Hierachy of Organization and Tissue Types
1/14
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Specialized Cells
Cells that perform a specific function. They have structures that allow them to perform their specific function.
Tissues
Groups of specialized cells
Epithelial Tissue
Tightly packed cells that line the surfaces of the body.
Types:
Exterior (skin epithelia)
Interior (columor epithelia)
Lining of stomach, intestine, mouth, lungs, etc
Connective tissue
Tissues that build support structures for organs. They often form external matrixes of collagen fibres.
Types
Bone
Cartilage, Tendons, Ligaments
Fat
Blood
Muscle Tissue
Long fibrous tissue that can contract and provide movement. They are attached to bones and surrounds the digestive tract, blood vessels, and forms the heart.
Types:
Skeletal
Smooth
Cardiac
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that allows for the respone to internal and external stimuli. It forms the brain and nerves, and connects to the sensory receptors and muscles.
Epithelial (skin) cells
Tightly packed - Protects against foreign invaders from entering and prevents important molecules from escaping.
Layered - for protective barrier
Thin - so many layers can form since these cells wear away easily
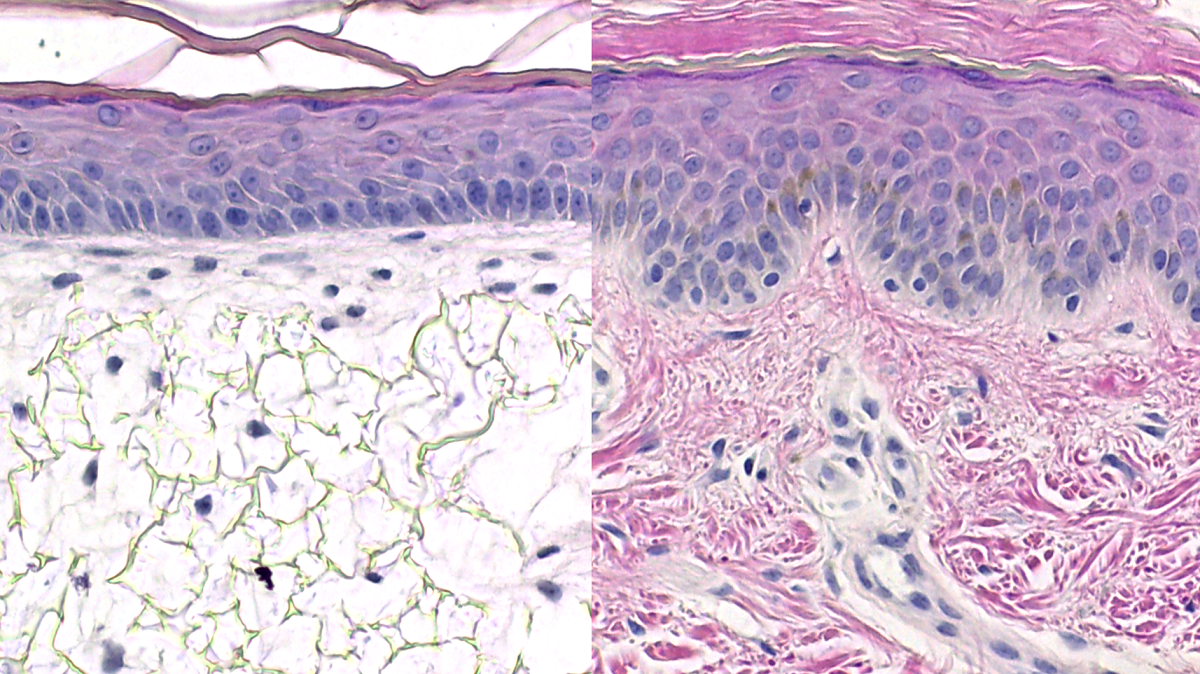
Inner epithelial cells
Cilia (respiratory) - Sweeps out toxins/dirt out of trachea
Golgi-rich - To secrete mucous to help the digestive and respiratory system
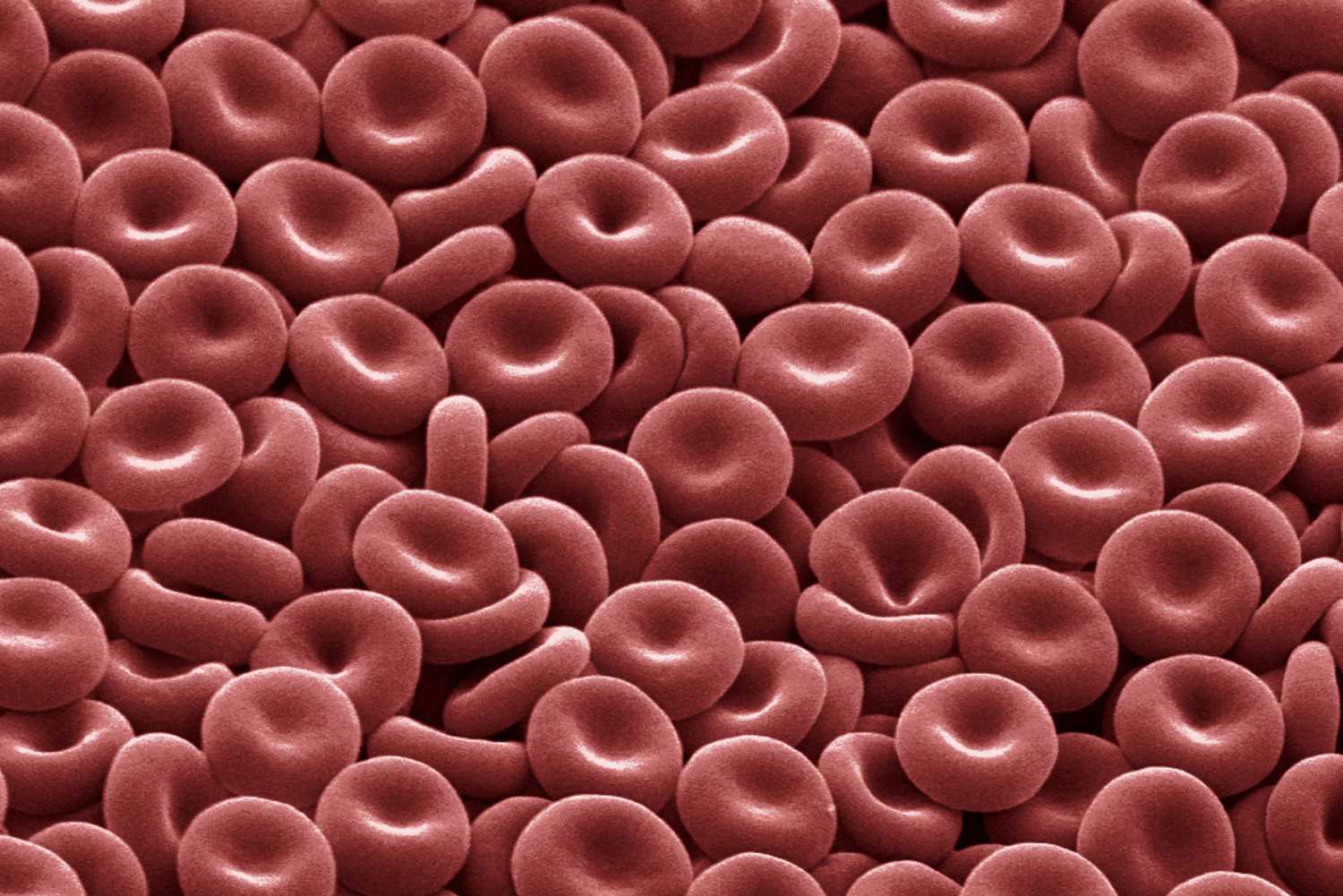
Red blood cells
Cells that contain hemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood.
Smooth - easily passes through vessels
Concave shape - to increase surface area so more oxygen can be transported
No nucleus or membranes - to maximize space for oxygen; thinning of the cell
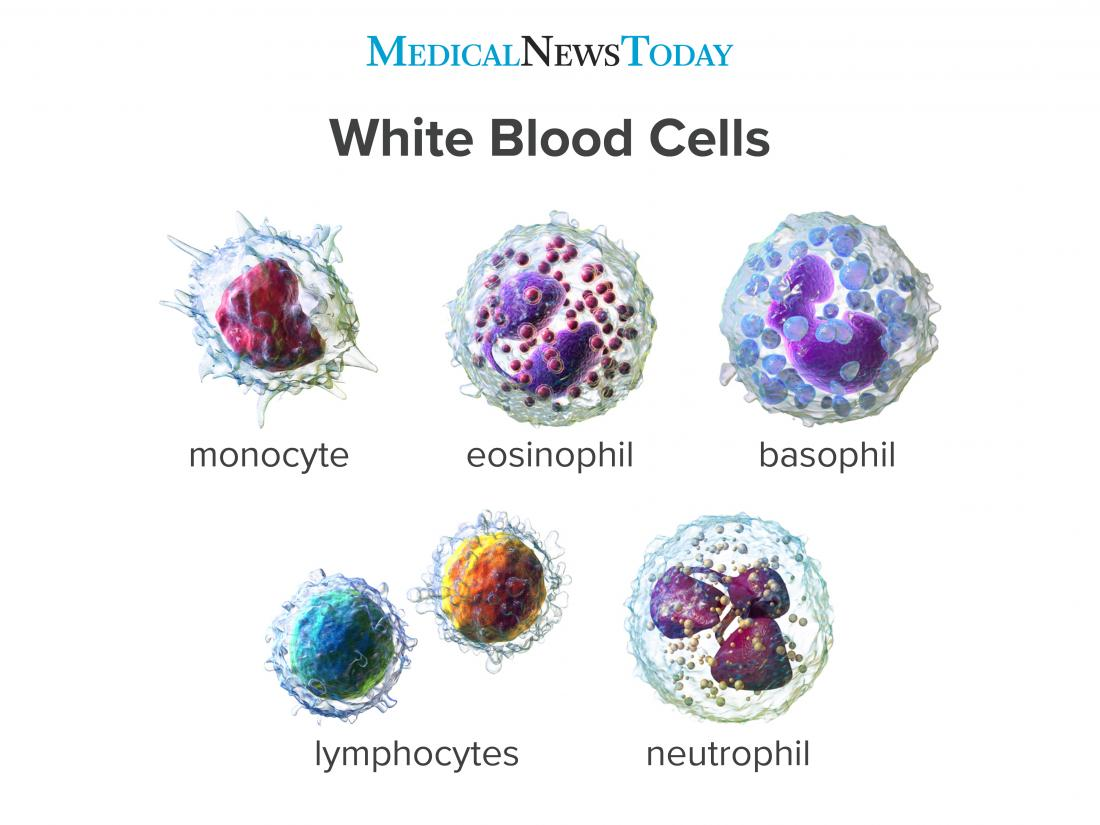
White blood cells
Cells that are able to engulf/swallow invading bacteria to fight infection by digesting them with enzymes. They can destroy damaged old cells in the body.
Flexible cell membrane - to consume invaders
Ribosome rich - To form proteins to attack invaders
Lysosome rich - to break down substances absorbed
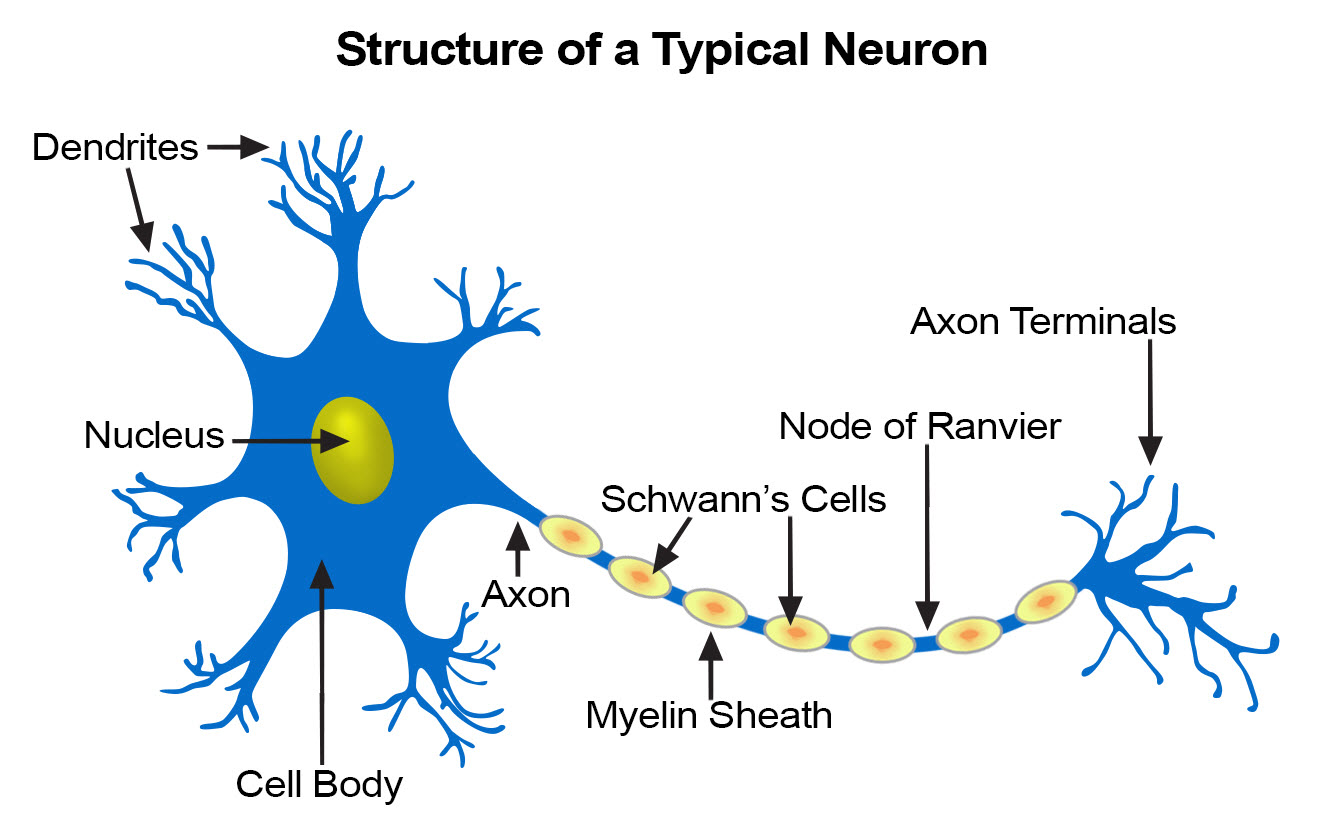
Nerve cells
Cells that conduct electrical impulses to coordinate body activities.
Long body (axon) - to rapidly carry nerve impulses to the brain
Dendrites - allows for communication between cells
Mitochondria rich - to fuel the rapid impulses
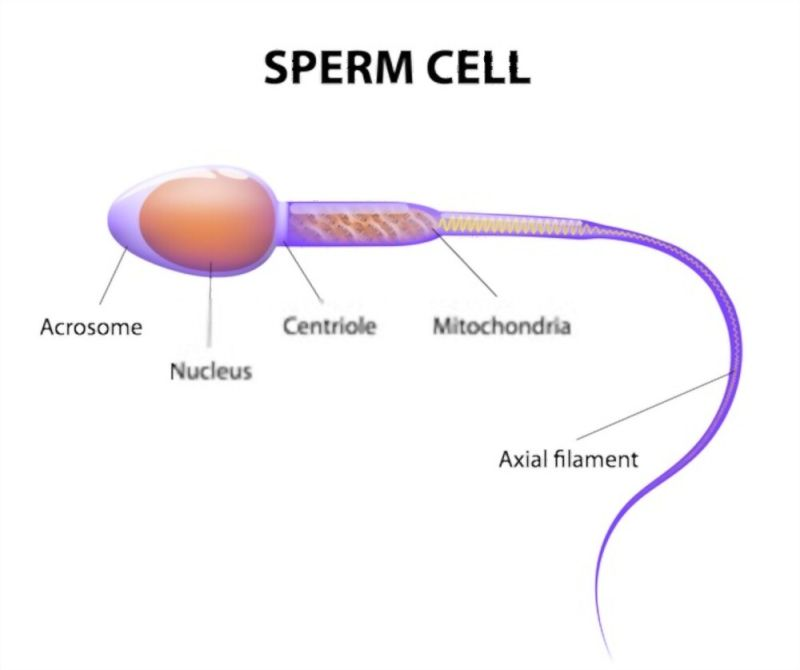
Sperm cells
Cells that carry DNA of the male parent to join with DNA of the female parent
Head - pointed to pierce egg wall
Cap on head (acrosome) - contains digestive material to break down egg membrane
Mitochondria rich tail - to fuel propulsion of tail
Tail - long and thin to propel forward
Small - so more of them can be produced
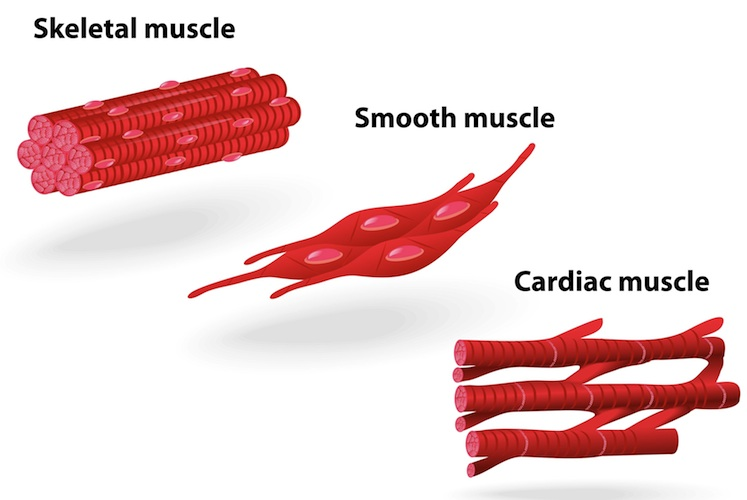
Muscle cells
Three types:
Skeletal (connects to bones and joints)
Cardiac (heart)
Visceral/smooth (inside blood vessels and internal organs)
Produces movement and maintains posture due to muscles contracting and relaxing.
They form long fibres that have a striped/striated appearance
Fat cells
Cells that store extra materials from food that can be turned into energy later.
Provides insulation
Surrounds vital organs and tissues
Fills sharp angles between bones and muscle
Goblet cells
Column shaped cells that secrete mucus. They are found in intestinal and respiratory tracks.