AP Biology Exam Review
1/330
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
331 Terms
polymer
many monomers
ionic bond
formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
dehydration synthesis
molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule
hydrolysis
breakdown of a compound by adding water
element
cant be broken down
compound
two or more elements
electronegativity
attraction of an atom for the electrons of a covalent bond
nonpolar covalent
equal sharing of electrons
polar covalent
unequal sharing of electrons
polar
part negative part positive
hydrogen bond
attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom
covalent bond
bond that shares a pair of electrons from atom to atom
cohesion
attraction between molecules of the same substance
adhesion
attraction between molecules of different substances
hydrophobic
water hating
hydrophilic
water loving
H2O polarity
H positive O negative
monomer
subunit for polymers
van der waals
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that results from changing charges
solvent
dissolving agent of a solution
solution
two or more substances
solute
dissolved by solvent
hydronium
H+
hydroxide
OH-
acid
substance that increases the H+ concentration of a solution
pH scale
high number high OH-, low number high H+
nucleotide
five carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
nucleic acid
DNA and RNA
amino acids
monomers of proteins
polypeptide
chain of amino acids
lipids
nonpolar fats and oils, store energy and build cell membrane
phospholipids
hydrophobic head, hydrophilic tail
isomer
compounds with the same formula but different structures
DNA
directions for its own replecation, stores genetic info, deoxyribose sugar, antiparallel, ATCG, double strand
RNA
messenger to create proteins, ribose sugar, AUCG, single strand
monosaccharides
monomer of carbs
dipeptide
two amino acids bonded together
peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids
levels of protein structure
primary, secondary (alpha helix, beta sheet), tertiary, quaternary
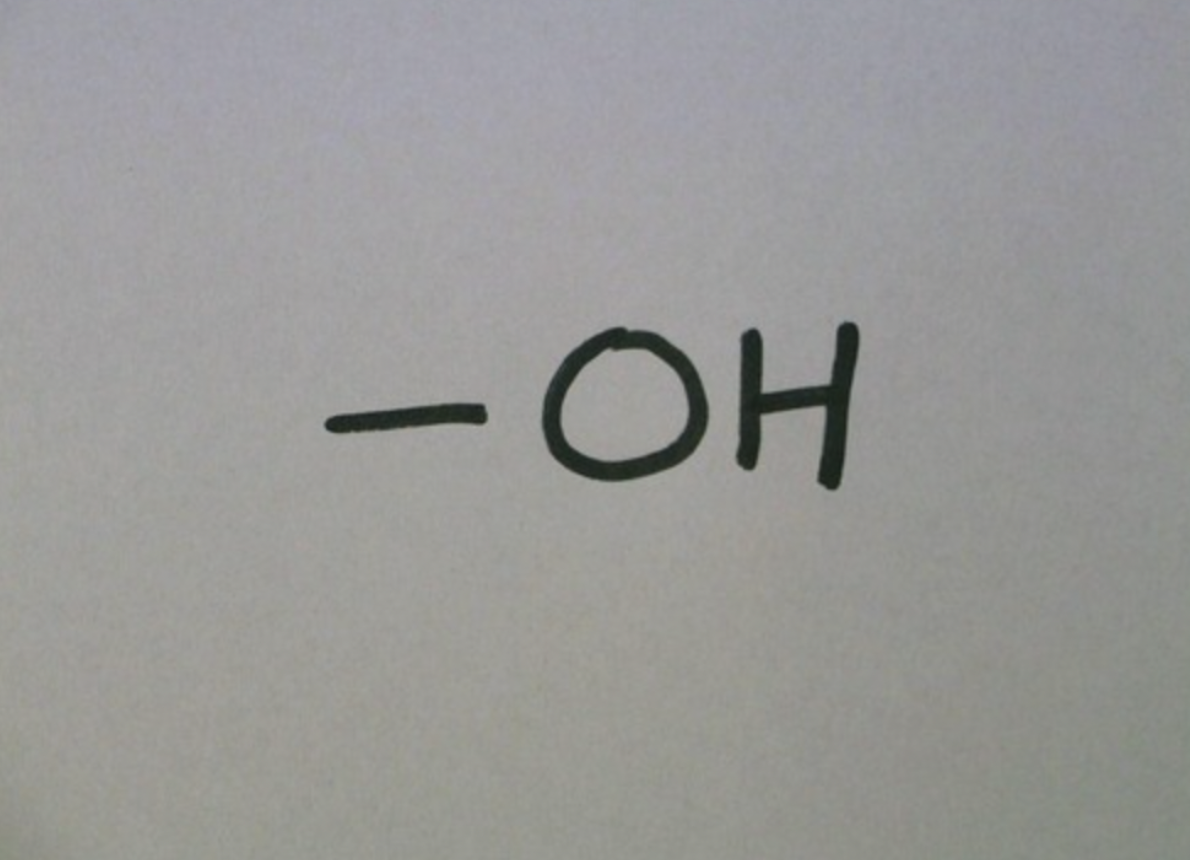
hydroxyl
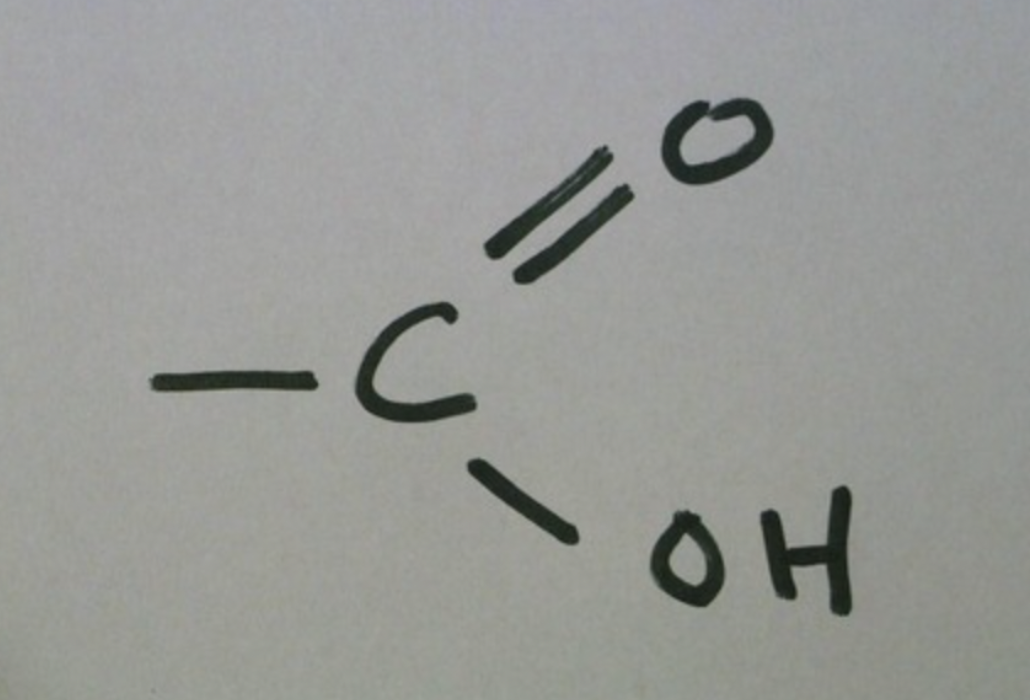
carboxyl
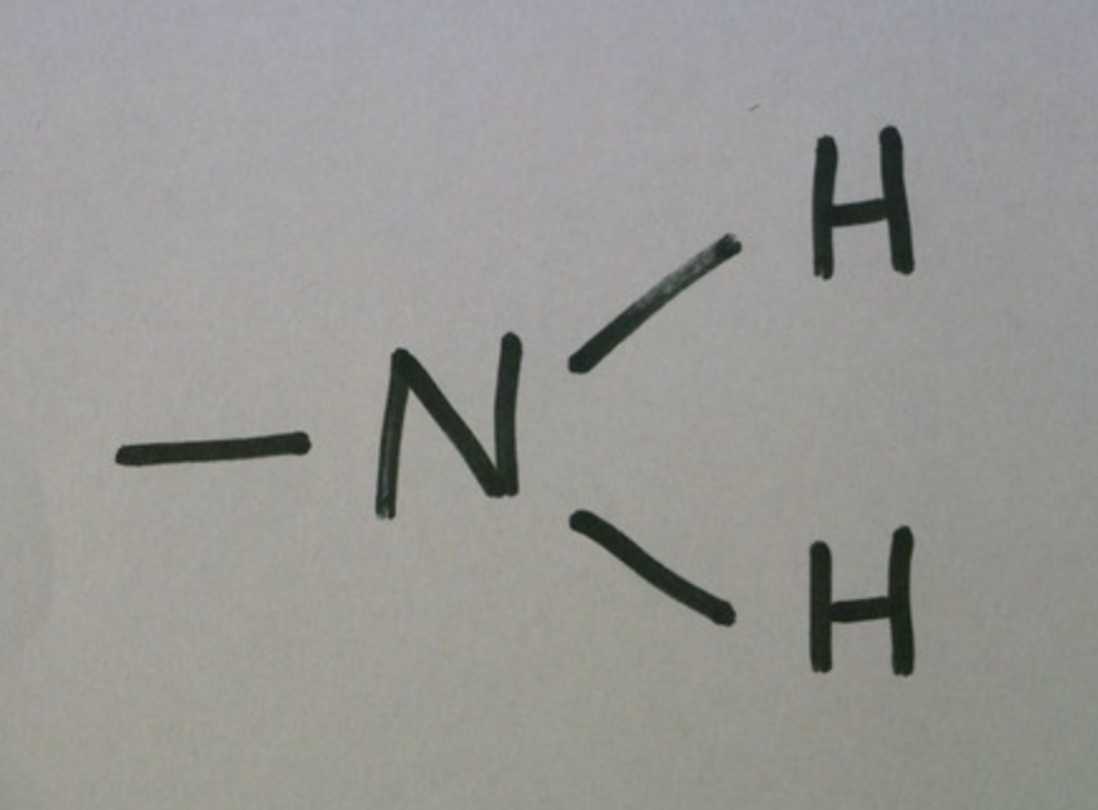
amino
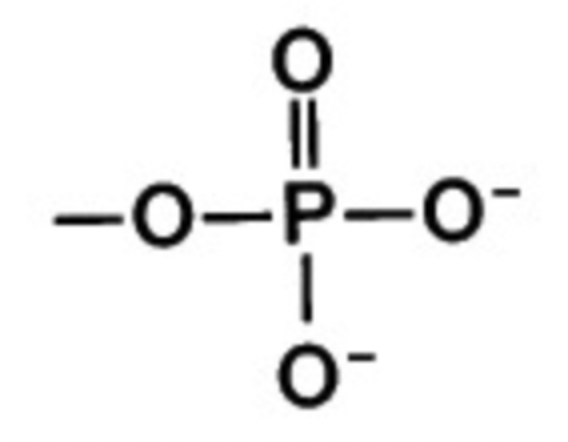
phosphate
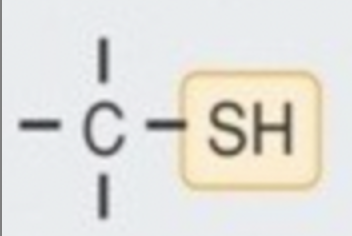
sulfhydryl
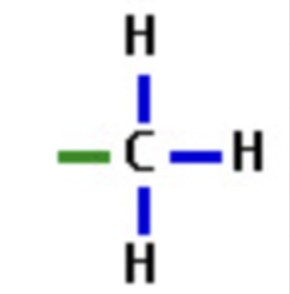
methyl
carbohydrates
energy and structure
proteins
structure, enzymes, cell communication, movement
buffer
solution that minimizes changes in pH when extraneous acids or bases are added to the solution
eukaryotes
organisms made up of one or more cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, DNA in nucleus
prokaryotes
Single celled organisms that do not contain nuclei and instead store DNA in the nucleoid, no membrane-bound organelles
plasma membrane
selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cell, "fluid mosaic" made of phospholipids, macromolecules, and proteins
cell wall
made up of carbs, surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms
cytoplasm
jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
cytosol
fluid portion of cytoplasm
ribosomes
site of protein synthesis, either found in the cytoplasm or on the rough ER, not membrane bound, made of rRNA and proteins
rough ER
membrane tubes studded with ribosomes; proteins are synthesized and packaged for possible export to the golgi
smooth ER
membrane tubes with no ribosomes; detoxifies cell, stores calcium ions, and is involved in lipid synthesis
golgi complex
flattened membrane-bound sacs, receives and modifies proteins, preparing them for possible export out of the cell
mitochondria
double-membraned organelle, site of cellular respiration, or ATP energy production
lysosomes
membraneous sac of hydrolytic enzymes used to digest macromolecules or break them down to reusable materials (monomers), acidic pH
vacuoles
membrane bound sac with a variety of uses; can store water/macromolecules, release waste, etc
chloroplasts
plant cells, a double membraned organelle that is the site of photosynthesis
nuclear envelope
double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
nuclear pores
channels in the nuclear envelope that allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus, connecting layers of the double membrane
nucleoid
dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell
nucleoli
dense masses of RNA and protein that manufacture ribosomes, lots located in the nucleus
food vacuoles
fuses with lysosomes, uses enzymes to digest food
contractile vacuoles
works to pump excess water out of a cell
central vacuoles (plants)
formed by the merging of smaller vacuoles, play a major role in plant growth, store inorganic ions
hydrolytic enzymes
found in lysosomes that speed up/aid in the breakdown of chemical bonds through hydrolysis
cilia
locomotor appendages that are short and numerous, can move fluid and receive signals
flagella
locomotor appendages that are long and whip-like, move like a fish tale, not many
plasmodesmata
channels through plant cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
lumen
the space inside of an organelle, the space in the rough ER
secretory proteins
destined for release from the cell
peripheral proteins
loosely bound to the membrane surface or attached to an integral protein
intergral proteins
penetrate the lipid bilayer, usually spans the entire membrane
thylakoid
folded membrane compartments in stacks called grana, light dependent photosyntheisis reactions
stroma
fluid between inner chloroplast membrane and outer thylakoids, carbon fixation reactions
microvilli
projections that increase the cells surface area
microtubules
hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that makes up part of the cytoskeleton in all eukaryotic cells
cytoskeletons
network whos components are made of proteins that holds the cell together, helps to keep its shape, aids in movement
centrosome
region where the cells microtubules are initiated
chromatin
material consisting of DNA and proteins, visible as chromosomes in dividing cells
endoplasmic reticulum
network of membrane tubes in cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
osmosis
diffusion specifically for water, going from less concentrated solution to more for equilibrium
isotoic
free water = solution, flacid
hypotonic
free water > solution, low concentration moves to high, turgid
hypertonic
free water < solution, high concentration moves to low, plasmolysis
fluid mosaic model
proteins bobbing in a fluid lipid bilayer of phospholipids, held together by hydrophobic interactions
aquaporins
channel proteins to help water get through plasma membrane
diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentration, small nonpolar molecules
concentration gradient
region along which the density of a substance increases/decreases
passive transport
moving down concentration gradient, doesnt require energy
facilitated diffusion
high to low concentration with transport proteins, hydrophilic and charged ions
active transport
requires energy to move molecule up concentration gradient
membrane potential
voltage across a membrane
endocytosis
vesicle forms and transports macromolecules into cell (phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor mediated endocytosis)
exocytosis
vesicle transports macromolecules out of plasma membrane
cholesterol
steroid, randomly wedged between phospholipids, regulates bilayer fluidity