MCAT General Chemistry
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Formal Charge Equation
Valence electron - 0.5 bonding electrons (sticks) - free electrons (dots)
Molecular Geometry: 2 groups represent what
sp - Linear
Molecular Geometry: 3 groups represent what
sp2 - Trigonal planar
Molecular Geometry: 4 groups represent what
sp3 - Tetrahedral
What are the INTRAmolecular forces
Ionic bonds, Covalent bonds, Metallic Bond, Coordinate Covalent Bond
INTRAmolecular forces: The longer the distance between atoms and less electrons shared
The weaker the bond
Breaking a bond is what kind if process?
Endothermic
Ionic Bond
Bond between particles of opposite charges. Transfer of Electrons
Ionic bonds in aqueous solutions
Will separate; electrolytes
Covalent Bond
Formed between atoms of opposite charge with high electronegativity. Share electrons
Metallic Bond
Bond between metals. Atoms with low electronegativity
Coordinate Covalent Bond
Donate both electrons to bond
What are the INTERmolecular forces?
Ion-Dipole force, Dipole-Dipole, Dispersion Forces and Hydrogen Bonding
INTERmolecular forces: The larger the charge
The stronger the bond
INTERmolecular forces: The smaller the charge
The weaker the bond
Ion-Dipole force
Ion bonds with polar molecule. Molecule will orient to the opposite charge to bond
The larger the ionic charge & dipole
The larger the force
Dipole - Dipole
Bond between two polar molecule
The more polar the molecule in dipole - dipole
The stronger the force generated
Dipole Induced Dipole
Bond between a polar and non-polar molecule
London Dispersion
Bond between any and all molecules
Hydrogen Bonding
Bonding with very polar molecules. Nitrogen, Oxygen or Fluorine
Enthalpy
Energy stored
Forming a bond is what kind if process?
Exothermic
Reactants being higher than products in regards to enthalpy is what?
Exothermic
Reactants being lower than products in regards to enthalpy is what?
Endothermic
Entropy
Potential randomness
How can you alter randomness?
Increasing volume, Increasing temperature, increasing the amount
Gibbs Free Energy
Measure of if there is enough energy available to do work in chemical process
In Gibbs Free Energy: Reactants higher than products is what?
Spontaneous, Exergonic
Delta G is what in a spontaneous, exergonic process?
Negative
Delta G is what in a non-spontaneous, endergonic process?
Positive
In Gibbs Free Energy: Reactants lower than products is what?
Non-spontaneous, Endergonic
Gibbs Free Energy Equation
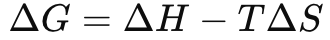
The stronger the IMF
The stronger the phase of matter
Phases of matter from High to Low IMF
Solids > Liquids > Gases > Ideal Gases
Gas to liquid is
Condensation
Liquid to Solid is
Freezing
Solid to Liquid is
Melting
Liquid to Gas is
Boiling (Vapor)
Solid to Gas is
Sublimation
Gas to Solid is
Deposition
When Heat is absorbed
Kinetic Energy and Entropy increases
When Heat is released
Kinetic Energy and Entropy decreases
Heat of Fusion Equation
q = n * delta H
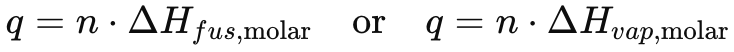
Specific Heat Equation
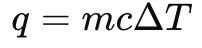
IMF are __ proportional to Volume
Indirectly
IMF are __ proportional to Pressure
Indirectly
External Pressure and IMF are __ proportional to Density
Directly
External Temperature is ___ proportional to Density
Indirectly
External Temperature is ___ proportional to Vapor Pressure
Directly
IMF is __ to Vapor Pressure
Indirectly
What effect does external pressure have on Vapor Pressue?
No effect
External Pressure and IMF are __ proportional to boiling point
Directly
External Pressure and IMF are __ proportional to melting/freezing point
Directly
Solution
Homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances
In terms of solute: A strong electrolyte
Breaks apart completely
In terms of solute: A weak electrolyte
Breaks apart “sort of”
In terms of solute: A non-electrolyte
Doesn’t break at all
Van’t Hoff Factor (i)
The number of particles electrolytes break into.
Solubility
Amount of something that can dissolve at certain temperatures
Unsaturated
Concentration of Solute is less than solvent
Saturated
Concentration of Solute is equal to solvent
Supersaturated
Concentration of Solute is greater than solvent
Solid & Liquid solubility is directly proportional to
Temperature
Gaseous solubility is directly proportional to __, and indirectly proportional to
Temperature, Pressure
Boyles Law
Pressure is inversely proportional to Volume V α 1/P
Charles Law
Temperature is directly proportional to volume V α T
Amonton’s Law
Temperature is directly proportional to Pressure P α T
Combined Gas Law
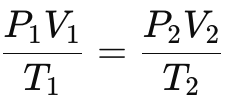
Ideal Gas Law
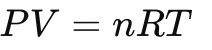
Mole Fraction
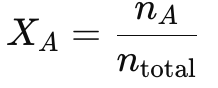
Dalton’s Law
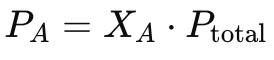
Grahm’s Law
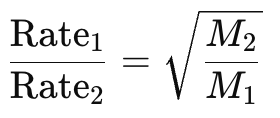
What determines Delta H & Delta G
Difference of reactant energy and product energy
What is Activation Energy (Ea)
The difference between reactant energy and highest energy transition state.
Rate determining step
Highest peak, also the slowest
Rate Law Equation
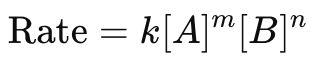
How is a reaction in equilibrium?
When the forward and reverse rates are equal
K > 1
In equilibrium products are favored
K = 1
In equilibrium neither are favored
K < 1
In equilibrium reactants are favored
What does the Reaction Quotient (Q) describe?
The distance from equilibrium
Q > K
Too much product, shifts toward reactants
Q = K
In equilibrium
Q < K
Too much reactant, shifts toward products
What is a Brønsted Acid
Donate a proton
What is a Brønsted Base
Accepts a proton
What is a Lewis Acid
Accepts electron pairs, acts as an electrophile
What is a Lewis Base
Donates electron pairs, acts as an nucleophile. Are ligands and chelates
What are some characteristics of acids?
They usually have a more electronegative atom bonded to H. They can have large positive charge.
What are some characteristics of a base?
They usually have less electronegative atoms with lone pairs.
What is an Amphoteric Compound?
Compound with both characteristics of acids and bases
General rules for identifying an acid?
More positive charge, High in electronegativity, large atomic size
General rules for identifying a base?
More negative charge, low electronegativity, small atomic size
What are the strong acids?
H2SO4, HClO4, HClO3, HNO3, HCl, HBr, HI
What are the strong bases?
O2- , OH-, OR- , NH2- ,NR2-, H- ,R-
Characteristics of Strong Acids
Dissociate completely, Ka > 1, produces weak conjugate base. Products are favored in equilibrium
Characteristics of Weak Acids
Dissociate partially, Ka < 1, equilibrium favors the reactants. Produces strong conjugate bases
Characteristics of Strong Bases
Dissociate completely, Ka > 1, produces weak conjugate acids, equilibrium favors products