Materials Elastomeric Impression
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
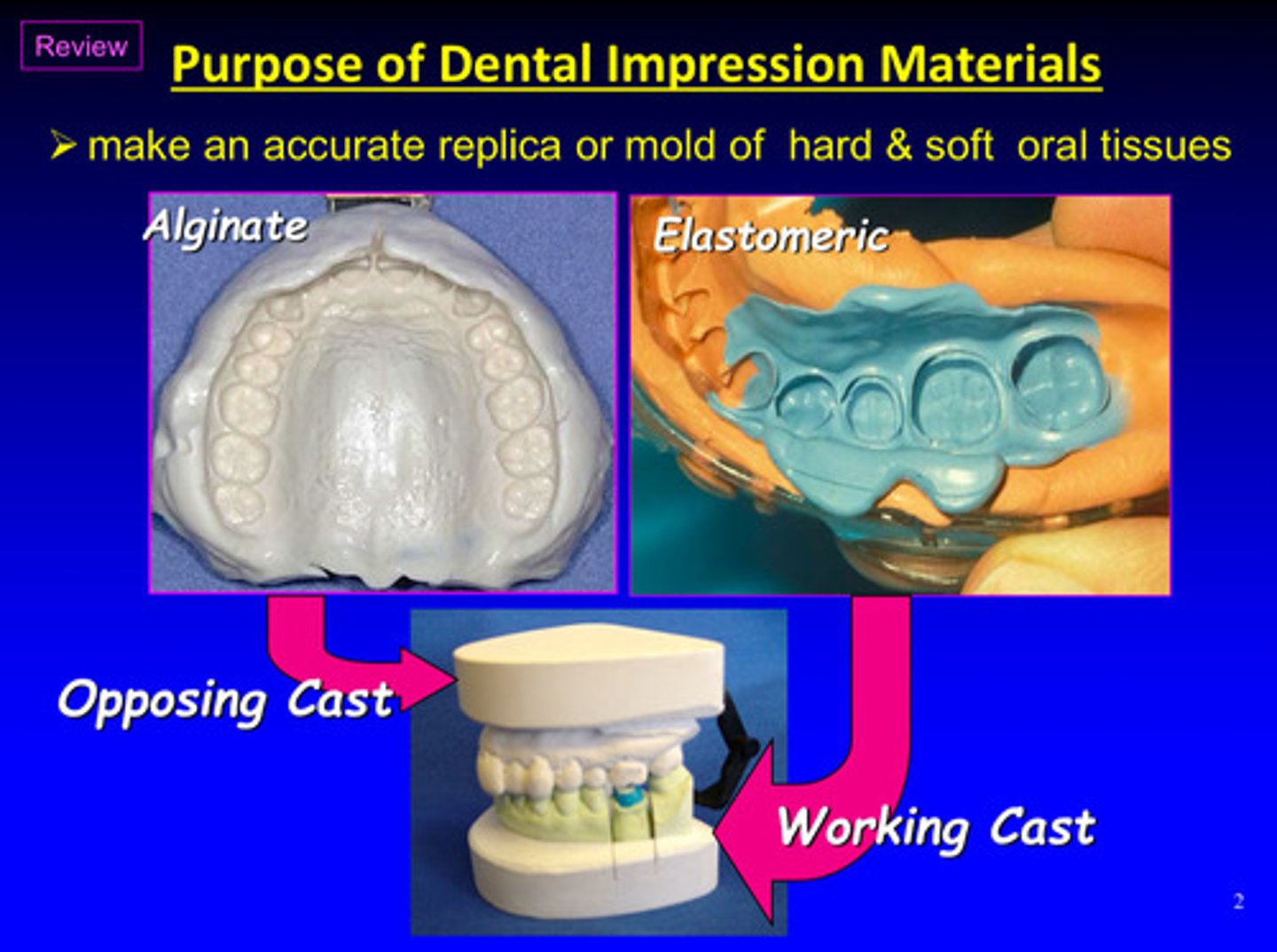
what is the purpose of dental impression materials
to make an accurate replica or mold of hard & soft oral tissues
what are the 4 nonaqueous elastomers
1) polysulfide
2) silicone
3) polyether
4) polyvinyl siloxane (addition silicone)
what are the properties of polyether and polyvinyl siloxane (rigid or flexible)
flexible
what is the setting reaction of polyether and polyvinyl siloxane
chemical and irreversible
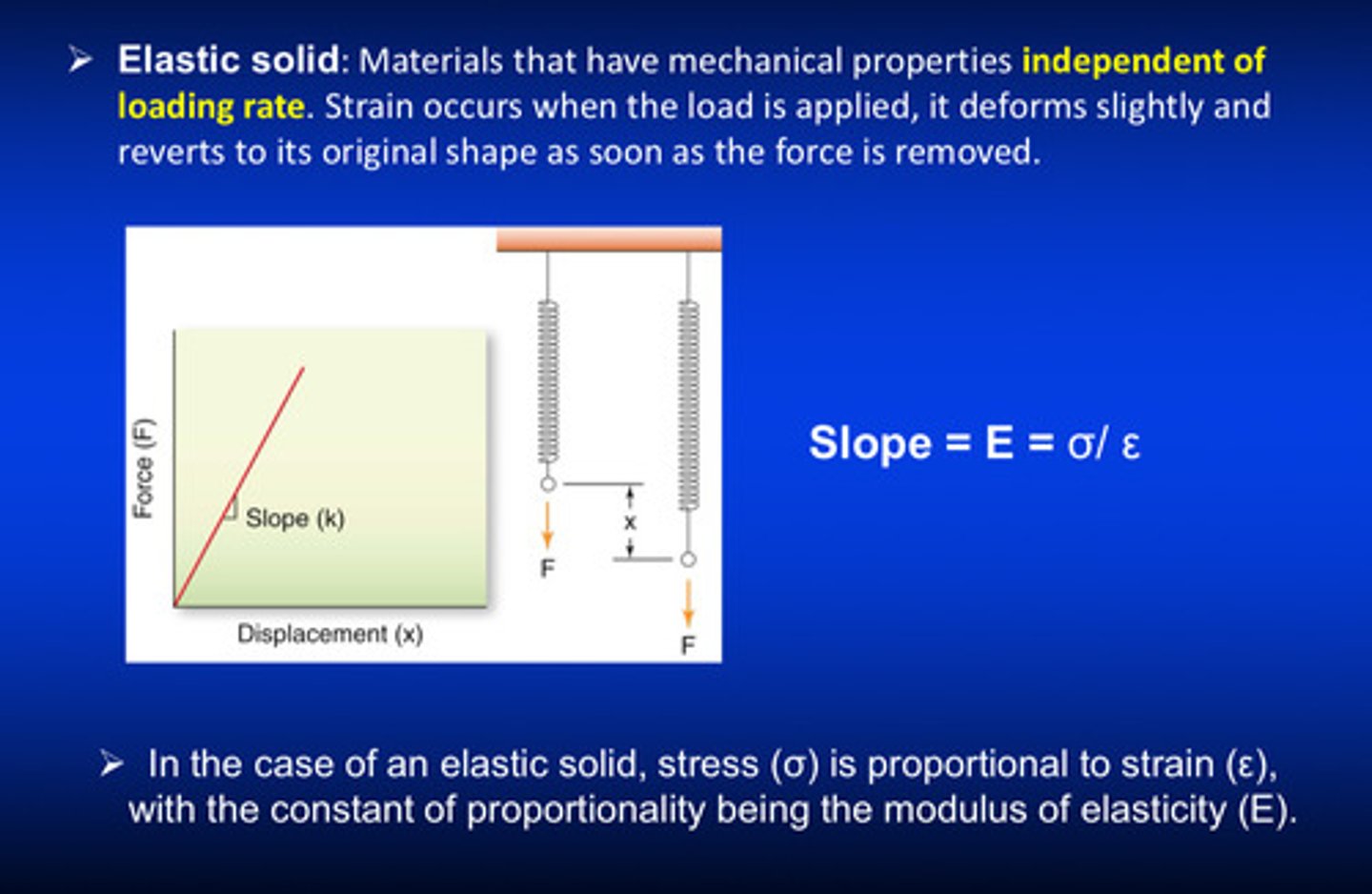
what is an elastic solid
materials that have mechanical properties independent of loading rate
strain occurs when the load is applied, but an elastic solid will deform slightly and…
revert to its original shape as soon as the force is removed
in the case of an elastic solid, stress is proportional to…
strain (constant of proportionality is the modulus of elasticity)
viscous fluid resists what
movement of an object through the fluid
viscous fluid are materials that exhibit a _____ in response when a load is applied
lag
a viscous fluid can be viewed as a dash pot with a piston moving through a viscous fluid; when the fluid-filled cylinder is pulled, the rate of strain is proportional to the _______ and the constant of proportionality is the __________ of the fluid
stress; viscosity
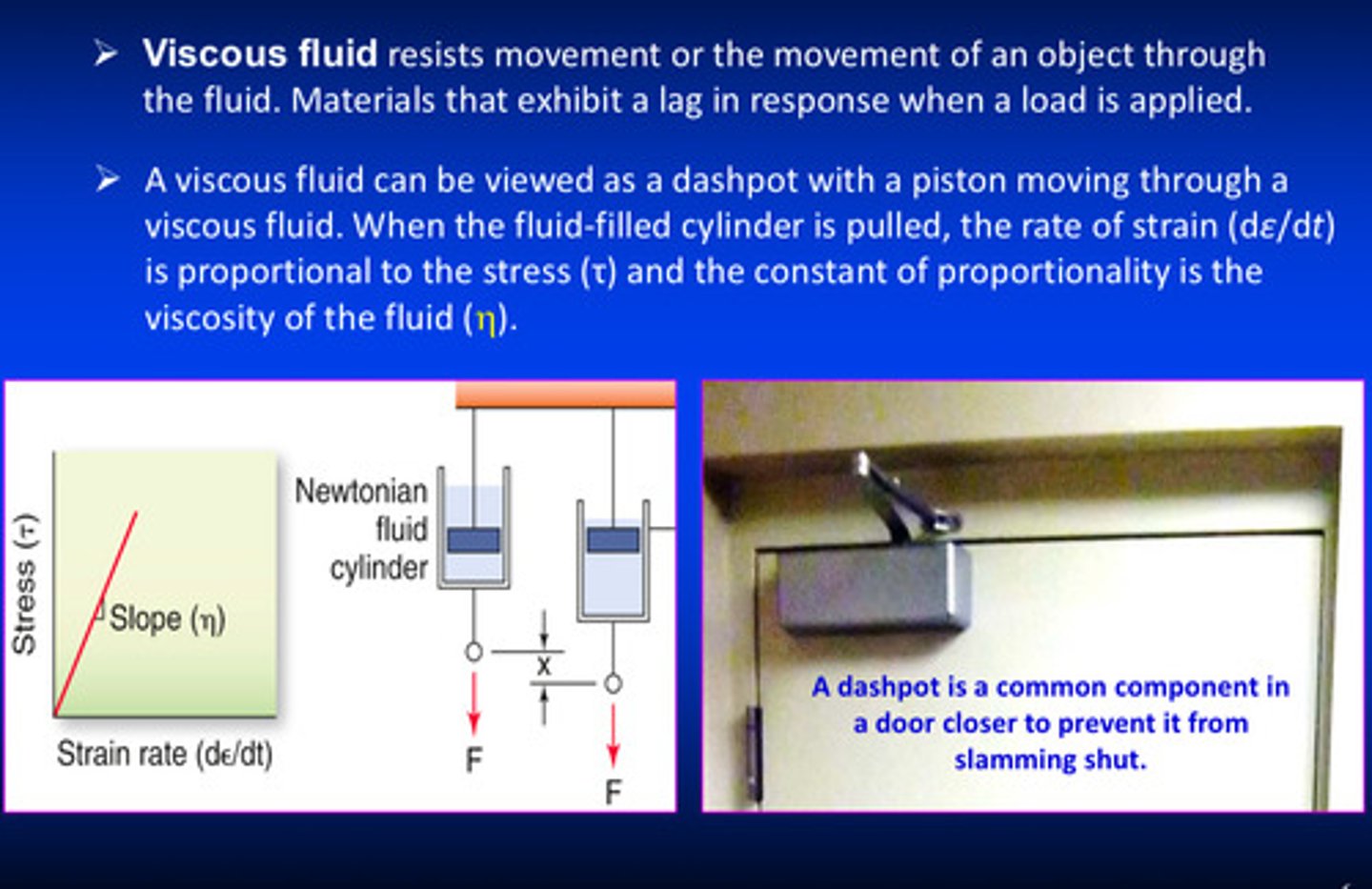
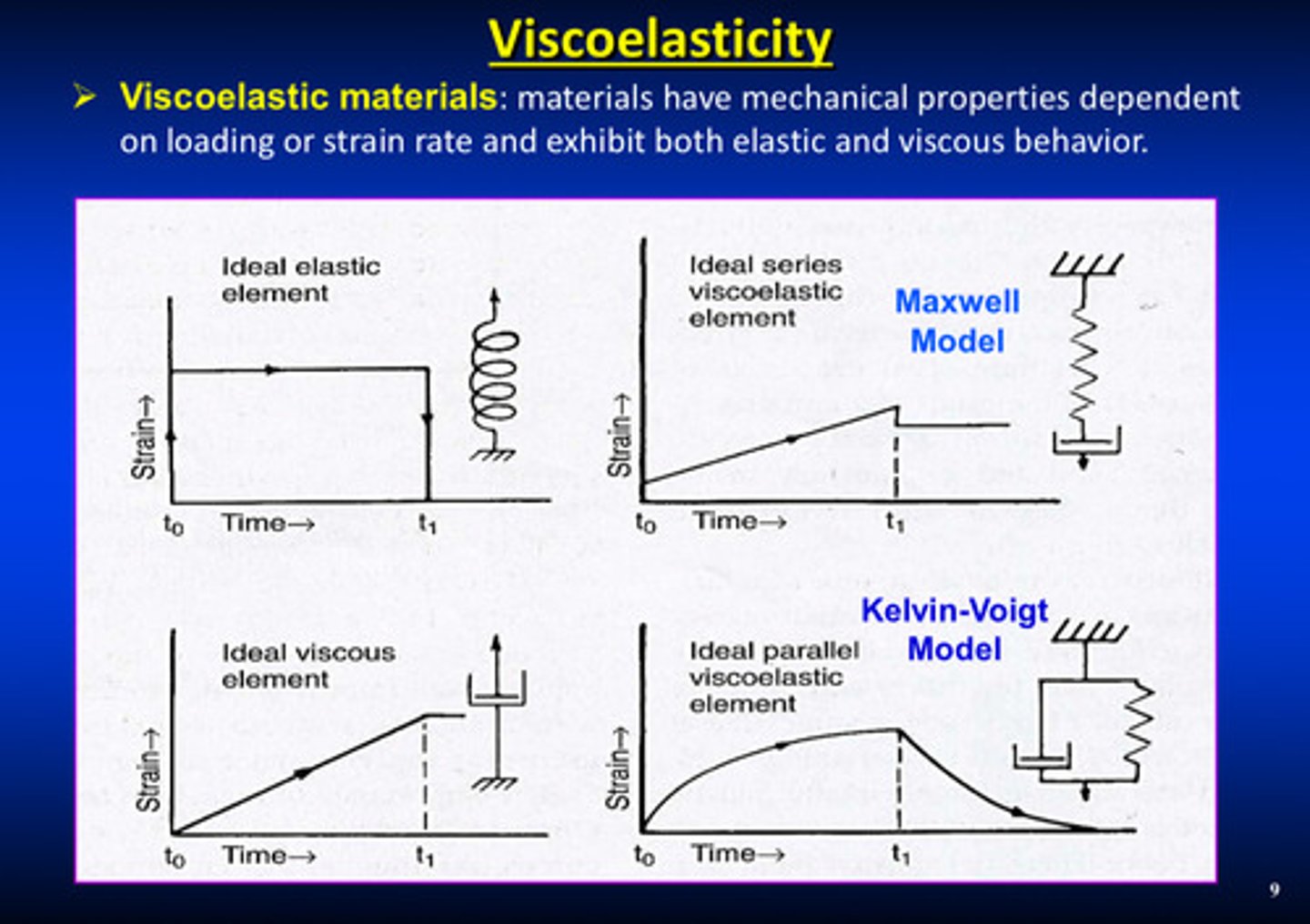
what is the maxwell model
a purely viscous damper (dash pot) and a purely elastic spring connect in series
in the maxwell model, if the material is put under a constant strain, what happens to the stresses
the stresses gradually relax
the deformation of the elastic element in the maxwell model would be the the spring-back deformation that occurs instantaneously, but the deformation of the viscous element would ____ ________/_____ with time as long as the stress is applied
not change/grow
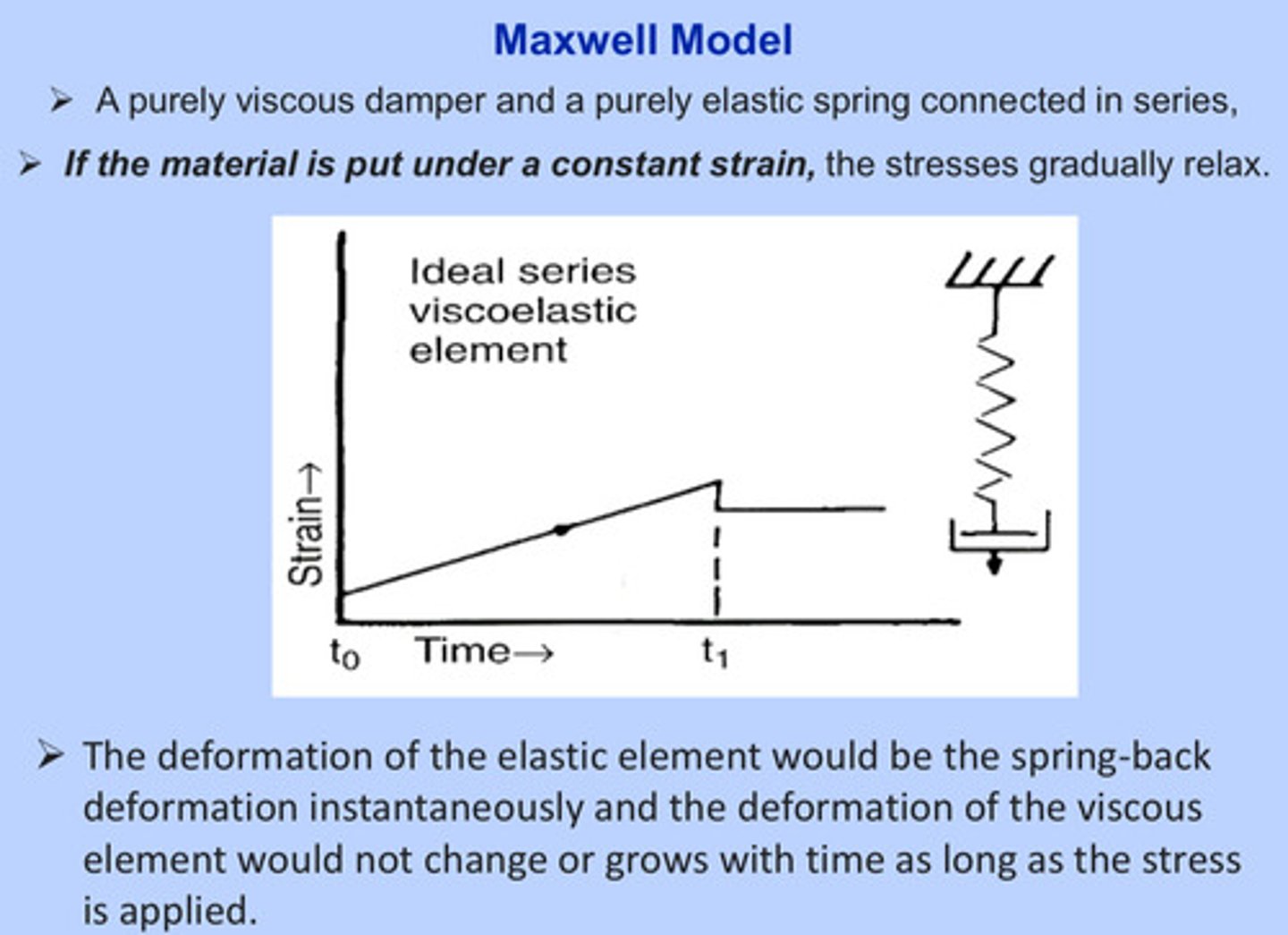
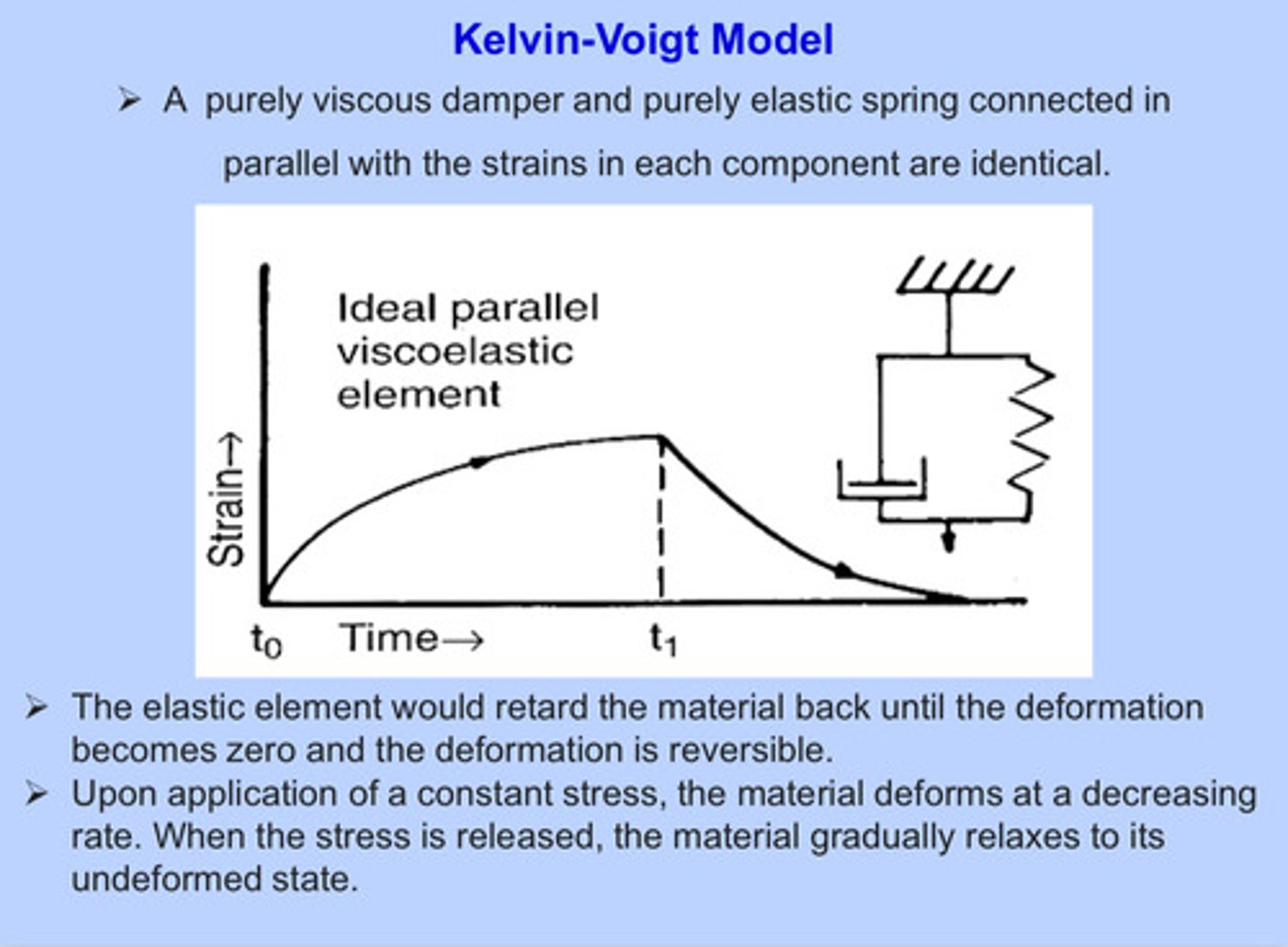
what is the kelvin-voigt model
a purely viscous damper (dash pot) and purely elastic spring connected in parallel with the strains in each component being identical
the elastic element in the kelvin-voigt model would ______ the material back until the deformation becomes zero and the deformation is reversible
retard
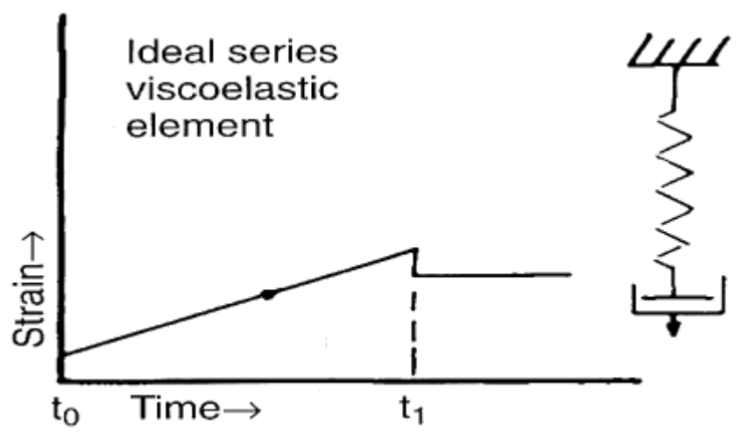
which model is this
maxwell model
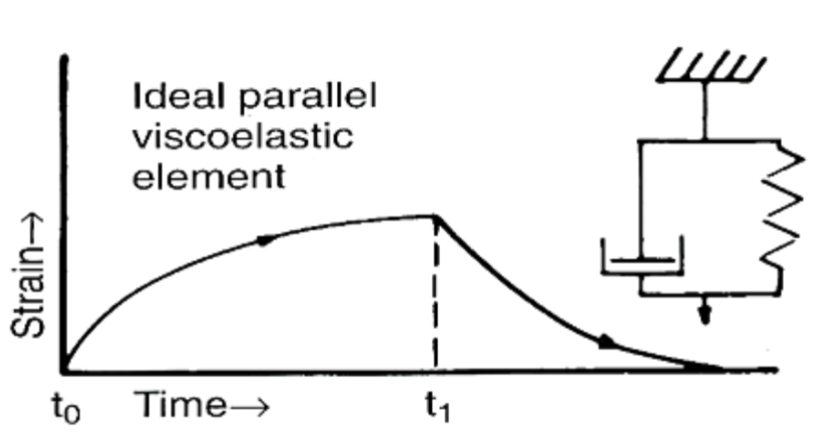
which model is this
kevin-voigt model
upon application of a constant stress in the kelvin-voigt model, the material deforms at a ____________ rate; when the stress is released, the material gradually relaxes to its ______________ state
decreasing; undeformed
what are viscoelastic materials
materials that have mechanical properties dependent on loading or strain rate and exhibit both elastic and viscous behavior
viscoelasticity is a ___________ rearrangement
molecular
materials that have properties dependent on the strain rate are better characterized by what
by relating stress or strain as a function of time
what is stress relaxation
the reduction in stress in a material subjected to constant strain
what is creep
the increase in strain in a material under constant stress
what is viscosity defined as
the resistance of a fluid to flow equal to the stress divided by the strain rate (viscosity = stress / strain rate)

although the viscosity of a fluid is proportional to the _______ _______, the proportionality differs for different fluids
shear rate
fluids can be classified as what 3 categories depending on how their viscosity varies with shear rate
1) newtonian
2) pseudoplastic
3) dilatant
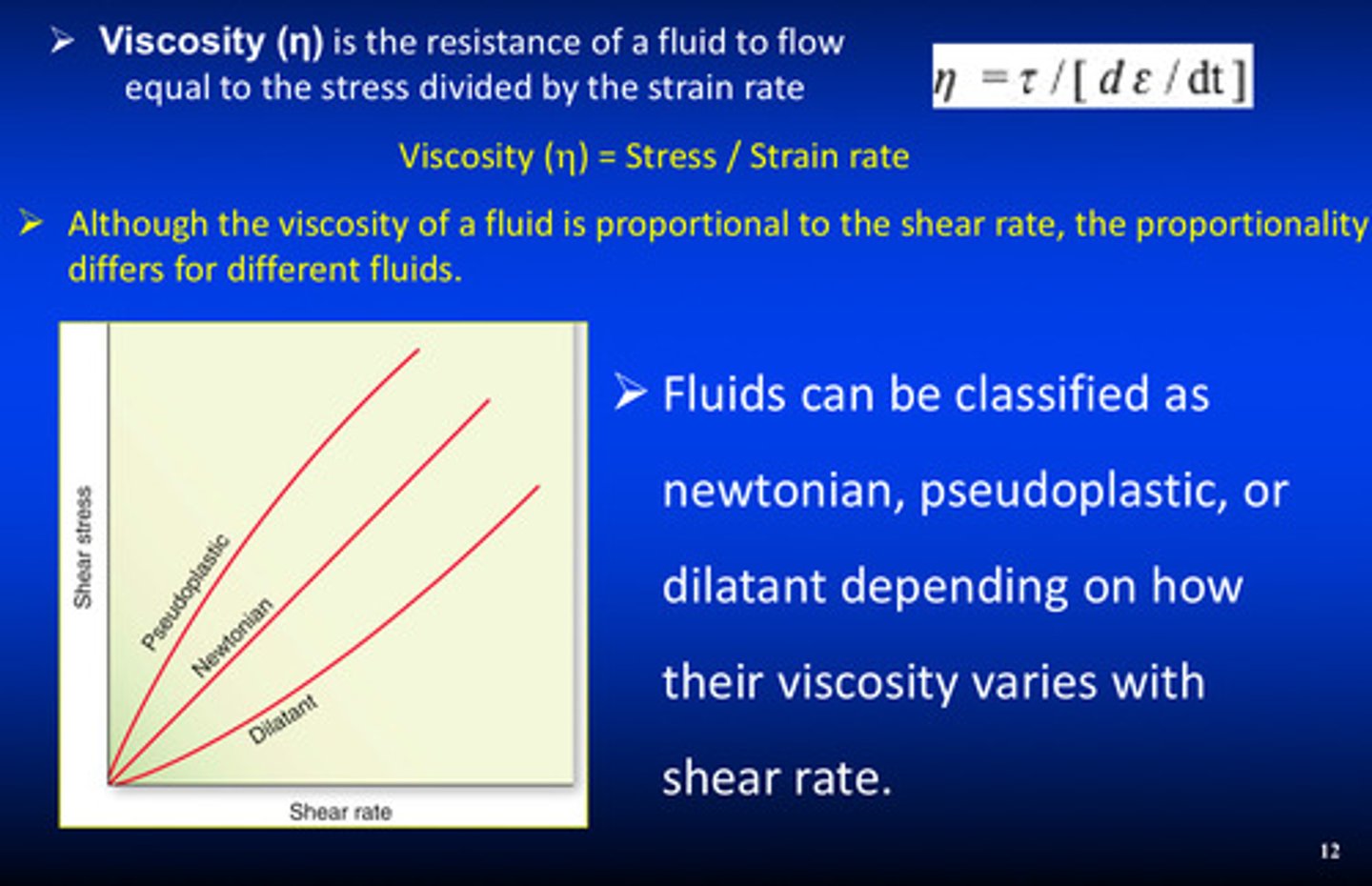
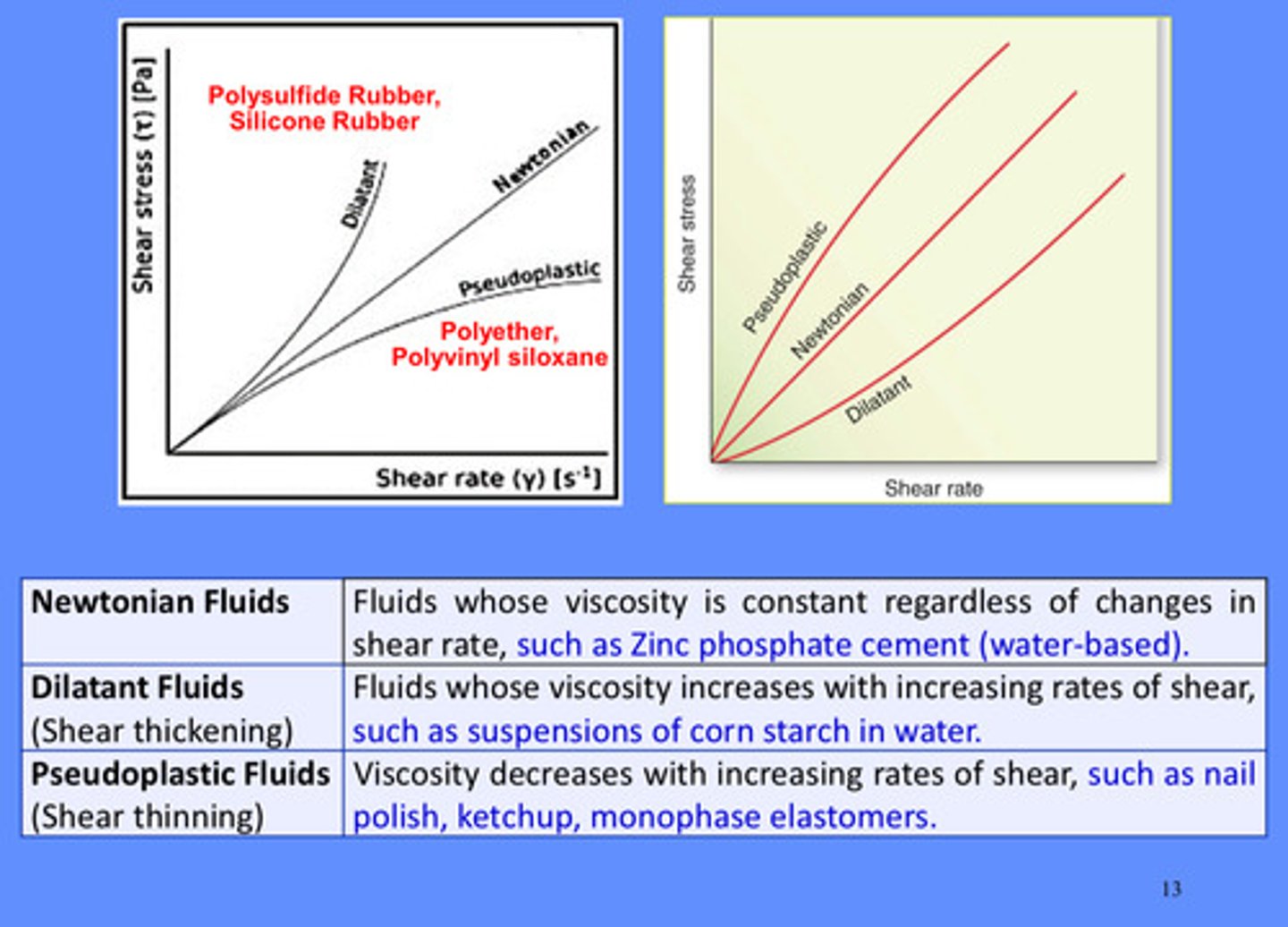
newtonian fluids: fluids whose viscosity is ________ regardless of changes in shear rate, such as…
constant; zinc phosphate cement (water-based)
_________ / ___________ = viscosity
stress/strain
Newtonian fluids; fluids whose viscosity is _________ regardless of changes in shear rate, such as…
constant; zinc phosphate cement
dilatant fluids: fluids whose viscosity _______ with _________ rates of shear, such as suspensions of corn starch in water
inc; increasing
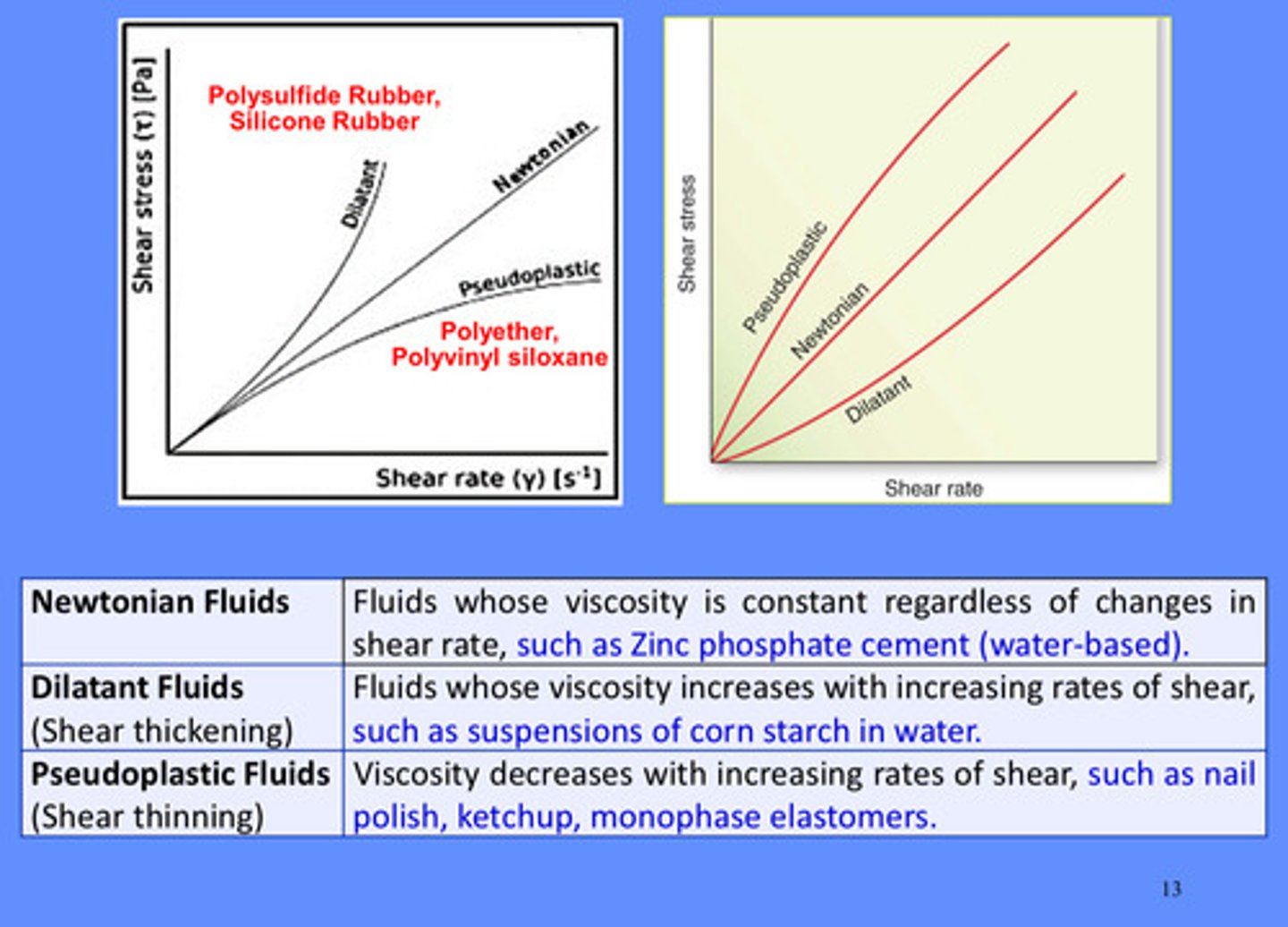
pseudoplastic fluids: fluids whose viscosity ________ with ___________ rates of shear, such as nail polish, ketchup, monophase elastomers
dec; inc
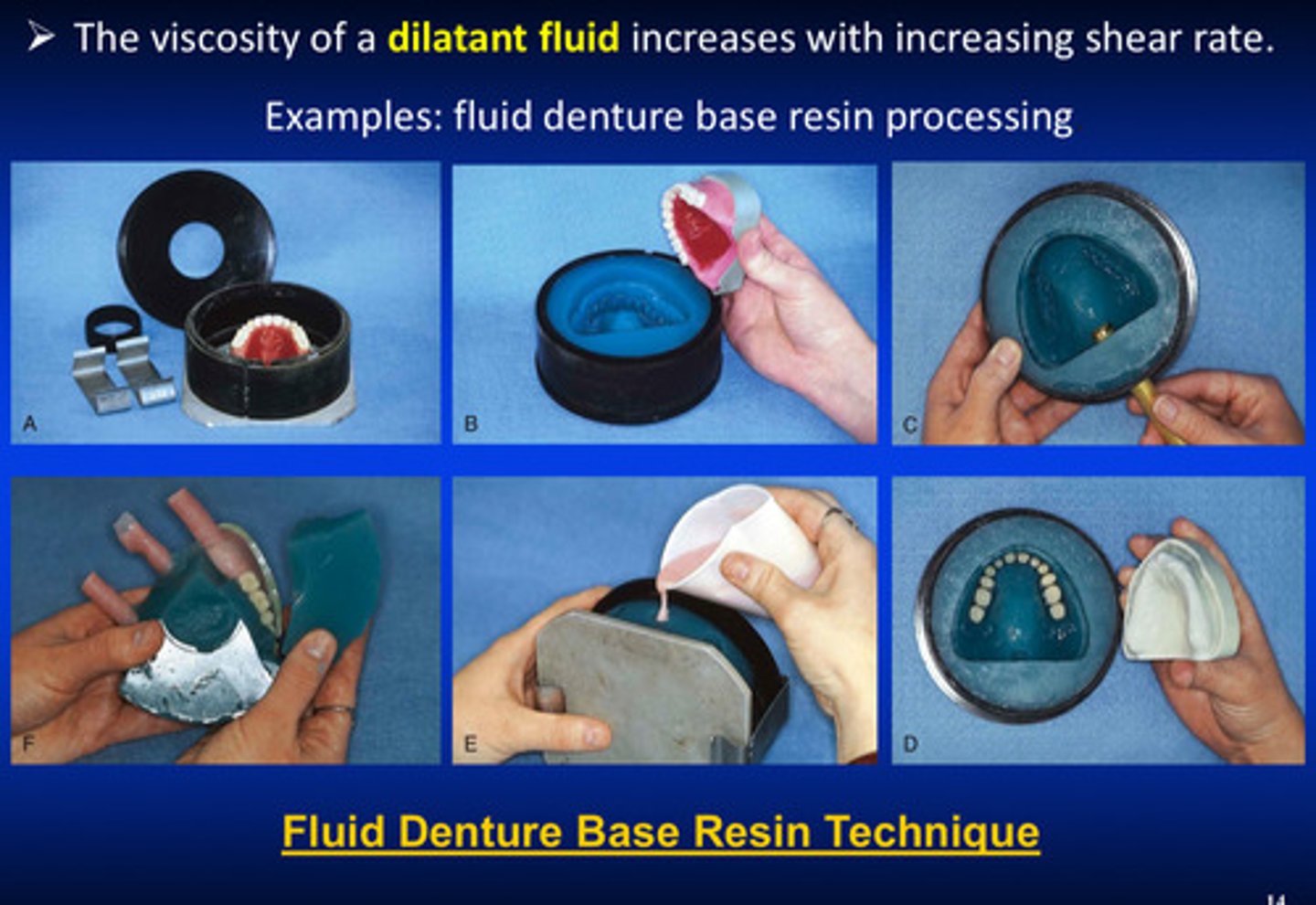
the viscosity of a dilatant fluid increases with what
inc w shear rate (ex: fluid denture base resin processing)
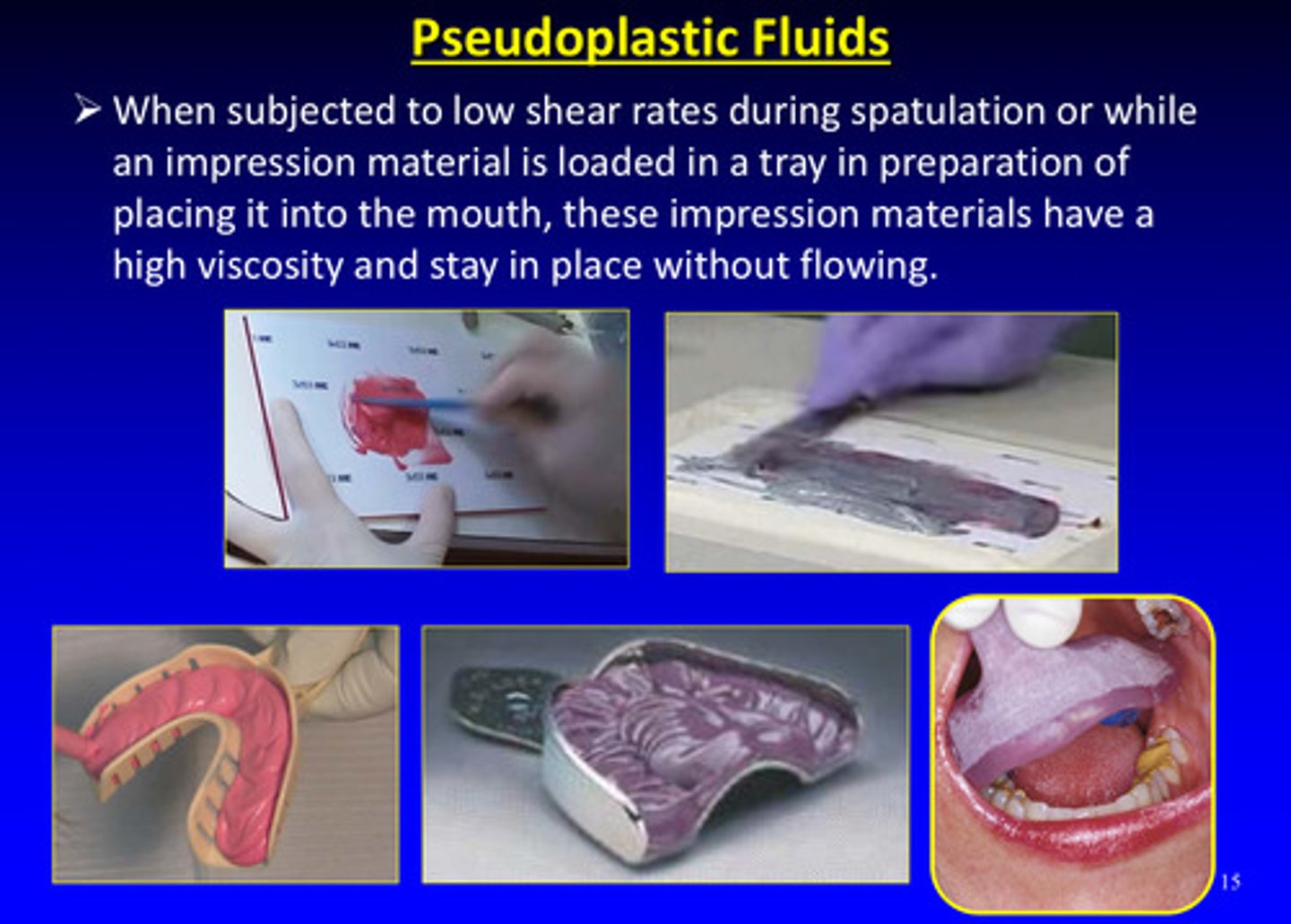
what kind of fluid does this describe: when subjected to low shear rates during spatulation or while an impression material is loaded in a tray in preparation of placing it into the mouth, these impression materials have a high viscosity and stay in place without flowing
pseudoplastic fluids
when using a syringe to deliver material, there are _________ shear rates encountered within the mixing tip
higher
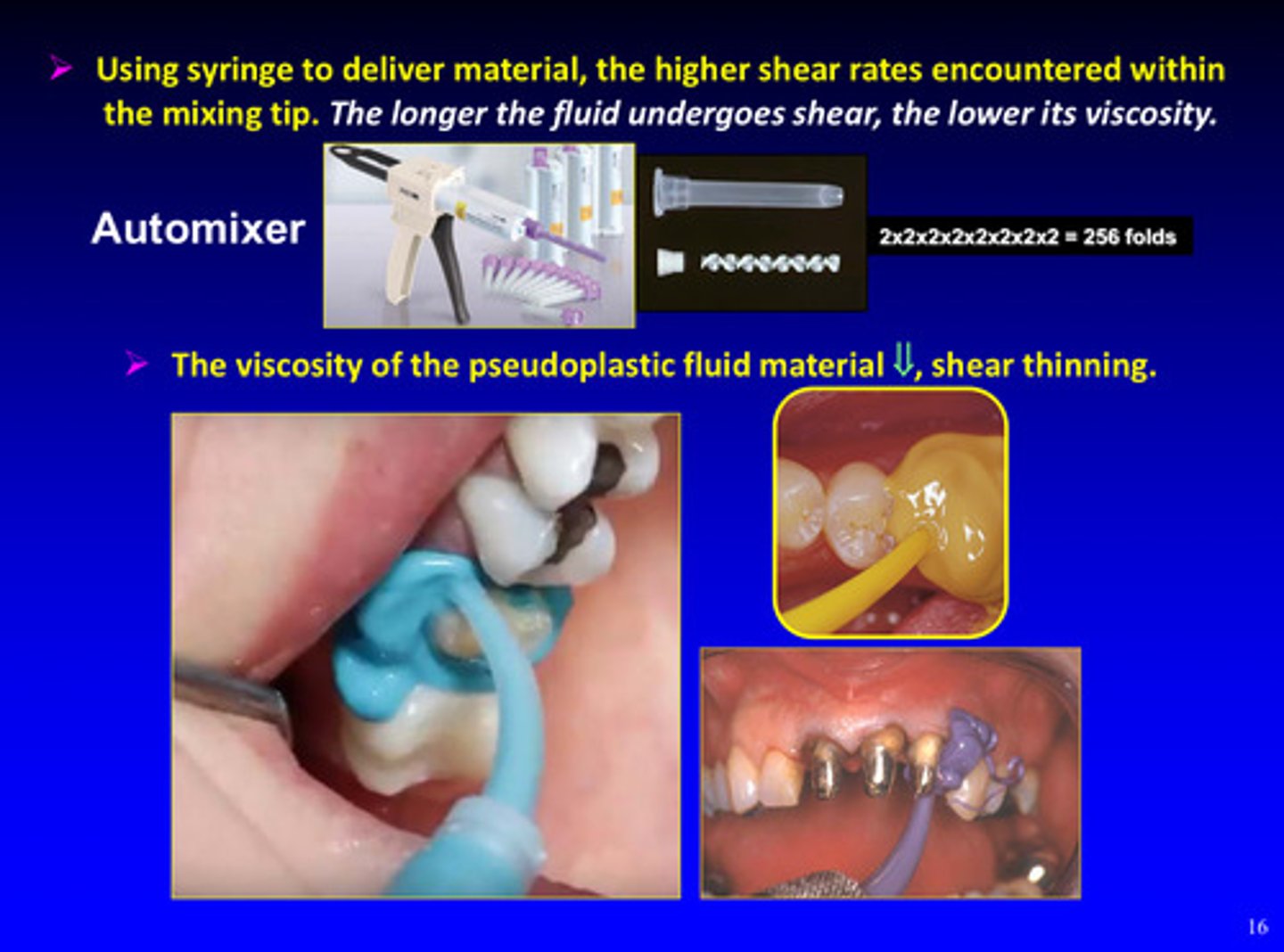
the longer the pseudoplastic fluid undergoes shear, the lower its…
viscosity
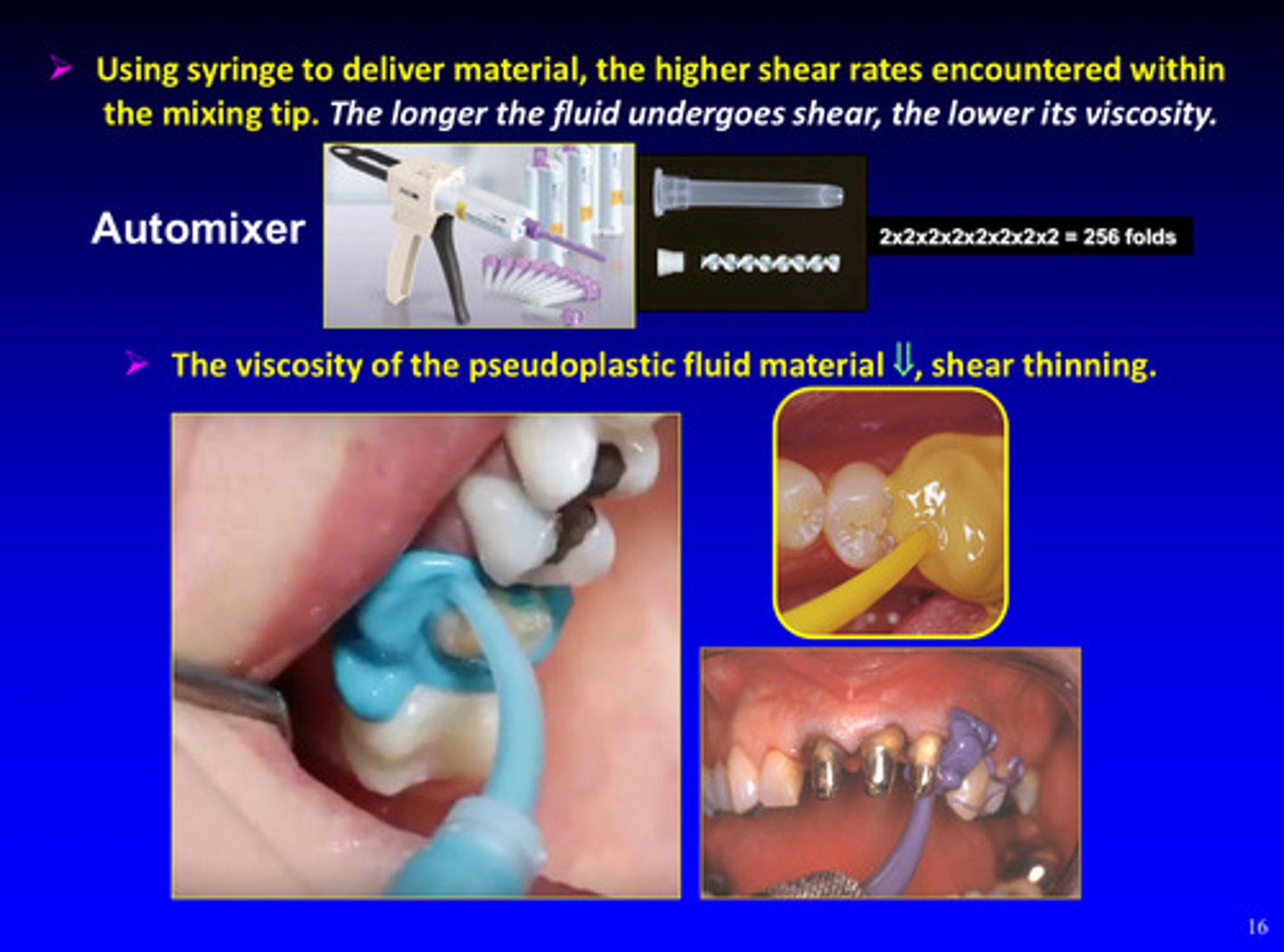
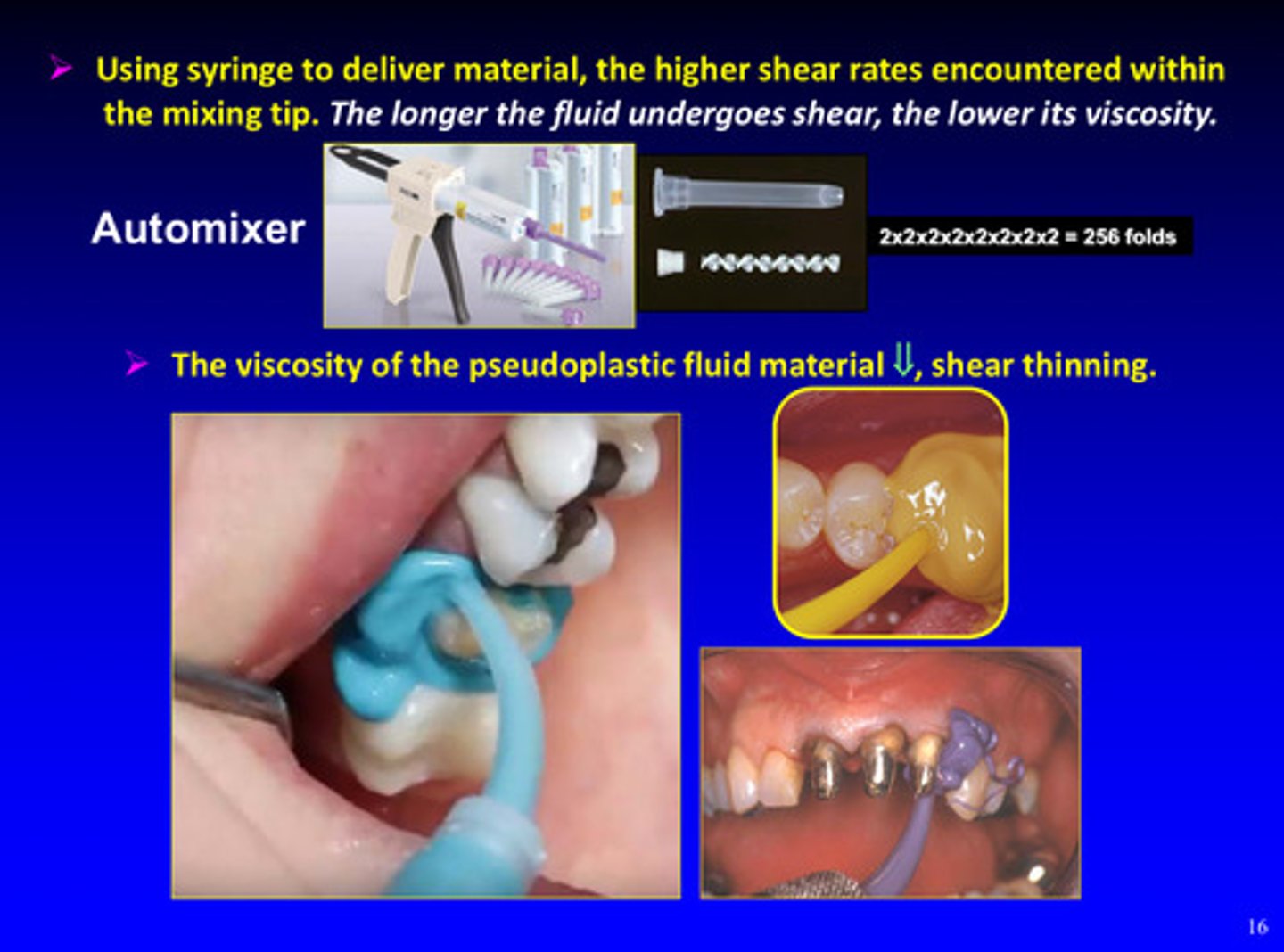
the viscosity of the pseudoplastic fluid material decreases shear __________
thinning
the high shear rates encountered as pseudoplastic fluids pass through the syringe tips, the viscosity _________ by as much as tenfold
decreases
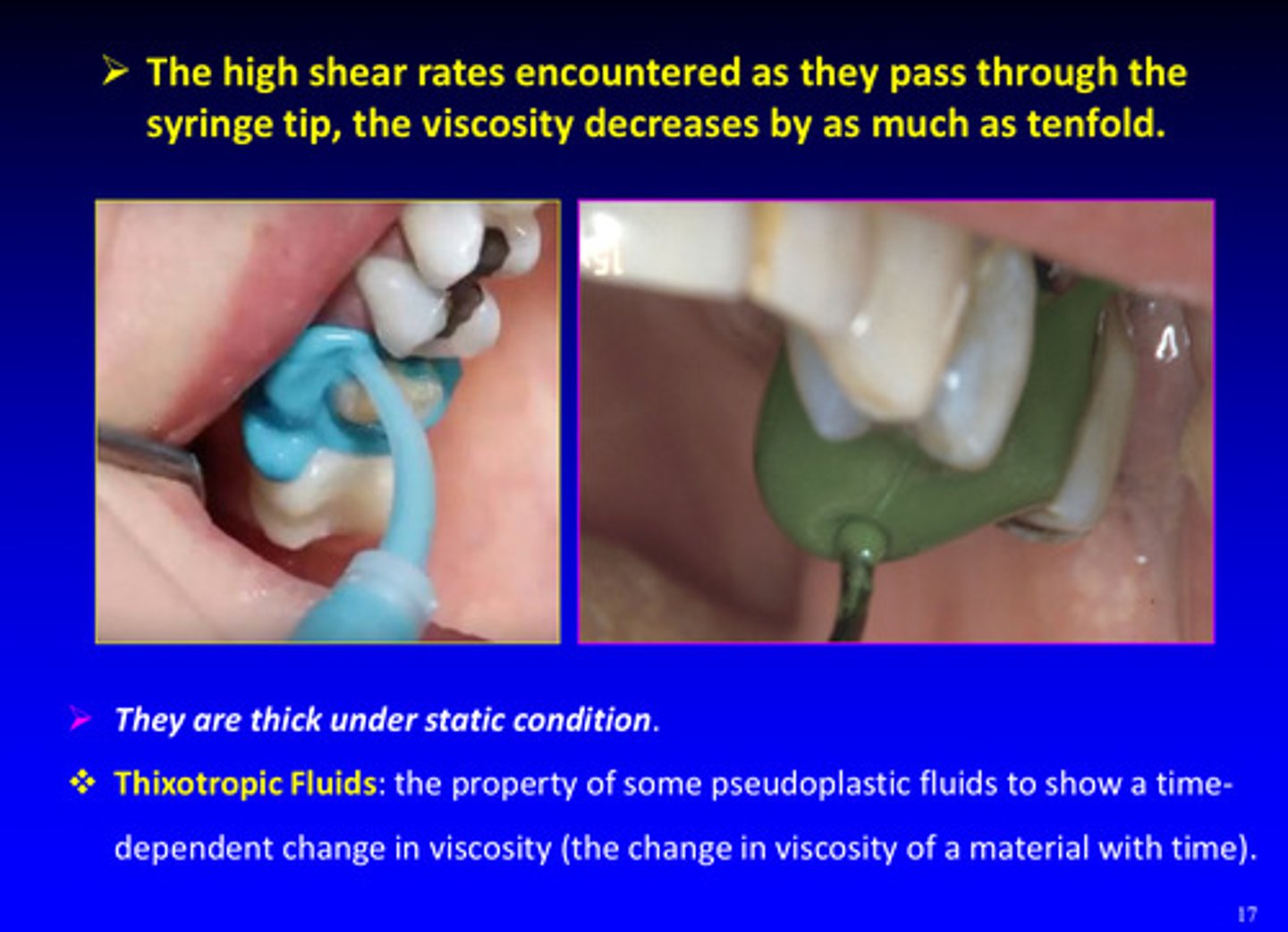
pseudoplastic fluids are _______ under static condition
thick
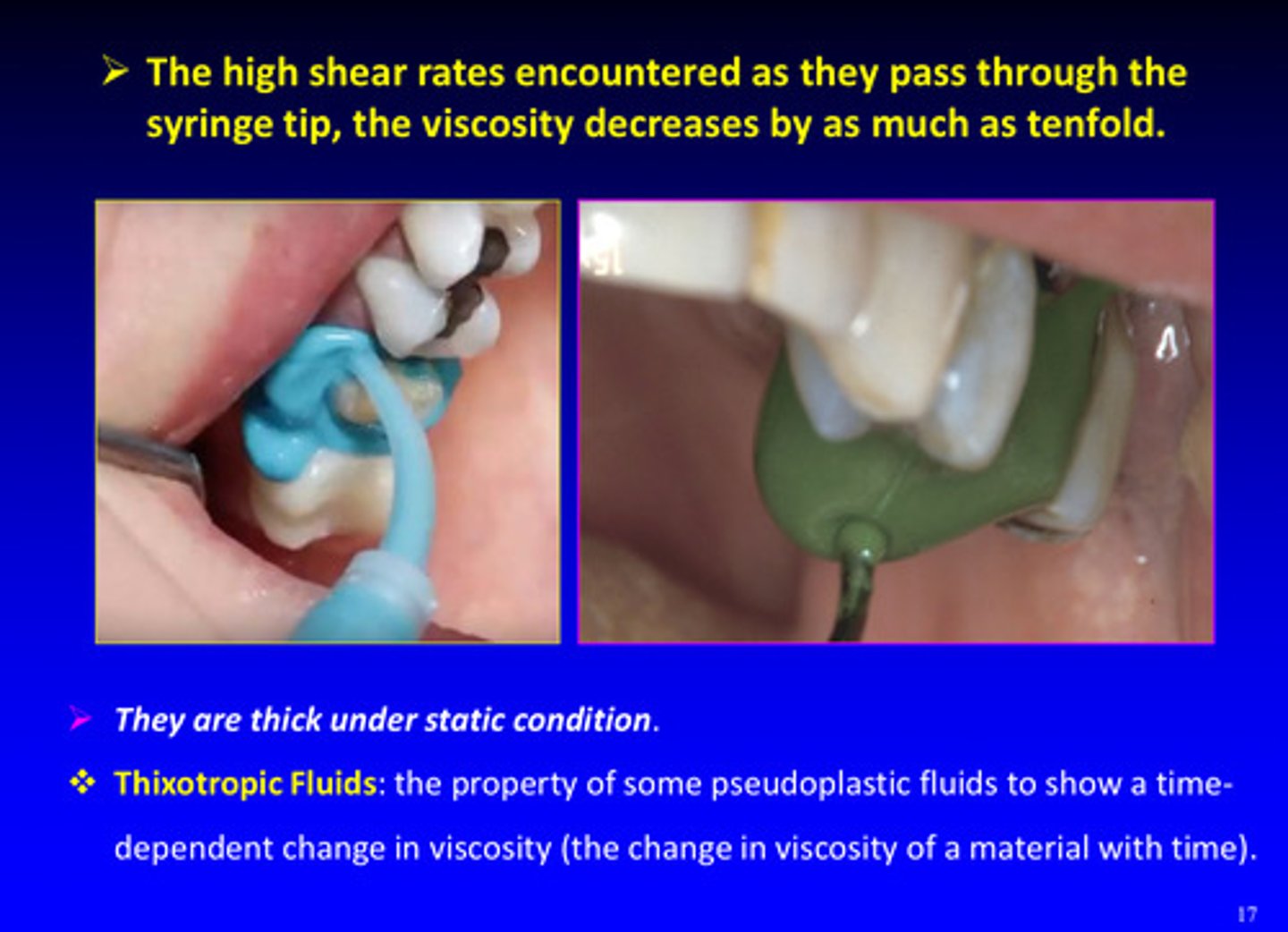
what are thixotropic fluids
the property of some pseudoplastic fluids to show a time-dependent change in viscosity (the change in viscosity of a material with time)
what are the 2 relevant nonaqueous elastomers we are focusing on
polyvinyl siloxane (PVS, VPS) and polyether
what are the 6 requirements for an elastomeric impression material
1) flow properly under load
2) good detail reproduction
3) adequate tear strength
4) high elastic recovery
5) good dimensional stability
6) gypsum compatibility

general formulation of elastic impression materials
matrix (continuous phase) and filler (dispersed phase)
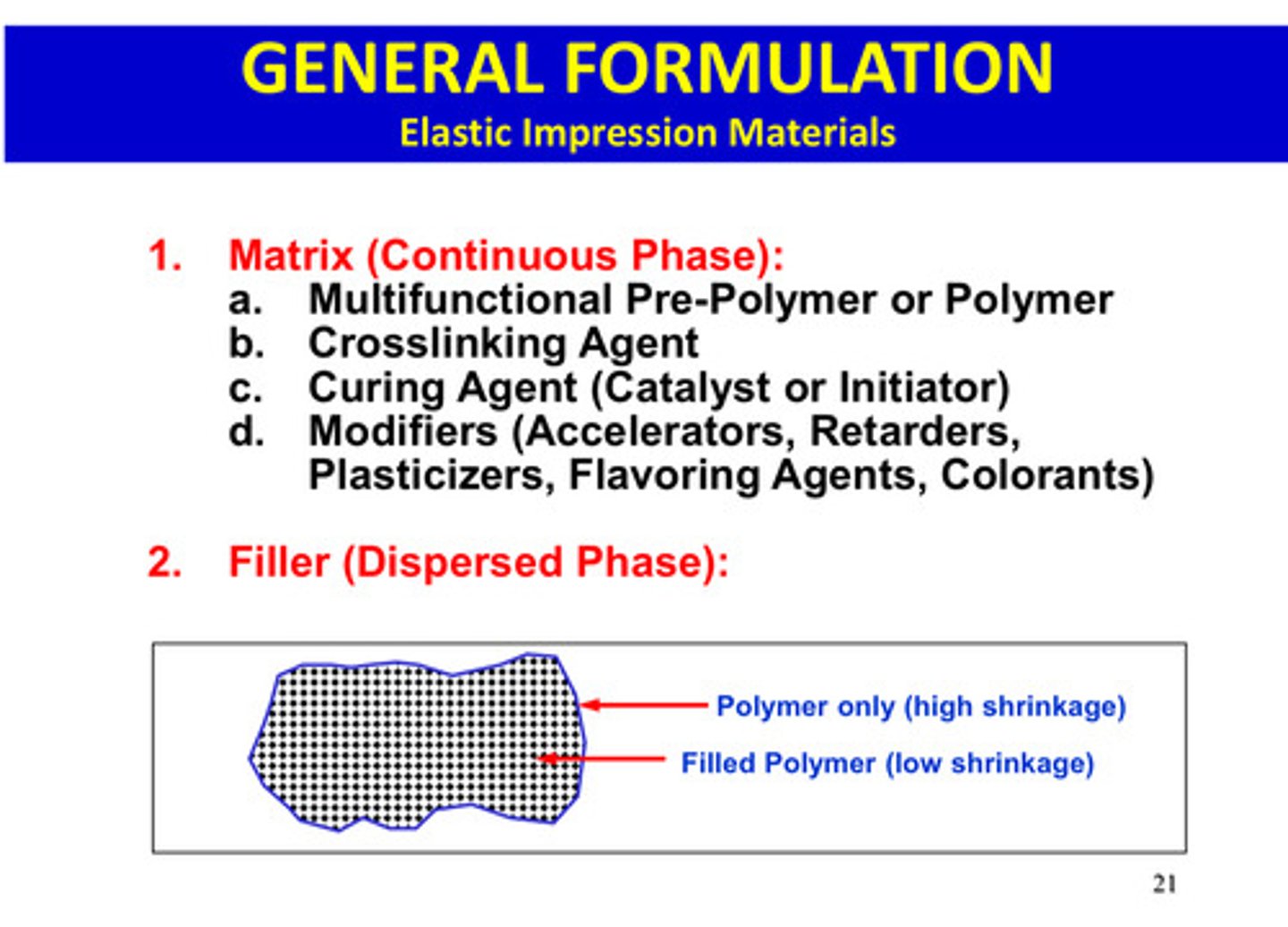
what are the components of matrix in elastic impression materials
multifunctional pre-polymer or polymer
crosslinking agent
curing agent (catalyst or initiator)
modifiers (accelerators, retarders, plasticizers, flavoring agents, colorants)
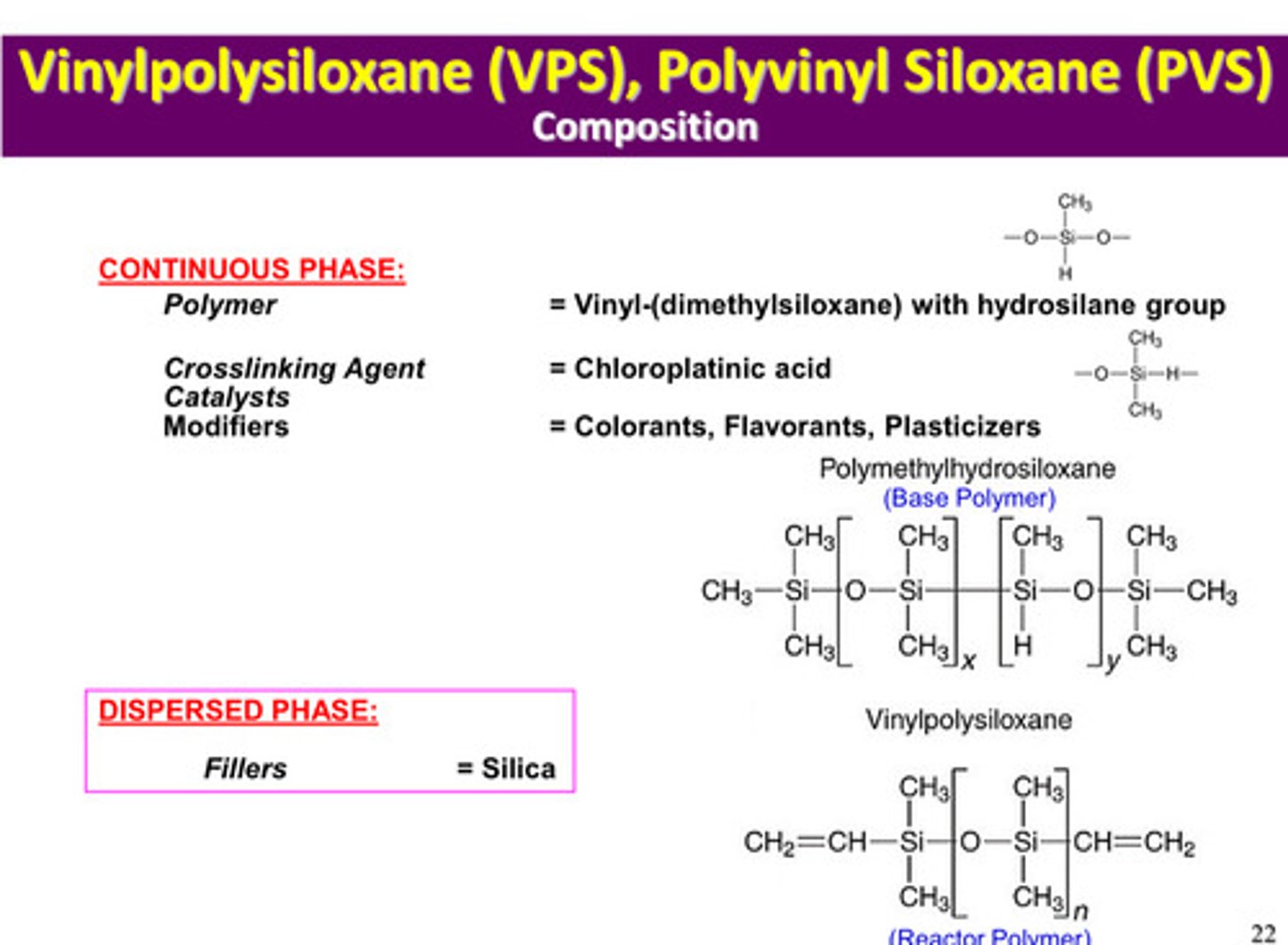
in PVS or VPS, what is the polymer of the continuous phase/matrix
vinyl-(dimethylsiloxane) with hydrosilane group
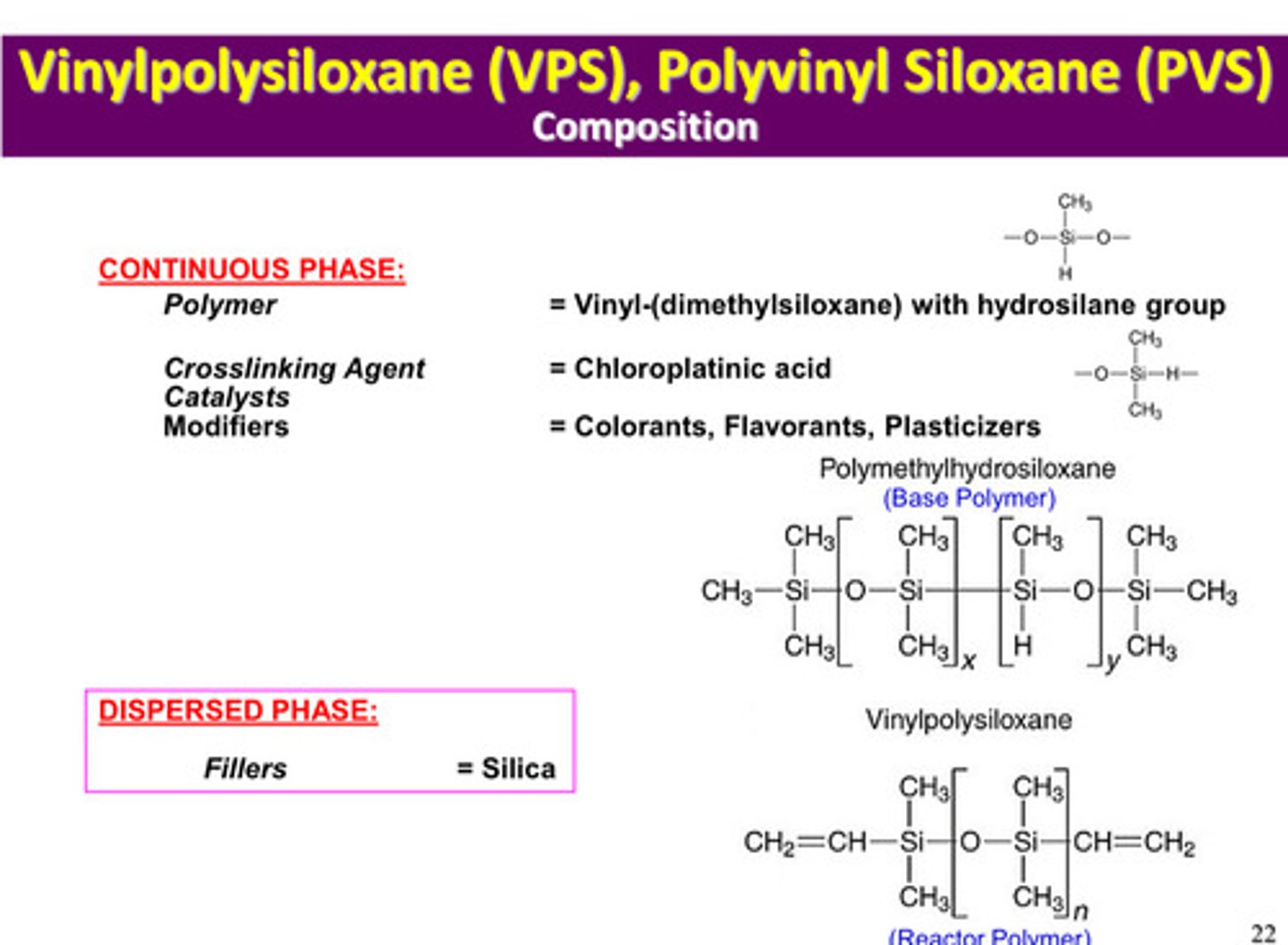
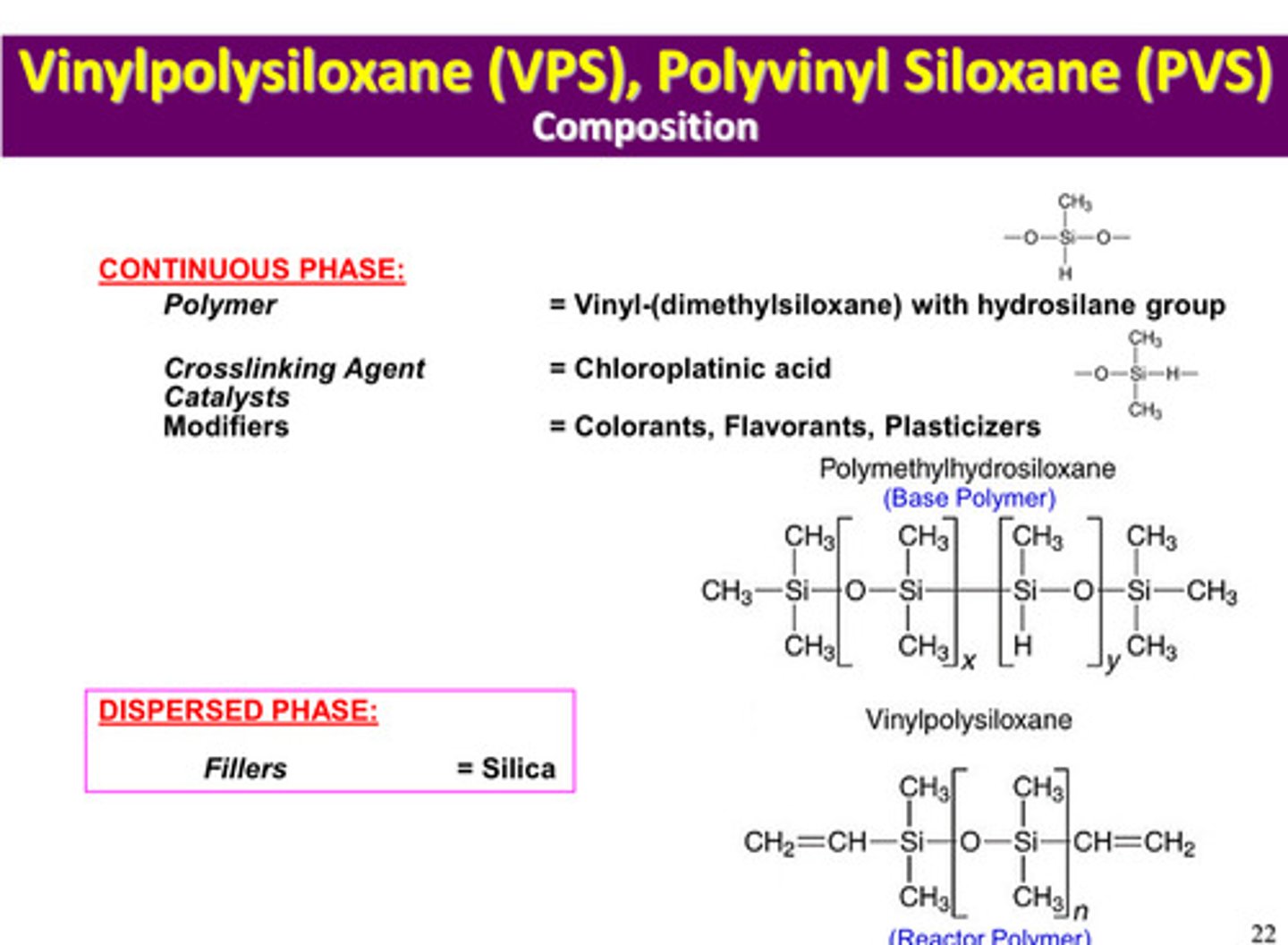
in PVS or VPS, what is the crosslinking agent/catalyst of the continuous phase/matrix
chloroplatinic acid
in PVS or VPS, what are the modifiers of the continuous phase/matrix
colorants, flavorants, plasticizers
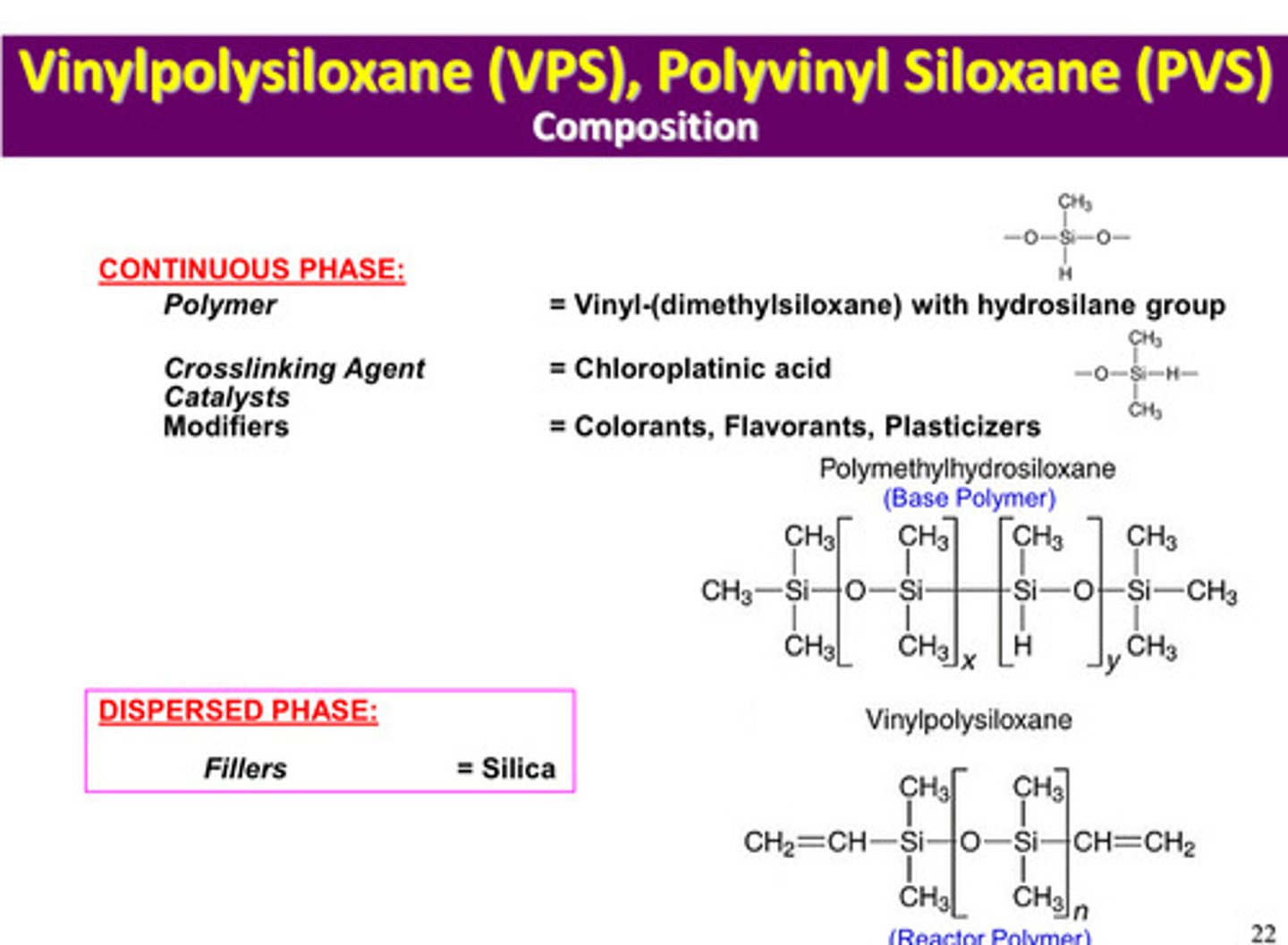
in PVS or VPS, what is the filler of the dispersed phase/filler
silica
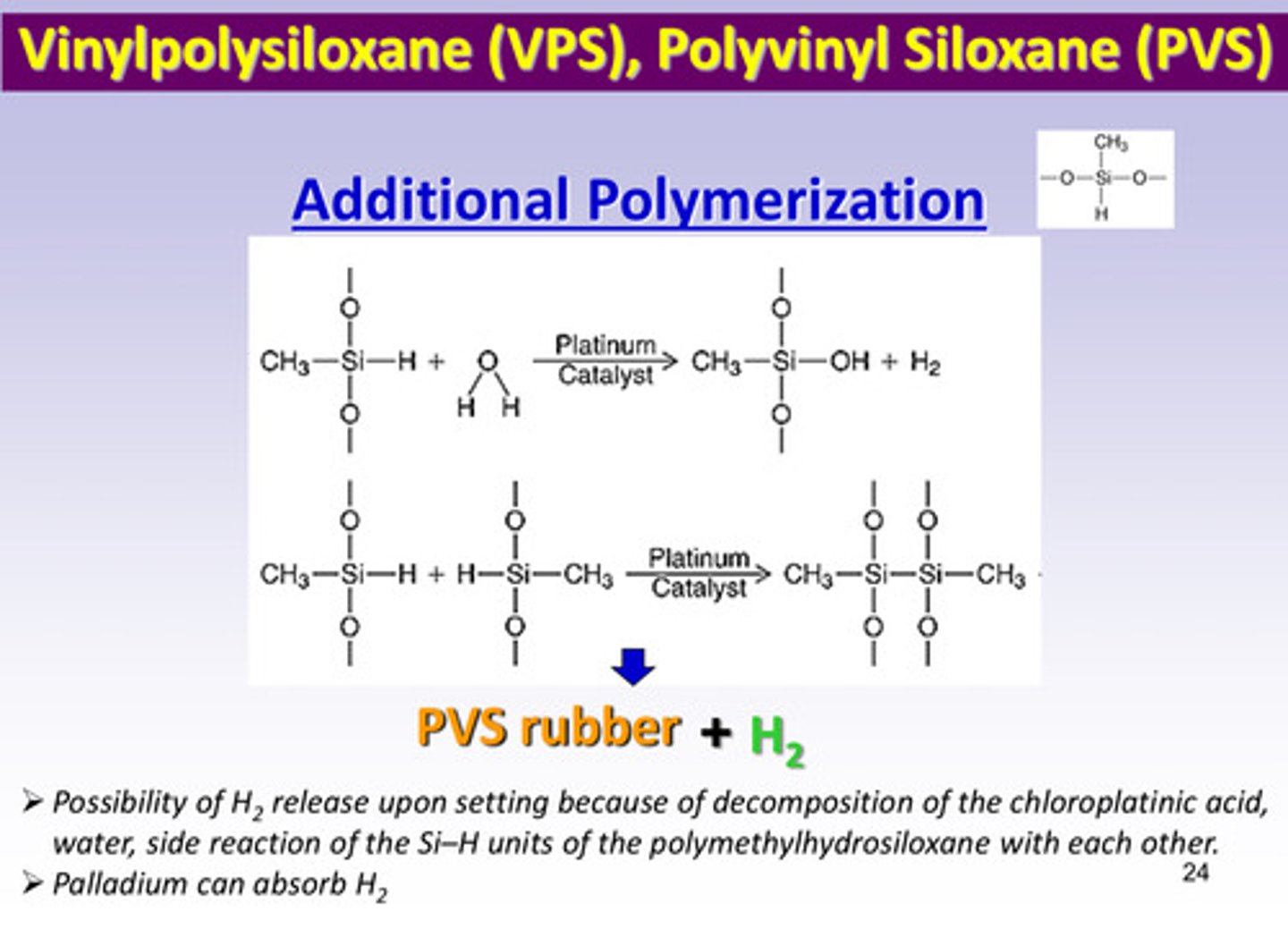
what kind of polymerization reaction occurs between the reactor polymer and the hydrosilane group of VPS/PVS
addition polymerization (product is PVS rubber with no by product)
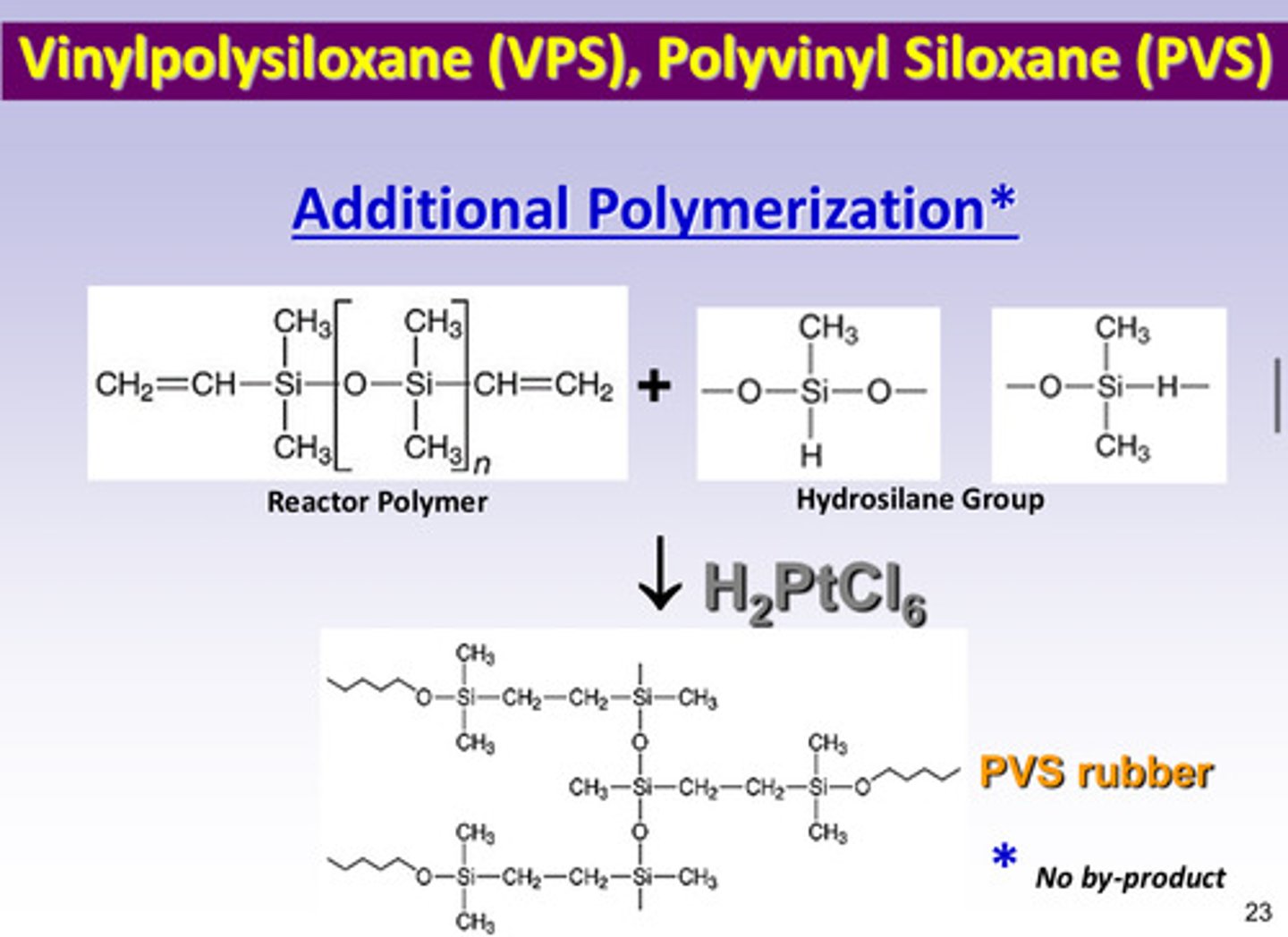
in addition polymerization, there is no by-product, but there is the possibility of ____ gas release upon setting because of what 3 things…
H2 gas; bc of decomposition of the chloroplatinic acid, water, and side rxn of Si-H units of polymethylhydrosiloxane with each other
what can absorb the H2 that is released by the addition polymerization reaction of VPS/PVS
palladium (ingredient that can be included in the impression material)
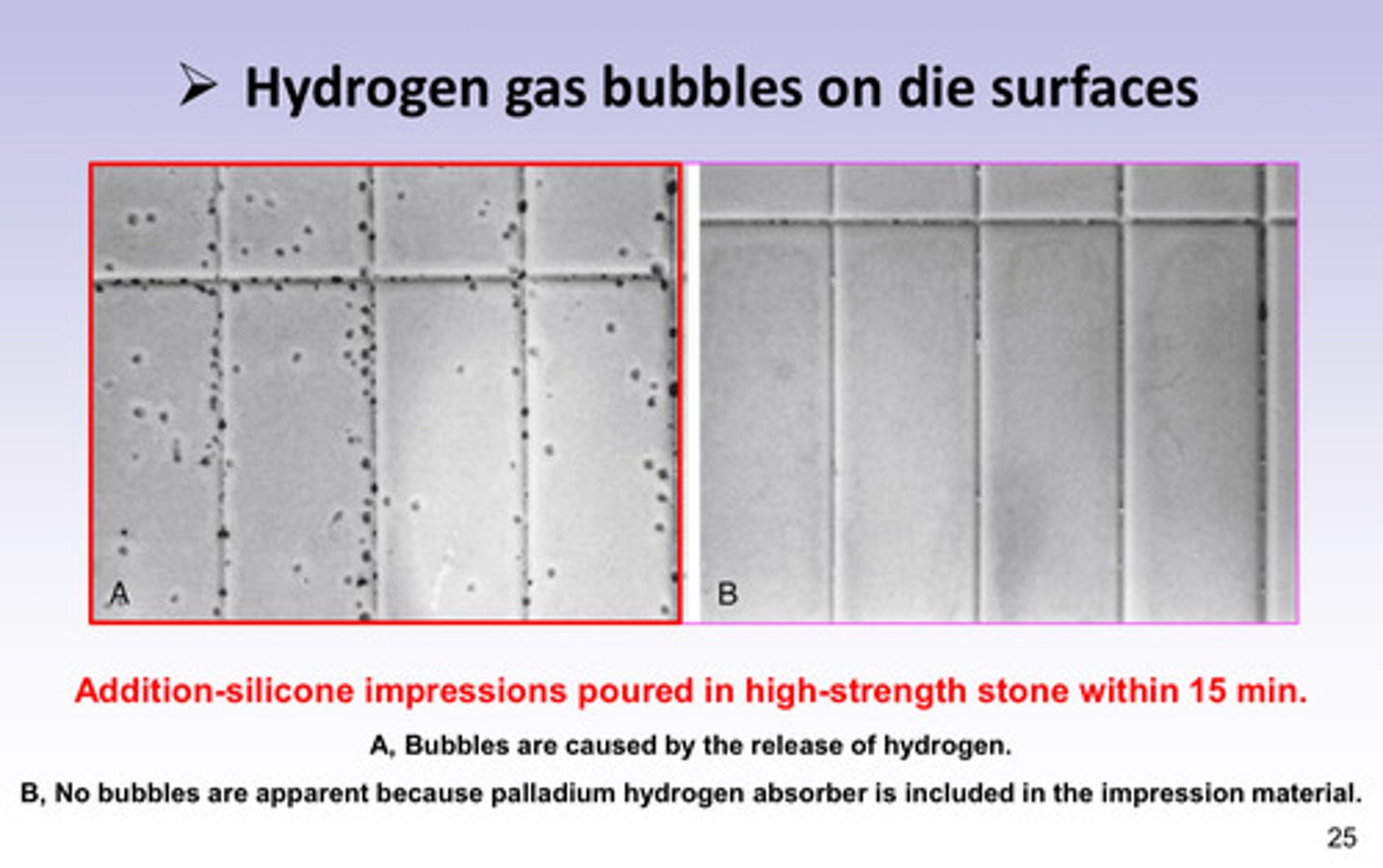
addition-silicone impressions should be poured in _________________ within __________ min
high-strength stone; 15
what are the 5 advantages of PVS/VPS
1) clean and pleasant for the patient
2) highly accurate
3) highly dimensional stability
4) delayed 30-60 min before casting
5) possible multiple pours
examples of hydrogen gas bubbles on die surface
A: bubbles caused by release of H2
B: no bubbles apparent because palladium hydrogen absorber is included in impression material
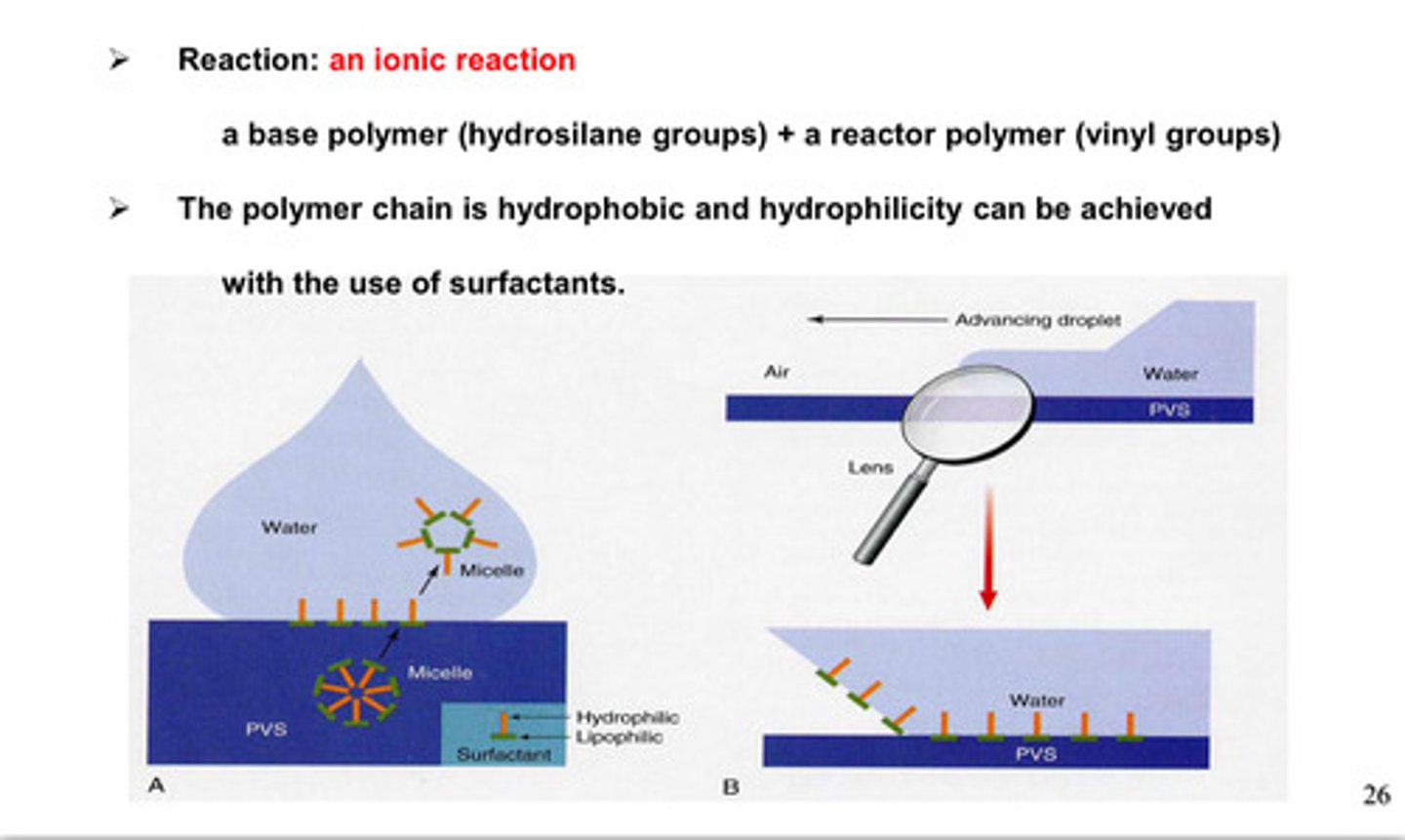
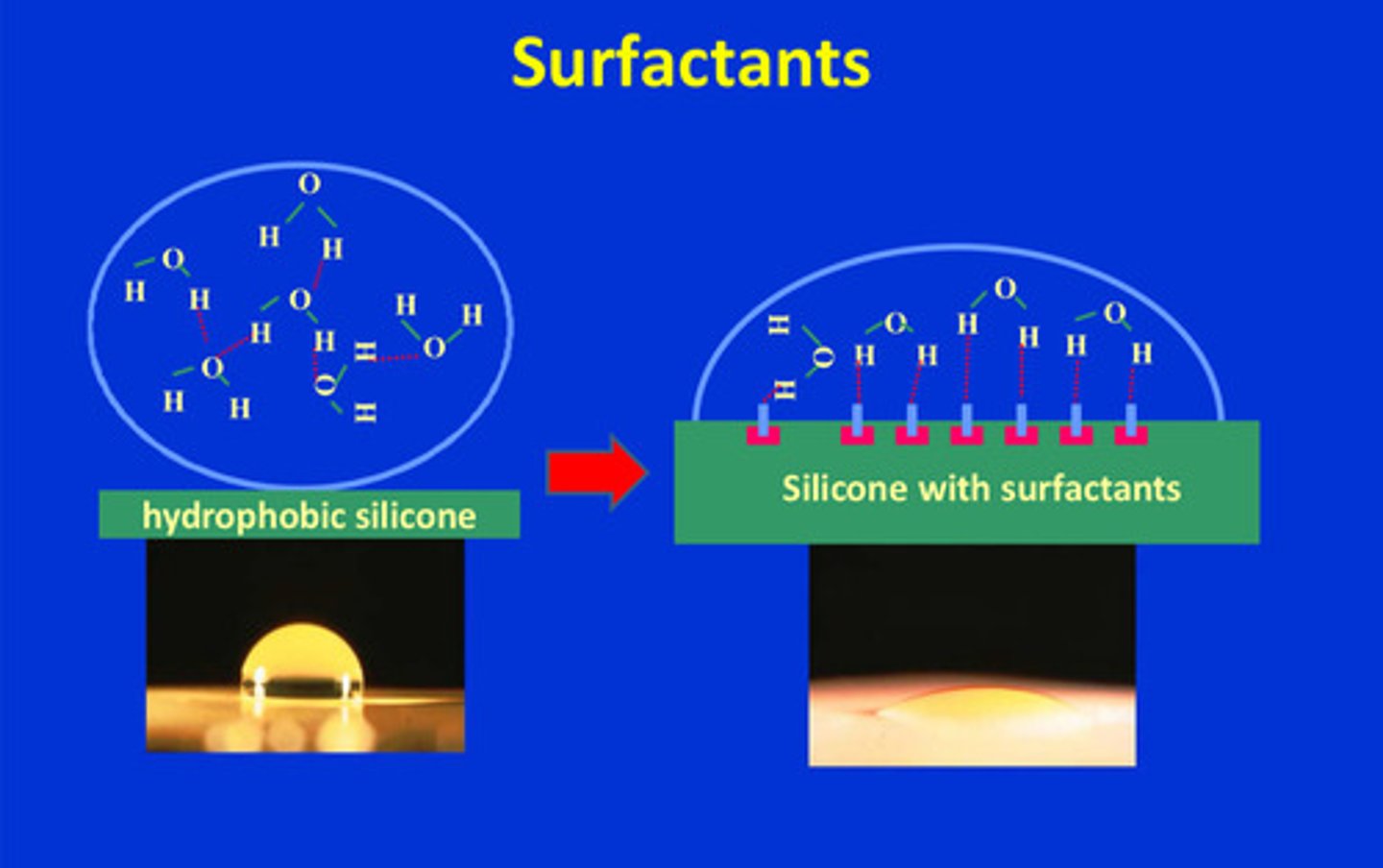
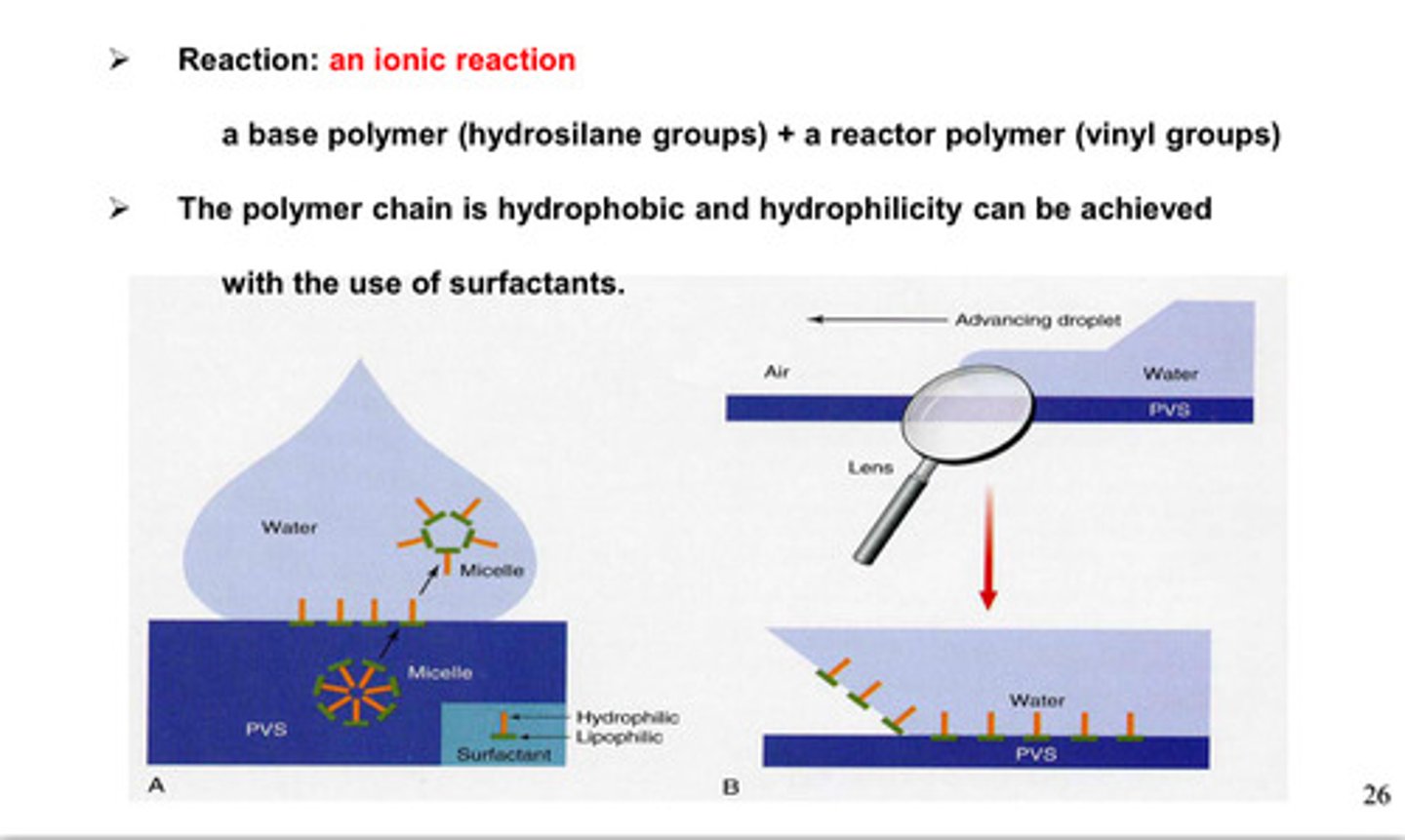
the polymer chain in VPS/PVS is ___________ and ___________ can be achieved w the use of surfactants
hydrophobic; hydrophilicity
what kind of reaction occurs between the base polymer (hydrosilane group) and reactor polymer (vinyl group) in VPS/PVS
ionic rxn
what are the 3 disadvantages of PVS/VPS
1) expensive
2) hydrogen gas bubbles on die surfaces
3) sulfur in rubbers (latex) inhibits polymerization
example of surfactant use
in clinical situation, residual monomers in acrylic provisional and composite cores have a similar _____________ effect on the set of PVS like latex gloves
inhibiting
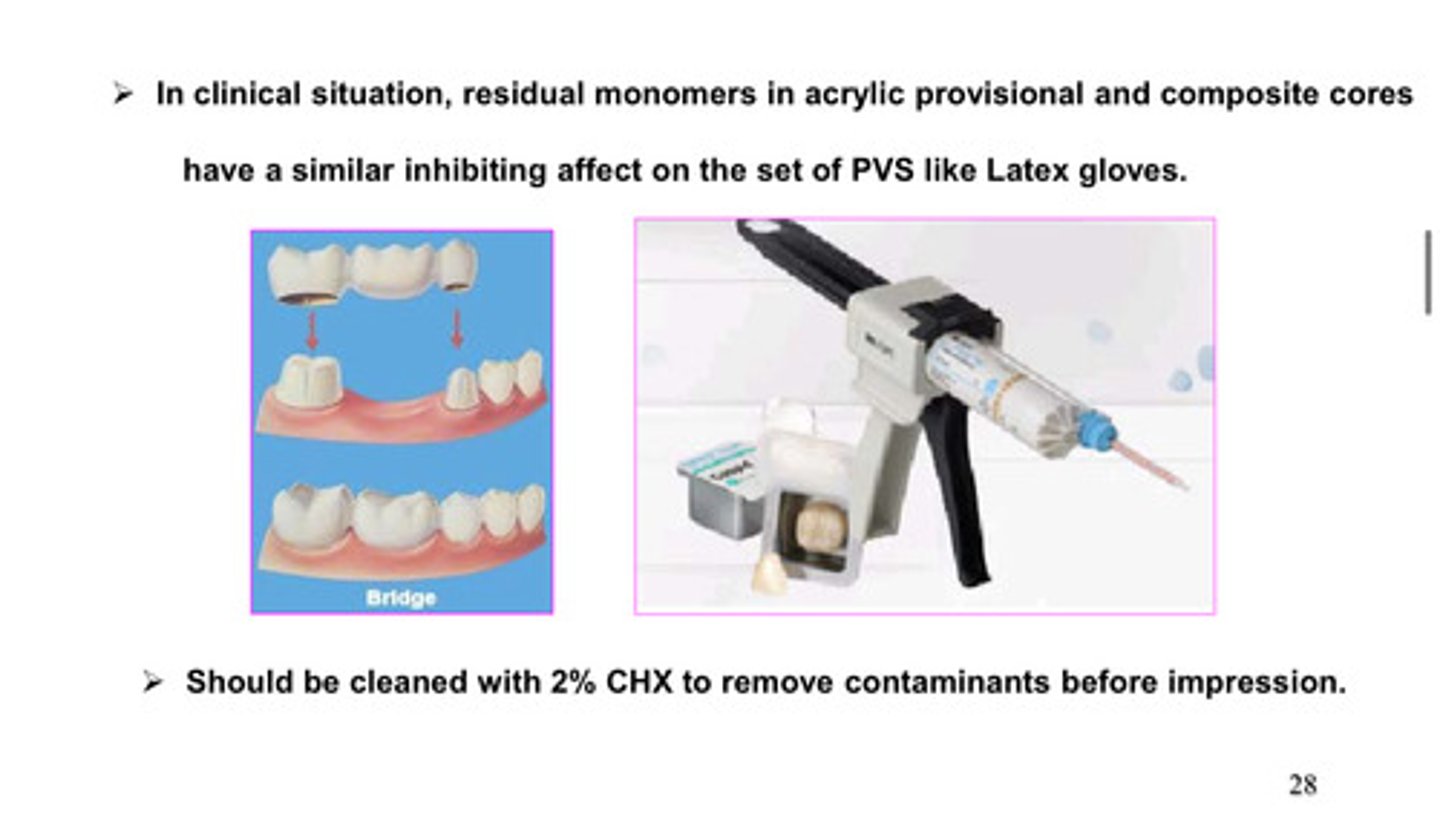
acrylic provisional and composite cores should be cleaned with what to remove contaminants before impression
2% CHX
options of mixing and delivery systems for elastomeric materials (3)
2 pastes on mixing pad, in mixing gun, in mixing machine

why is VPS/PVS the best impression material for dimensional stability
pouring should be delayed 30-60 minutes for H2 out-gassing and pouring can be delayed up to 7-10 days

the polymer chain are ___________ and ___________ can be achieved with the use of _____________
hydrophobic; hydrophilicity; surfactants
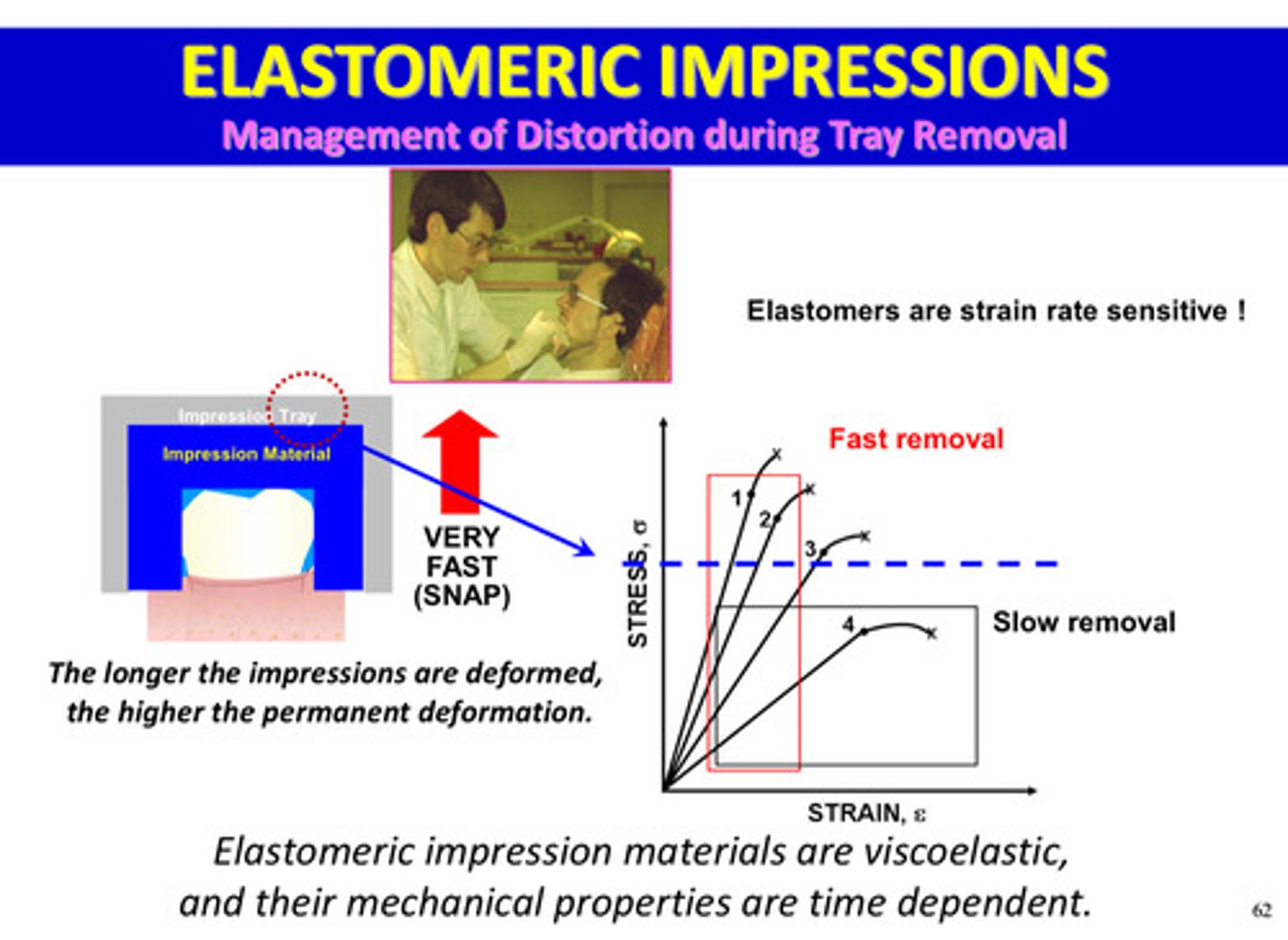
elastomers are strain rate ____________
sensitive
stiffness of VPS/PVS material makes what difficult
removal

most material is dispensed using what mixing/delivery systems
auto-mixing gun and mixing tips

all of the elastomeric impression materials showed linear viscoelastic behavior exhibiting __________ _____________ after 50 hrs of creep recovery
permanent deformation
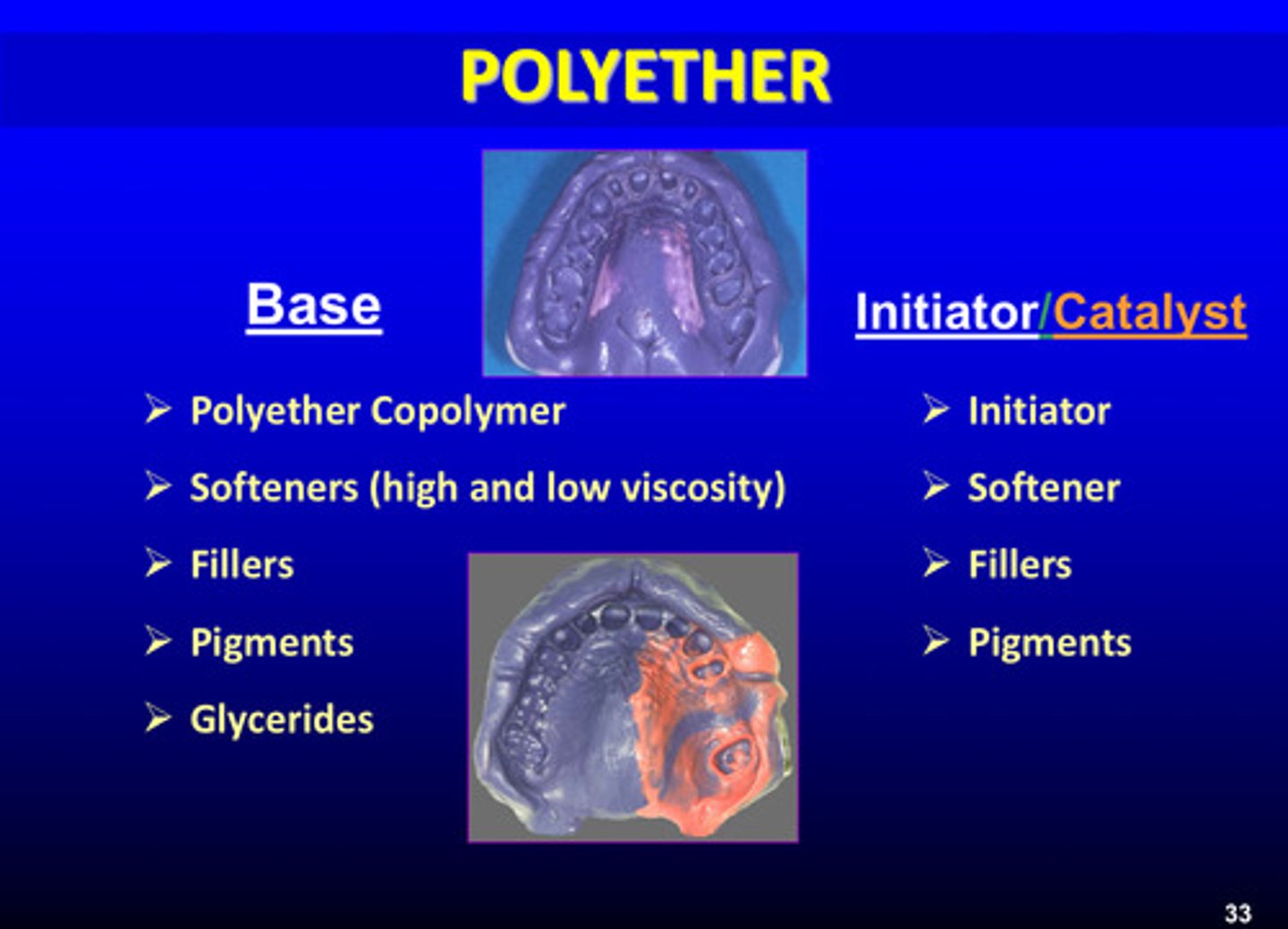
what are the 5 components of the base of polyether impression material
1) polyether copolymer
2) softeners (high and low viscosity)
3) fillers
4) pigments
5) glycerides
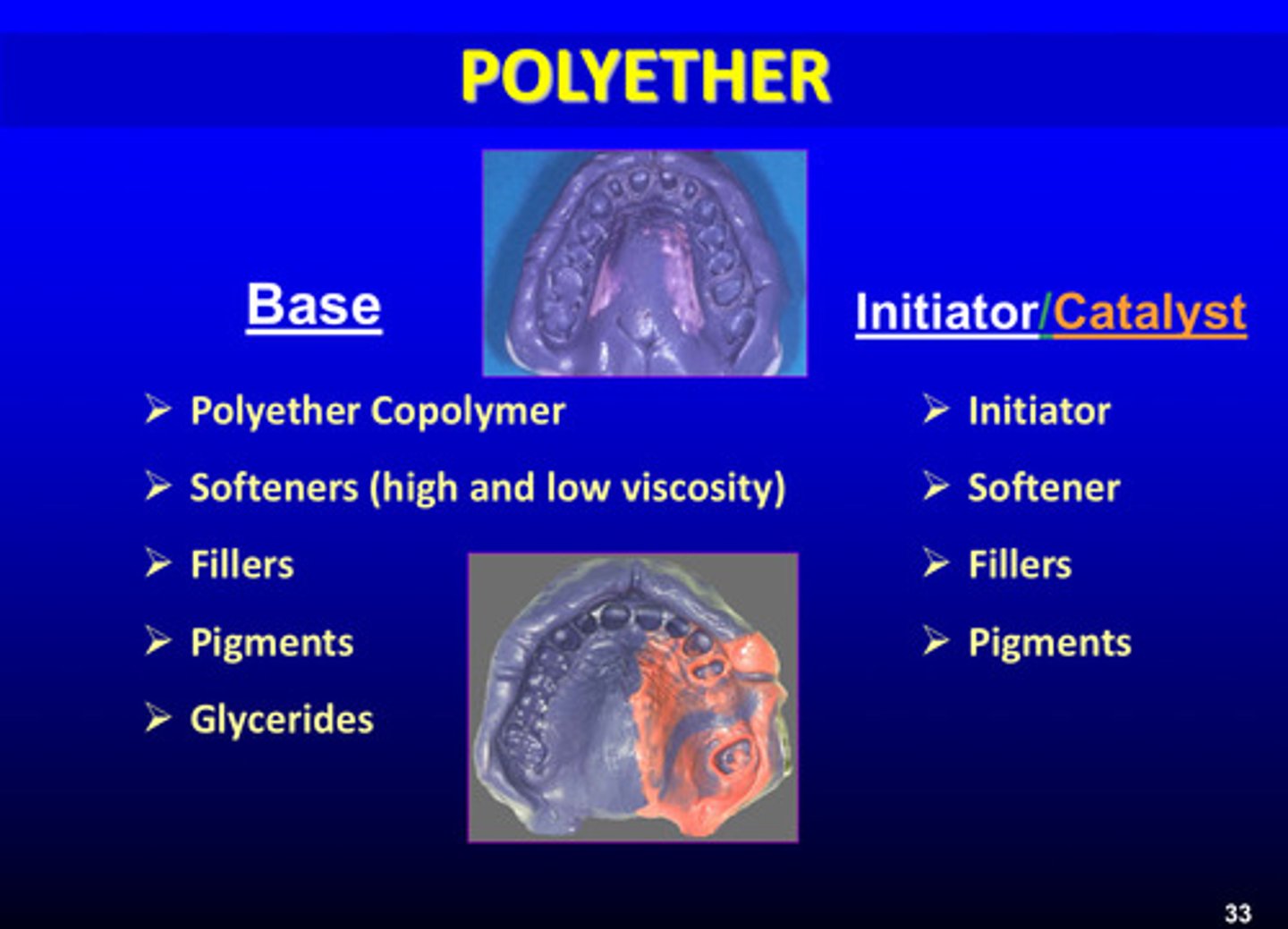
what are the 4 components of the initiator/catalyst of polyether impression materials
1) initiator
2) softener
3) fillers
4) pigments
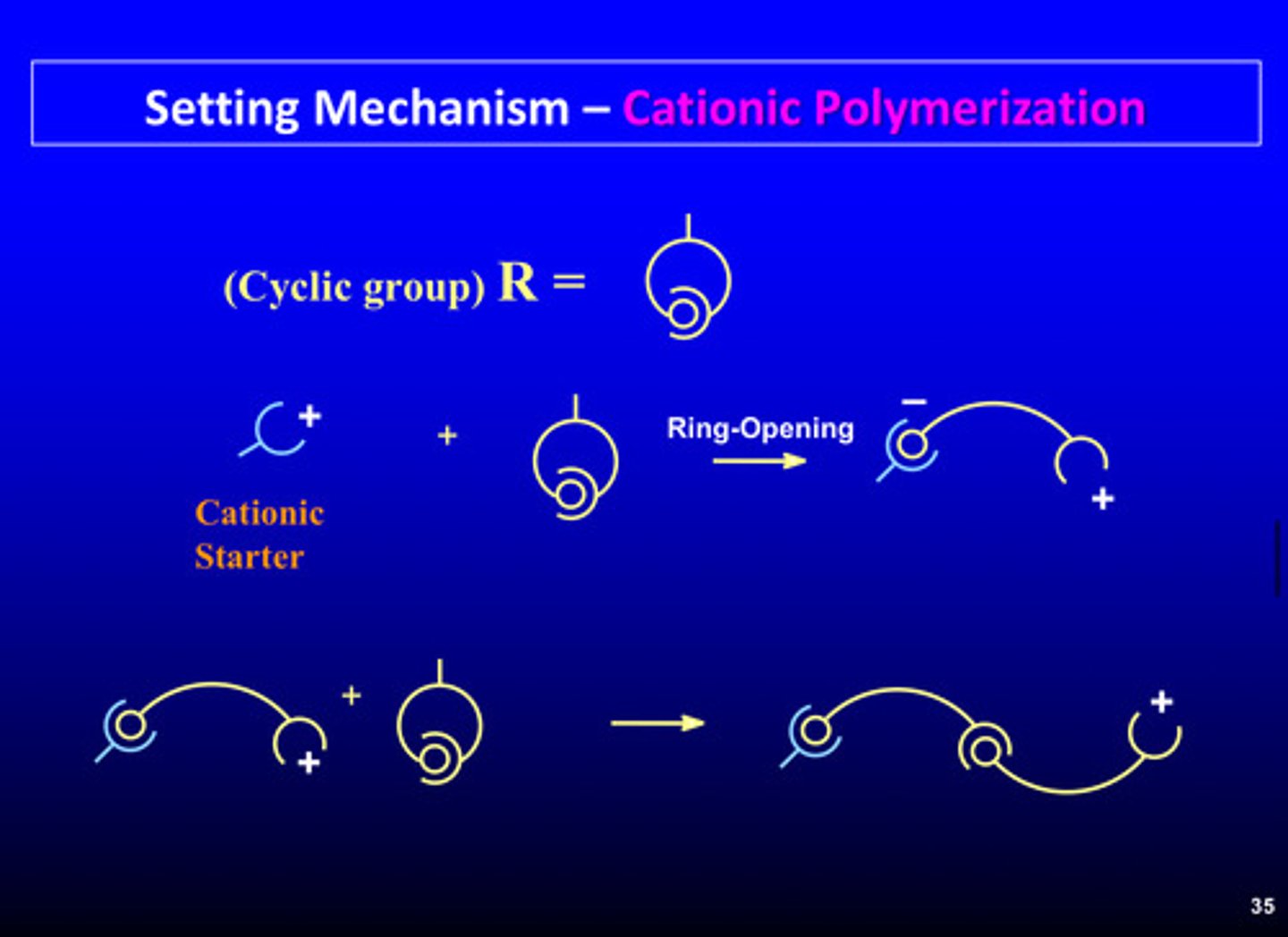
what kind of polymerization reaction occurs for polyether rubbers
cationic polymerization
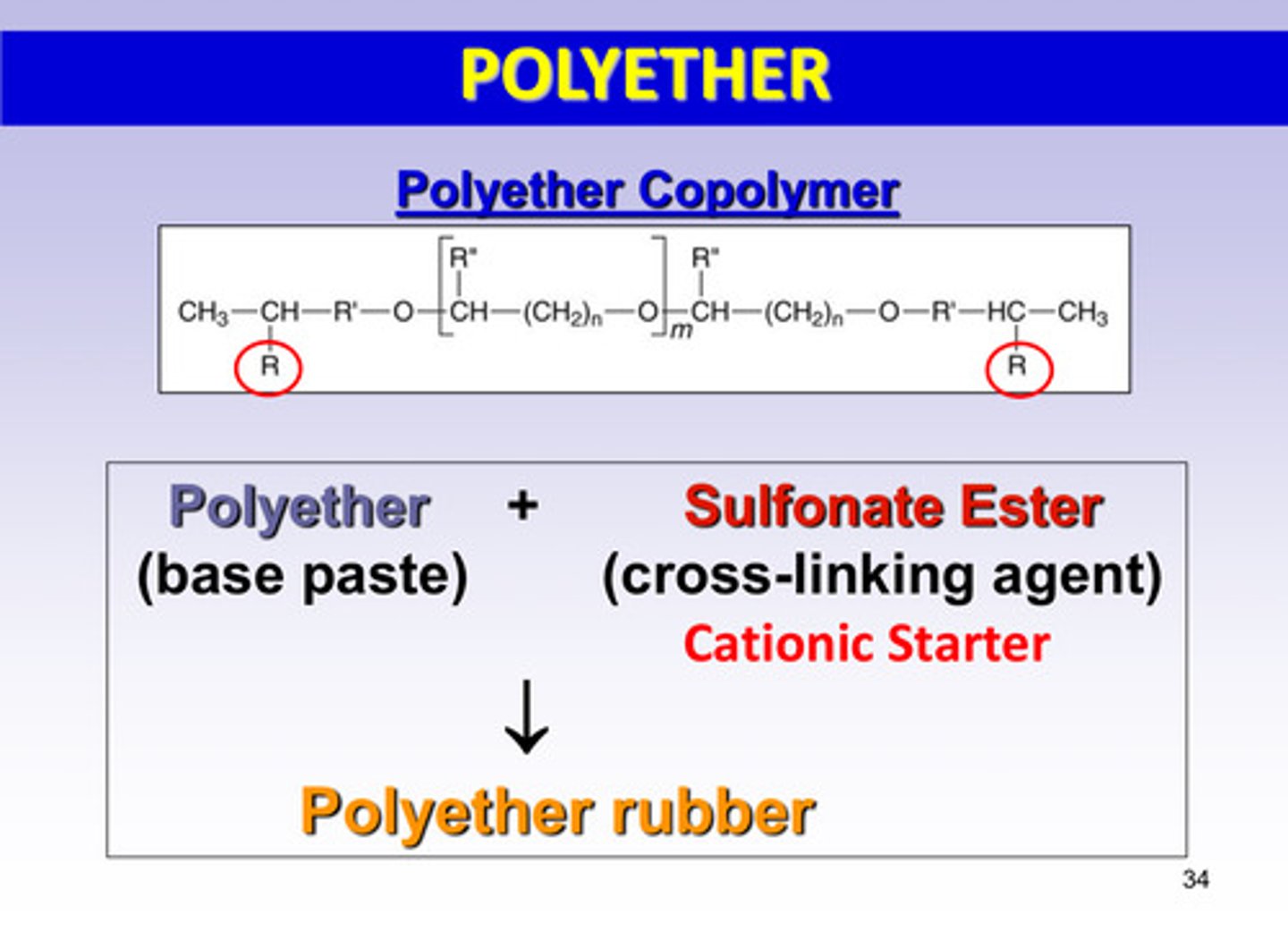
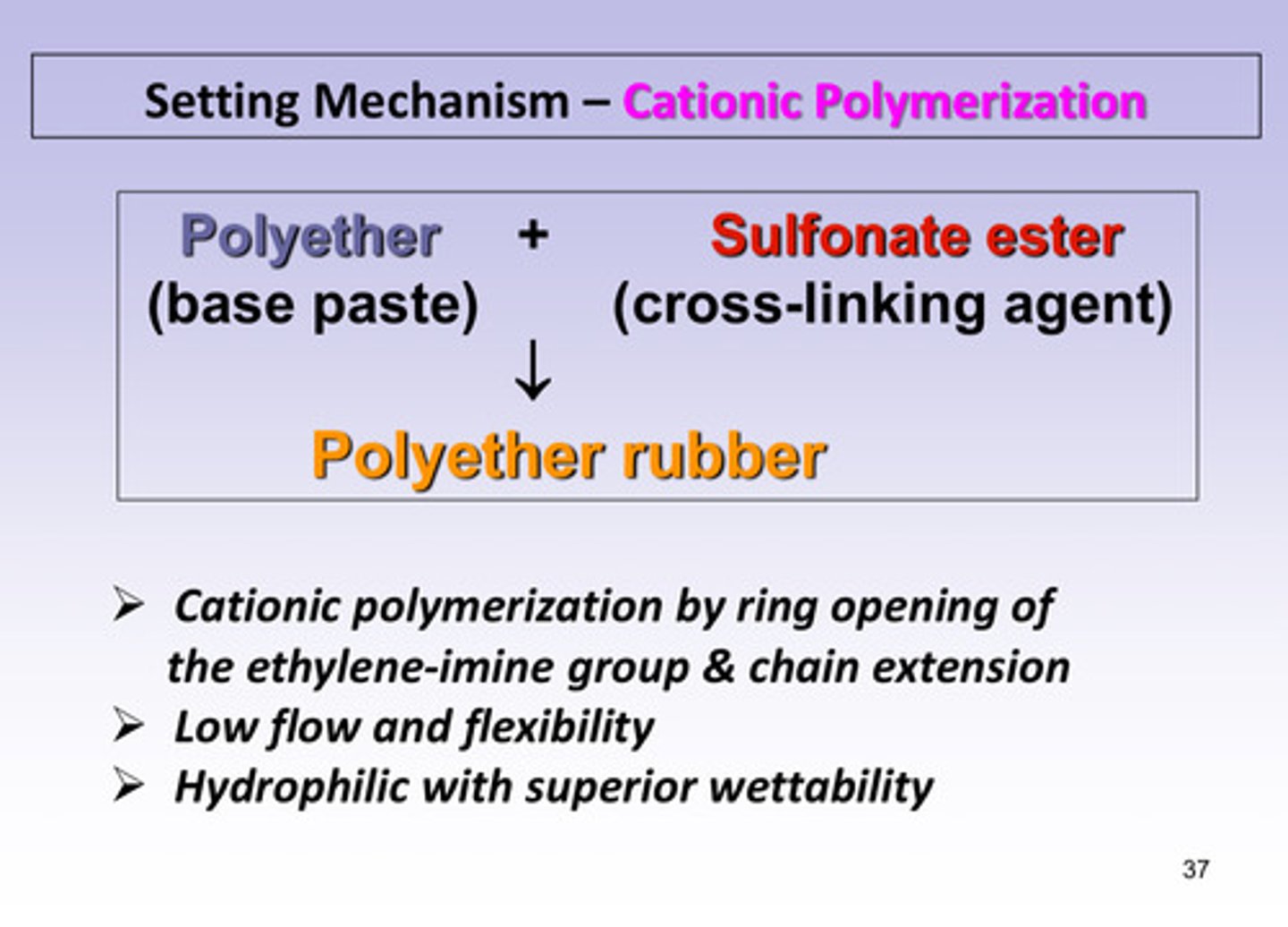
what 2 reactants undergo the polymerization reaction to form the polyether rubber
polyether (base paste) + sulfonate ester (cross-linking agent/cationic starter)
polyether rubber is formed through cationic polymerization by ______ __________ of the ethylene-imine group and _______ __________
ring opening; chain extension
example of cationically induced polyaddition for polyether material
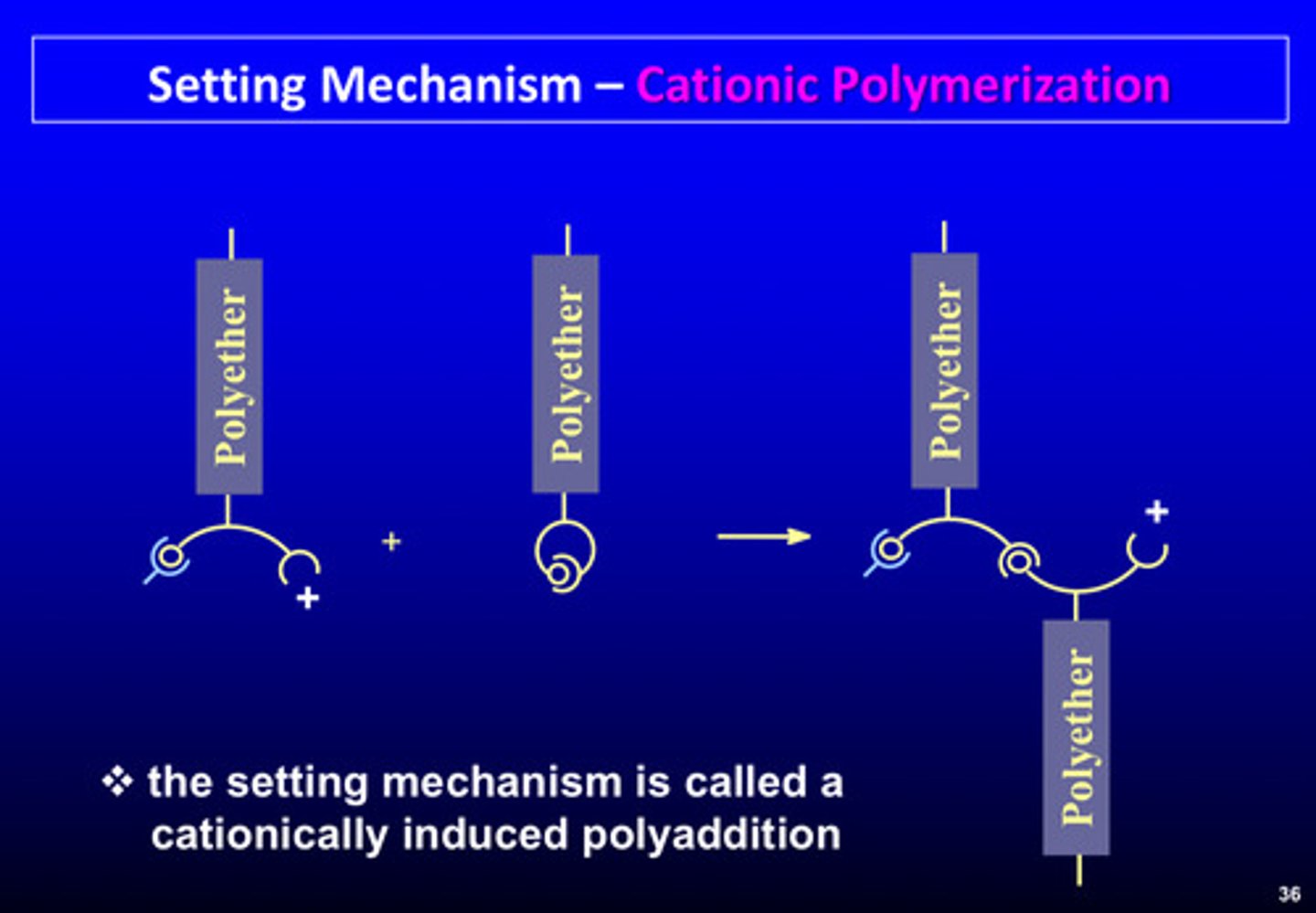
what are the 2 characteristics of polyether rubber
1) low flow and flexibility
2) hydrophilic with superior wettability
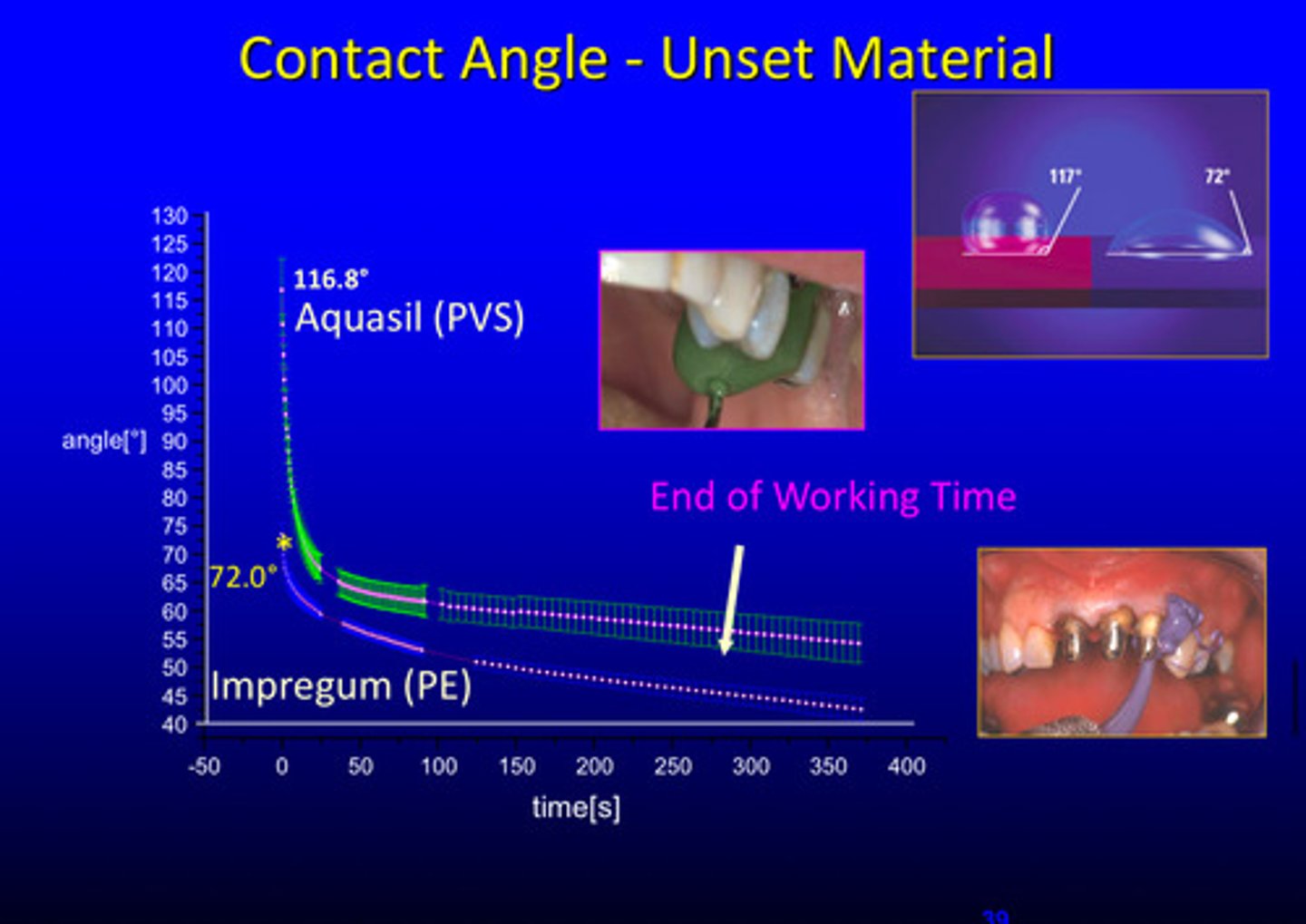
contact angle changes of unset material will… (inc/dec w time)
dec (72) as time inc (to the end of working time)
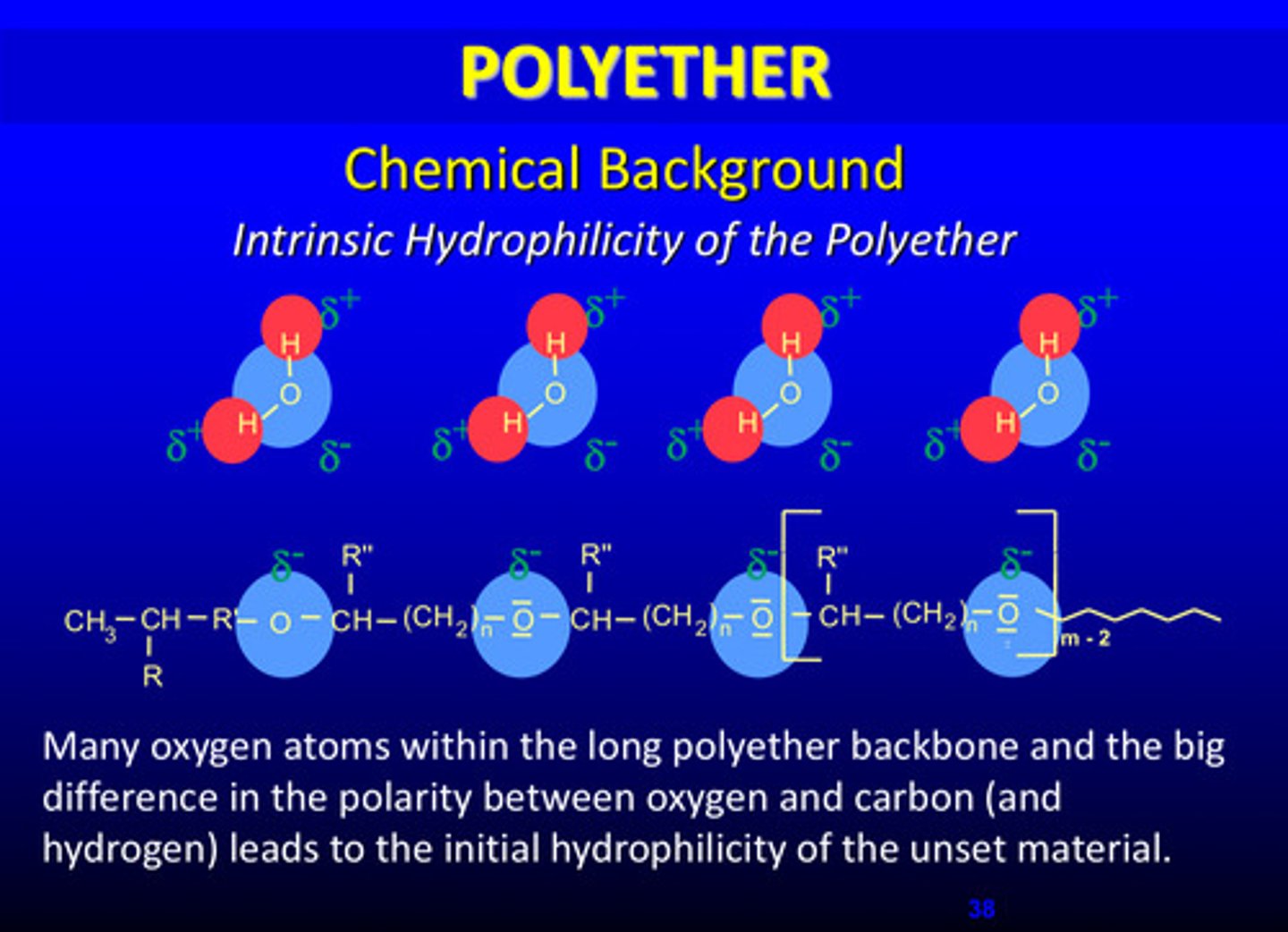
describe the chemical background of the intrinsic hydrophilicity of the polyether
many oxygen atoms within the long polyether backbone and a big difference in the polarity between oxygen and carbon (and hydrogen) leads to initial hydrophilicity of the unset material
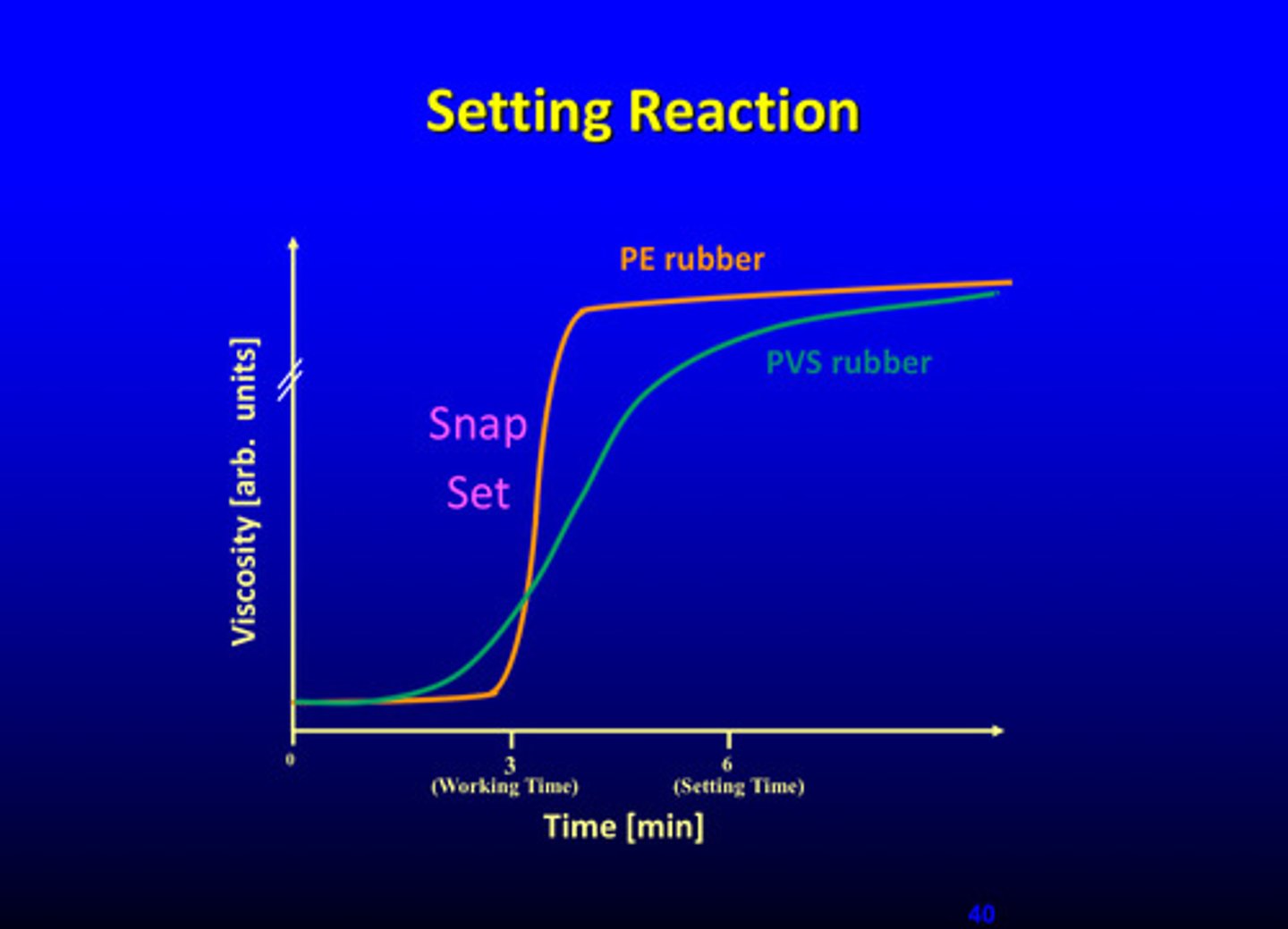
viscosity changes during setting reaction, compare PE and PVS rubber
PE rubber has higher viscosity than PVS
what are 5 polyether rubber manipulation and technique considerations
1) excellent impression accuracy and dimensional stability
2) stiff and therefore difficult to remove without rocking
3) break seal and rock slightly to prevent tearing: LOW tear resistance
4) negatively affected by H2O, saliva, and blood: since hydrophilic, moisture increases marginal discrepancy and increased water absorption occurs if thinning agents are used
5) can be dispensed from automated extruder and mixer (ESPECIALLY PentaMix)

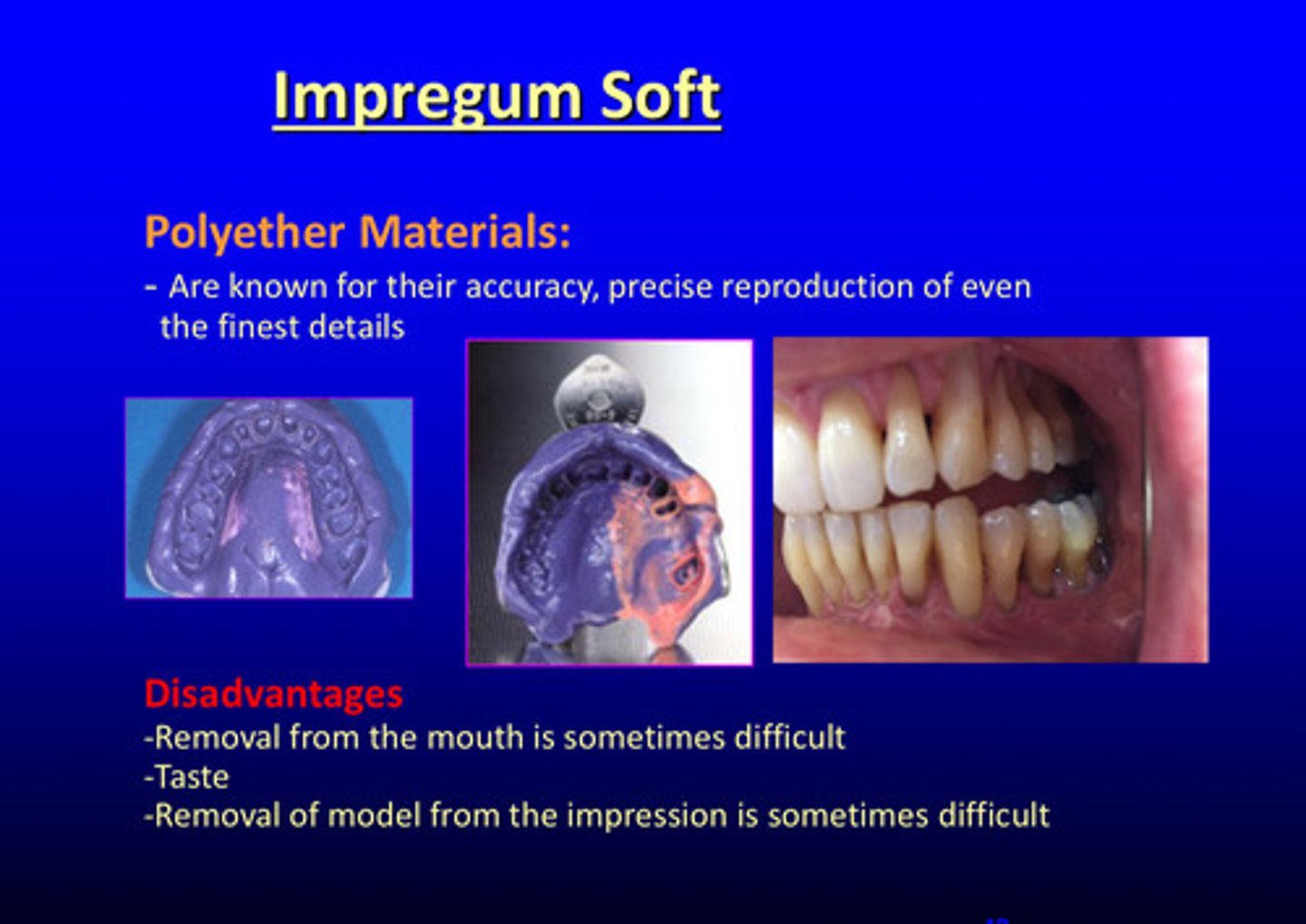
what are polyether materials known for
their accuracy and precise reproduction of even the finest details
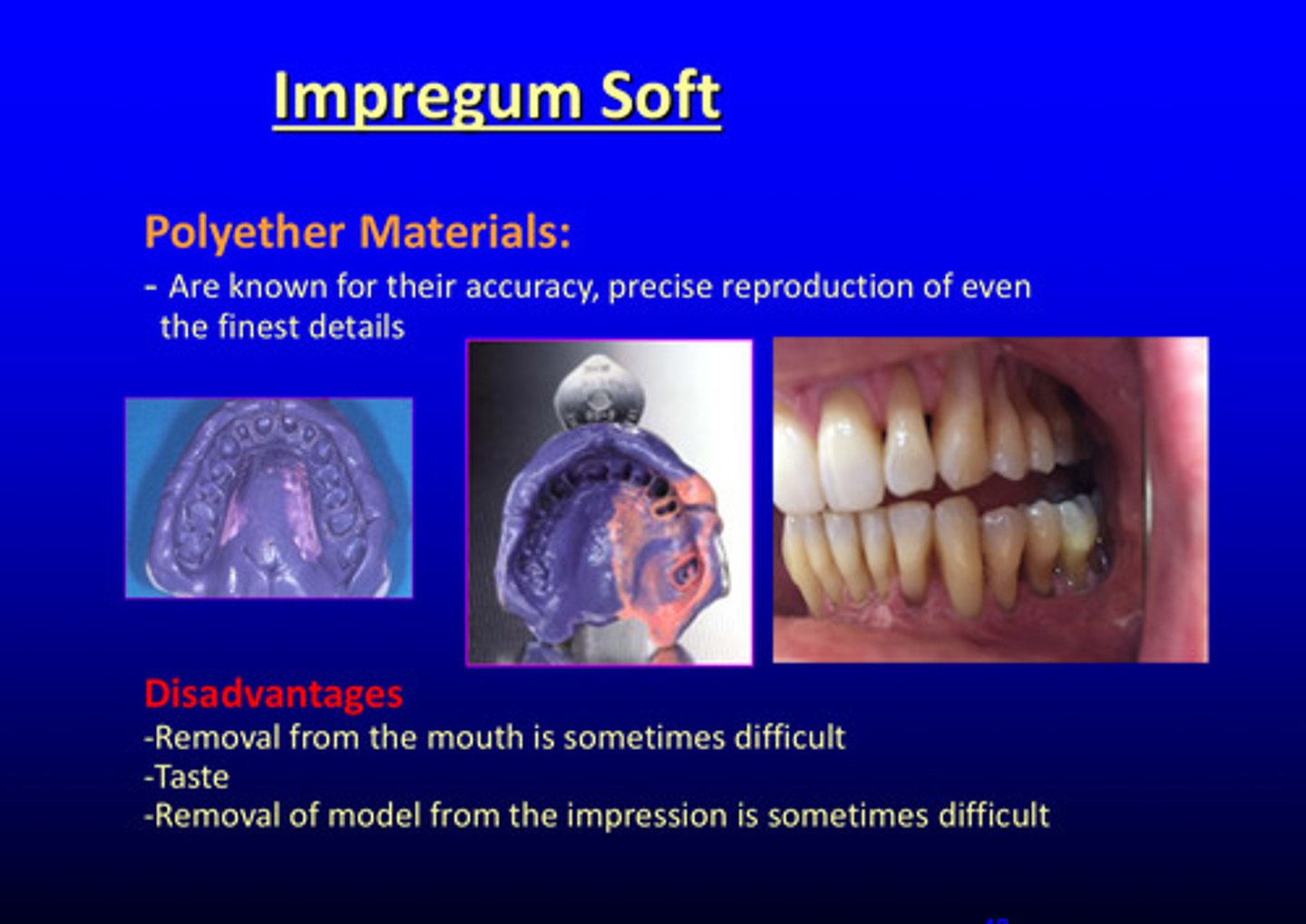
what are the 3 disadvantages of polyether materials
1) removal from the mouth is sometimes difficult
2) taste
3) removal of model from the impression can be difficult
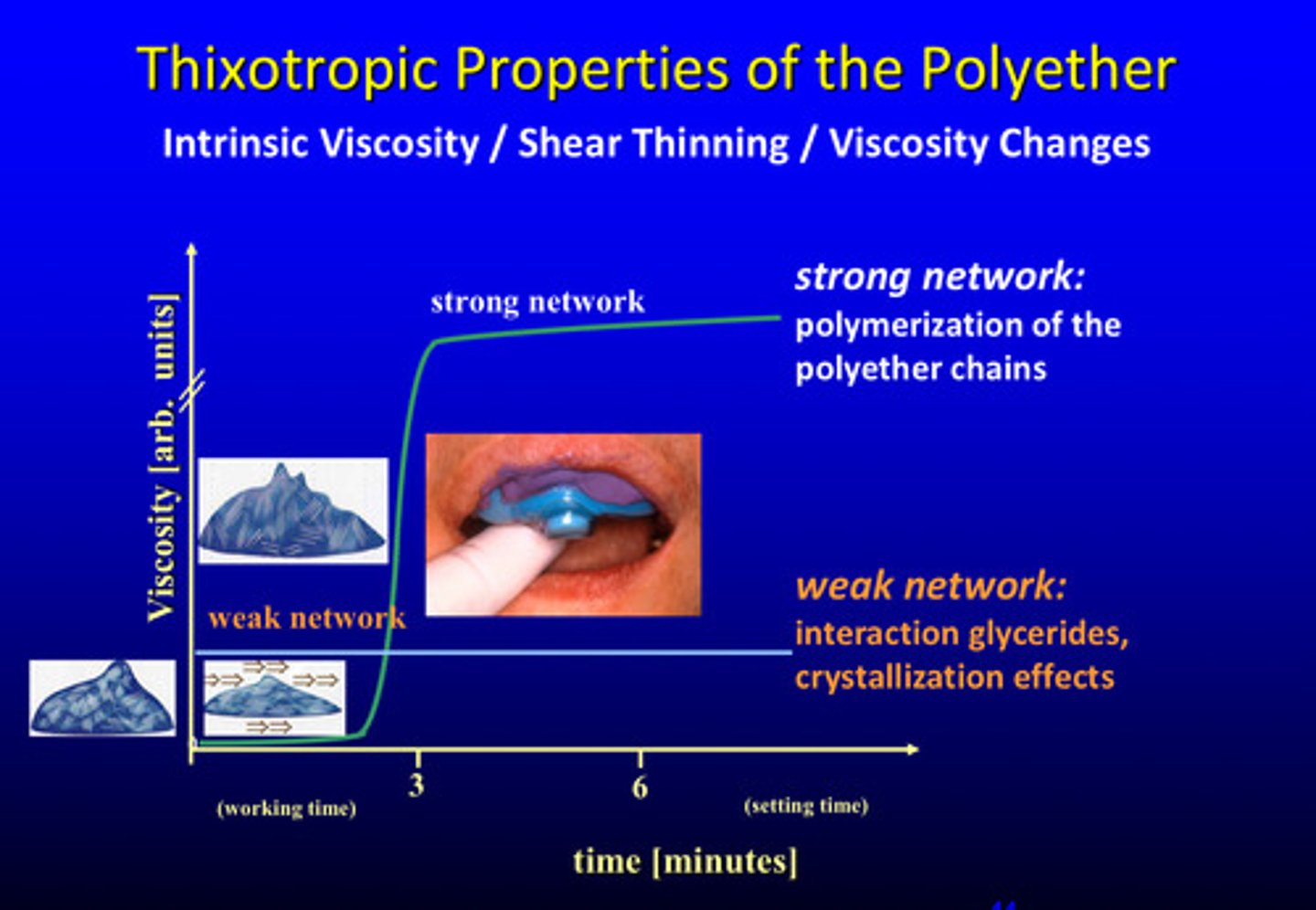
what are the thixotropic properties of the polyether (3)
intrinsic viscosity, shear thinning, and viscosity changes
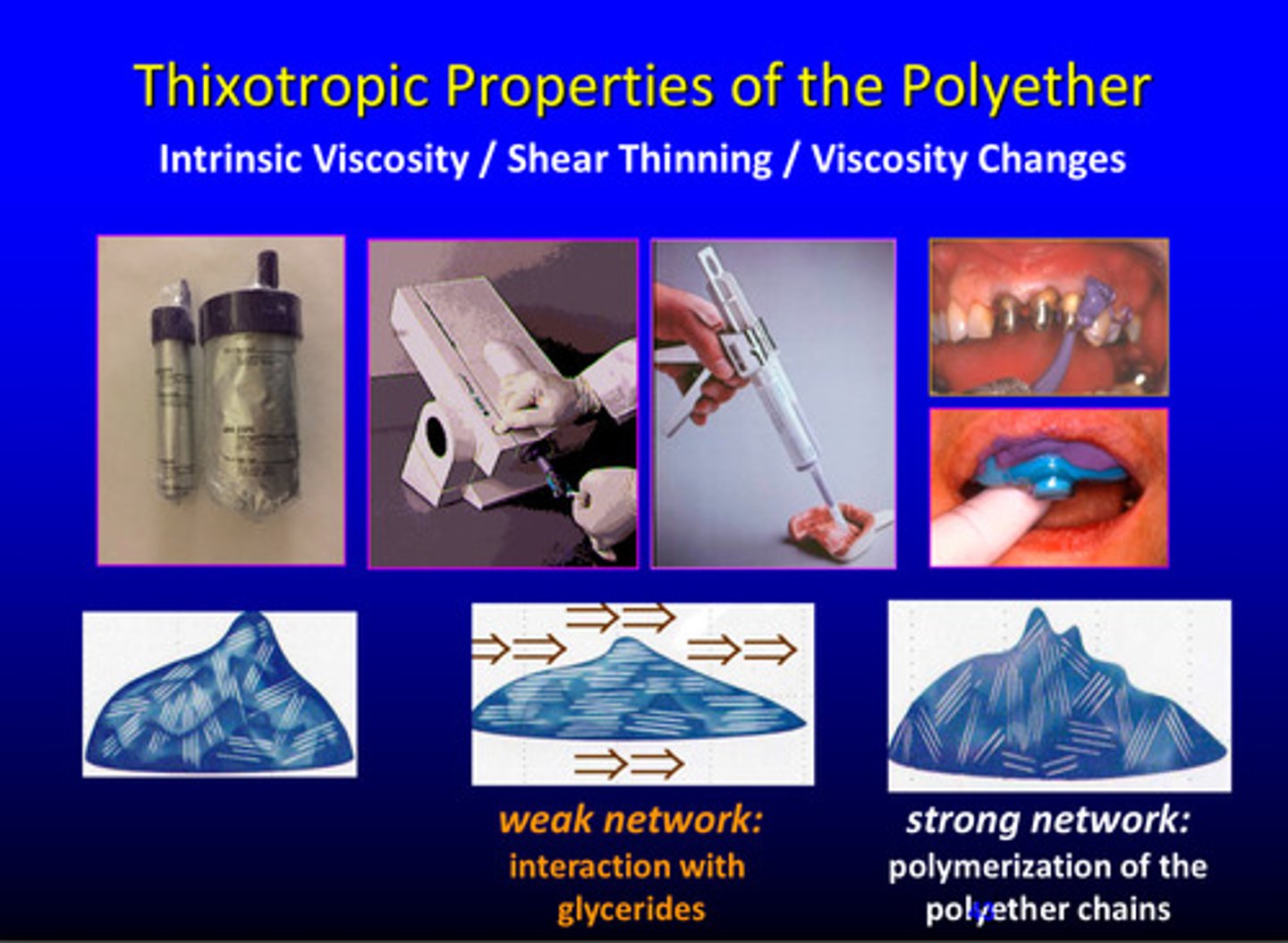
what is the weak network of the polyether
interaction with glycerides
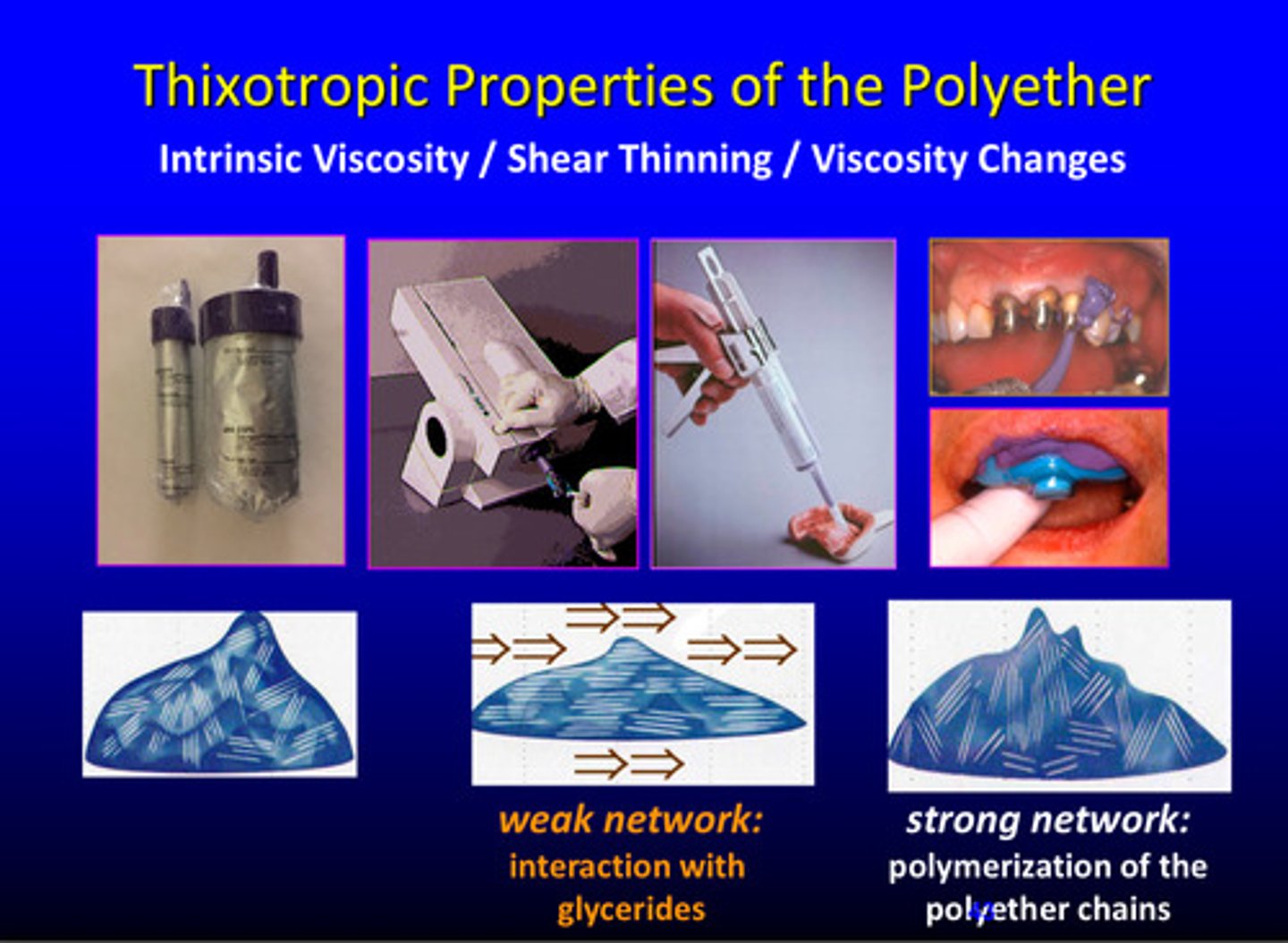
what is the strong network of the polyether
polymerization of the polyether chains
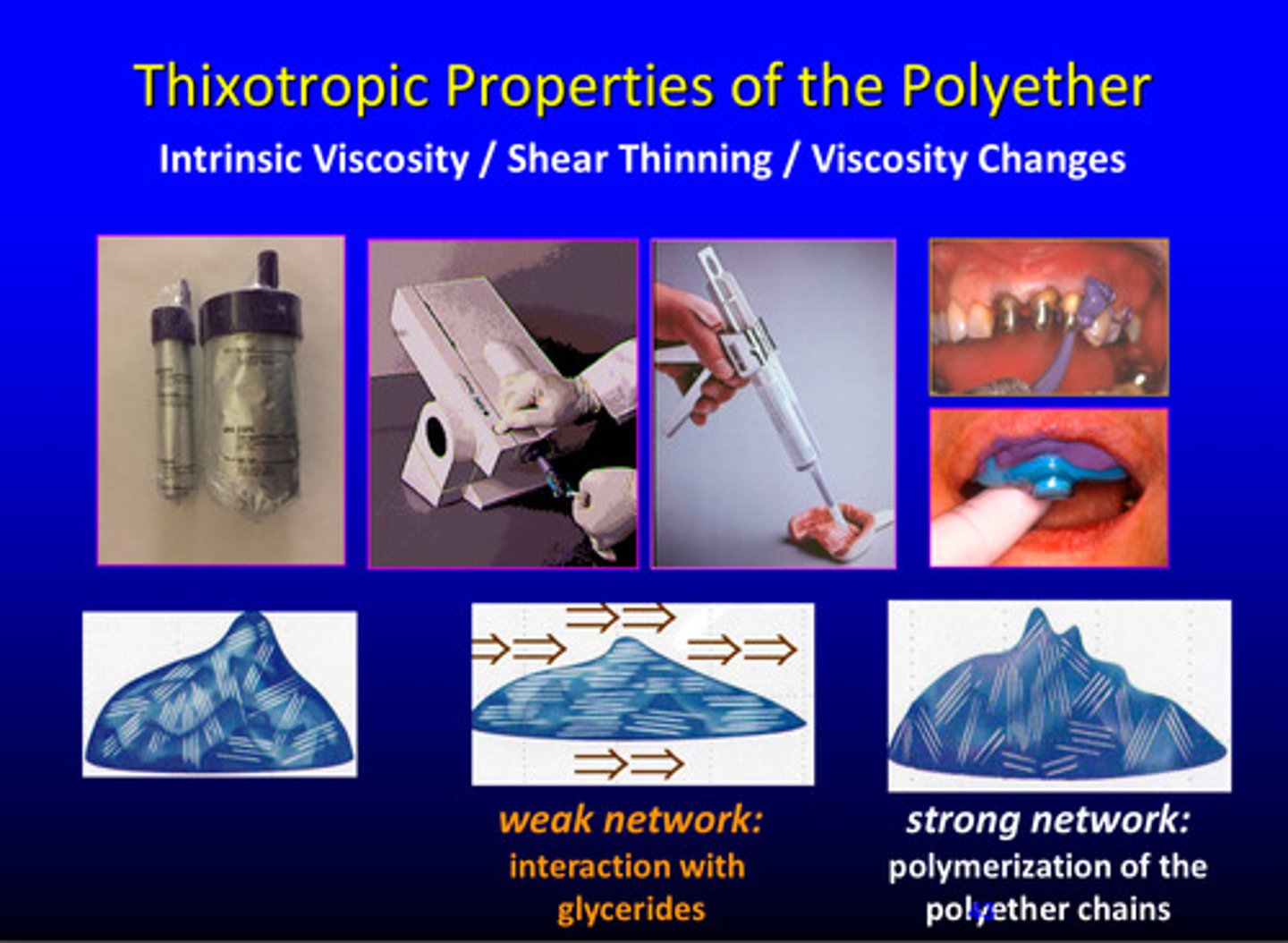
strong vs weak network of polyether
strong polymerization of polyether chains
weak interaction glycerides, crystallization effect
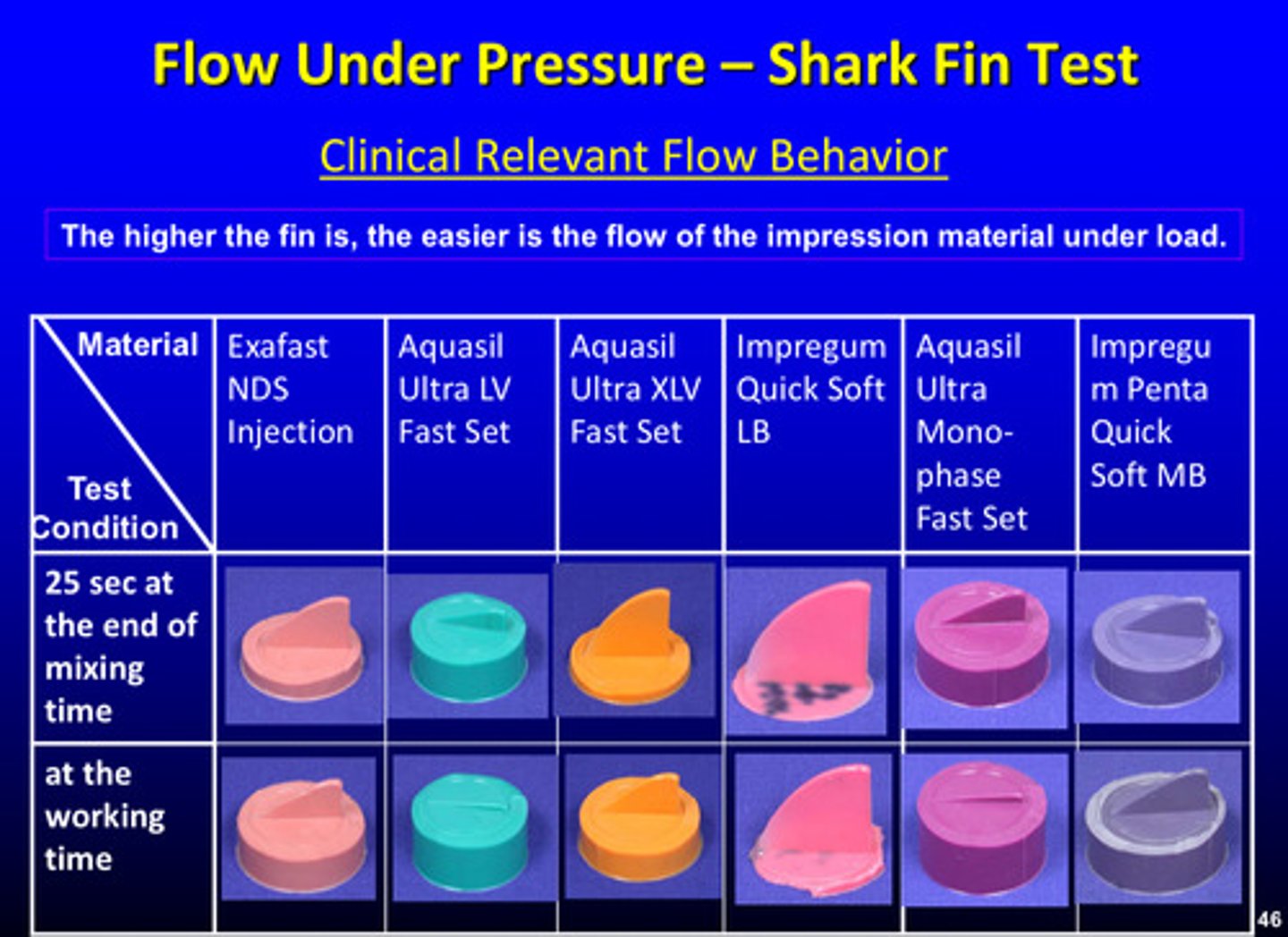
describe the shark fin test
material is loaded into the circular recess and loaded at the selected time to allow the material to flow UP the tapered slit; after setting, the mold is disassembled and the height of the shark fin is determined by profilometry
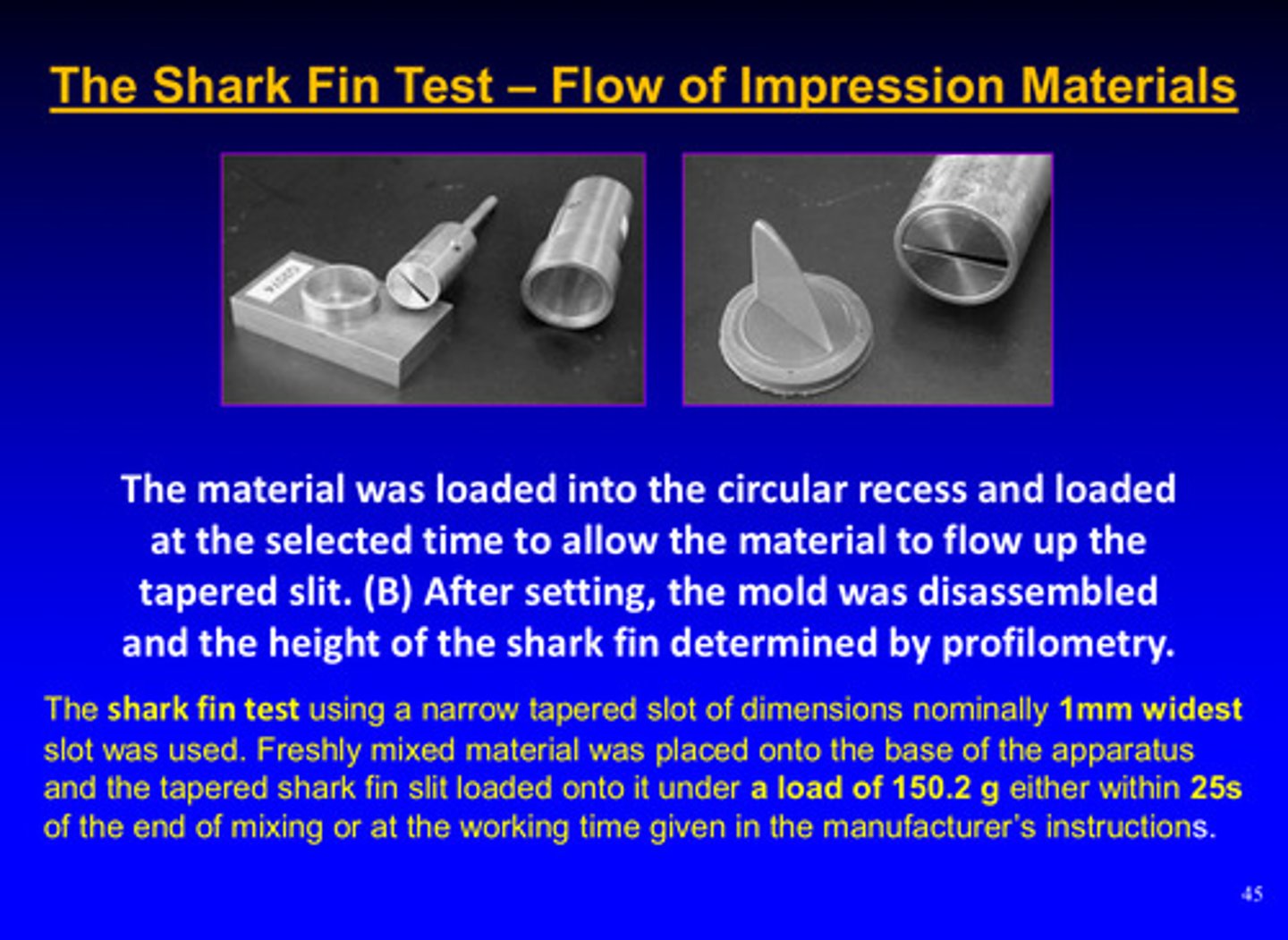
shark fin test: the higher the fin is, the easier…
the flow of the impression material under load
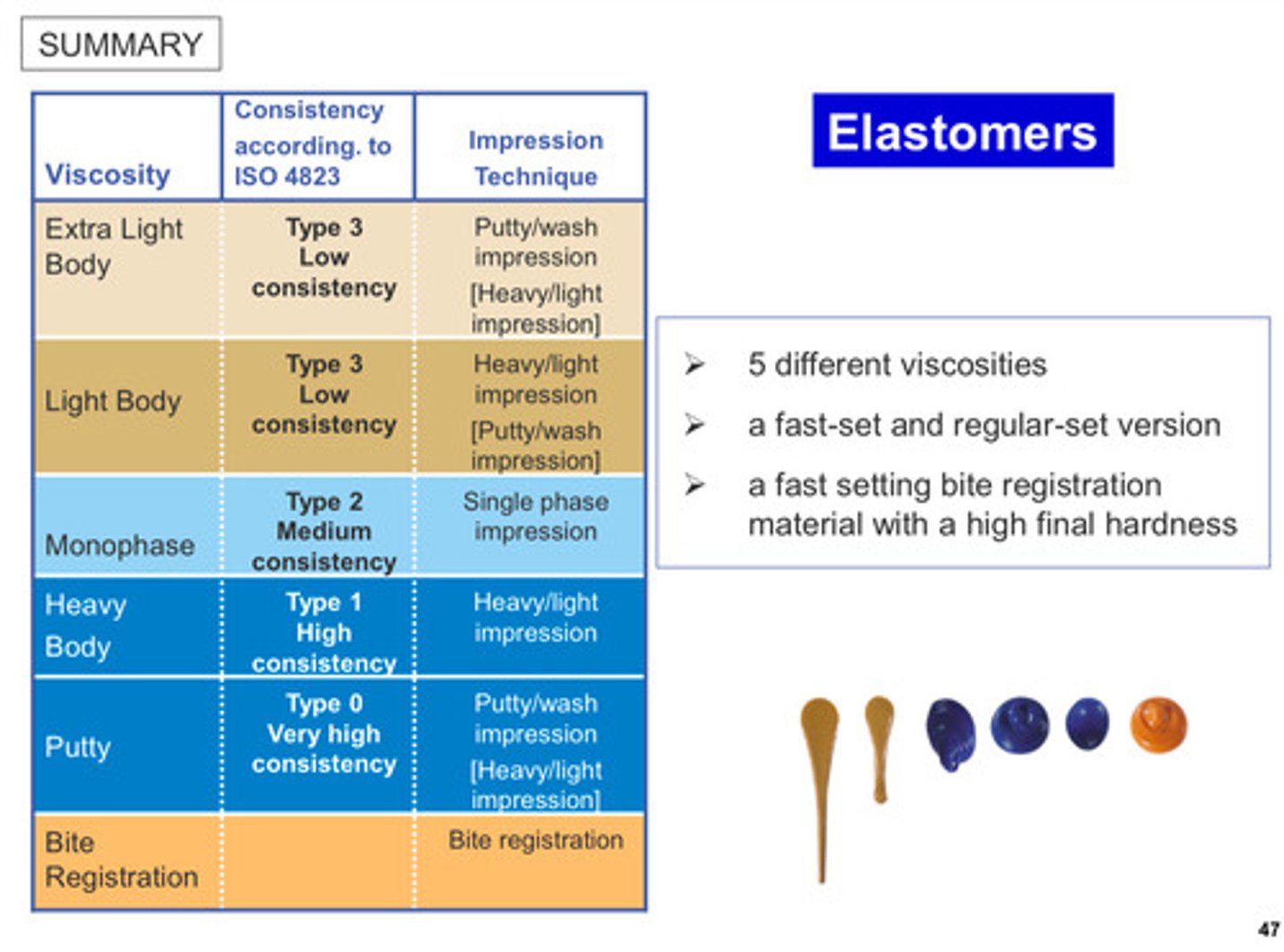
summary of elastomers with different viscosities (3 points)
1) 5 different viscosities
2) fast-set and regular-set version
3) fast setting bite registration material with a high final hardness
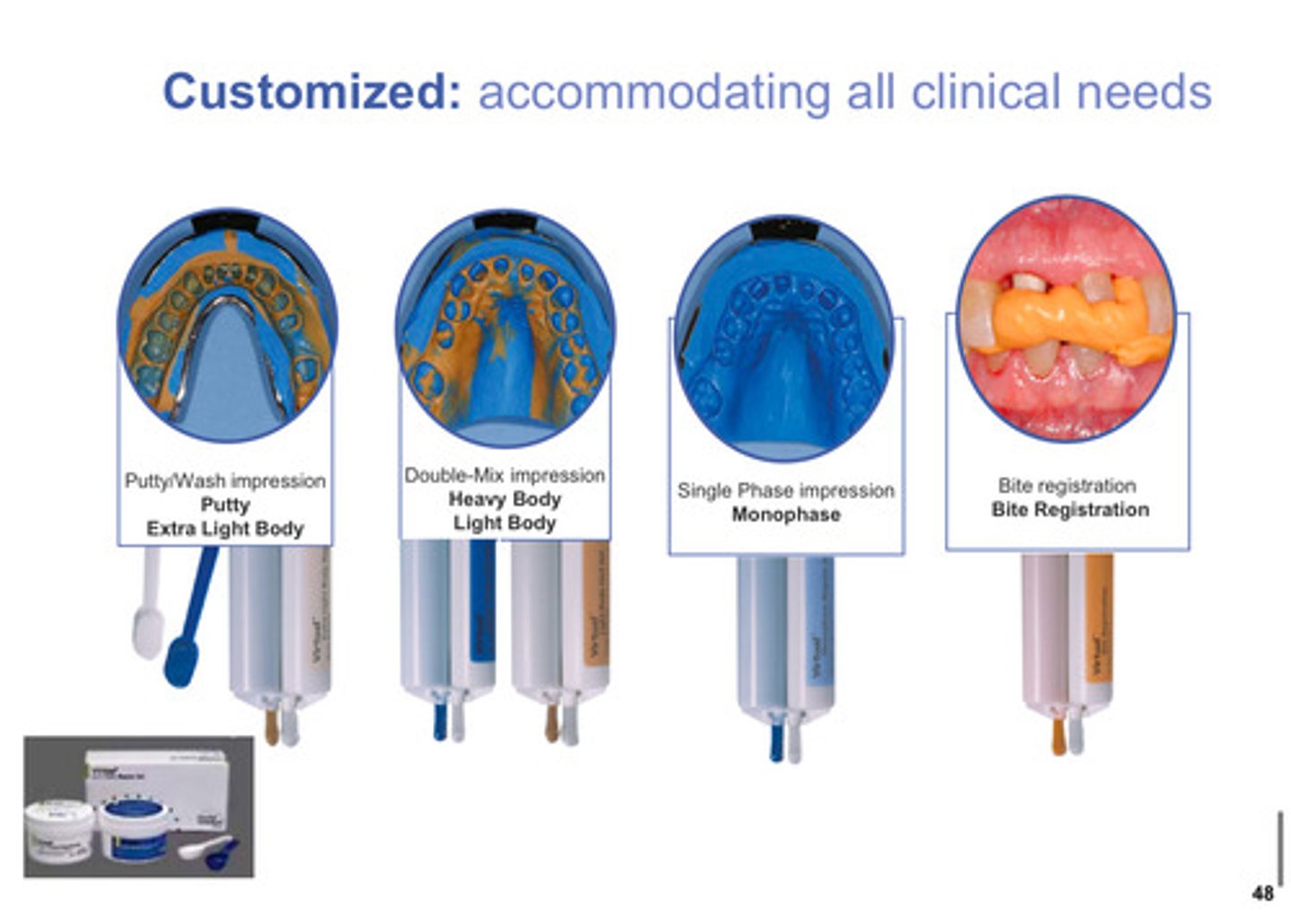
elastomers can be _________ to accommodate all clinical needs
customized
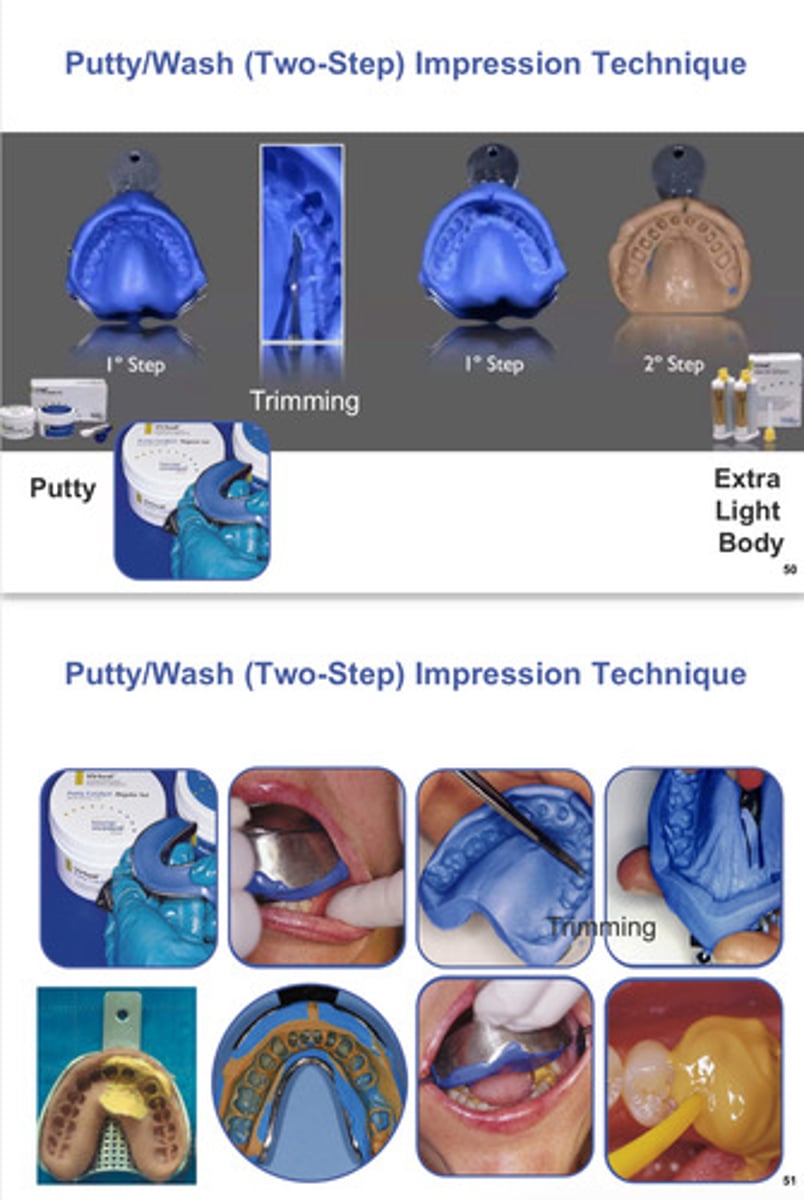
putty/wash (2 step) impression technique, what materials are needed
putty impression/trim → extra light body
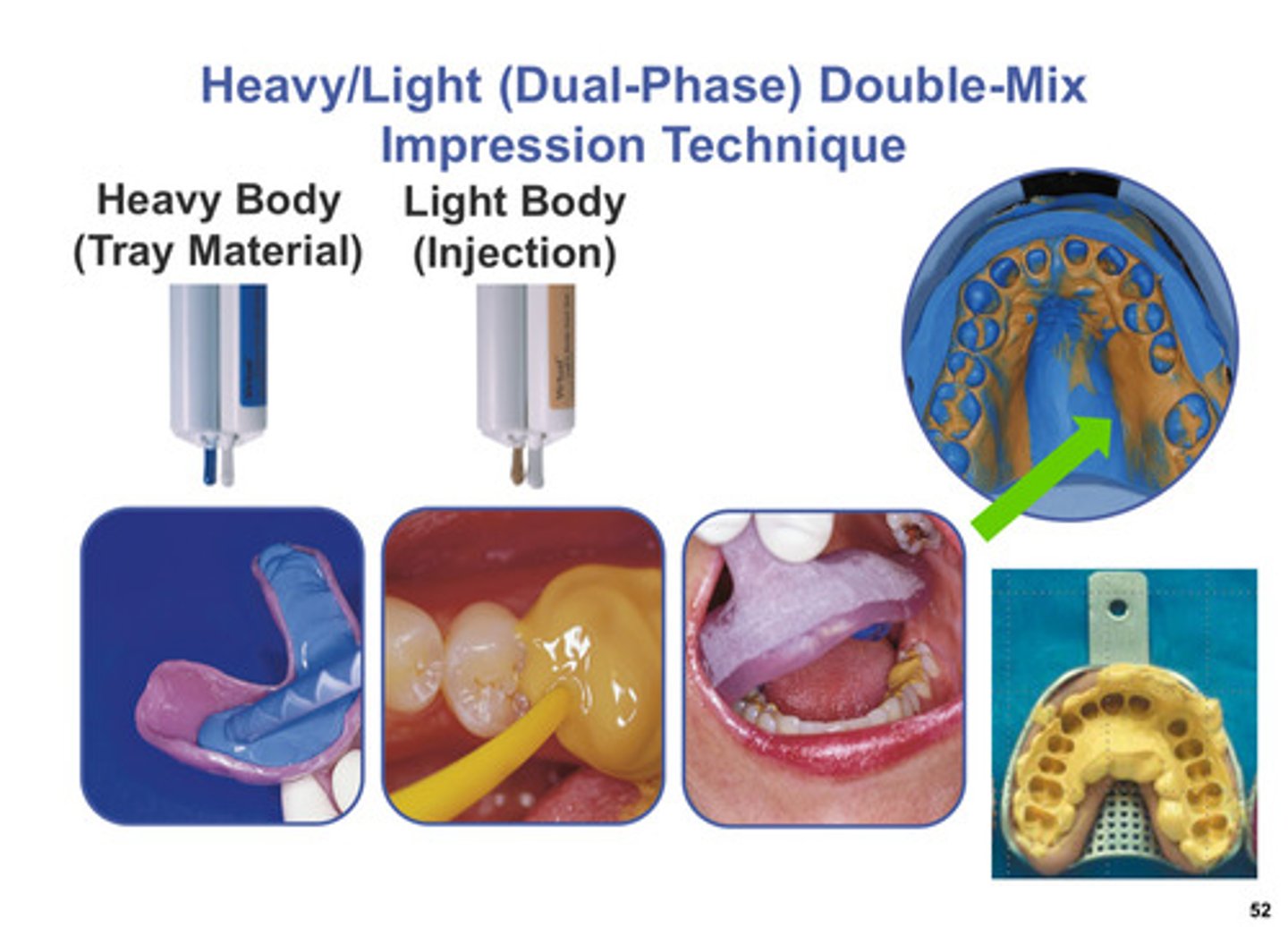
heavy/light (dual phase) double mix impression technique
place heavy body in tray and light body on teeth, then take impression
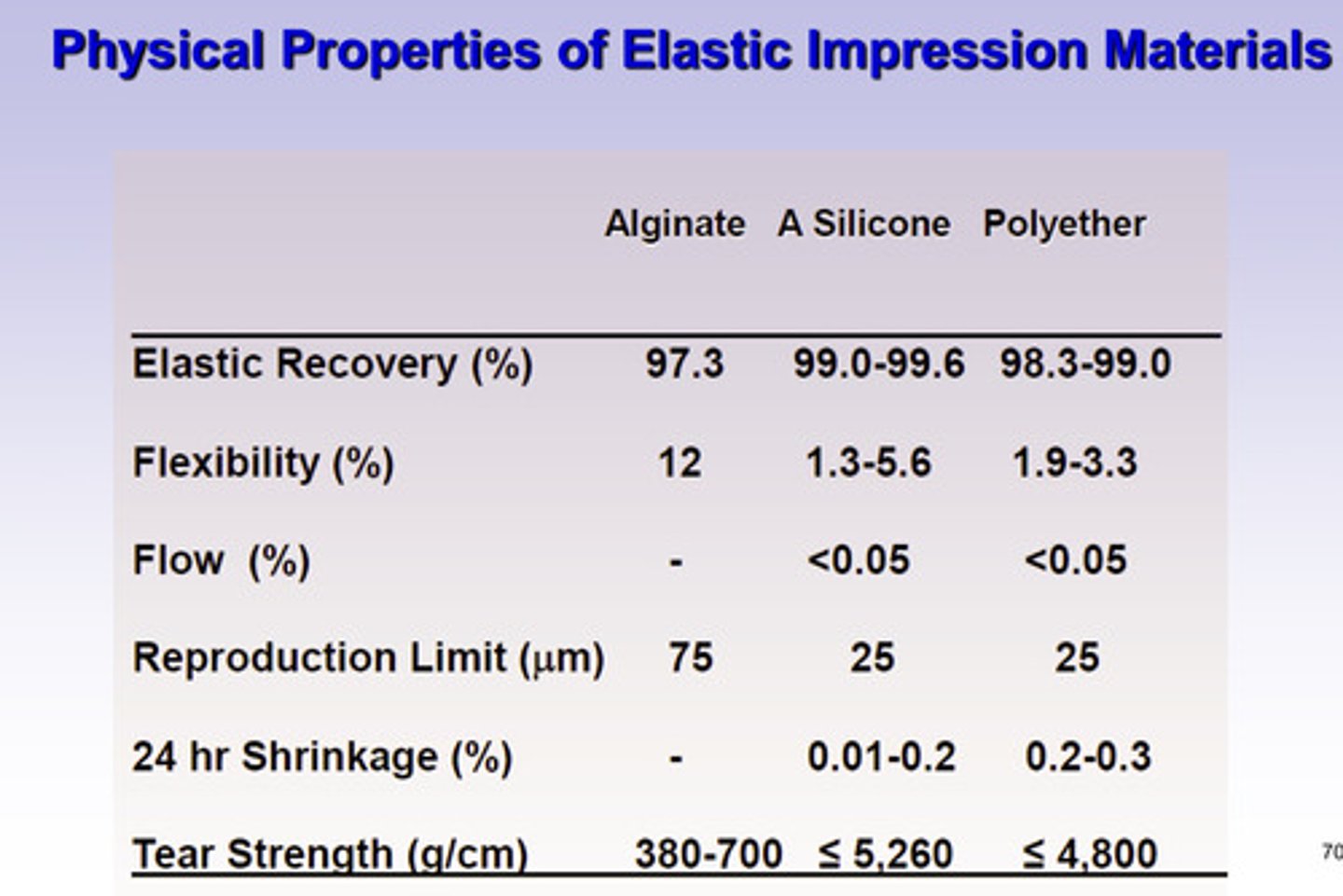
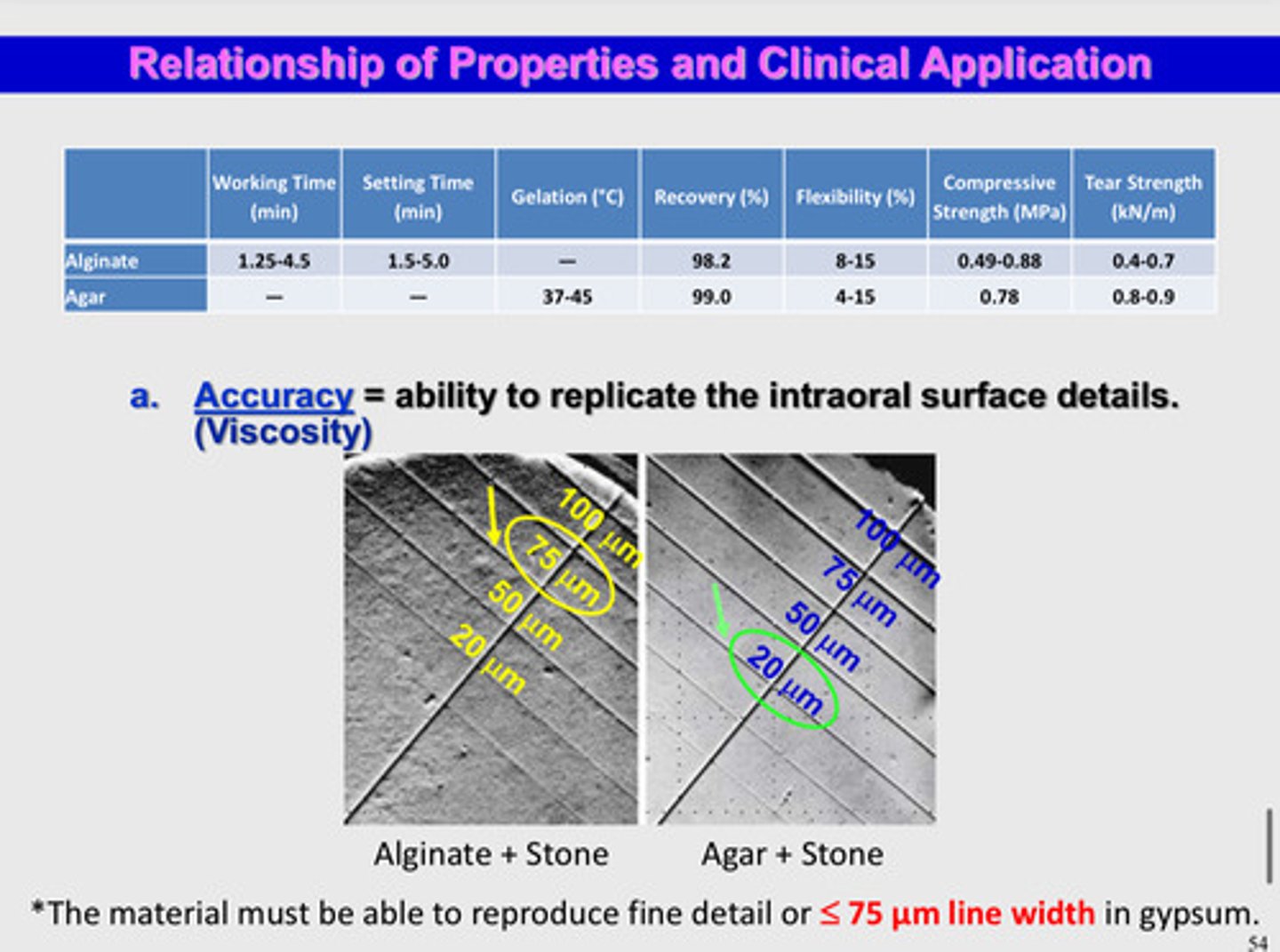
recall for alginate hydrocolloid: in terms of accuracy, the material must be able to reproduce fine detail or _______ line width in gypsum
75 um
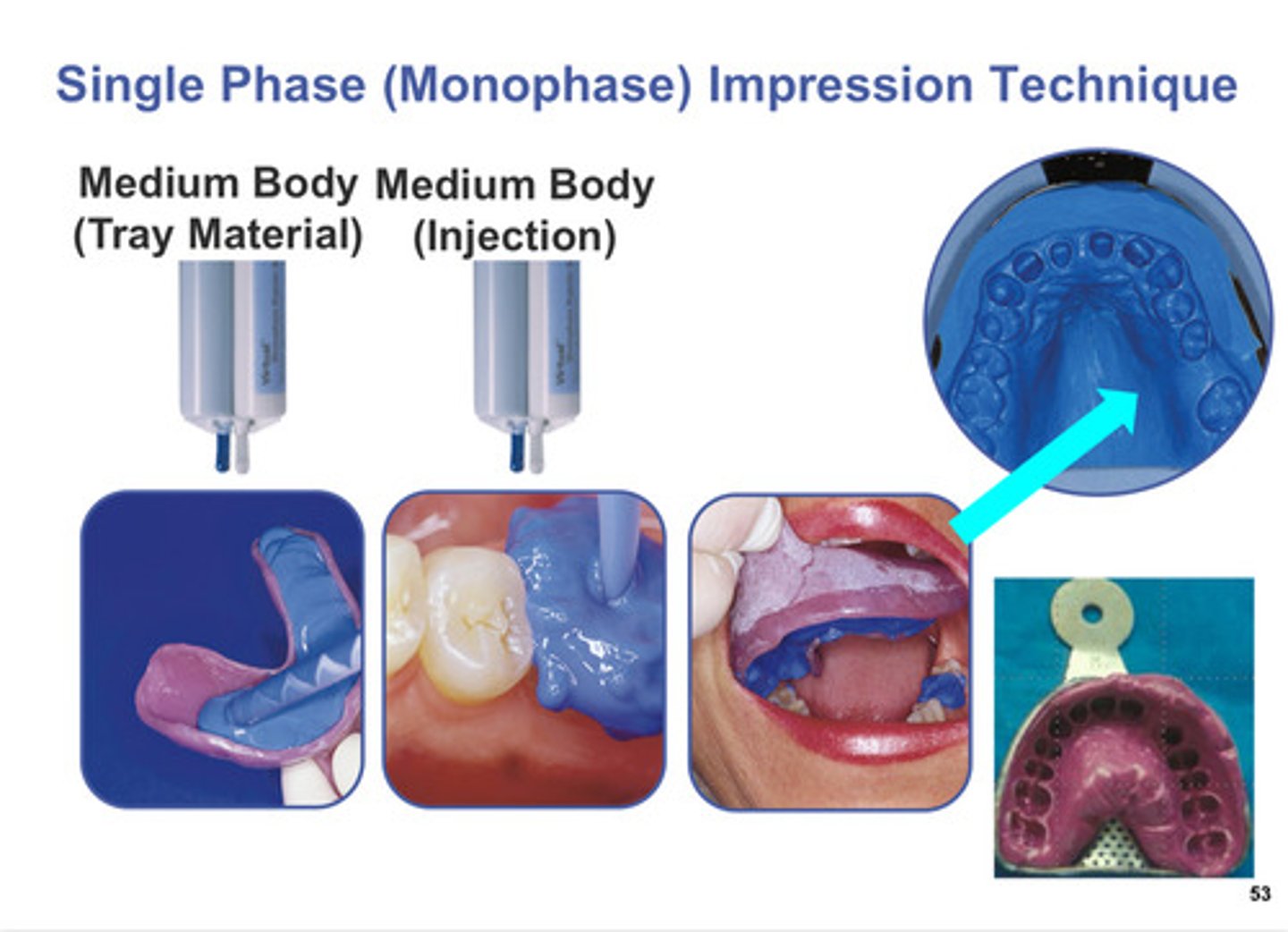
single phase (monophase) impression technique, you use what type of “body”
Medium body: put into tray and pt mouth, then take impression
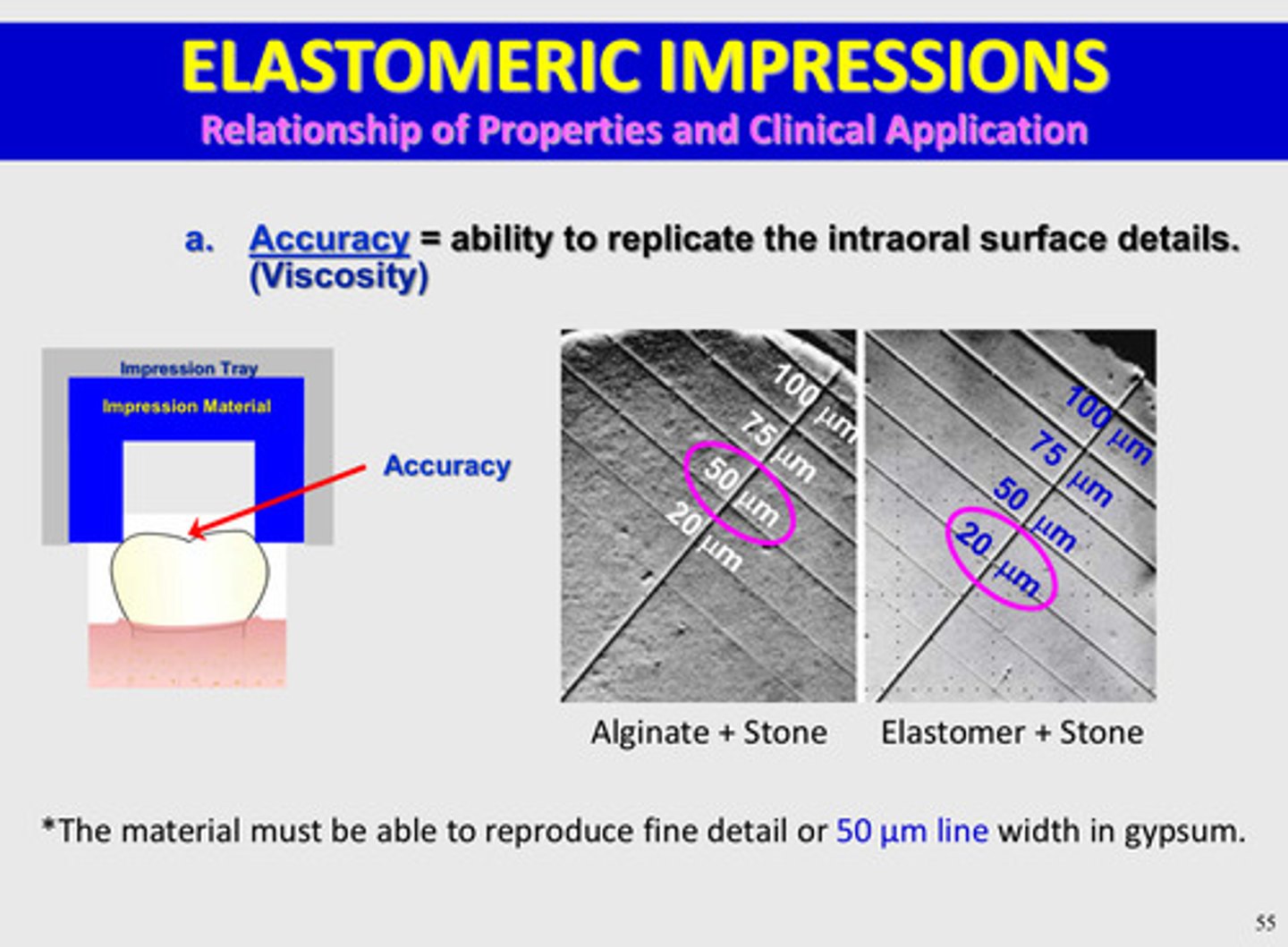
for elastomer: in terms of accuracy, the material must be able to reproduce fine detail or _______ line width in gypsum
50 um
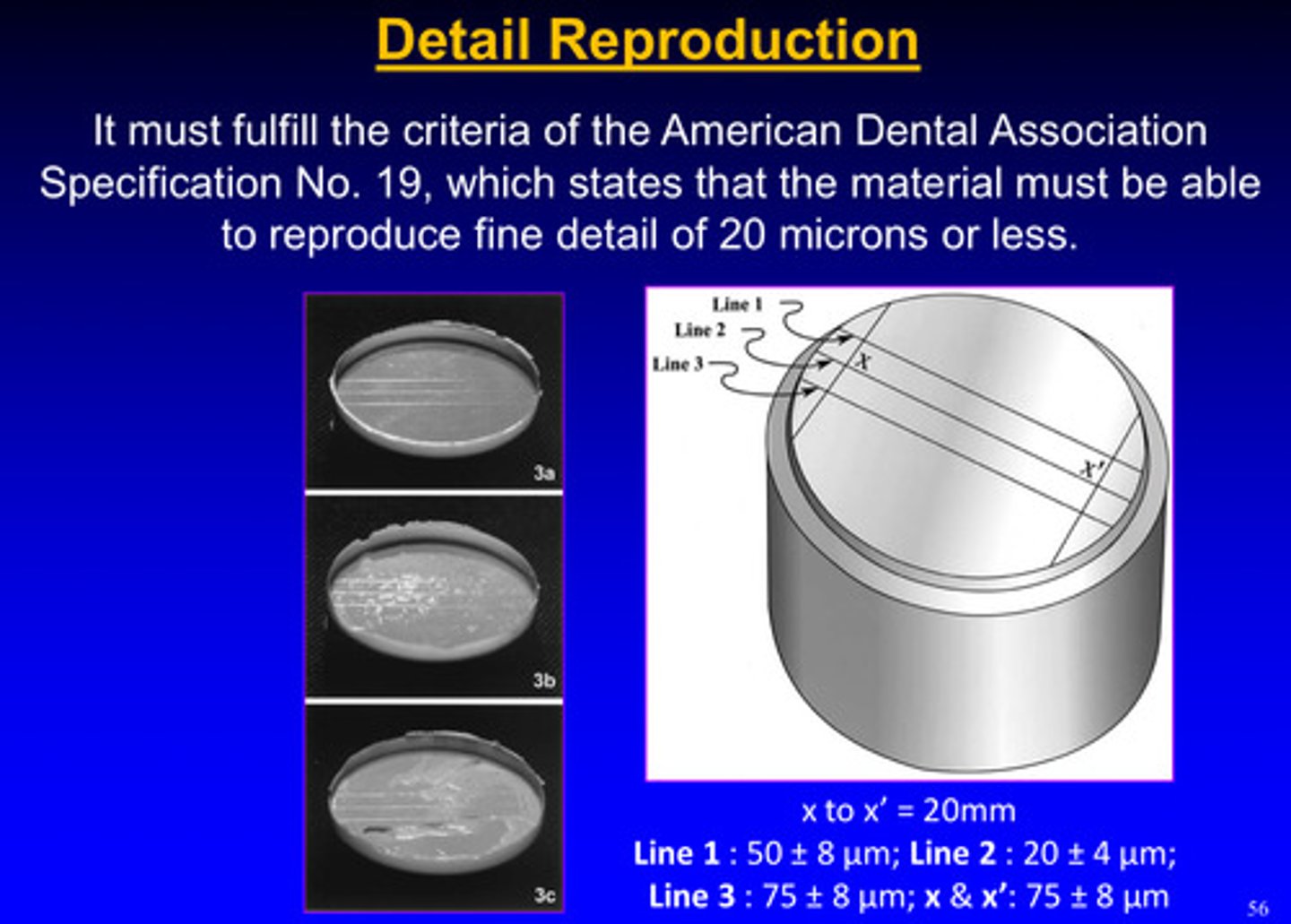
what is the ideal level of detail reproduction of elastomers
material must be able to reproduce fine detail of
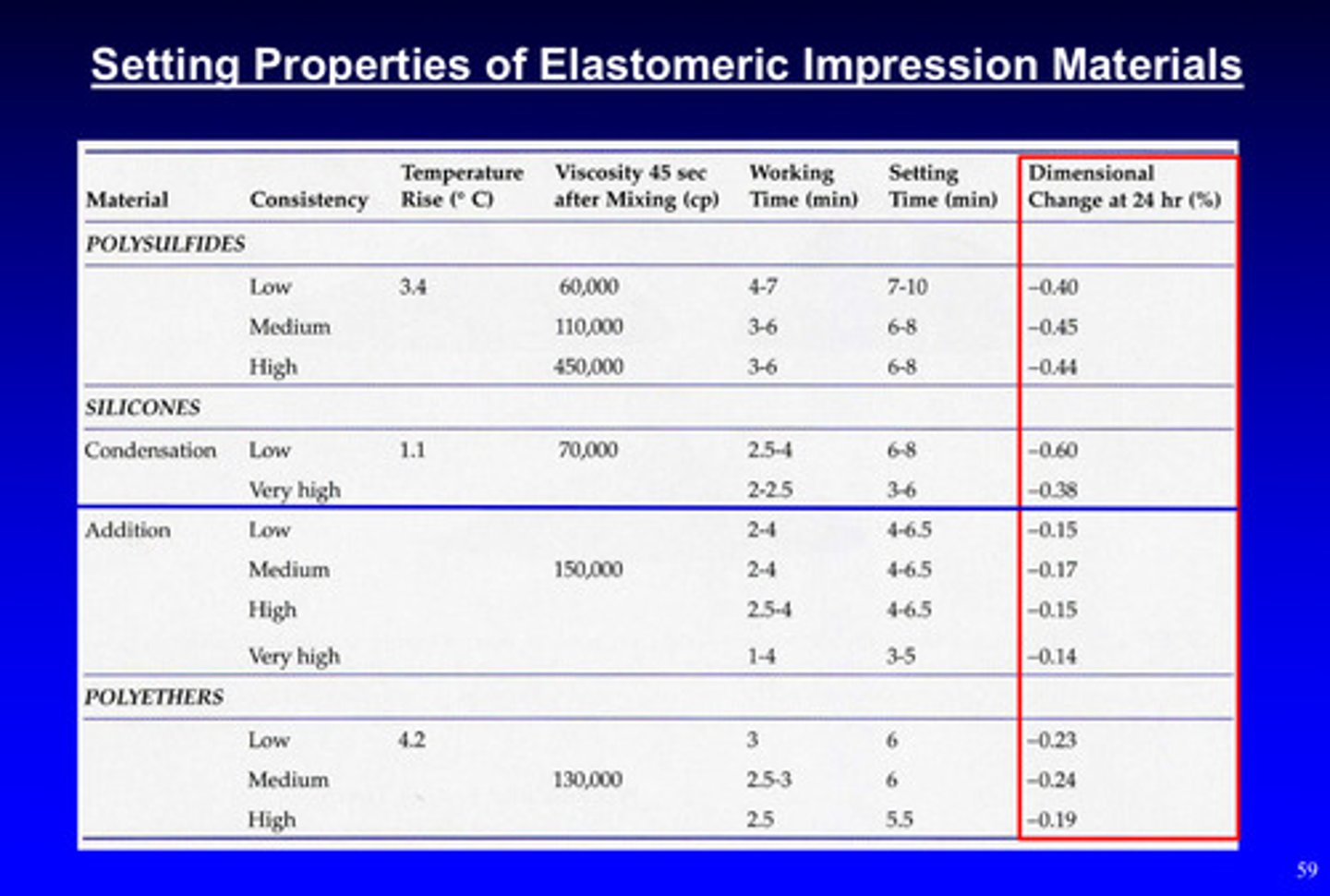
dimensional change of elastomeric impression materials
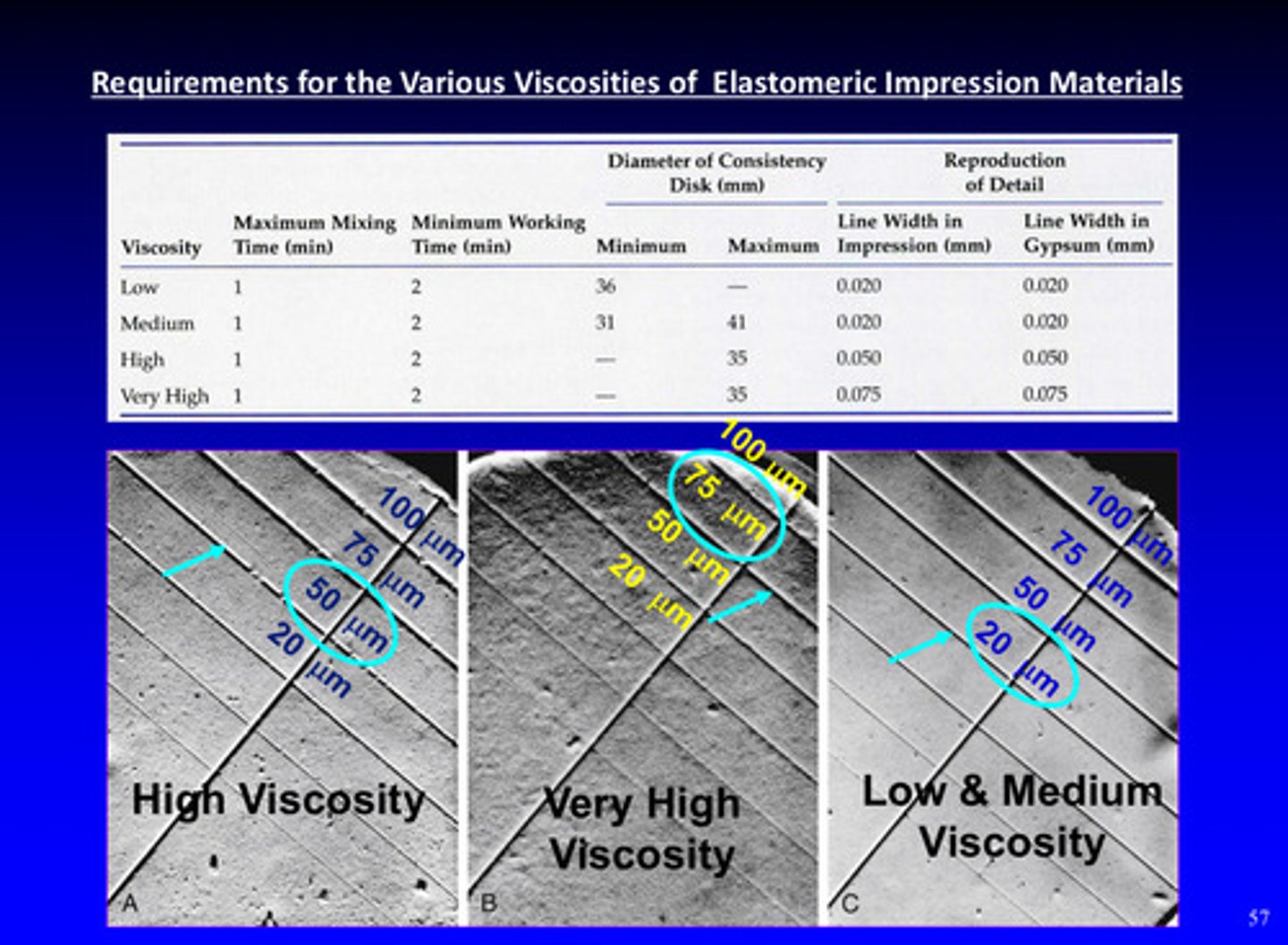
requirements of various viscosities of elastomeric impression materials
very high viscosity: 75 um
high viscosity: 50 um
low/medium viscosity: 20 um
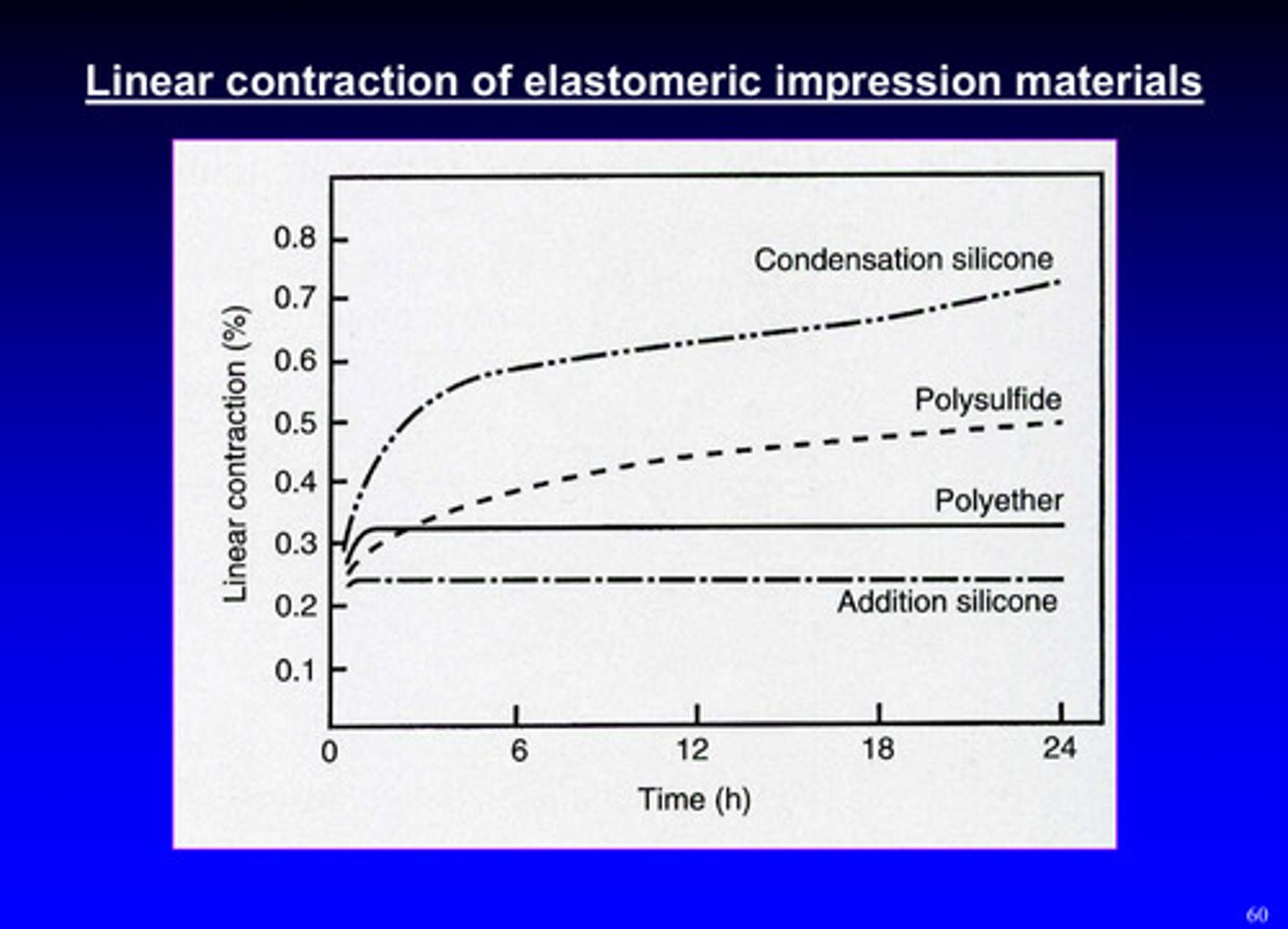
linear contraction of elastomeric impression materials, rank highest to lowest linear contraction including the following:
condensation silicone, addition silicone, polyether, polysulfide
condensation silicone > polysulfide > polyether > addition silicone
elastomeric impression materials are viscoelastic, and their mechanical properties are ______ dependent, meaning…
time; the longer the impressions are deformed, the higher the permanent deformation
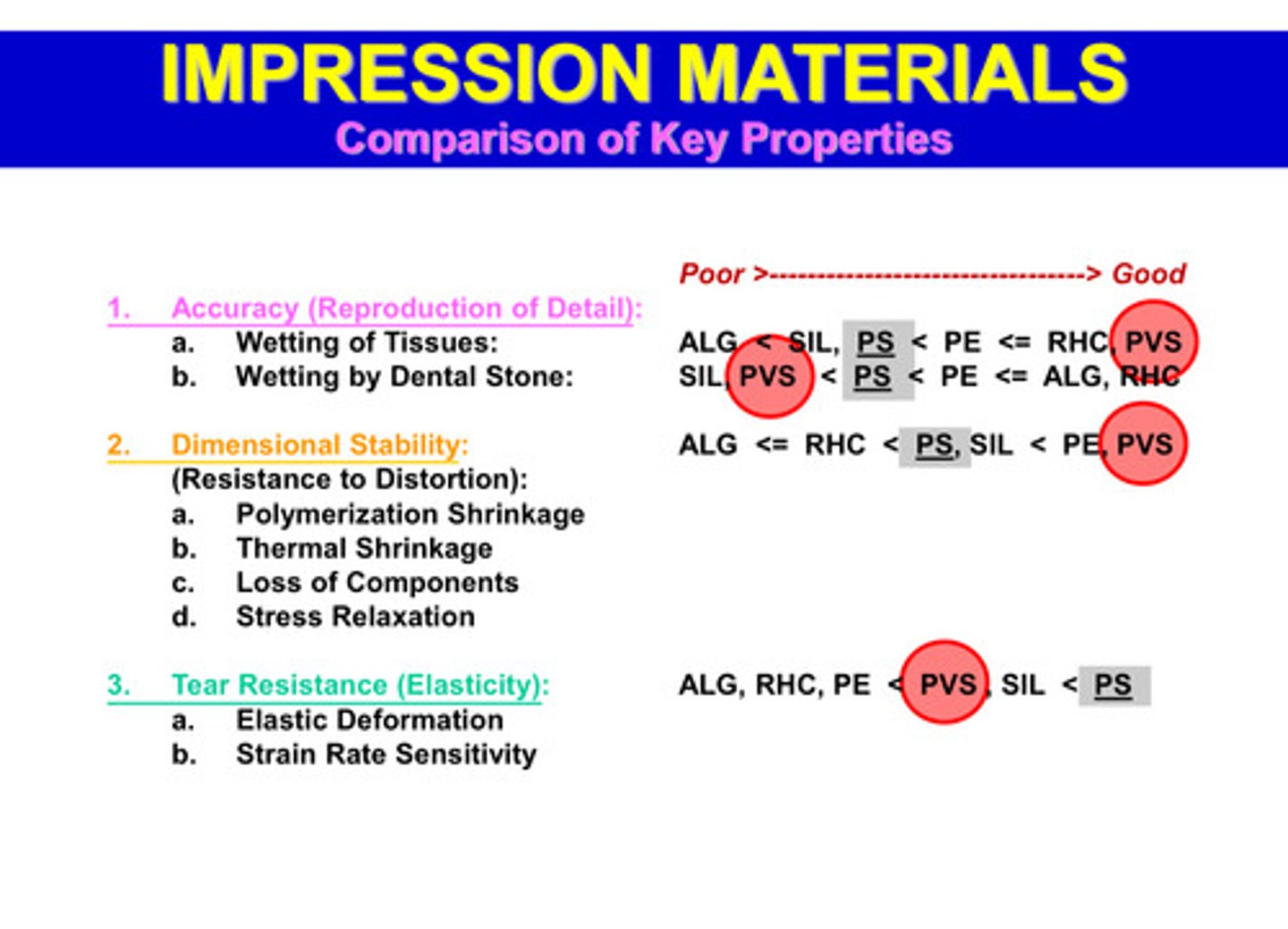
when thinking of the key properties of PVS, it is better than most materials in two things…
better at wetting of tissues, better dimensional stability
comparison of key properties of PE and PVS have higher …….. compared to alginate
PE, PVS have higher accuracy, dimensional stability, and tear resistance
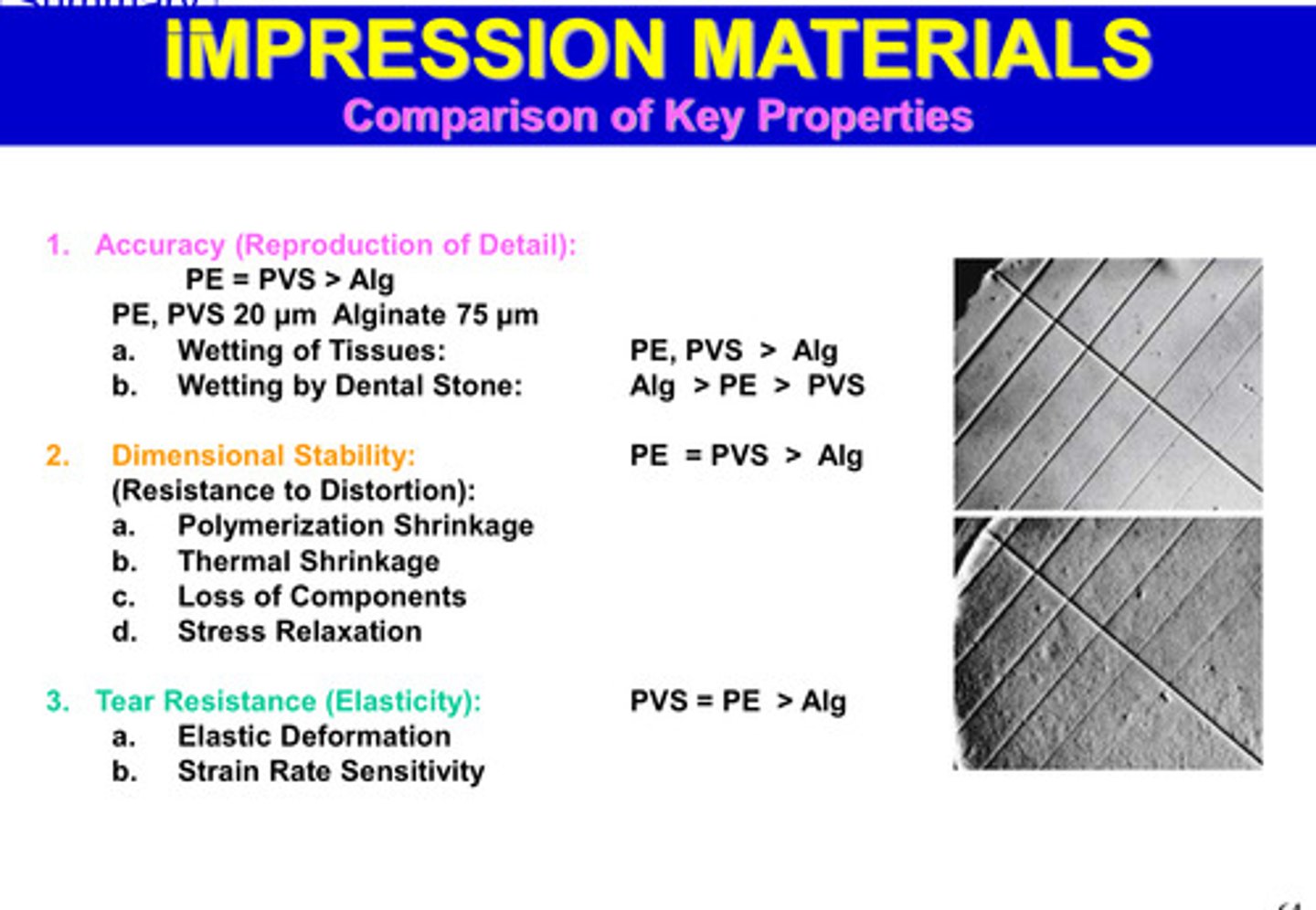
alginate is more _______ and has a higher _____________ rate
flexible; reproduction