OChem Unit 3 (Alkenes/Alkynes)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
reactions of conjugated dienes
1) pi electrons attack the electrophile, forming resonance stabilized carbocation intermediate
2) the nucleophile attacks both carbocations, forming a 1-2 (direct) product and a 1-4 (indirect) product
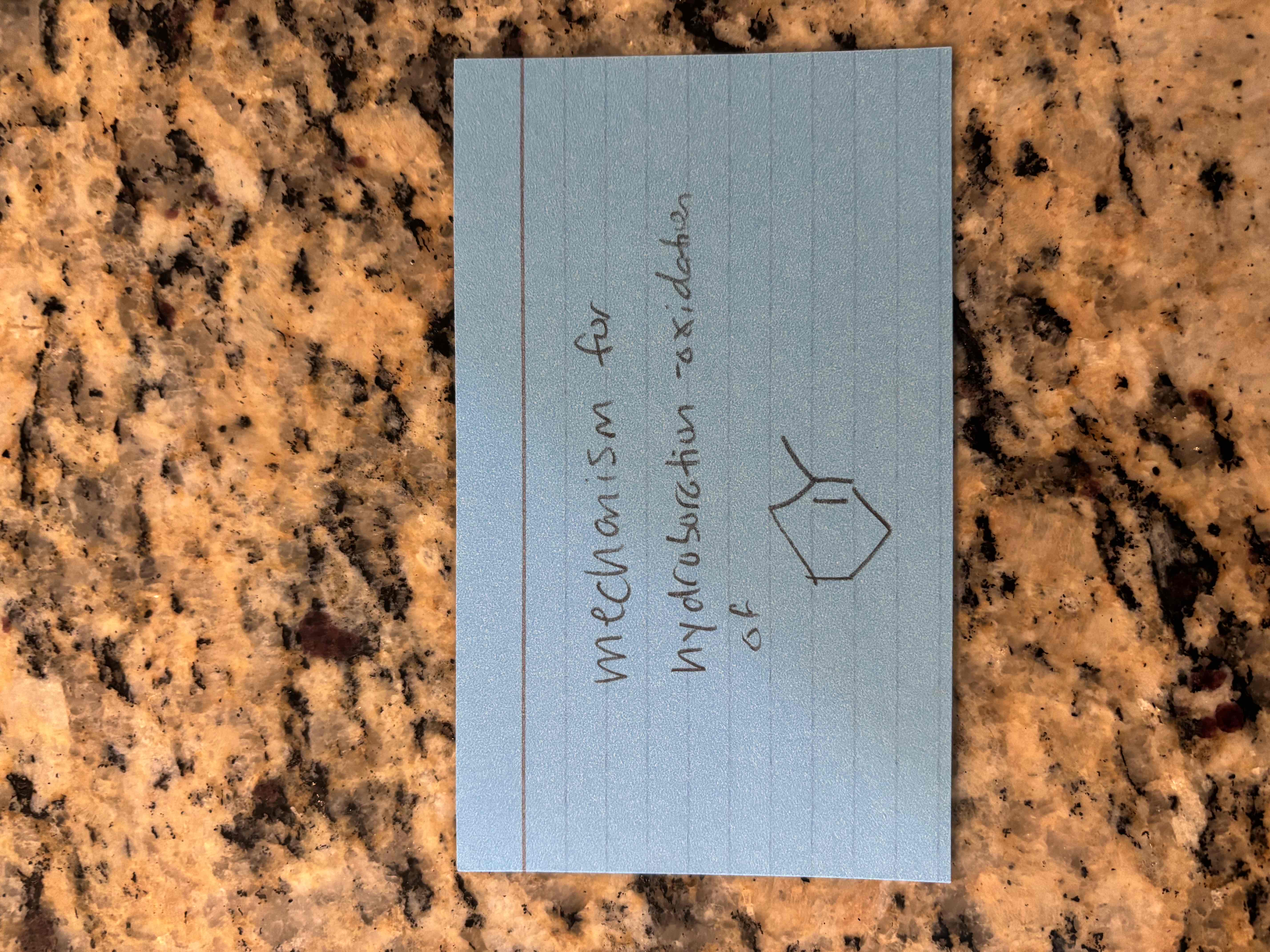
major vs minor products
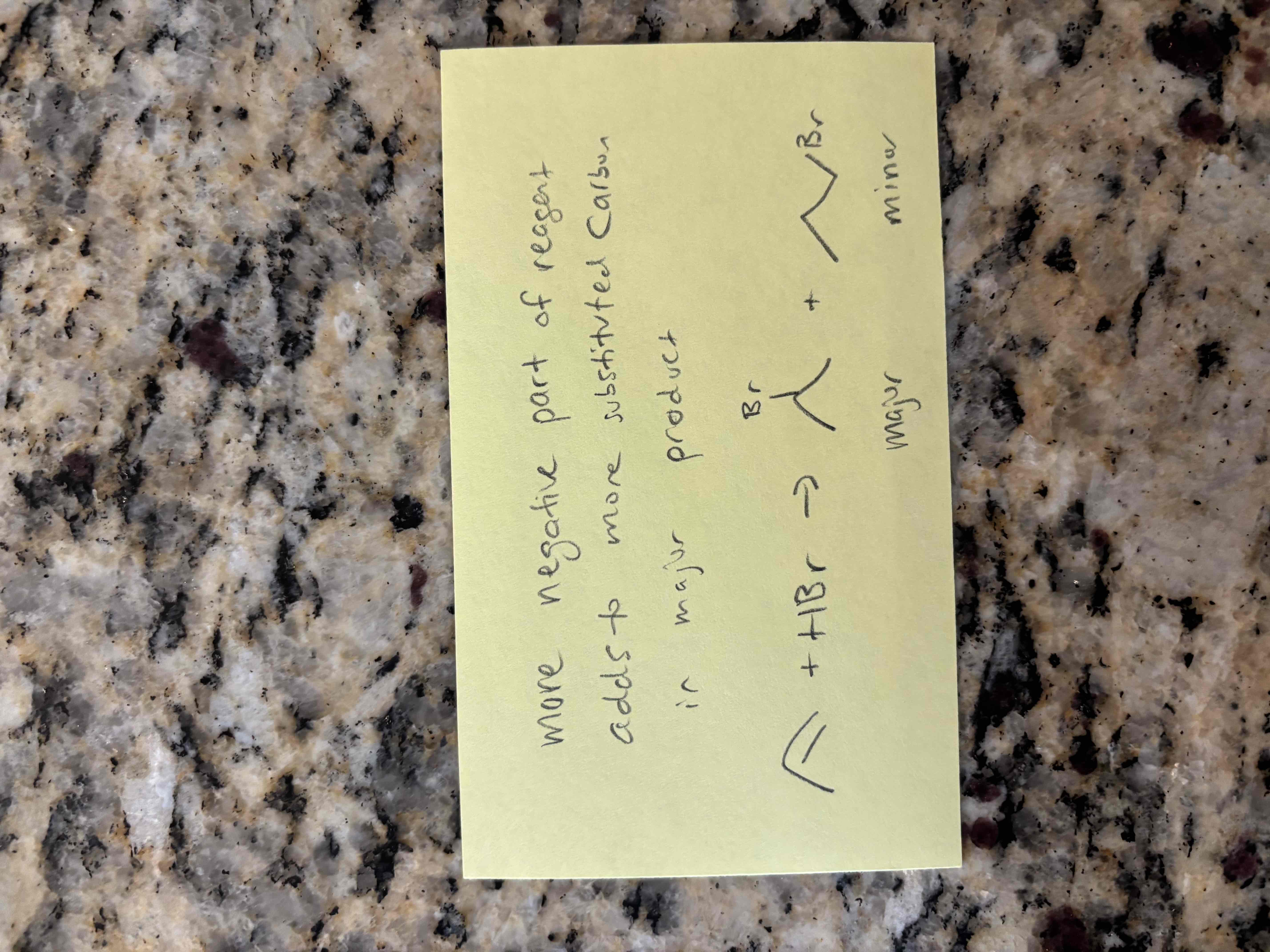
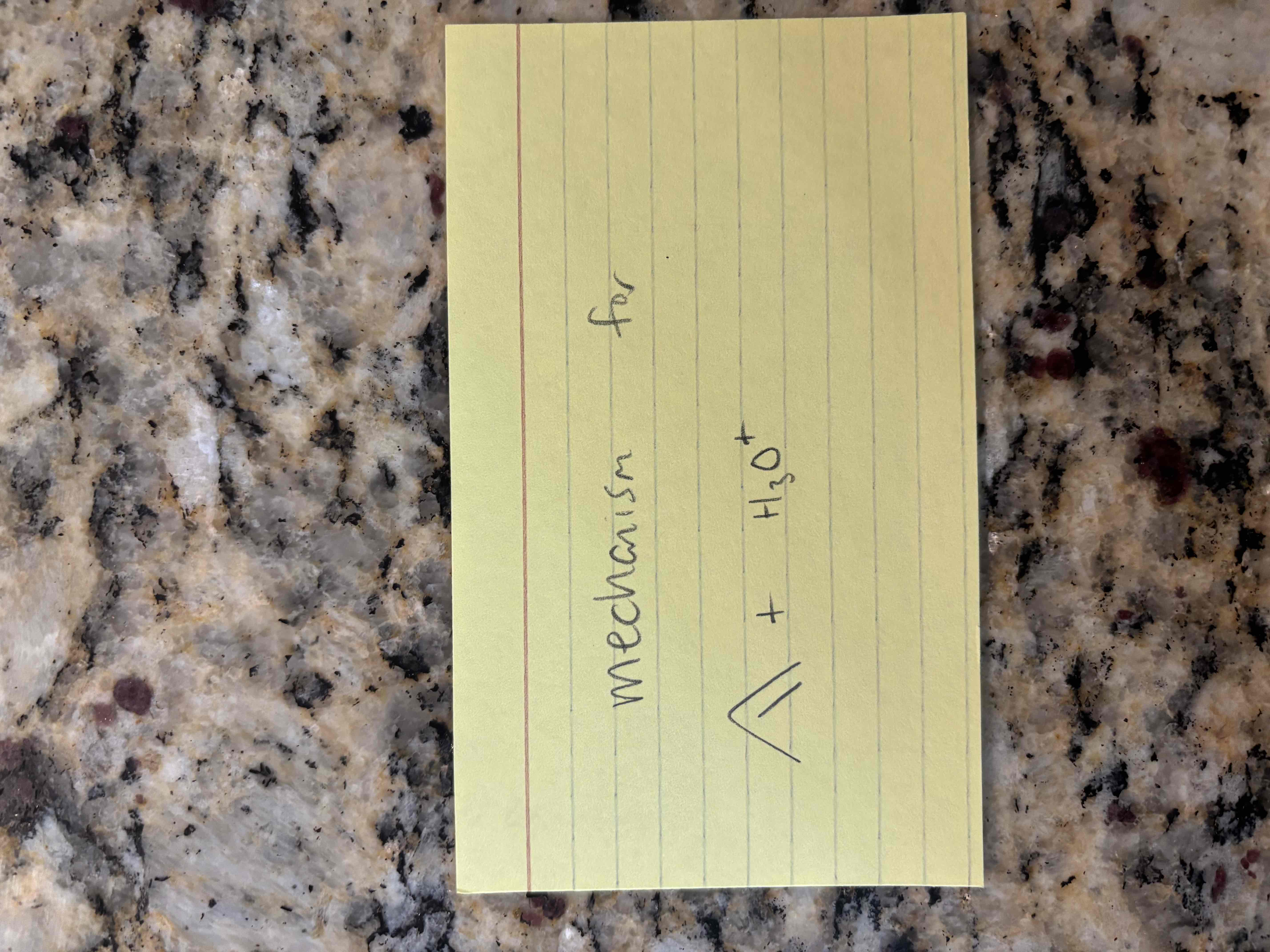



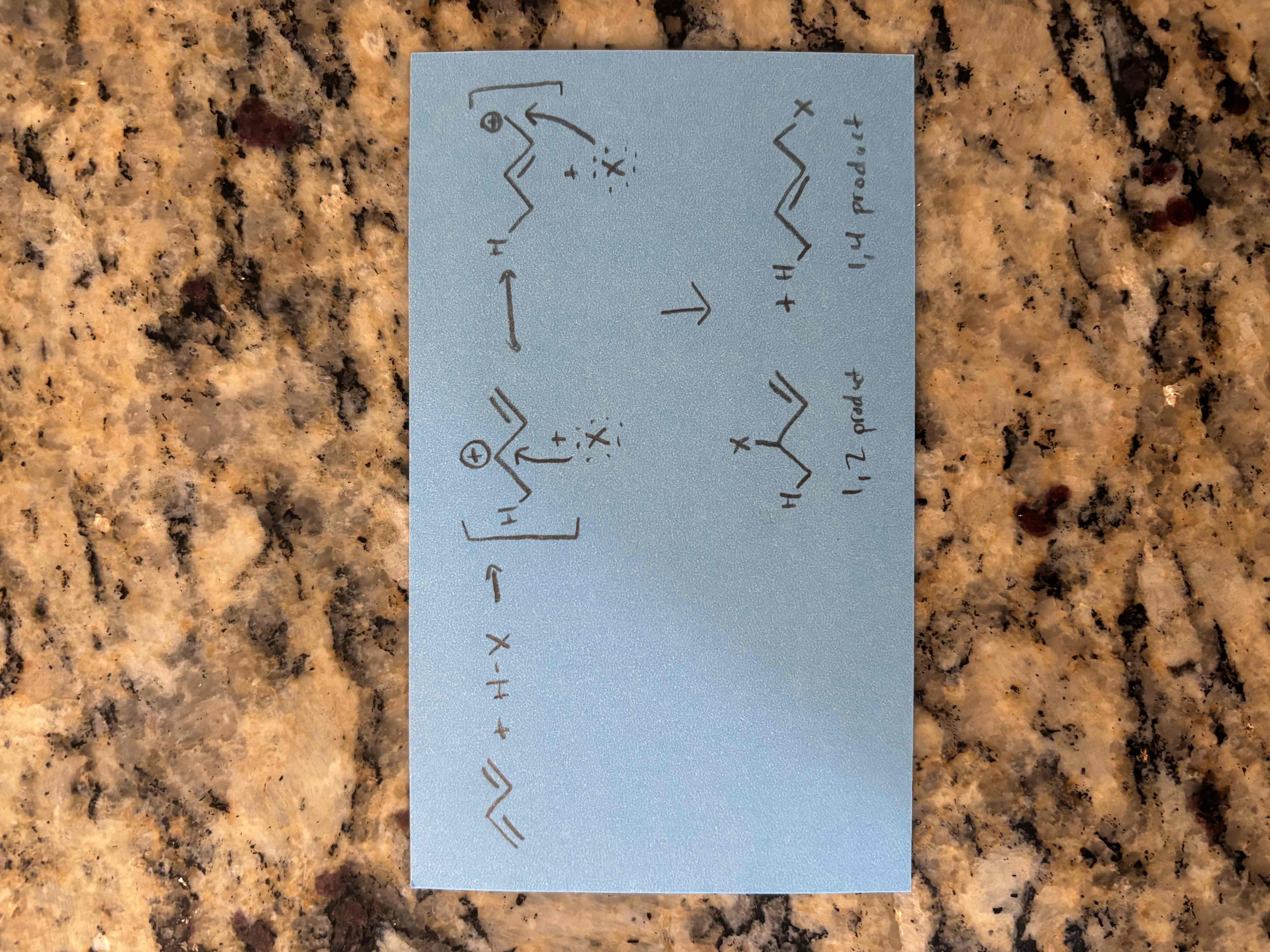
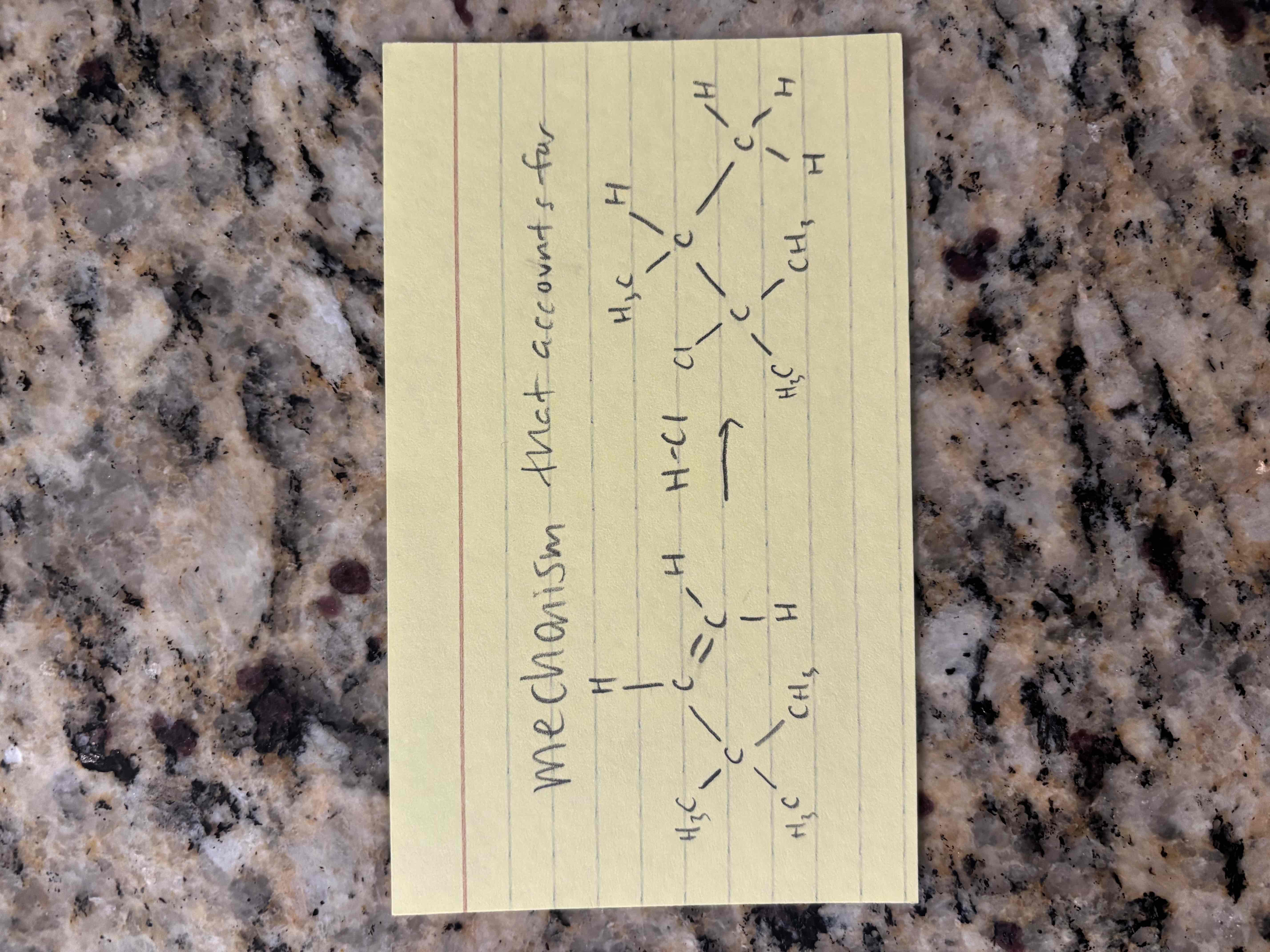
hydride/alkyl shifts
hydride shift - hydrogen shifts down a carbon to switch which carbon has a positive charge
alkyl shift - same as hydride shift but an alkyl group shifts
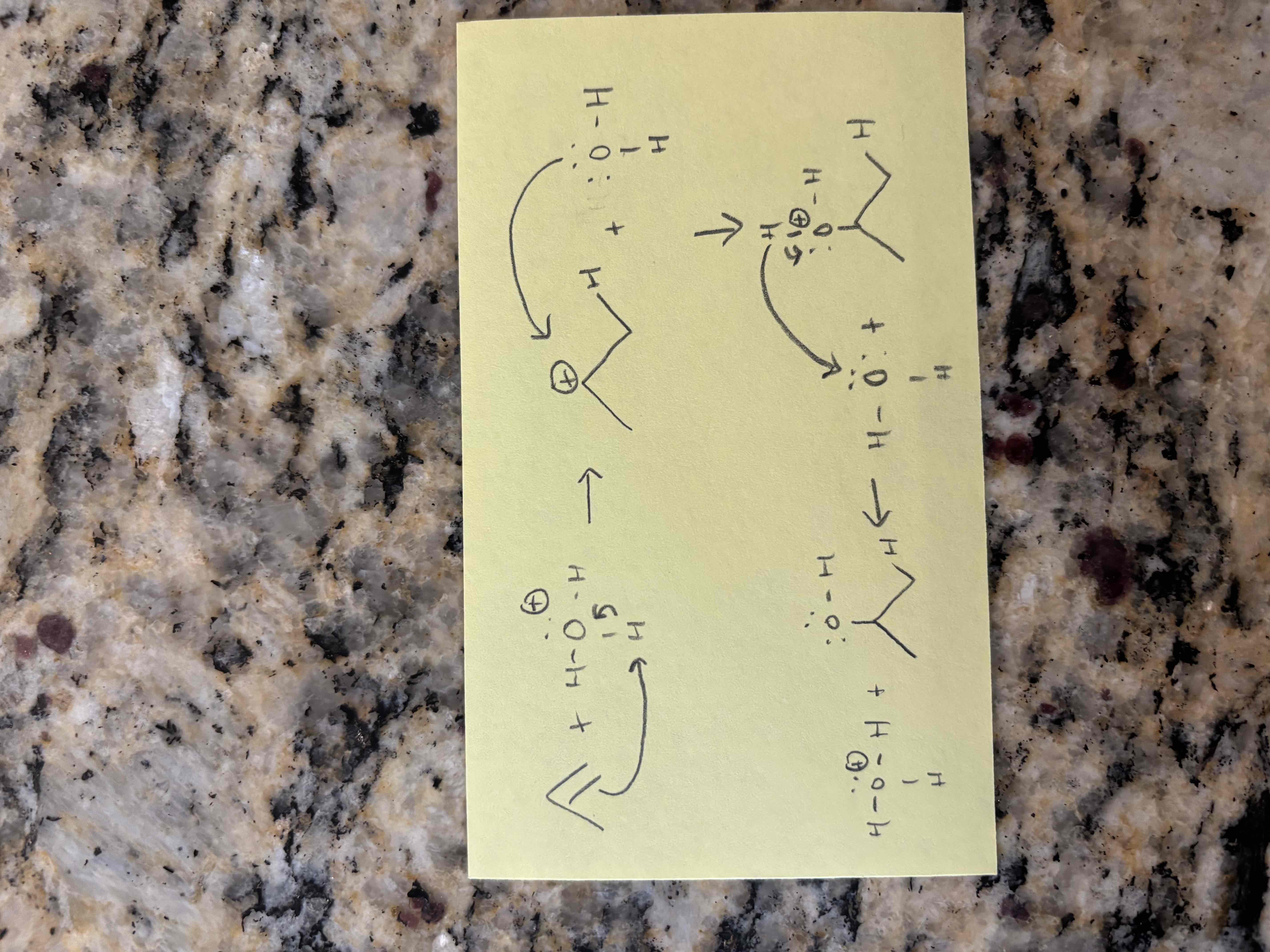
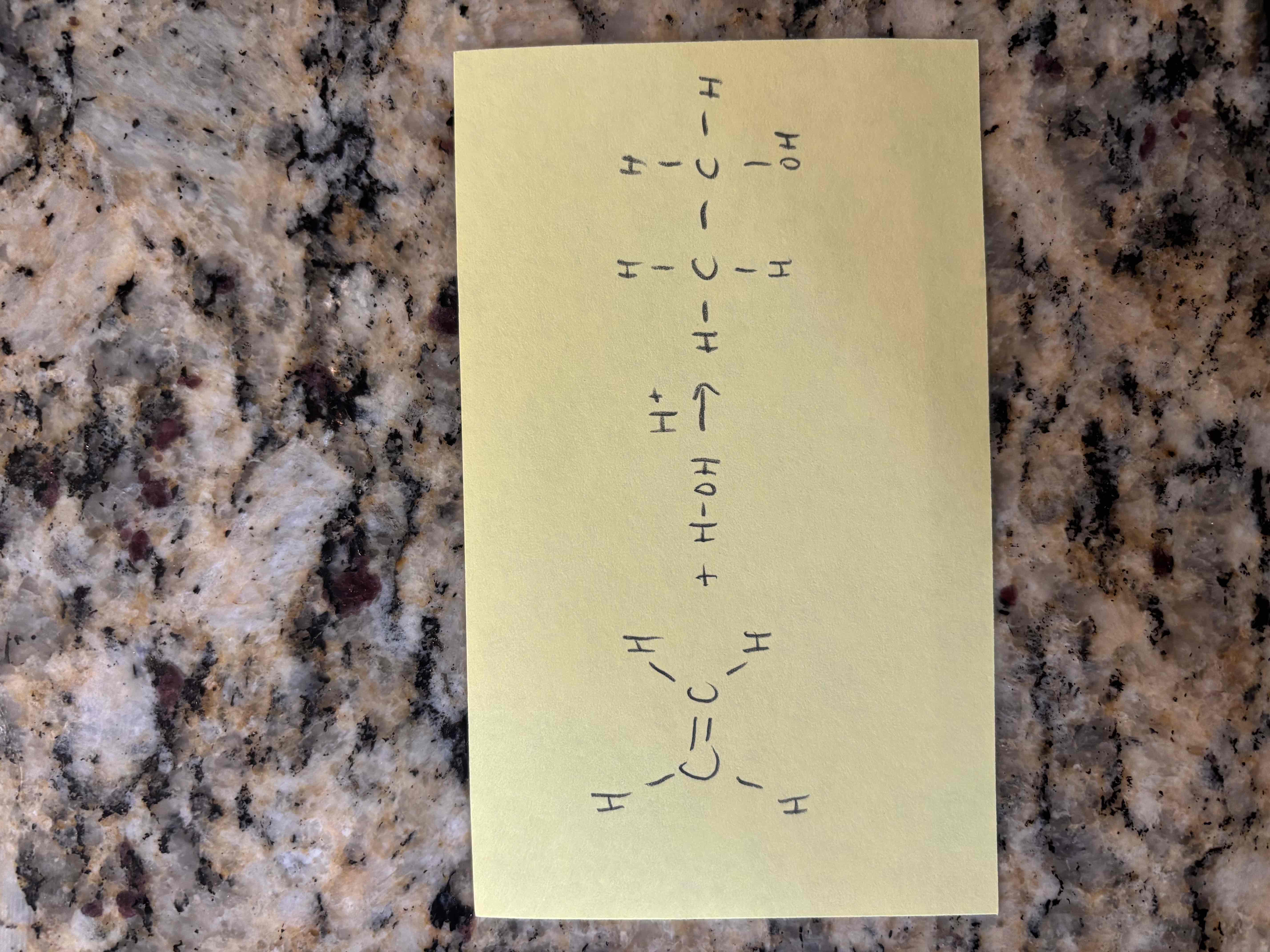
hydration of alkenes
additional of water to an alkene
new sigma bonds form to h and oh
requires an acid catalyst
acetylene

propylene
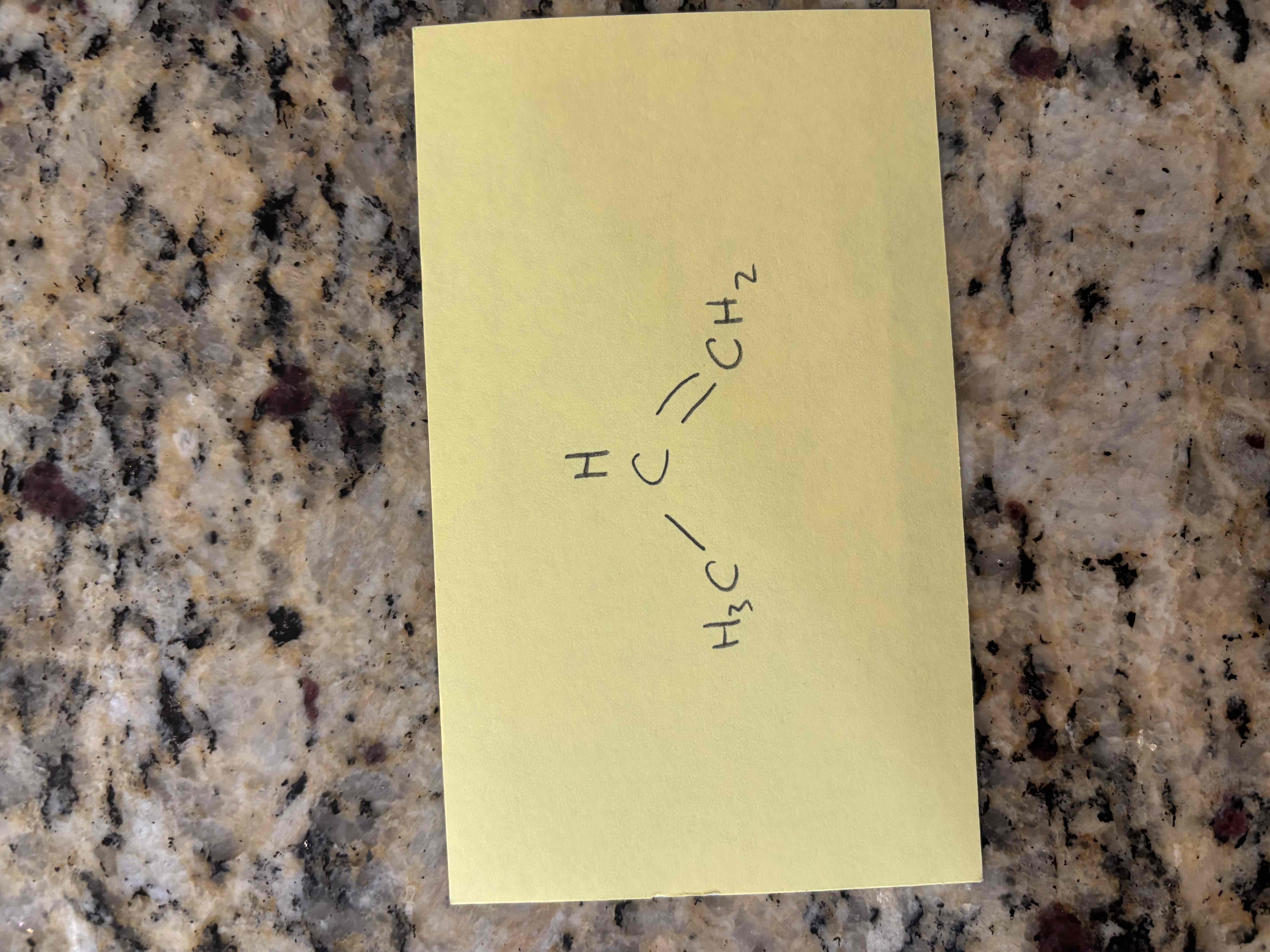
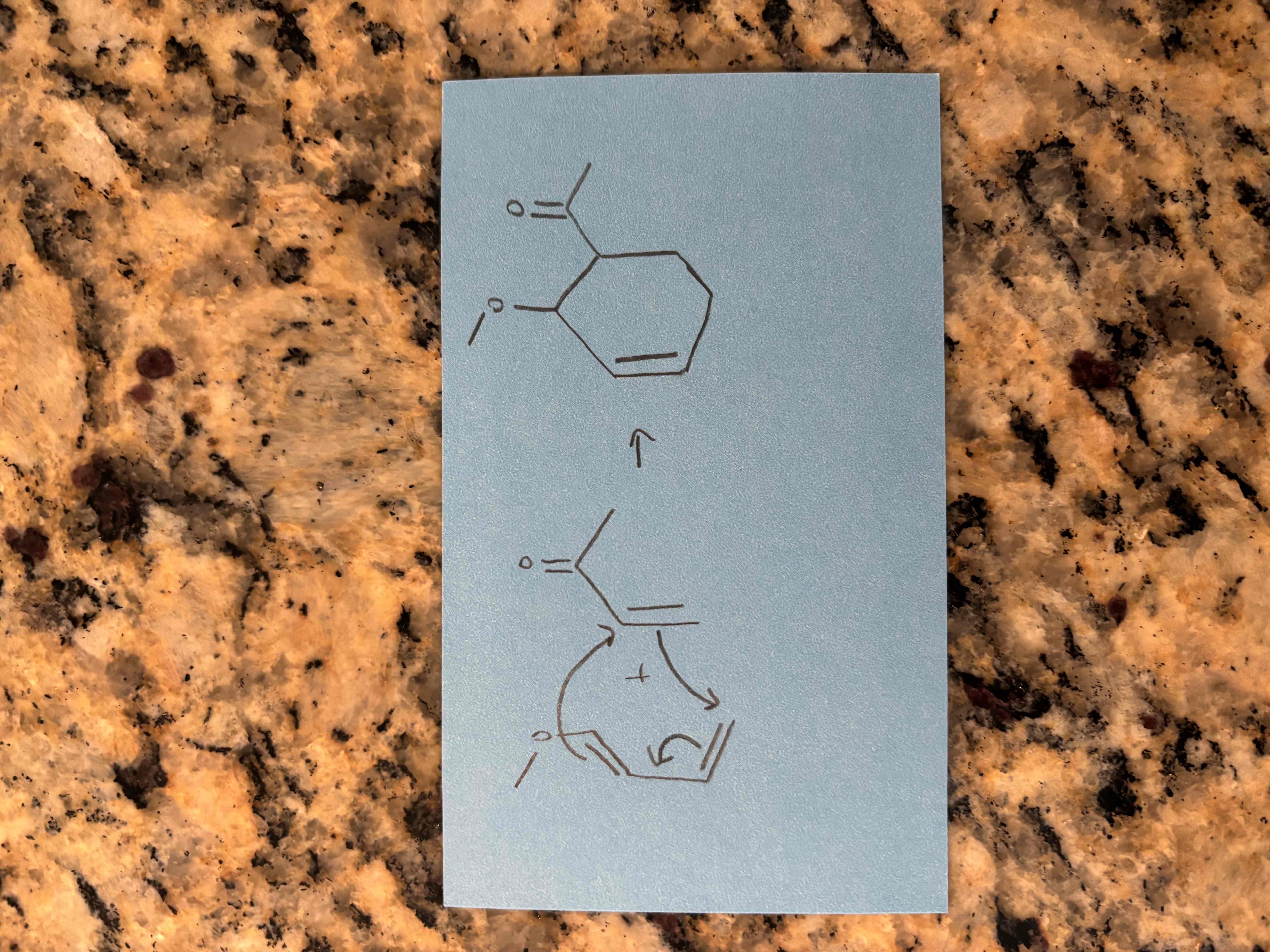
diels-alder reactions (cycloaddition)
a conjugated diene reacts with another molecule that has a pi bond to form a ring structure
bond breaking and making occur simultaneously
no carbocation intermediate
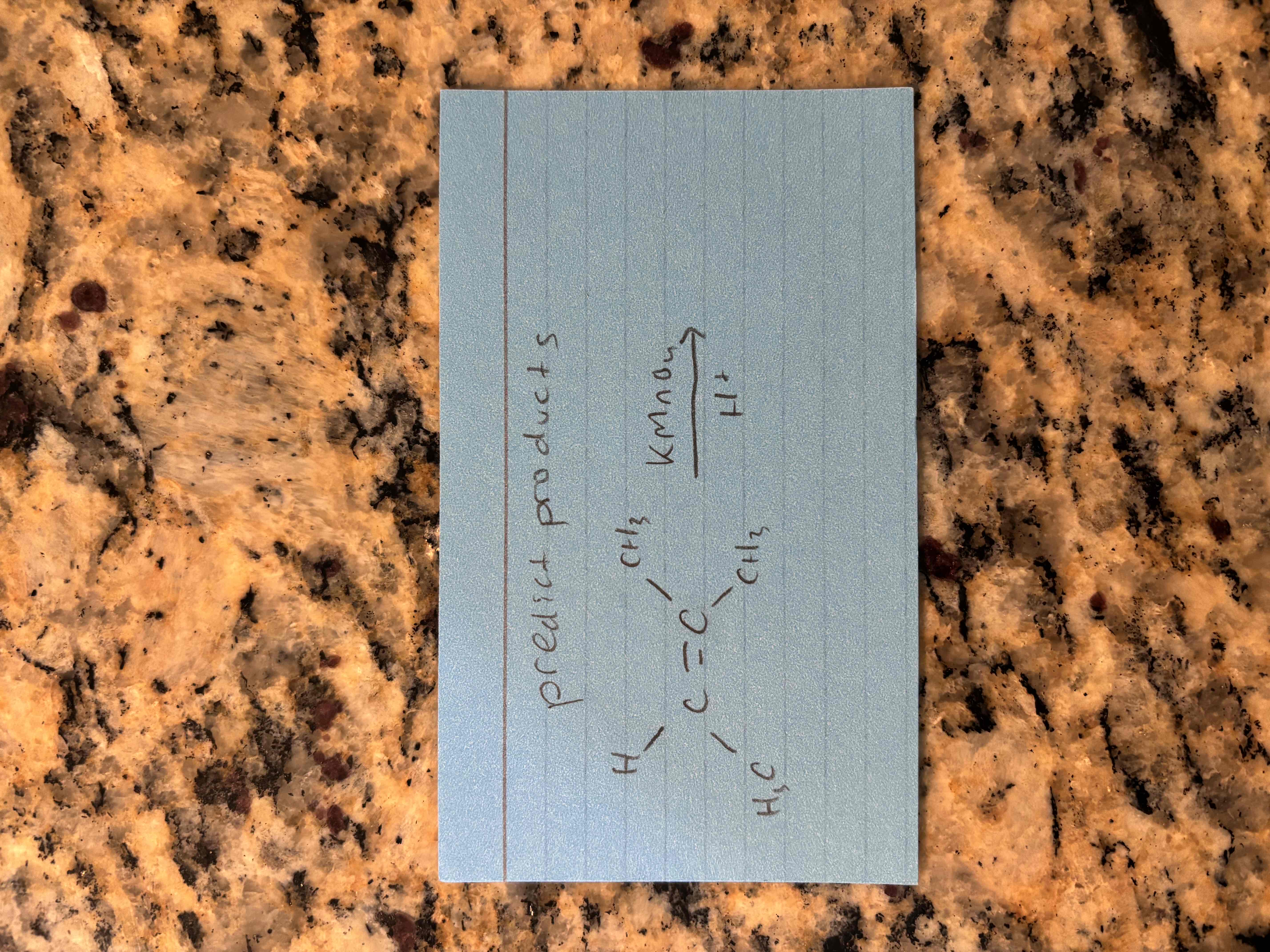
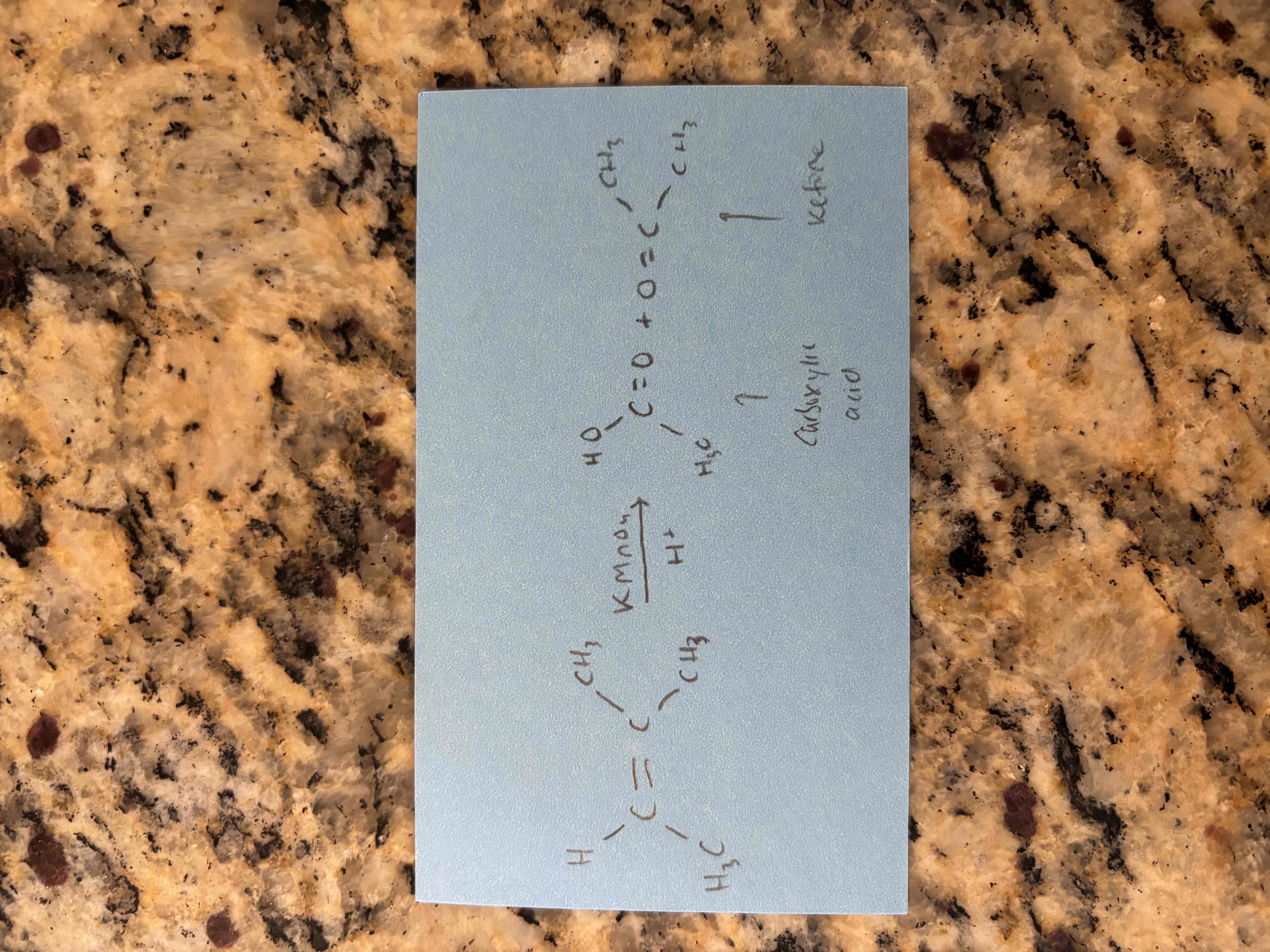
oxidation with permanganate in an acidic solution
breaks c=c bond and forms 2 c=o bonds
“snip and cap”
produces carboxylic acids and ketones
aldehydes are oxidized to carboxylic acids (h becomes oh)
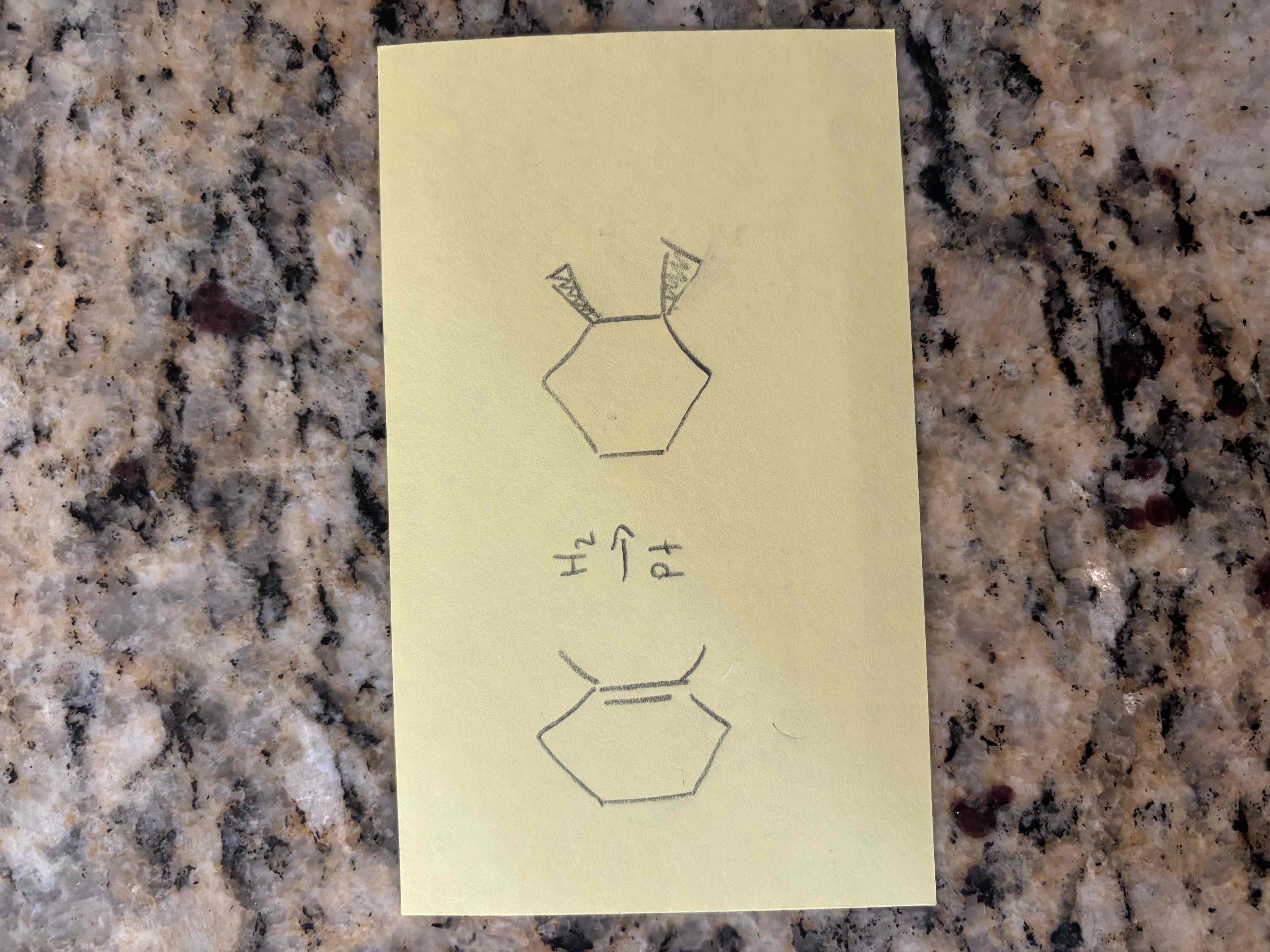
alkene hydrogenation example
isopropyl

cumulated

(e) / (z)
distinguish between tri or tetra substituted configurational alkenes
(e)- higher priority groups on opposite sides
(z)- higher priority groups on same side
the higher priority group has the higher atomic number at the first point of difference
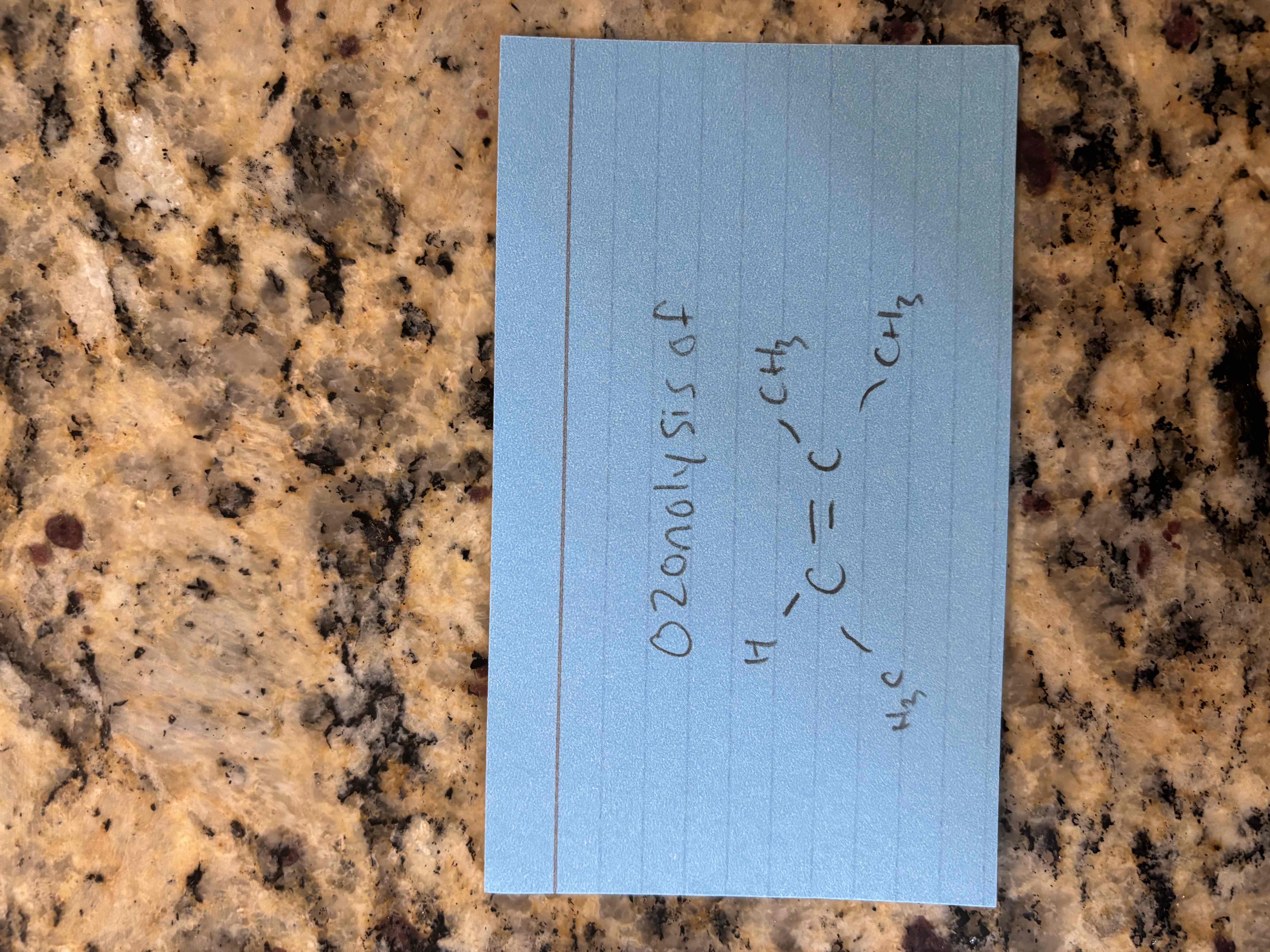
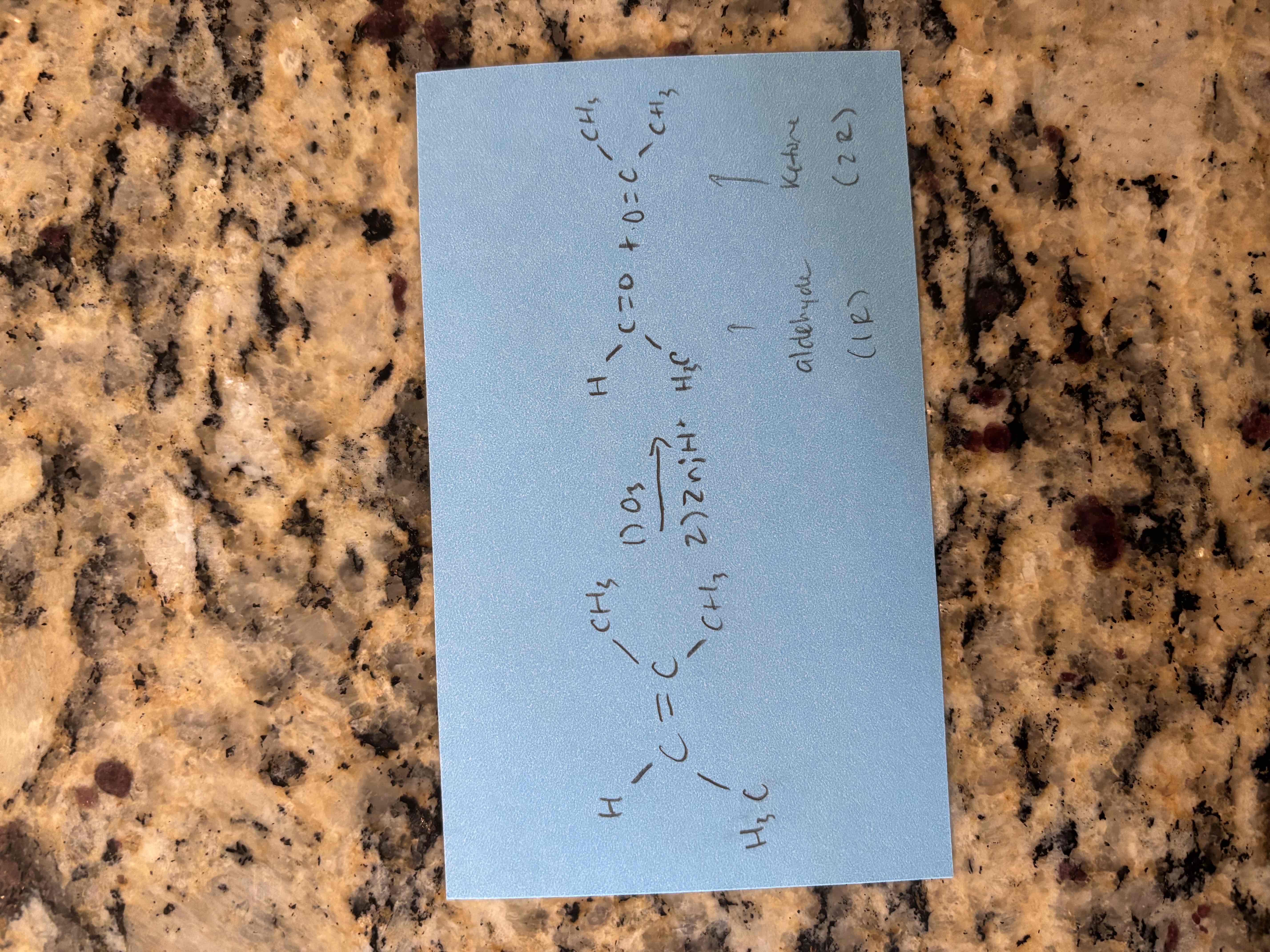
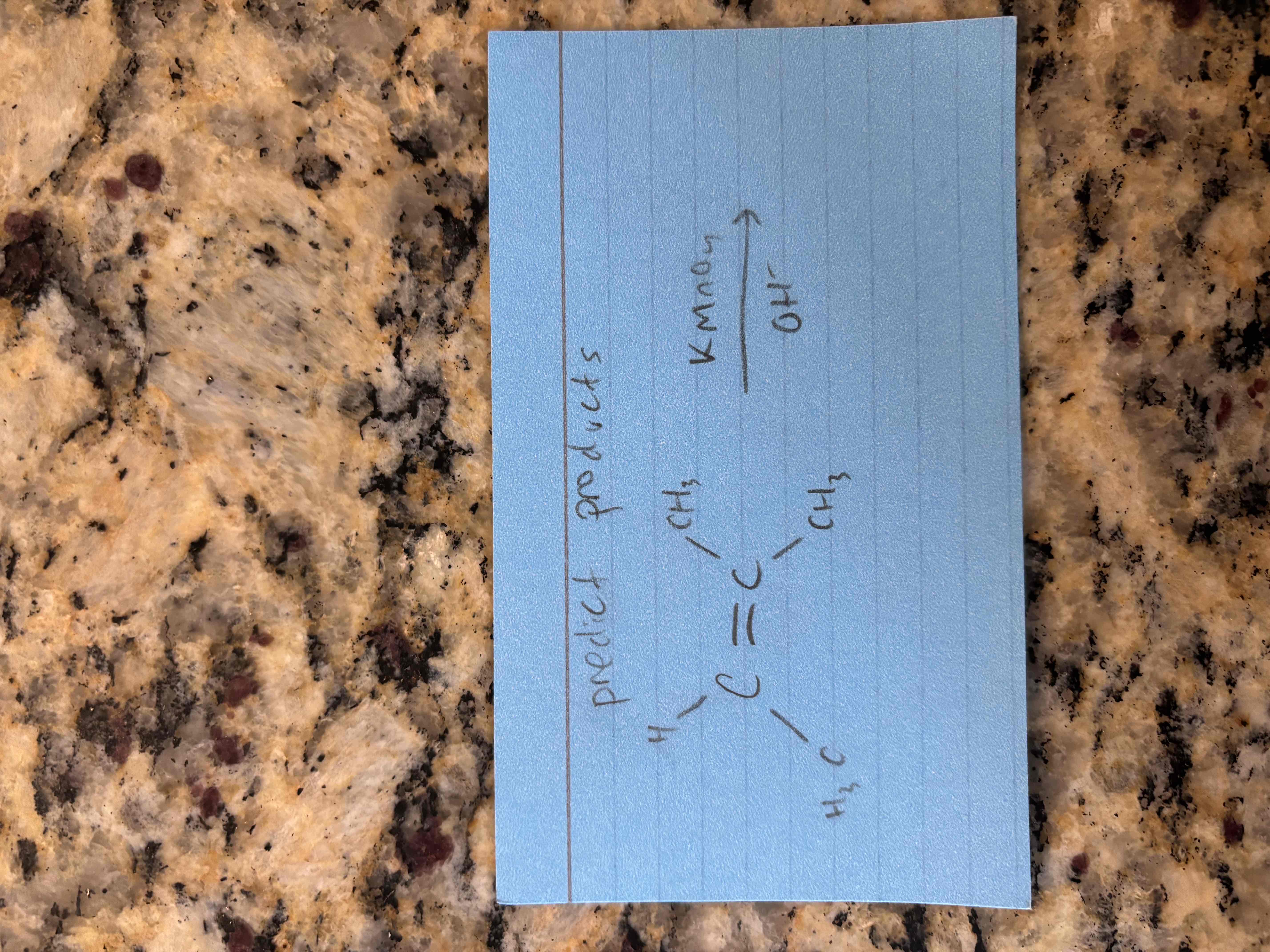
oxidation with permanganate in a basic solution
breaks c=c bond and adds oh groups to each carbon
also called dihydroxylation
syn addition (oh groups add to same side of ring)
produces glycol (compound with 2 adjacent oh groups)
hydrogenation of alkenes
additional of h2 to an alkene
2 new sigma bonds to hydrogens
hydrogens add to same side of a ring
requires a catalyst (ni, pt, pd)
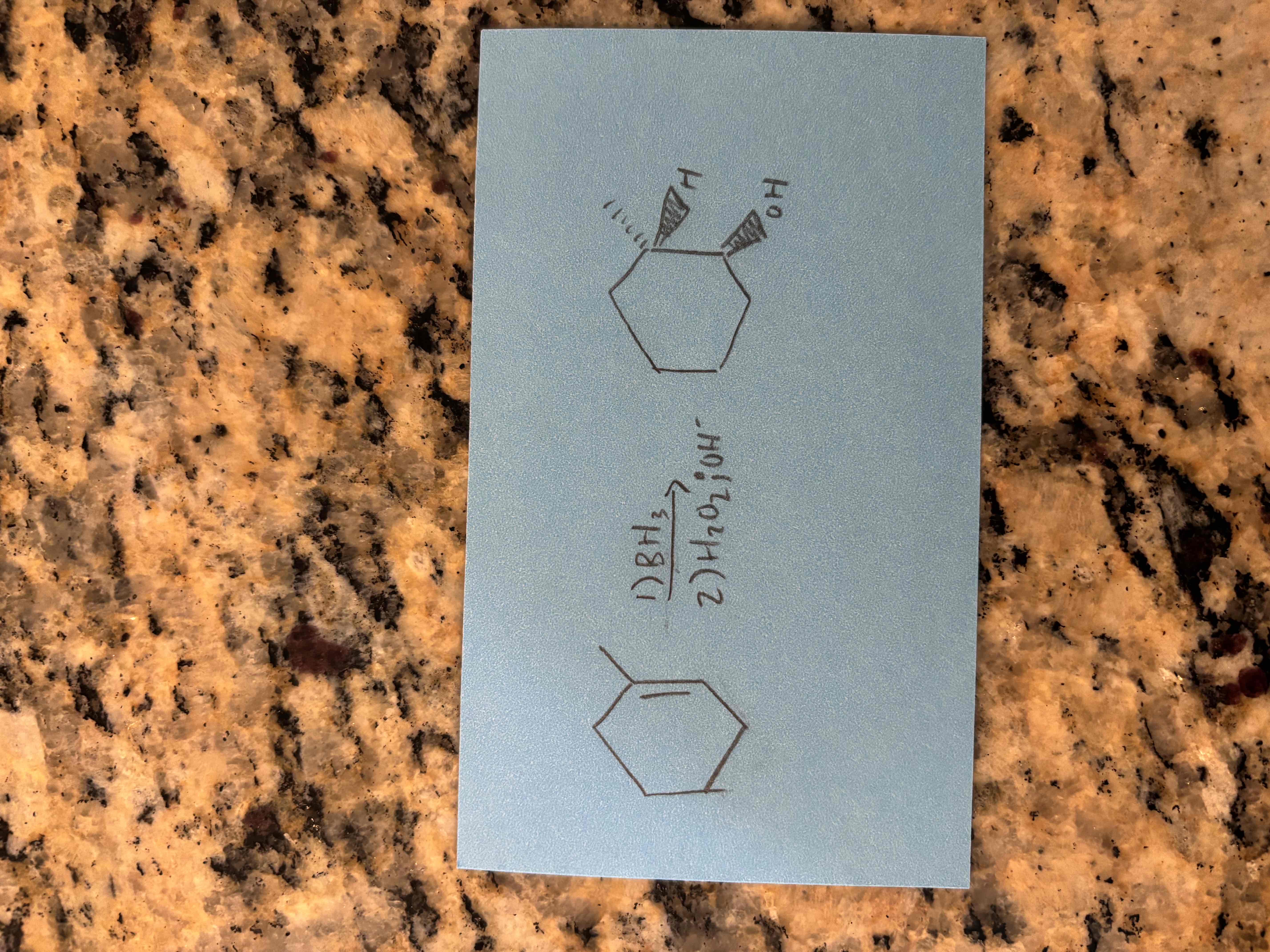
difference between acid catalyzed hydration and hydroboration oxidation of alkenes
acid catalyzed hydration - forms markovnikov product (oh on more substituted carbon)
hydroboration oxidation - forms anti-markovnikov product (oh on less substituted carbon)
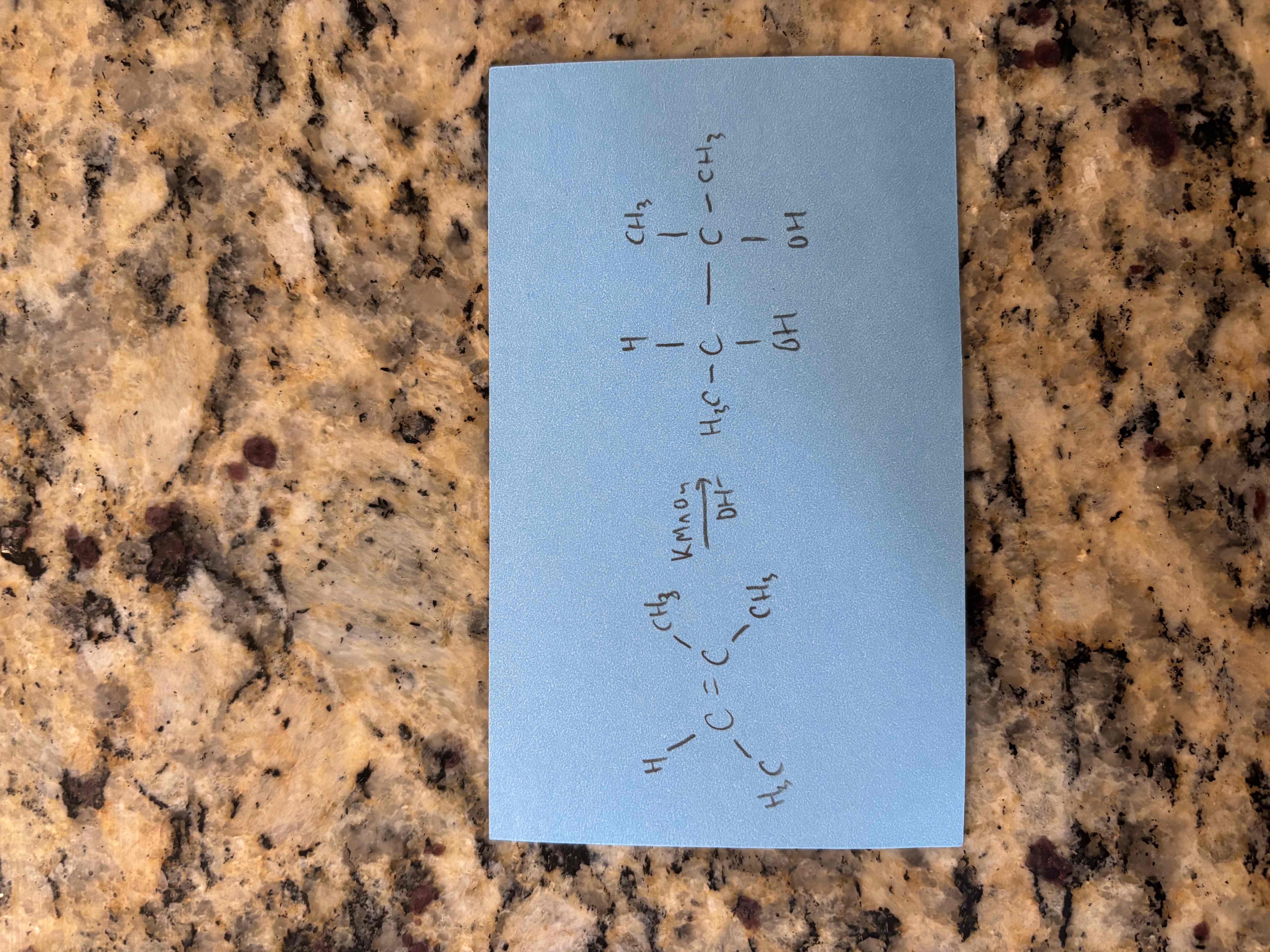
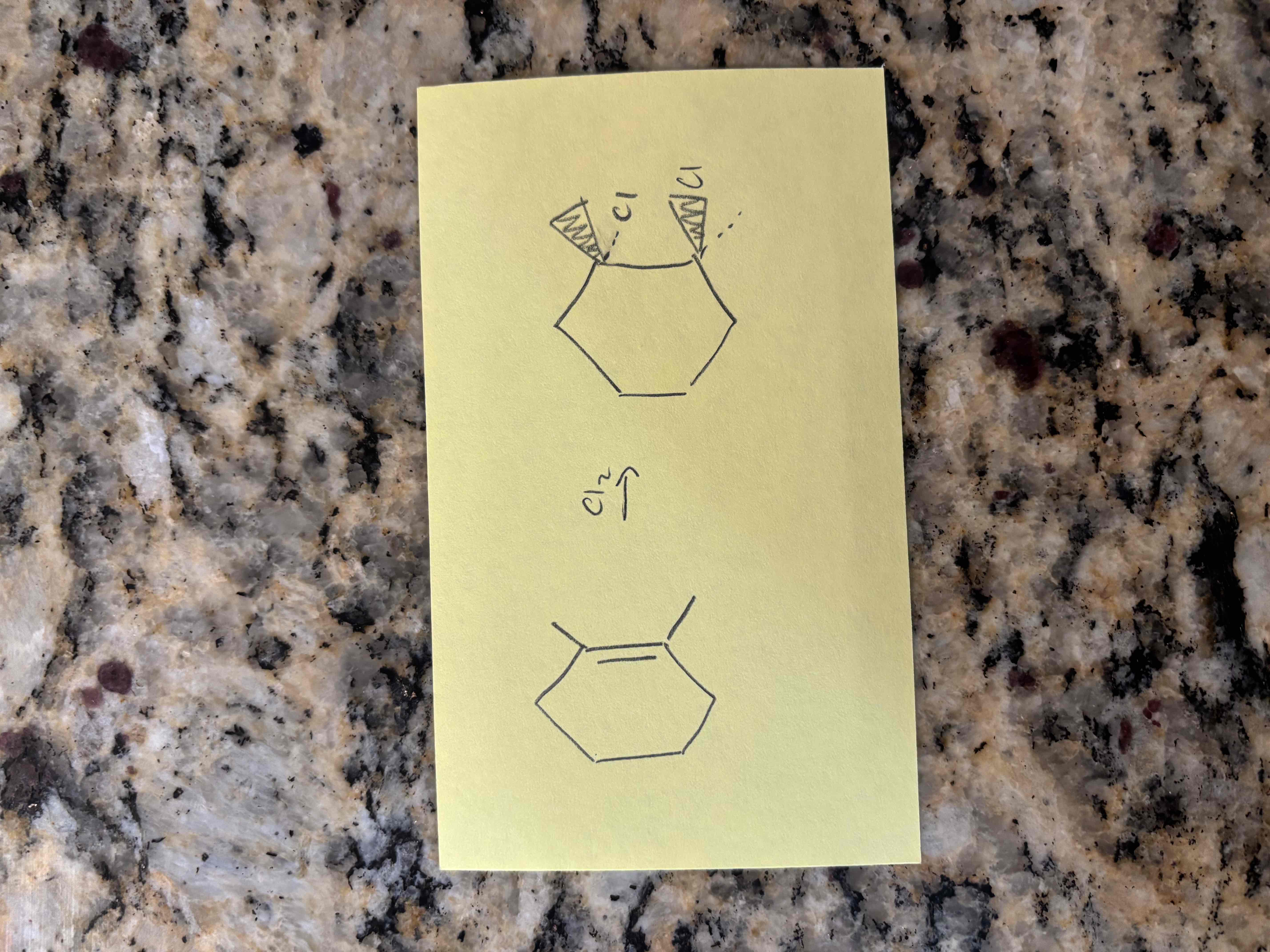
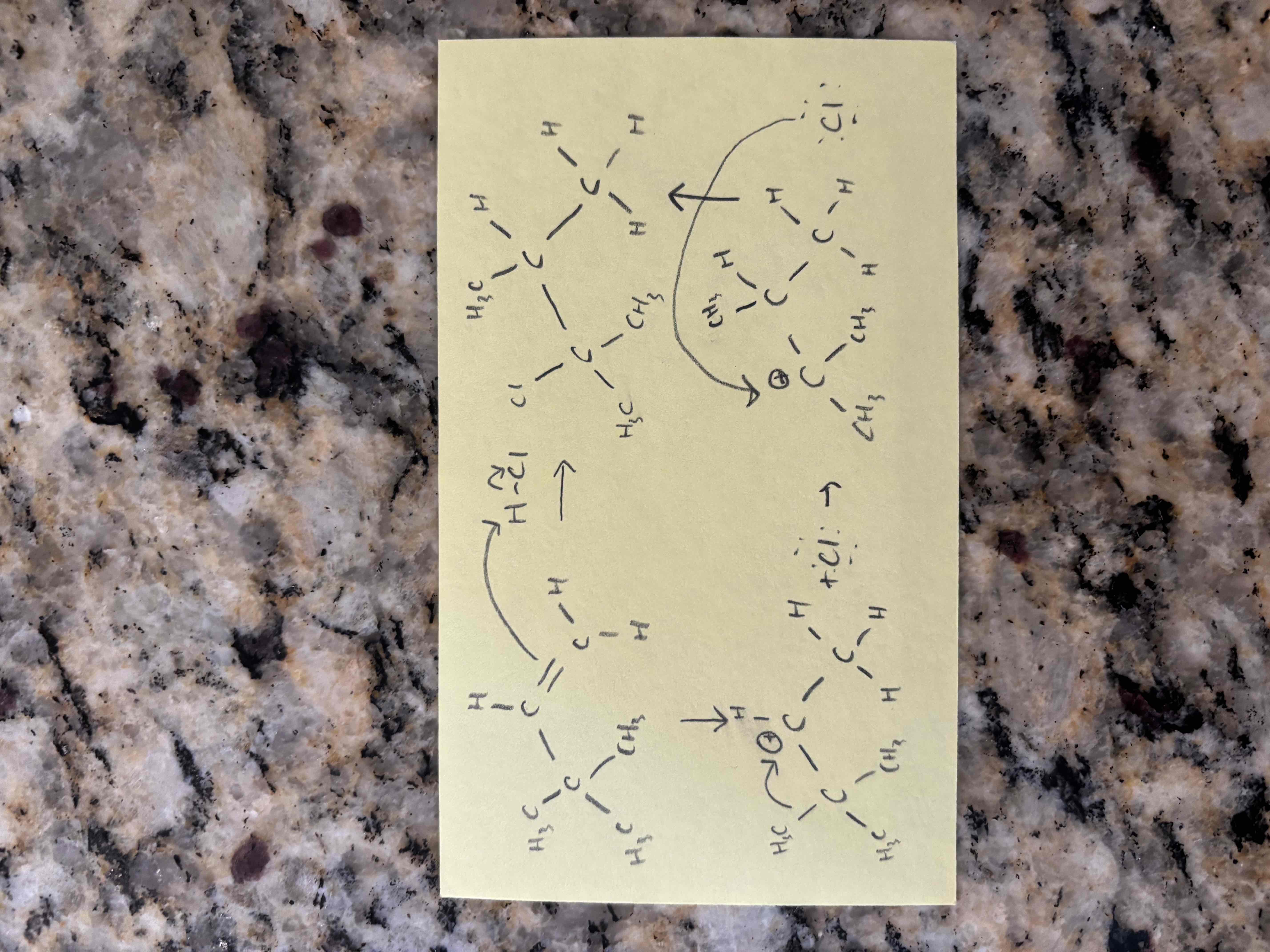
alkene halogenation
additional of a halogen to an alkene
2 new sigma bonds to halogen
halogens add to opposite sides of a ring
allyl

alkene hydroboration-oxidation reactions
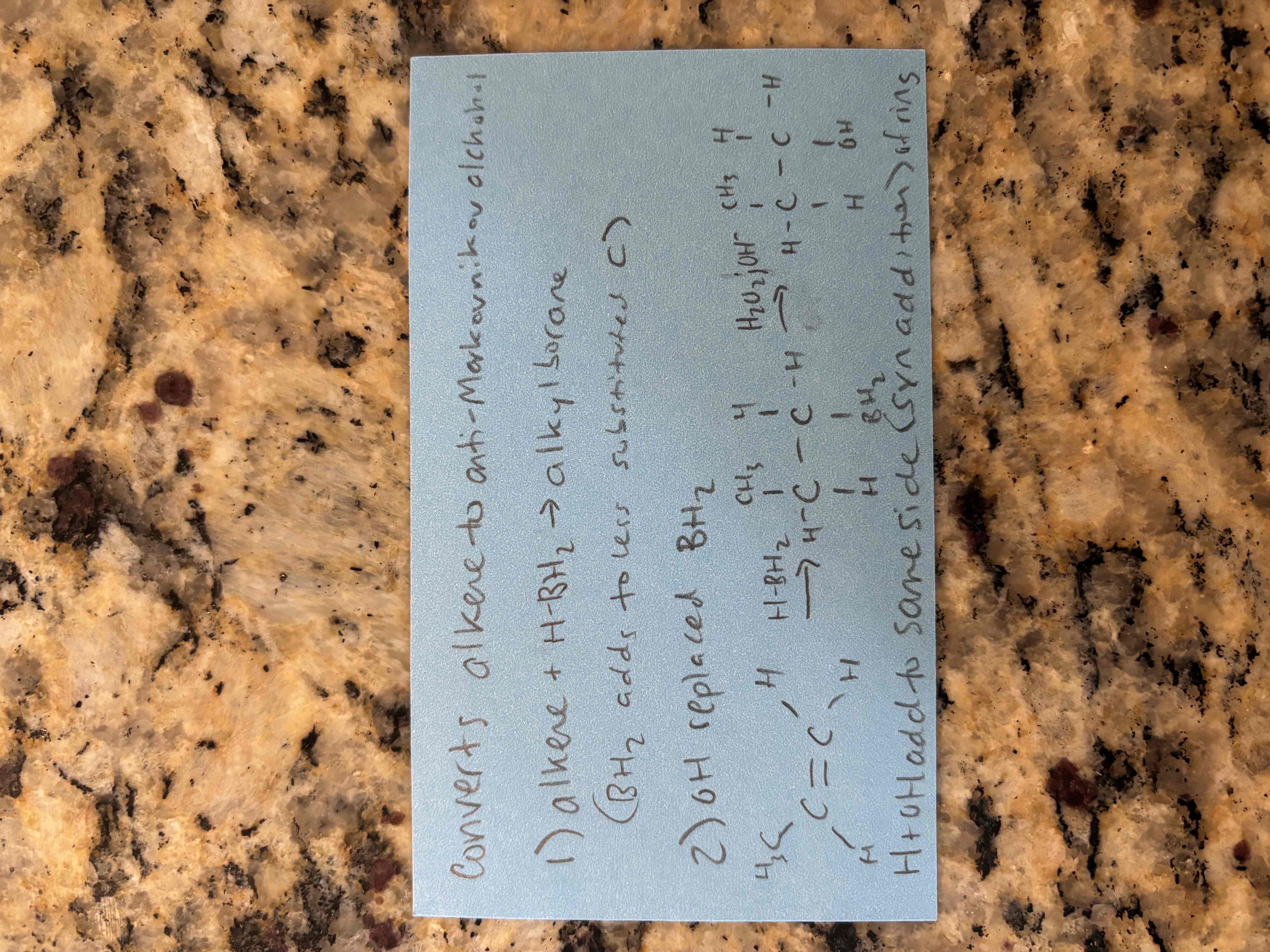
isolated/non-conjugated

ozonolysis
breaks c=c bond and forms 2 c=o bonds
forms aldehydes and ketones
1st step) ozone (o3)
2nd step) zinc in acid (zn;h+)
methylene

sec-butyl
alkene halogenation example
acid reaction with an alkene
new sigma bond with hydrogen
new sigma bond with anion
cis/trans
distinguish between disubstituted configurational alkene isomers
cis - same side
trans - opposite sides
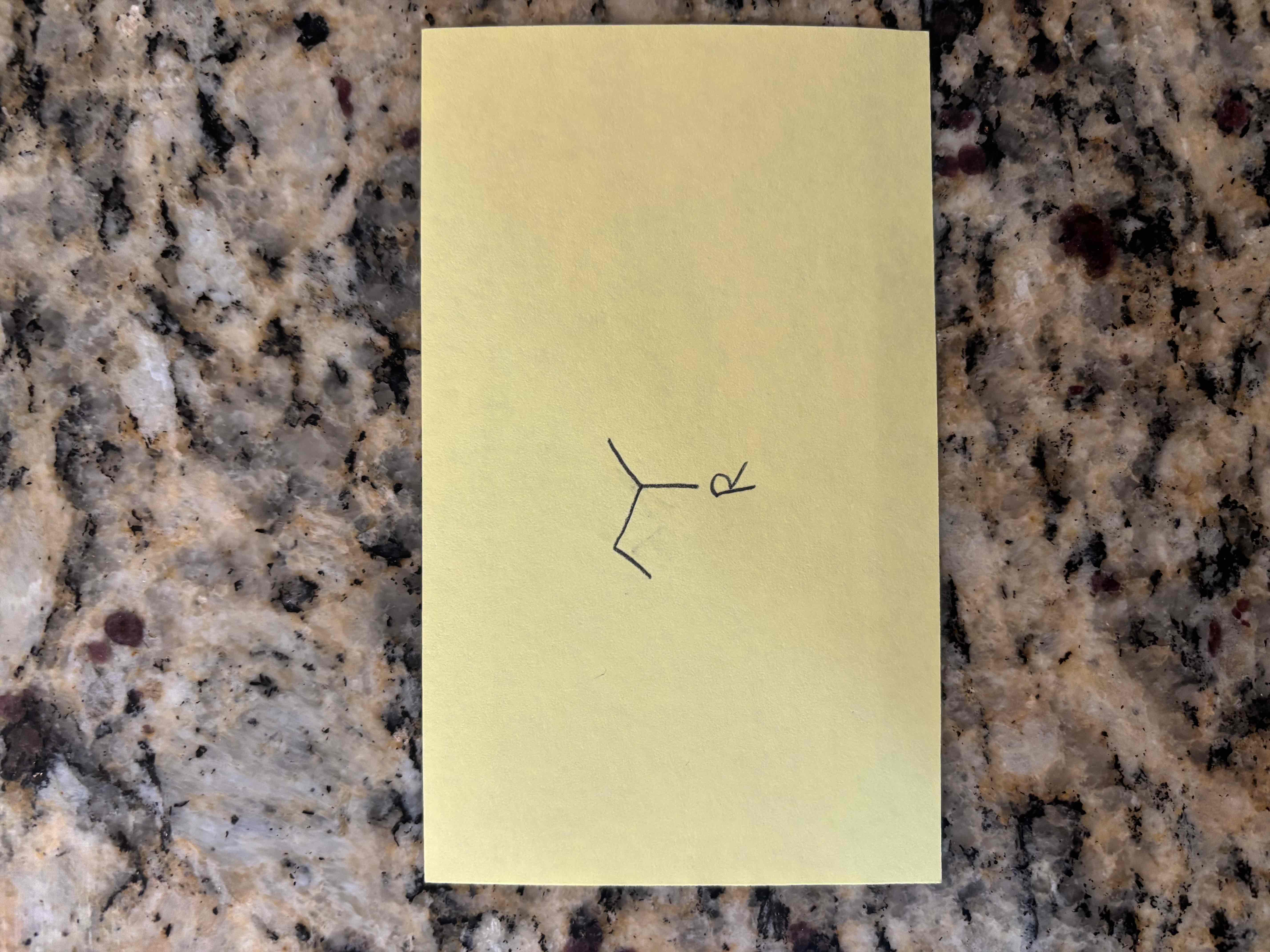
isobutyl

electrophilic addition mechanisms
1) pi electrons attack electrophile and form carbocation intermediate
2) nucleophile attacks carbocation
3 [only occurs in acid catalyzed hydration]) product loses a proton to regenerate catalyst (deprotonization)
ethylene


vinyl

conjugated

alkene hydration example
regioselective vs regiospecific
regioselective - both major and minor products form
regiospecific - only one product forms

1 vs 2 equivalents
1 equivalent - is the amount of reagent needed to react with 1 mole of reactant, 1 pi bond is broken
2 equivalents - twice the amount of reagent as 1 equivalent, 2 pi bonds are broken
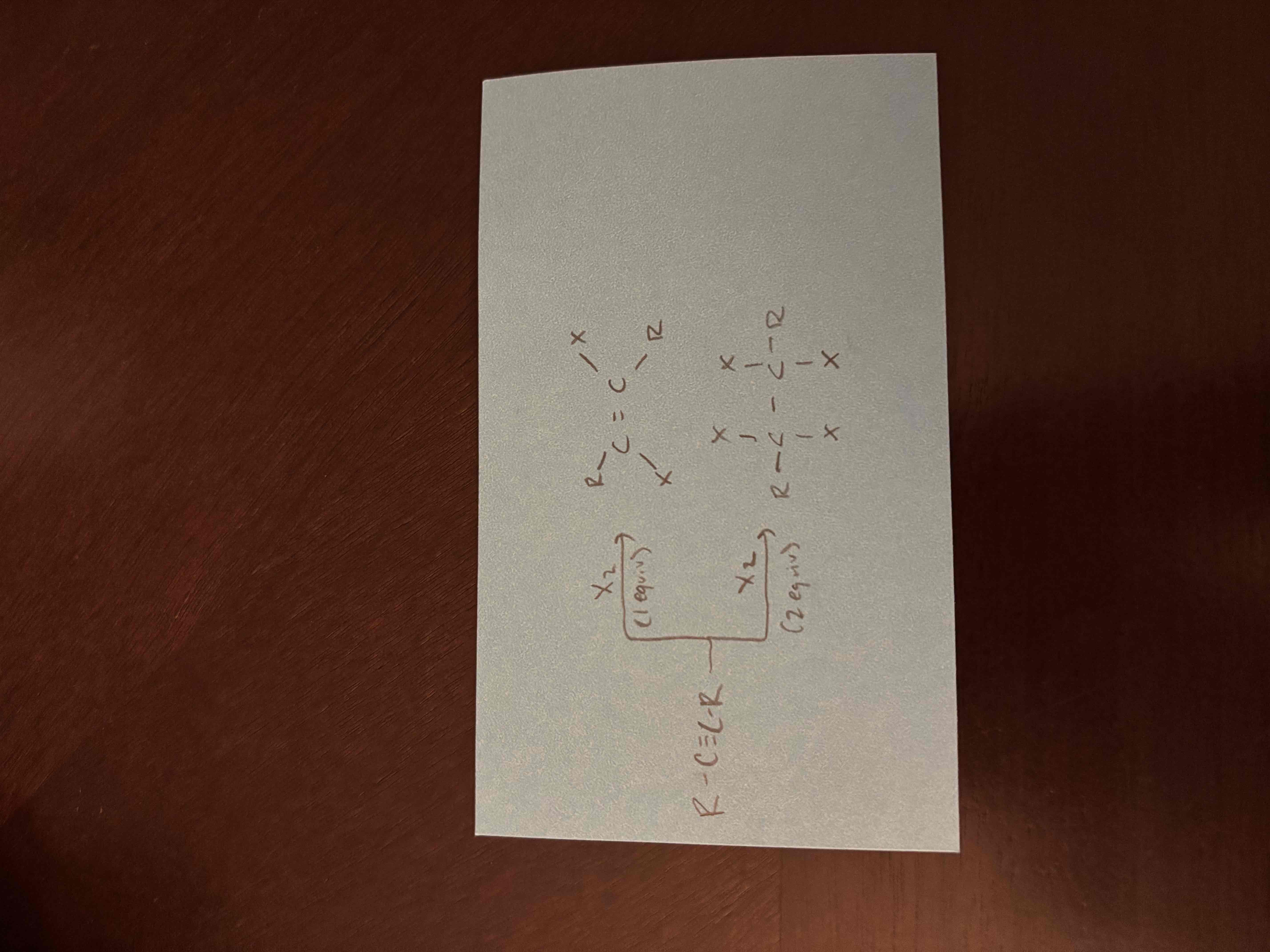
halogenation of alkynes
1 equivalent - 2 halogens are added on opposite sides, 1 pi bond is broken
2 equivalents - 4 halogens added, 2 pi bonds broken

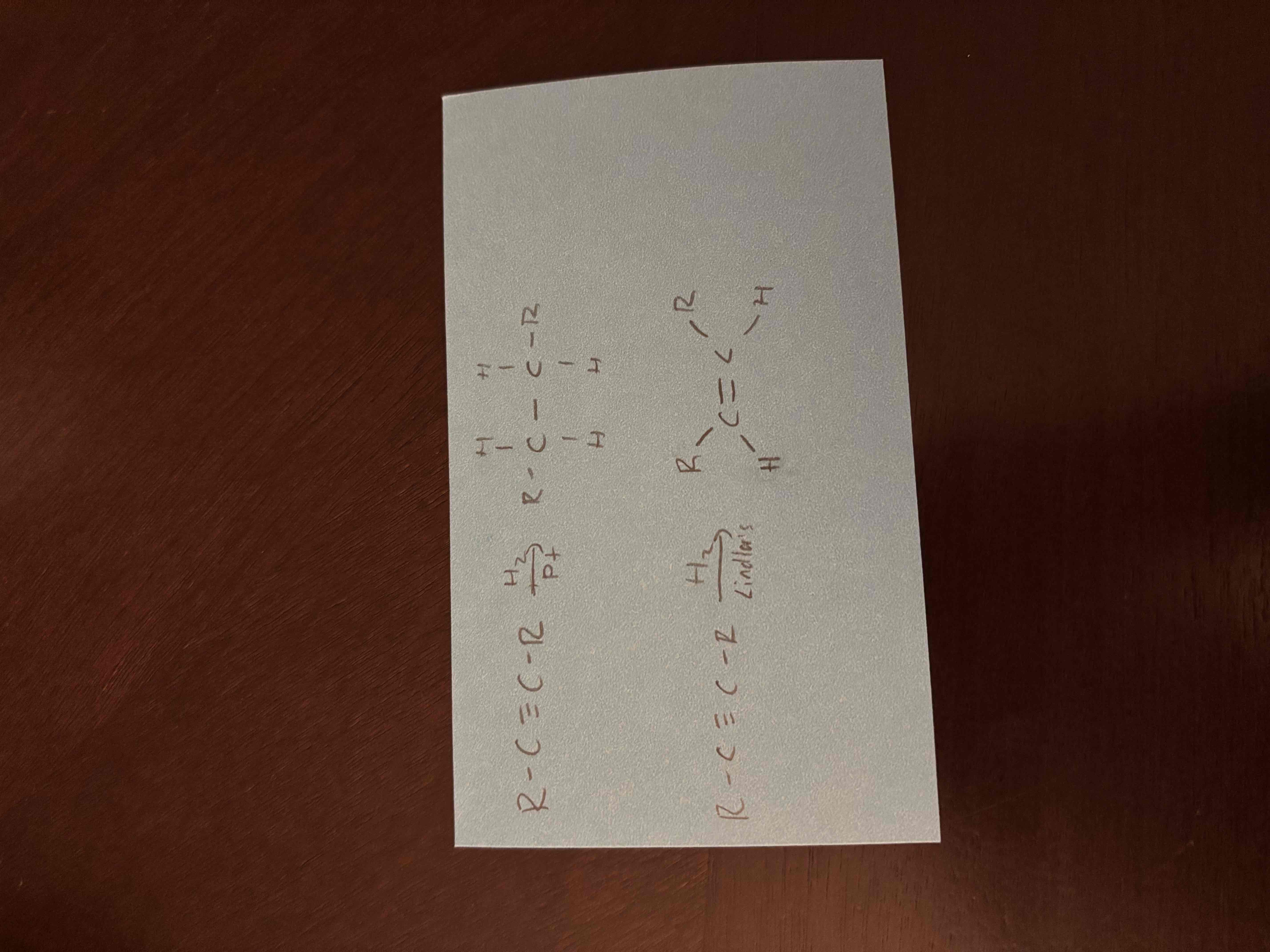
Ni/Pt vs Lindlar’s catalyst
both catalysts for hydrogenation of alkynes
Ni/Pt - produces alkane (complete hydrogenation)
Lindlar’s constant - produces alkene (partial hydrogenation)

hydrohalogenation of alkynes
electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides (hx)
markovnikov addition (x adds to more substituted carbon)
hydrohalogenation of unsymmetrical alkynes leads to isomers

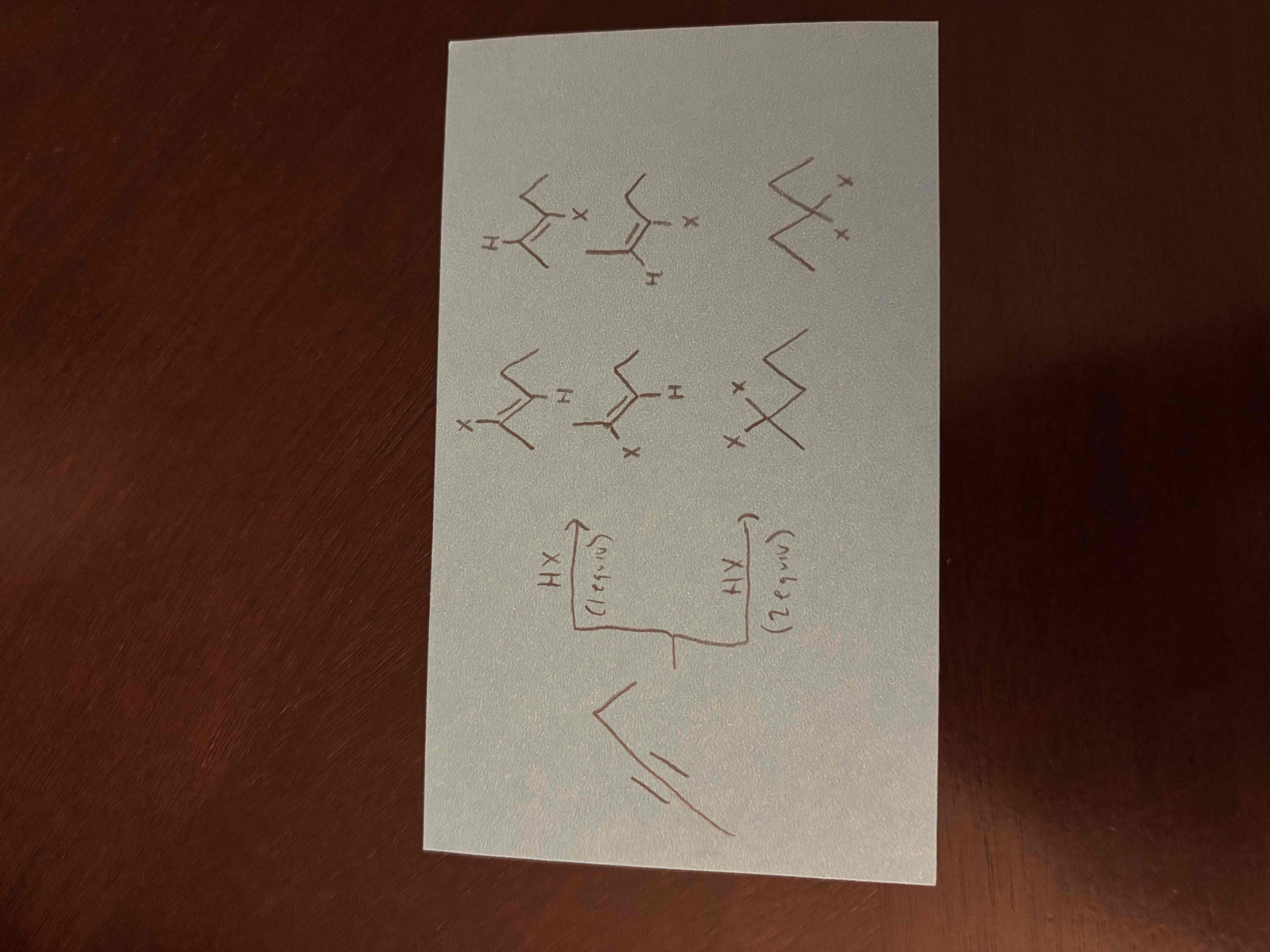
hydration of alkynes


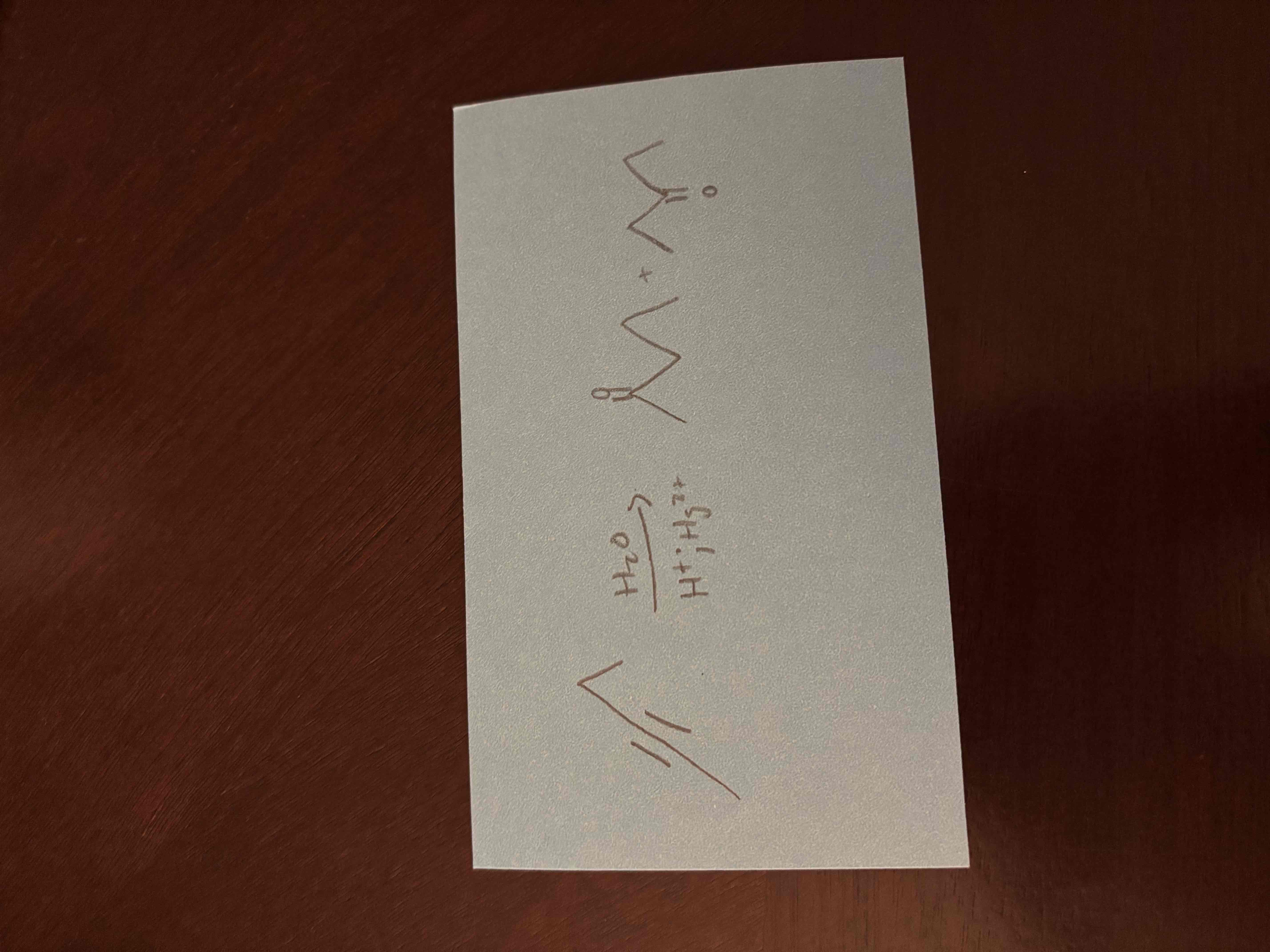


hydroboration-oxidation of alkynes


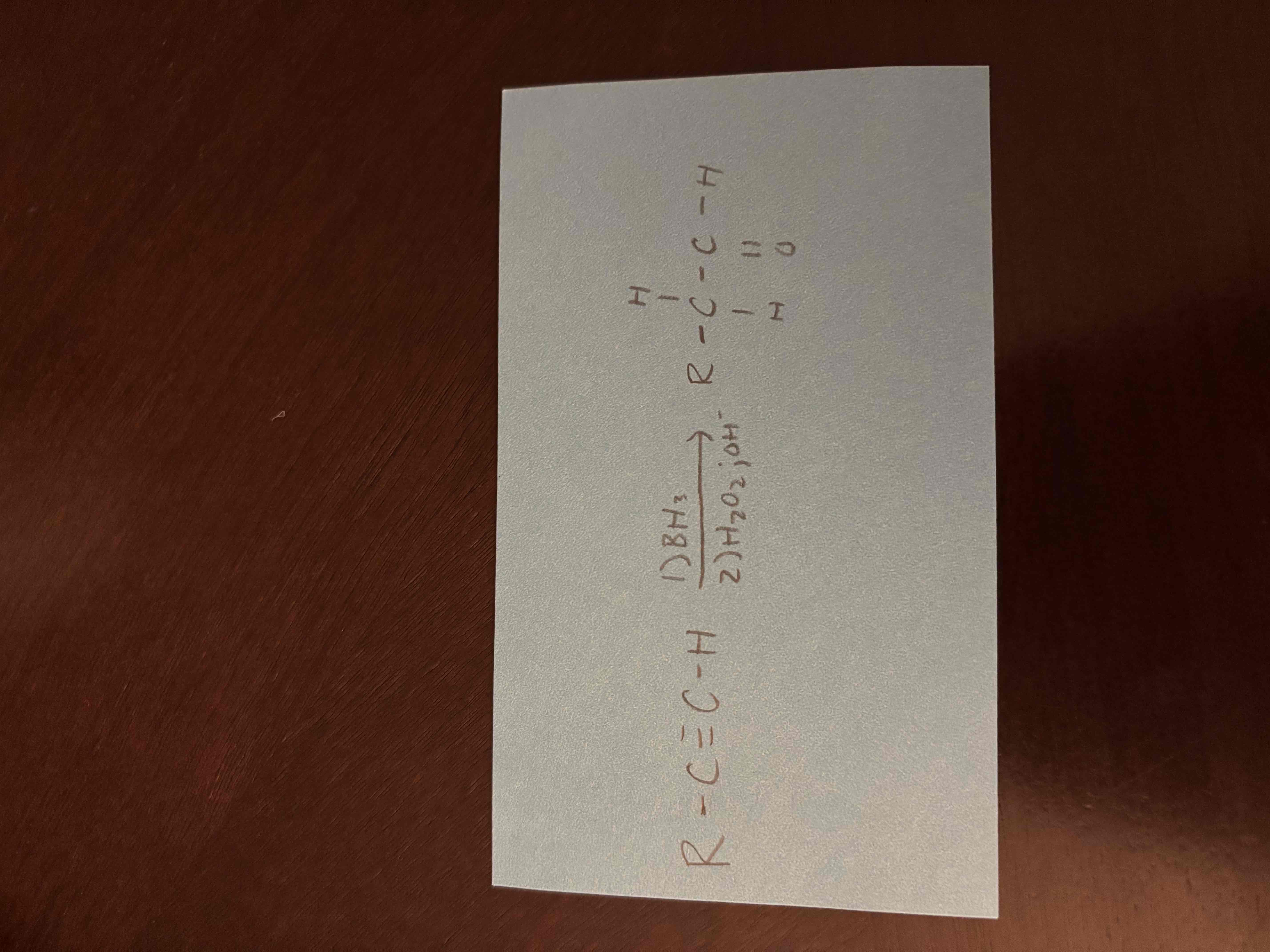
difference between hydration and hydroboration oxidation of alkynes
hydration forms markovnikov product (double bond to oxygen on the more substituted carbon)
hydroboration oxidation forms anti-markovnikov product (double bond to oxygen on the less substituted carbon)
carboxylic acid
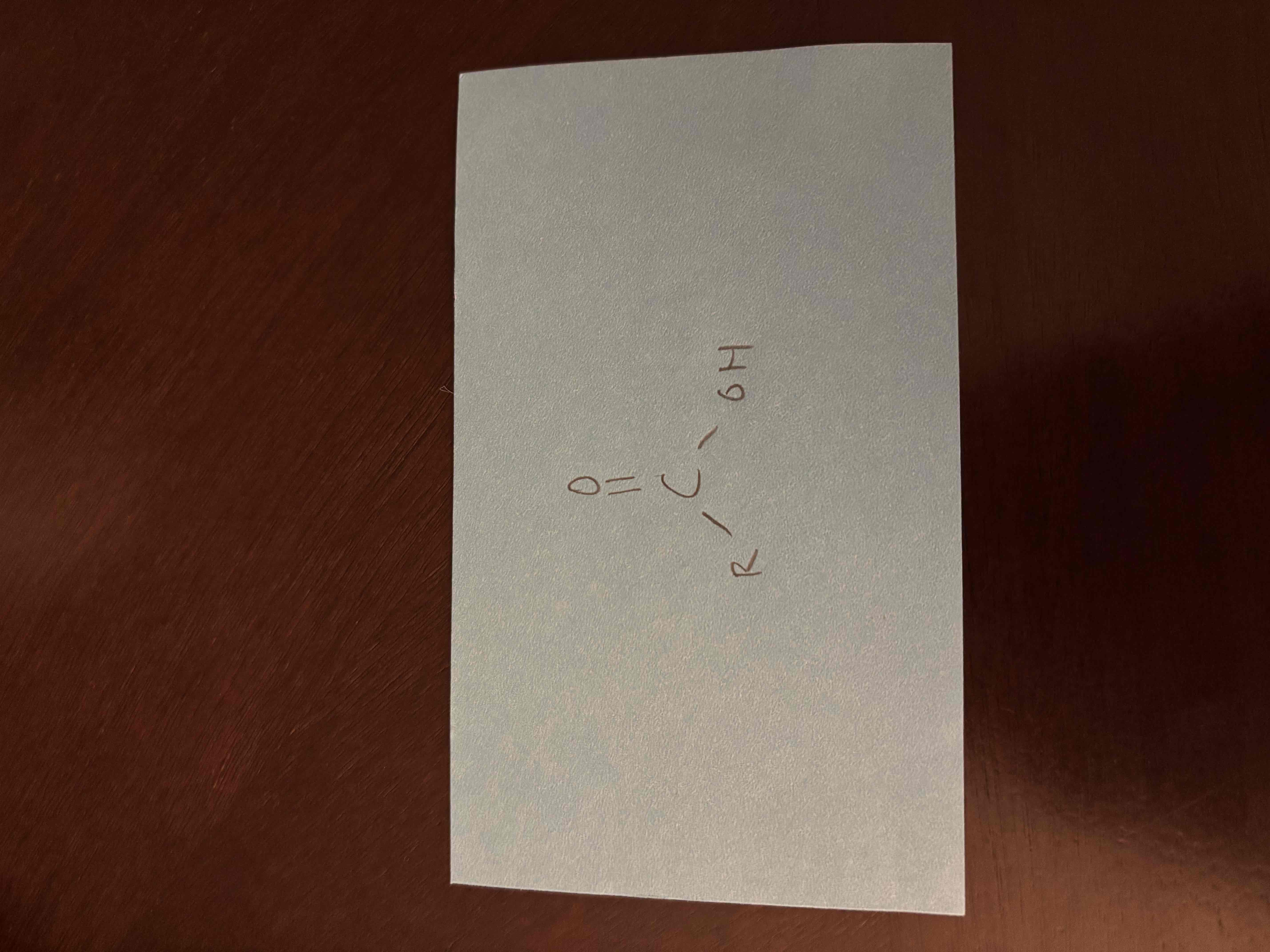
glycol
a type of alcohol where 2 hydroxyl groups are on adjacent carbons
aldehyde

ketone
