Pre-Calculus Unit 1-3
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
function
each element in A is assigned to only one element in B
function A represents
input, independent, cause
function B represents
output, dependent, effect
vertical line test
test used to determine if a relation is a function - line must touch only 1 point vertically
horizontal line test
a test used to determine if the inverse of a relation is a function OR 1 to 1
if there are two solutions, is it a function?
no, it must only have one
what cannot be in the denominator of a function?
0
what is the range of a fractional function?
All real numbers, except for 0
what is the domain of a fractional function?
All real numbers, except for the root of the denominator
a closed circle means
greater than or equal to OR less than or equal to
a open circle mean
greater than OR less than
even degree
y-axis symmetry / ends behave the same: f(-x) = f(x)
odd degree
origin symmetry / ends behave opposite: f(-x) = -x
linear function
f(x) = mx + b
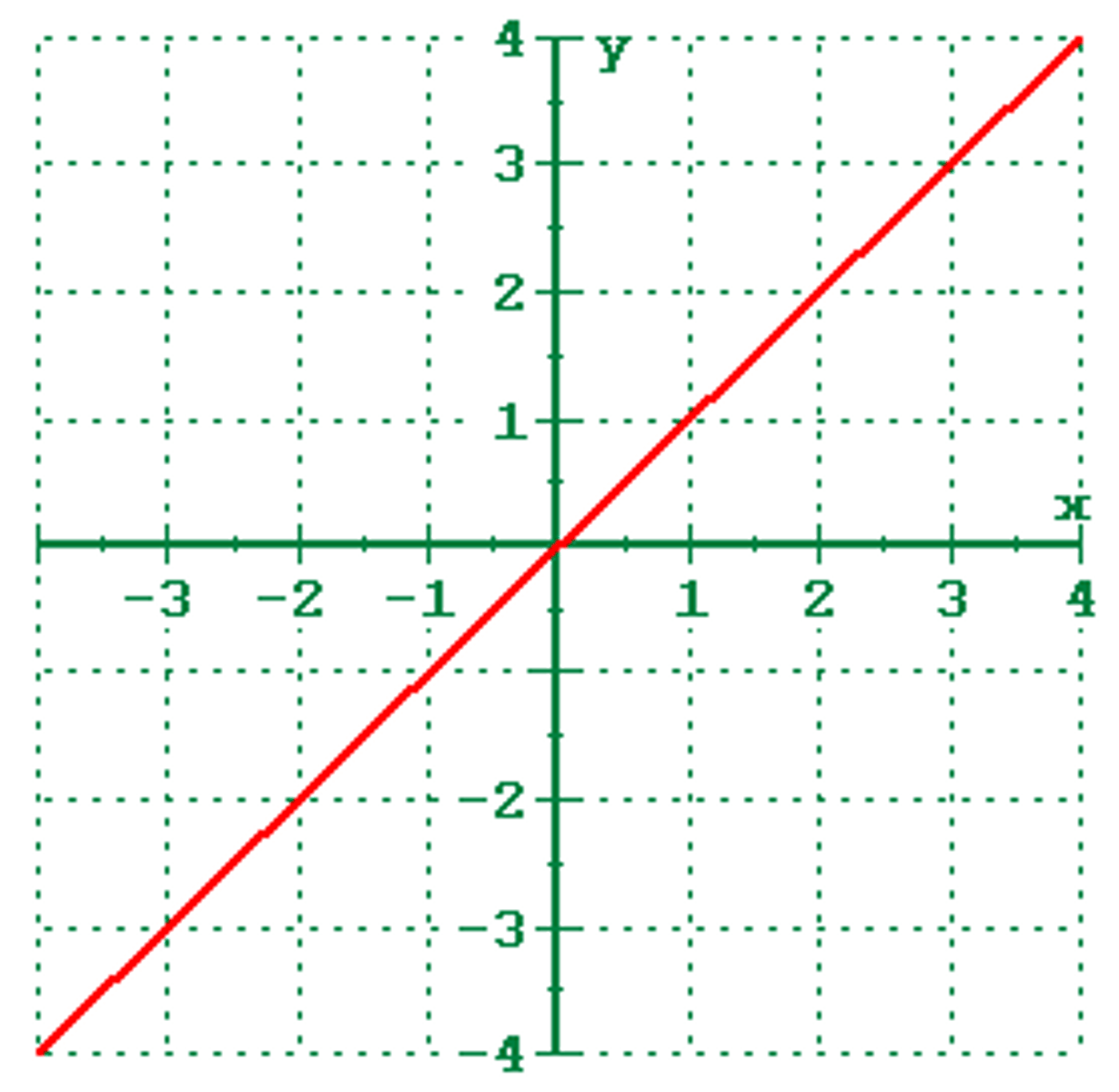
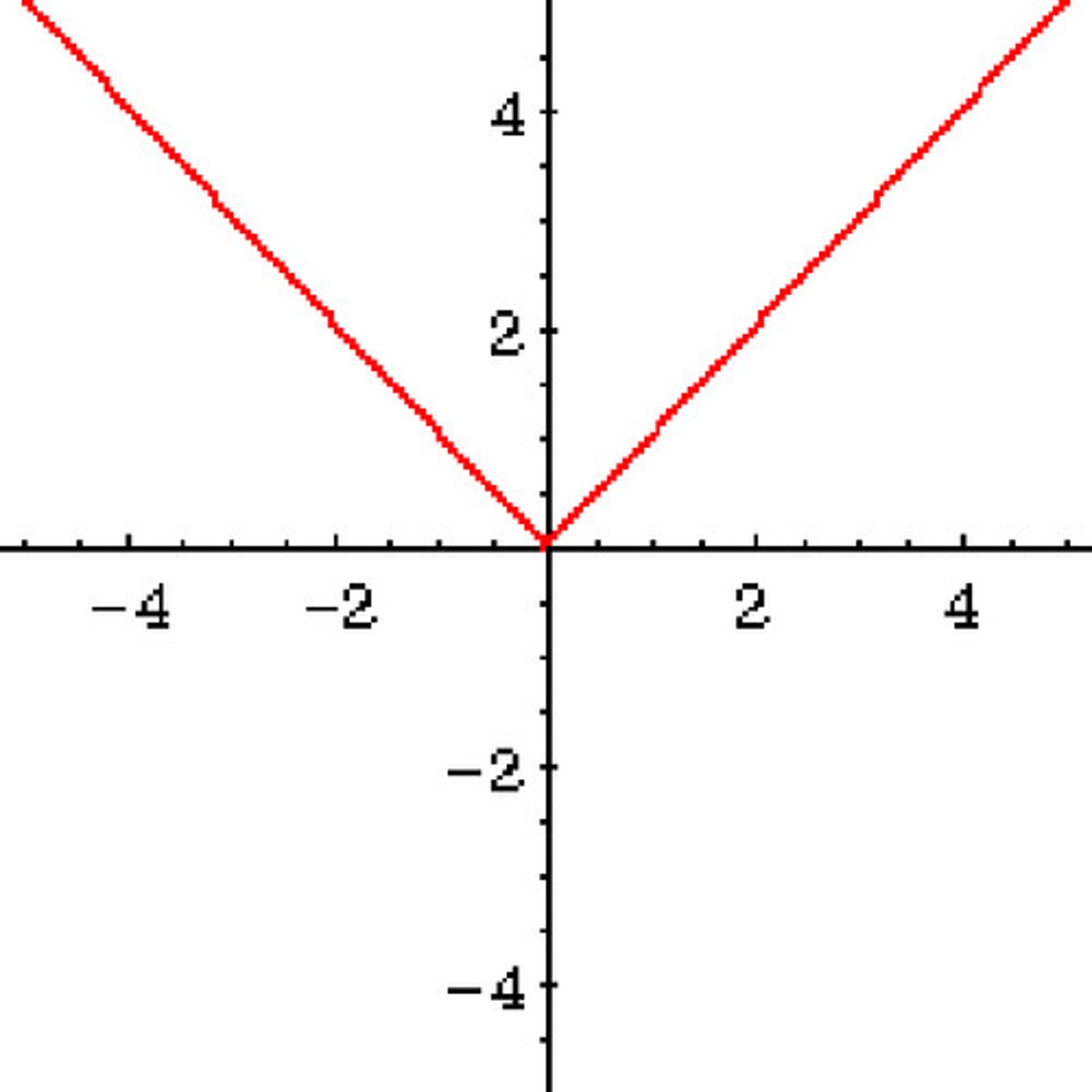
absolute value function
f(x) = a|x-h| + k
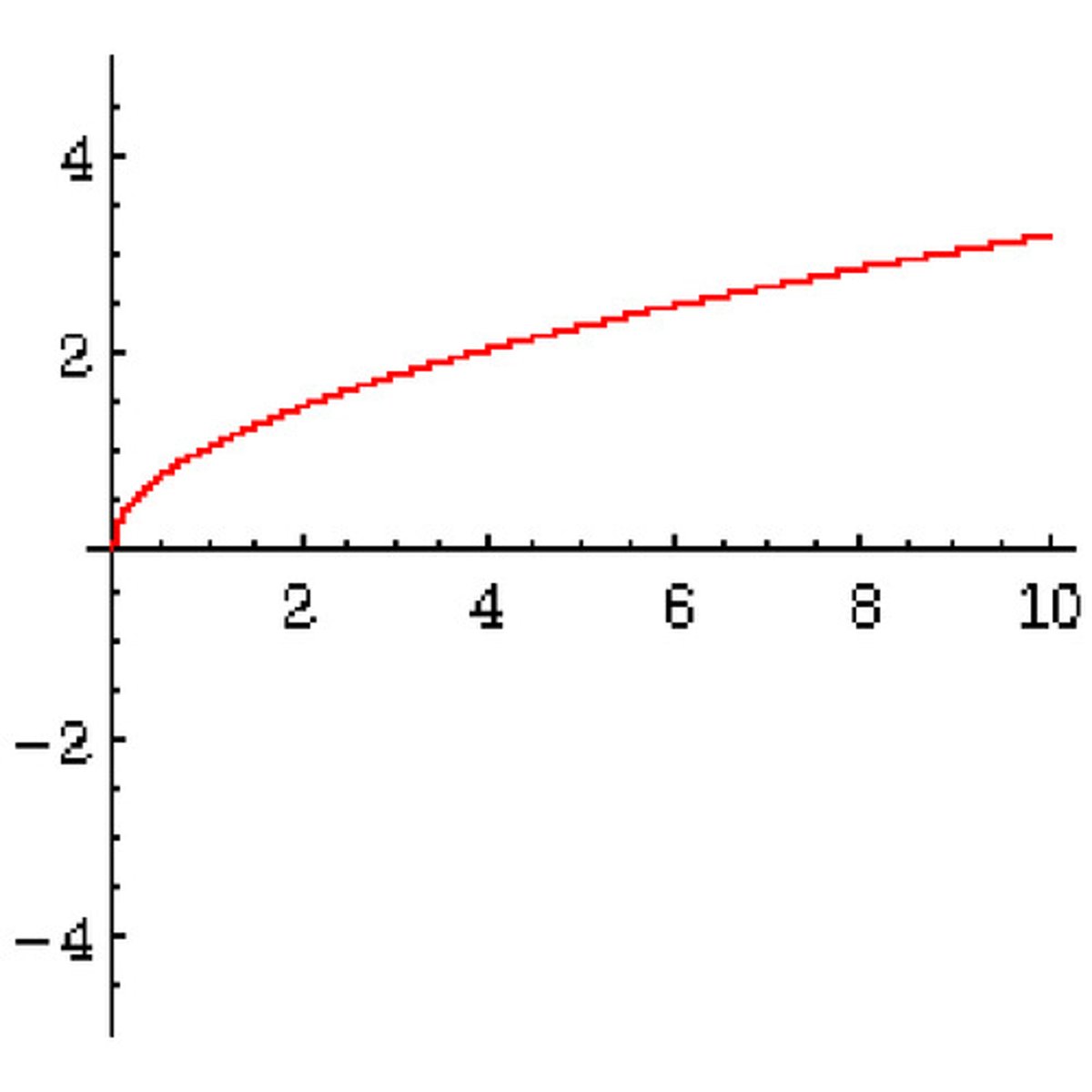
square root function
f(x) = a√x-h +k
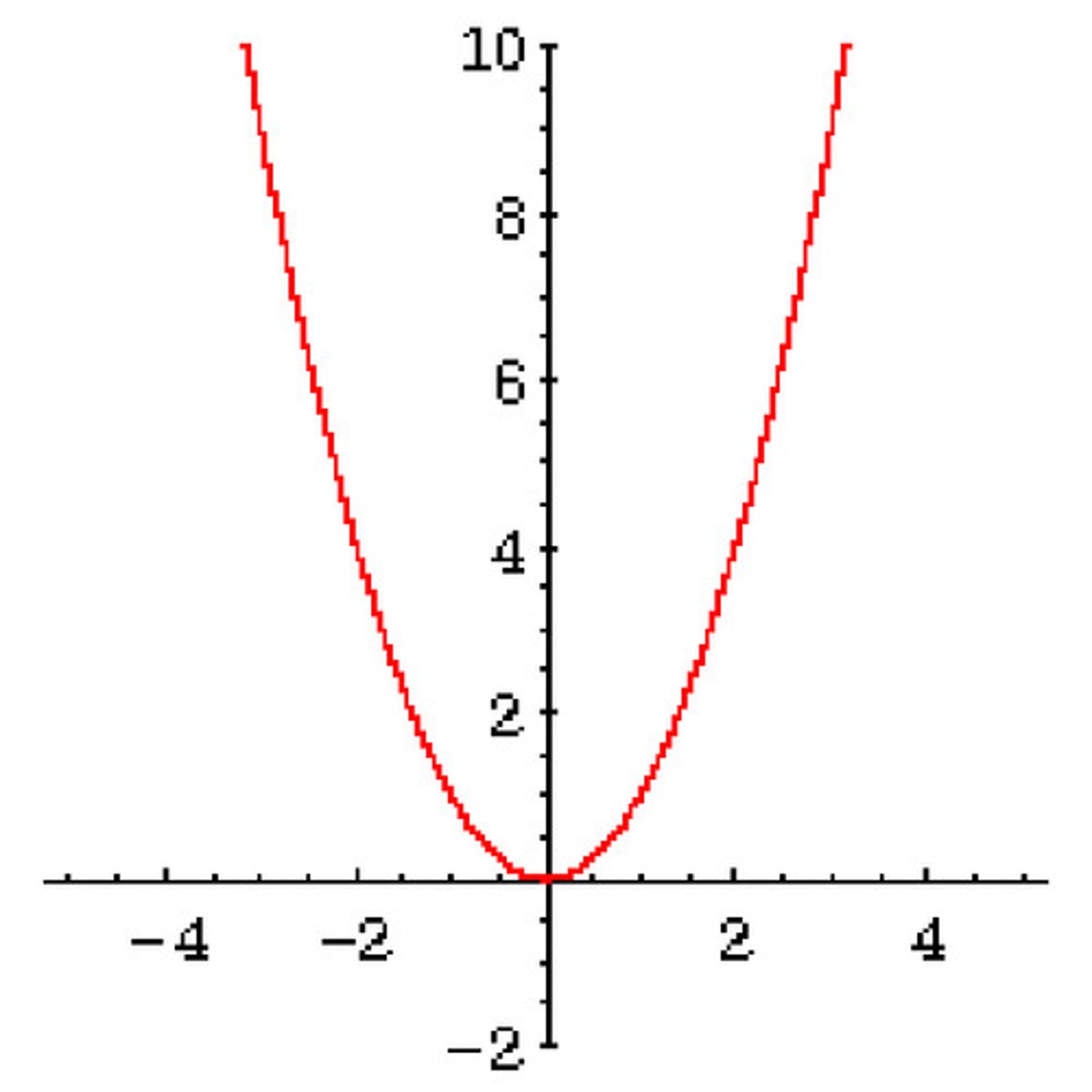
quadratic function
f(x) = a(x-h)^2 +k
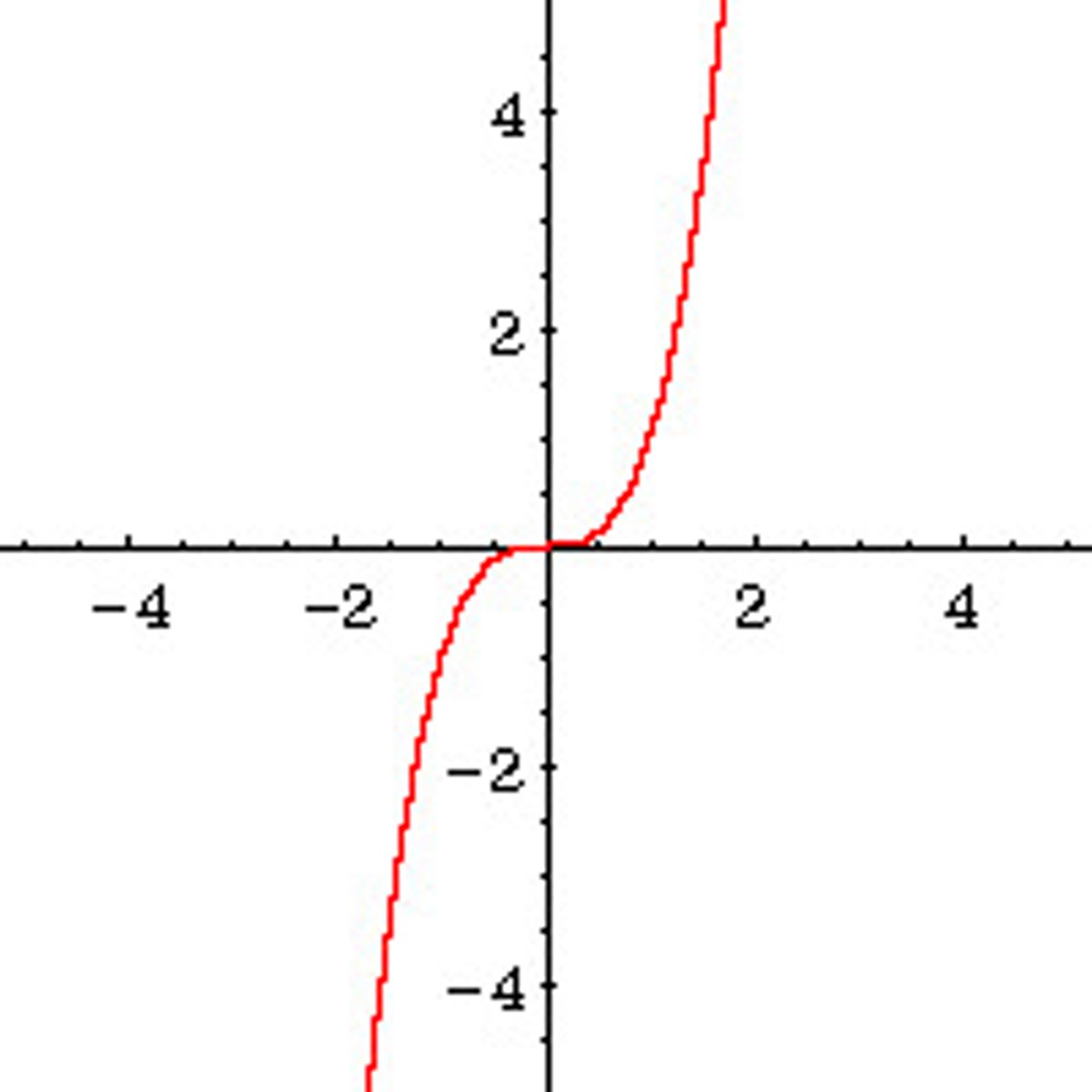
cubic function
f(x) = a(x-h)^3 + k
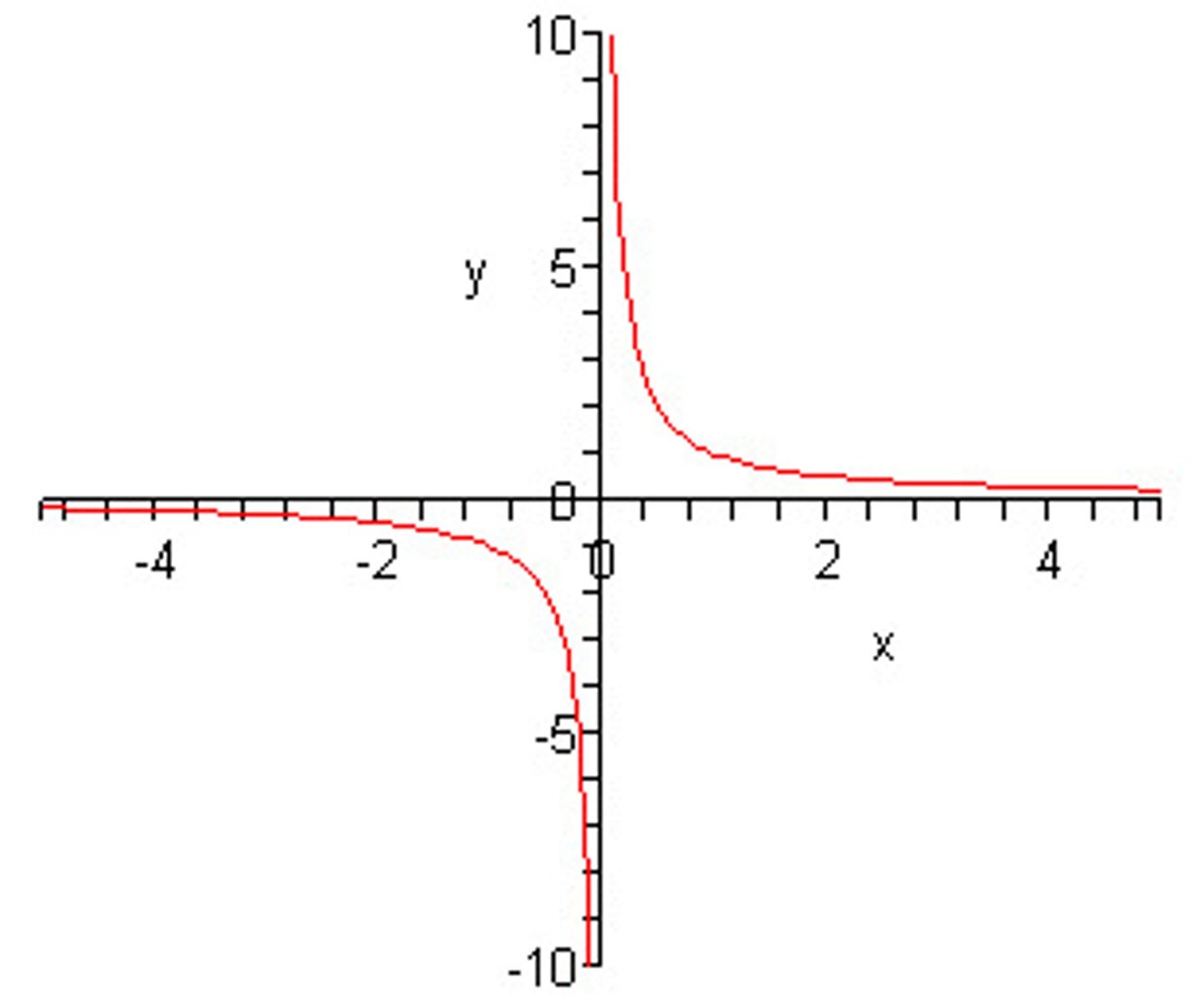
rational function
f(x) = (a/x-h) +k
horizontal shift
f(x - h) OR f(x + h)
vertical shift
f(x) + k
nonrigid transformation (stretch/compression)
"a" value
x-axis reflection
-f(x)
y-axis reflection
f(-x)
f ○ g (x)
f(g(x))
how to find domain of square root function?
set to 0 and solve
if f ○ g (x) equals x, f and g are _____
inverses
how do you find the inverse of a function?
swap x and y
what switches between a function and its inverse?
the domain and range
standard form
f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c
what does c represent in standard form?
the y-intercept
parent quadratic function (function, domain, range, y-intercept, axis of symmetry, minimum)
y = x^2
D: (-∞, +∞)
R: [0, +∞)
y-int: 0
A.O.S: x = 0
minimum: at 0
how to find vertex in standard form
(-b/2a, f(-b/2a))
vertex form
f(x) = a(x-h)^2 + k
vertex: (h,k)
how do you find x-intercepts?
y = 0
how do you find y-intercepts?
x = 0
How to go from standard to vertex form
complete the square
even multiplicity
bounces on x-axis
odd multiplicity
crosses the x-axis
ways to factor
AC method, grouping, cubes, quadratic formula, GCF
when is a function continuous?
if there are no gaps, jumps, or sharp turns
steps for long division of polynomials (4)
1) add in any placeholders
2) look at 1st two numbers and find what makes them equal
3) distribute
4) swap signs then add
steps for synthetic division of polynomials (3)
1) find x = 0 (the zero)
2) bring down 1st number
3) multiple by the zero and add the numbers
what does the degree tell you?
how many solutions there are
how to list possible rational real zeros
factors of constant/factors of leading coefficient
Descartes rule of signs
count sign changes - negative/positive real roots
compare the degrees: Denominator = Numerator (horizontal and vertical asymptotes)
horizontal: leading coefficient
vertical: Denominator = o
compare the degrees: Denominator > Numerator (horizontal and vertical asymptotes)
horizontal: y = 0; +k
vertical: Denominator = o
compare the degrees: Denominator < Numerator (horizontal and vertical asymptotes)
horizontal: none; divide for slant
vertical: Denominator = o
what does a cancelled factor become?
a hole, a removable discontinutity
horizontal asymptote is a
what happens eventually (can be crossed)
vertical asymptote is a
brick wall (can't be crossed or touched)
steps to graph rational functions (6)
1) simplify
2) find and sketch asymptotes
3) plot x and y-intercepts
4) plot at least 1 point on either side of asymptote
5) use smooth curves
6) to find slant use long division
f(x) = a^x
a > o (always positive) - a ≠ 1 - cannot be imaginary
make a ______ to graph exponential growth
table
natural base e equals approximately
2.718
A = p(1 + r/n)^nt
A = new amount
p = principal (initial)
r = rate (decimal)
t = time (years)
n = number of times it compounds
A = pe^rt
continuously compounded
n = 1 (annual)
half life means
time it takes for element to decay in half
Change of base: loga(X)
logX/loga
loge(X) equals
natural log: ln(x)
if X is negative in log(X), what does it equal?
it does not exist (DNE)
B^E = N
logB(N) = E
logarithmic property: loga(1) = 0
a^0 = 1
logarithmic property: loga(a) = 1
a^1 = a
logarithmic property: loga(a^x) = x
a^x = a^x
logarithmic property: log(a^x) = log(a^y)
x = y
steps to graph logs (4)
1) change to exponential
2) select 'y' values 1st
3) use a table
4) find domain and range (D = the zero; R = all real numbers usually)
logarithmic property: loga(uv)
loga(u) +loga(v)
logarithmic property: loga(u/v)
loga(u) - loga(v)
logarithmic property: loga(u^v)
vloga(u)
steps to solve exponential and logarithmic equations (2)
1) rewrite in a form that allows solving for exponents/logs
2) one to one form (a^x = a^y so x=y)