Chapter 31 - regulation of transcription and chromatin structure
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the basic chemical properties of membrane lipids?
- amphipathic
- hydrophobic tail
- hydrophilic head
Translation
RNA -> protein
protein
the primary functional products of gene expression
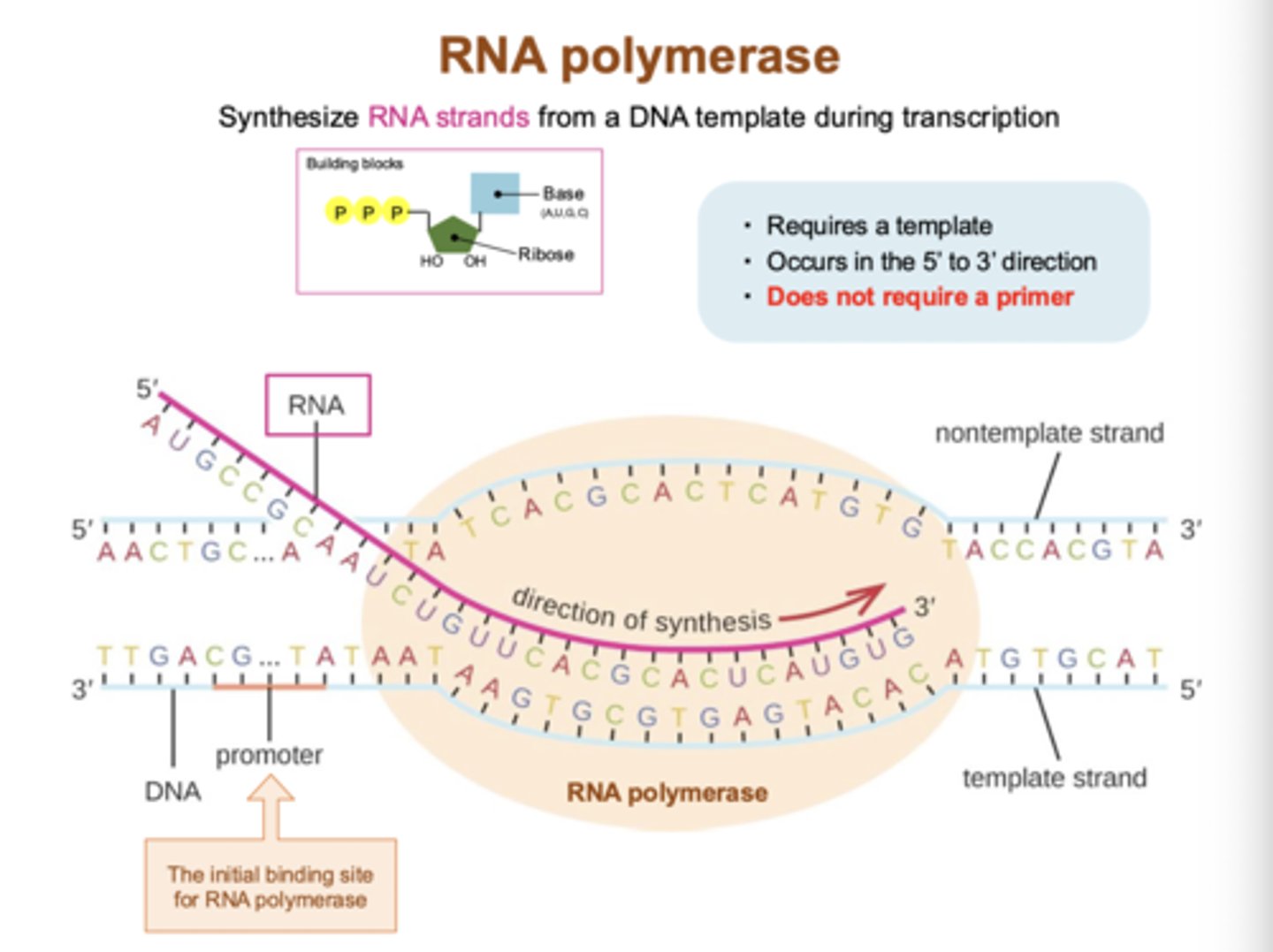
What are the key properties of RNA polymerase? What role does the promoter play in transcription?
enzyme that converts lactose to galactose and glucose?
β-galactosidase
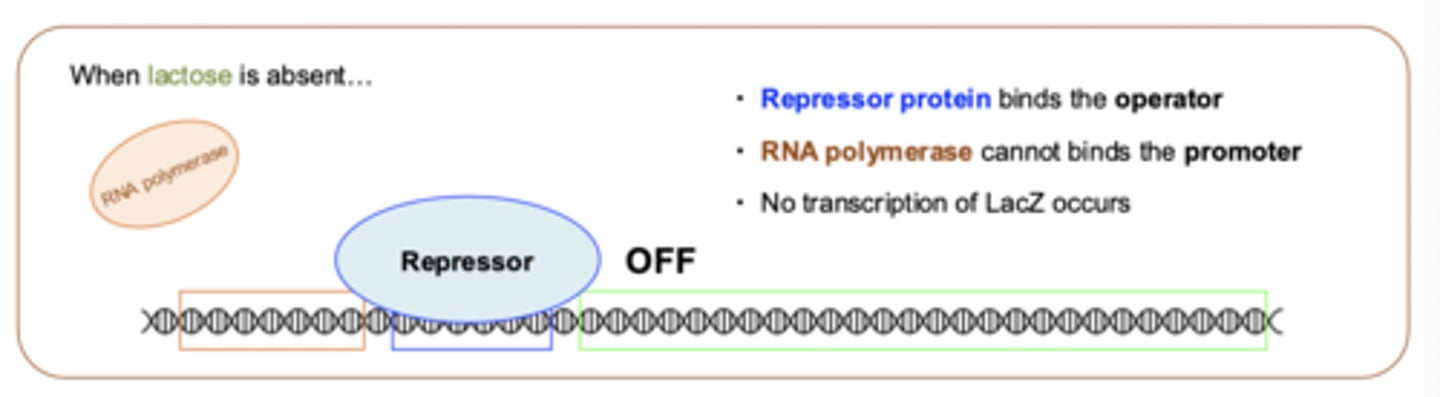
Lac operon when lactose is absent?
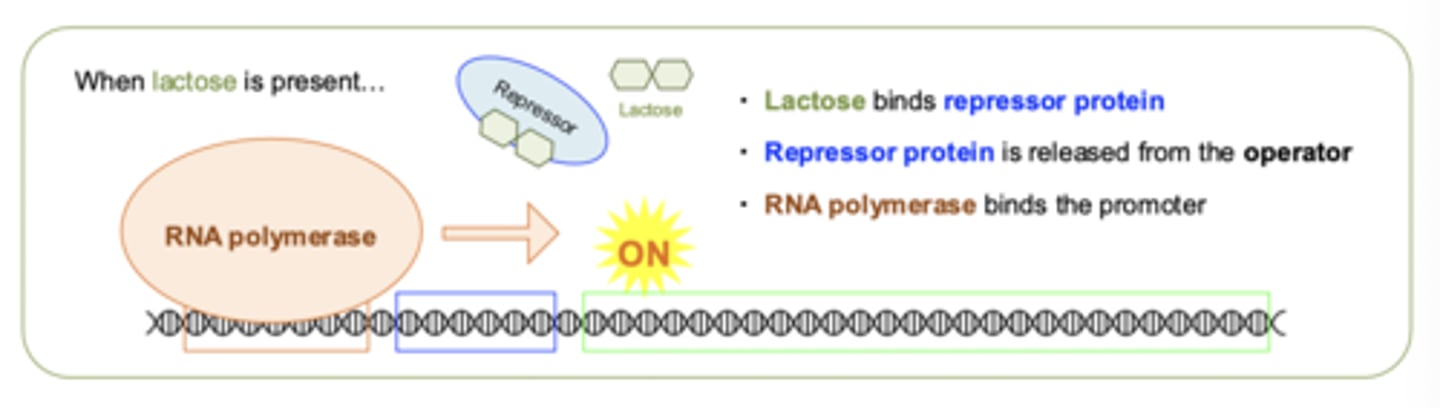
Lac operon when lactose is present?
What does lac Z code for?
B-galactosidase enzyme (which breaks down lactose into galactose and glucose)
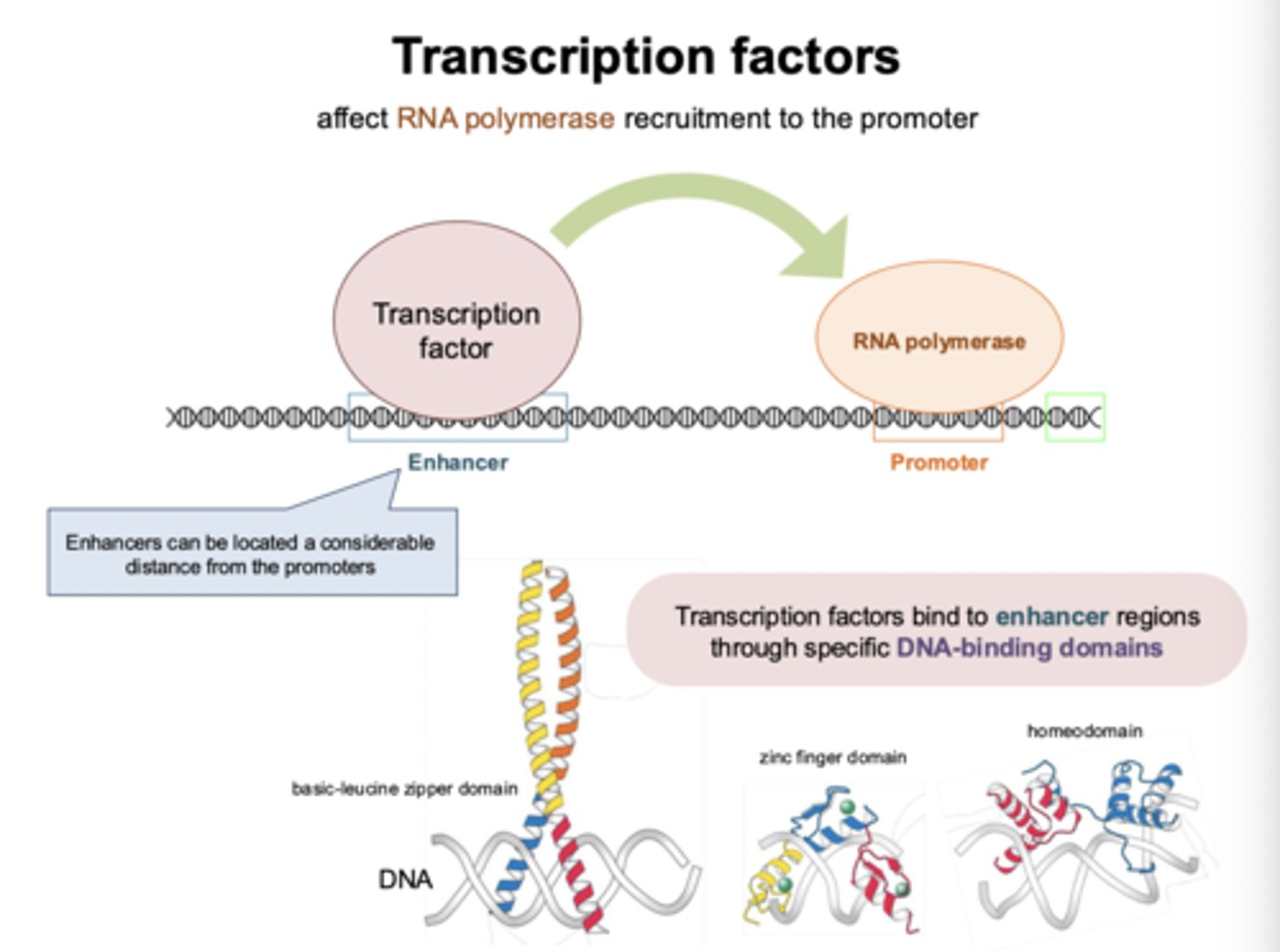
What are the key features of transcription factors?
TFs affect RNA polymerase recruitment to the promoter by binding to enhancer regions through specific DNA-binding domains
- ex: repressors and activators
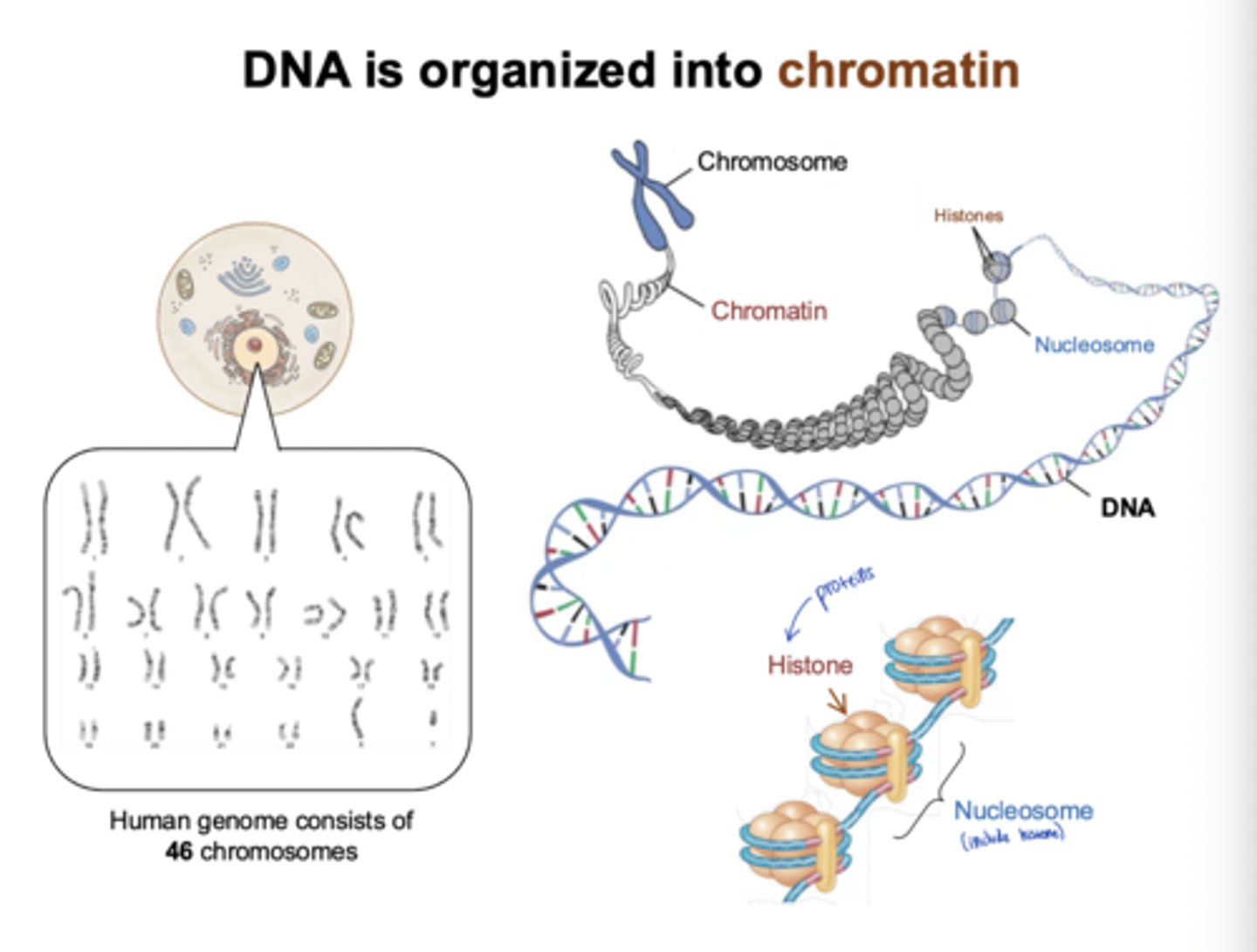
How is DNA organized into chromatin, and what is the role of histone proteins?
DNA wraps around histone proteins to form nucleosomes
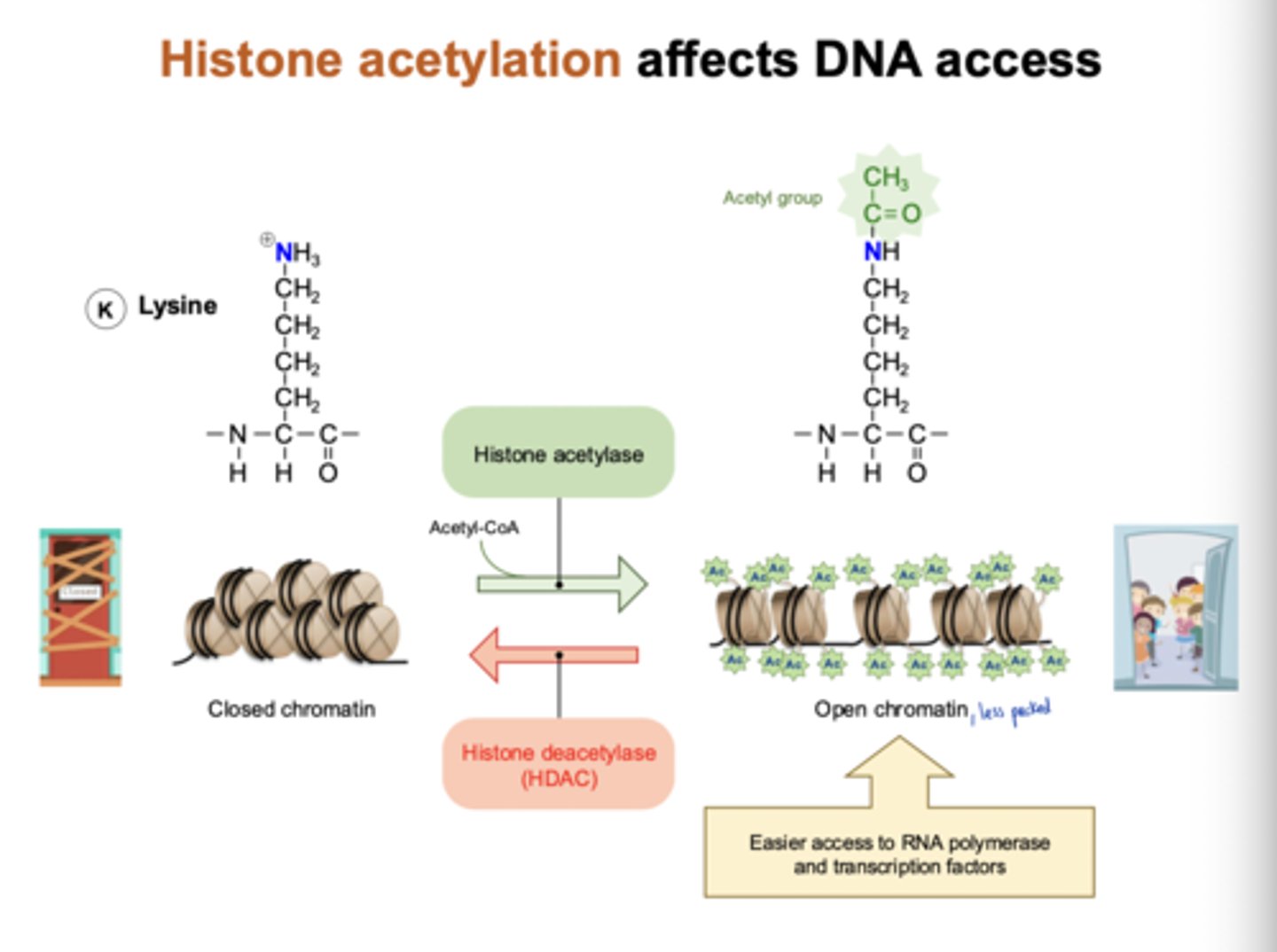
How does acetylation of histone generally affect gene transcription?
histone acetylation opens chromatin
- open chromatin is easier to access by RNA pol and TFs
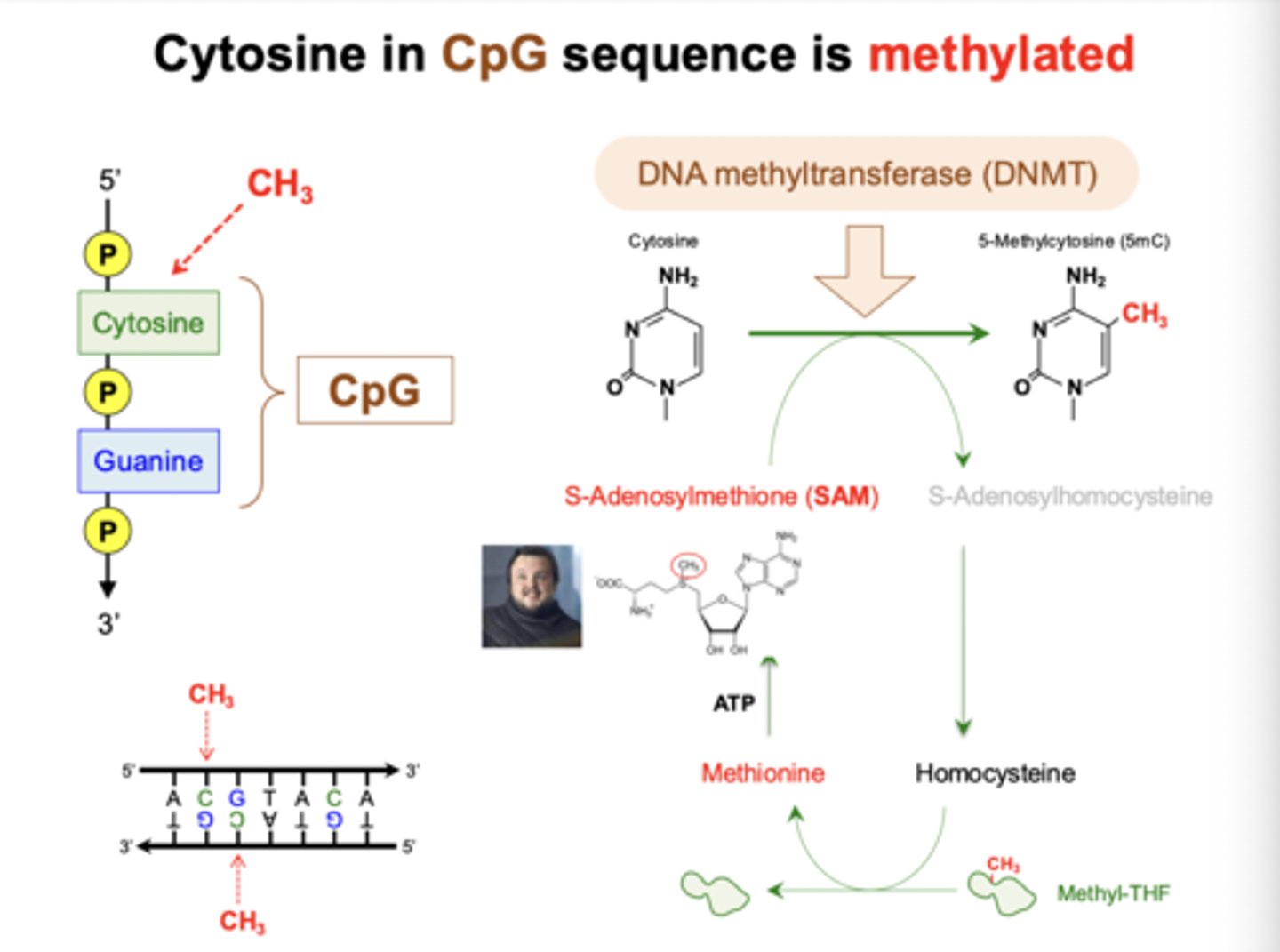
What are the key properties of DNA methylation, and which enzymes control the methylation status of DNA?
- DNMT enzyme adds methyl group
- does not disturb G-C pairing
- affects DNA-protein interactions
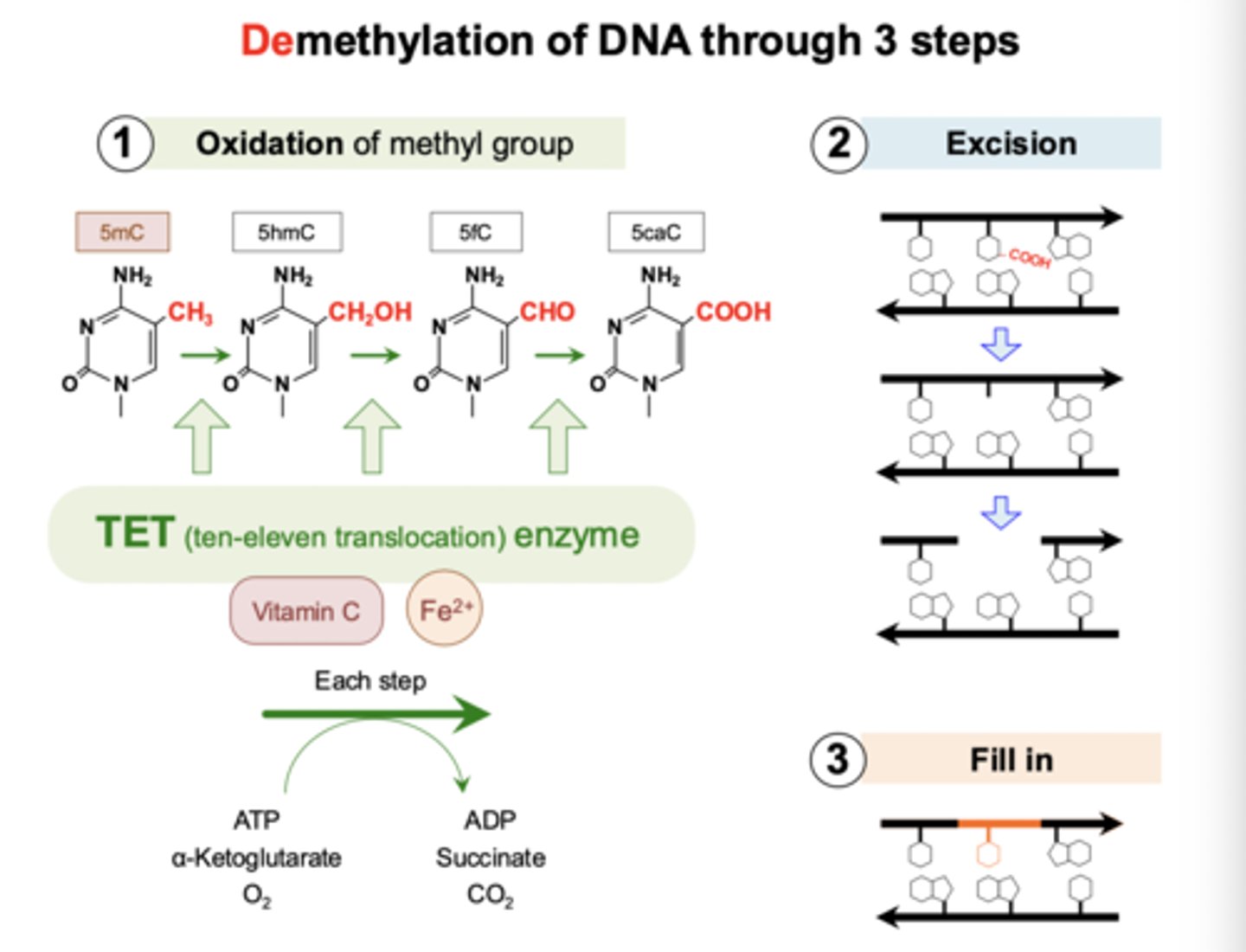
What enzyme is used for DNA demethylation
TET
What generally happens to methylated DNA?
Methylated DNA (gene) is generally inactivate (transcription is repressed)
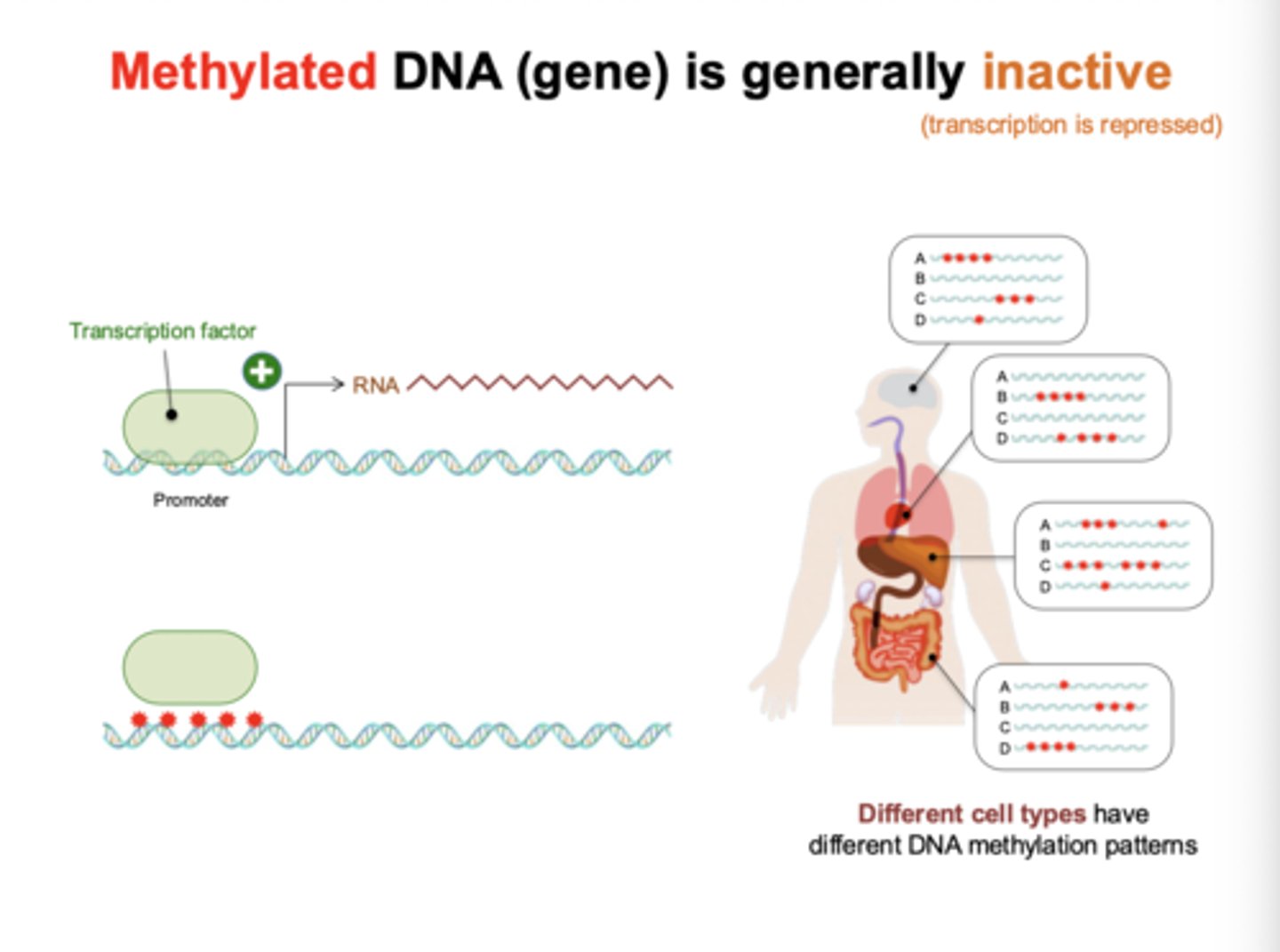
genes general idea
different genes are expressed in different tissues
what % of cells contain identical DNA sequences
more than 99%
What is the initial binding site of RNA polymerase
the promoter
Where can enhancers be located?
enhancers can be located a considerable distance from the promoter
What do TFs bind to?
enhancer region
How many chromosomes does the human genome consist of?
46 chromosomes
chemical modification of histone proteins influence ______ and ______
chromatin structure and gene expression
Name of methylated cytosine
- cofactor used
cytosine -> 5-methycytosine
- uses SAM to add methyl group
CpG sequence and methylation
- CpG sequence: cytosine preceding guanine in DNA
- cytosine in CpG sequence is often methylated
unique quality of DNA methylation
DNA methylated can be inherited
- DNMT1 maintains DNA methylation patterns