IMAG1131 - chapter 1a ppt
1/253
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
254 Terms
Organisms are made up of….
systems
Systems are made up of….
organs
Organs are made up of….
tissues
Tissues are made up of….
cells
Cells are made up of….
molecules
Molecules are made up of….
atoms
four tissue types
epithelial
connective
muscular
nervous
a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity
epithelial tissue
example of epithelial tissue
epidermis
support tissues that bind together and support structures
connective tissue
example of connective tissue
bones, tendons
tissue that provides movement
muscular tissue
types of muscular tissue
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
tissues that provide communication and control of body functions via signal conduction
nervous tissue
10 anatomical systems
circulatory
digestive
respiratory
integumentary
urinary
reproductive
nervous
muscular
endocrine
skeletal
bodily system that distributes oxygen to cells & transports waste products from cells
circulatory system
bodily system involved with absorption of nutrients & elimination of waste
digestive system
bodily system that supplies oxygen & eliminates carbon dioxide
respiratory system
anatomical system that eliminates carbon dioxide
respiratory system
system that transports waste products from cells
circulatory system
bodily system that protects the body & eliminates waste through perspiration
integumentary system
how does the integumentary system eliminate waste?
perspiration
which bodily system protects the body?
integumentary system
bodily system that regulates blood content & eliminates waste products
urinary system
the urinary system regulates what content?
blood content
bodily system that reproduces an organism
reproductive system
bodily system that regulates bodily activities
muscular system
bodily system that allows for movement
muscular system
another word for smooth muscle
visceral
this bodily system is made up of ductless glands
endocrine system
bodily system that regulates body activities via hormones
endocrine system
bodily system consisting of BONES
skeletal system
how many bones does an adult have?
206
number of bones in axial skeleton
80
number of bones in appendicular skeleton
126
what two skeletons make up the skeletal system?
axial & appendicular
skeleton consisting of the central axis of the body
axial skeleton
bones included in axial skeleton
skull, vertebral column, ribs, sternum
bones included in appendicular skeleton
limbs, shoulder and pelvic girdles
which skeleton includes the ribs?
axial skeleton
which skeleton includes the pelvic girdle?
appendicular skeleton
study of bones
osteology
study of joints
arthrology
4 categories of bones
long
short
flat
irregular
limbs are what type of bone?
long
bones longer than wide
long
category of bones with peculiar shapes
irregular
examples of irregular bones
vertebrae, facial bones, pelvic bones
the facial bones are examples of what classification of bone?
irregular
primary ossification center of long bones
diaphysis
widening of body adjacent to epiphyseal plate; site of bone growth in length
metaphysis
Secondary ossification center at ends of long bone
epiphysis
layer of cartilage between diaphysis and epiphysis
epiphyseal plate
“body” of long bones
diaphysis
generally freely movable or diarthrodial joints
synovial
7 types of synovial joints
gliding
hinge
pivot
condyloid
saddle
ball & socket
hinge
another term for gliding joint
plane joint
another term for pivot joint
trochoid
another term for condyloid joint
ellipsoid
another term for saddle joint
sellar
another term for ball & socket joint
spheroidal
2 types of hinge joints
ginglymus & bicondylar
intercarpal, intermetacarpal, and carpometacarpal joint types
plane (gliding)
elbow joint & interphalangeal joints type
ginglymus (hinge)
TMJ & knee joint types
bincondylar (hinge)
proximal & distal radioulnar joint type
trochoid (pivot)
c1-2 joint type
trochoid (pivot)
wrist joint type
ellipsoid (condyloid)
metacarpophalangeal joints (1st to 5th) joint type
ellipsoid (condyloid)
1st carpometacarpal joint (thumb) joint type
sellar (saddle)
hip joint type
spheroidal (ball & socket)
shoulder joint type
spheroidal (ball & socket)
Which of the following joints is classified as trichoidal or pivot?
a. wrist joint
b. proximal radioulnar
c. metacarpophalangeal
d. shoulder
proximal radioulnar
Which of the following joints is classified as ellipsoidal or condyloid?
a. wrist
b. ankle
c. interphalangeal
d. hip
interphalangeal
Which of the following joints is classified as bicondylar (hinge)?
a. metacarpophalangeal
b. first carpometacarpal joint
c. proximal radioulnar joint
d. knee
knee
Describes the body part as seen by the image receptor or other recording medium, such as a fluoroscopic screen
radiographic view
Refers to a specific body position, such as supine, prone, recumbent, erect or Trendelenburg
radiographic position
Restricted to the discussion of the patient’s physical position
radiographic position
Restricted to the discussion of a radiograph or image
radiographic view
Restricted to the discussion of the path of the central ray
radiographic position
lying on the back
supine
lying face downward
prone
lying down in any position
recumbent
decubitus
lying down with a horizontal beam (named for side down)
upright
erect
facing the image receptor
PA projection
facing the radiographic tube
AP projection
body facing away from the image receptor
AP projection
body facing away from the radiographic tube
PA projection
in anterior oblique (torso) positions, the body is facing what?
image receptor
body rotated with the left anterior portion closest to the image receptor
left anterior oblique
body rotated with the right anterior portion closest to the image receptor
right anterior oblique
RAO
right anterior oblique
LAO
left anterior oblique
with posterior oblique positions (torso), the body is facing what?
radiographic tube
body rotated with left posterior portion closest to the image receptor
left posterior oblique
body rotated with right posterior portion closest to the image receptor
right posterior oblique
RPO
right posterior oblique
LPO
left posterior oblique
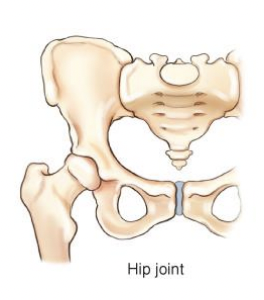
joint type
spheroidal (ball and socket)