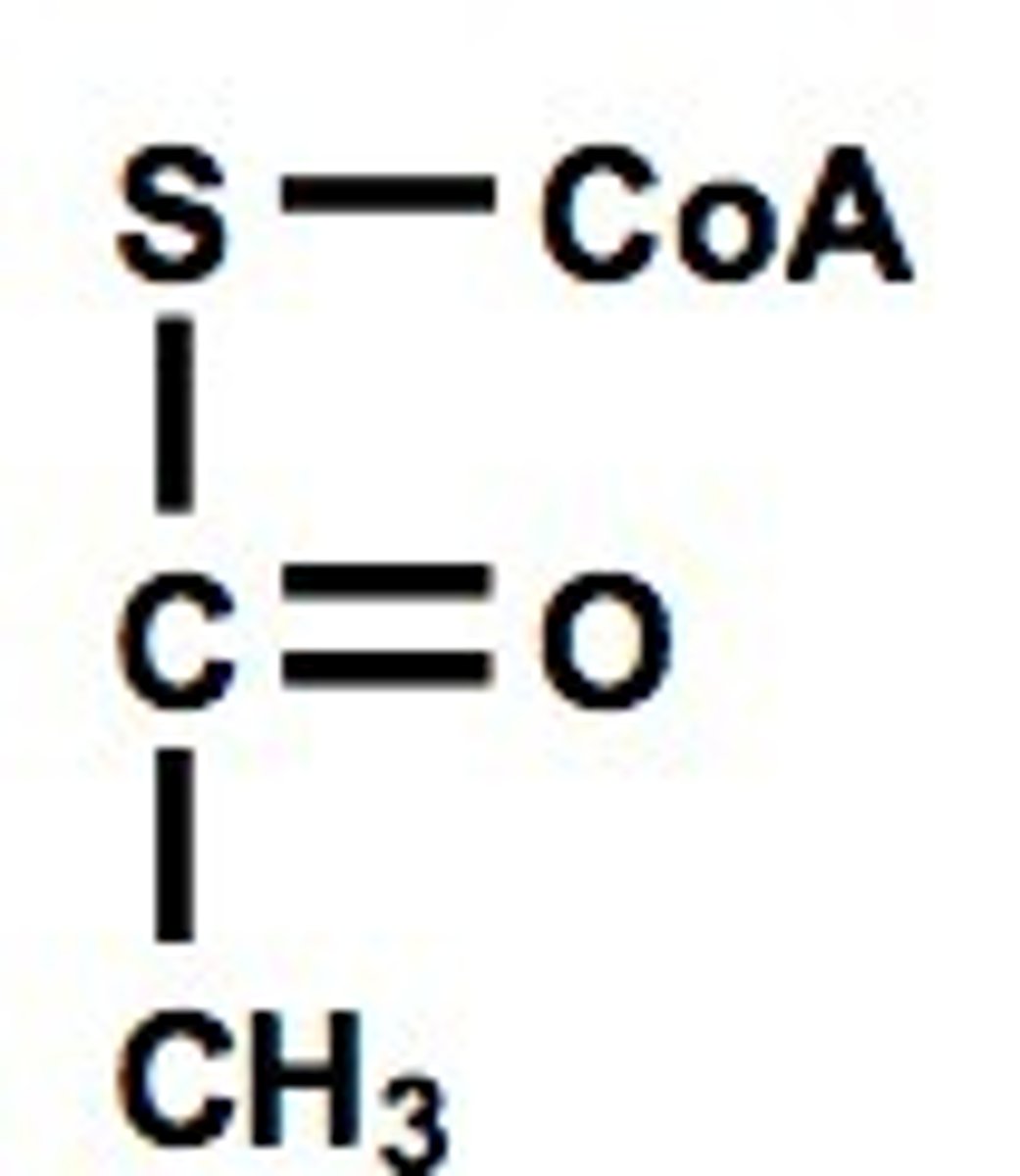
Citric acid
A 6-carbon compound that results when the 4-carbon compound that is the starting material joins with acetyl CoA; also known as citrate